Intranasal Delivery of Granisetron to the Brain via Nanostructured Cubosomes-Based In Situ Gel for Improved Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Emesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Design and Optimization of Experiments
2.2.2. Formulation of Granisetron-Loaded Cubosomes (GS-CBS)
2.2.3. GS-CBS Characterization and Optimization
Particle Diameter and Zeta Potential Analysis
Measurement of Entrapment Efficiency
2.2.4. Characterization of the Optimized GS-CBS Formulation
Morphological Evaluation
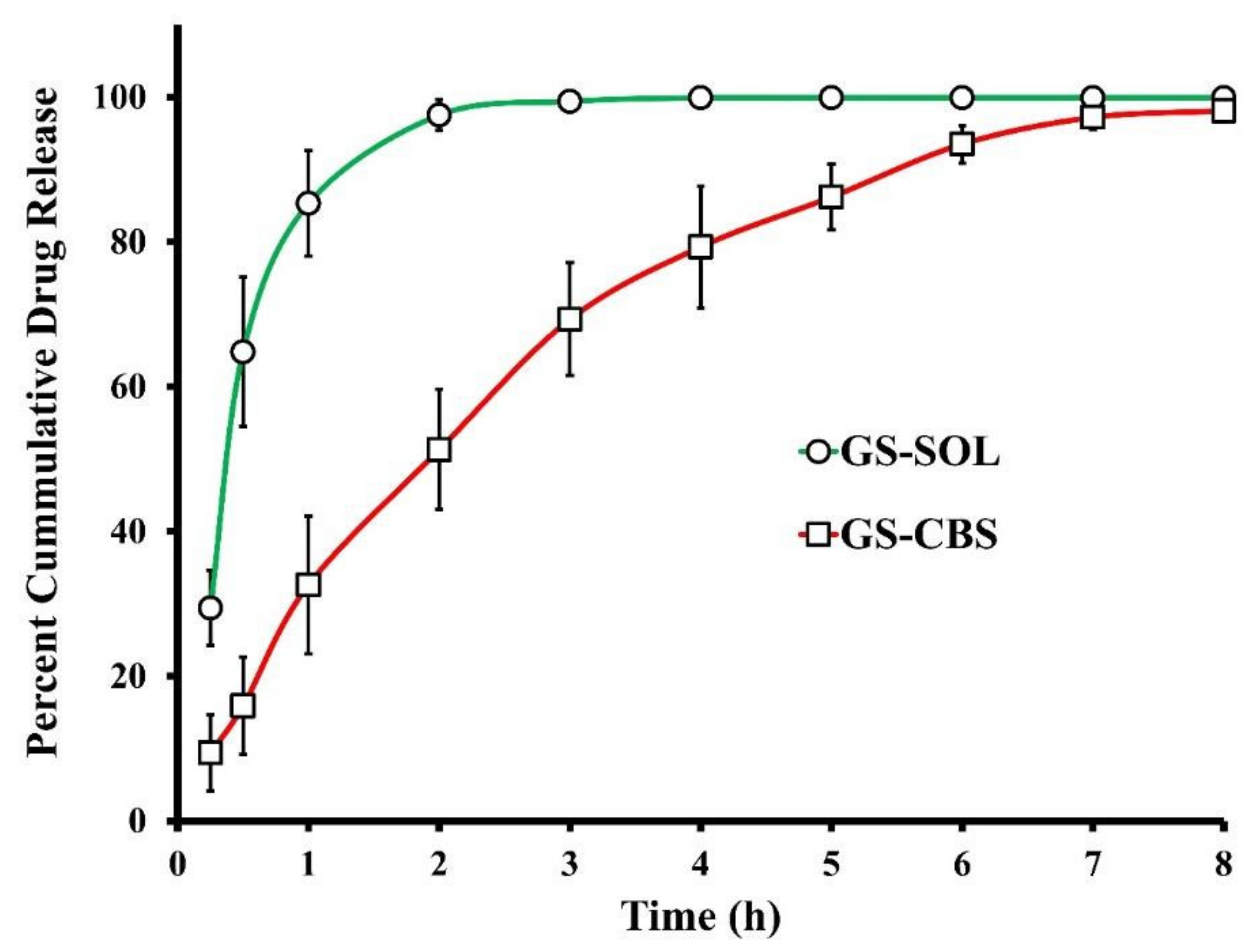
In Vitro Release of GS
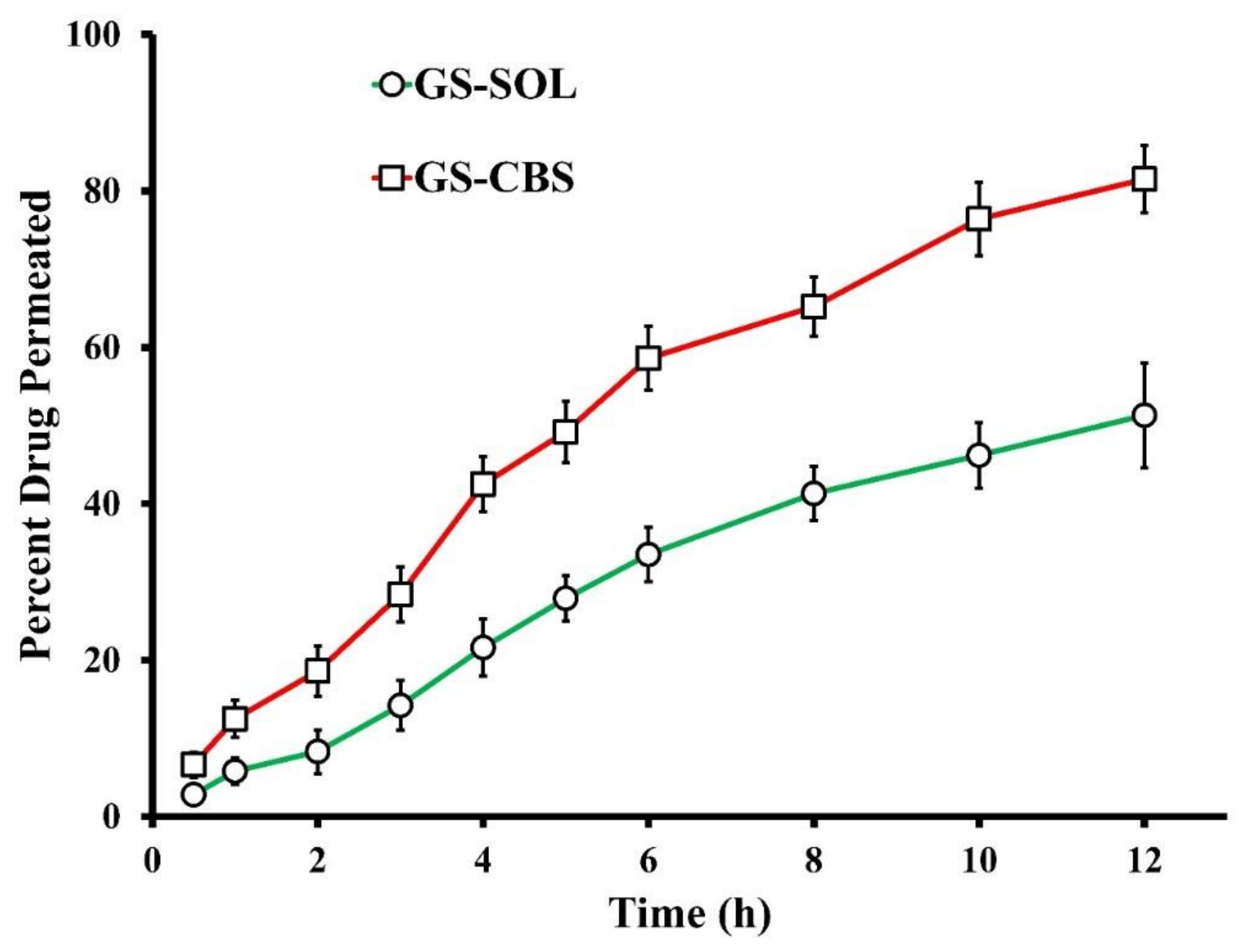
Ex Vivo Permeation of GS
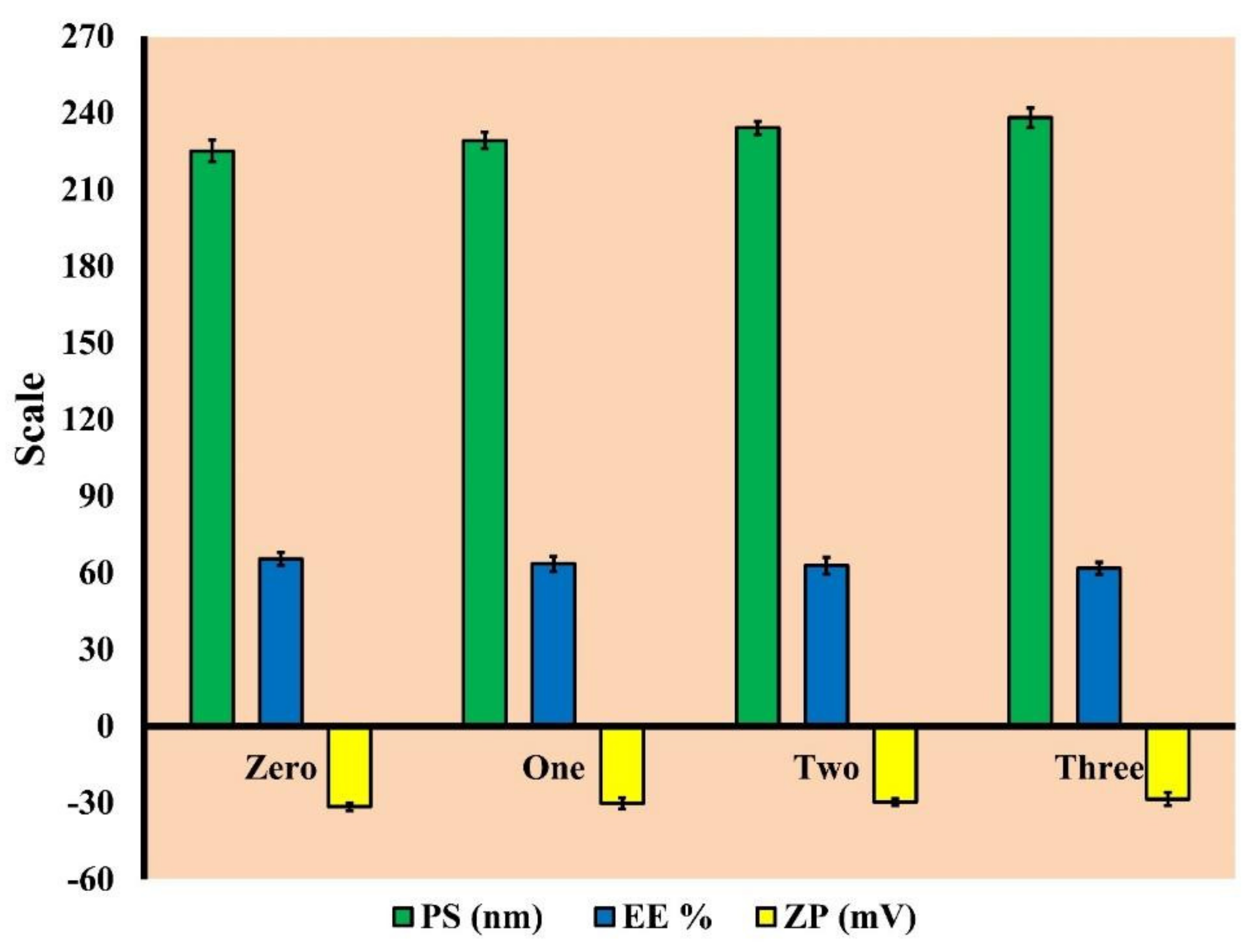
Short-Term Stability
Preparation of GS-CBS Thermosensitive Gel
2.2.5. Evaluation of pH
2.2.6. In Vivo Studies
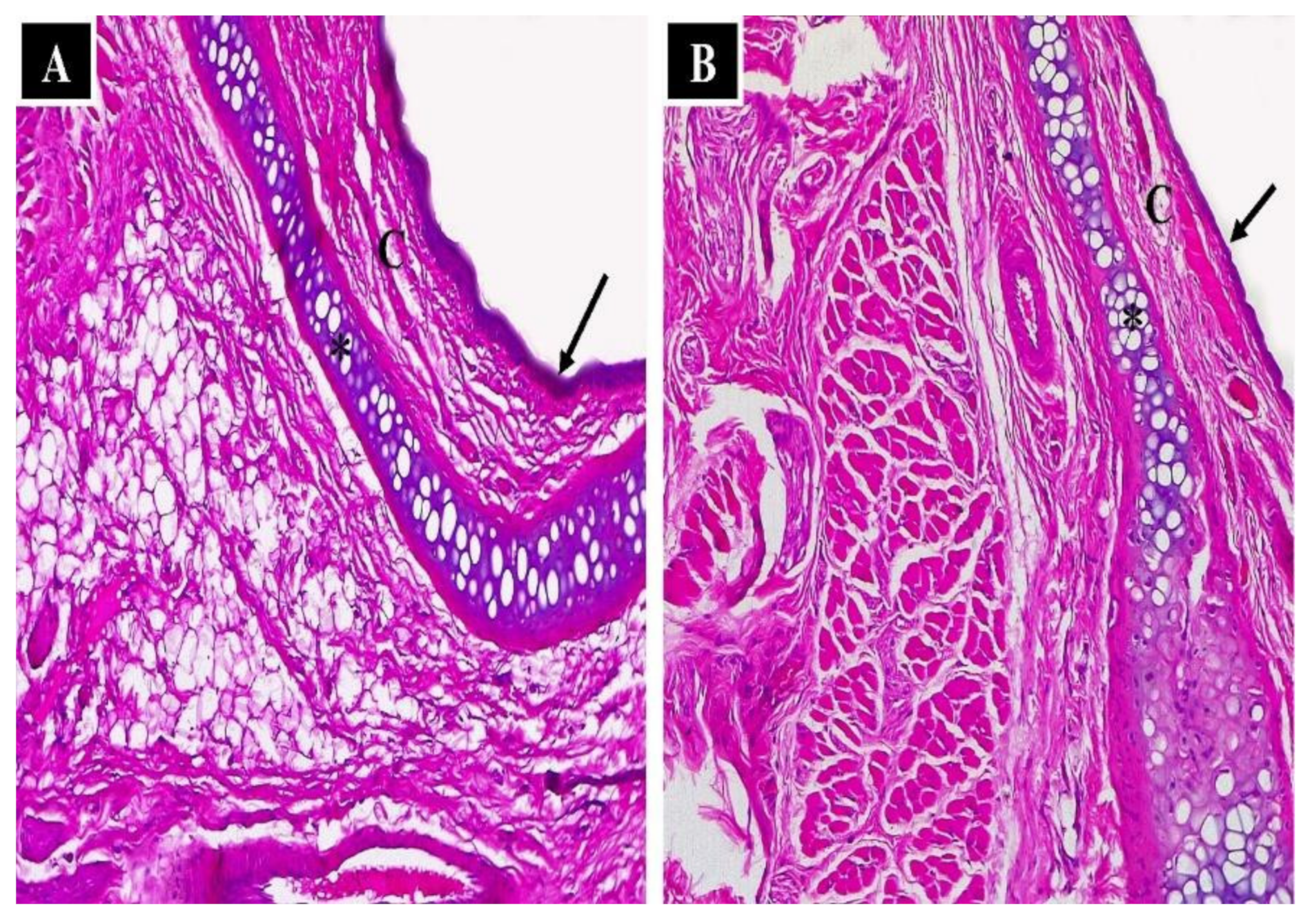
Histopathological Evaluation
In Vivo Biodistribution Analysis
Sample Preparation for Analysis
Chromatographic Conditions
Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
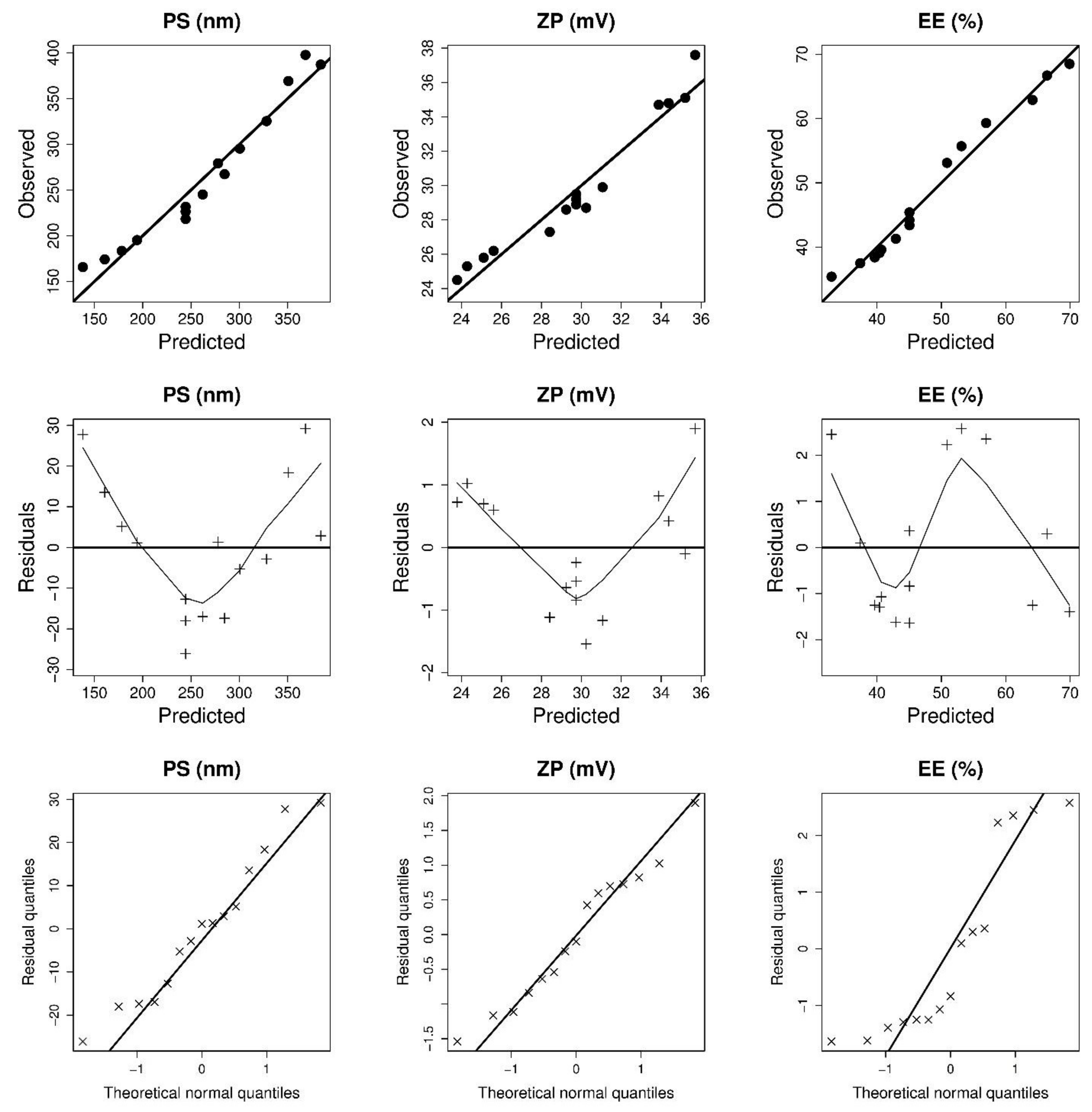
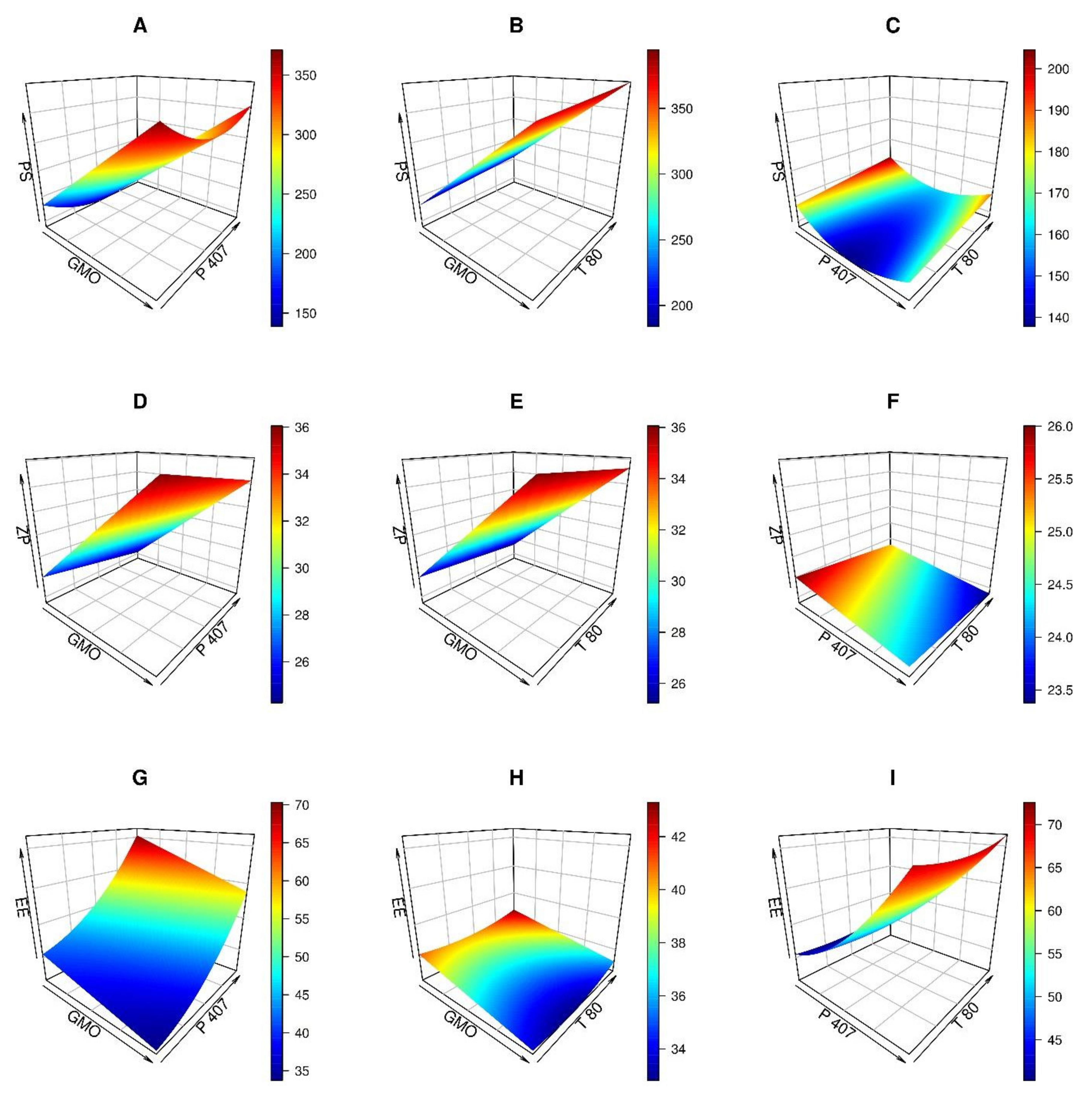
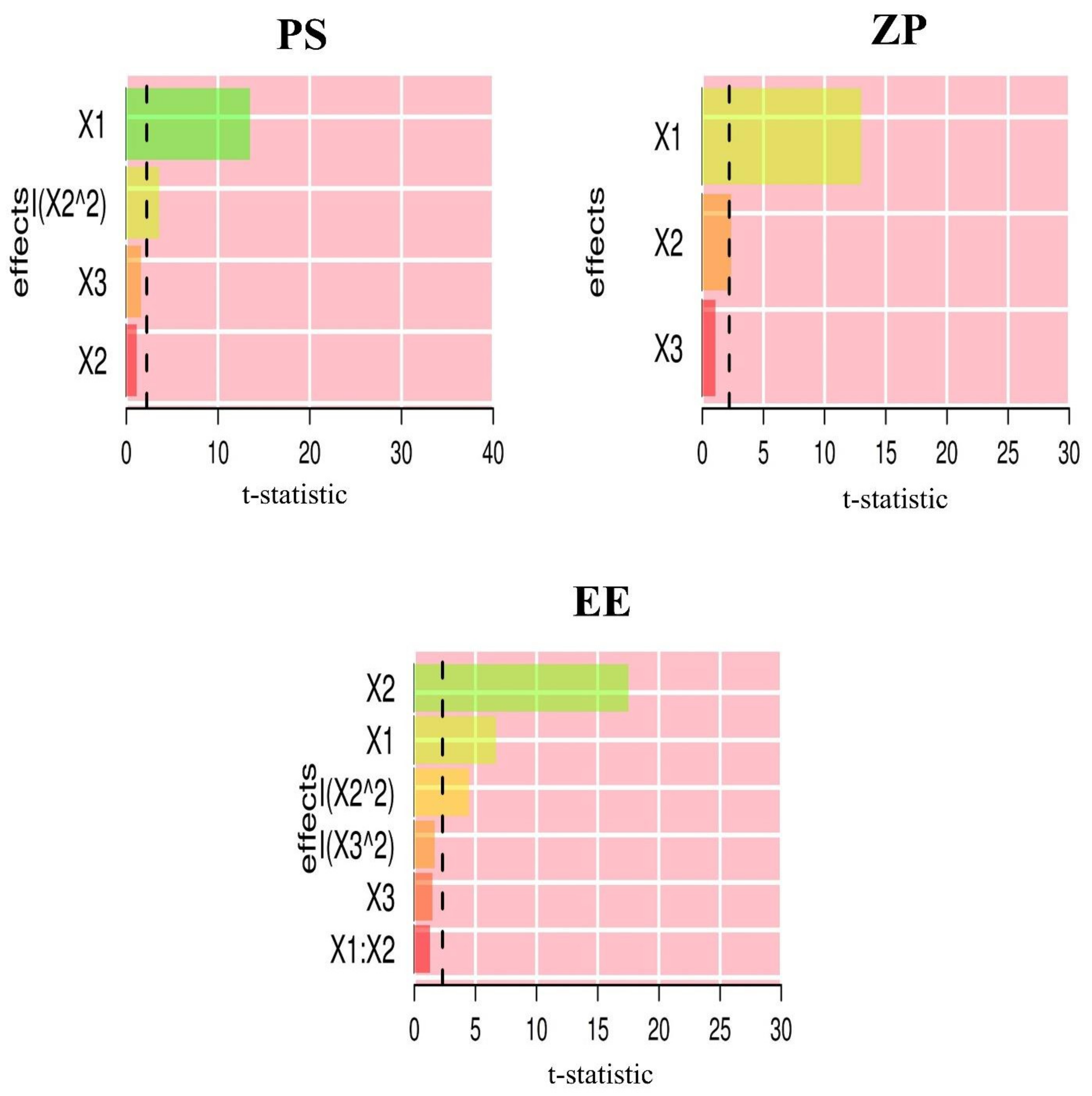
3.1. Experimental Design and Optimization
3.1.1. Analysis of Particle Size (PS)
3.1.2. Analysis of Zeta Potential (ZP)
3.1.3. Analysis of Entrapment Efficiency (EE)
3.1.4. Formulation Optimization
3.2. Characterization of Optimized GS-CBS
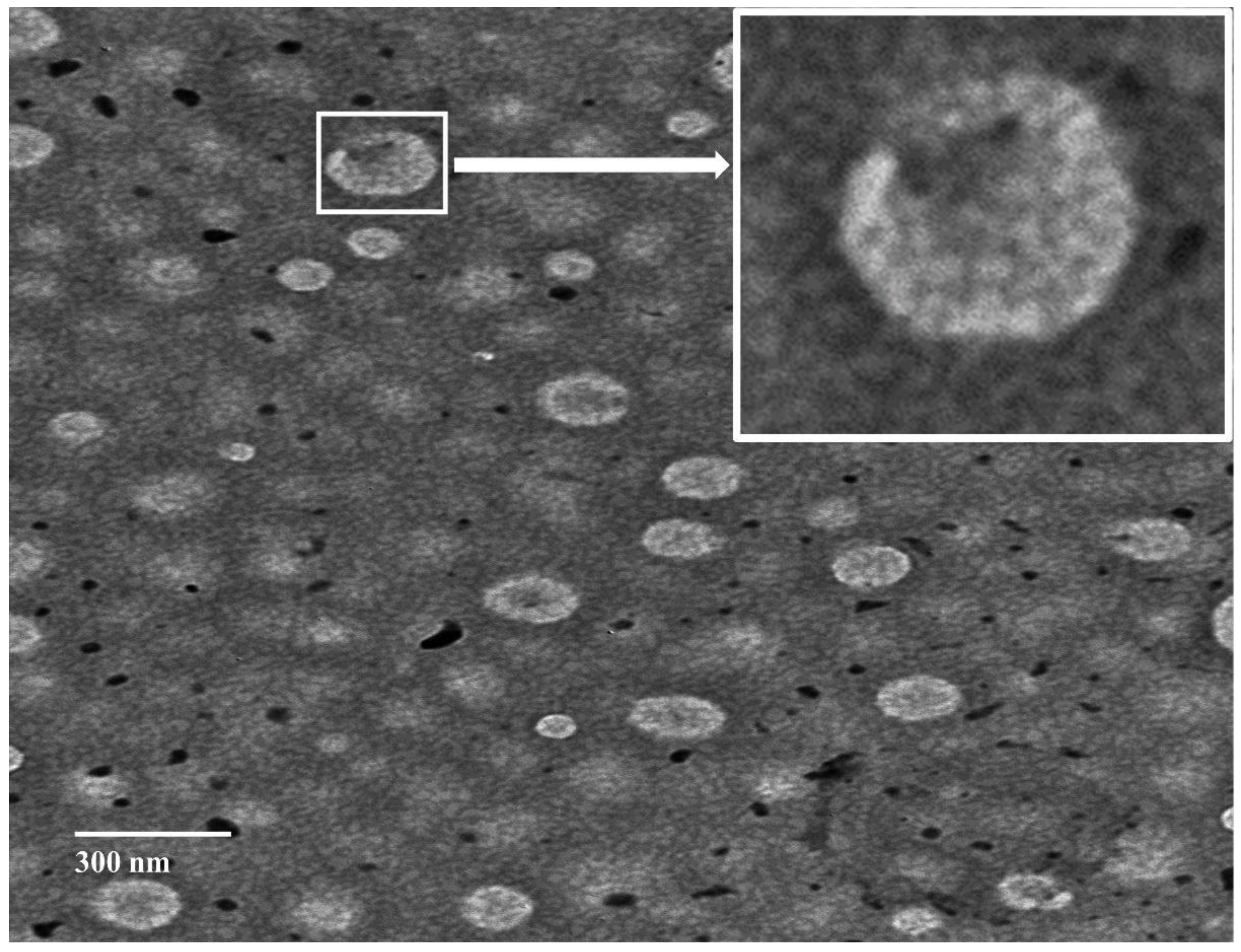
3.2.1. Morphological Evaluation
3.2.2. In Vitro Release of GS
3.2.3. Ex Vivo Permeation of GS
3.2.4. Short-Term Stability
3.2.5. Evaluation of pH
3.2.6. Nasal Histopathological Studies
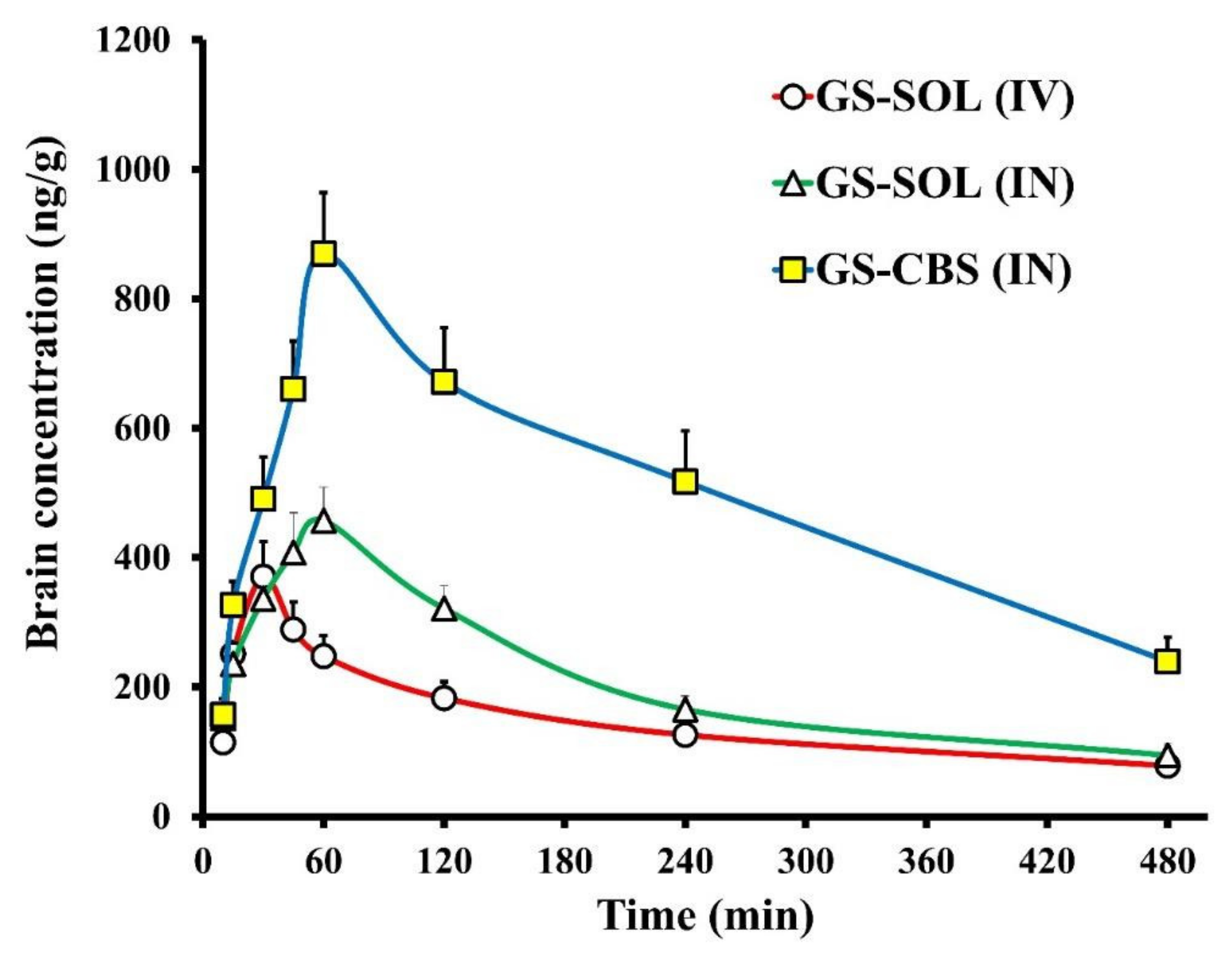
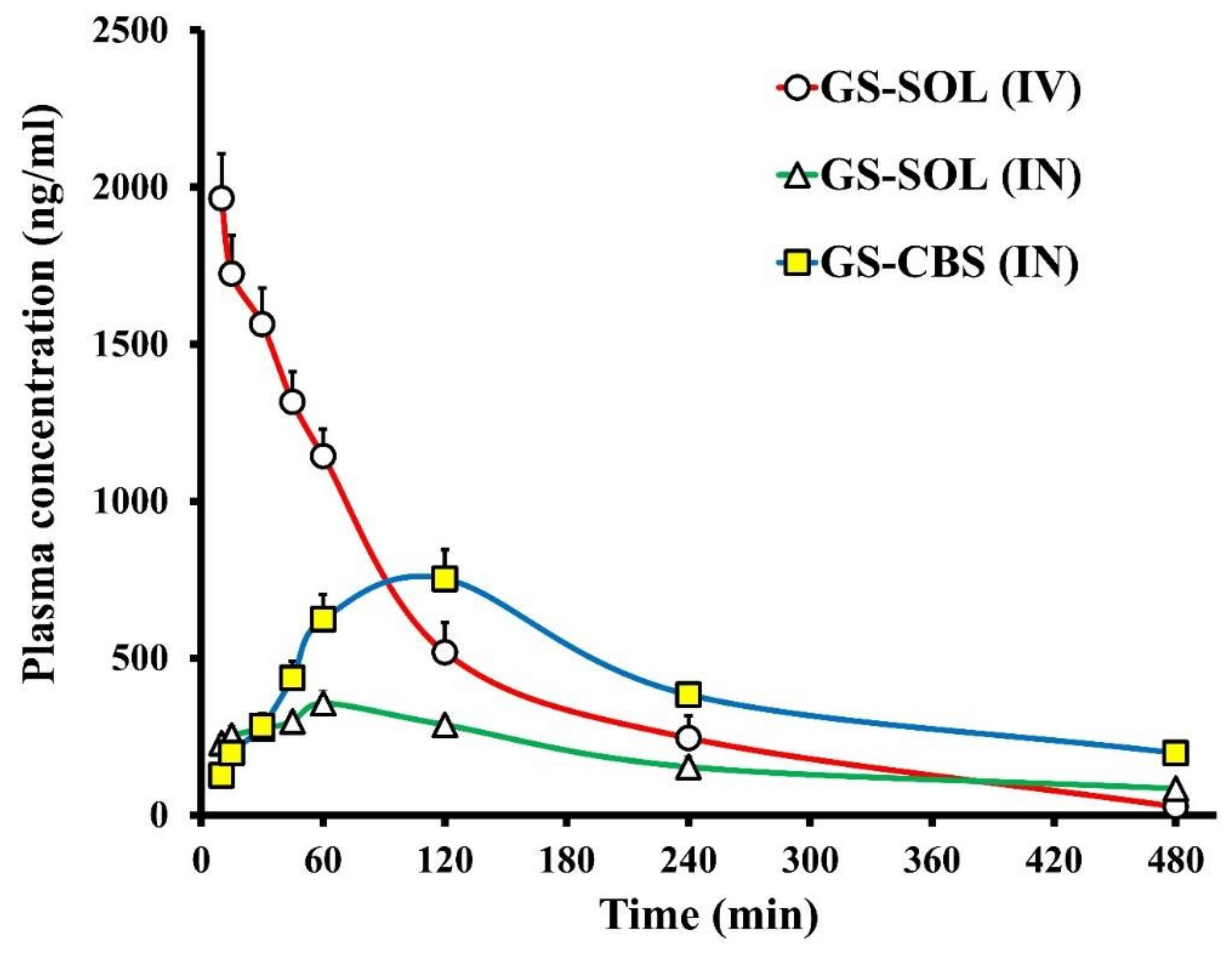
3.2.7. In Vivo Biodistribution Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schnell, F.M. Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: The importance of acute antiemetic control. Oncologist 2003, 8, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeim, A.; Dy, S.M.; Lorenz, K.A.; Sanati, H.; Walling, A.; Asch, S.M. Evidence-based recommendations for cancer nausea and vomiting. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, K.; Kasper, C.; Schmoll, H.-J. Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: Current and new standards in the antiemetic prophylaxis and treatment. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roila, F.; Warr, D.; Aapro, M.; Clark-Snow, R.A.; Einhorn, L.; Gralla, R.J.; Herrstedt, J.; Saito, M.; Tonato, M. Delayed emesis: Moderately emetogenic chemotherapy (single-day chemotherapy regimens only). Support. Care Cancer 2010, 19, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yarker, Y.E.; McTavish, D.J.D. Granisetron. Drugs 1994, 48, 761–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; El-Setouhy, D.A.; Badawi, A.A.E.