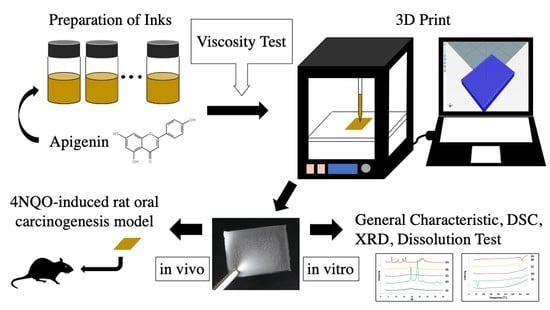
Three-Dimensional Printing of an Apigenin-Loaded Mucoadhesive Film for Tailored Therapy to Oral Leukoplakia and the Chemopreventive Effect on a Rat Model of Oral Carcinogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
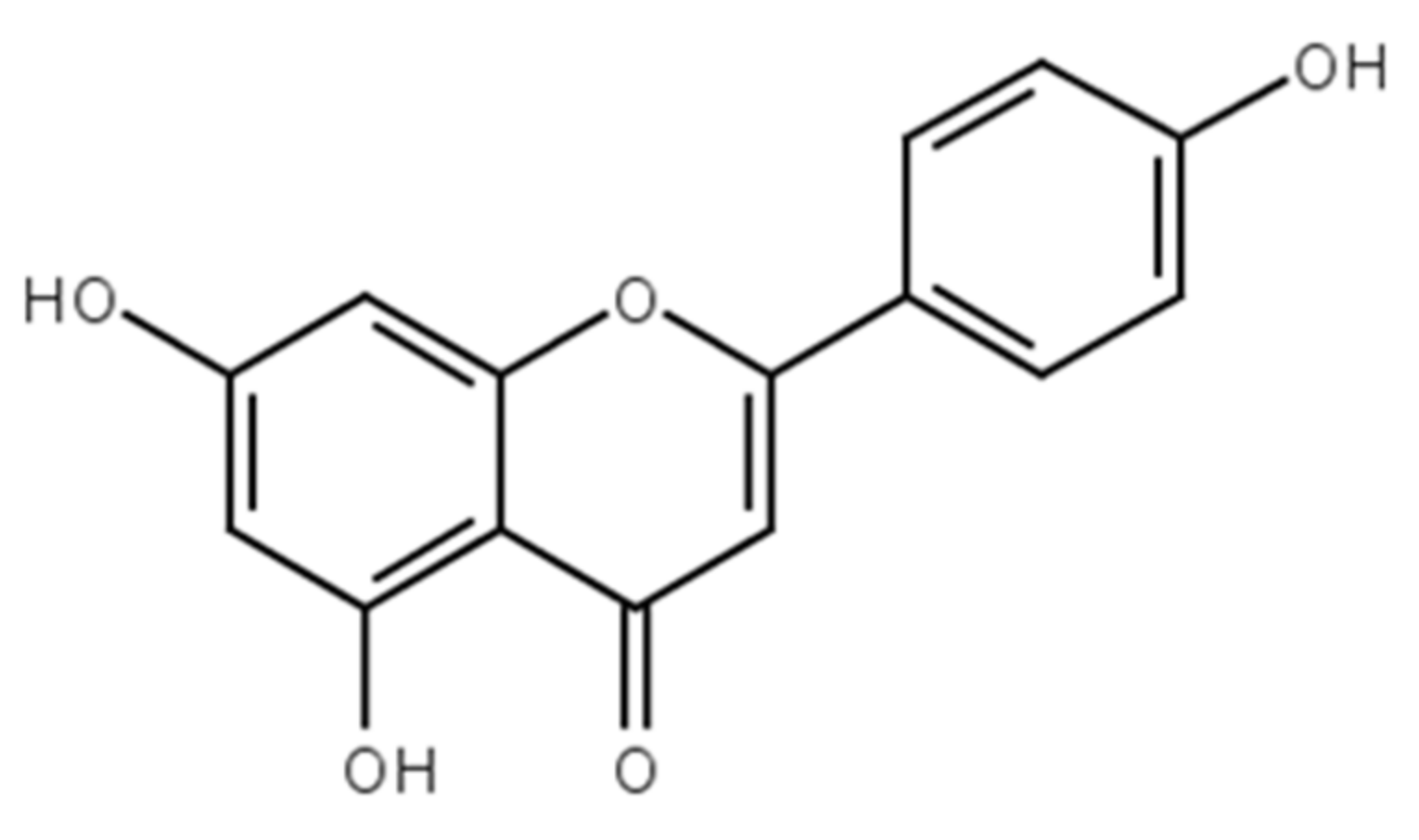
2.2. Preparation of Inks for Apigenin-Loaded Film
2.3. Viscous Property of Printer Ink
2.4. 3D Design and Fabrication of Apigenin-Loaded Film
2.5. Measurement of Film Weights and Thickness
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.7. Powder X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.8. Dissolution Test
2.9. In Vivo Chemoprevention Potential of the Apigenin-Loaded Film
2.9.1. Animal Experimental Protocol
2.9.2. Histopathological Examination
2.9.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Property of Printer Ink
3.2. Characterization of Apigenin-Loaded Film
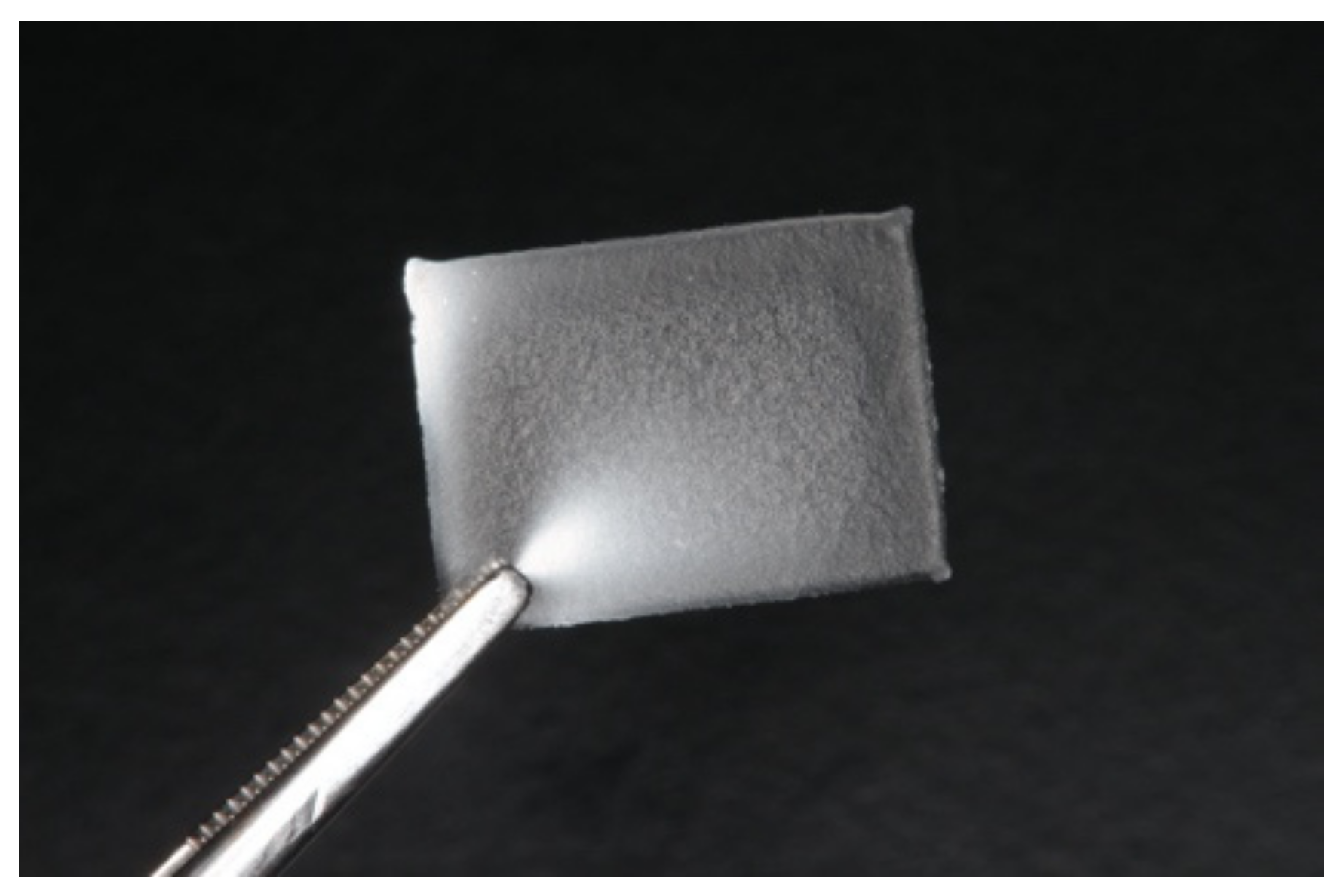
3.2.1. General Characteristics of Apigenin-Loaded Film
3.2.2. DSC
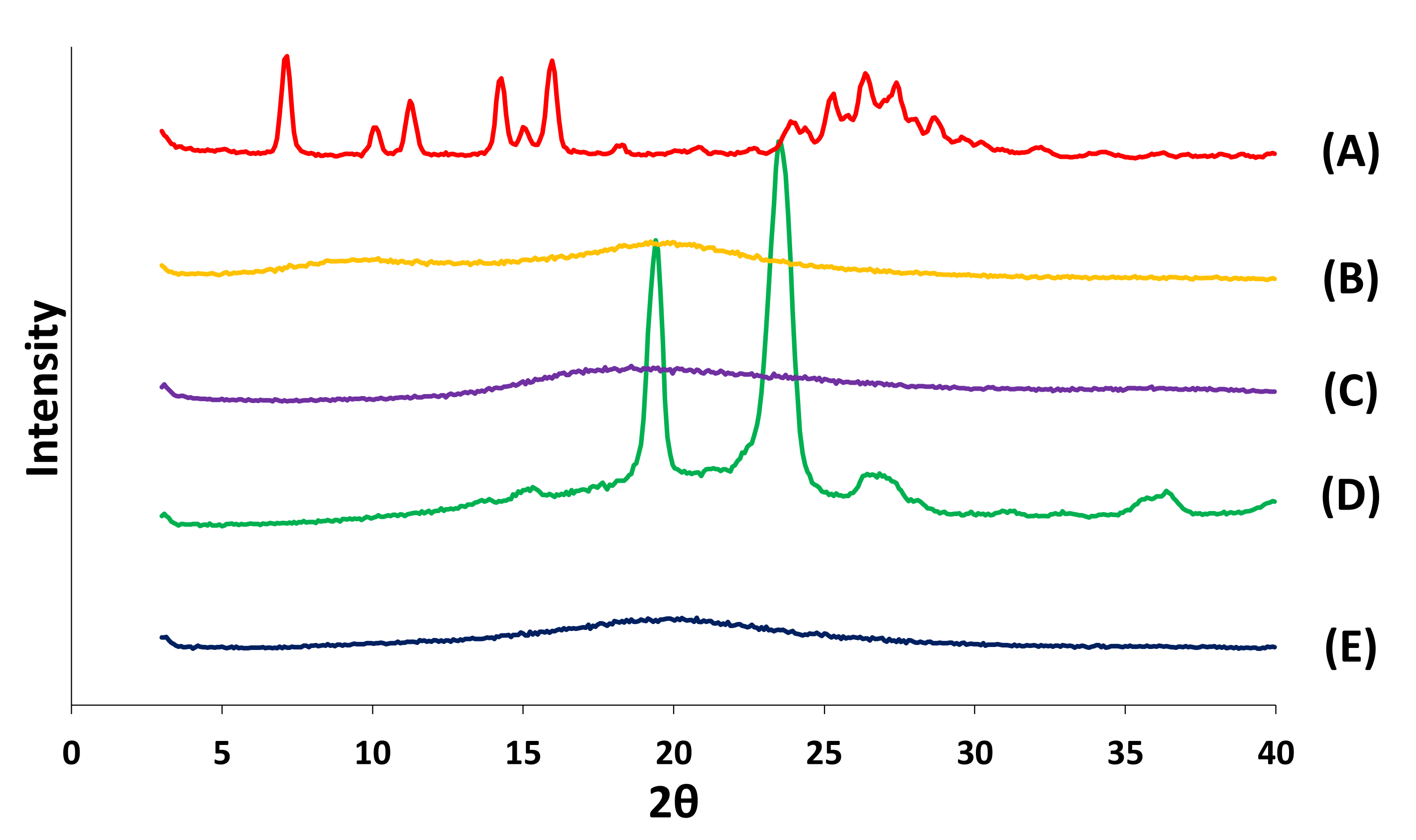
3.2.3. XRD
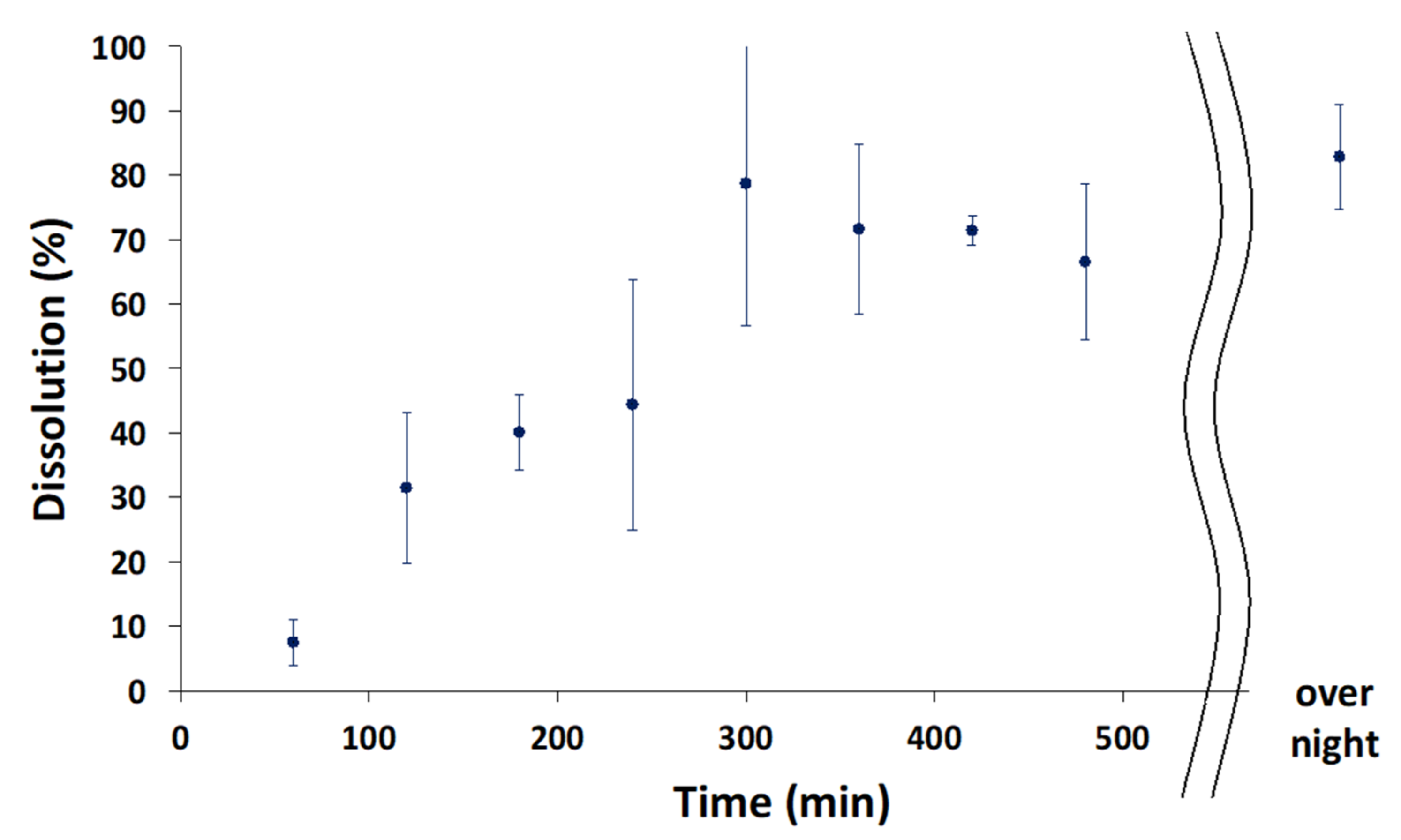
3.2.4. Dissolution Test
3.3. Chemoprevention for the Rat Tongue Carcinoma Induced by 4NQO
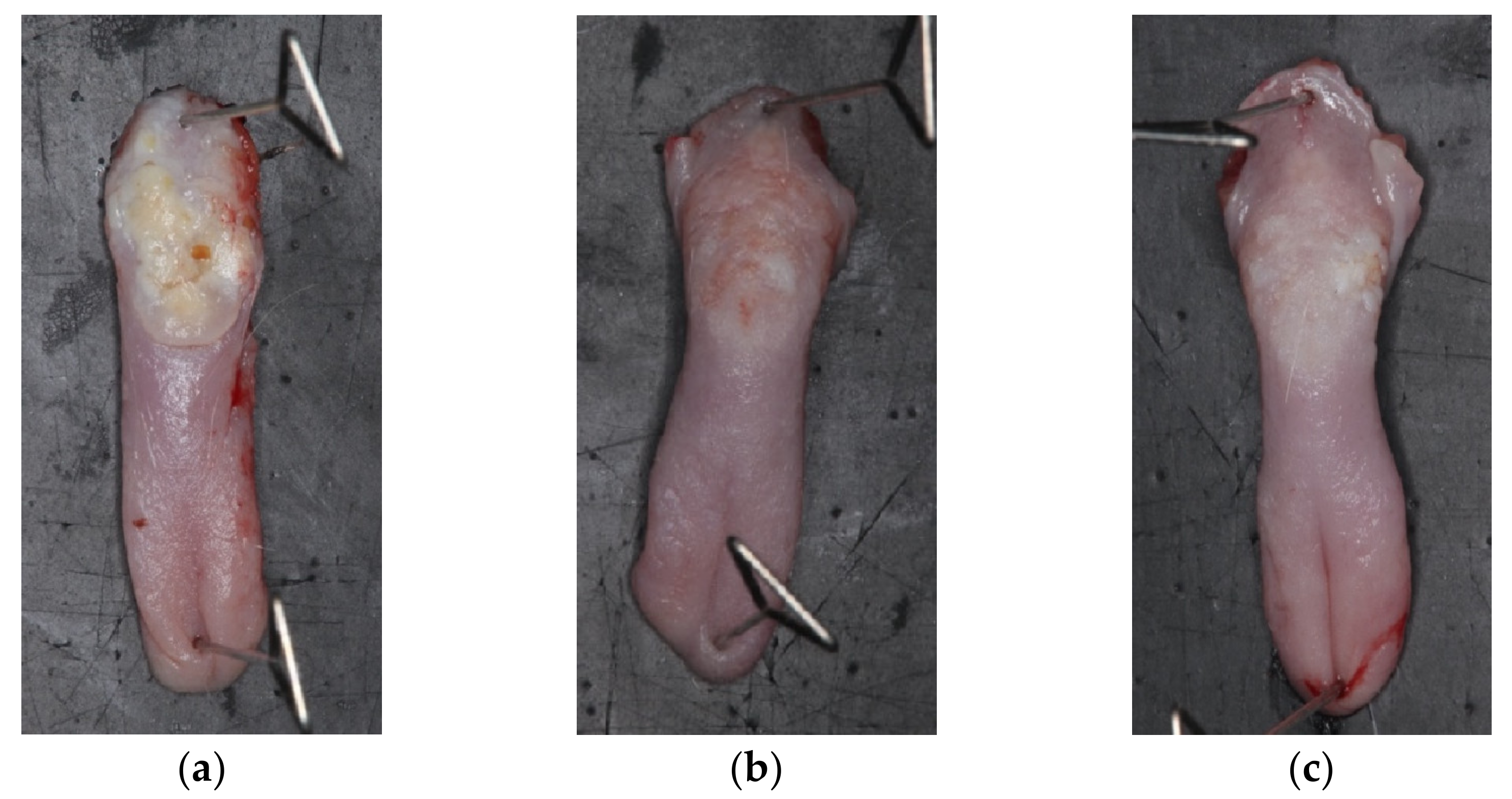
3.3.1. General Observation
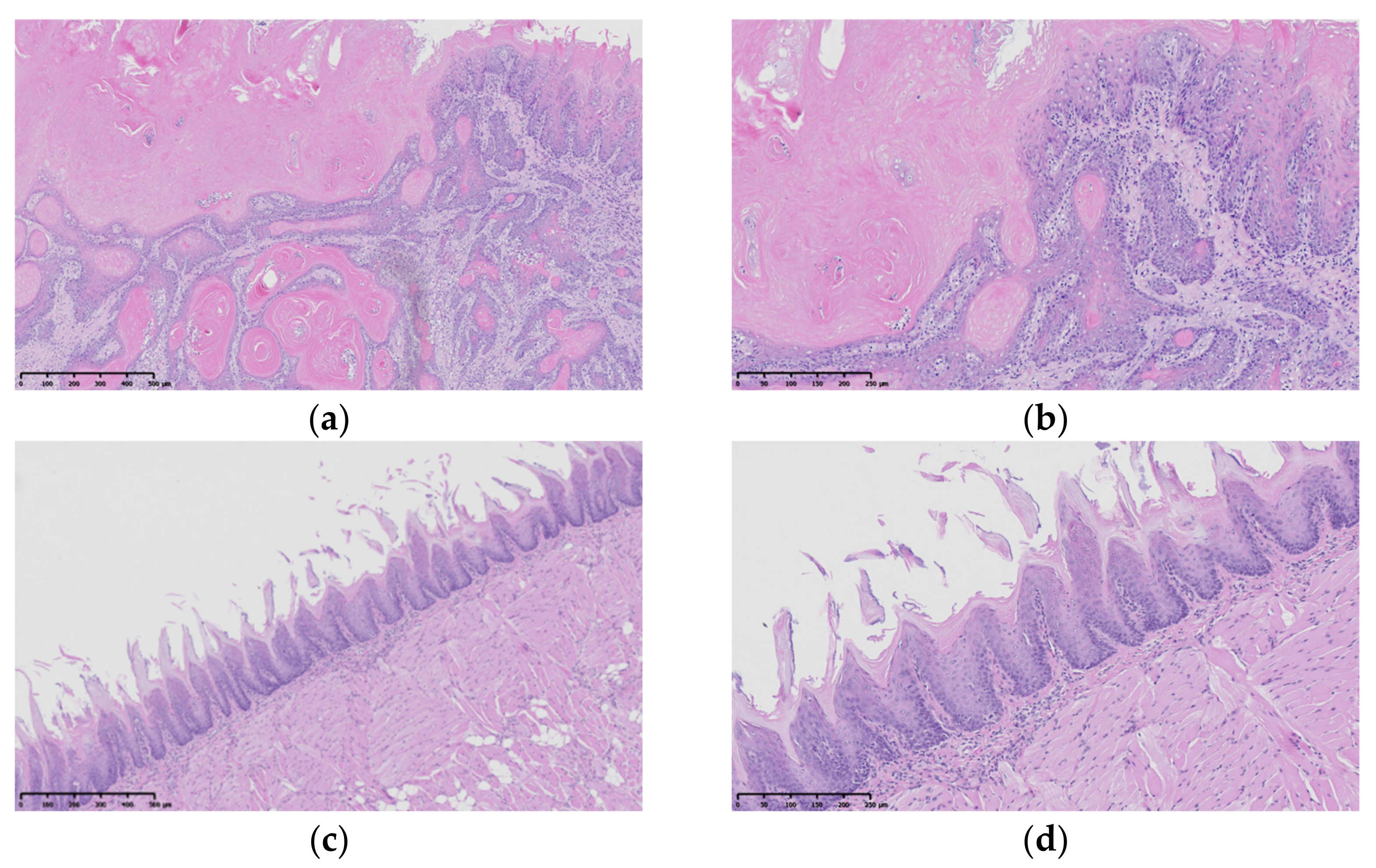
3.3.2. Histopathological Assessment
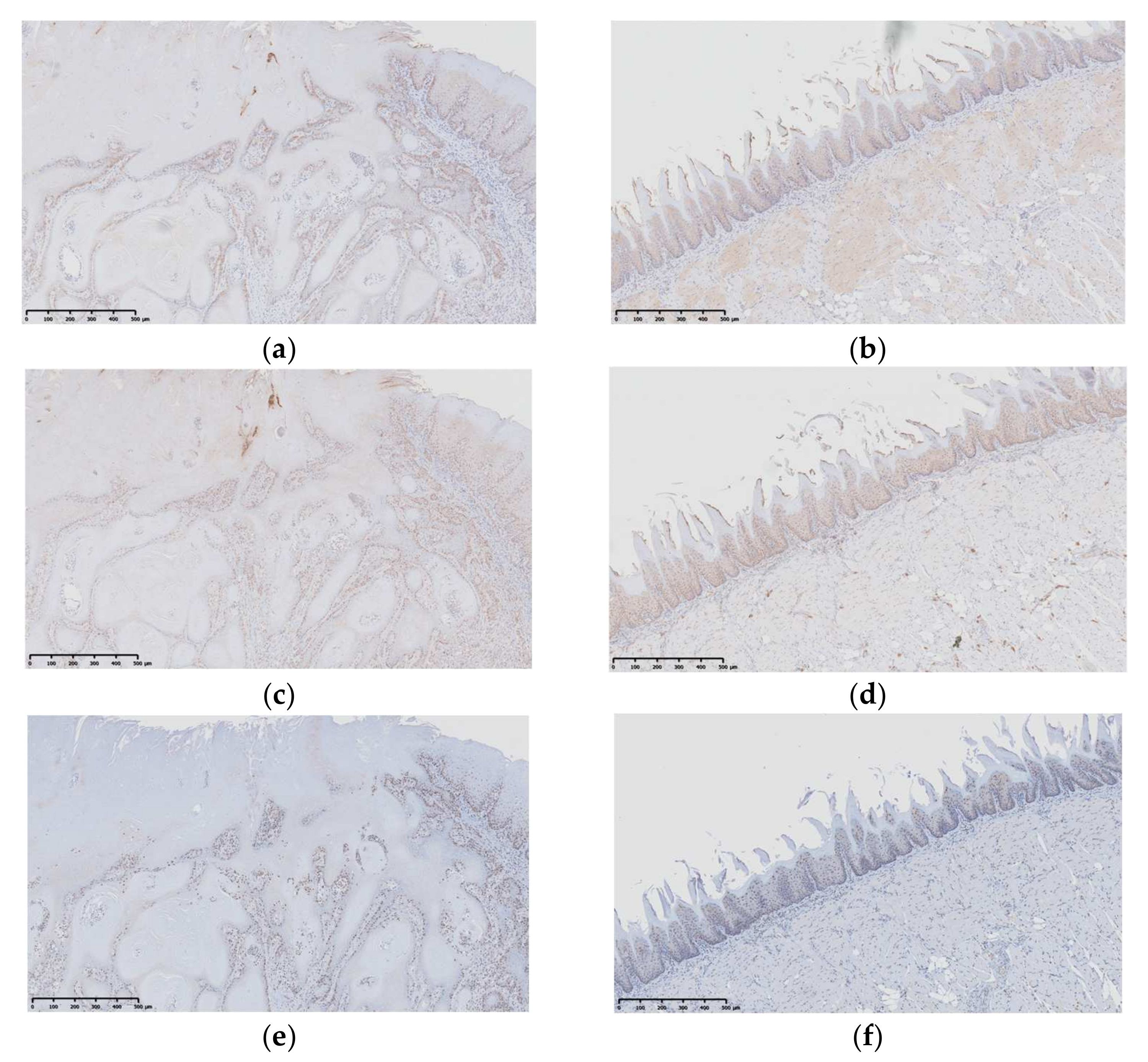
3.3.3. IHC Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamróz, W.; Szafraniec, J.; Kurek, M.; Jachowicz, R. 3D Printing in Pharmaceutical and Medical Applications—Recent Achievements and Challenges. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aguilar-de-Layva, Á.; Linares, V.; Casas, M.; Caraballo, I. 3D Printed Drug Delivery Systems Based on Natural Products. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenfield, S.J.; Awad, A.; Madla, C.M.; Hatton, G.B.; Firth, J.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Shaping the Future: Recent Advances of 3D Printing in Drug Delivery and Healthcare. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, J.; Madurawe, R.D.; Moore, C.M.V.; Khan, M.A.; Khairuzzaman, A. A New Chapter in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: 3D-printed Drug Products. Adv. Drug Deliv Rev. 2017, 108, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkasabgy, N.A.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Maged, A. 3D Printing: An Appealing Route for Customized Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, S.A.; Burley, J.C.; Alexander, M.R.; Yang, J.; Roberts, C.J. 3D Printing of Five-in-one Dose Combination Polypill with Defined Immediate and Sustained Release Profiles. J. Control. Release 2015, 217, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Cui, M.