Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles for Topical Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Deproteinized Natural Rubber Latex
2.2. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles
2.3. Preparation of Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles
2.4. Determination of the Content of Silver Nanoparticles in Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film
2.5. Surface pH
2.6. Mechanical Properties
2.7. Swelling Ratio and Erosion
2.8. Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis
2.10. X-ray Diffraction
2.11. In Vitro Release of Silver Nanoparticles from Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film
2.12. In Vitro Skin Permeation of Silver Nanoparticles from Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film
2.13. Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation
2.14. Statistic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of the Content of Silver Nanoparticles in Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film
3.2. Surface pH
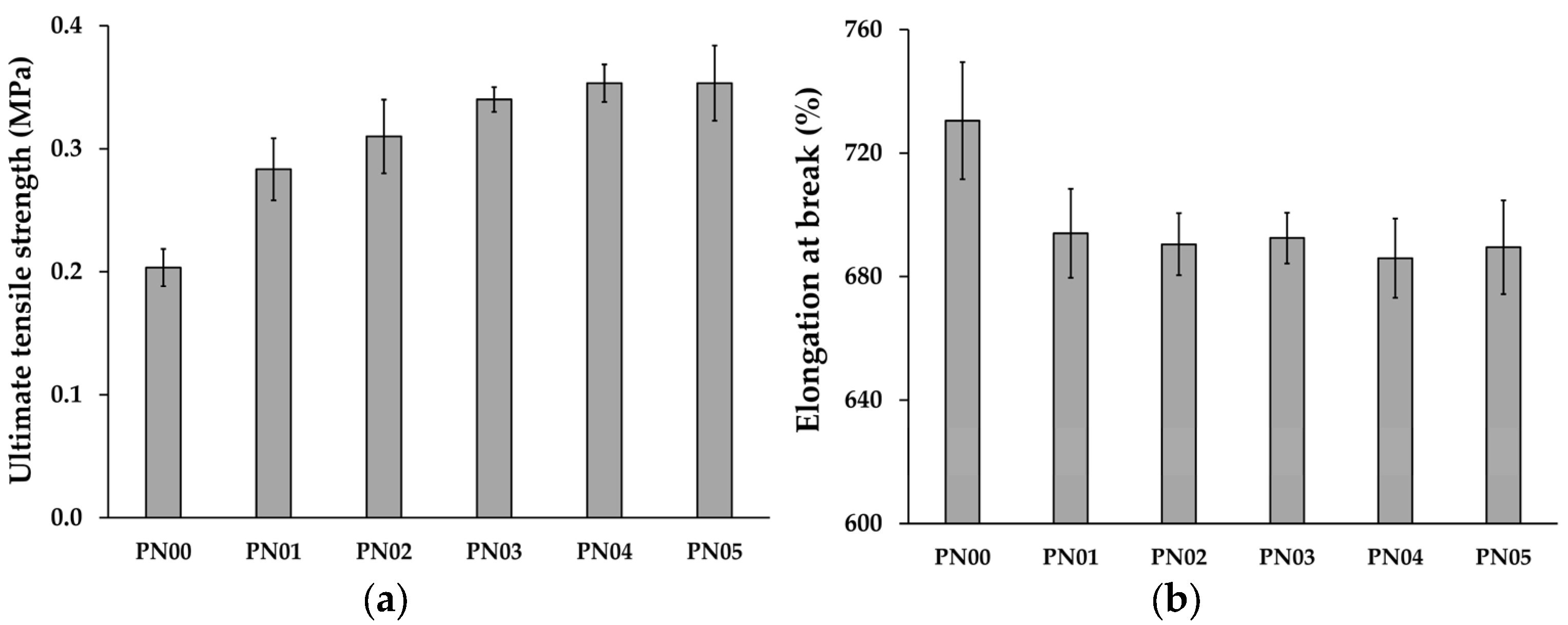
3.3. Mechanical Properties
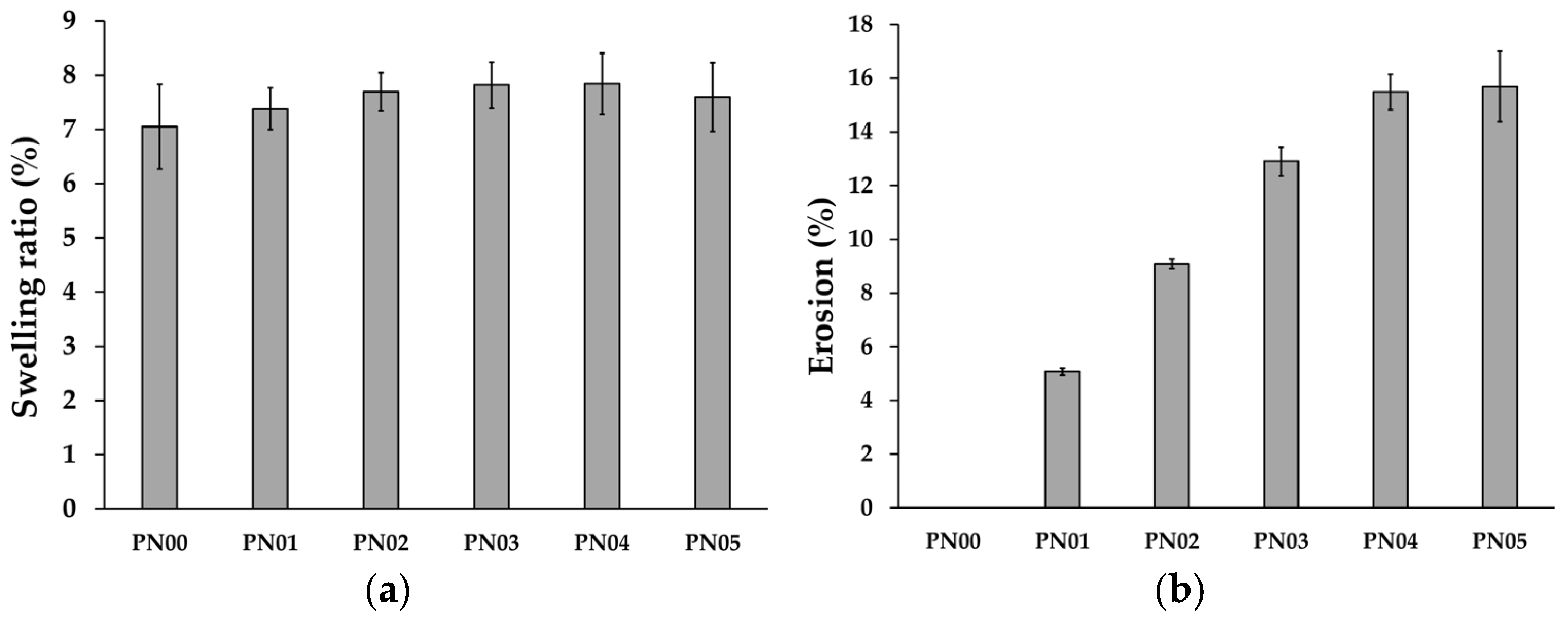
3.4. Swelling Ratio and Erosion
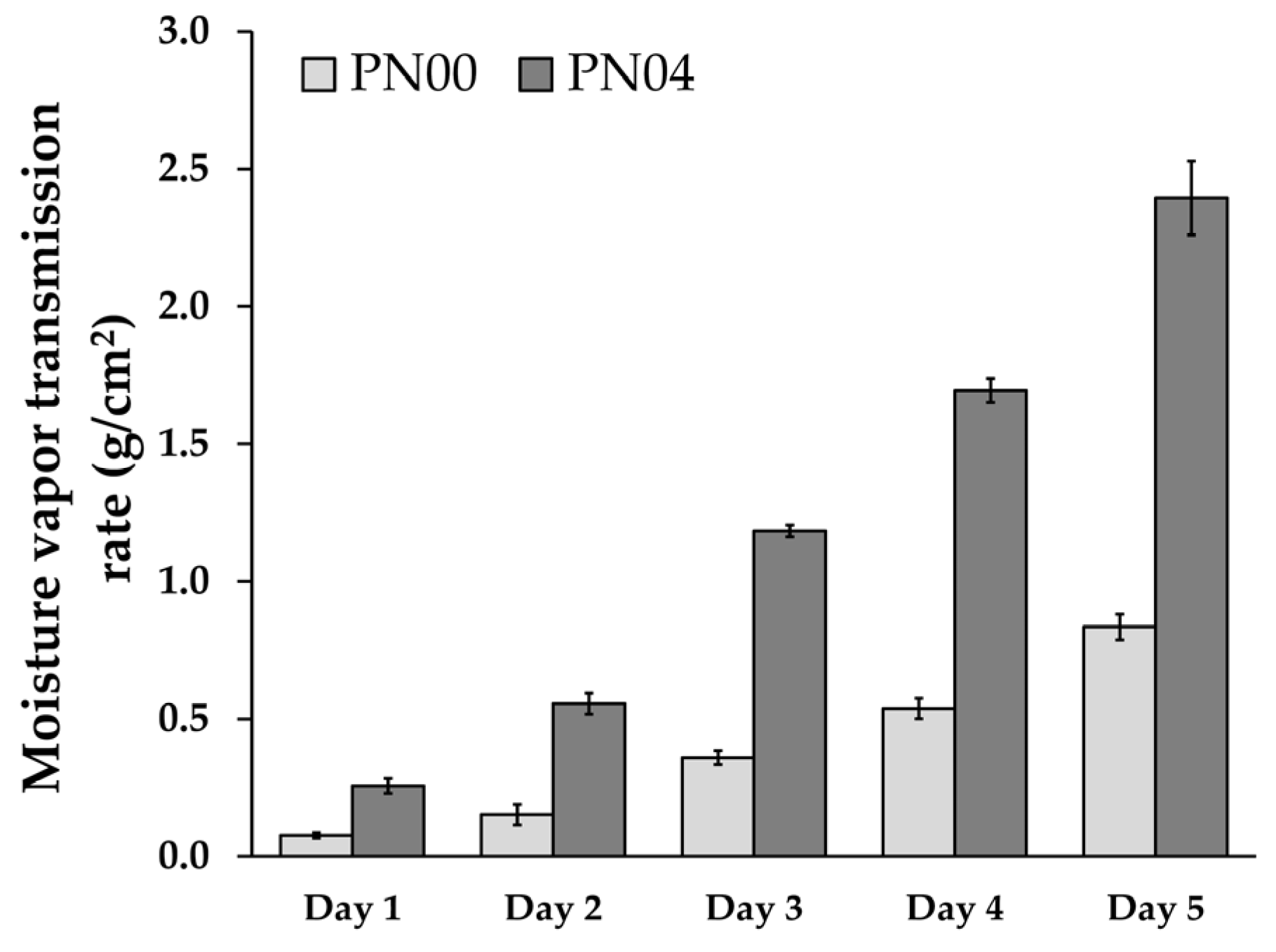
3.5. Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate
3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis
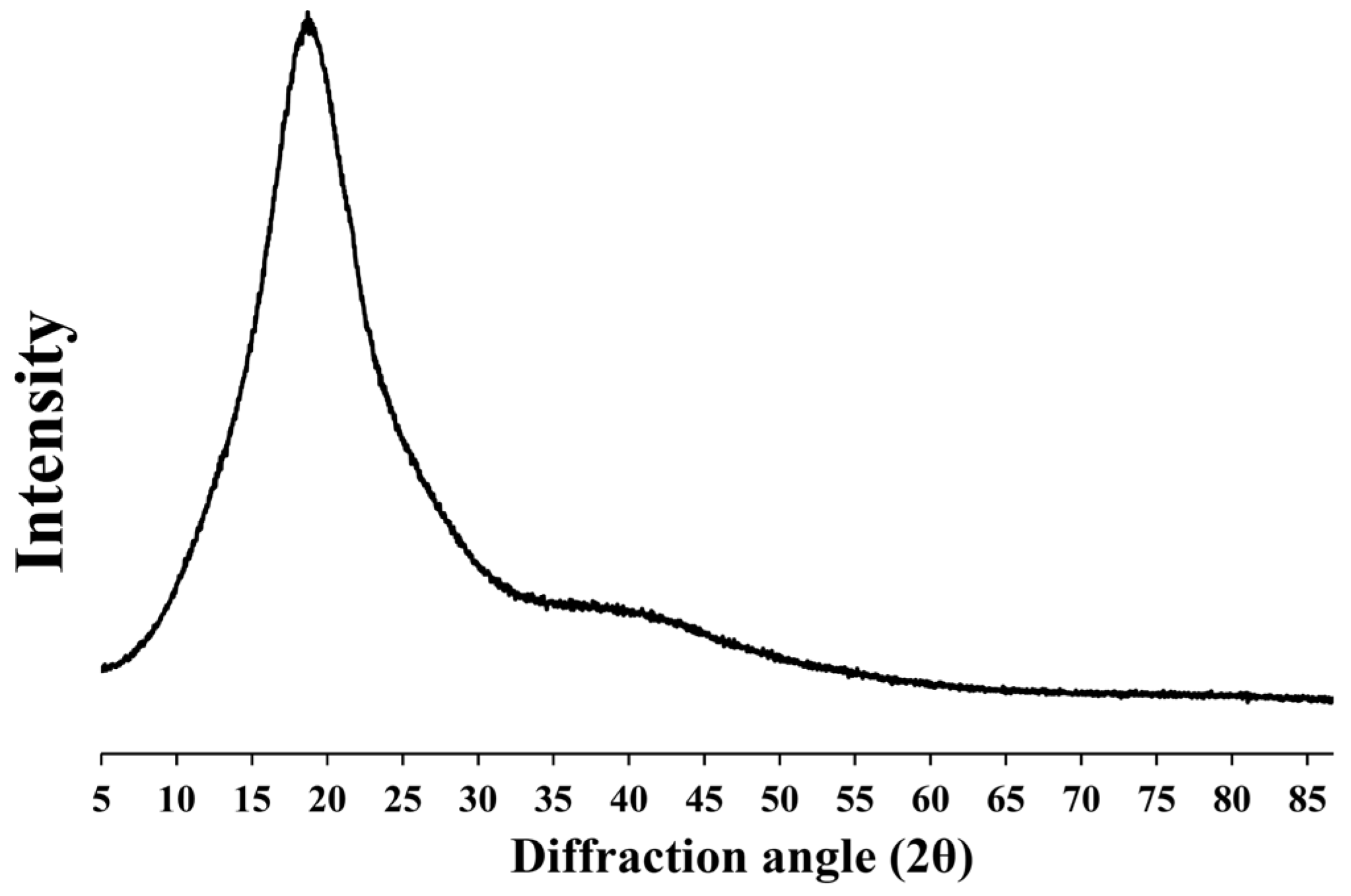
3.7. X-ray Diffraction
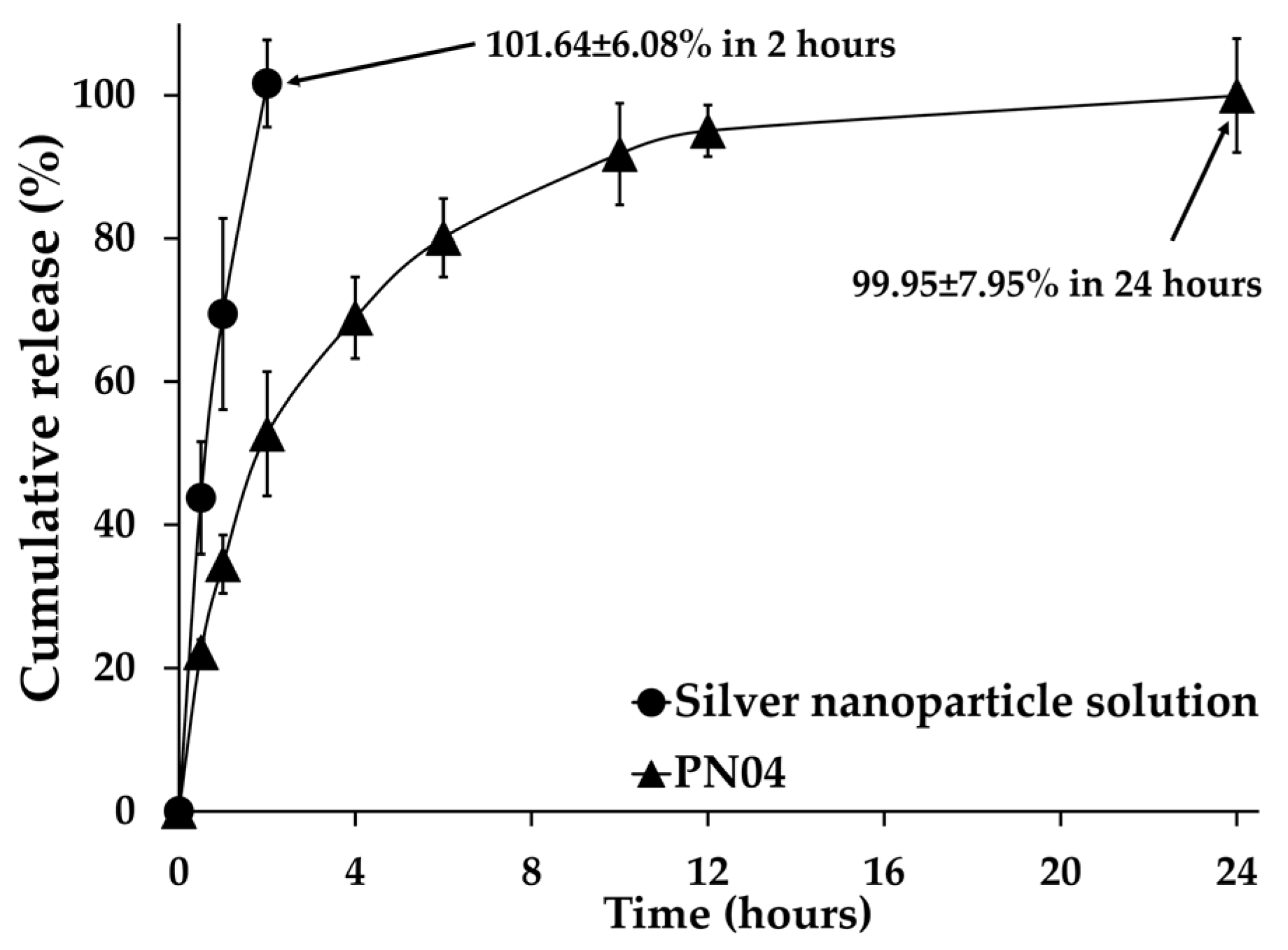
3.8. In Vitro Release of Silver Nanoparticles from Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film
3.9. In Vitro Skin Permeation of Silver Nanoparticles from Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film
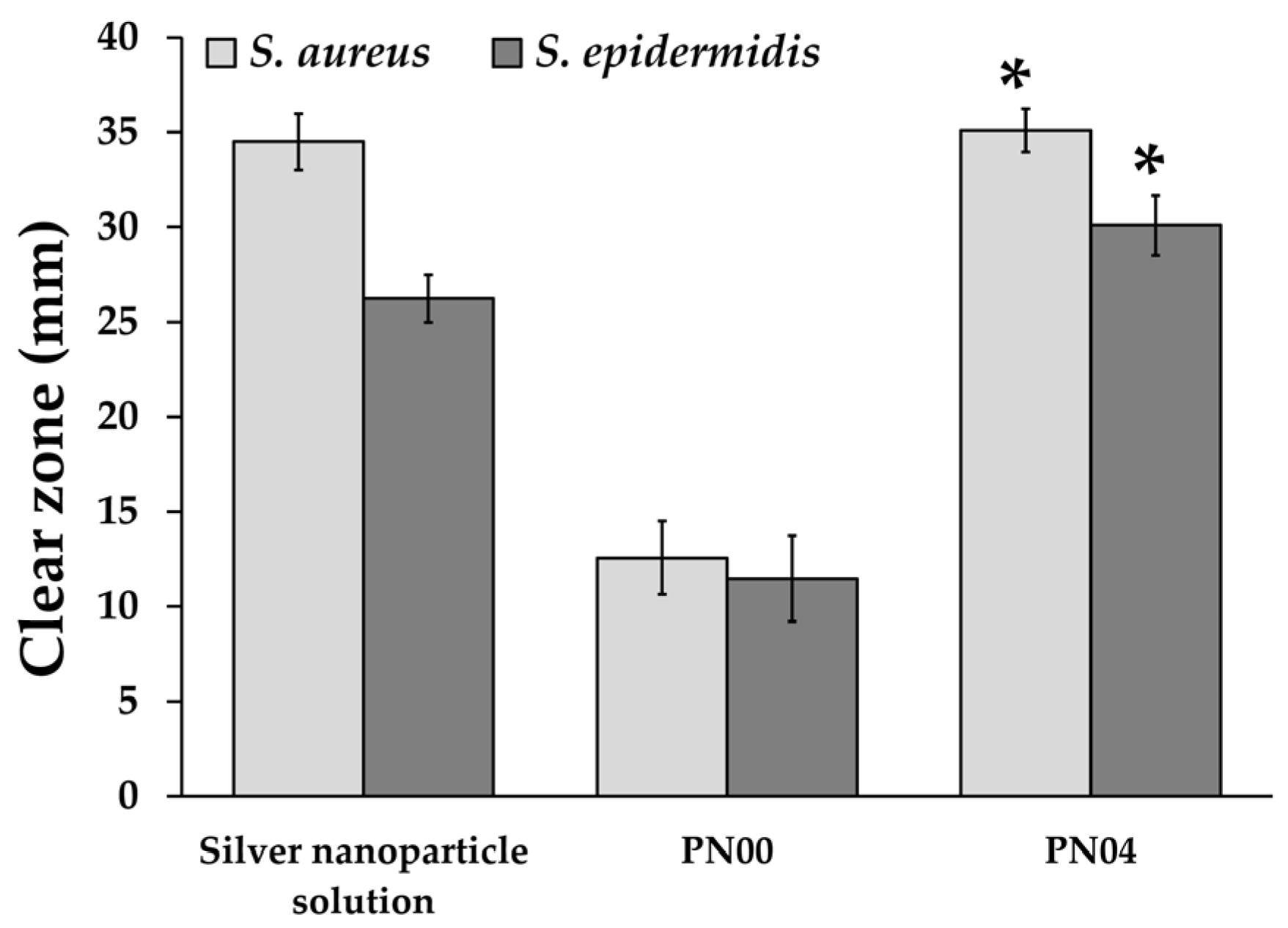