-L.; El-Nabarawi, M.A. Provesicular granisetron hydrochloride buccal formulations: In vitro evaluation and preliminary investigation of in vivo performance. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 60, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, V.; Garg, T.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.K. Development and evaluation of a sublingual film of the antiemetic granisetron hydrochloride. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2014, 44, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmonem, R.; El Nabarawi, M.; Attia, A. Development of novel bioadhesive granisetron hydrochloride spanlastic gel and insert for brain targeting and study their effects on rats. Drug Deliv. 2017, 25, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, A.M.; Tadros, M.I.; Alaa-Eldin, A.A. Spray-dried silica xerogel nanoparticles as a promising gastroretentive carrier system for the management of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9619–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhuria, S.V.; Hanson, L.R.; Frey, W.H., II. Intranasal delivery to the central nervous system: Mechanisms and experimental considerations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1654–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, S.S.; Nasr, M.; Ahmed, R.F.; Badawy, S.S.; Mansour, S. Intranasally administered in situ gelling nanocomposite system of dimenhydrinate: Preparation, characterization and pharmacodynamic applicability in chemotherapy induced emesis model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.I.; Beg, S.; Samad, A.; Baboota, S.; Kohli, K.; Ali, J.; Ahuja, A.; Akbar, M. Strategy for effective brain drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 40, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türker, S.; Onur, E.; Ózer, Y. Nasal route and drug delivery systems. Pharm. Weekbl. Sci. Ed. 2004, 26, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsenosy, F.M.; Abdelbary, G.A.; Elshafeey, A.H.; Elsayed, I.; Fares, A.R. Brain Targeting of Duloxetine HCL via Intranasal Delivery of Loaded Cubosomal Gel: In vitro Characterization, ex vivo Permeation, and in vivo Biodistribution Studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9517–9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgatte, U.C.; Kumbhar, A.B.; Chaudhari, P.D. Development of in situ gel for nasal delivery: Design, optimization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2014, 21, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, N.M.; Awad, G.A.; Mortada, N.D.; Abd Elhady, S.S. Enhanced bioavailability of metoclopramide HCl by intranasal administration of a mucoadhesive in situ gel with modulated rheological and mucociliary transport properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 32, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonvico, F.; Clementino, A.; Buttini, F.; Colombo, G.; Pescina, S.; Guterres, S.