Preparation, In Vitro Characterization, and Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Polymeric pH-Responsive Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of CS/CP/PVAcPAa Hydrogels
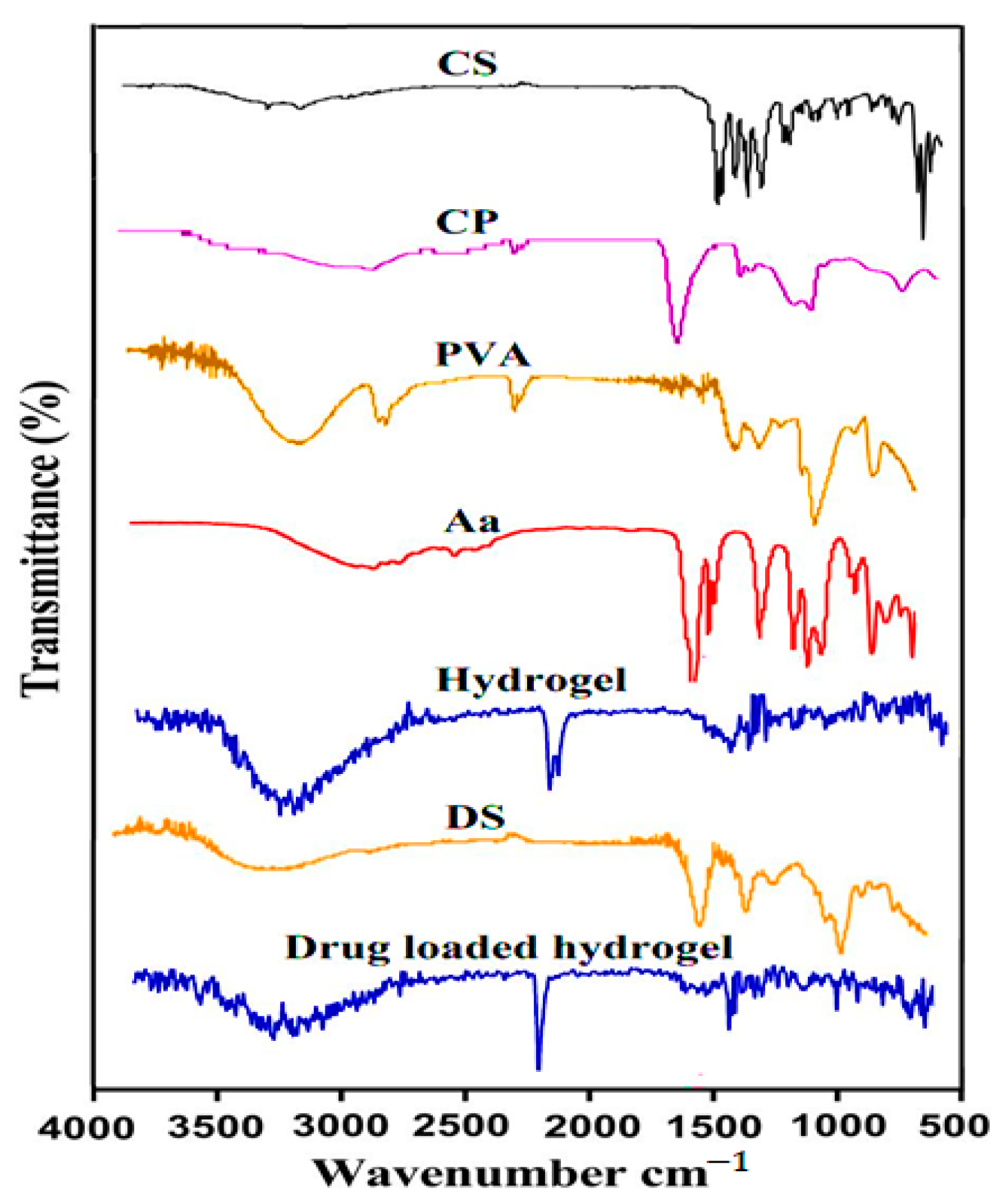
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
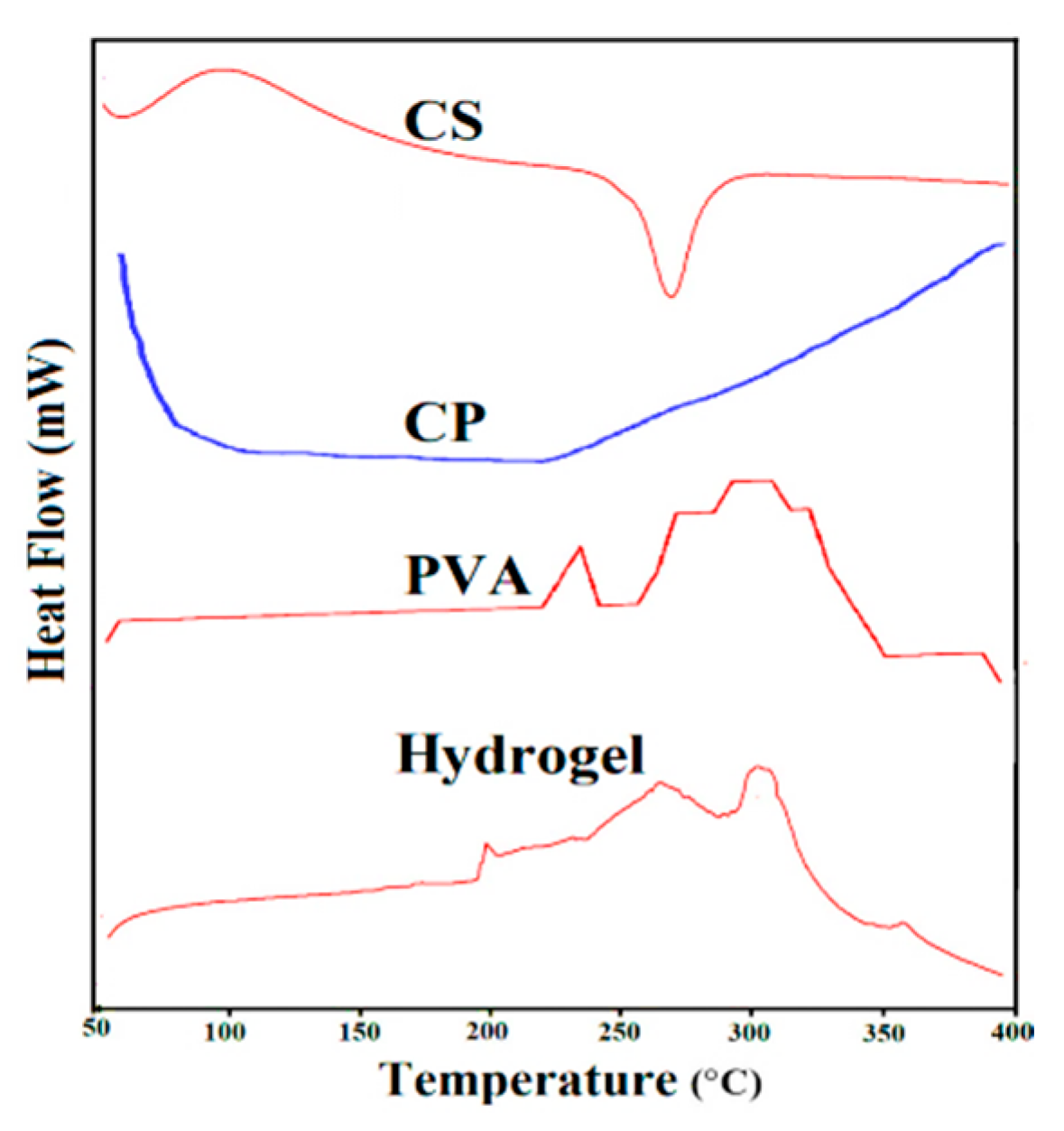
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
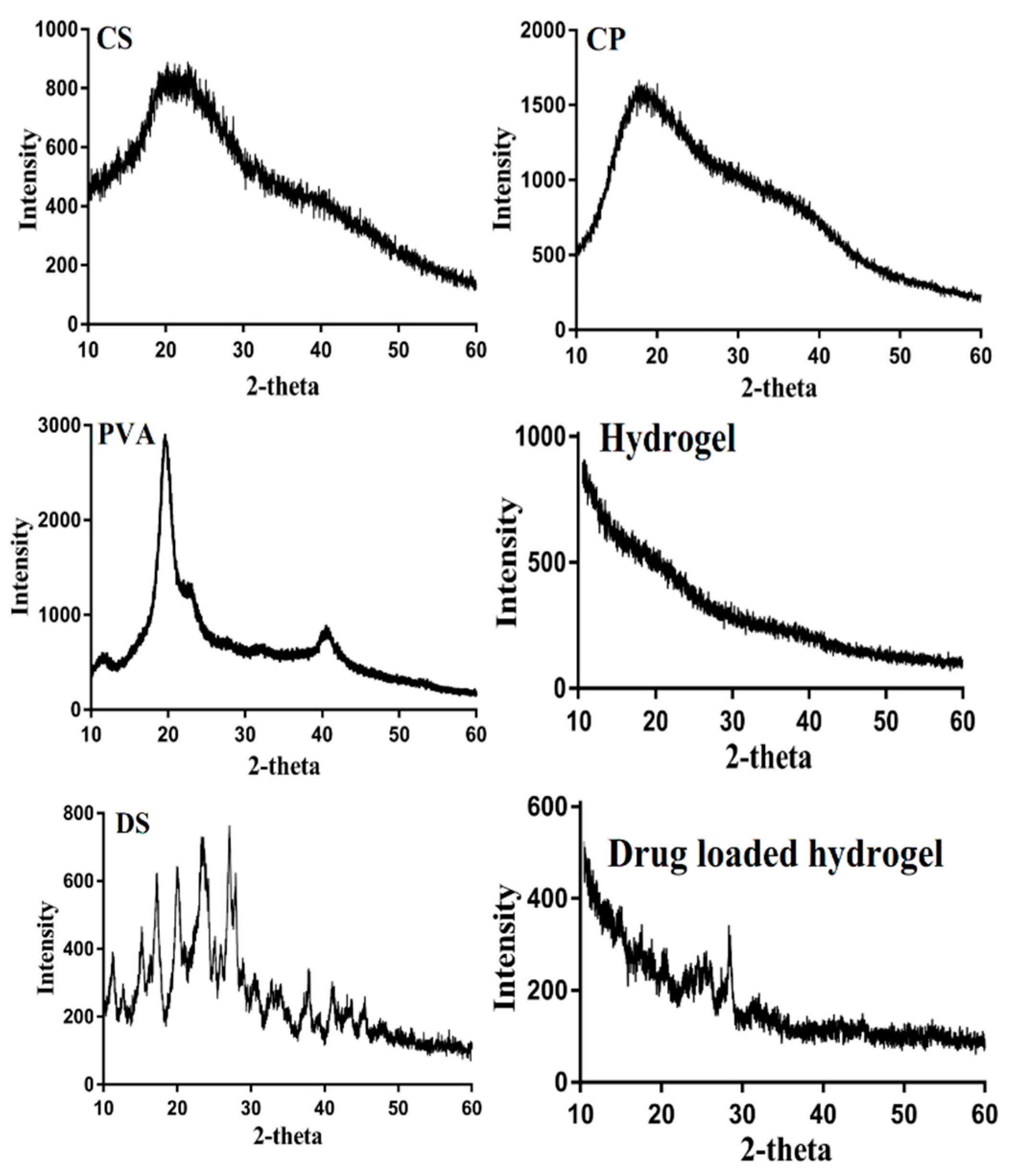
2.6. X-ray Diffraction Studies
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
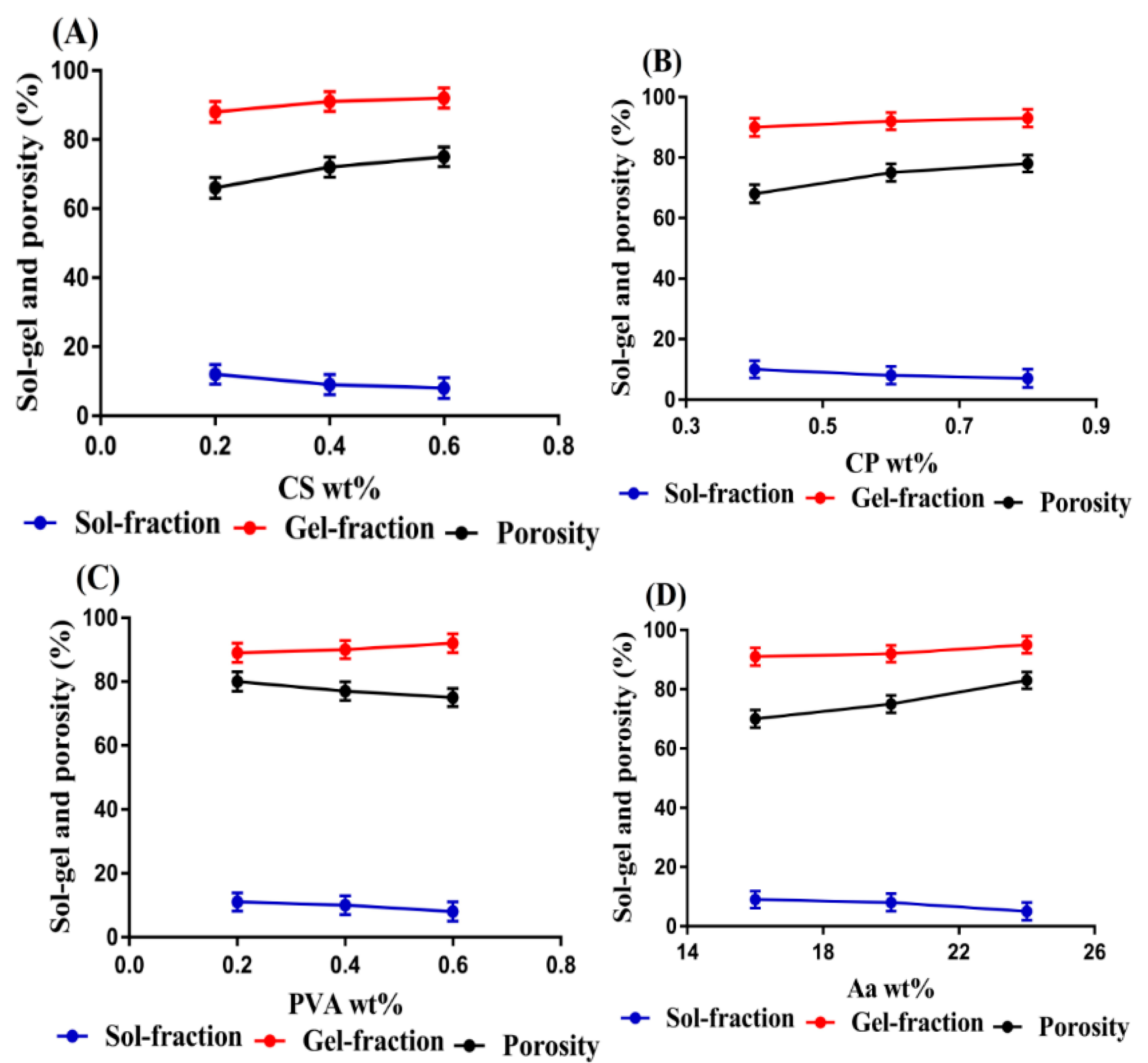
2.8. Sol–Gel Fraction
2.9. Porosity Study
2.10. Biodegradation Study
2.11. Swelling Study
2.12. Polymer Volume Fraction
2.13. Drug Loading
2.14. Drug Release Studies
2.15. Kinetic Modeling
2.16. Cytotoxicity Study
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of CS/CP/PVAcPAa Hydrogels
3.2. FTIR
3.3. TGA
3.4. DSC
3.5. X-ray Diffraction Studies
3.6. SEM
3.7. Sol–Gel Fraction
3.8. Porosity Study
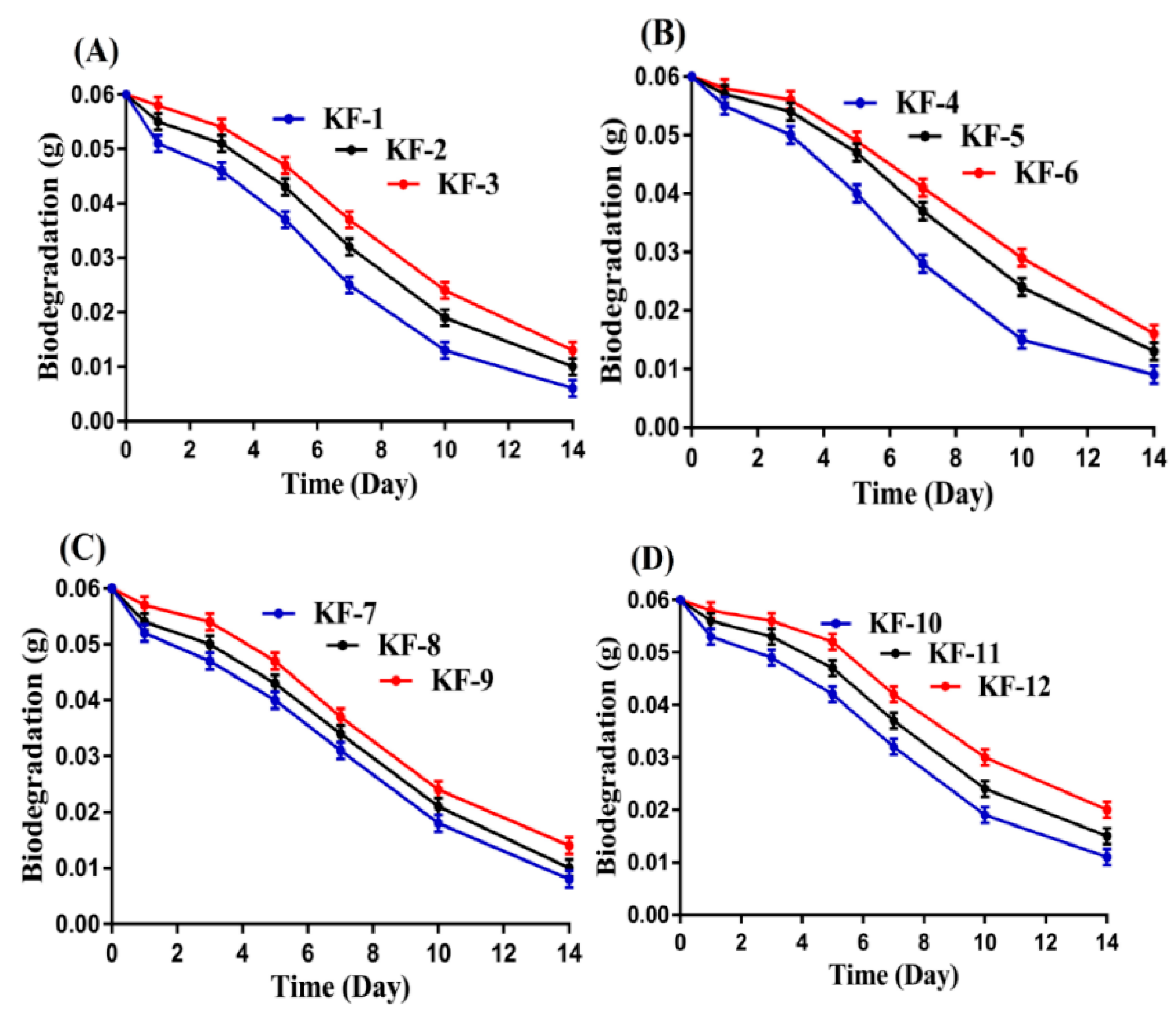
3.9. Biodegradation Study
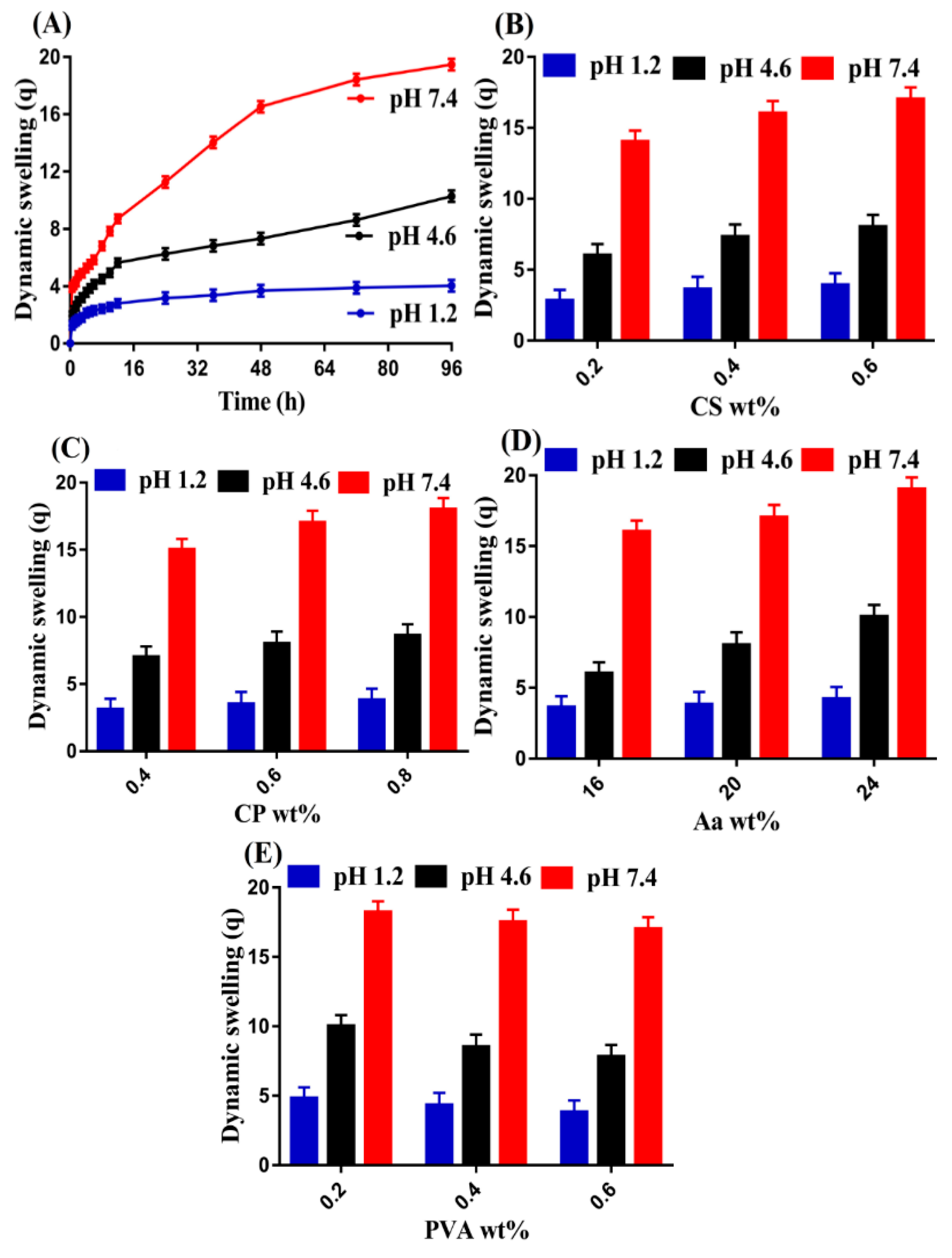
3.10. Swelling Study
3.10.1. Effect of pH
3.10.2. Effect of CS/CP/PVA/ and Aa
3.11. Polymer Volume Fraction
3.12. Drug Loading
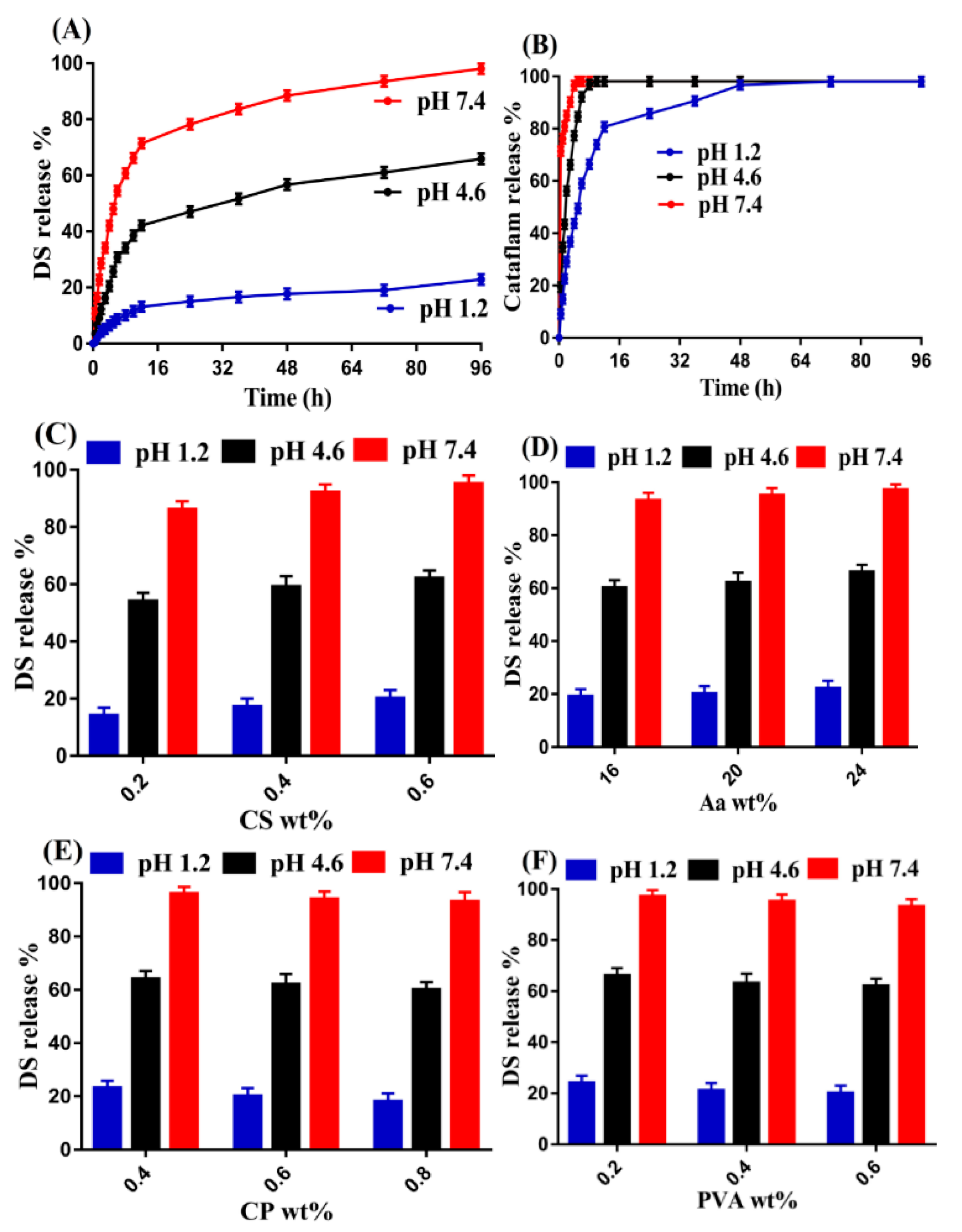
3.13. Drug Release Studies
3.13.1. Effect of pH
3.13.2. Effect of CS/CP/PVA/ and Aa
3.14. Kinetic Modeling
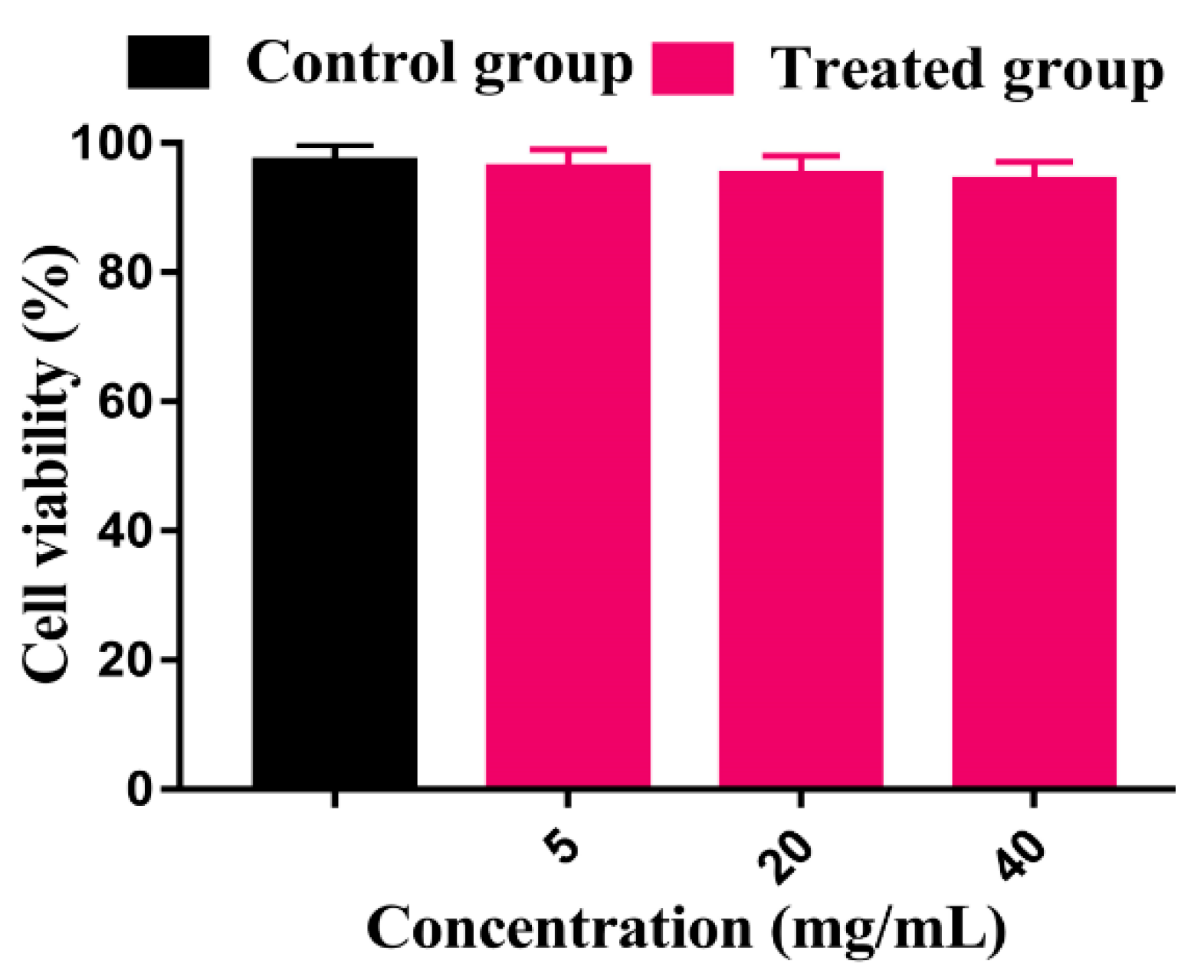
3.15. Cytotoxicity Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barakat, N.S.; Ahmad, A.A. Diclofenac sodium loaded-cellulose acetate butyrate: Effect of processing variables on microparticles properties, drug release kinetics and ulcerogenic activity. J. Microencapsul. 2008, 25, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, P.A.; Sorkin, E.M. Diclofenac sodium. Drugs 1988, 35, 244–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohel, M.; Amin, A.F. Formulation optimization of controlled release diclofenac sodium microspheres using factorial design. J. Control. Release 1998, 51, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; Delgadillo, R.M.V. Design, fabrication and drug release potential of dual stimuli-responsive composite hydrogel nanoparticle interfaces. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 204, 111819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamidi, N.; Velasco Delgadillo, R.M.; Barrera, E.V. Covalently Functionalized Carbon Nano-Onions Integrated Gelatin Methacryloyl Nanocomposite Hydrogel Containing γ-Cyclodextrin as Drug Carrier for High-Performance pH-Triggered Drug Release. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Luo, F.; Qian, Z. Efficient inhibition of colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis by drug loaded micelles in thermosensitive hydrogel composites. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3095–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, T.R.; Kohane, D.S. Hydrogels in drug delivery: Progress and challenges. Polymer 2008, 49, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Minhas, M.U.; Badshah, S.F.; Naeem, A.; Khan, K.U.; Fahad, M. Nanogels as drug-delivery systems: A comprehensive overview. Ther. Deliv. 