Lipid Nanoparticles as Promising Carriers for mRNA Vaccines for Viral Lung Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. mRNA Vaccination and Mechanism of Action of mRNA
2.1. Background of mRNA Vaccines
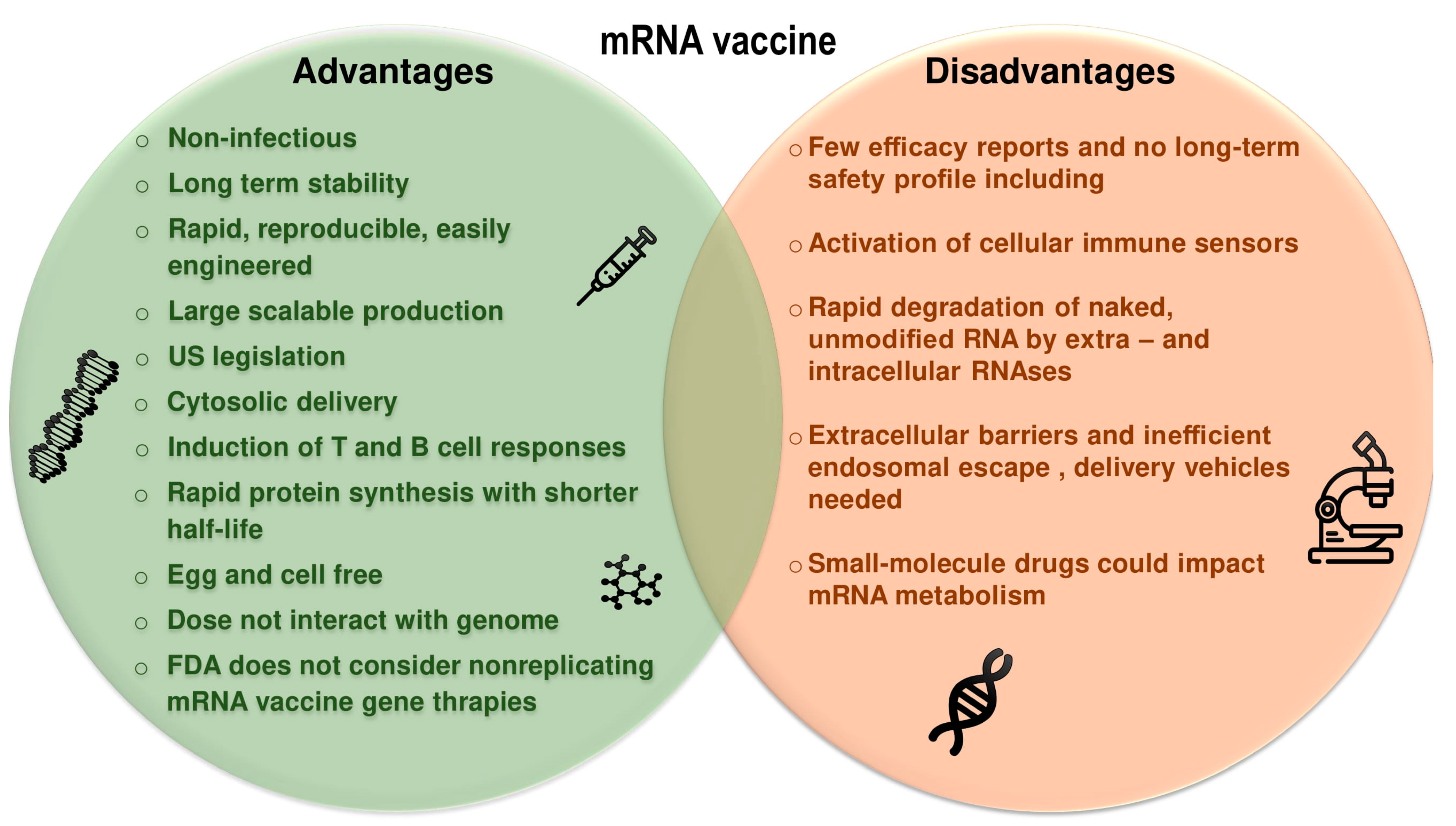
2.2. Therapeutic Considerations of mRNA Vaccines
3. Combining Nanoparticles with mRNA Vaccines
4. Nanoparticles as Carriers
Nanoparticle Delivery Systems
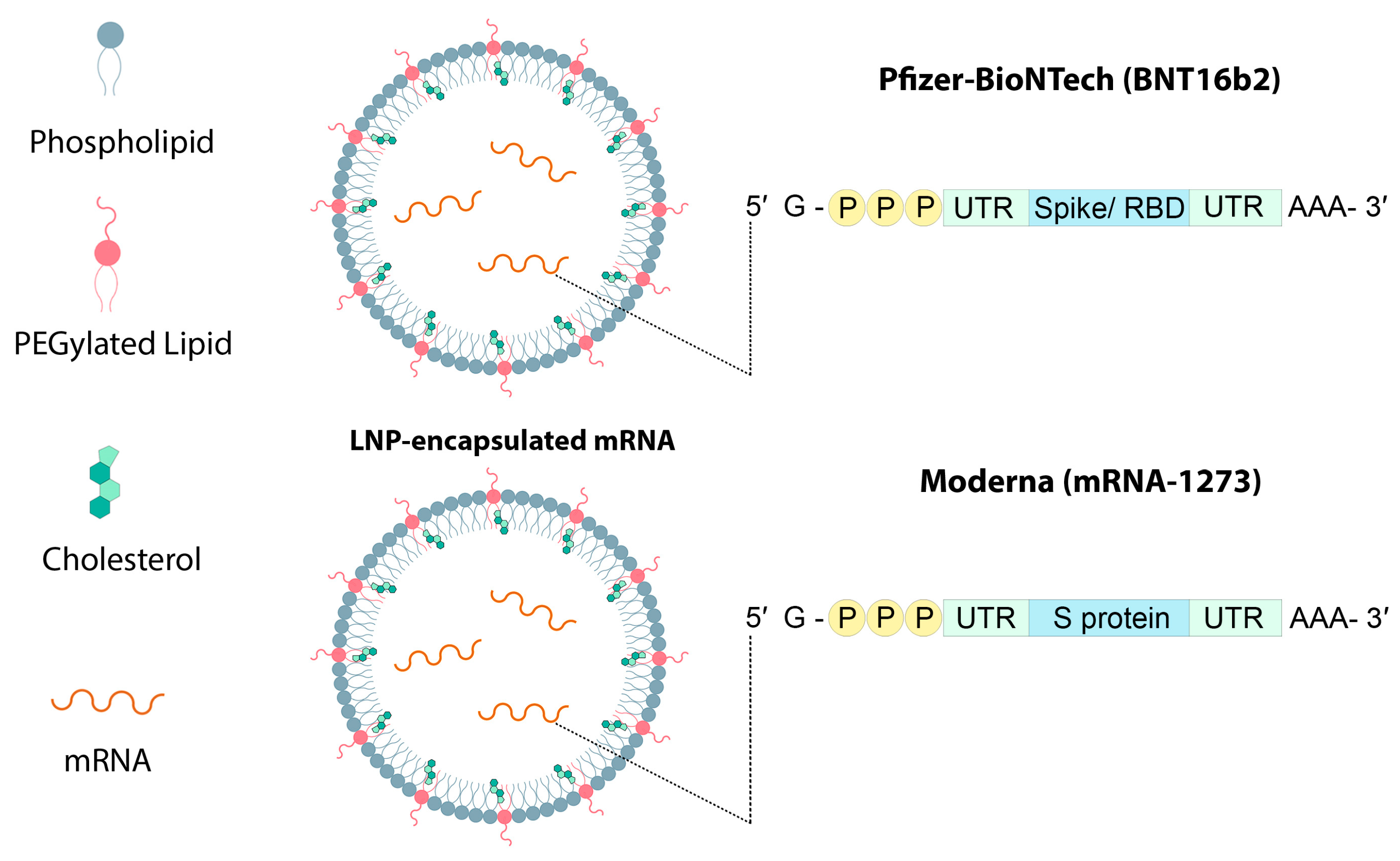
5. Lipid Nanoparticles Used in mRNA Vaccines and Their Delivery Systems
