A Novel Control Method of Enterococcus faecalis by Co-Treatment with Protamine and Calcium Hydroxide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture Medium
2.2. Microorganisms
2.3. Antimicrobial Agents
2.4. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Protamine against E. faecalis
2.4.1. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of E. faecalis to Protamine
2.4.2. Evaluation of Growth Inhibition Ability of Protamine against E. faecalis
2.5. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Calcium Hydroxide against E. faecalis
2.5.1. Evaluation Test of Calcium Hydroxide Tolerance of E. faecalis
2.5.2. Effect of Treatment with Calcium Hydroxide on the Metabolic Activity of E. faecalis
2.6. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Co-Treatment with Protamine and Calcium Hydroxide
2.6.1. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity
2.6.2. Evaluation of the Effect on the Surface Structure of E. faecalis
2.7. Investigation of Antimicrobial Mechanism of Action
2.7.1. Observation of Cell Membrane Damage Using Live/Dead Staining
2.7.2. Investigation of Localization Sites of Protamine in Bacteria
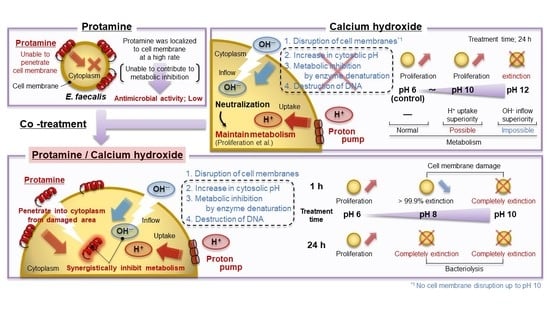
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Activity of Protamine against E. faecalis
3.1.1. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of E. faecalis to Protamine
3.1.2. Growth Inhibition Ability of Protamine against E. faecalis