2019, 10, 697–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Tanaka, T. Phase transition in polymer gels induced by visible light. Nature 1990, 346, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T.; Uragami, T.; Nakamae, K. Biomolecule-sensitive hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T.; Asami, N.; Uragami, T. A reversibly antigen-responsive hydrogel. Nature 1999, 399, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Mya, K.Y.; Ni, X.; He, C.; Leong, K.W.; Li, J. Dynamic and static light scattering studies on self-aggregation behavior of biodegradable amphiphilic poly (ethylene oxide)− Poly [(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate]− Poly (ethylene oxide) triblock copolymers in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 5920–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, X.J.; Tan, Y.X.; Li, Z.; Teo, L.S.; Goh, S.H.; Li, J. Biodegradable thermogelling poly (ester urethane) s consisting of poly (lactic acid)–thermodynamics of micellization and hydrolytic degradation. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Lei, M.; Liu, S.-X.; Zhao, Q. Smart hydrogel-based optical fiber SPR sensor for pH measurements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 261, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N. Fundamentals on pH-and temperature-sensitive delivery systems. PAPERBACK APV 1993, 33, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Baït, N.; Grassl, B.; Benaboura, A. Dynamic Rheology Study of In-situ Gelation Process of Polyacrylamide-Montmorillonite Composite Hydrogels. In International Symposium on Materials and Sustainable Development; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 378–384. [Google Scholar]
- Peppas, N.; Torres-Lugo, M.; Pacheco-Gomez, J.; Foss, A.; Huang, Y.; Ichikawa, H.; Leobandung, W. Intelligent hydrogels and their biotechnological and separation applications. In Radiation Synthesis of Intelligent Hydrogels and Membranes for Separation Purposes; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2000; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Putnam, D.A.; Shiah, J.-G.; Kopeček, J. Intracellularly biorecognizable derivatives of 5-fluorouracil: Implications for site-specific delivery in the human condition. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 52, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, A.-M.; Ciolacu, D.; Neamtu, A.; Mungiu, O.C.; Stoica, B.; Vasile, C. Cellulose/chondroitin sulfate hydrogels: Synthesis, drug loading/release properties and biocompatibility. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2010, 44, 369. [Google Scholar]