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Nicoli, S. Surface-modified nanocarriers for nose-to-brain delivery: From bioadhesion to targeting. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.; Ghorab, M.K.; Abdelazem, A. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cubosomes containing 5-fluorouracil for liver targeting. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 5, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, C.V.; Vishwapathi, V.K.; Quarshie, A.; Moinuddin, Z.; Page, J.; Kendrekar, P.; Mashele, S.S. Self-assembled lipid cubic phase and cubosomes for the delivery of aspirin as a model drug. Langmuir 2017, 33, 9907–9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballa, S.A.; El Garhy, O.H.; Abdelkader, H. Cubosomes: Composition, preparation, and drug delivery applications. J. Adv. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahirrao, M.; Shrotriya, S. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cubosomal in situ nasal gel containing resveratrol for brain targeting. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, H.A.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Kamel, A.O.; Hady, M.A.; Awad, G.A. Phospholipid based colloidal poloxamer–nanocubic vesicles for brain targeting via the nasal route. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 100, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, H.M.; Elkomy, M.H.; El Menshawe, S.F.; Salem, H.F. Transfersomal nanovesicles for nose-to-brain delivery of ofloxacin for better management of bacterial meningitis: Formulation, optimization by Box-Behnken design, characterization and in vivo pharmacokinetic study. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 101304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soetaert, K. plot3D: Plotting Multi-Dimensional Data, R Package Version 1.1.1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=plot3D (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- Panda, D.; Eid, H.; Elkomy, M.; Khames, A.; Hassan, R.; El-Ela, F.A.; Yassin, H. Berberine Encapsulated Lecithin–Chitosan Nanoparticles as Innovative Wound Healing Agent in Type II Diabetes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, H.M.; Ali, A.A.; Ali, A.M.A.; Eissa, E.M.; Hassan, R.M.; Abo El-Ela, F.I.; Hassan, A.H. Potential Use of Tailored Citicoline Chitosan-Coated Liposomes for Effective Wound Healing in Diabetic Rat Model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 555–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkomy, M.H.; Alruwaili, N.K.; Elmowafy, M.; Shalaby, K.; Zafar, A.; Ahmad, N.; Alsalahat, I.