3.10. Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Zhu, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles of different particle size against Vibrio Natriegens. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvekar, P.; Palaskar, J.; Metgud, S.; Maria, R.; Dutta, S. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of silver nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus. Biomater. Investig. Dent. 2020, 7, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodoth, A.K.; Ghate, V.M.; Lewis, S.A.; Prakash, B.; Badalamoole, V. Pectin-based silver nanocomposite film for transdermal delivery of donepezil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneewattanapinyo, P.; Monton, C.; Pichayakorn, W.; Dangmanee, N.; Wunnakup, T.; Suksaeree, J. Plaster gel loaded with silver nanoparticle-mediated Ganoderma applanatum: From fabrication to evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maneewattanapinyo, P.; Pichayakorn, W.; Monton, C.; Dangmanee, N.; Wunnakup, T.; Suksaeree, J. Effect of ionic liquid on silver-nanoparticle-complexed Ganoderma applanatum and its topical film formulation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suksaeree, J.; Thuengernthong, A.; Pongpichayasiri, K.; Maneewattanapinyo, P.; Settharaksa, S.; Pichayakorn, W. Formulation and evaluation of matrix type transdermal patch containing silver nanoparticles. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 4369–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, D.; Ahmed, M.R.; Gomathi, K.; Chitra, K.; Sehgal, P.K.; Jayakumar, R. Dermal wound healing processes with curcumin incorporated collagen films. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoksan, R.; Chirachanchai, S. Silver nanoparticle-loaded chitosan–starch based films: Fabrication and evaluation of tensile, barrier and antimicrobial properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigurupati, S.; Mughal, M.R.; Okun, E.; Das, S.; Kumar, A.; McCaffery, M.; Seal, S.; Mattson, M.P. Effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles on the growth of keratinocytes, fibroblasts and vascular endothelial cells in cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2194–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, W.; Harrison, J. An Evaluation of Wound Healing Efficacy of a Film Dressing Made from Polymer-integrated Amnion Membrane. Organogenesis 2020, 16, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, N.B.; Sant’Ana Pegorin, G.; Boratto, M.H.; de Barros, N.R.; de Oliveira Graeff, C.F.; Herculano, R.D. Biomedical applications of natural rubber latex from the rubber tree Hevea brasiliensis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 126, 112126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banpean, A.; Paradee, N.; Sirivat, A.; Niamlang, S. Deproteinized natural rubber as an electrically controllable, transdermal drug-delivery patch. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3745–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayadevan, J.; Unnikrishnan, G. Novel membranes from physico-chemically modified deproteinized natural rubber latex: Development, characterisation and drug permeation. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 14179–14187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayadevan, J.; Alex, R.; Gopalakrishnapanicker, U. Deproteinised natural rubber latex grafted poly(dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate)–poly(vinyl alcohol) blend membranes: Synthesis, properties