- Nikumbh, K.V.; Sevankar, S.G.; Patil, M.P. Formulation development, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of microemulsion-based gel loaded with ketoprofen. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, E.A.; Loutfy, S.A.; Hussein, Y.; Kenawy, E.-R.S. Recent advances in PVA-polysaccharide based hydrogels and electrospun nanofibers in biomedical applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozens, E.J.; Roohpour, N.; Gautrot, J.E. Comparative adhesion of chemically and physically crosslinked poly (acrylic acid)-based hydrogels to soft tissues. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 146, 110250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Ali, L.; Khalid, I.; Rashid, H. Controlled delivery of valsartan by cross-linked polymeric matrices: Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 487, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, S.; Buabeid, M.A.; Ullah, K.; Murtaza, G.; Mannan, A.; Khan, S.A. Synthesis, Characterization and Safety Profiling of Eudragit-Based pH-Responsive Hydrogels: A Promising Platform for Colonic Delivery of Losartan Potassium. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, K.; Sohail, M.; Buabeid, M.A.; Murtaza, G.; Ullah, A.; Rashid, H.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, S.A. Pectin-based (LA-co-MAA) semi-IPNS as a potential biomaterial for colonic delivery of oxaliplatin. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, K.; Sohail, M.; Mannan, A.; Rashid, H.; Shah, A.; Murtaza, G.; Khan, S.A. Facile Synthesis of Chitosan Based-(AMPS-co-AA) Semi-IPNs as a Potential Drug Carrier: Enzymatic Degradation, Cytotoxicity, and Preliminary Safety Evaluation. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfraz, R.M.; Khan, H.U.; Mahmood, A.; Ahmad, M.; Maheen, S.; Sher, M. Formulation and evaluation of mouth disintegrating tablets of atenolol and atorvastatin. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, K.; Khan, S.A.; Murtaza, G.; Sohail, M.; Azizullah; Manan, A.; Afzal, A. Gelatin-based hydrogels as potential biomaterials for colonic delivery of oxaliplatin. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 556, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, M.A.; Sohail, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Sarfraz, R.M.; Khan, S.; de Matas, M.; Hussain, Z.; Abbasi, M.; Shah, S.A.; Kousar, M.; et al. HEMA based pH-sensitive semi IPN microgels for oral delivery; a rationale approach for ketoprofen. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Costa-Júnior, E.; Pereira, M.M.; Mansur, H.S. Properties and biocompatibility of chitosan films modified by blending with PVA and chemically crosslinked. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, H.; Tulain, U.R.; Azam, F.; Qureshi, J. Thiolation of arabinoxylan and its application in the fabrication of pH-sensitive thiolated arabinoxylan grafted acrylic acid copolymer. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badshah, S.F.; Akhtar, N.; Minhas, M.U.; Khan, K.U.; Khan, S.; Abdullah, O.; Naeem, A. Porous and highly responsive cross-linked β-cyclodextrin based nanomatrices for improvement in drug dissolution and absorption. Life Sci. 2021, 267, 118931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ranjha, N.M. Effect of degree of cross-linking on swelling and on drug release of low viscous chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 2014, 71, 2133–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Chiu, I.-H.; Hung, M.-C.; Vu, Q.L.; Lin, I.; Wu, P.-C. In Vitro Evaluation of Smart and pH-Sensitive Chondroitin Sulfate/Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery. Gels 2022, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Khalid, S.H.; Qadir, M.I.; Massud, A.; Ali, M.; Khan, I.U.; Saleem, M.; Iqbal, M.S.; Asghar, S.; Gul, H. Water uptake and drug release behaviour of methyl methacrylate-co-itaconic acid [P(MMA/IA)] hydrogels cross-linked with methylene bis-acrylamide. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Sahlin, J.J. A simple equation for the description of solute release. III. Coupling of diffusion and relaxation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, F.; Qi, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Z.; Cai, G.; Zhang, X. Epidermal growth factor receptor aptamer-conjugated polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticles enhance salinomycin delivery to osteosarcoma and cancer stem cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispim, E.; Piai, J.; Fajardo, A.; Ramos, E.; Nakamura, T.; Nakamura, C.; Rubira, A.; Muniz, E. Hydrogels based on chemically modified poly (vinyl alcohol)(PVA-GMA) and PVA-GMA/chondroitin sulfate: Preparation and characterization. Express Polym. Lett. 2012, 6, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, R.M.; Khan, M.U.; Mahmood, A.; Akram, M.R.; Minhas, M.U.; Qaisar, M.N.; Ali, M.R.; Ahmad, H.; Zaman, M. Synthesis of co-polymeric network of carbopol-g-methacrylic acid nanogels drug carrier system for gastro-protective delivery of ketoprofen and its evaluation. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2020, 59, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, M.U.; Ahmad, M.; Ali, L.; Sohail, M. Synthesis of chemically cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol-co-poly (methacrylic acid) hydrogels by copolymerization; a potential graft-polymeric carrier for oral delivery of 5-fluorouracil. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 21, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Chi, L.; Fuchs, H. A new approach for the fabrication of an alternating multilayer film of poly (4-vinylpyridine) and poly (acrylic acid) based on hydrogen bonding. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 1997, 18, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.M.; Vavia, P.R. Diclofenac-loaded biopolymeric nanosuspensions for ophthalmic application. Nanomedicine 2009, 5, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, I.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.; Barkat, K.; Sohail, M. Cross-Linked Sodium Alginate-g-poly(Acrylic Acid) Structure: A Potential Hydrogel Network for Controlled Delivery of Loxoprofen Sodium. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.F.; Shen, S.S.; Lu, S.C. Synthesis and characterization of chondroitin sulfate-methacrylate hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 52, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, G.O.K.; Tan, Y.T.F.; Peh, K.K. Hydrophilic polymer solubilization on norfloxacin solubility in preparation of solid dispersion. Powder Technol. 2014, 256, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, K.F.; Richter, A.; Ludwig, S.; Zimmermann, J.; Kressler, J.; Kuckling, D.; Adler, H.J. Poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (acrylic acid) hydrogels: FT-IR spectroscopic characterization of crosslinking reaction and work at transition point. Acta Polym. 1999, 50, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkat, K.; Ahmad, M.; Usman Minhas, M.; Khalid, I.; Nasir, B. Development and characterization of pH-responsive polyethylene glycol-co-poly (methacrylic acid) polymeric network system for colon target delivery of oxaliplatin: Its acute oral toxicity study. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 1806–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrutkar, J.R.; Gattani, S.G. Chitosan-chondroitin sulfate based matrix tablets for colon specific delivery of indomethacin. AAPS Pharmscitech 2009, 10, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Shao, Y.-F.; Minhas, M.U.; Wu, P.-C. Formulation and in-vitro characterization of pH-responsive semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels for controlled release of ketorolac tromethamine. Gels 2021, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminabhavi, T.M.; Naik, H.G. Pervaporation separation of water/dimethylformamide mixtures using poly(vinyl alcohol)-g-polyacrylamide copolymeric membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Dhiman, A. Functionalization of carbopol with NVP for designing antibiotic drug loaded hydrogel dressings for better wound management. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Res. 2019, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Ma, H.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, A. pH-sensitive sodium alginate/poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel beads prepared by combined Ca2+ crosslinking and freeze-thawing cycles for controlled release of diclofenac sodium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 46, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-T.; Huang, C.-P.; Lee, Y.-D. Synthesis and characterizations of amphiphilic poly (l-lactide)-grafted chondroitin sulfate copolymer and its application as drug carrier. Biomol. Eng. 2007, 24, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhail, M.; Li, X.-R.; Liu, J.-Y.; Hsieh, W.-C.; Lin, Y.-W.; Wu, P.