5.1. Ionizable Lipids
5.2. Cationic Lipids
5.3. Other Types of Lipids That Can Be Used in mRNA Delivery Systems Based on Nanoparticles
5.4. Lipid-Bound Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)
5.5. Cholesterol
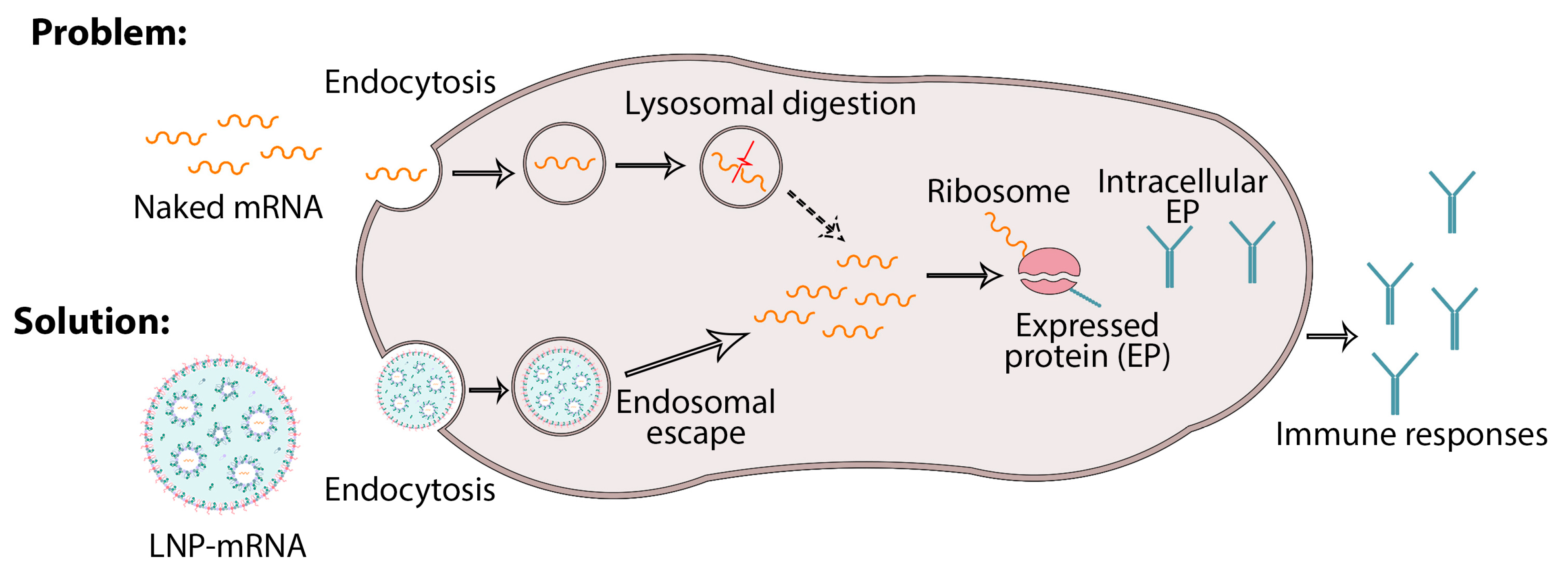
6. Nanodelivery Systems Based on Lipid Nanoparticles
- (1)
- Promotion of the release of mRNA from the endosome to the cytoplasm;
- (2)
- Control of the uptake of mRNA into the target host cell.
