Imaging of Gαq Proteins in Mouse and Human Organs and Tissues
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Organs from CD1 Mice
2.2. Acute Asthma Model and Preparation of Fixated Lung Tissue
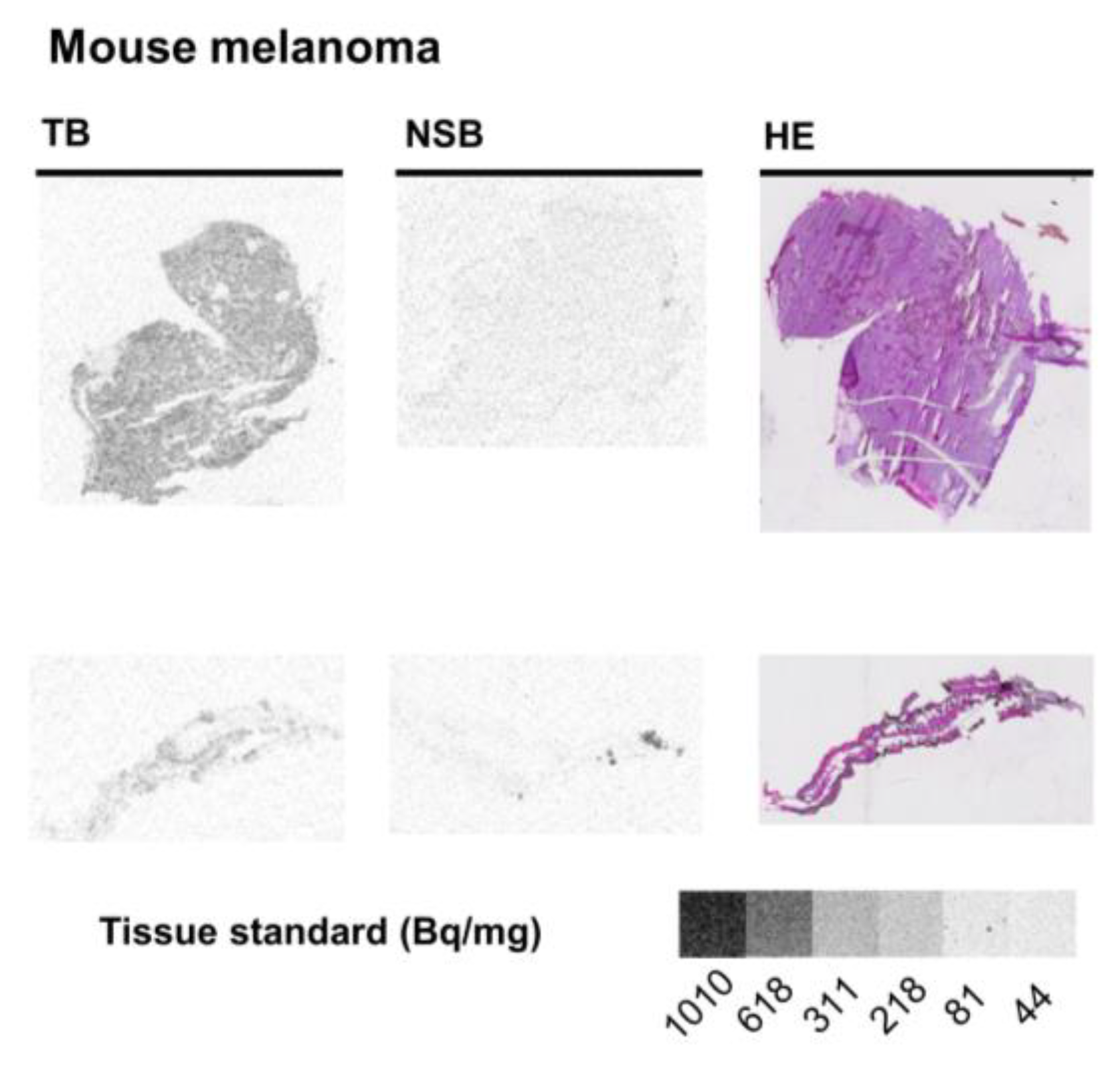
2.3. Mouse Melanoma
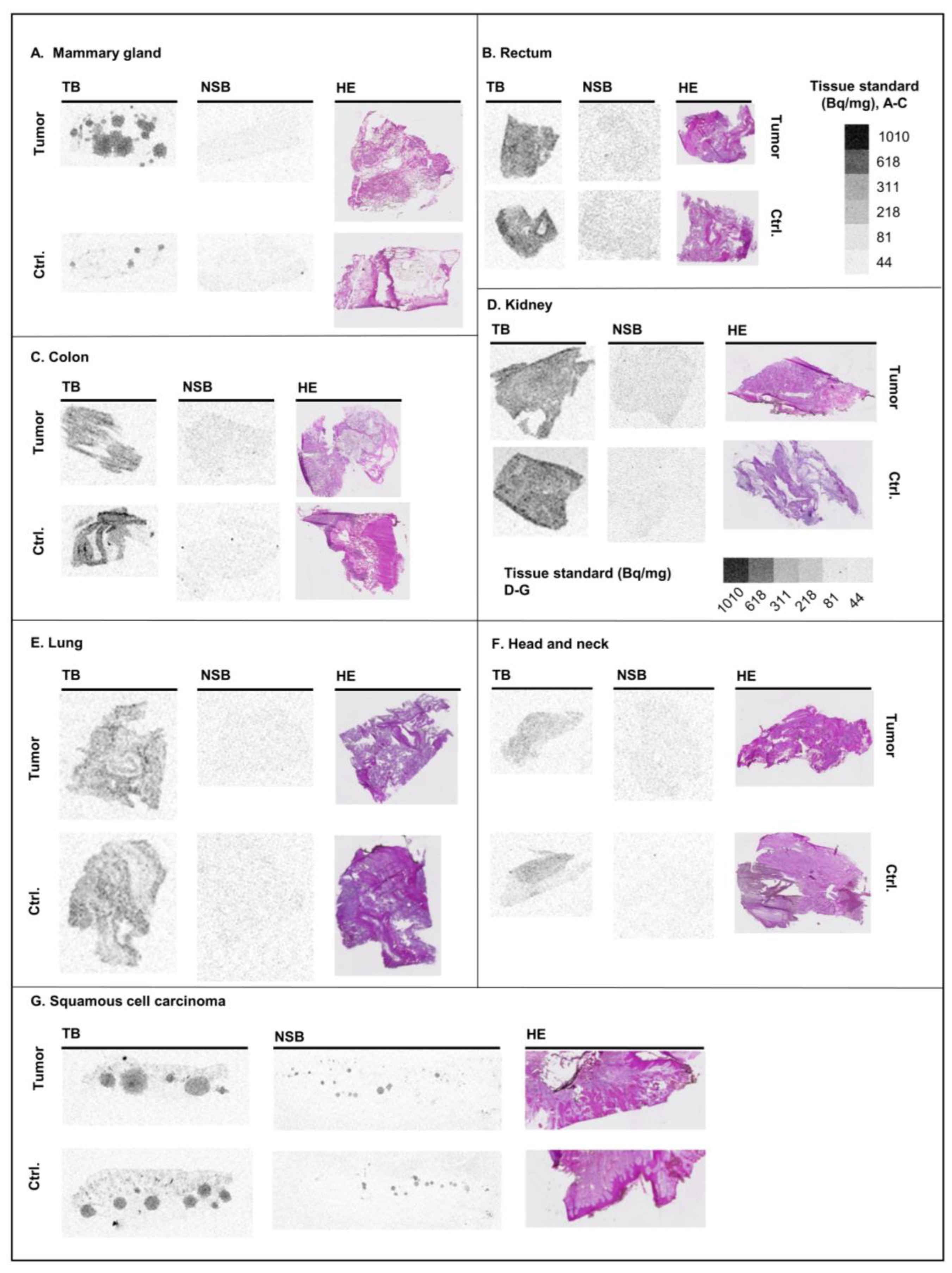
2.4. Human Cancer Samples
2.5. Cryosectioning
2.6. Histological Staining of Samples
2.7. Autoradiography
2.8. Densitometric Analysis
3. Results
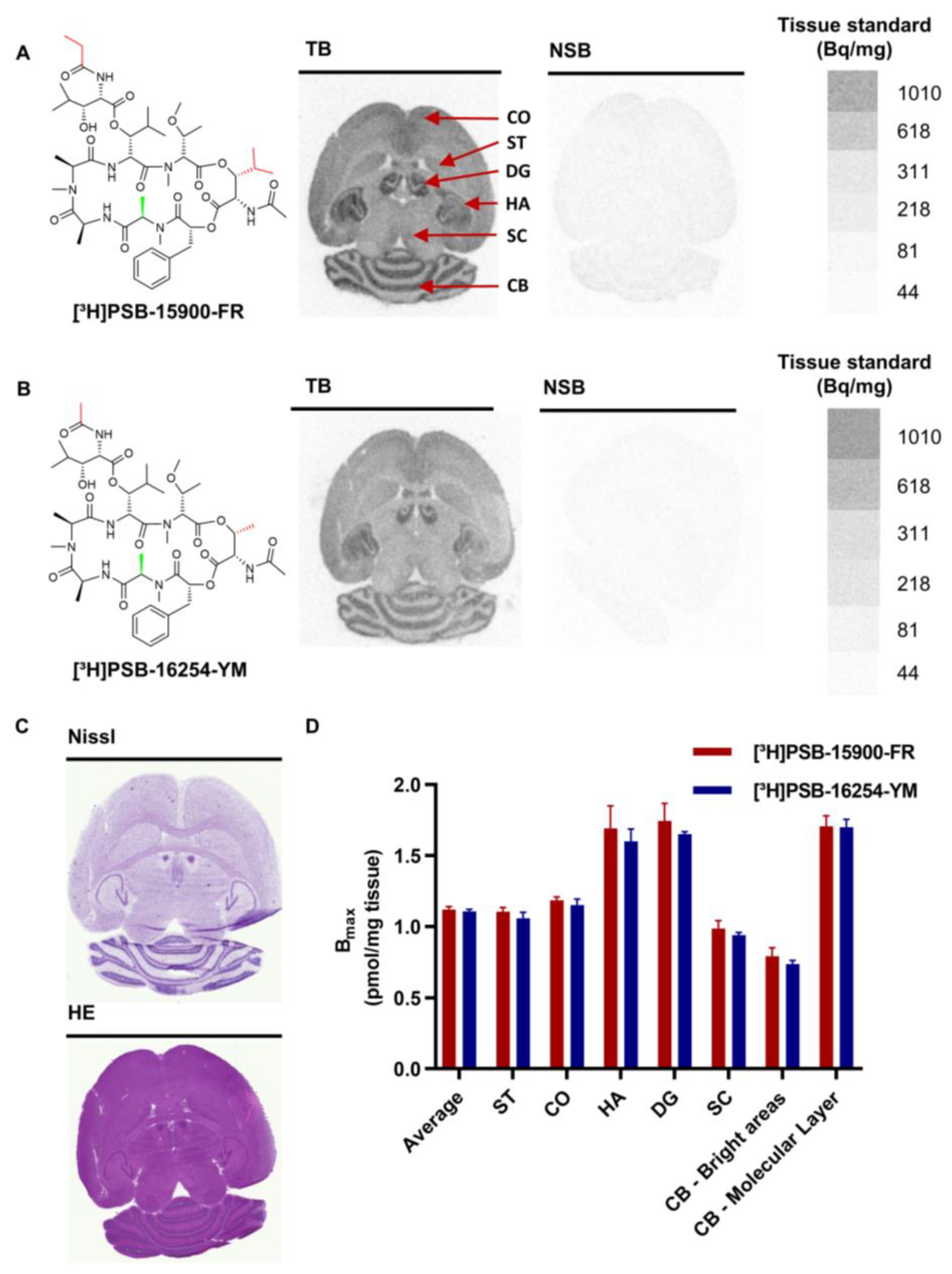
3.1. Autoradiography of Gαq Proteins in Healthy Mouse Brain
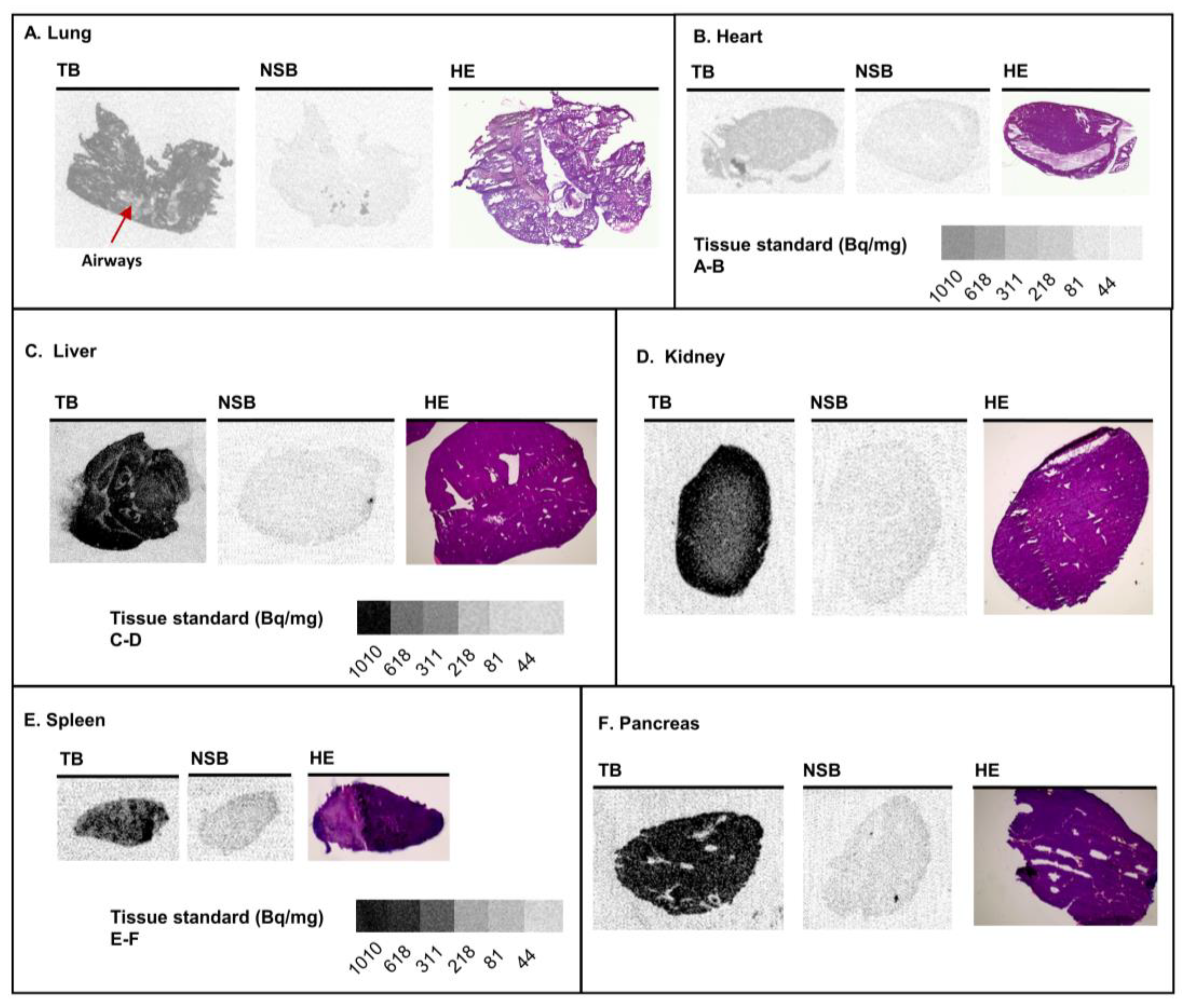
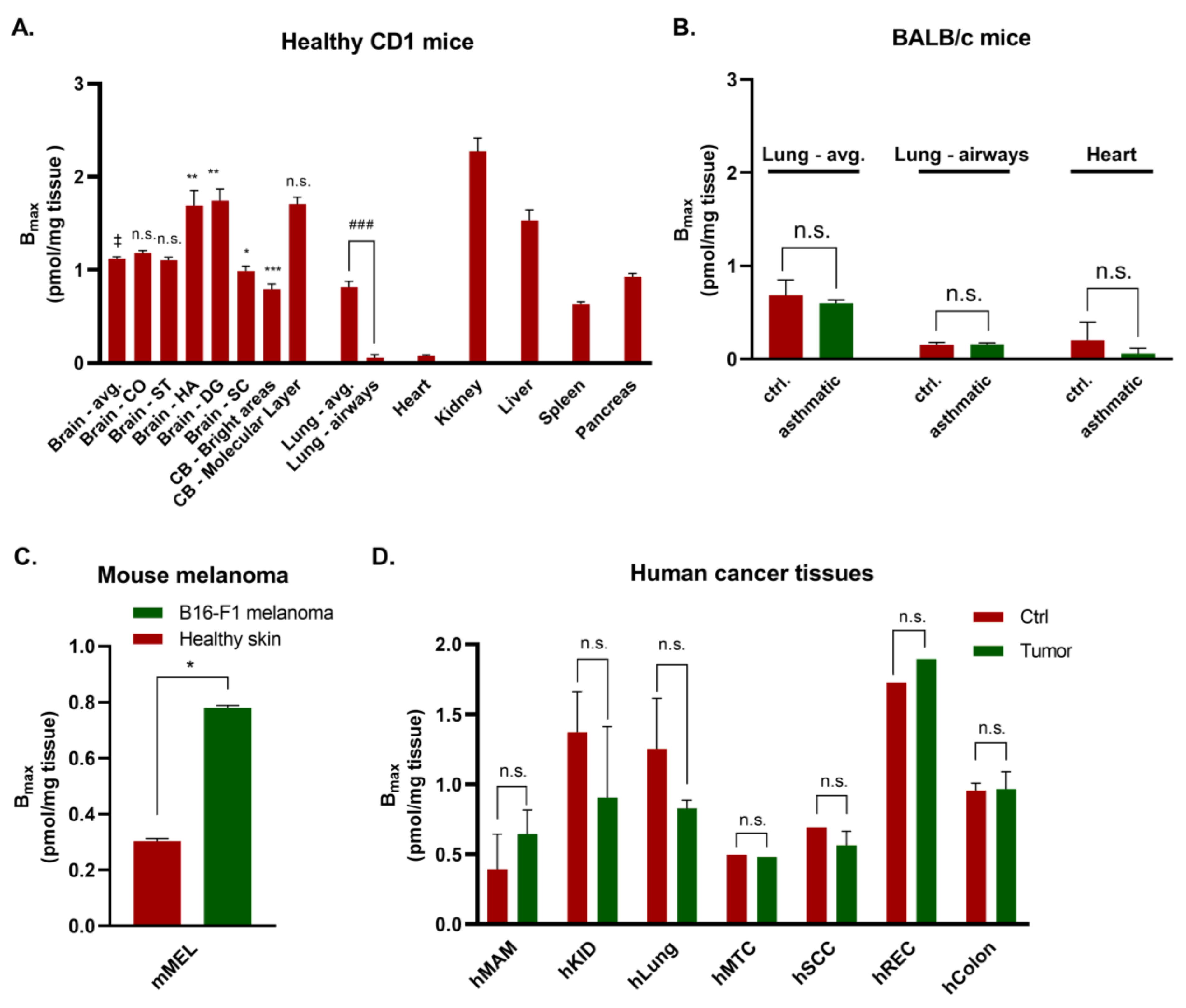
3.2. Various Organs from Healthy Mice
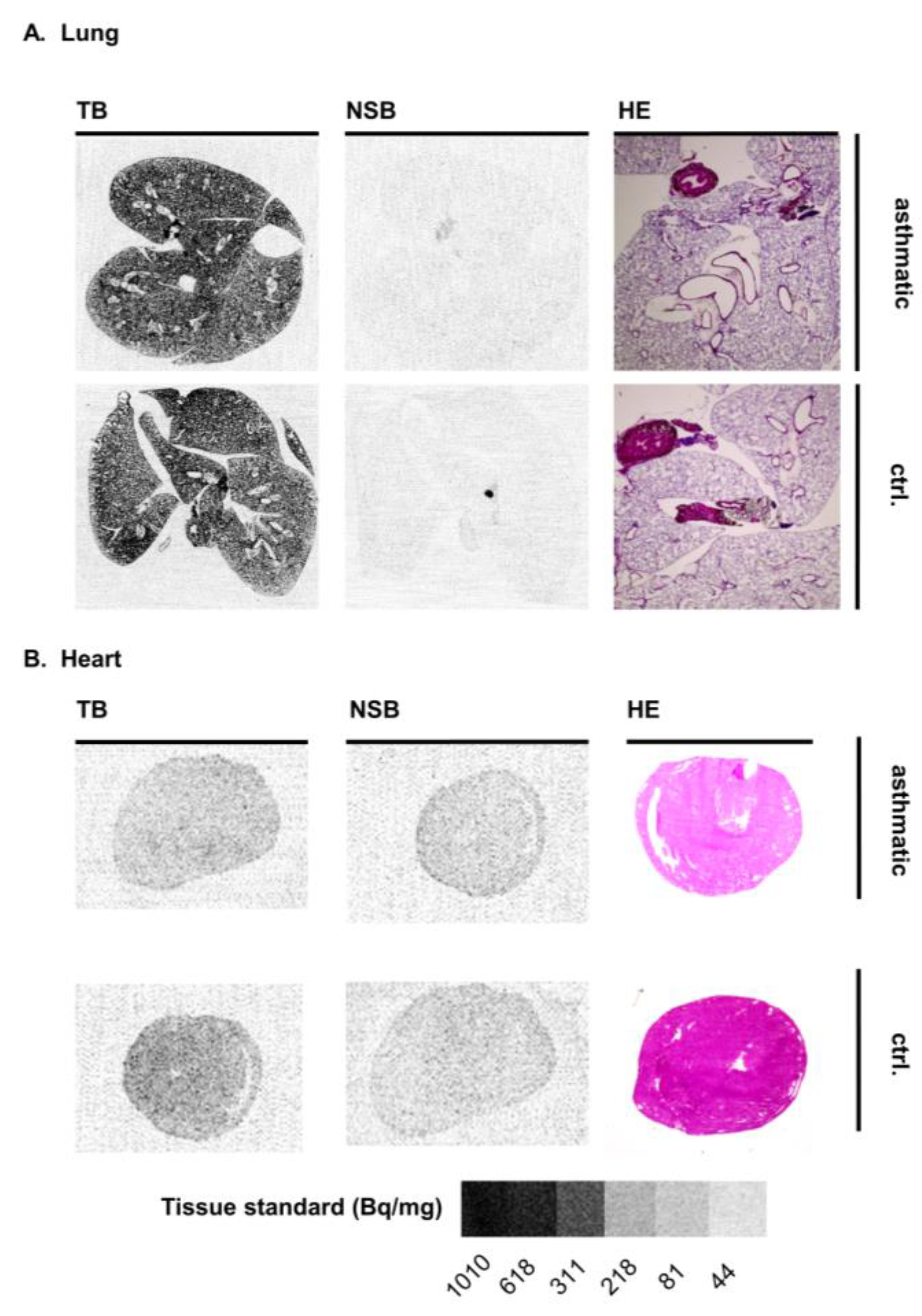
3.3. Mouse Disease Models
3.4. Human Tissues
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oldham, W.M.; Hamm, H.E. Heterotrimeric G protein activation by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.I.; Strathmann, M.P.; Gautam, N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science 1991, 252, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milligan, G.; Kostenis, E. Heterotrimeric G-proteins: A short history. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147 (Suppl. S1), S46–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.J.; Chae, H.Z.; Rhee, S.G.; Exton, J.H. Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature 1991, 350, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offermanns, S.; Simon, M.I. Gα15 and Gα16 couple a wide variety of receptors to phospholipase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 15175–15180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.K.; Yung, L.Y.; Chan, J.S.; Chan, J.H.; Wong, C.S.; Wong, Y.H. Gα14 links a variety of G(i)- and G(s)-coupled receptors to the stimulation of phospholipase C. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 132, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D158–D169. [CrossRef]
- Needleman, S.B.; Wunsch, C.D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1970, 48, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avet, C.; Mancini, A.; Breton, B.; Le Gouill, C.; Hauser, A.S.; Normand, C.; Kobayashi, H.; Gross, F.; Hogue, M.; Lukasheva, V.; et al. Effector membrane translocation biosensors reveal G protein and βarrestin coupling profiles of 100 therapeutically relevant GPCRs. Elife 2022, 11, e74101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Raimondi, F.; Kadji, F.M.N.; Singh, G.; Kishi, T.; Uwamizu, A.; Ono, Y.; Shinjo, Y.; Ishida, S.; Arang, N.; et al. Illuminating G-protein-coupling selectivity of GPCRs. Cell 2019, 177, 1933–1947.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amatruda, T.T.; Steele, D.A.; Slepak, V.Z.; Simon, M.I. G alpha 16, a G protein alpha subunit specifically expressed in