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Eissa, E.M.; Eid, H.M. Surface-Modified Bilosomes Nanogel Bearing a Natural Plant Alkaloid for Safe Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Inflammation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Eblovi, N.; Rasi, S.; Drechsler, M.; Di Gregorio, G.M.; Menegatti, E.; Cortesi, R. Lipid-based supramolecular systems for topical application: A preformulatory study. AAPS PharmSci. 2003, 5, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkomy, M.H.; Elmowafy, M.; Shalaby, K.; Azmy, A.F.; Ahmad, N.; Zafar, A.; Eid, H.M. Development and machine-learning optimization of mucoadhesive nanostructured lipid carriers loaded with fluconazole for treatment of oral candidiasis. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkomy, M.H.; El Menshawe, S.F.; Eid, H.M.; Ali, A.M.A. Development of a nanogel formulation for transdermal delivery of tenoxicam: A pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic modeling approach for quantitative prediction of skin absorption. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 43, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkomy, M.H.; Elmenshawe, S.F.; Eid, H.; Ali, A.M.A. Topical ketoprofen nanogel: Artificial neural network optimization, clustered bootstrap validation, and in vivo activity evaluation based on longitudinal dose response modeling. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3294–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, H.M.; Elkomy, M.H.; El Menshawe, S.F.; Salem, H.F. Development, optimization, and in vitro/in vivo characterization of enhanced lipid nanoparticles for ocular delivery of ofloxacin: The influence of pegylation and chitosan coating. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019, 20, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, H.M.; Naguib, I.A.; Alsantali, R.I.; Alsalahat, I.; Hegazy, A.M. Novel Chitosan-Coated Niosomal Formulation for Improved Management of Bacterial Conjunctivitis: A Highly Permeable and Efficient Ocular Nanocarrier for Azithromycin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 3027–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callens, C.; Ceulemans, J.; Ludwig, A.; Foreman, P.; Remon, J. Rheological study on mucoadhesivity of some nasal powder formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 55, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Enin, H.A.A.; Elkomy, M.H.; Naguib, I.A.; Ahmed, M.F.; Alsaidan, O.A.; Alsalahat, I.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Eid, H.M. Lipid Nanocarriers Overlaid with Chitosan for Brain Delivery of Berberine via the Nasal Route. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seju, U.; Kumar, A.; Sawant, K. Development and evaluation of olanzapine-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for nose-to-brain delivery: In vitro and in vivo studies. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 4169–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirogi, R.V.S.; Kandikere, V.N.; Shukla, M.; Mudigonda, K.; Maurya, S.; Boosi, R. Quantification of granisetron in human plasma by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkomy, M.H.; Abou-Taleb, H.A.; Eid, H.M.; Yassin, H.A. Fabrication and In Vitro/In Vivo Appraisal of Metronidazole Intra-Gastric Buoyant Sustained-Release Tablets in Healthy Volunteers. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Wani, T.A.; Raish, M. Application of Box–Behnken design for ultrasonic-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Paeonia emodi. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.P.; Pawara, D.D.; Gudewar, C.S.; Tekade, A.R. Nanostructured cubosomes in an in situ nasal gel system: An alternative approach for the controlled delivery of donepezil HCl to brain. J. Liposome Res. 2018, 29, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.; Aboelwafa, A.A.; Elshafeey, A.H.; Elsayed, I. Central composite optimization of ocular mucoadhesive cubosomes for enhanced bioavailability and controlled delivery of voriconazole. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboud, H.M.; Hassan, A.H.; Ali, A.A.; Abdel-Razik, A.-R.H. Novel in situ gelling vaginal sponges of sildenafil citrate-based cubosomes for uterine targeting. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsi, N.M.; Abdelbary, G.A.; Ahmed, M. Silver sulfadiazine based cubosome hydrogels for topical treatment of burns: Development and in vitro/in vivo characterization. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, J.-C. Drug transport to brain with targeted nanoparticles. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illum, L. (Ed.) Intranasal delivery to the central nervous system. In Blood-Brain Barrier in Drug Discovery: Optimizing Brain Exposure of CNS Drugs and Minimizing Brain Side Effects for Peripheral Drugs; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 535–565. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahman, F.E.; Elsayed, I.; Gad, M.K.; Badr, A.; Mohamed, M.I. Investigating the cubosomal ability for transnasal brain targeting: In vitro optimization, ex vivo permeation and in vivo biodistribution. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 490, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohyeldin, S.M.; Mehanna, M.M.; Elgindy, N.A. Superiority of liquid crystalline cubic nanocarriers as hormonal transdermal vehicle: Comparative human skin permeation-supported evidence. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motwani, S.K.; Chopra, S.; Talegaonkar, S.; Kohli, K.; Ahmad, F.J.; Khar, R.K. Chitosan–sodium alginate nanoparticles as submicroscopic reservoirs for ocular delivery: Formulation, optimisation and in vitro characterisation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkomy, M.H.; El-Gazayerly, O.N.; Abdelrahman, A.A. The influence of solid/solvent interfacial interactions on physicochemical and mechanical properties of ofloxacin. J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 16, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamma, R.; Elsayed, I. Transfersomal lyophilized gel of buspirone HCl: Formulation, evaluation and statistical optimization. J. Liposome Res. 2013, 23, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muheem, A.; Shakeel, F.; Warsi, M.H.; Jain, G.K.; Ahmad, F.J. A Combinatorial statistical design approach to optimize the nanostructured cubosomal carrier system for oral delivery of ubidecarenone for management of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: In vitro–in vivo investigations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 3050–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.I.; Baboota, S.; Ahuja, A.; Ali, M.; Ali, J.; Sahni, J.K. Intranasal infusion of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) containing CNS acting drug and estimation in brain and blood. Drug Deliv. 2013, 20, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, M.; Bhatt, G.K. An overview: Formulation and product development of nasal spray. World J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 6, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, N.; Abbas, Z. Mucoadhesive in situ gels as nasal drug delivery systems: An overview. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 7, 168–180. [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan, H.S.; Mahajan, M.S.; Nerkar, P.P.; Agrawal, A. Nanoemulsion-based intranasal drug delivery system of saquinavir mesylate for brain targeting. Drug Deliv. 2013, 21, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragagni, M.; Mennini, N.; Maestrelli, F.; Cirri, M.; Mura, P. Comparative study of liposomes, transfersomes and ethosomes as carriers for improving topical delivery of celecoxib. Drug Deliv. 2012, 19, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; He, Q. The interaction of nanoparticles with plasma proteins and the consequent influence on nanoparticles behavior. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göppert, T.M.; Müller, R.H. Polysorbate-stabilized solid lipid nanoparticles as colloidal carriers for intravenous targeting of drugs to the brain: Comparison of plasma protein adsorption patterns. J. Drug Target. 2005, 13, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Independent Variables | Levels | ||||||
| (−1) | (0) | (1) | |||||
| X1: GMO (w/v %) a | 3 | 5 | 7 | ||||
| X2: P 407 (w/w %) b | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | ||||