7. Treatment and Prevention of Viral Infectious Diseases of the Lungs
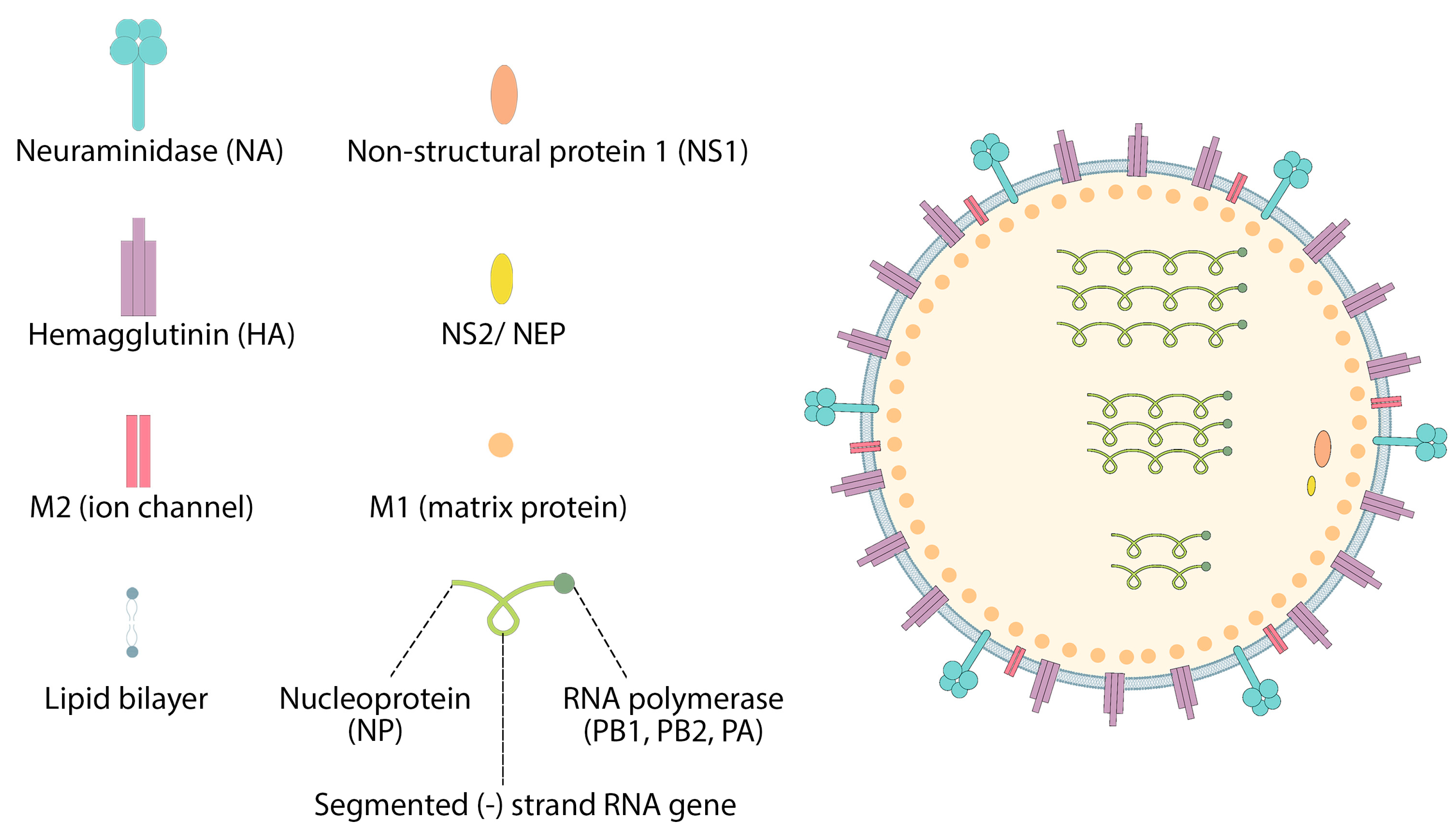
7.1. Influenza
7.2. Coronavirus
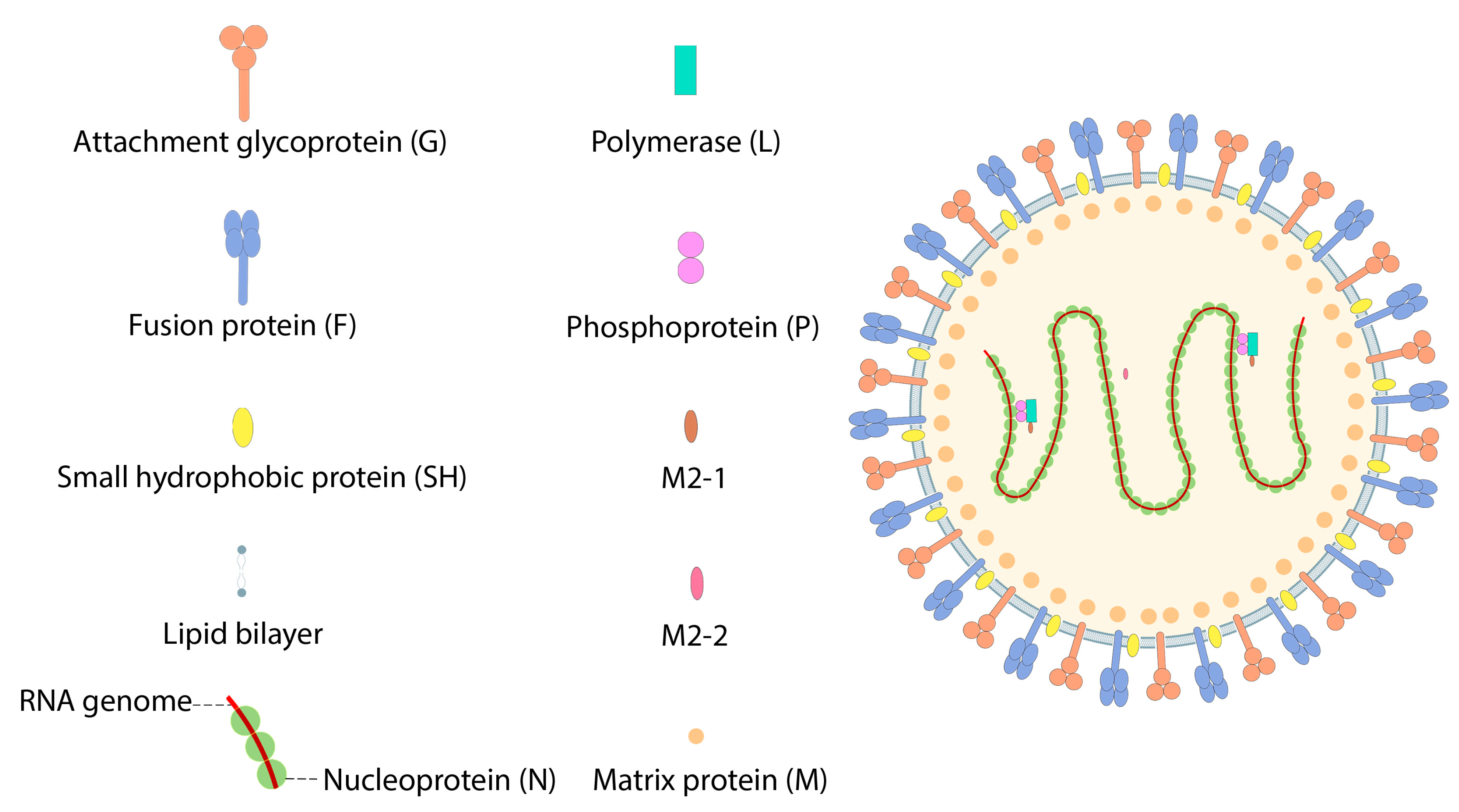
7.3. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
8. Using Particles as a Delivery System
8.1. LNPs as a Delivery System
8.2. VLPs as a Delivery System
9. Challenges
10. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bruinsma, R.F.; Wuite, G.J.L.; Roos, W.H. Physics of viral dynamics. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2021, 3, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, V.; Greber, U.F. The endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response—Homeostasis, cell death and evolution in virus infections. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 45, fuab016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, M.; Mostafaei, S.; Aghaei, A.; Hosseini, N.; Darabi, H.; Nouri, M.; Etemadi, A.; Neill, A.O.; Nahand, J.S.; Mirzaei, H.; et al. The association between HPV gene expression, inflammatory agents and cellular genes involved in EMT in lung cancer tissue. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, S.S.; Fenniri, H.; Singh, B. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2007, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Maruggi, G.; Shan, H.; Li, J. Advances in mRNA Vaccines for Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.; Weissman, D.; Whitehead, K.A. mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases: Principles, delivery and clinical translation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 817–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Zhang, C.; Walker, P.G.; Dong, Y. Formulation and Delivery Technologies for mRNA Vaccines. In Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Gao, G.F. mRNA vaccines: A matter of delivery. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 32, 100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, N.A.C.; Kester, K.E.; Casimiro, D.; Gurunathan, S.; DeRosa, F. The promise of mRNA vaccines: A biotech and industrial perspective. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C. Design and application of nanoparticles as vaccine adjuvants against human corona virus infection. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 219, 111454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroudian, M.; Azhdari, M.H.; Goodarzi, N.; O’Sullivan, D.; Donnelly, S.C. Smart Nanotherapeutics and Lung Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doroudian, M.; MacLoughlin, R.; Poynton, F.; Prina-Mello, A.; Donnelly, S.C. Nanotechnology based therapeutics for lung disease. Thorax 2019, 74, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, L.; Kruger, H.G.; Maguire, G.E.M.; Govender, T.; Parboosing, R. The role of nanotechnology in the treatment of viral infections. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2017, 4, 105–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, D.; Biswasroy, P.; Goyal, A.; Ghosh, G.; Rath, G. Recent Advancement in Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery System against Viral Infections. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroudian, M.; Armstrong, M.E.; Donnelly, S.C. Nano-Based Therapies for Acute and Chronic Lung Diseases. In Biotechnology Applied to Inflammatory Diseases: Cellular Mechanisms and Nanomedicine; Ribeiro de Araujo, D., Carneiro-Ramos, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 271–286. [Google Scholar]
