Bentonite- and Palygorskite-Based Gels for Topical Drug Delivery Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Synthesis of DCF and Preparation of DCF Nanosuspension
2.2.2. DCF Nanosuspension Characterization
2.2.3. Preparation of DCF Nanosuspension-Loaded Hydrogels
2.2.4. Rheological Analysis
2.2.5. Solid State Characterization
2.2.6. In Vitro Release Study of DCF Nanosuspension-Loaded Hydrogels
2.2.7. In Vitro Skin Penetration/Permeation
2.2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
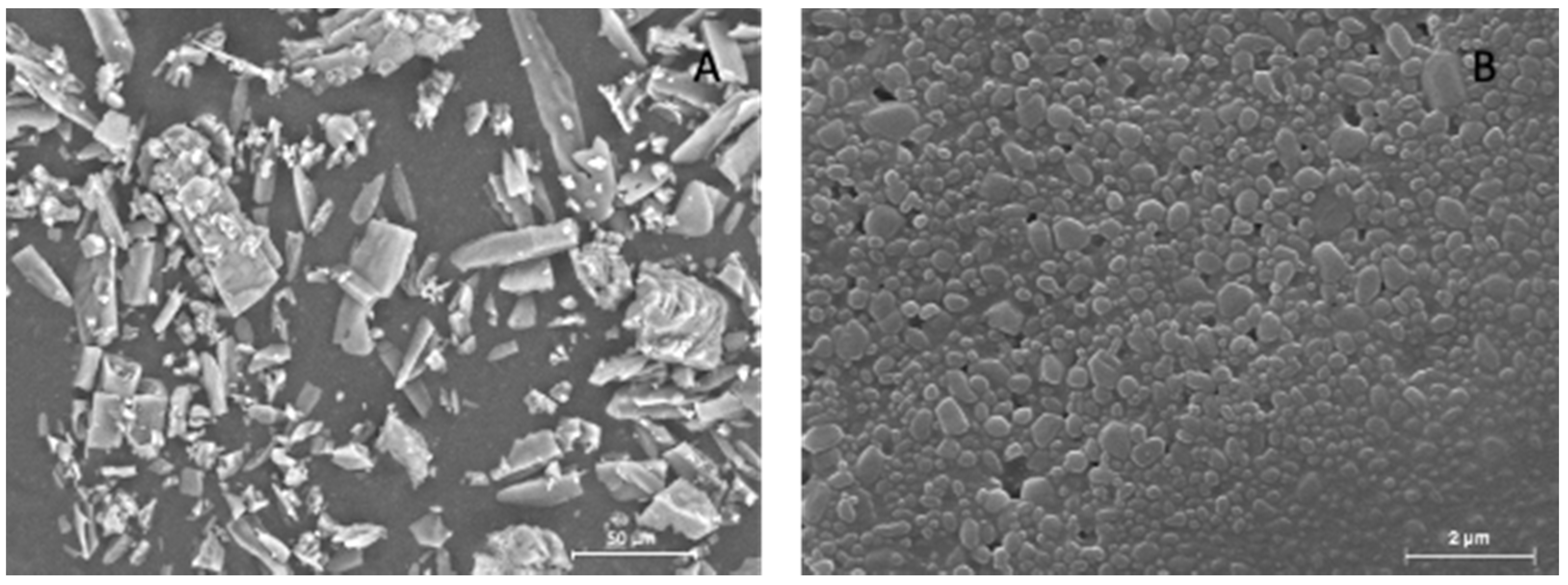
3.1. DCF Nanosuspension Characterization
3.2. Rheological Properties
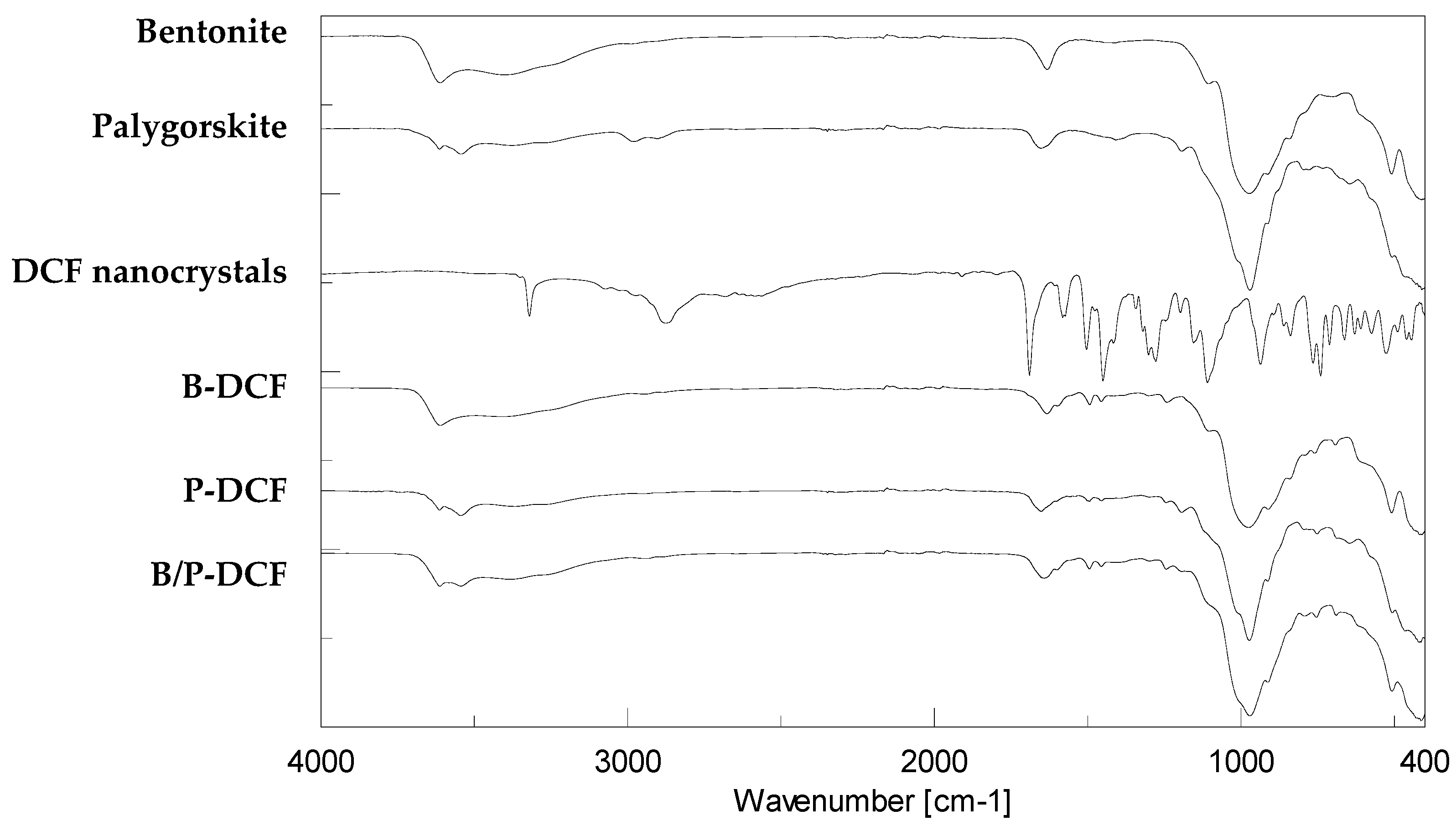
3.3. Solid State Characterization
3.4. In Vitro Release Study of DCF Nanocrystals-Loaded Hydrogels
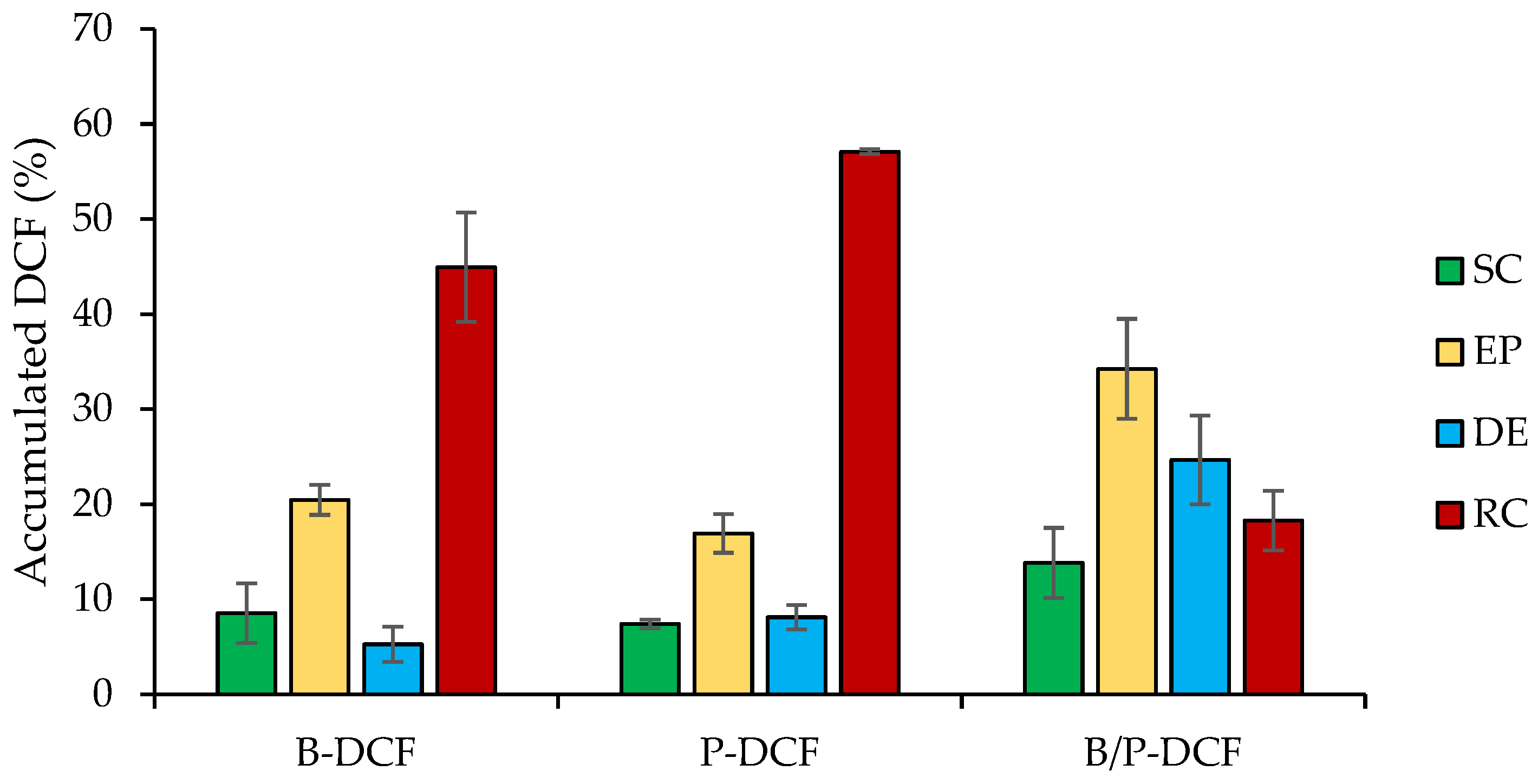
3.5. In-Vitro Skin Penetration/Permeation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Villén, F.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; López-Galindo, A.; Cerezo, P.; Viseras, C. Design and characterization of spring water hydrogels with natural inorganic excipients. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 197, 105772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.I.; Kanczler, J.M.; Yang, X.B.; Attard, G.S.; Oreffo, R.O. Clay gels for the delivery of regenerative microenvironments. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3304–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardziński, P.J. On the impact of intermolecular interactions between the quaternary ammonium ions on interlayer spacing of quat-intercalated montmorillonite: A molecular mechanics and ab-initio study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, A. From structure evolution of palygorskite to functional material: A review. Micropor Mesopor Mat. 2022, 333, 111765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, F. Effects of pH on the gel properties of montmorillonite, palygorskite and montmorillonite-palygorskite composite clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonton, T.C.; Komarneni, S.; Roy, R. Gelling