hematopoietic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5587–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Ho, M.K.C.; Wong, Y.H. A hematopoietic perspective on the promiscuity and specificity of Galpha16 signaling. Neurosignals 2009, 17, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Fang, L.; Xie, X. Development of a universal high-throughput calcium assay for G-protein- coupled receptors with promiscuous G-protein Galpha15/16. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offermanns, S.; Zhao, L.P.; Gohla, A.; Sarosi, I.; Simon, M.I.; Wilkie, T.M. Embryonic cardiomyocyte hypoplasia and craniofacial defects in G alpha q/G alpha 11-mutant mice. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 4304–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Raamsdonk, C.D.; Griewank, K.G.; Crosby, M.B.; Garrido, M.C.; Vemula, S.; Wiesner, T.; Obenauf, A.C.; Wackernagel, W.; Green, G.; Bouvier, N.; et al. Mutations in GNA11 in uveal melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onken, M.D.; Makepeace, C.M.; Kaltenbronn, K.M.; Kanai, S.M.; Todd, T.D.; Wang, S.; Broekelmann, T.J.; Rao, P.K.; Cooper, J.A.; Blumer, K.J. Targeting nucleotide exchange to inhibit constitutively active G protein α subunits in cancer cells. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaao6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthey, M.; Roberts, R.; Seidinger, A.; Simon, A.; Schröder, R.; Kuschak, M.; Annala, S.; König, G.M.; Müller, C.E.; Hall, I.P.; et al. Targeted inhibition of Gq signaling induces airway relaxation in mouse models of asthma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaag2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, G.; Mamazhakypov, A.; Schermuly, R.T.; Rajagopal, S. The role of G protein-coupled receptors in the right ventricle in pulmonary hypertension. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettschureck, N.; Rütten, H.; Zywietz, A.; Gehring, D.; Wilkie, T.M.; Chen, J.; Chien, K.R.; Offermanns, S. Absence of pressure overload induced myocardial hypertrophy after conditional inactivation of Gαq/Gα11 in cardiomyocytes. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuschak, M.; Namasivayam, V.; Rafehi, M.; Voss, J.H.; Garg, J.; Schlegel, J.G.; Abdelrahman, A.; Kehraus, S.; Reher, R.; Küppers, J.; et al. Cell-permeable high-affinity tracers for Gq proteins provide structural insights, reveal distinct binding kinetics, and identify small molecule inhibitors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 177, 1898–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfacini, D.; Patt, J.; Annala, S.; Harpsøe, K.; Eryilmaz, F.; Reher, R.; Crüsemann, M.; Hanke, W.; Zhang, H.; Tietze, D.; et al. Rational design of a heterotrimeric G protein α subunit with artificial inhibitor sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 