- Aghasadeghi, M.R.; Heidari, H.; Sadat, S.M.; Irani, S.; Amini, S.; Siadat, S.D.; Fazlhashemy, M.E.; Zabihollahi, R.; Atyabi, S.M.; Momen, S.B.; et al. Lamivudine-PEGylated chitosan: A novel effective nanosized antiretroviral agent. Curr. HIV Res. 2013, 11, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroudian, M.; O’Neill, A.; O’Reilly, C.; Tynan, A.; Mawhinney, L.; McElroy, A.; Webster, S.S.; MacLoughlin, R.; Volkov, Y.; Michelle, E.A.; et al. Aerosolized drug-loaded nanoparticles targeting migration inhibitory factors inhibit Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced inflammation and biofilm formation. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 2933–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroudian, M.; O’ Neill, A.; Mac Loughlin, R.; Prina-Mello, A.; Volkov, Y.; Donnelly, S.C. Nanotechnology in pulmonary medicine. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2021, 56, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kontodimas, K.; Bosmann, M. Nanomedicine: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach to COVID-19. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 648005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, A.; Allawadhi, P.; Khurana, I.; Allwadhi, S.; Weiskirchen, R.; Banothu, A.K.; Chhabra, D.; Joshi, K.; Bharani, K.K. Role of nanotechnology behind the success of mRNA vaccines for COVID-19. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liang, Y.; Huang, L. Development and Delivery Systems of mRNA Vaccines. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 718753. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinkazemi, H.; Samani, S.; O’Neill, A.; Soezi, M.; Moghoofei, M.; Azhdari, M.H.; Aavani, F.; Nazbar, A.; Keshel, S.H.; Doroudian, M. Applications of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles against Breast Cancer. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 6493458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamford, D.H.; Grimes, J.M.; Stuart, D.I. What does structure tell us about virus evolution? Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005, 15, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, G.T.; Mahiny, A.J.; Vlatkovic, I. COVID-19 mRNA vaccines: Platforms and current developments. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1850–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Yang, K.; Li, R.; Zhang, L. mRNA Vaccine Era-Mechanisms, Drug Platform and Clinical Prospection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, R.; Lentacker, I.; De Smedt, S.C.; Dewitte, H. The dawn of mRNA vaccines: The COVID-19 case. J. Control. Release 2021, 333, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines—A new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlake, T.; Thess, A.; Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Kallen, K.J. Developing mRNA-vaccine technologies. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, J.B.; Mason, P.W.; Geall, A.; Mandl, C.W. RNA-based vaccines. Vaccine 2012, 30, 4414–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, P.S.; Rudra, A.; Miao, L.; Anderson, D.G. Delivering the Messenger: Advances in Technologies for Therapeutic mRNA Delivery. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 710–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, A.; Aljabbari, A.; Lokras, A.; Foged, C.; Thakur, A. Opportunities and Challenges in the Delivery of mRNA-based Vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharavi, A.T.; Hanjani, N.A.; Movahed, E.; Doroudian, M. The role of macrophage subtypes and exosomes in immunomodulation. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iavarone, C.; O’Hagan, D.T.; Yu, D.; Delahaye, N.F.; Ulmer, J.B. Mechanism of action of mRNA-based vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2017, 16, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruggi, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Ulmer, J.B.; Yu, D. mRNA as a Transformative Technology for Vaccine Development to Control Infectious Diseases. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichmuth, A.M.; Oberli, M.A.; Jaklenec, A.; Langer, R.; Blankschtein, D. mRNA vaccine delivery using lipid nanoparticles. Ther. Deliv. 2016, 7, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, R.; Lentacker, I.; De Smedt, S.; Dewitte, H. Three decades of messenger RNA vaccine development. Nano Today 2019, 28, 100766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosigkeit, S.; Meng, M.; Grunwitz, C.; Gomes, P.; Kreft, A.; Hayduk, N.; Heck, R.; Pickert, G.; Ziegler, K.; Abassi, Y.; et al. Monitoring Translation Activity of mRNA-Loaded Nanoparticles in Mice. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 3909–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Sun, X. Recent advances in mRNA vaccine delivery. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 5338–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, C.; De Koker, S.; Saelens, X.; Vanham, G.; Grooten, J. Challenges and advances towards the rational design of mRNA vaccines. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Weissman, D. Recent advances in mRNA vaccine technology. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 65, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Sun, X.; Aikins, M.E.; Moon, J.J. Non-viral COVID-19 vaccine delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 169, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L. Nanoparticle approaches against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2021, 25, 100964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, K.; Shelling, A.N.; Wu, Z. Nanotechnology-Enabled COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, C.; Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Roth, G.; Becker, C.; Dam, T.C.; Verdurmen, W.P.; Brock, R.; Probst, J.; Schlake, T. Protein expression from exogenous mRNA: Uptake by receptor-mediated endocytosis and trafficking via the lysosomal pathway. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Lillard, J.W., Jr. Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.K.; Islam, M.R.; Choudhury, Z.S.; Mostafa, A.; Kadir, M.F. Nanotechnology based approaches in cancer therapeutics. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzea, C.; Pacheco, I.I.; Robbie, K. Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: Sources and toxicity. Biointerphases 2007, 2, MR17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.A.A.; Saleh, A.M. Applications of nanoparticle systems in drug delivery technology. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, T.; Sabliov, C.M. Nanodelivery of bioactive components for food applications: Types of delivery systems, properties, and their effect on ADME profiles and toxicity of nanoparticles. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panyam, J.; Labhasetwar, V. Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to cells and tissue. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Biazar, E.; Jafarpour, M.; Montazeri, M.; Majdi, A.; Aminifard, S.; Zafari, M.; Akbari, H.R.; Rad, H.G. Nanotoxicology and nanoparticle safety in biomedical designs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczewska, A.Z.; Niemirowicz, K.; Markiewicz, K.H.; Car, H. Nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 1020–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.d.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudramurthy, G.R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sinniah, U.R.; Ghasemzadeh, A. Nanoparticles: Alternatives against Drug-Resistant Pathogenic Microbes. Molecules 2016, 21, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahin, N.; Anwar, R.; Tewari, D.; Kabir, M.T.; Sajid, A.; Mathew, B.; Uddin, M.S.; Aleya, L.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Nanoparticles and its biomedical applications in health and diseases: Special focus on drug delivery. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 19151–19168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepeda-Cervantes, J.; Cruz-Reséndiz, A.; Sampieri, A.; Carreón-Nápoles, R.; Sánchez-Betancourt, J.I.; Vaca, L. Incorporation of ORF2 from Porcine Circovirus Type 2(PCV2) into genetically encoded nanoparticles as a novel vaccine using a self-aggregating peptide. Vaccine 2019, 37, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.S.; June, C.H.; Langer, R.; Mitchell, M.J. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkington, E.H.; Suys, E.J.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Wheatley, A.K.; Zukancic, D.; Algarni, A.; Al-Wassiti, H.; Davis, T.P.; Pouton, C.W.; Kent, S.J.; et al. From influenza to COVID-19: Lipid nanoparticle mRNA vaccines at the frontiers of infectious diseases. Acta Biomater. 2021, 131, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Jia, L.