In Situ-Forming Gels Loaded with Stimuli-Responsive Gated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Local Sustained Drug Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. General Techniques
2.3. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSNs)
2.4. Synthesis of S1 and S2
2.5. Synthesis of S3
2.6. Synthesis of In Situ-Forming Gels
2.7. Cargo Release Studies
2.8. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.9. Cell Culture Conditions
2.10. WST-1 Cell Viability Assay
2.11. Live Confocal Microscopy of Cells Treated with MSN-Loaded Gels
3. Results and Discussion
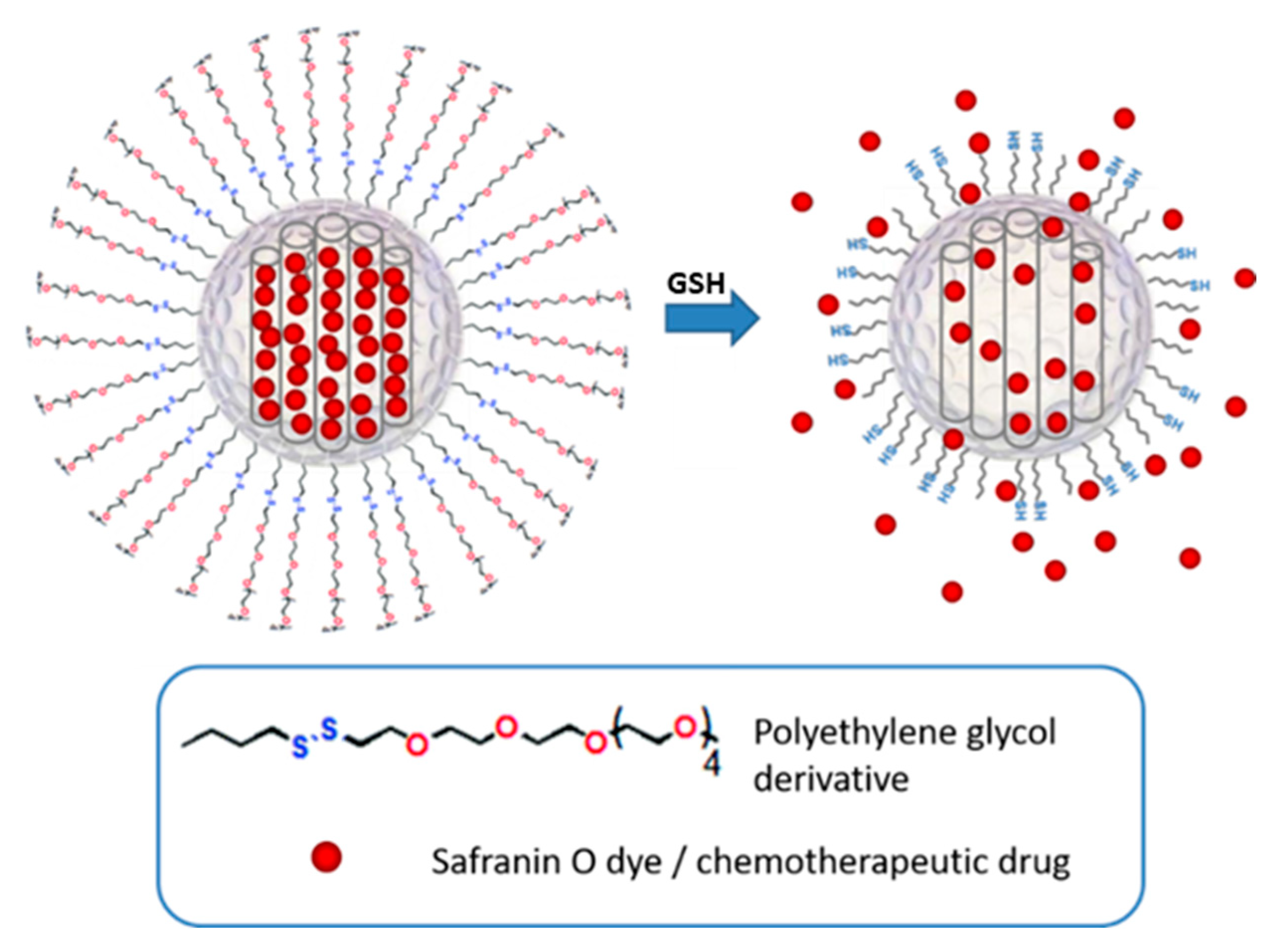
3.1. Design and Synthesis of Gated MSNs
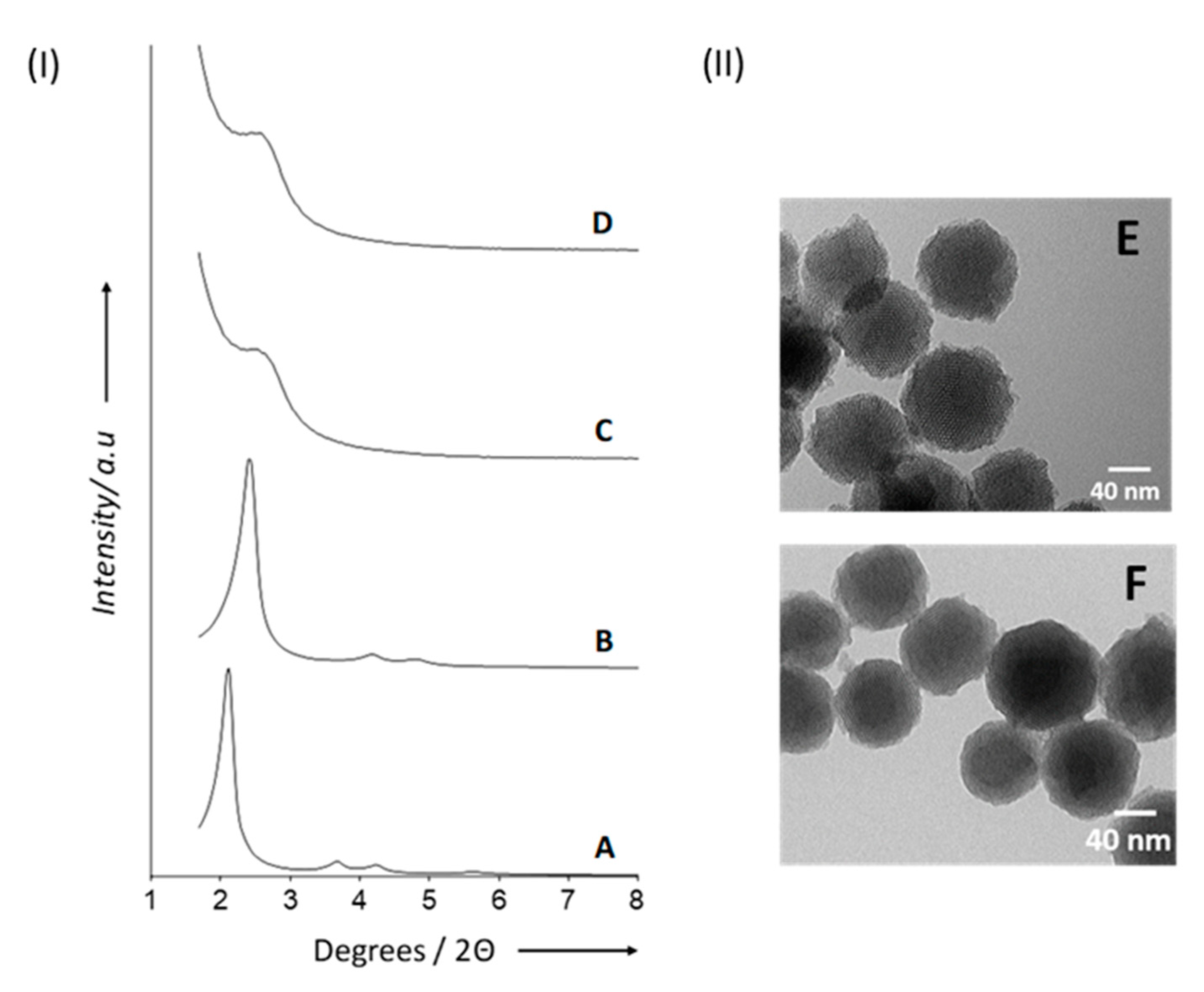
3.2. Characterization of the Materials
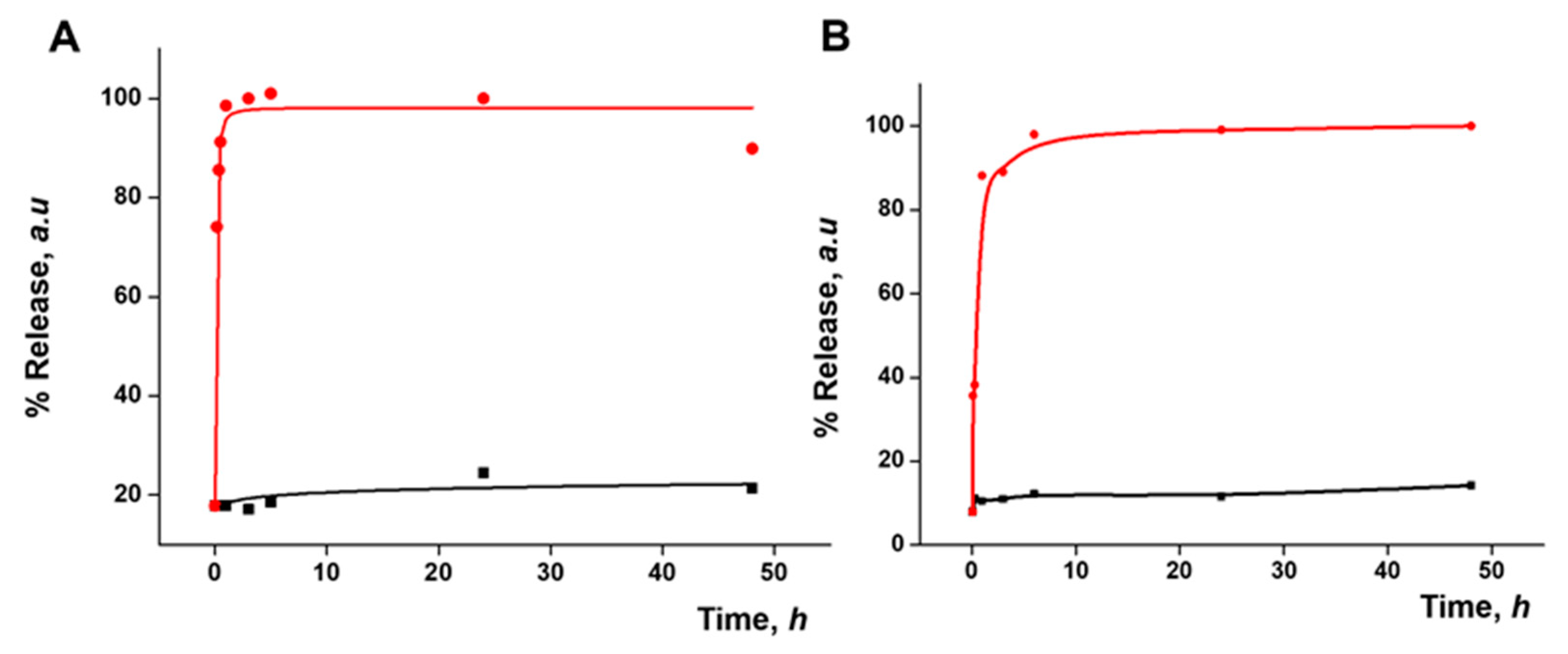
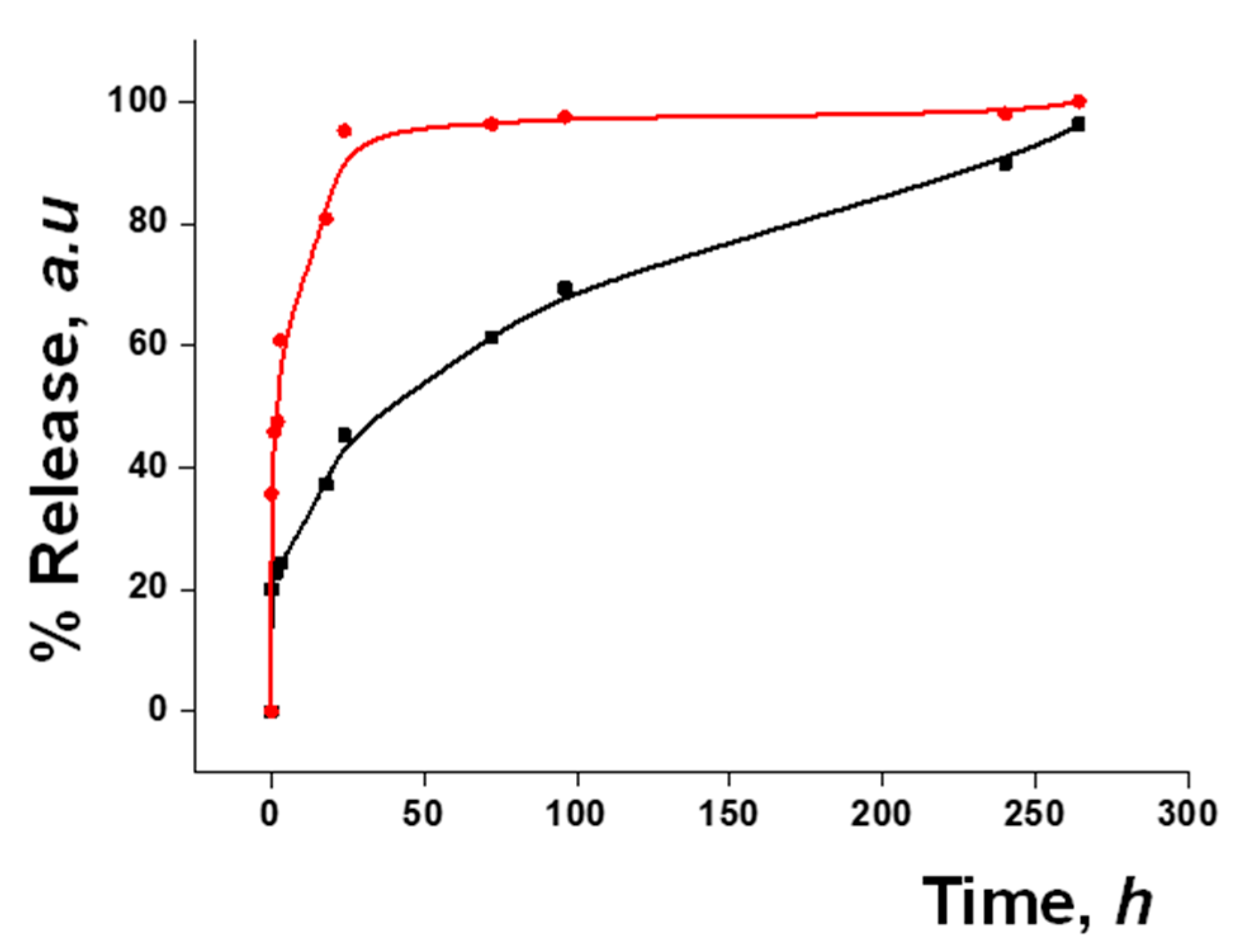
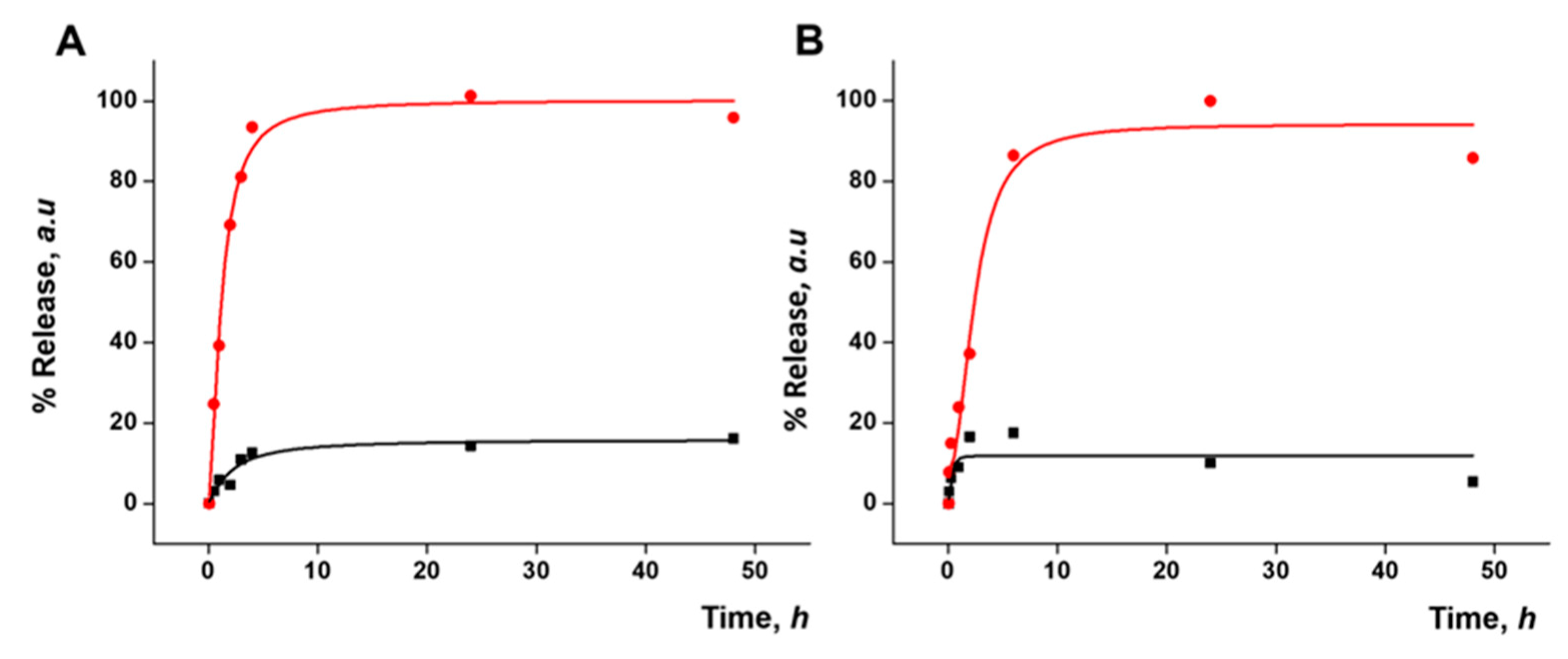
3.3. Functional Redox-Responsive Controlled Release
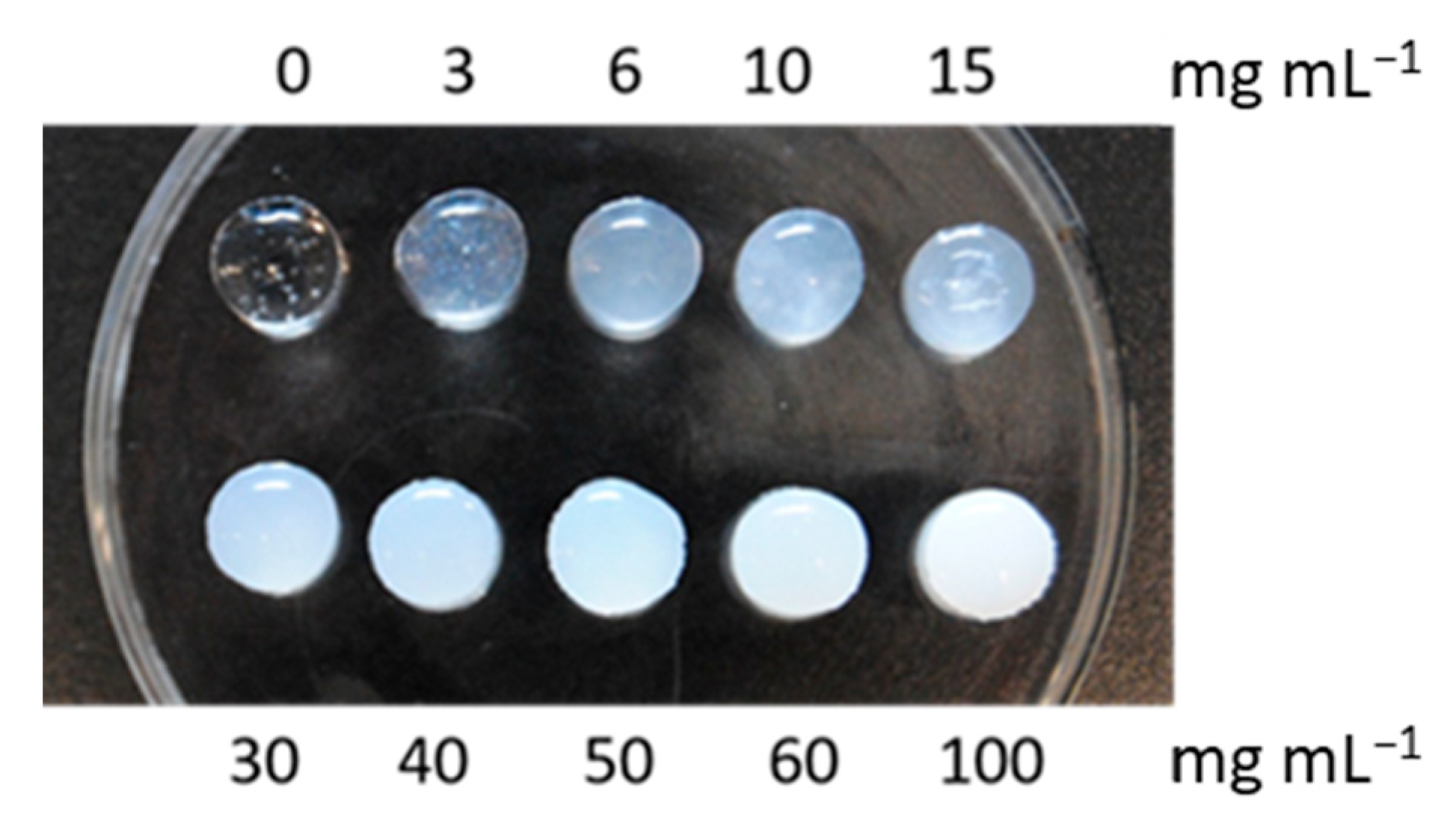
3.4. Design and Characterization of In Situ-Forming Gels
3.5. Gated Response of Nanoparticles Inside the HA Gel Matrix
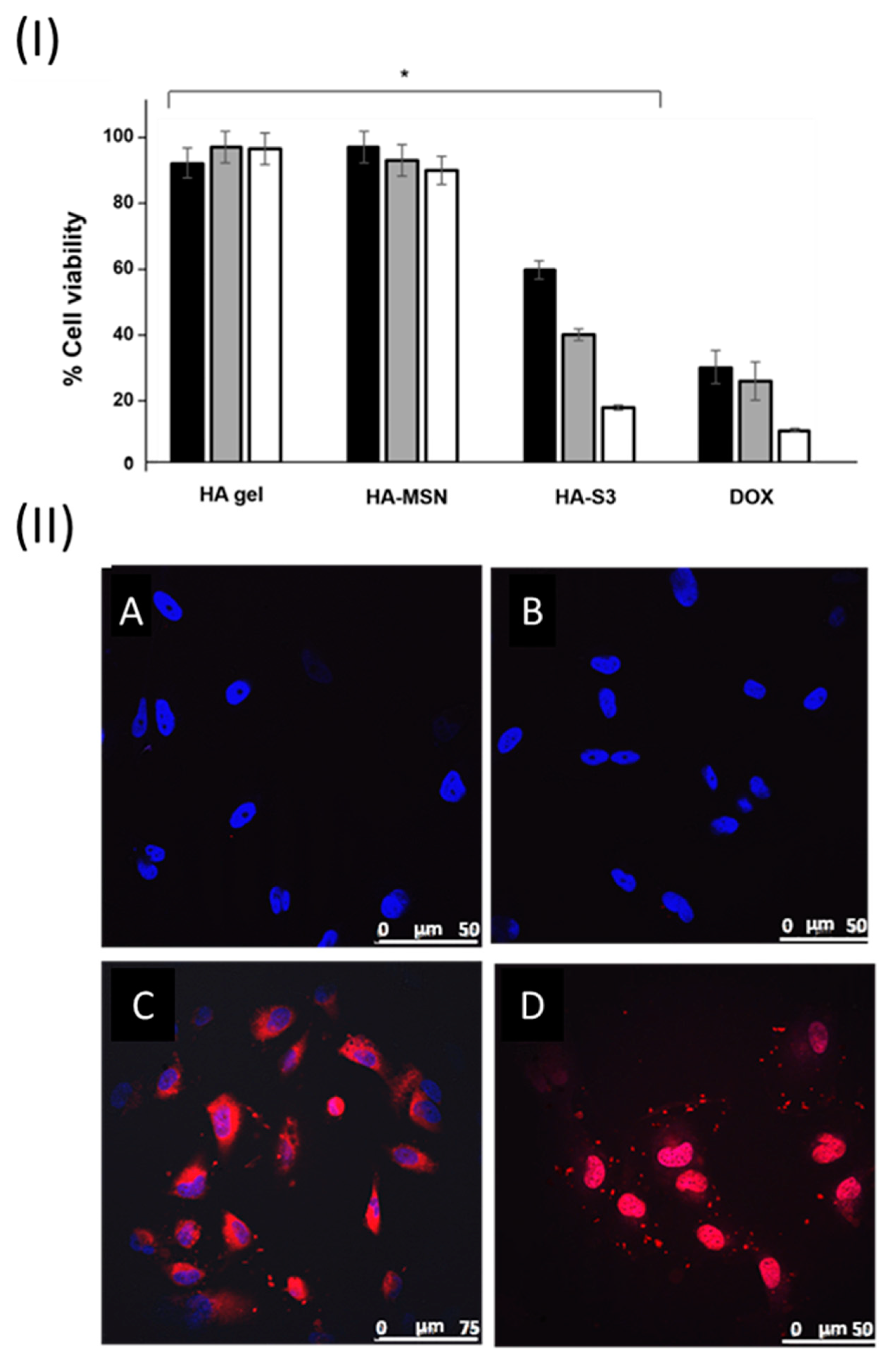
3.6. Cellular Studies
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. In Vivo bio-safety evaluations and diagnostic/therapeutic applications of chemically designed mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3144–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asefa, T.; Tao, Z. Biocompatibility of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 2265–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganath, S.H.; Kee, L.; Krantz, W.B.; Chow, P.K.-H.; Wang, C.