5747–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patt, J.; Alenfelder, J.; Pfeil, E.M.; Voss, J.H.; Merten, N.; Eryilmaz, F.; Heycke, N.; Rick, U.; Inoue, A.; Kehraus, S.; et al. An experimental strategy to probe Gq contribution to signal transduction in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, J.H.; Nagel, J.; Rafehi, M.; Guixà-González, R.; Malfacini, D.; Patt, J.; Kehraus, S.; Inoue, A.; König, G.M.; Kostenis, E.; et al. Unraveling binding mechanism and kinetics of macrocyclic Gαq protein inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 173, 105880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Xiao, P.; Lei, S.; Deng, F.; Xiao, G.G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. How is mRNA expression predictive for protein expression? A correlation study on human circulating monocytes. Acta Biochem. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.H.; Toussaint, M.; Teodoro, R.; Dukić-Stefanović, S.; Kranz, M.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Moldovan, R.-P.; Brust, P. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a novel 18F-labeled radiotracer for PET imaging of the adenosine A2A receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, R.I.; Tam, F.W.; Unwin, R.J.; Bailey, M.A. Purinergic signaling in kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallon, V.; Unwin, R.; Inscho, E.W.; Leipziger, J.; Kishore, B.K. Extracellular nucleotides and P2 receptors in renal Function. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 211–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, A.S.; Trauelsen, M.; Rudenko, O.; Hjorth, S.A.; Schwartz, T.W. GPCR-mediated signaling of metabolites. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 777–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlavan, S.; Oberhofer, M.; Sauer, B.; Ruppenthal, S.; Tian, Q.; Scholz, A.; Kaestner, L.; Lipp, P. Gαq and Gα11 contribute to the maintenance of cellular electrophysiology and Ca2+ handling in ventricular cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignola, A.M.; Kips, J.; Bousquet, J. Tissue remodeling as a feature of persistent asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 1041–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annala, S.; Feng, X.; Shridhar, N.; Eryilmaz, F.; Patt, J.; Yang, J.; Pfeil, E.M.; Cervantes-Villagrana, R.D.; Inoue, A.; Häberlein, F.; et al. Direct targeting of Gαq and Gα11 oncoproteins in cancer cells. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaau5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrage, R.; Schmitz, A.-L.; Gaffal, E.; Annala, S.; Kehraus, S.; Wenzel, D.; Büllesbach, K.M.; Bald, T.; Inoue, A.; Shinjo, Y.; et al. The experimental power of FR900359 to study Gq-regulated biological processes. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, J.G.; Tahoun, M.; Seidinger, A.; Voss, J.H.; Kuschak, M.; Kehraus, S.; Schneider, M.; Matthey, M.; Fleischmann, B.K.; König, G.M.; et al. Macrocyclic Gq Protein Inhibitors FR900359 and/or YM-254890-Fit for Translation? ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mouse Tissues | Human Tissues | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Mouse Organs | Bmax ± SEM (pmol/mg of Tissue) | Cancer Samples | Bmax ± SEM (pmol/mg of Tissue) |
| Brain—average | 1.12 ± 0.02 | Mammary gland—control | 0.39 ± 0.25 |
| Brain—striatum | 1.11 ± 0.03 | Mammary gland—tumor | 0.65 ± 0.17 |
| Brain—cortex | 1.18 ± 0.02 | Kidney—control | 1.37 ± 0.29 |
| Brain—hip. sulc. | 1.69 ± 0.16 | Kidney—tumor | 0.90 ± 0.51 |
| Brain—gyr. dent. | 1.74 ± 0.12 | Lung—control | 1.25 ± 0.36 |
| Brain— superior colliculus | 0.99 ± 0.06 | Lung—tumor | 0.83 ± 0.06 |
| Cerebellum— Bright areas | 0.79 ± 0.06 | Head and neck—control | 0.50 |
| Cerebellum— Molecular layer | 1.71 ± 0.07 | Head and neck—tumor | 0.48 |
| Lung—average | 0.81 ± 0.07 | Skin—control | 0.69 |
| Lung—airways | 0.06 ± 0.03 | Skin—squamous cell carcinoma | 0.56 ± 0.10 |
| Heart | 0.08 ± 0.01 | Rectum—control | 1.73 |
| Kidney | 2.27 ± 0.14 | Rectum—tumor | 1.89 |
| Liver | 1.53 ± 0.12 | Colon—control | 0.96 ± 0.05 |
| Spleen | 0.63 ± 0.02 | Colon—tumor | 0.97 ± 0.12 |
| Pancreas | 0.93 ± 0.04 | ||
| Mouse disease models | |||
| Lung control—full | 0.69 ± 0.17 | ||
| Lung asthmatic—full | 0.60 ± 0.04 | ||