-C. Fabrication of alginate based microgels for drug-sustained release: In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, L.; Ahmad, M.; Usman, M.; Yousuf, M. Controlled release of highly water-soluble antidepressant from hybrid copolymer poly vinyl alcohol hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 2014, 71, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Zafar, N.; Lebaz, N.; Mahmood, A.; Elaissari, A. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-based hydrogel copolymeric for controlled delivery of galantamine hydrobromide in Dementia. Processes 2020, 8, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarika, P.R.; James, N.R.; kumar P.R., A.; Raj, D.K. Preparation, characterization and biological evaluation of curcumin loaded alginate aldehyde-gelatin nanogels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 68, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, R.R.; Elella, M.H.A.; Sabaa, M.W. Synthesis, characterization and applications of N-quaternized chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.B. Synthesis and properties of silk sericin-g-poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) superabsorbent hydrogel. Polym. Bull. 2011, 66, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkat, K.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Khalid, I.; Malik, N.S. Chondroitin sulfate-based smart hydrogels for targeted delivery of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer: Preparation, characterization and toxicity evaluation. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 6271–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullad, A.G.; Manjeshwar, L.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Novel pH-Sensitive Hydrogels Prepared from the Blends of Poly(vinyl alcohol) with Acrylic Acid-graft-Guar Gum Matrixes for Isoniazid Delivery. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 7323–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmin, N.; Al-Mamun, M.; Jalil, R.-U. A novel method to study the effect of PH and excipients on water uptake and swelling behaviour of carbopol polymers. Bangl. Pharm. J. 2010, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Şanlı, O.; Ay, N.; Işıklan, N. Release characteristics of diclofenac sodium from poly (vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate and poly (vinyl alcohol)-grafted-poly (acrylamide)/sodium alginate blend beads. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Bajpai, A.K.; Kulkarni, R.A. Preparation, characterization, and water-sorption study of polyvinyl alcohol based hydrogels with grafted hydrophilic and hydrophobic segments. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 95, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, P.S.K.; Mohan, Y.M.; Sreeramulu, J.; Raju, K.M. Semi-IPNs of starch and poly(acrylamide-co-sodium methacrylate): Preparation, swelling and diffusion characteristics evaluation. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tabakha, M.M.; Khan, S.A.; Ashames, A.; Ullah, H.; Ullah, K.; Murtaza, G.; Hassan, N. Synthesis, Characterization and Safety Evaluation of Sericin-Based Hydrogels for Controlled Delivery of Acyclovir. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, I.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Barkat, K. Synthesis and evaluation of chondroitin sulfate based hydrogels of loxoprofen with adjustable properties as controlled release carriers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilgin, P.; Ozay, H.; Ozay, O. Synthesis and characterization of pH responsive alginate based-hydrogels as oral drug delivery carrier. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, G.M.; Zhu, J.-B. Studies on drug release kinetics from ibuprofen–carbomer hydrophilic matrix tablets: Influence of co-excipients on release rate of the drug. J. Control. Release 1999, 57, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, O.; Minhas, M.U.; Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, S.; Barkat, K.; Ahmad, A. Synthesis, optimization, and evaluation of polyvinyl alcohol-based hydrogels as controlled combinatorial drug delivery system for colon cancer. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 3348–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of potassium chloride release from compressed, hydrophilic, polymeric matrices: Effect of entrapped air. J. Pharm. Sci. 1983, 72, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankaew, R.; Rodkate, N.; Lamlertthon, S.; Rutnakornpituk, B.; Wichai, U.; Ross, G.; Rutnakornpituk, M. “Smart” carboxymethylchitosan hydrogels crosslinked with poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) and poly (acrylic acid) for controlled drug release. Polym. Test. 2015, 42, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
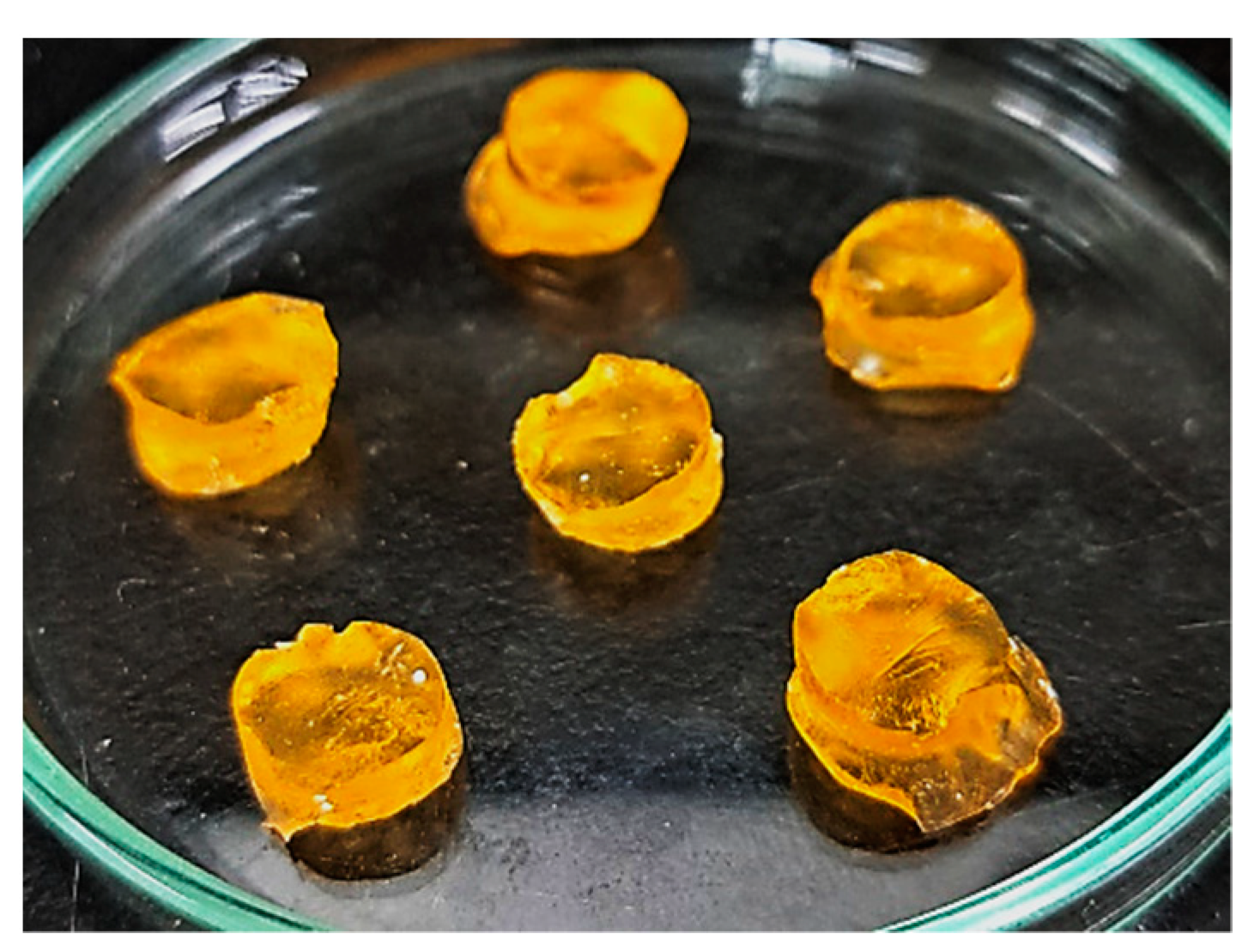




| F. Code | Polymer CS g/100 g | Polymer CP g/100 g | Polymer PVA g/100 g | Monomer Aa g/100 g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KF-1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 20 |
| KF-2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 20 |
| KF-3 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 20 |
| KF-4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 20 |
| KF-5 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 20 |
| KF-6 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 20 |
| KF-7 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 20 |
| KF-8 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 20 |
| KF-9 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 20 |
| KF-10 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 16 |
| KF-11 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 20 |
| KF-12 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 24 |
| Formulation Code | Polymer Volume Fraction | Drug-Loaded (mg)/450 mg of Dry Gel | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH1.2 | pH 4.6 | pH 7.4 | Weight Method | Extraction Method | |
| KF-1 | 0.303 | 0.166 | 0.071 | 152.2 ± 0.3 | 150.6 ± 0.2 |