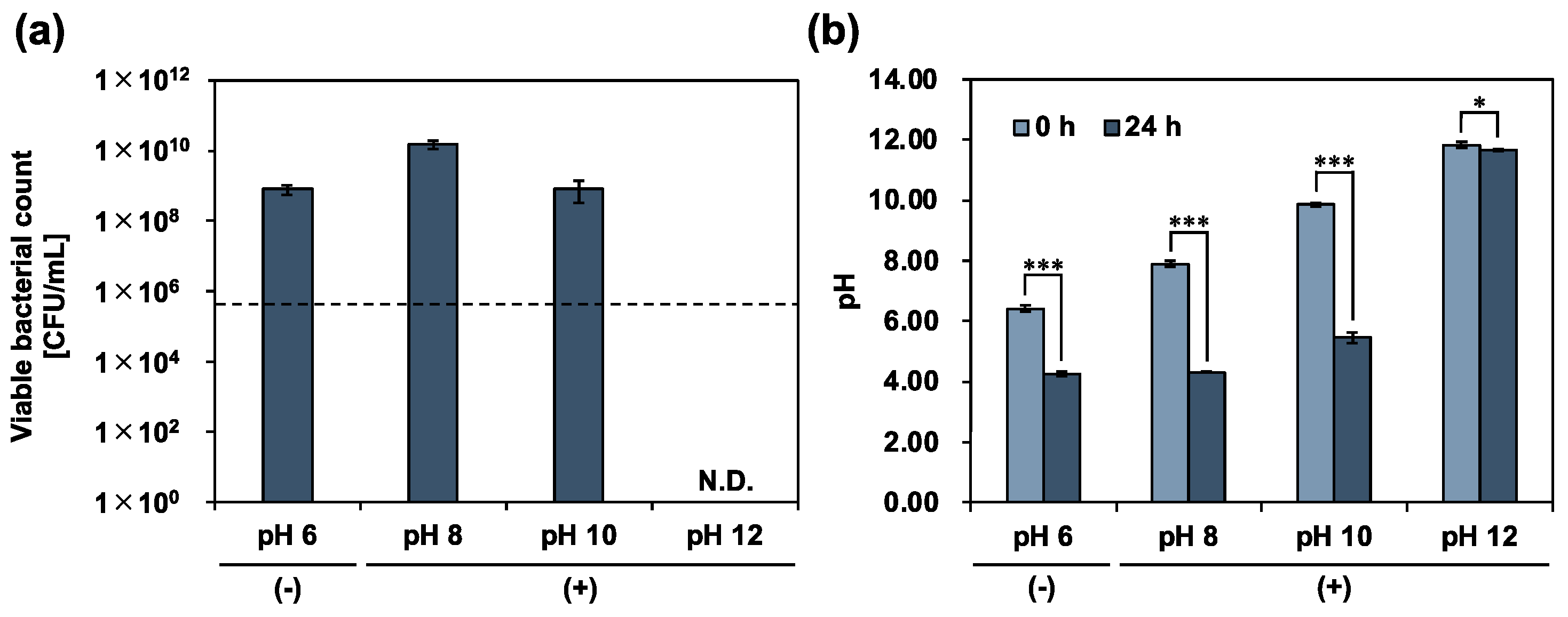
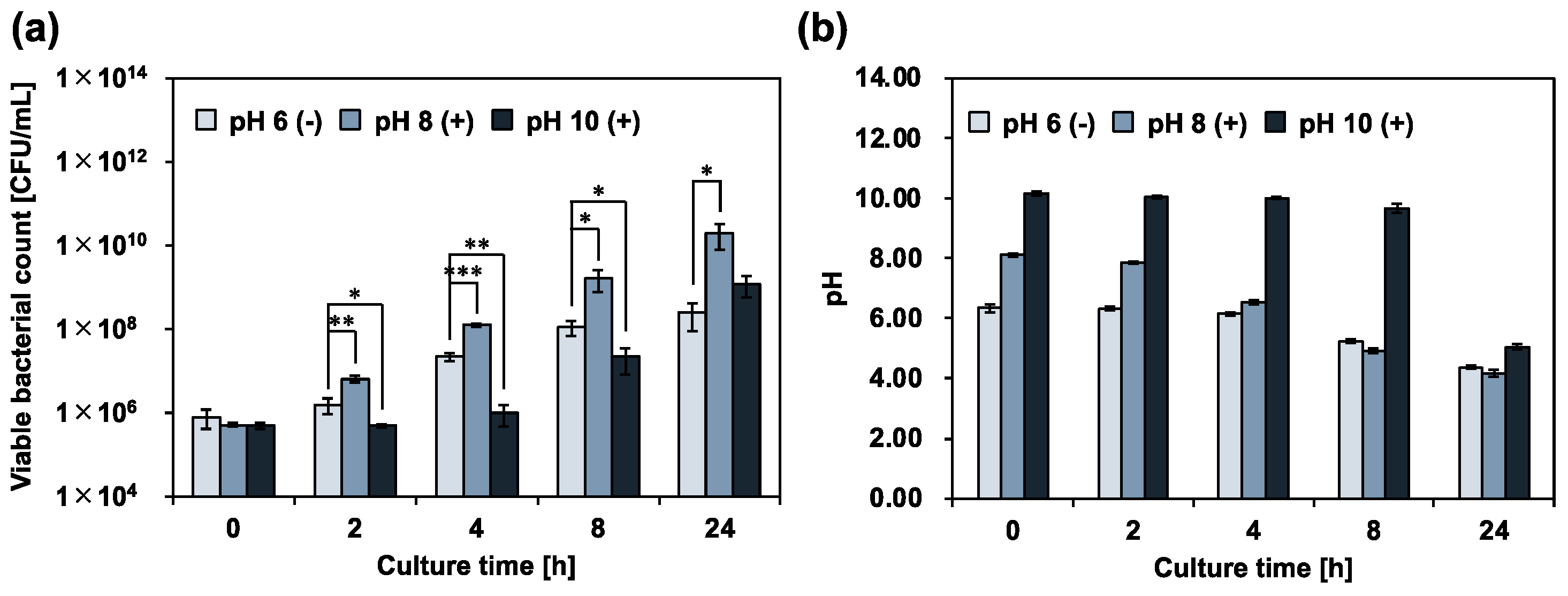
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity of Calcium Hydroxide against E. faecalis
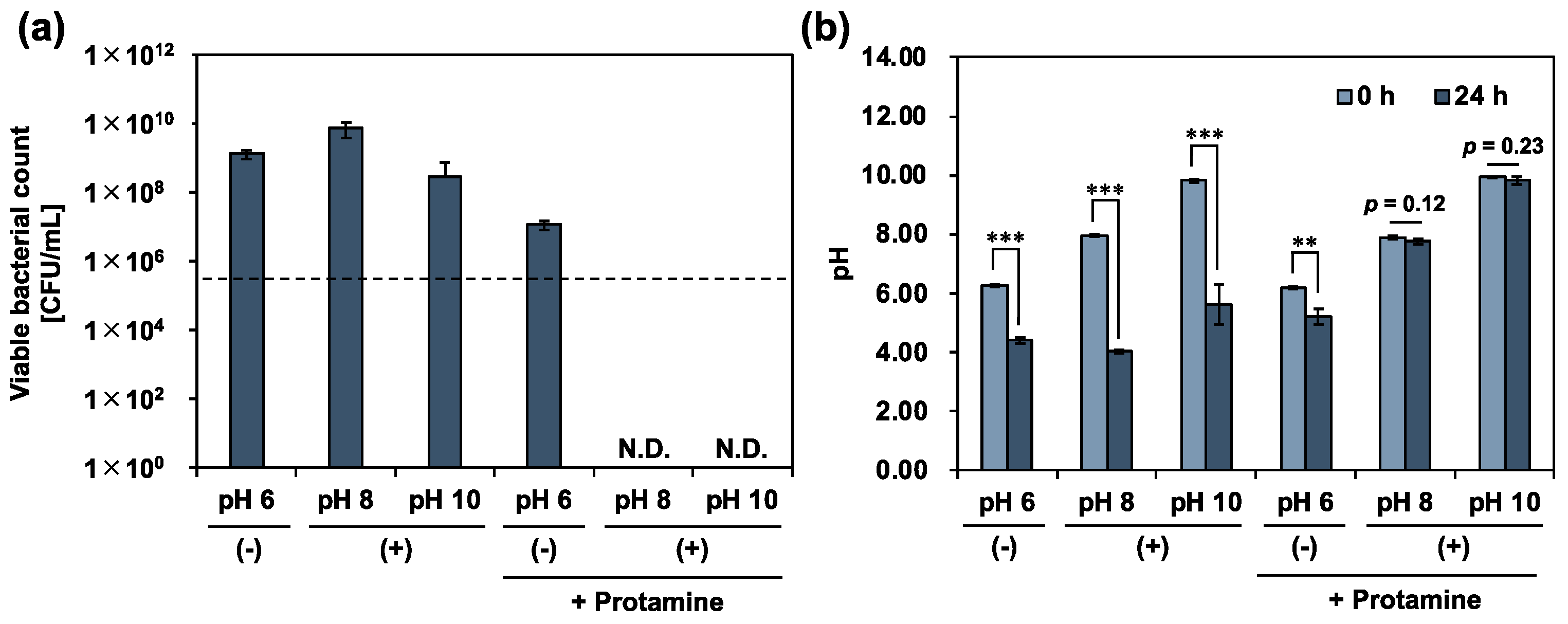
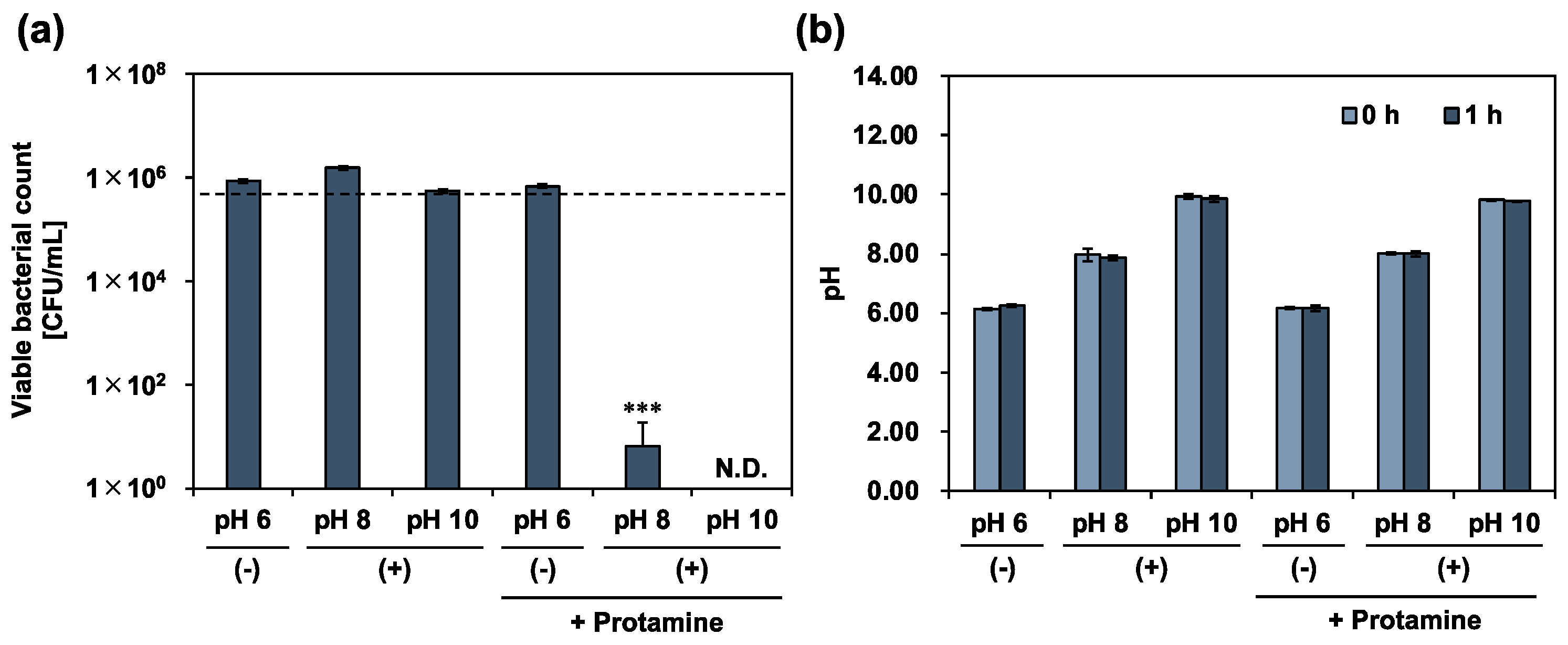
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity of Co-Treatment with Protamine and Calcium Hydroxide
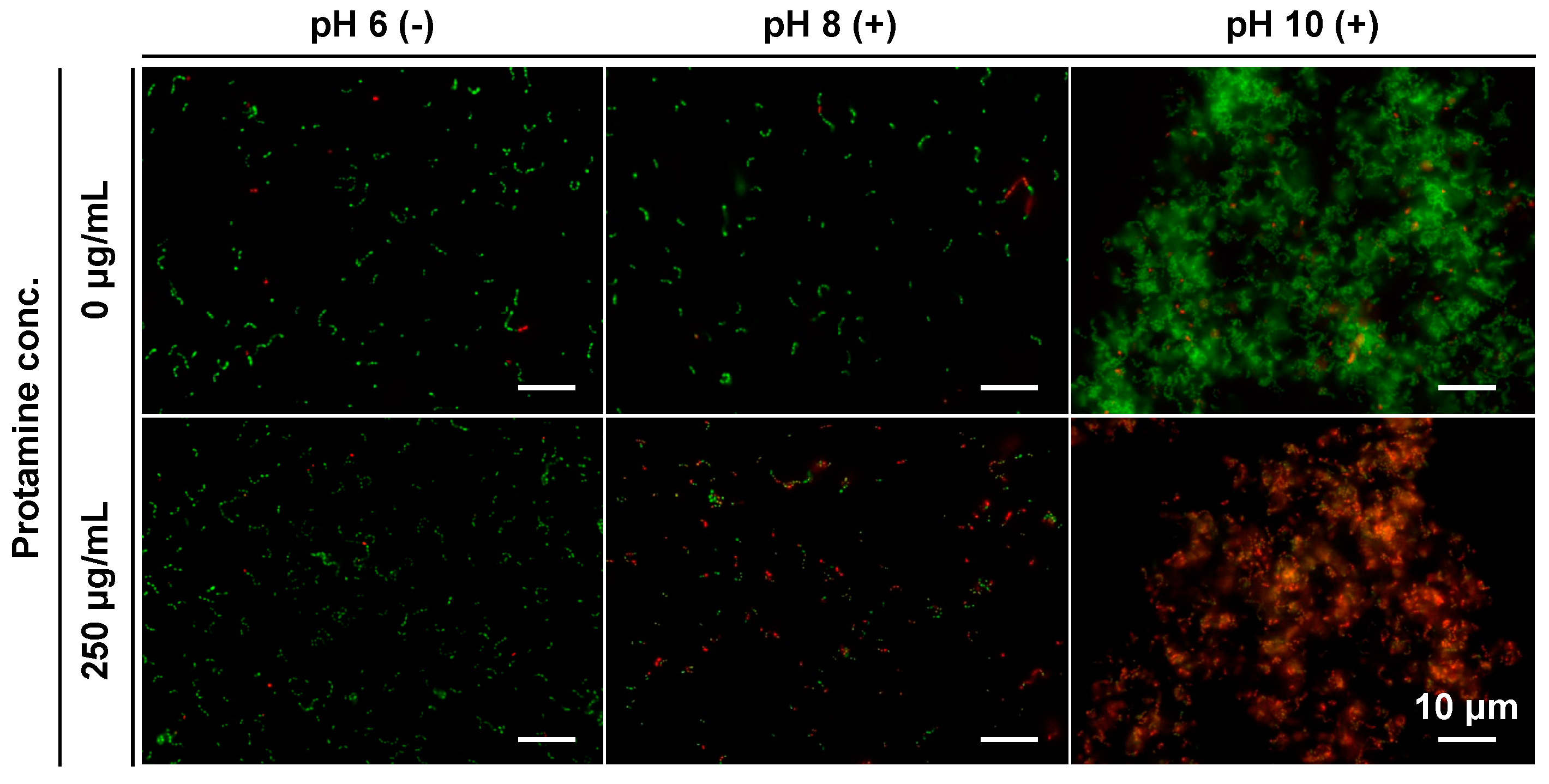
3.4. Investigation of Antimicrobial Mechanism of Action
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qian, W.; Ma, T.; Ye, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hao, P. Microbiota in the apical root canal system of tooth with apical periodontitis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Lin, B.; Liu, F.; Zhao, W. Role of Enterococcus faecalis in refractory apical periodontitis: From pathogenicity to host cell response. J. Oral Microbiol. 2023, 15, 2184924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Dummer, P.M.H. Properties and applications of calcium hydroxide in endodontics and dental traumatology. Int. Endod. J. 2011, 44, 697–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, E. Antimicrobial effect of calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament in root canal treatment: A literature review—Part I. In vitro studies. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2014, 39, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamifar, K.; Tondari, A.; Saghiri, M.A. Endodontic Periapical Lesion: An Overview on the Etiology, Diagnosis and Current Treatment Modalities. Eur. Endod. J. 2020, 5, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Guo, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xu, H.H.K.; Ren, B.; Peng, X.; Weir, M.D.; Li, M.; Cheng, L. The inhibitory effect of quaternary ammonium salt on bacteria in root canal. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, C.H.; Schwartz, S.A.; Beeson, T.J.; Owatz, C.B. Enterococcus faecalis: Its role in root canal treatment failure and current concepts in retreatment. J. Endod. 2006, 32, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, F.; Shakir, M. The Influence of Enterococcus faecalis as a Dental Root Canal Pathogen on Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Corbella, S.; Sequeira-Byron, P.; Tsesis, I.; Rosen, E.; Lolato, A.; Taschieri, S. Endodontic procedures for retreatment of periapical lesions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 10, CD005511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajo, K.; Komori, R.; Ishikawa, S.; Ueno, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Iwami, Y.; Takahashi, N. Resistance to acidic and alkaline environments in the endodontic pathogen Enterococcus faecalis. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 21, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Davies, J.K.; Sundqvist, G.; Figdor, D. Mechanisms involved in the resistance of Enterococcus faecalis to calcium hydroxide. Int. Endod. J. 2002, 35, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portenier, I.; Haapasalo, H.; Rye, A.; Waltimo, T.; Orstavik, D.; Haapasalo, M. Inactivation of root canal medicaments by dentine, hydroxylapatite and bovine serum albumin. Int. Endod. J. 2001, 34, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anija, R.; Kalita, C.; Bhuyan, A.C.; Hussain, M.D.I.; Saikia, A.; Das, L. Comparative evaluation of the concentration-dependent effect of proton-pump inhibitor in association with calcium hydroxide and chlorhexidine on Enterococcus faecalis: An in vitro study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2021, 25, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boparai, J.K.; Sharma, P.K. Mini Review on Antimicrobial Peptides, Sources, Mechanism and Recent Applications. Protein Pept. Lett. 2020, 27, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurkiewicz-Pisarek, A.; Baran, J.; Ciach, T. Antimicrobial Peptides: Challenging Journey to the Pharmaceutical, Biomedical, and Cosmeceutical Use. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Y.; Yan, Z.-B.; Meng, Y.-M.; Hong, X.-Y.; Shao, G.; Ma, J.-J.; Cheng, X.-R.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Fu, C.-Y. Antimicrobial peptides: Mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.T.; Gill, T.A. Solubility and antimicrobial efficacy of protamine on Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli as influenced by pH. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, S.Y. Antimicrobial Activity of Protamine against Oral Microorganisms. Biocontrol Sci. 2015, 20, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiki, M.; Honda, M. The investigation of synergistic activity of protamine with conventional antimicrobial agents against oral bacteria. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 523, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeise, K.D.; Woods, R.J.; Huffnagle, G.B. Interplay between Candida albicans and Lactic Acid Bacteria in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Impact on Colonization Resistance, Microbial Carriage, Opportunistic Infection, and Host Immunity. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e0032320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T. Adaptability of Lactic Acid Bacteria to Unusual Environment. Jpn. J. Dairy Food Sci. 1994, 43, A-25–A-34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Booth, V. Antimicrobial Peptide Mechanisms Studied by Whole-Cell Deuterium NMR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Flanagan, T.W.; Kharouf, N.; Bertsch, C.; Mancino, D.; Haikel, Y. Antimicrobial Proteins: Structure, Molecular Action, and Therapeutic Potential. Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpe, S.; Bakker, E.P. Requirement of a large K+-uptake capacity and of extracytoplasmic protease activity for protamine resistance of Escherichia coli. Arch. Microbiol. 1997, 167, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspedon, A.; Groisman, E.A. The antibacterial action of protamine: Evidence for disruption of cytoplasmic membrane energization in Salmonella typhimurium. Microbiology 1996, 142 Pt 12, 3389–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| MIC [μg/mL] | MBC [μg/mL] |
|---|---|
| 250 | >1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abe, Y.; Honda, M. A Novel Control Method of Enterococcus faecalis by Co-Treatment with Protamine and Calcium Hydroxide. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061629
Abe Y, Honda M. A Novel Control Method of Enterococcus faecalis by Co-Treatment with Protamine and Calcium Hydroxide. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(6):1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061629
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbe, Yu, and Michiyo Honda. 2023. "A Novel Control Method of Enterococcus faecalis by Co-Treatment with Protamine and Calcium Hydroxide" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 6: 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061629
APA StyleAbe, Y., & Honda, M. (2023). A Novel Control Method of Enterococcus faecalis by Co-Treatment with Protamine and Calcium Hydroxide. Pharmaceutics, 15(6), 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061629