| Lung control—airways | 0.15 ± 0.02 | ||
| Lung asthmatic—airways | 0.16 ± 0.02 | ||
| Heart—control | 0.21 ± 0.19 | ||
| Heart—asthmatic | 0.06 ± 0.06 | ||
| Mouse—skin | 0.30 ± 0.01 | ||
| Mouse—melanoma | 0.78 ± 0.01 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voss, J.H.; Al-Hroub, H.; Gedschold, R.; Dietrich, J.M.; Gaffal, E.; Toma, M.; Kehraus, S.; König, G.M.; Brust, P.; Fleischmann, B.K.; et al. Imaging of Gαq Proteins in Mouse and Human Organs and Tissues. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010057
Voss JH, Al-Hroub H, Gedschold R, Dietrich JM, Gaffal E, Toma M, Kehraus S, König GM, Brust P, Fleischmann BK, et al. Imaging of Gαq Proteins in Mouse and Human Organs and Tissues. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoss, Jan H., Haneen Al-Hroub, Robin Gedschold, Jennifer M. Dietrich, Evelyn Gaffal, Marieta Toma, Stefan Kehraus, Gabriele M. König, Peter Brust, Bernd K. Fleischmann, and et al. 2023. "Imaging of Gαq Proteins in Mouse and Human Organs and Tissues" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010057
APA StyleVoss, J. H., Al-Hroub, H., Gedschold, R., Dietrich, J. M., Gaffal, E., Toma, M., Kehraus, S., König, G. M., Brust, P., Fleischmann, B. K., Wenzel, D., Deuther-Conrad, W., & Müller, C. E. (2023). Imaging of Gαq Proteins in Mouse and Human Organs and Tissues. Pharmaceutics, 15(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010057