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, K.; Wen, H.; Jia, D.; Hou, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, X.; et al. Preparation and Investigation of Novel Gastro-floating Tablets with 3D Extrusion-based Printing. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwuosa, T.C.; Soares, C.; Gollwitzer, V.; Habashy, R.; Timmins, P.; Alhnan, M.A. On Demand Manufacturing of Patient-specific Liquid Capsules via Coordinated 3D Printing and Liquid Dispensing. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 118, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyanes, A.; Madla, C.M.; Umerji, A.; Piñeiro, G.D.; Montero, J.M.G.; Diaz, M.J.L.; Barcia, M.G.; Taherali, F.; Sánchez-Pintos, P.; Couce, M.-L.; et al. Automated Therapy Preparation of Isoleucine Formulations Using 3D Printing for the Treatment of MSUD: First Single-centre, Prospective, Crossover Study in Patients. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahham, N.; Fina, F.; Marcuta, C.; Kraschew, L.; Mohr, W.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W.; Goyanes, A. Selective Laser Sintering 3D Printing of Orally Disintegrating Printlets Containing Ondansetron. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panraksa, P.; Qi, S.; Udomsom, S.; Tipduangta, P.; Rachtanapun, P.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Jantrawut, P. Characterization of Hydrophilic Polymers as a Syringe Extrusion 3D Printing Material for Orodispersible Film. Polymers 2021, 13, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftheriadis, G.K.; Ritzoulis, C.; Bouropoulos, N.; Tzetzis, D.; Andreadis, D.A.; Boetker, J.; Rantanen, J.; Fatouros, D.G. Unidirectional Drug Release from 3D Printed Mucoadhesive Buccal Films Using FDM Technology: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 144, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagami, T.; Yoshimura, N.; Goto, E.; Noda, T.; Ozeki, T. Fabrication of Muco-Adhesive Oral films by the 3D Printing of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose-Based Catechin-Loaded Formulation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 1898–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seoane-Viaño, I.; Ong, J.J.; Luzardo-Álvarez, A.; González-Barcia, M.; Basit, A.W.; Otero-Espinar, F.J.; Goyanes, A. 3D Printed Tacrolimus Suppositories for the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagami, T.; Hayashi, N.; Sakai, N.; Ozeki, T. 3D Printing of Unique Water-soluble Polymer-based Suppository Shell for Controlled Drug Release. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 568, 118494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Yu, X.; Jin, Y. 3D Printing of Vaginal Rings with Personalized Shapes for Controlled Release of Progesterone. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 539, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagami, T.; Goto, E.; Kida, R.; Hirose, K.; Noda, T.; Ozeki, T. Lyophilized Ophthalmologic Patches as Novel Corneal Drug Formulations Using a Semi-solid Extrusion 3D Printer. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 617, 121448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, A.; Marti, B.M.; Sauret-Jackson, V.; Darwood, A. 3D Printing in Dentistry. Br. Dent. J. 2015, 219, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alifui-Segbaya, F.; Williams, R.J.; George, R. Additive Manufacturing: A Novel Method for Fabricating Cobalt—Chromium Removable Partial Denture Frameworks. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2017, 25, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Tunchel, S.; Blay, A.; Kolerman, R.; Mijiritsky, E.; Shibli, J.A. 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing Single Titanium Dental Implants: A Prospective Multicenter Study with 3 Years of Follow-Up. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016, 8590971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, T.T.; Reis, A.C. Fabrication of Dental Implants by the Additive Manufacturing Method: A Systematic Review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, D., III; Eidson, R.S.; Rudek, I.; Bencharit, S. In-office Fabrication of Dental Implant Surgical Guides Using Desktop Stereolithographic Printing and Implant Treatment Planning Software: A Clinical Report. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Yang, C.; Chen, K.; Zhang, S. Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Chinese Customized Three-Dimensionally Printed Total Temporomandibular Joint Prostheses: A Prospective Case Series Study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2021, 74, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelet, J.T.; Jouan, R.; Prade, V.; Francisco, C.; Jaby, P.; Gleizal, A. Place of 3D printing in Facial Epithesis. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 118, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Shan, W.; Shen, J. Fabrication and Evaluation of Dental Fillers Using Customized Molds via 3D Printing Technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 562, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, S. Update from the 4th Edition of the World Health Organization of Head and Neck Tumours: Tumours of the Oral Cavity and Mobile Tongue. Head Neck Pathol. 2017, 11, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reibel, J.; Gale, N.; Hille, J. Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders and Oral Epithelial Dysplasia. Who Classification of Head and Neck Tumours, 4th ed.; El-Naggar, A.K., Chan, J.K.C., Grandis, J.R., Takata, T., Slootweg, P.J., Eds.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017; pp. 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders: A Comprehensive Review on Clinical Aspects and Management. Oral Oncol. 