and application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1821–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suksaeree, J.; Bumroongrat, C.; Polraksa, N.; Taweepreda, W.; Phaechamud, T.; Pichayakorn, W. Deproteinization of natural rubber latex and its pale-colored thin films. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichayakorn, W.; Suksaeree, J.; Taweepreda, W. Improved deproteinization process for protein-free natural rubber latex. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 844, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichayakorn, W.; Suksaeree, J.; Boonme, P.; Taweepreda, W.; Ritthidej, G.C. Preparation of deproteinized natural rubber latex and properties of films formed by itself and several adhesive polymer blends. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 13393–13404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monton, C.; Sampaopan, Y.; Pichayakorn, W.; Panrat, K.; Suksaeree, J. Herbal transdermal patches made from optimized polyvinyl alcohol blended film: Herbal extraction process, film properties, and in vitro study. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 69, 103170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Manjón, A.; Chichkov, B.N.; Barcikowski, S. Influence of water temperature on the hydrodynamic diameter of gold nanoparticles from laser ablation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 2499–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmudin, L.; Suharyadi, E.; Utomo, A.B.S.; Abraha, K. Optical properties of silver nanoparticles for surface plasmon resonance (SPR)-based biosensor applications. J. Mod. Phys. 2015, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanpui, P.; Murugadoss, A.; Prasad, P.V.D.; Ghosh, S.S.; Chattopadhyay, A. The antibacterial properties of a novel chitosan–Ag-nanoparticle composite. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 124, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Lu, T.; Zhang, P.; Jing, X. Preparation and antibacterial effects of PVA-PVP hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-F.; Tsao, K.-T. Preparation and properties of nanocomposite hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles by ex situ polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 3653–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid-Wendtner, M.-H.; Korting, H.C. The pH of the skin surface and its impact on the barrier function. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 19, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukić, M.; Pantelić, I.; Savić, S.D. Towards optimal pH of the skin and topical formulations: From the current state of the art to tailored products. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias Murbach, H.; Jaques Ogawa, G.; Azevedo Borges, F.; Romeiro Miranda, M.C.; Lopes, R.; Roberto de Barros, N.; Guedes Mazalli, A.V.; Gonçalves da Silva, R.; Ferreira Cinman, J.L.; de Camargo Drago, B.; et al. Ciprofloxacin release using natural rubber latex membranes as carrier. Int. J. Biomat. 2014, 2014, 157952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimala, K.; Mohan, Y.M.; Sivudu, K.S.; Varaprasad, K.; Ravindra, S.; Reddy, N.N.; Padma, Y.; Sreedhar, B.; MohanaRaju, K. Fabrication of porous chitosan films impregnated with silver nanoparticles: A facile approach for superior antibacterial application. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saijun, D.; Nakason, C.; Kaesaman, A.; Klinpituksa, P. Water absorption and mechanical properties of water-swellable natural rubber. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2009, 31, 561. [Google Scholar]