properties of sepiolite versus montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 1988, 3, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Galindo, A.; Viseras, C.; Aguzzi, C.; Cerezo, P. Chapter 13—Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Uses of Fibrous Clays. In Developments in Clay Science; Galàn, E., Singer, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 299–324. [Google Scholar]
- Aguzzi, C.; Viseras, C.; Cerezo, P.; Rossi, S.; Ferrari, F.; López-Galindo, A.; Caramella, C. Influence of dispersion conditions of two pharmaceutical grade clays on their interaction with some tetracyclines. Appl. Clay Sci. 2005, 30, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carazo, E.; Borrego-Sánchez, A.; García-Villén, F.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Cerezo, P.; Aguzzi, C.; Viseras, C. Advanced Inorganic Nanosystems for Skin Drug Delivery. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugrahani, I.; Utami, D.; Ibrahim, S.; Nugraha, Y.P.; Uekusa, H. Zwitterionic cocrystal of diclofenac and l-proline: Structure determination, solubility, kinetics of cocrystallization, and stability study. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 117, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Sinico, C.; Ennas, G.; Marongiu, F.; Marongiu, G.; Fadda, A.M. Diclofenac nanosuspensions: Influence of preparation procedure and crystal form on drug dissolution behaviour. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 373, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pireddu, R.; Sinico, C.; Ennas, G.; Marongiu, F.; Muzzalupo, R.; Lai, F.; Fadda, A.M. Novel nanosized formulations of two diclofenac acid polymorphs to improve topical bioavailability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pireddu, R.; Schlich, M.; Marceddu, S.; Valenti, D.; Pini, E.; Fadda, A.M.; Lai, F.; Sinico, C. Nanosuspensions and Microneedles Roller as a Combined Approach to Enhance Diclofenac Topical Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlich, M.; Casula, L.; Musa, A.; Pireddu, R.; Pitzanti, G.; Cardia, M.C.; Valenti, D.; Marceddu, S.; Fadda, A.M.; De Luca, M.A.; et al. Needle-Free Jet Injectors and Nanosuspensions: Exploring the Potential of an Unexpected Pair. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, M.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Casula, L.; Barbosa, R.D.M.; Sandri, G.; Cardia, M.C.; Lai, F.; Viseras, C. Clay-Based Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Vehicles of Curcumin Nanocrystals for Topical Application. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Shin, G.H.; Park, H.J. Solid lipid nanoparticles loaded thermoresponsive pluronic–xanthan gum hydrogel as a transdermal delivery system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 135, 46004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Ullah, S.; Alnuwaiser, M.A.; Rehman, F.U.; Selim, S.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Farid, A. Formulation and Evaluation of Chitosan-Gelatin Thermosensitive Hydrogels Containing 5FU-Alginate Nanoparticles for Skin Delivery. Gels 2022, 8, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, A.; Amaro, M.I.; Healy, A.M.; Cabral, L.M.; de Sousa, V.P. Comparative evaluation of rivastigmine permeation from a transdermal system in the Franz cell using synthetic membranes and pig ear skin with in vivo-in vitro correlation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 512, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pireddu, R.; Caddeo, C.; Valenti, D.; Marongiu, F.; Scano, A.; Ennas, G.; Lai, F.; Fadda, A.M.; Sinico, C. Diclofenac acid nanocrystals as an effective strategy to reduce in vivo skin inflammation by improving dermal drug bioavailability. Coll. Surf. B. 2016, 143, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, M.; Dhake, A.S.; Sharma, S.