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Deng, J.; Zhu, A.; Ma, L.; Li, W.; et al. The nano delivery systems and applications of mRNA. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 227, 113910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehendale, R.; Joshi, M.; Patravale, V.B. Nanomedicines for treatment of viral diseases. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2013, 30, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfagih, I.M.; Aldosari, B.; AlQuadeib, B.; Almurshedi, A.; Alfagih, M.M. Nanoparticles as Adjuvants and Nanodelivery Systems for mRNA-Based Vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschmann, M.D.; Carrasco, M.J.; Alishetty, S.; Paige, M.; Alameh, M.G.; Weissman, D. Nanomaterial Delivery Systems for mRNA Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenmaker, L.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Verbeke, R.; Kersten, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J.A. mRNA-lipid nanoparticle COVID-19 vaccines: Structure and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, B.N.; Alfagih, I.M.; Almurshedi, A.S. Lipid Nanoparticles as Delivery Systems for RNA-Based Vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99 Pt A, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Jin, Y.; Chivukula, P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Clamme, J.P.; Mahato, R.I.; Ng, D.; Ying, W.; et al. Effect of PEGylation on biodistribution and gene silencing of siRNA/lipid nanoparticle complexes. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, S.; Goodarzi, N.; Doroudian, M.; Movahed, E. Potential COVID-19 therapeutic approaches targeting angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; An updated review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Lobato, M.; López-Estévez, A.M.; Cordeiro, A.S.; Dacoba, T.G.; Crecente-Campo, J.; Torres, D.; Alonso, M.J. Nanotechnologies for the delivery of biologicals: Historical perspective and current landscape. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ryu, J.H. Influenza Viruses: Innate Immunity and mRNA Vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 710647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, J.; Thwaites, R.S.; Openshaw, P.J.M. Seasonal and pandemic influenza: 100 years of progress, still much to learn. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Szutkowska, B.; Kierzek, E. Anti-Influenza Strategies Based on Nanoparticle Applications. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, J.; Lazzaro, S.; Habbeddine, M.; Schmidt, K.E.; Baumhof, P.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Madden, T.D.; Hope, M.J.; Heidenreich, R.; et al. Unmodified mRNA in LNPs constitutes a competitive technology for prophylactic vaccines. NPJ Vaccines 2017, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freyn, A.W.; Ramos da Silva, J.; Rosado, V.C.; Bliss, C.M.; Pine, M.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Madden, T.D.; de Souza Ferreira, L.C.; Weissman, D.; et al. A Multi-Targeting, Nucleoside-Modified mRNA Influenza Virus Vaccine Provides Broad Protection in Mice. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 1569–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, A.; Juranek, S.; Brossart, P. Clinical and immunological effects of mRNA vaccines in malignant diseases. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, I.; Liu, M.A.; Peden, K.; Zhou, T.; Kang, H.N. Development of mRNA Vaccines: Scientific and Regulatory Issues. Vaccines 2021, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorza, F.B.; Pardi, N. New Kids on the Block: RNA-Based Influenza Virus Vaccines. Vaccines 2018, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, J.; Moghoofei, M.; Doroudian, M.; Abiri, R. Genomic Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 during the early phase of the pandemic in Asia. Preprints 2020, 2020050100. [Google Scholar]