- de Barros, N.R.; Miranda, M.C.R.; Borges, F.A.; de Mendonça, R.J.; Cilli, E.M.; Herculano, R.D. Oxytocin sustained release using natural rubber latex membranes. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2016, 22, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesar, M.B.; Borges, F.A.; Bilck, A.P.; Yamashita, F.; Paulino, C.G.; Herculano, R.D. Development and characterization of natural rubber latex and polylactic acid membranes for biomedical application. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Kao, W.J. Drug release kinetics and transport mechanisms of non-degradable and degradable polymeric delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejnik, A.; Kapuscinska, A.; Schroeder, G.; Nowak, I. Physico-chemical characterization of formulations containing endomorphin-2 derivatives. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 1719–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, S.; Murawala, P.; Shiras, A.; Pokharkar, V.; Prasad, B.L.V. Gellan gum capped silver nanoparticle dispersions and hydrogels: Cytotoxicity and in vitro diffusion studies. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal drug delivery: Innovative pharmaceutical developments based on disruption of the barrier properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larese, F.F.; D’Agostin, F.; Crosera, M.; Adami, G.; Renzi, N.; Bovenzi, M.; Maina, G. Human skin penetration of silver nanoparticles through intact and damaged skin. Toxicology 2009, 255, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroli, B.; Ennas, M.G.; Loffredo, F.; Isola, M.; Pinna, R.; Arturo