-H. Hydrogel matrix entrapping PLGA-paclitaxel microspheres: Drug delivery with near zero-order release and implantability advantages for malignant brain tumour chemotherapy. Pharma. Res. 2009, 26, 2101–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, T.; Benny, O.; Joki, T.; Menon, L.G.; Machluf, M.; Abe, T.; Carroll, R.S.; Black, P.M. Novel local drug delivery system using thermoreversible gel in combination with polymeric microspheres or liposomes. Anticancer. Res. 2010, 30, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Wang, Q.; Shen, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Duan, Y. Thermoresponsive nanocomposite gel for local drug delivery to suppress the growth of glioma by inducing autophagy. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzione, M.; Garciulo, N.; Cauto, D.; Liguori, B.; Cerruti, P.; Amendola, E.; Lavprgna, M.; Buonocore, G.G. Peculiarities of vanillin release from amino-functionalized mesoporous silica embedded into biodegradable composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamachi, Y.; Bastakoti, B.P.; Alshehi, S.M.; Miyamoto, N.; Nakato, T.; Yamauchi, Y. Thermo-responsive hydrogels containing mesoporous silica toward controlled and sustainable releases. Mat. Lett. 2016, 168, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, C.P.; Apolinario, L.M.; Favaro, W.J.; Paula, A.J.; Duran, N. Doxorubicin-Functionalized Silica Nanoparticles Incorporated into a Thermoreversible Hydrogel and Intraperitoneally Administered Result in High Prostate Antitumor Activity and Reduced Cardiotoxicity of Doxorubicin. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J. Preparation of chitosan/mesoporous silica nanoparticle composite hydrogels for sustained co-delivery of biomacromolecules and small chemical drugs. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2013, 14, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuñiga, E.; Belmar, L.; Toledo, L.; Torres, C.; Rivas, B.L.; Sanchez, S.A.; Urbano, B.F. Rhodamine-loaded surface modified mesoporous silica particles embedded into a thermoresponsive composite hydrogel for prolonged release. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 95, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Deng, H.; Xiao, L.; Qin, C.; Du, Y.; Shi, X. A study of chitosan hydrogel with embedded mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded by ibuprofen as a dual stimuli-responsive drug release system for surface coating of titanium implants. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dong, X.; Kei, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, D.; Chen, H.; Xiao, X. Polysaccharides/mesoporous silica nanoparticles hybrid composite hydrogel beads for sustained drug delivery. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 3095–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, N.K.; Fujiwara, M.; Tanaka, Y. Photocontrolled reversible release of guest molecules from coumarin-modified mesoporous si. Nature 2003, 421, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza, A.; Guisasola, E.; Ruiz-Hernandez, E.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetically Triggered Multidrug Release by Hybrid Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermayer, S.; Weiss, V.; Hermann, A.; Schmidt, A.; Datz, S.; Müller, K.; Wagner, E.; Bein, T.; Bräuchle, C. Multifunctional polymer-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7953–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Guo, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Gan, Y. Biofunctionalized polymer-lipid supported mesoporous silica nanoparticles for release of chemotherapeutics in multidrug resistant cancer cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3650–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardos, A.; Aznar, E.; Coll, C.; Martínez-Mañez, R.; Barat, J.M.; Marcos, M.D.; Sancenón, F.; Benito, A.; Soto, J. Controlled release of vitamin B2 using mesoporous materials functionalized with amine-bearing gate-like scaffoldings. J. Control. Release 2008, 131, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Liu, F.; Shao, Q.; Min, Y.Z.; Costa, M.; Yeow, E.K.L.; Xing, B.G. Drug Delivery: Enzyme-Responsive Cell-Penetrating Peptide Conjugated Mesoporous Silica Quantum Dot Nanocarriers for Controlled Release of Nucleus-Targeted Drug Molecules and Real-Time Intracellular Fluorescence Imaging of Tumor Cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardos, A.; Mondragón, L.; Aznar, E.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Soto, J.; Barat, J.M.; Pérez-Payá, E.; Guillem, C.; et al. Enzyme-Responsive Intracellular Controlled Release Using Nanometric Silica Mesoporous Supports Capped with “Saccharides”. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6353–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Cheng, F.; Zhou, R.; Cao, J.; Li, J.; Burda, C.; Min, Q.; Zhu, J.-J. DNA-Hybrid-Gated Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers for Dual-Targeted and MicroRNA-Responsive Controlled Drug Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2371–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, J.A.; O’Malley, W.; Kubeil, M.; Graham, B.; Stephan, H.; Spiccia, L. Nanomaterials: Applications in cancer imaging and therapy. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, H18–H40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, W.J. Nanoparticles in Biological Systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1242–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Barnes, J.C.; Bosoy, A.; Stoddart, J.F.