| X3:T 80 (w/w %) b | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| Run | GMO (w/v %) | P 407(w/w %) | T 80 (w/w %) | Y1: Particle Size (nm) | Y2: Entrapment Efficiency (%) | Y3: Zeta Potential (mV) | Y4: Polydispersity Index c |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 218.3 ± 2.4 | 43.4 ± 2.7 | (−) 29.5 ± 1.4 | 0.452 ± 0.13 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 267.3 ± 3.1 | 66.7 ± 3.2 | (−) 27.3 ± 2.1 | 0.051 ± 0.03 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 226.4 ± 2.6 | 44.2 ± 2.8 | (−) 28.9 ± 1.5 | 0.472 ± 0.15 |
| 4 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 183.5 ± 1.9 | 68.5 ± 3.1 | (−) 24.5 ± 1.3 | 0.437 ± 0.21 |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 369.1 ± 3.7 | 41.3 ± 2.5 | (−) 34.8 ± 2.3 | 0.494 ± 0.17 |
| 6 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 245.1 ± 2.7 | 62.9 ± 2.4 | (−) 28.6 ± 2.5 | 0.274 ± 0.09 |
| 7 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 195.3 ± 2.3 | 39.1 ± 1.8 | (−) 26.2 ± 1.3 | 0.428 ± 0.22 |
| 8 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 295.2 ± 4.2 | 38.4 ± 2.1 | (−) 28.7 ± 2.4 | 0.476 ± 0.16 |
| 9 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 165.8 ± 1.6 | 53.1 ± 2.7 | (−) 25.8 ± 1.2 | 0.433 ± 0.24 |
| 10 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 325.3 ± 2.9 | 39.6 ± 2.3 | (−) 35.1 ± 3.1 | 0.198 ± 0.08 |
| 11 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 279.2 ± 3.1 | 37.5 ± 1.8 | (−) 29.9 ± 2.6 | 0.518 ± 0.25 |
| 12 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 387.1 ± 3.9 | 35.4 ± 2.6 | (−) 37.6 ± 3.2 | 0.854 ± 0.31 |
| 13 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 397.6 ± 2.5 | 59.3 ± 2.9 | (−) 34.7 ± 2.1 | 0.071 ± 0.04 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 231.7 ± 3.8 | 45.4 ± 2.4 | (−) 29.2 ± 3.3 | 0.194 ± 0.11 |
| 15 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 174.2 ± 2.4 | 55.7 ± 3.1 | (−) 25.3 ± 1.7 | 0.492 ± 0.21 |
| Source | PS | ZP | EE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | F | p-Value | |
| Model | 205.09 | <0.0001 | 152.80 | <0.0001 | 104.05 | <0.0001 |
| X1: GMO (w/v %) | 746.25 | <0.0001 | 439.97 | <0.0001 | 64.53 | <0.0001 |
| X2: P 407 (w/w %) | 6.73 | 0.0267 | 14.77 | 0.0027 | 473.33 | <0.0001 |
| X3: T 80 (w/w %) | 8.50 | 0.0154 | 3.67 | 0.0818 | 4.41 | 0.0689 |
| X1 X2 | 12.10 | 0.0083 | ||||
| X22 | 58.87 | <0.0001 | 67.71 | <0.0001 | ||
| X32 | 4.29 | 0.0720 | ||||
| Lack of Fit | 1.45 | 0.4703 | 5.36 | 0.1670 | 7.02 | 0.1298 |
| Model | Reduced Quadratic | Linear | Reduced Quadratic | |||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.9831 | 0.9702 | 0.9779 | |||
| R2 | 0.9880 | 0.9766 | 0.9873 | |||
| %CV | 1.85 | 2.20 | 10.48 | |||
| Predicted R2 | 0.9730 | 0.9508 | 0.9416 | |||
| Adequate precision | 43.7095 | 33.9851 | 30.8347 | |||
| Standard deviation | 0.0012 | 0.0008 | 14,008.91 | |||