López-Quintela, M. Penetration of metallic nanoparticles in human full-thickness skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; He, J.; Xue, J.; Ding, W. Efficient fabrication of transparent antimicrobial poly(vinyl alcohol) thin films. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, D.; Momin, B.; Palamthodi, S.; Lele, S.S. Physicochemical and functional properties of chitosan-based nano-composite films incorporated with biogenic silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; He, H.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, P.; Xie, J.; Lu, Z. Controllable in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles on multilayered film-coated silk fibers for antibacterial application. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 461, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, L.M.; Phillips, T.J. Wound healing update. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2012, 31, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Code | Concentration of Silver Nanoparticle Solution (ppm) | Length of Immersion (Hours) | Content of Silver Nanoparticles in Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film (µg/cm2) | Surface pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PN00 | - | - | - | 7.22 ± 0.06 |
| PN01 | 1000 | 24 | 7.25 ± 0.88 † | 7.04 ± 0.06 |
| PN02 | 2000 | 24 | 12.03 ± 0.86 † | 7.02 ± 0.04 |
| PN03 | 3000 | 24 | 16.97 ± 0.65 † | 7.00 ± 0.09 |
| PN04 | 3000 | 48 | 20.81 ± 0.97 † | 7.02 ± 0.06 |
| PN05 | 3000 | 72 | 21.03 ± 0.72 ‡ | 7.04 ± 0.13 |
| R2 | n | Release Rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Order | First Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer–Peppas | ||