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2590–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doane, T.L.; Burda, C. The unique role of nanoparticles in nanomedicine: Imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2885–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, P.-Z.; Nguyen, K.T.; Wang, X.-J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tan, N.S.; Zhao, Y. Biocompatible, Uniform, and Redispersible Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer-Targeted Drug Delivery In Vivo. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2450–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; Cai, K. Redox-Responsive Nanocarrier Based on Heparin End-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Tumor Therapy in Vitro and in Vivo. Langmuir 2014, 30, 7867–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Karambelkar, A.; Gu, L.; Lin, K.; Miller, J.S.; Chen, C.S.; Sailor, M.J.; Bhatia, S.N. Bioresponsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Triggered Drug Release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19582–19585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Mai, W.X.; Zhang, H.; Xue, M.; Xia, T.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zink, J.I.; et al. Codelivery of an Optimal Drug/siRNA Combination Using Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles to Overcome Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer In Vitro and in Vivo. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.-Y.; Trewyn, B.G.; Jeftinija, D.M.; Jeftinija, K.; Xu, S.; Jeftinija, S.; Lin, V.S.-Y. A Mesoporous Silica Nanosphere-Based Carrier System with Chemically Removable CdS Nanoparticle Caps for Stimuli-Responsive Controlled Release of Neurotransmitters and Drug Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4451–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, C.; Mondragón, L.