| Vesicle Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) | Entrapment Efficiency% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental value | 225.2 | (−) 31.6 | 65.4 |
| Predicted value | 242.8 | (−) 28.5 | 63.6 |
| Prediction error (%) £ | 7.82 | 9.81 | 2.75 |
| Formulation | Cumulative GS Permeated at 12 h (μg/cm2) | Permeability Coefficient (cm/h) | Flux (Jss) (µg cm−2 h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GS-SOL | 615.6 ± 41.3 | 0.02704 ± 0.00013 | 27.1 ± 1.67 |
| GS-CBS | 978.4 ± 51.9 | 0.04589 ± 0.00043 | 45.9 ± 3.84 |
| Formulation | Tissue/Organ | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (min) | t1/2 (min) | Ke (min−1) | AUC0–t (ng/mL·min) | AUCbrain/AUCblood | Cbrain/Cblood at 30 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS-SOL (IV) | Brain | 370.8 | 30 | 301 | 0.0023 | 105,670 | 0.46 | 0.237 |
| Blood | 1964 | 10 | 77 | 0.0090 | 227,502 | |||
| GS-SOL in situ gel (IN) | Brain | 457.2 | 60 | 188 | 0.0037 | 127,598 | 1.12 | 1.228 |
| Blood | 356 | 60 | 200 | 0.0035 | 113,892 | |||
| GS-CBS in situ gel (IN) | Brain | 869.4 | 60 | 231 | 0.0030 | 316,669 | 1.26 | 1.733 |
| Blood | 752 | 120 | 193 | 0.0036 | 252,287 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eissa, E.M.; Elkomy, M.H.; Eid, H.M.; Ali, A.A.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Alsubaiyel, A.M.; Naguib, I.A.; Alsalahat, I.; Hassan, A.H. Intranasal Delivery of Granisetron to the Brain via Nanostructured Cubosomes-Based In Situ Gel for Improved Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Emesis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071374
Eissa EM, Elkomy MH, Eid HM, Ali AA, Abourehab MAS, Alsubaiyel AM, Naguib IA, Alsalahat I, Hassan AH. Intranasal Delivery of Granisetron to the Brain via Nanostructured Cubosomes-Based In Situ Gel for Improved Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Emesis. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(7):1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071374
Chicago/Turabian StyleEissa, Essam M., Mohammed H. Elkomy, Hussein M. Eid, Adel A. Ali, Mohammed A. S. Abourehab, Amal M. Alsubaiyel, Ibrahim A. Naguib, Izzeddin Alsalahat, and Amira H. Hassan. 2022. "Intranasal Delivery of Granisetron to the Brain via Nanostructured Cubosomes-Based In Situ Gel for Improved Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Emesis" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 7: 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071374
APA StyleEissa, E. M., Elkomy, M. H., Eid, H. M., Ali, A. A., Abourehab, M. A. S., Alsubaiyel, A. M., Naguib, I. A., Alsalahat, I., & Hassan, A. H. (2022). Intranasal Delivery of Granisetron to the Brain via Nanostructured Cubosomes-Based In Situ Gel for Improved Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Emesis. Pharmaceutics, 14(7), 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071374