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Stability studies on aqueous and oily ophthalmic solutions of diclofenac. Yakugaku Zasshi 2009, 129, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Romero, G.B.; Chen, R.; Keck, C.M.; Müller, R.H. Industrial concentrates of dermal hesperidin smartCrystals®--production, characterization & long-term stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 482, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Chemeda, Y.C.; Christidis, G.E.; Khan, N.M.T.; Koutsopoulou, E.; Hatzistamou, V.; Kelessidis, V.C. Rheological properties of palygorskite–bentonite and sepiolite–bentonite mixed clay suspensions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 90, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckham, P.F.; Rossi, S. The colloidal and rheological properties of bentonite suspensions. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 1999, 82, 43–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, H.; Keren, R. Rheology of Na-Rich Montmorillonite Suspension as Affected by Electrolyte Concentration and Shear Rate. Clays Clay Min. 2001, 49, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neaman, A.; Singer, A. Rheology of Mixed Palygorskite-Montmorillonite Suspensions. Clays Clay Min. 2000, 48, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Villén, F.; Faccendini, A.; Aguzzi, C.; Cerezo, P.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Rossi, S.; Grisoli, P.; Ruggeri, M.; Ferrari, F.; Sandri, G.; et al. Montmorillonite-norfloxacin nanocomposite intended for healing of infected wounds. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5051–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccendini, A.; Ruggeri, M.; Rossi, S.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Aguzzi, C.; Grisoli, P.; Viseras, C.; Sandri, G.; Ferrari, F. Norfloxacin loaded electrospun scaffolds: Montmorillonite nanocomposite vs. free drug. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carazo, E.; Borrego-Sánchez, A.; García-Villén, F.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Viseras, C.; Cerezo, P.; Aguzzi, C. Adsorption and characterization of palygorskite-isoniazid nanohybrids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kang, Y.; Mu, B.; Wang, A. Attapulgite/bentonite interactions for methylene blue adsorption characteristics from aqueous solution. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 237, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pireddu, R.; Sinico, C.; Ennas, G.; Schlich, M.; Valenti, D.; Murgia, S.; Marongiu, F.; Fadda, A.M.; Lai, F. The effect of diethylene glycol monoethyl ether on skin penetration ability of diclofenac acid nanosuspensions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 162, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| DCF Nanosuspension Composition | Characterization | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | % (w/w) | Mean Diameter (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
| DCF | 1.0 | 287.8 ± 10.1 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | −26.8 ± 0.7 |
| Poloxamer 188 | 0.5 | |||
| Water | 98.5 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruggeri, M.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Casula, L.; Sandri, G.; Perioli, L.; Cardia, M.C.; Lai, F.; Viseras, C. Bentonite- and Palygorskite-Based Gels for Topical Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041253
Ruggeri M, Sánchez-Espejo R, Casula L, Sandri G, Perioli L, Cardia MC, Lai F, Viseras C. Bentonite- and Palygorskite-Based Gels for Topical Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(4):1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041253
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuggeri, Marco, Rita Sánchez-Espejo, Luca Casula, Giuseppina Sandri, Luana Perioli, Maria Cristina Cardia, Francesco Lai, and César Viseras. 2023. "Bentonite- and Palygorskite-Based Gels for Topical Drug Delivery Applications" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 4: 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041253
APA StyleRuggeri, M., Sánchez-Espejo, R., Casula, L., Sandri, G., Perioli, L., Cardia, M. C., Lai, F., & Viseras, C. (2023). Bentonite- and Palygorskite-Based Gels for Topical Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics, 15(4), 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041253