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Marcos, M.D.; Soto, J.; Amorós, P.; Pérez-Payá, E. Enzyme-Mediated Controlled Release Systems by Anchoring Peptide Sequences on Mesoporous Silica Supports. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2138–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, C.; De La Torre, C.; Gorbe, M.; Aznar, E.; Sancenón, F.; Murguía, J.R.; Martinez-Mañez, R.; Marcos, M.D.; Amoros, P. Gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the controlled delivery of drugs in cancer cells. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3753–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Narayanan, K.; Lee, F.; Hyun Bae, K.; Gao, S.; Kurisawa, M. Enzyme-mediated hyaluronic acid-tyramine hydrogels for the propagation of human embryonic stem cells in 3D. Acta Biomater. 2015, 24, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Noriega, A.; Hastings, C.L.; Ozbakir, B.; O Donnell, K.E.; O Brien, F.J.; Storm, G.; Hennink, W.E.; Duffy, G.P.; Ruiz-Hernández, E. Hyperthermia-induced drug delivery from thermosensitive liposomes encapsulated in an injectable hydrogel for local chemotherapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Miller, L.M.; Di Pasqua, A.J. Biocompatibility of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles? Comments Inorg. Chem. 2016, 36, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, L.; Sandhu, J.K.; Harper, M.-E.; Cuperlovic-Culf, M. Role of Glutathione in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Therapies. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorna, C.F.; Oshiroa, C.; Marshe, S.; Hernandez-Boussardb, T.; McLeodd, H.; Kleina, T.E.; Altmana, R.B. Doxorubicin pathways: Pharmacodynamics and adverse effects. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2011, 21, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z. Thermo-sensitive hydrogels for delivering biotherapeutic molecules: A review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Tong, J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Y.; Tian, M. Recent advances in thermo-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2979–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghauri, Z.H.; Islam, A.; Qadir, M.A.; Gull, N.; Haider, B.; Khan, R.U.; Riaz, T. Development and evaluation of pH-sensitive biodegradable ternary blended hydrogel films (chitosan/guar gum/PVP) for drug delivery application. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Qiu, L.; Sheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Deng, L.; Li, X.; Bradley, M.; Zhang, R. Biodegradable pH-responsive hydrogels for controlled dual-drug release. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, H.R.; Clegg, J.R.; Peppas, N.A. Analyte-Responsive Hydrogels: Intelligent Materials for Biosensing and Drug Delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; An, Q.; Tong, W.; Li, H.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhang, Y. A new way to promote molecular drug release during medical treatment: A polyelectrolyte matrix on a piezoelectric-dielectric energy conversion substrate. Small 2018, 14, 1802136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shergalis, A.; Bankhead, A.; Luesakul, U.; Muangsin, N.; Neamati, N. Current Challenges and Opportunities in Treating Glioblastoma. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 412–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Solid | SBET (m2 g−1) | Total Pore Volume 1 (cm3 g−1) | Pore Size 1,2 (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSNs | 919.62 | 0.91 | 3.22 |