2020, 102, 104550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuribayashi, Y.; Tsushima, F.; Morita, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Sakurai, J.; Uesugi, A.; Sato, K.; Oda, S.; Sakamoto, K.; Harada, H. Long-term Outcome of Non-surgical Treatment in Patients with Oral Leukoplakia. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amagasa, T.; Yamashiro, M.; Ishikawa, H. Oral Leukoplakia Related to Malignant Transformation. Oral Sci. Int. 2006, 3, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmstrup, P.; Dabelsteen, E. Oral Leukoplakia—to Treat or Not to Treat. Oral Dis. 2016, 22, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodi, G.; Franchini, R.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Varoni, E.M.; Sardella, A.; Kerr, A.R.; Carrassi, A.; McDonald, L.C.I.; Worthington, H.V. Interventions for Treating Oral Leukoplakia to Prevent Oral Cancer. Cochrane Datebase Syst. Rev. 2016, 7, CD001829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Venegas, G.; Sánchez-Carballido, M.A.; Suárez, C.D.; Gómez-Mora, J.A.; Bonneau, N. Effects of Flavonoids on Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 686–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, M.; Fujiwara, N.; Takahashi, N.; Shibuya, Y.; Masuda, S. Food-Derived Compound Apigenin and Luteolin Modulate mRNA Splicing of Introns with Weak Splice Sites. iScience 2019, 22, 336–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniatis, T.; Reed, R. An Extensive Network of Coupling among Gene Expression Machines. Nature 2002, 416, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millevoi, S.; Vagner, S. Molecular Mechanisms of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 3′ End Processing Regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 38, 2757–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orphanides, G.; Reinberg, D. A Unified Theory of Gene Expression. Cell 2002, 108, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scotti, M.M.; Swanson, M.S. RNA Mis-splicing in Disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Sanada, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Nowak, D.; Nagata, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Sato, Y.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Kon, A.; Nagasaki, M.; et al. Frequent Pathway Mutations of Splicing Machinery in Myelodysplasia. Nature 2011, 478, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Tanaka, T.; Hirose, Y.; Yamaguchi, F.; Kohno, H.; Toida, M.; Hara, A.; Sugie, S.; Shibata, T.; Mori, H. Dietary Garcinol Inhibits 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide-induced Tongue Carcinogenesis in Rats. Cancer Lett. 2005, 221, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Afifi, N.; Alabsi, A.; Kaid, F.; Bakri, M.; Ramanathan, A. Prevention of Oral Carcinogenesis in Rats by Dracaena Cinnabari Resin Extracts. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 2287–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.A.P.; Moura, C.F.G.; Gollucke, A.P.B.; Ferreira, M.S.; Catharino, R.R.; Aguiar, O., Jr.; Spadari, R.C.; Barbisan, L.F.; Ribeiro, D.A. Chemopreventive Activity of Apple Extract Following Medium-Term Oral Carcinogenesis Assay Induced by 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Rouby, D.H. Histological and Immunohistochemical Evaluation of the Chemopreventive Role of Lycopene in Tongue Carcinogenesis Induced by 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide. Arch. Oral Biol. 2011, 56, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, D.A.; Kitakawa, D.; Domingues, M.A.C.; Cabral, L.A.G.; Marques, M.E.A.; Salvadori, D.M.F. Survivin and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Production During 4NQO-induced Rat Tongue Carcinogenesis: A Possible Relationship. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2007, 83, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elemoso, A.; Shalunov, G.; Balakhovsky, Y.M.; Ostrovskiy, A.Y.; Khesuani, Y.D. 3D Bioprinting: The Roller Coaster Ride to Commercialization. Int. J. Bioprint. 2020, 6, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoane-Viaño, I.; Trenfield, S.J.; Basit, A.W.; Goyanes, A. Translating 3D printed Pharmaceuticals: From Hype to Real-world Clinical Applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Dhawan, N.; Sharma, H.; Vaidya, S.; Vaidya, B. Bioadhesive Polymers: Novel Tool for Drug Delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2014, 42, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanović, M.; Petrović, M.; Cvijić, S.; Tomić, N.; Stojanović, D.; Ibrić, S.; Uskoković, P. 3D Printed Buccal Films for Prolonged-Release of Propranolol Hydrochloride: Development, Characterization and Bioavailability Prediction. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speer, I.; Preis, M.; Breitkreutz, J. Novel Dissolution Method for Oral Film Preparations with Modified Release Properties. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Lv, J.; Yang, W.; Pi, X.; Lin, W.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, W.; Pang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Lv, Z.; et al. Preparation and Application of Subdivided Tablets Using 3D Printing for Precise Hospital Dispensing. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 149, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Kovacevic, T.; Madden, P.; Coupland, V.H.; Sperandio, M.; Odell, E.; Møller, H. Factors Predicting Malignant Transformation in Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders among Patients Accrued over a 10-year Period in South East England. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-H.; Lin, P.-Y.; Lin, C.