| KF-2 | 0.277 | 0.136 | 0.062 | 178.4 ± 0.2 | 177.2 ± 0.4 |
| KF-3 | 0.256 | 0.125 | 0.058 | 194.1 ± 0.4 | 193.2 ± 0.3 |
| KF-4 | 0.318 | 0.174 | 0.076 | 143.3 ± 0.6 | 142.1 ± 0.5 |
| KF-5 | 0.284 | 0.146 | 0.067 | 164.6 ± 0.1 | 162.8 ± 0.1 |
| KF-6 | 0.277 | 0.136 | 0.062 | 178.4 ± 0.2 | 177.2 ± 0.4 |
| KF-7 | 0.208 | 0.105 | 0.053 | 205.1 ± 0.6 | 203.4 ± 0.1 |
| KF-8 | 0.250 | 0.130 | 0.059 | 187.2 ± 0.5 | 185.3 ± 0.3 |
| KF-9 | 0.277 | 0.136 | 0.062 | 178.4 ± 0.2 | 177.2 ± 0.4 |
| KF-10 | 0.312 | 0.172 | 0.074 | 146.1 ± 0.4 | 144.4 ± 0.5 |
| KF-11 | 0.277 | 0.136 | 0.062 | 178.4 ± 0.2 | 177.2 ± 0.2 |
| KF-12 | 0.225 | 0.096 | 0.046 | 219.6 ± 0.1 | 209.1 ± 0.4 |
| F. Code | Zero-Order r2 | First Order r2 | Higuchi r2 | Korsmeyer–Peppas | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r2 | n | ||||
| KF-1 | 0.9321 | 0.9943 | 0.9860 | 0.9132 | 0.5278 |
| KF-2 | 0.9672 | 0.9987 | 0.9665 | 0.9240 | 0.5460 |
| KF-3 | 0.9080 | 0.9812 | 0.9792 | 0.9429 | 0.5193 |
| KF-4 | 0.9731 | 0.9889 | 0.9812 | 0.9782 | 0.5012 |
| KF-5 | 0.9187 | 0.9973 | 0.9932 | 0.9672 | 0.5567 |
| KF-6 | 0.9672 | 0.9987 | 0.9665 | 0.9240 | 0.5460 |
| KF-7 | 0.9874 | 0.9894 | 0.9710 | 0.9621 | 0.6064 |
| KF-8 | 0.9656 | 0.9950 | 0.9903 | 0.9893 | 0.5864 |
| KF-9 | 0.9672 | 0.9987 | 0.9665 | 0.9240 | 0.5460 |
| KF-10 | 0.9939 | 0.9991 | 0.9845 | 0.9782 | 0.6187 |
| KF-11 | 0.9672 | 0.9987 | 0.9665 | 0.9240 | 0.5460 |
| KF-12 | 0.9757 | 0.9884 | 0.9863 | 0.9824 | 0.5983 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suhail, M.; Liu, J.-Y.; Hung, M.-C.; Chiu, I.-H.; Minhas, M.U.; Wu, P.-C. Preparation, In Vitro Characterization, and Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Polymeric pH-Responsive Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Release. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091864
Suhail M, Liu J-Y, Hung M-C, Chiu I-H, Minhas MU, Wu P-C. Preparation, In Vitro Characterization, and Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Polymeric pH-Responsive Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Release. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(9):1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091864
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuhail, Muhammad, Jia-Yu Liu, Ming-Chia Hung, I-Hui Chiu, Muhammad Usman Minhas, and Pao-Chu Wu. 2022. "Preparation, In Vitro Characterization, and Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Polymeric pH-Responsive Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Release" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 9: 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091864
APA StyleSuhail, M., Liu, J.-Y., Hung, M.-C., Chiu, I.-H., Minhas, M. U., & Wu, P.-C. (2022). Preparation, In Vitro Characterization, and Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Polymeric pH-Responsive Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Release. Pharmaceutics, 14(9), 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091864