| S1 | 475.18 | 0.43 | - |
| S2 | 102.01 | 0.24 | - |
| Solid | αSaf O (mmol g−1 SiO2) | αDOX (mmol g−1 SiO2) | αPEG (mmol g−1 SiO2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S2 | 0.24 | - | 0.49 |
| S3 | - | 0.21 | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de la Torre, C.; Coll, C.; Ultimo, A.; Sancenón, F.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Ruiz-Hernández, E. In Situ-Forming Gels Loaded with Stimuli-Responsive Gated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Local Sustained Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041071
de la Torre C, Coll C, Ultimo A, Sancenón F, Martínez-Máñez R, Ruiz-Hernández E. In Situ-Forming Gels Loaded with Stimuli-Responsive Gated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Local Sustained Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(4):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041071
Chicago/Turabian Stylede la Torre, Cristina, Carmen Coll, Amelia Ultimo, Félix Sancenón, Ramón Martínez-Máñez, and Eduardo Ruiz-Hernández. 2023. "In Situ-Forming Gels Loaded with Stimuli-Responsive Gated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Local Sustained Drug Delivery" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 4: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041071
APA Stylede la Torre, C., Coll, C., Ultimo, A., Sancenón, F., Martínez-Máñez, R., & Ruiz-Hernández, E. (2023). In Situ-Forming Gels Loaded with Stimuli-Responsive Gated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Local Sustained Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 15(4), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041071