-K.; Chi, L.-Y. Effects of Oral Exercise on Tongue Pressure in Taiwanese Older Adults in Community Day Care Centers. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.; Gao, Y.; Qian, S. Preparation of Apigenin Nanocrystals Using Supercritical Antisolvent Process for Dissolution and Bioavailability Enhancement. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, D.; Davis, M.; Walker, G.M.; Lyons, J.G.; Higginbotham, C.L. The Effect of Cooling on the Degree of Crystallinity, Solid-State Properties, and Dissolution Rate of Multi-Component Hot-Melt Extruded Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aldawsari, M.F.; Ahmed, M.M.; Fatima, F.; Anwer, M.K.; Katakam, P.; Khan, A. Development and Characterization of Calcium-Alginate Beads of Apigenin: In Vitro Antitumor, Antibacterial, and Antioxidant Activities. Mar. Drugs. 2021, 19, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Badry, M.; Hassan, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Elsaghir, H. Performance of Poloxamer 407 as Hydrophilic Carrier on the Binary Mixtures with Nimesulide. FARMACIA 2013, 61, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Jangdey, M.S.; Gupta, A.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S. Development and Optimization of Apigenin-loaded Transfersomal System for Skin Cancer Delivery: In Vitro Evaluation. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, T.; Ishigamori, R. Understanding Carcinogenesis for Fighting Oral Cancer. J. Oncol. 2011, 2011, 603740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-koshab, M.; Alabsi, A.M.; Bakri, M.M.; Naicker, M.S.; Seyedan, A. Chemopreventive Activity of Tualang Honey Against Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma—in Vivo. Oral Surg Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2020, 129, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, D.L.; Horn, T.L.; Johnson, W.D.; Peng, X.; Lubet, R.A.; Steele, V.E. Suppression of Rat Oral Carcinogenesis by Agonists of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor γ. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thandavamoorthy, P.; Balan, R.; Subramaniyan, J.; Arumugam, M.; Johmn, B.; Krishnan, G.; Ramasamy, E.; Mani, G.K.; Rajendran, R.; Thiruvengadam, D. Alleviative Role of Rutin Against 4-Nitroquinoline-1-Oxide (4-NQO) Provoked Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Experimental Animal Model. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 8, 899–906. [Google Scholar]