| Silver nanoparticle solution | 0.9616 | 0.9844 | 0.9888 | - | 69.752 ± 6.083 * |
| Porous deproteinized natural rubber film loaded with silver nanoparticles (PN04) | 0.7920 | 0.9902 | 0.9342 | 0.315 ± 0.044 | 0.334 ± 0.063 ** |
| Lag Time (h) | Jss (µg/cm2/h) | Kp × 10−3 (cm/h) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silver nanoparticle solution | 2.61 | 0.092 ± 0.010 | 4.597 ± 0.525 |
| Porous deproteinized natural rubber film loaded with silver nanoparticles (PN04) | 2.66 | 0.089 ± 0.012 | 4.267 ± 0.575 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pichayakorn, W.; Maneewattanapinyo, P.; Monton, C.; Dangmanee, N.; Suksaeree, J. Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles for Topical Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15112603
Pichayakorn W, Maneewattanapinyo P, Monton C, Dangmanee N, Suksaeree J. Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles for Topical Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(11):2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15112603
Chicago/Turabian StylePichayakorn, Wiwat, Pattwat Maneewattanapinyo, Chaowalit Monton, Nattakan Dangmanee, and Jirapornchai Suksaeree. 2023. "Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles for Topical Drug Delivery" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 11: 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15112603
APA StylePichayakorn, W., Maneewattanapinyo, P., Monton, C., Dangmanee, N., & Suksaeree, J. (2023). Porous Deproteinized Natural Rubber Film Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles for Topical Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 15(11), 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15112603