- Najari, S.; Doroudian, M.; Ajouri, M.R.; Omidi, B. The Importance of SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Wastewater. J. Biosaf. 2021, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi Dehbidi, M.; Goodarzi, N.; Azhdari, M.H.; Doroudian, M. Mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes to combat COVID-19. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboubi Mehrabani, M.; Karvandi, M.S.; Maafi, P.; Doroudian, M. Neurological complications associated with COVID-19; molecular mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keech, C.; Albert, G.; Cho, I.; Robertson, A.; Reed, P.; Neal, S.; Plested, J.S.; Zhu, M.; Cloney-Clark, S.; Zhou, H.; et al. Phase 1–2 Trial of a SARS-CoV-2 Recombinant Spike Protein Nanoparticle Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2320–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, S.E.; Shurin, G.V.; Yost, M.; Anderson, A.; Pinto, L.; Wells, A.; Shurin, M.R.; Martinez, M.A. Differential Antibody Response to mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines in Healthy Subjects. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0034121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igyártó, B.Z.; Jacobsen, S.; Ndeupen, S. Future considerations for the mRNA-lipid nanoparticle vaccine platform. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2021, 48, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, S.P. Review of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines: BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273. J. Pharm. Pract. 2021, 35, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliprantis, A.O.; Shaw, C.A.; Griffin, P.; Farinola, N.; Railkar, R.A.; Cao, X.; Liu, W.; Sachs, J.R.; Swenson, C.J.; Lee, H.; et al. A phase 1, randomized, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the safety and immunogenicity of an mRNA-based RSV prefusion F protein vaccine in healthy younger and older adults. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 1248–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, F.S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Yi, H.; Kang, S.M.; Bozja, J.; Moore, M.L.; Compans, R.W. Viruslike particle vaccine induces protection against respiratory syncytial virus infection in mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcandalli, J.; Fiala, B.; Ols, S.; Perotti, M.; de van der Schueren, W.; Snijder, J.; Hodge, E.; Benhaim, M.; Ravichandran, R.; Carter, L.; et al. Induction of Potent Neutralizing Antibody Responses by a Designed Protein Nanoparticle Vaccine for Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Cell 2019, 176, 1420–1431.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markoutsa, E.; McGill, A.R.; Singer, A.; Jadhav, H.; Mohapatra, S.; Mohapatra, S.S. A multifunctional nanoparticle as a prophylactic and therapeutic approach targeting respiratory syncytial virus. Nanomedicine 2021, 32, 102325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espeseth, A.S.; Cejas, P.J.; Citron, M.P.; Wang, D.; DiStefano, D.J.; Callahan, C.; Donnell, G.O.; Galli, J.D.; Swoyer, R.; Touch, S.; et al. Modified mRNA/lipid nanoparticle-based vaccines expressing respiratory syncytial virus F protein variants are immunogenic and protective in rodent models of RSV infection. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, E.J.; Kwon, Y.M.; Lee, J.S.; Hwang, H.S.; Yoo, S.E.; Lee, Y.N.; Lee, Y.T.; Kim, M.C.; Cho, M.K.; Lee, Y.R.; et al. Virus-like nanoparticle and DNA vaccination confers protection against respiratory syncytial virus by modulating innate and adaptive immune cells. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pati, R.; Shevtsov, M.; Sonawane, A. Nanoparticle Vaccines against Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaumet, M.; Vargas, A.; Gurny, R.; Delie, F. Nanoparticles for drug delivery: The need for precision in reporting particle size parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, C.; Perche, F. Design and delivery of messenger RNA-based vaccines. Biochemist 2021, 43, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Gao, M.; Li, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.Q.; Xu, X. Next-Generation Vaccines: Nanoparticle-Mediated DNA and mRNA Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2001812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Li, T. Nanoparticle-Mediated Cytoplasmic Delivery of Messenger RNA Vaccines: Challenges and Future Perspectives. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, M.; Nawaz, M.; Papadimitriou, A.; Angerfors, A.; Camponeschi, A.; Na, M.; Hölttä, M.; Skantze, P.; Johansson, S.; Sundqvist, M.; et al. Linkage between endosomal escape of LNP-mRNA and loading into EVs for transport to other cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, A.; Wickner, P.G.; Saff, R.; Stone, C.A., Jr.; Robinson, L.B.; Long, A.A.; Wolfson, A.R.; Williams, P.; Khan, D.A.; Phillips, E.; et al. mRNA Vaccines to Prevent COVID-19 Disease and Reported Allergic Reactions: Current Evidence and Suggested Approach. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maus, A.; Strait, L.; Zhu, D. Nanoparticles as delivery vehicles for antiviral therapeutic drugs. Eng. Regen. 2021, 2, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
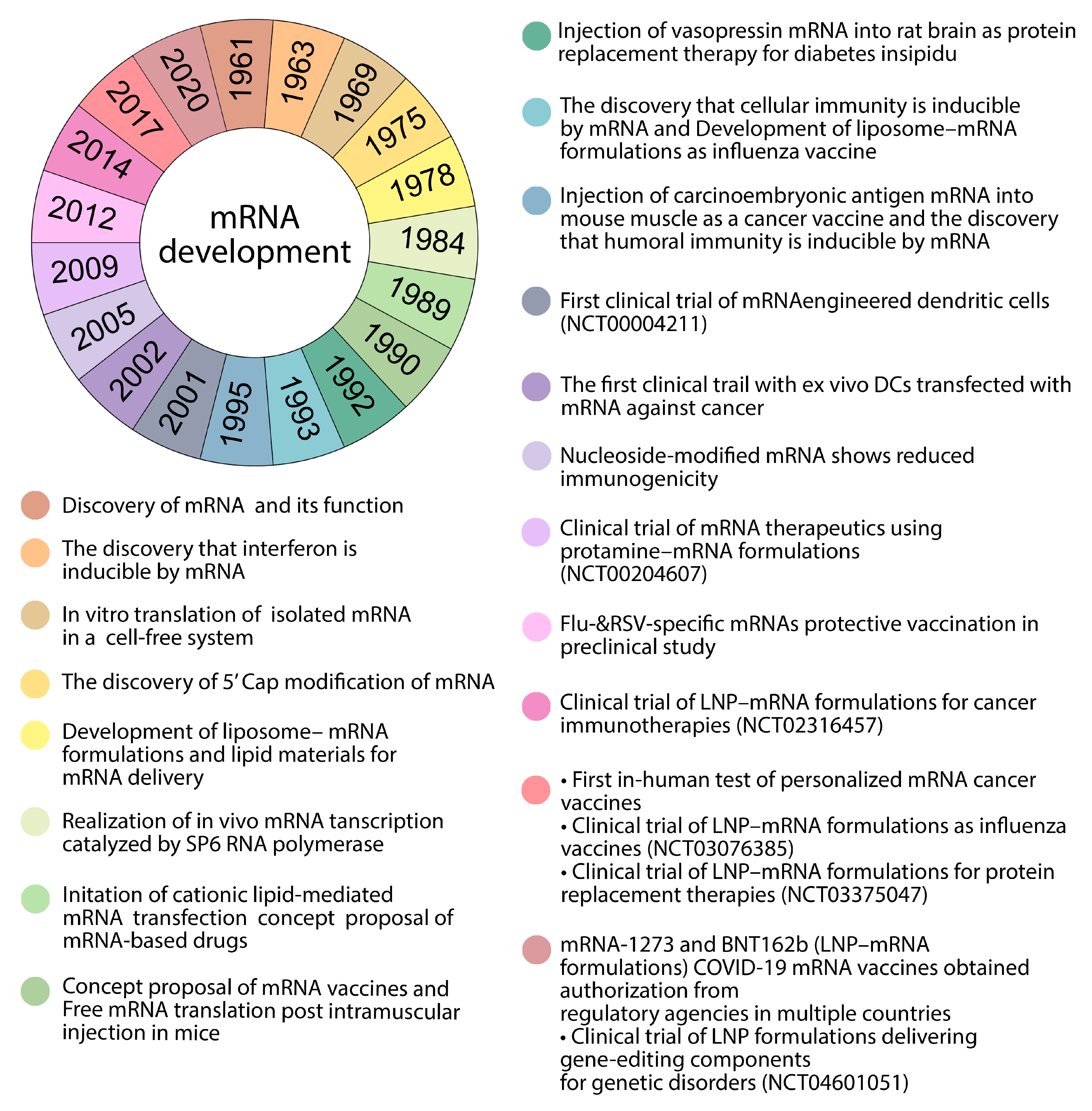
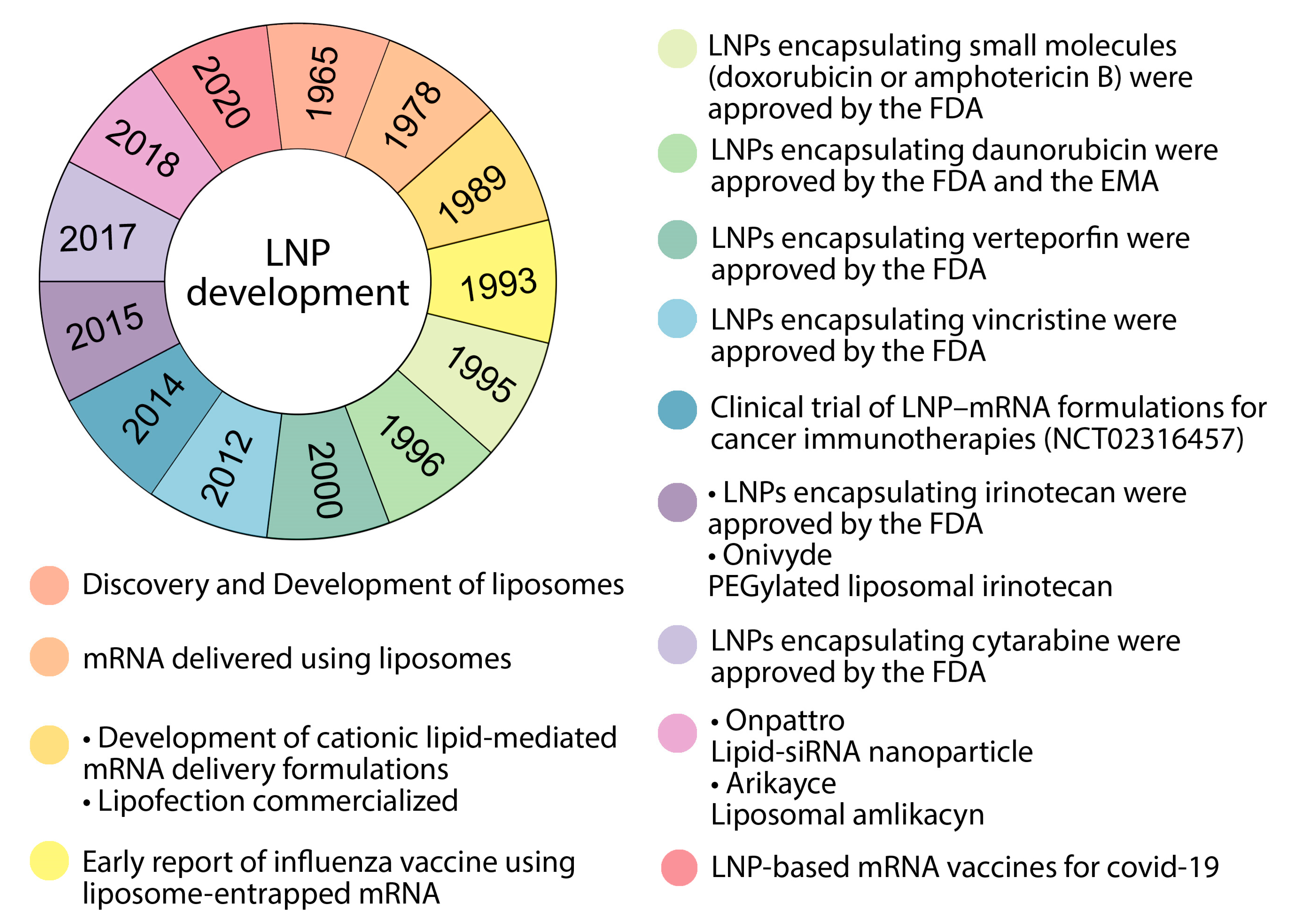


| Differences | Similarities | |
|---|---|---|
| LNP |
| Shape, particle size distribution, positive charge, lipid composition |
| Liposome |
| |
| Indication | Nanodelivery System Compositions | Route of Administration | In Vivo Model |
|---|---|---|---|
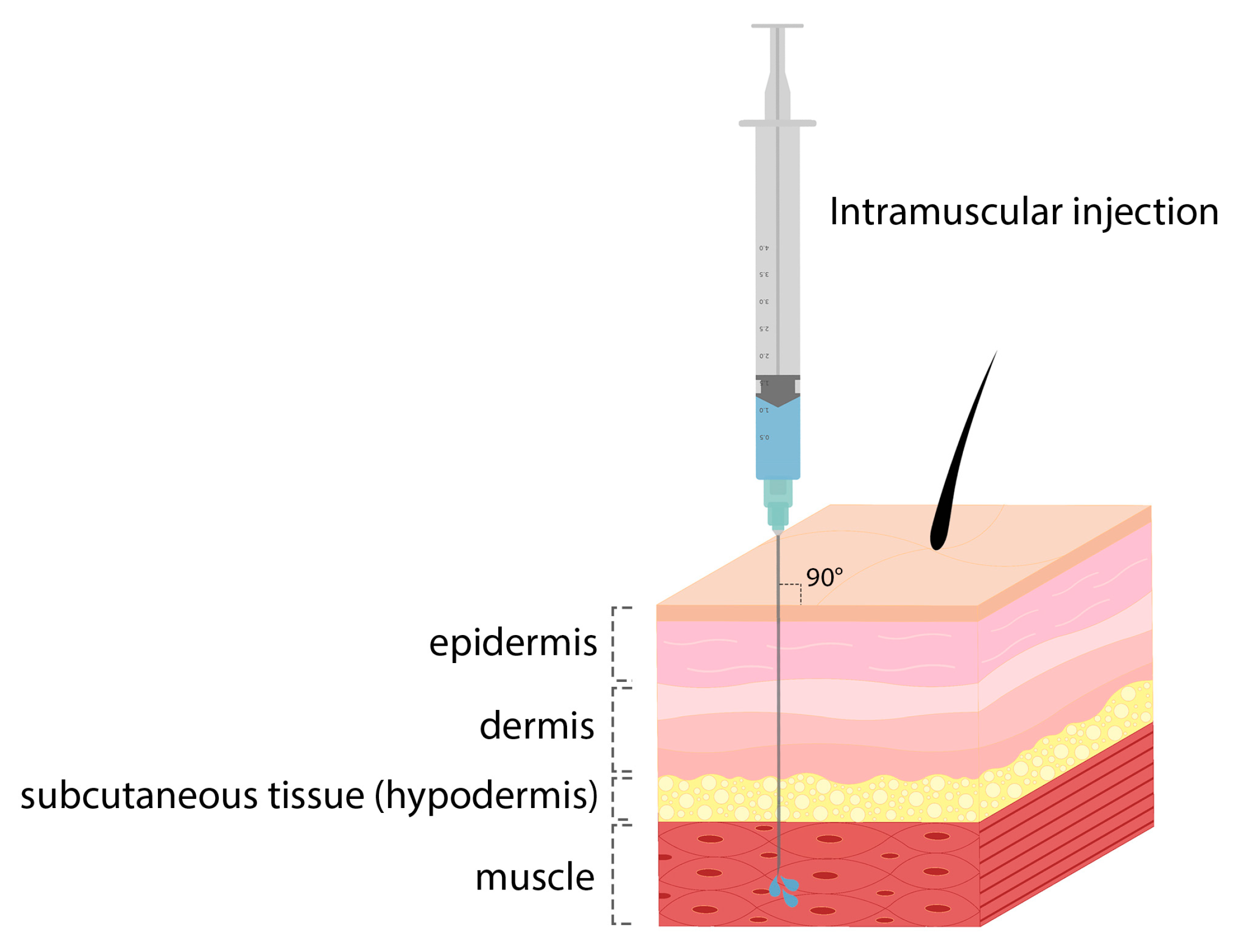
| Influenza virus | Ionizable lipid, DSPC, cholesterol, PEG lipid | Intramuscular | Rodents and NHPs |
| Influenza virus | DOTAP, DOPE, (DSPE-Mpeg2000), Mannose | Intranasal | Mice |
| COVID-19 | Ionizable lipid, DSPC, cholesterol, PEG lipid | Intramuscular | Mice and NHPs |
| Respiratory syncytial virus | Ionizable lipid, DSPC, cholesterol, PEG lipid | Intramuscular | Mice and cotton rats |
| Name | Funding Source | Disease | Encoded Antigen | Administration Route | Stage | ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA-1440 (nucleoside-modified) | Moderna Therapeutics | Influenza H10N8 | Haemagglutinin | i.m. | Phase I | NCT03076385 |
| mRNA-1851 (nucleoside-modified) | Moderna Therapeutics | Influenza H7N9 | Haemagglutinin | i.m. | Phase I | NCT03345043 |
| mRNA-1273 (perfusion-stabilized S protein mRNA vaccine) | Moderna Therapeutics/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) | COVID-19 | Spike | i.m. | Phase III | NCT04470427 |
| BNT162 (3 LNP-mRNA vaccines) | BioNTech/Pfizer | COVID-19 | Spike | i.m. | Phase III | NCT04537949 |
| BNT162b2 | Pfizer | SARS-CoV-2 | Spike | i.m. | Phase III (EUA and CMA) | NCT04368728 |
| CVnCoV | CureVac AG | SARS-CoV-2 | Spike | i.m. | Phase III | NCT04652102 |
| ARCT-021 | Arcturus Therapeutics | SARS-CoV-2 | Spike | i.m. | Phase II | NCT04728347 |
| mRNA-1345 | Moderna | RSV | F glycoprotein | i.m. | Phase I | NCT04528719 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hajiaghapour Asr, M.; Dayani, F.; Saedi Segherloo, F.; Kamedi, A.; Neill, A.O.; MacLoughlin, R.; Doroudian, M. Lipid Nanoparticles as Promising Carriers for mRNA Vaccines for Viral Lung Infections. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041127
Hajiaghapour Asr M, Dayani F, Saedi Segherloo F, Kamedi A, Neill AO, MacLoughlin R, Doroudian M. Lipid Nanoparticles as Promising Carriers for mRNA Vaccines for Viral Lung Infections. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(4):1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041127
Chicago/Turabian StyleHajiaghapour Asr, Mena, Fatemeh Dayani, Fatemeh Saedi Segherloo, Ali Kamedi, Andrew O’ Neill, Ronan MacLoughlin, and Mohammad Doroudian. 2023. "Lipid Nanoparticles as Promising Carriers for mRNA Vaccines for Viral Lung Infections" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 4: 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041127
APA StyleHajiaghapour Asr, M., Dayani, F., Saedi Segherloo, F., Kamedi, A., Neill, A. O., MacLoughlin, R., & Doroudian, M. (2023). Lipid Nanoparticles as Promising Carriers for mRNA Vaccines for Viral Lung Infections. Pharmaceutics, 15(4), 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041127









