A Comparative Study between A Protein Based Amorphous Formulation and Other Dissolution Rate Enhancing Approaches: A Case Study with Rifaximin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Amorphous Solid Dispersions by Spray Drying
2.3. Preparation of the Nanocrystalline Formulation by Wet Milling
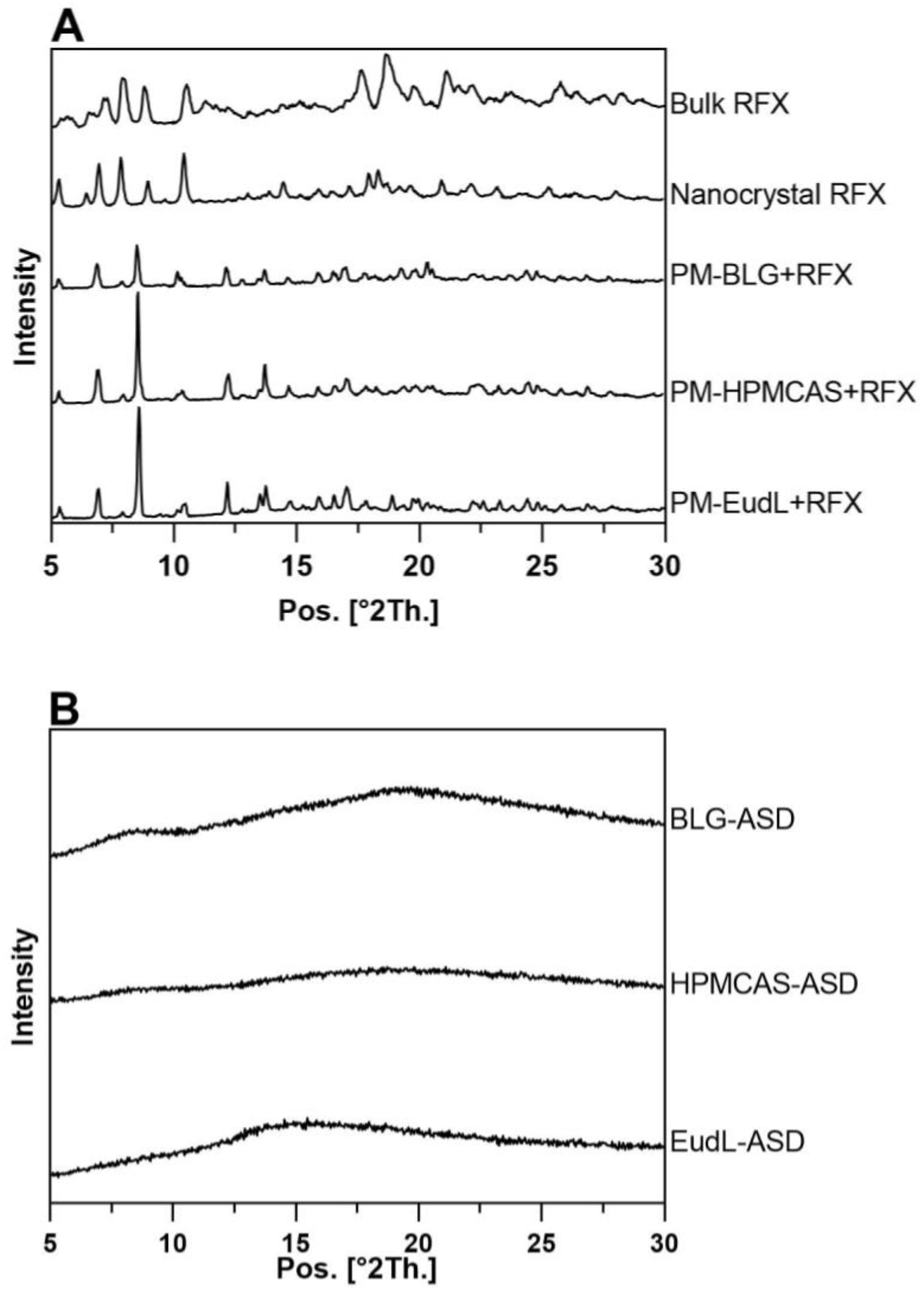
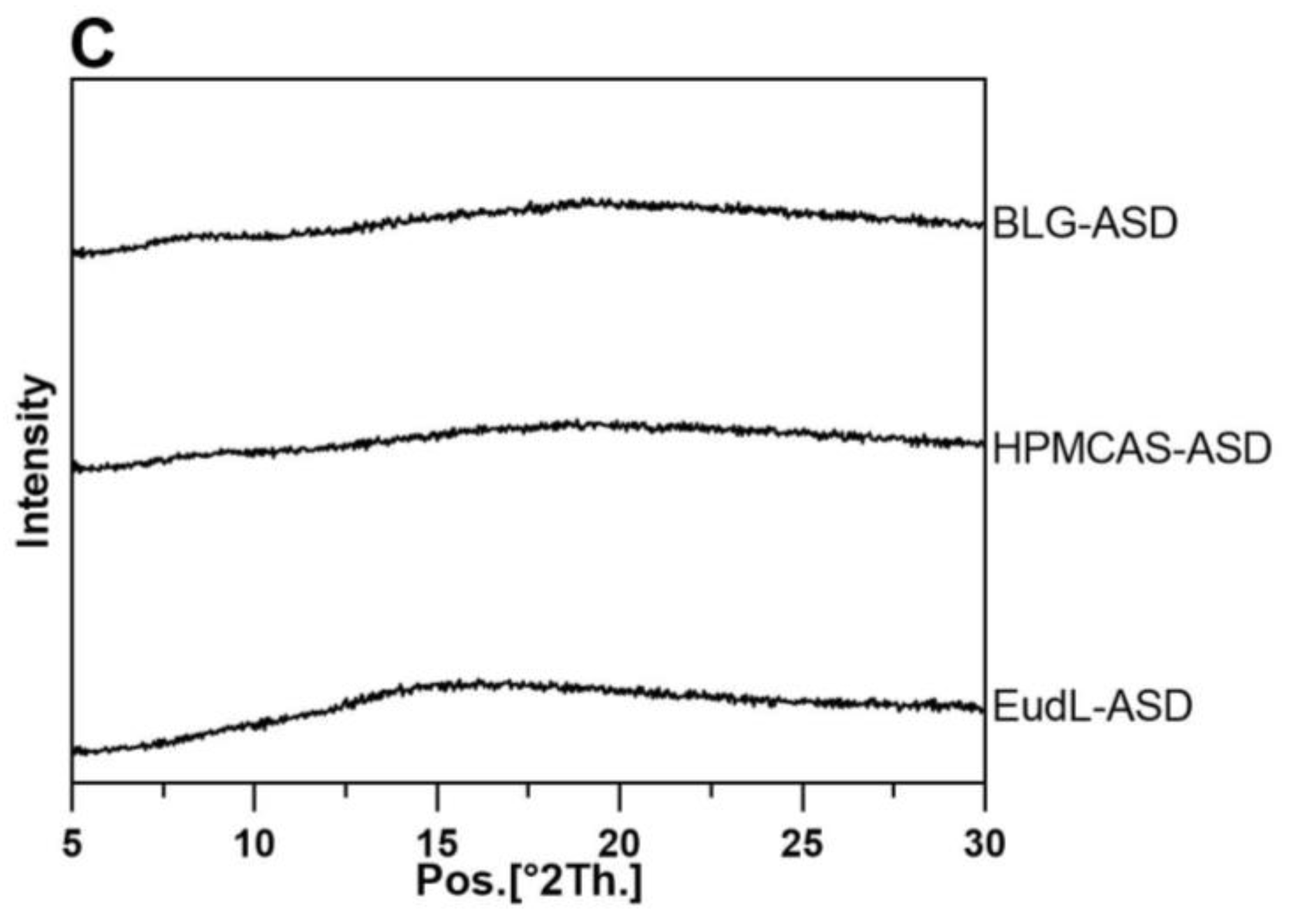
2.4. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
2.5. Modulated Differential Scanning Calorimetry (mDSC)
2.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
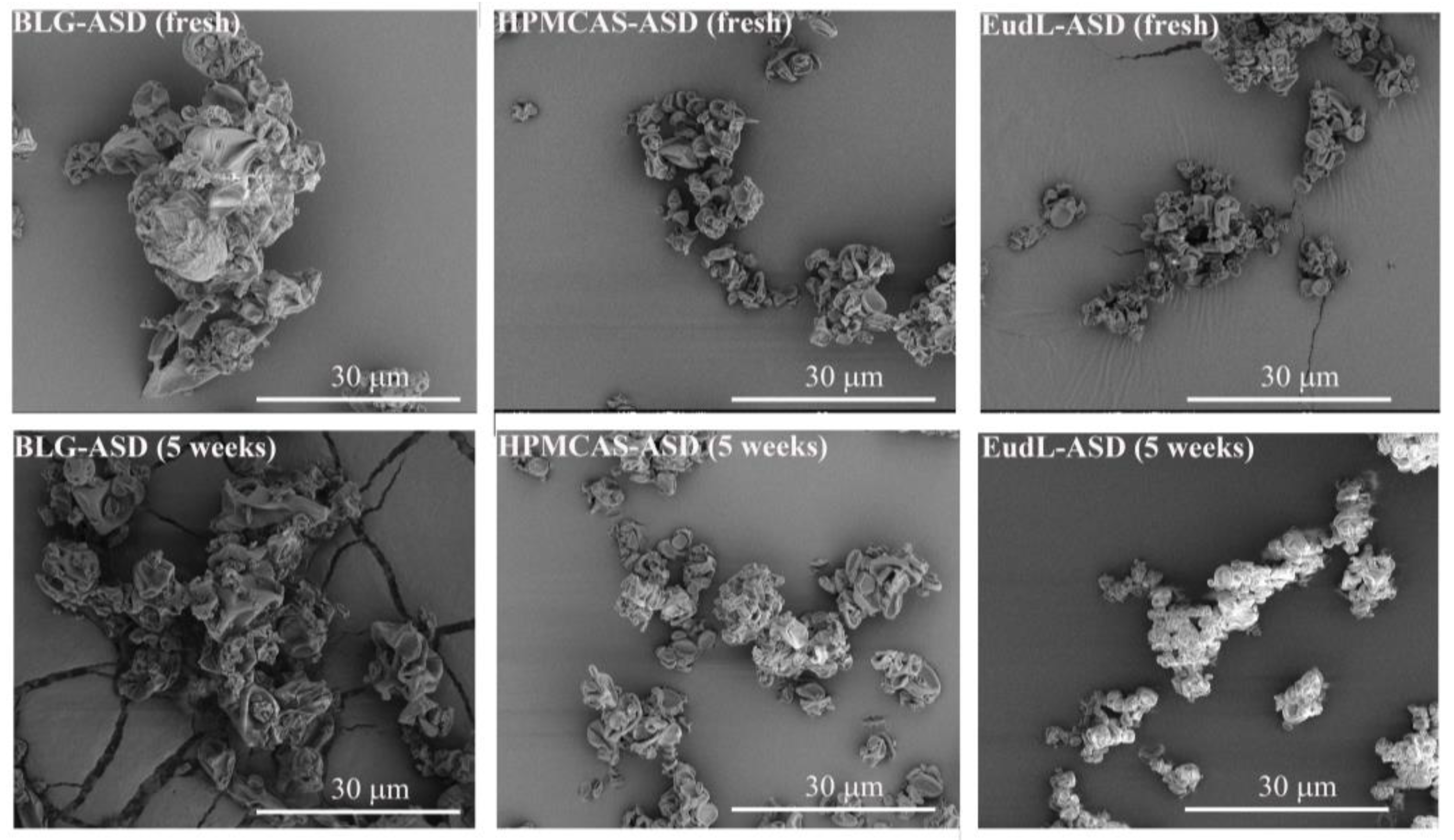
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.8. Physical Stability
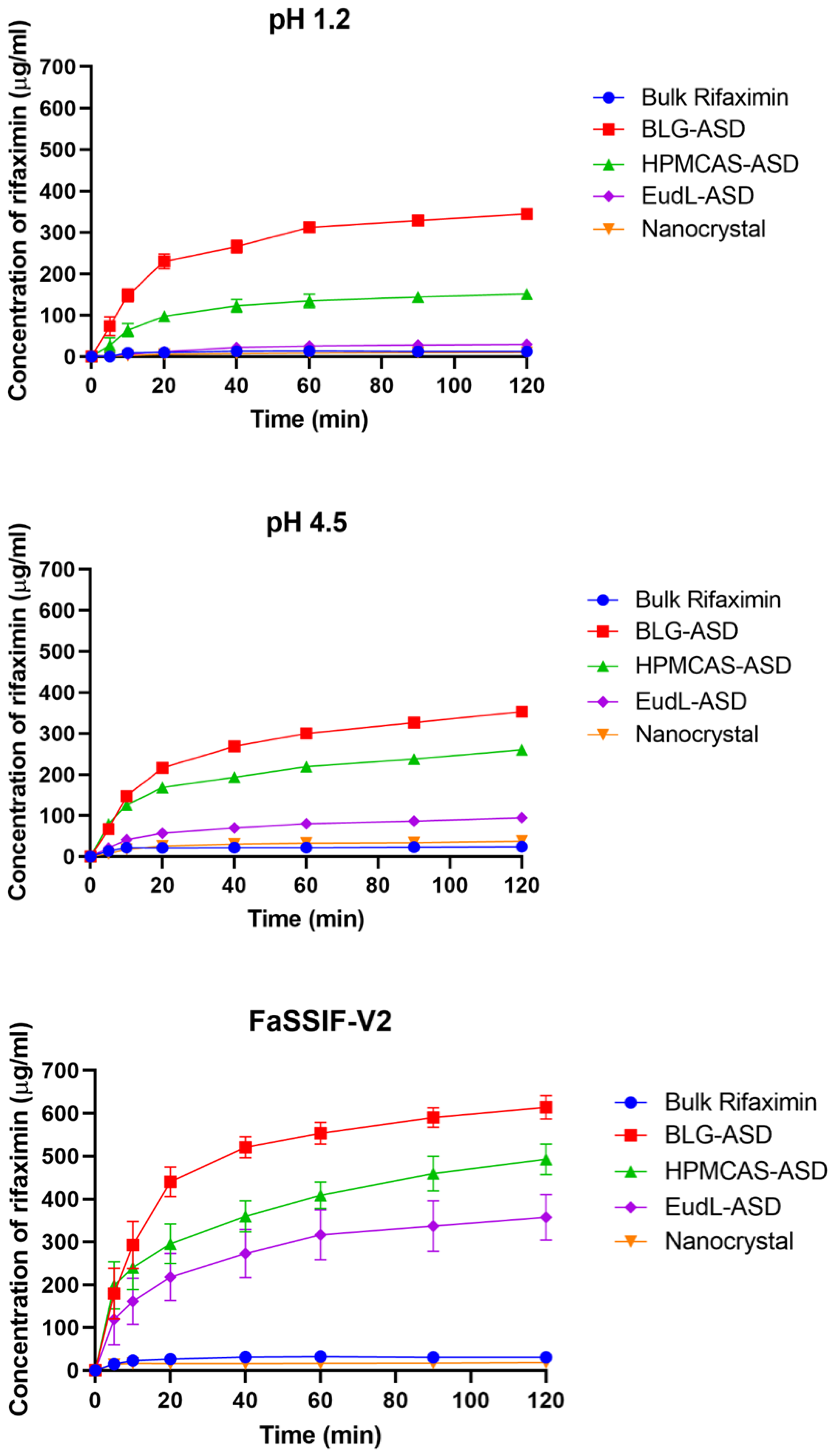
2.9. Powder Dissolution
2.10. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
3. Results
3.1. Solid-State Characterization and Physical Stability
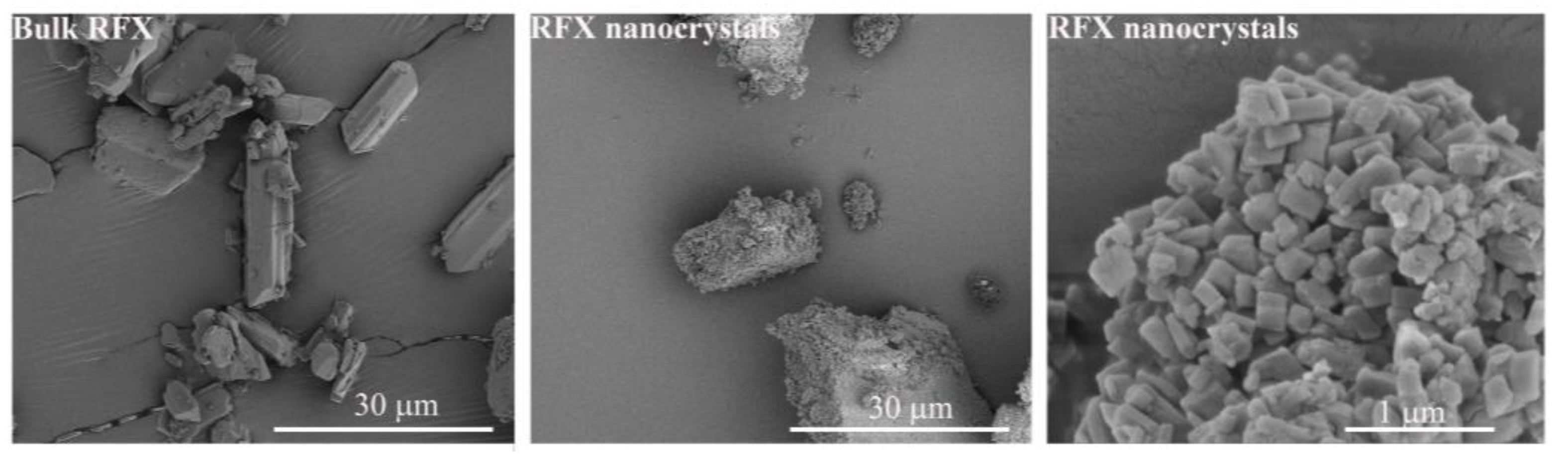
3.2. Morphology
3.3. Powder Dissolution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins: Basic science and product development. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarnes, A.; Ostergaard, J.; Jensen, S.S.; Aaltonen, J.; Rantanen, J.; Hirvonen, J.; Peltonen, L. Dissolution study of nanocrystal powders of a poorly soluble drug by UV imaging and channel flow methods. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.S.; Zhang, G.G.Z. Physical chemistry of supersaturated solutions and implications for oral absorption. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2016, 101, 122–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.D.; Lee, P.I. Probing the mechanisms of drug release from amorphous solid dispersions in medium-soluble and medium-insoluble carriers. J. Control Release 2015, 211, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Polymeric Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Review of Amorphization, Crystallization, Stabilization, Solid-State Characterization, and Aqueous Solubilization of Biopharmaceutical Classification System Class II Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapourani, A.; Andriotis, E.G.; Chachlioutaki, K.; Kontogiannopoulos, K.N.; Klonos, P.A.; Kyritsis, A.; Pavlidou, E.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Fatouros, D.G.; Barmpalexis, P. High-Drug-Loading Amorphous Solid Dispersions via In Situ Thermal Cross-Linking: Unraveling the Mechanisms of Stabilization. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 4393–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, M.M.; Tajber, L.; Tian, Y.; Olesen, N.E.; Jones, D.S.; Kozyra, A.; Lobmann, K.; Paluch, K.; Brennan, C.M.; Holm, R.; et al. Comparative Study of Different Methods for the Prediction of Drug-Polymer Solubility. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3408–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pas, T.; Vergauwen, B.; Van den Mooter, G. Exploring the feasibility of the use of biopolymers as a carrier in the formulation of amorphous solid dispersions—Part I: Gelatin. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2018, 535, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoder, M.; Abdelkader, H.; ElShaer, A.; Karam, A.; Najlah, M.; Alany, R.G. Efficient approach to enhance drug solubility by particle engineering of bovine serum albumin. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Bohr, A.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H.; Lobmann, K. Whey proteins as stabilizers in amorphous solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 128, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descombe, J.; Dubourg, D.; Picard, M.; Palazzini, E. Pharmacokinetic study of rifaximin after oral administration in healthy volunteers. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Res. 1994, 14, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beig, A.; Fine-Shamir, N.; Lindley, D.; Miller, J.M.; Dahan, A. Advantageous solubility-permeability interplay when using amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) formulation for the BCS class IV P-gp substrate rifaximin: Simultaneous increase of both the solubility and the permeability. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.; Dalal, S.K.; Jahagirdar, H.A. Solid Dispersion of Rifaximin. Patent EP2493456A2, 5 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kogawa, A.C.; Salgado, H.R.N. Status of rifaximin: A review of characteristics, uses and analytical methods. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 48, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraceni, P.; Vargas, V.; Solà, E.; Alessandria, C.; de Wit, K.; Trebicka, J.; Angeli, P.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Durand, F.; Pose, E. The use of rifaximin in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.S.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, W.L. β-Lactoglobulin influences human immunity and promotes cell proliferation. BioMed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7123587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.D.; Calvo, M. Interaction of Beta-Lactoglobulin with Retinol and Fatty-Acids and Its Role as a Possible Biological Function for This Protein—A Review. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscomi, G.C.; Campana, M.; Barbanti, M.; Grepioni, F.; Polito, M.; Confortini, D.; Rosini, G.; Righi, P.; Cannata, V.; Braga, D. Crystal forms of rifaximin and their effect on pharmaceutical properties. Crystengcomm 2008, 10, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Q.; Ueda, H.; Lobmann, K.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H. Organic acids as co-formers for co-amorphous systems—Influence of variation in molar ratio on the physicochemical properties of the co-amorphous systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 131, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merisko-Liversidge, E.; Liversidge, G.G.; Cooper, E.R. Nanosizing: A formulation approach for poorly-water-soluble compounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 18, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaka, S.R.K.; Bommana, M.M.; Desai, D.; Djordjevic, J.; Phuapradit, W.; Shah, N. Excipients for Amorphous Solid Dispersions. In Amorphous Solid Dispersions; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 123–161. [Google Scholar]
- Hiew, T.N.; Zemlyanov, D.Y.; Taylor, L.S. Balancing Solid-State Stability and Dissolution Performance of Lumefantrine Amorphous Solid Dispersions: The Role of Polymer Choice and Drug-Polymer Interactions. Mol. Pharmaceut. 2022, 19, 392–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittny, A.; Huwyler, J.; Puchkov, M. Mechanisms of increased bioavailability through amorphous solid dispersions: A review. Drug. Deliv. 2020, 27, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Materials | Tgs (°C) | Moisture Content (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh | 5 Weeks | ||
| Bulk RFX | 197.8 | ||
| BLG | 240.4 | ||
| HPMCAS | 121.6 | ||
| EudL | 187.0 | ||
| BLG-ASD | 200.1 | 3.9 | 5.7 |
| HPMCAS-ASD | 153.1 | 1.5 | 1.7 |