- Maggioni, D.; Garavello, W.; Rigolio, R.; Pignataro, L.; Gaini, R.; Nicolini, G. Apigenin Impairs Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth in Vitro Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Kaufman, P.D. Ki-67: More than a Proliferation Marker. Chromosoma 2018, 127, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincente, J.C.; Herrero-Zapatero, A.; Fresno, M.F.; López-Arranz, J.S. Expression of Cyclin D1 and Ki-67 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity: Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance. Oral Oncol. 2002, 38, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Katori, H.; Nozawa, A.; Tsukuda, M. Increased Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 and Ki-67 are Associated with Malignant Transformation of Pleomorphic Adenoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 2007, 34, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bôas, D.S.; Takiya, C.M.; Coelho-Sampaio, T.L.; Monção-Ribeiro, L.C.; Ramos, E.A.G.; Cabral, M.G.; dos Santos, J.N. Immunohistochemical Detection of Ki-67 is not Associated with Tumor-infiltrating Macrophages and Cyclooxygenase-2 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2010, 39, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingappan, K. NF-κB in Oxidative Stress. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colotta, F.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. Cancer-related Inflammation, the Seventh Hallmark of Cancer: Links to Genetic Instability. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Topal, A.; Alak, G.; Altun, S.; Erol, H.S.; Atamanalp, M. Evaluation of 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine and NFkB Activation, Oxidative Stress Response, Acetylcholinesterase Activity, and Histopathological Changes in Rainbow Trout Brain Exposed to Linuron. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 49, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Aznar-Cayuela, C.; Rubio, C.P.; Ceron, J.J.; López-Jornet, P. Evaluation of Salivary Nitric Oxide Levels and C-reactive Protein in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus and Burning Mouth Syndrome. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2017, 46, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardaro, N.; Vella, F.D.; Incalza, M.A.; Stasio, D.D.; Lucchese, A.; Contaldo, C.; Laudadio, C.; Petruzzi, M. Oxidative Stress and Oral Mucosal Diseases: An Overview. In Vivo 2019, 33, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Cai, W.; Zhao, S.; Shi, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Mao, Y.; He, B.; Hou, Y.; et al. Oxidative Stress-related Biomarkers in Saliva and Gingival Crevicular Fluid Associated with Chronic Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, R.B.; Cernelio, S.; Shenoy, R.P.; Gyawali, P.; Mukherjee, M. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense in Oral Lichen Planus and Oral Lichenoid Reaction. Scand J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2010, 70, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
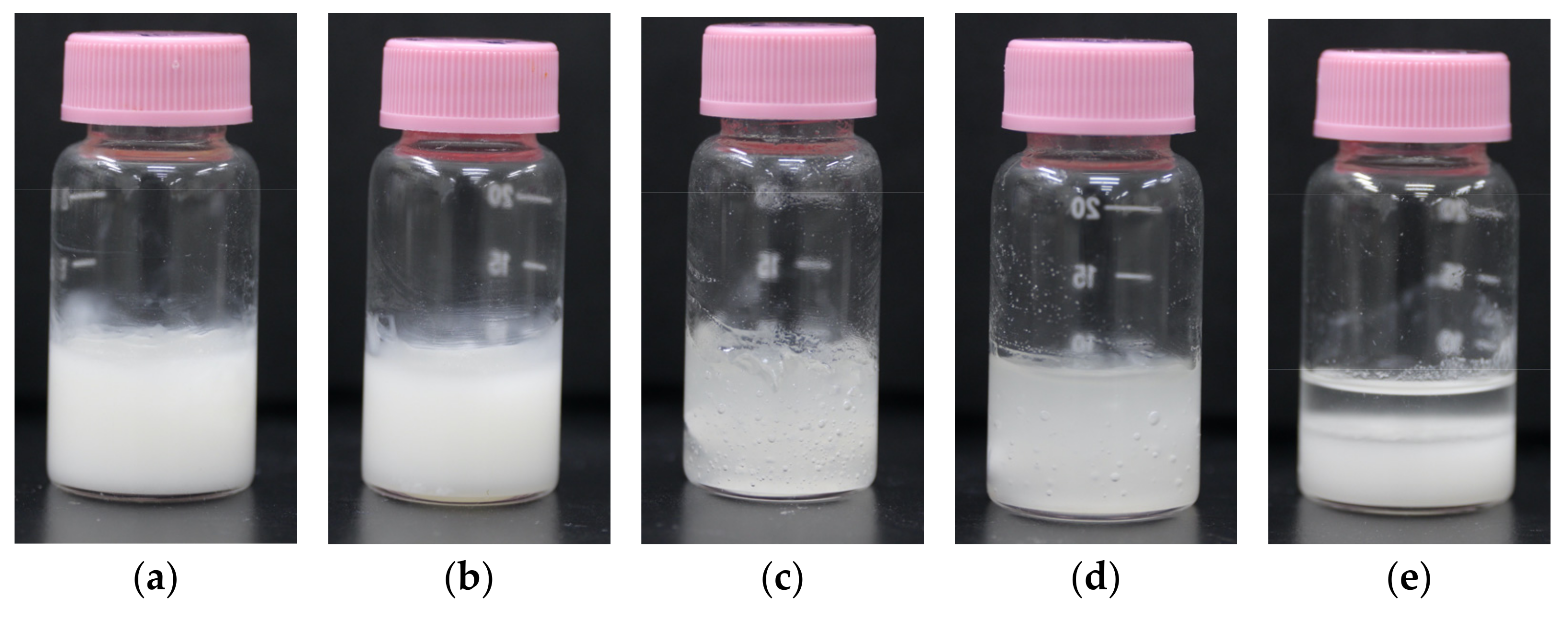

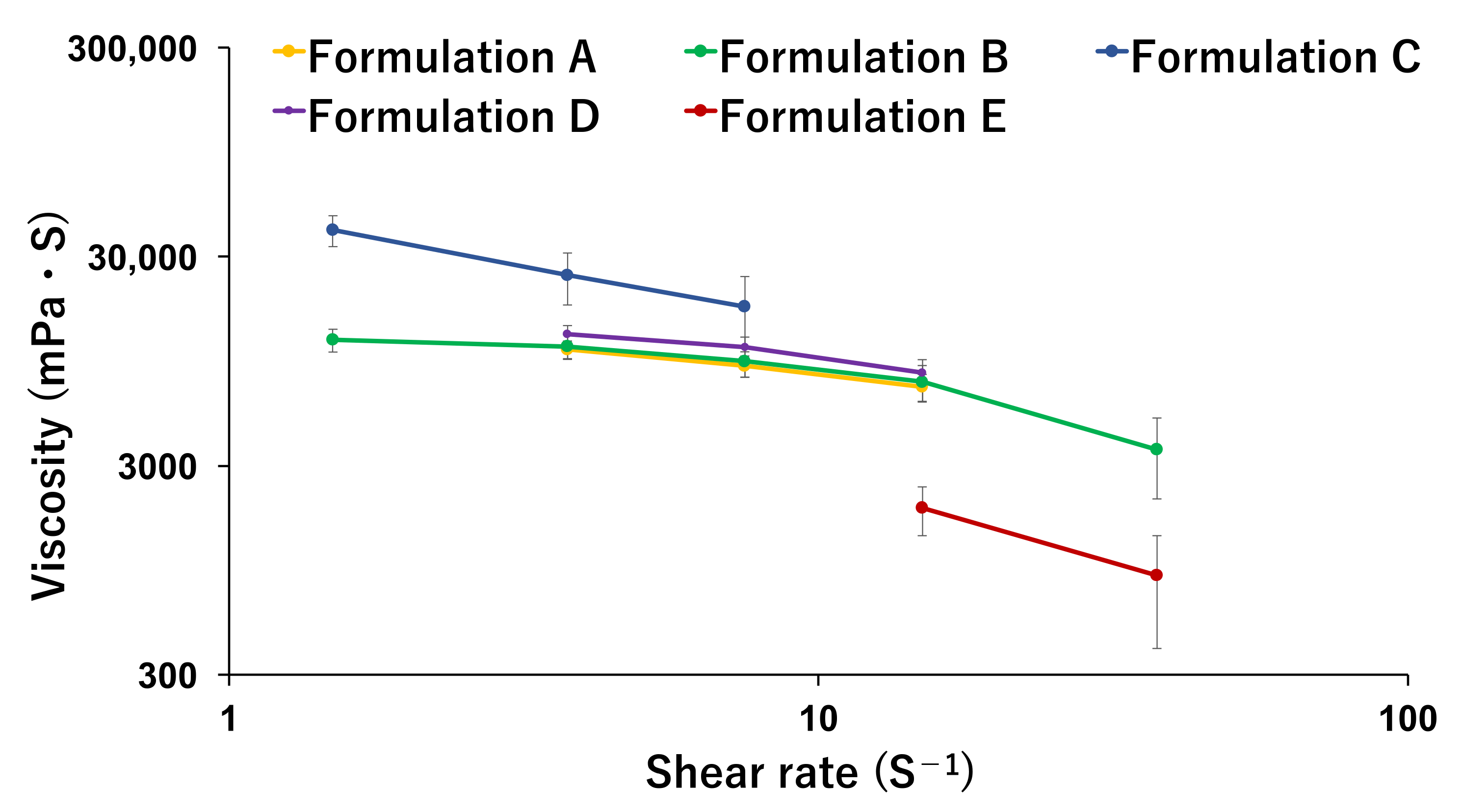