| EudL-ASD | 193.2 | 4.1 | 4.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuo, X.; Margrethe Brekstad Kjellin, M.; Schaal, Z.; Zhang, T.; Löbmann, K.; Leng, D. A Comparative Study between A Protein Based Amorphous Formulation and Other Dissolution Rate Enhancing Approaches: A Case Study with Rifaximin. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010126
Zhuo X, Margrethe Brekstad Kjellin M, Schaal Z, Zhang T, Löbmann K, Leng D. A Comparative Study between A Protein Based Amorphous Formulation and Other Dissolution Rate Enhancing Approaches: A Case Study with Rifaximin. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(1):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010126
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuo, Xuezhi, Maud Margrethe Brekstad Kjellin, Zarah Schaal, Tengyu Zhang, Korbinian Löbmann, and Donglei Leng. 2023. "A Comparative Study between A Protein Based Amorphous Formulation and Other Dissolution Rate Enhancing Approaches: A Case Study with Rifaximin" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 1: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010126
APA StyleZhuo, X., Margrethe Brekstad Kjellin, M., Schaal, Z., Zhang, T., Löbmann, K., & Leng, D. (2023). A Comparative Study between A Protein Based Amorphous Formulation and Other Dissolution Rate Enhancing Approaches: A Case Study with Rifaximin. Pharmaceutics, 15(1), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010126