| Composition | Apigenin (mg) | Ethanol (mL) | Water (mL) | CARBOPOL (mg) | Poloxamer (mg) | HPMC (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formulation A | 2.5 | 0 | 9.4 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Formulation B | 2.5 | 2.35 | 7.05 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Formulation C | 2.5 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Formulation D | 2.5 | 7.05 | 2.35 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Formulation E | 2.5 | 9.4 | 0 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Weight (mg) | Thickness (μm) | Drug (μg) |
|---|---|---|
| 159.7 ± 11.5 | 39.3 ± 2.7 | 163.0 ± 11.4 |
| Group | Survival Rate | Final Body Weight (g) a |
|---|---|---|
| CTRL | 5/6 (83.3%) | 484.4 ± 94.2 |
| Apigenin-loaded film | 6/6 (100%) | 576.6 ± 73.1 |
| Group | Normal | Hyperplasia | Dysplasia | Carcinoma |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (100%) |
| Apigenin-loaded film | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (50%) | 3 * (50%) |
| IHC Maker | Group | Mean ± SD (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ki-67 | CTRL | 4.42 ± 2.40 | <0.0001 * |
| Apigenin-loaded film | 2.54 ± 1.08 | ||
| NF-κB | CTRL | 13.77 ± 3.83 | 0.643 |
| Apigenin-loaded film | 12.30 ± 4.39 | ||
| 8-OHdG | CTRL | 12.20 ± 1.96 | 0.014 * |
| Apigenin-loaded film | 8.34 ± 4.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takashima, H.; Tagami, T.; Kato, S.; Pae, H.; Ozeki, T.; Shibuya, Y. Three-Dimensional Printing of an Apigenin-Loaded Mucoadhesive Film for Tailored Therapy to Oral Leukoplakia and the Chemopreventive Effect on a Rat Model of Oral Carcinogenesis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081575
Takashima H, Tagami T, Kato S, Pae H, Ozeki T, Shibuya Y. Three-Dimensional Printing of an Apigenin-Loaded Mucoadhesive Film for Tailored Therapy to Oral Leukoplakia and the Chemopreventive Effect on a Rat Model of Oral Carcinogenesis. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(8):1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081575
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakashima, Hiroyuki, Tatsuaki Tagami, Shinichiro Kato, Heeju Pae, Tetsuya Ozeki, and Yasuyuki Shibuya. 2022. "Three-Dimensional Printing of an Apigenin-Loaded Mucoadhesive Film for Tailored Therapy to Oral Leukoplakia and the Chemopreventive Effect on a Rat Model of Oral Carcinogenesis" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 8: 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081575
APA StyleTakashima, H., Tagami, T., Kato, S., Pae, H., Ozeki, T., & Shibuya, Y. (2022). Three-Dimensional Printing of an Apigenin-Loaded Mucoadhesive Film for Tailored Therapy to Oral Leukoplakia and the Chemopreventive Effect on a Rat Model of Oral Carcinogenesis. Pharmaceutics, 14(8), 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081575