Continuous Affinity Purification of Adeno-Associated Virus Using Periodic Counter-Current Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AAV Production
2.2. Screening of Elution Buffer
2.3. Batch Chromatography and Frontal Experiments
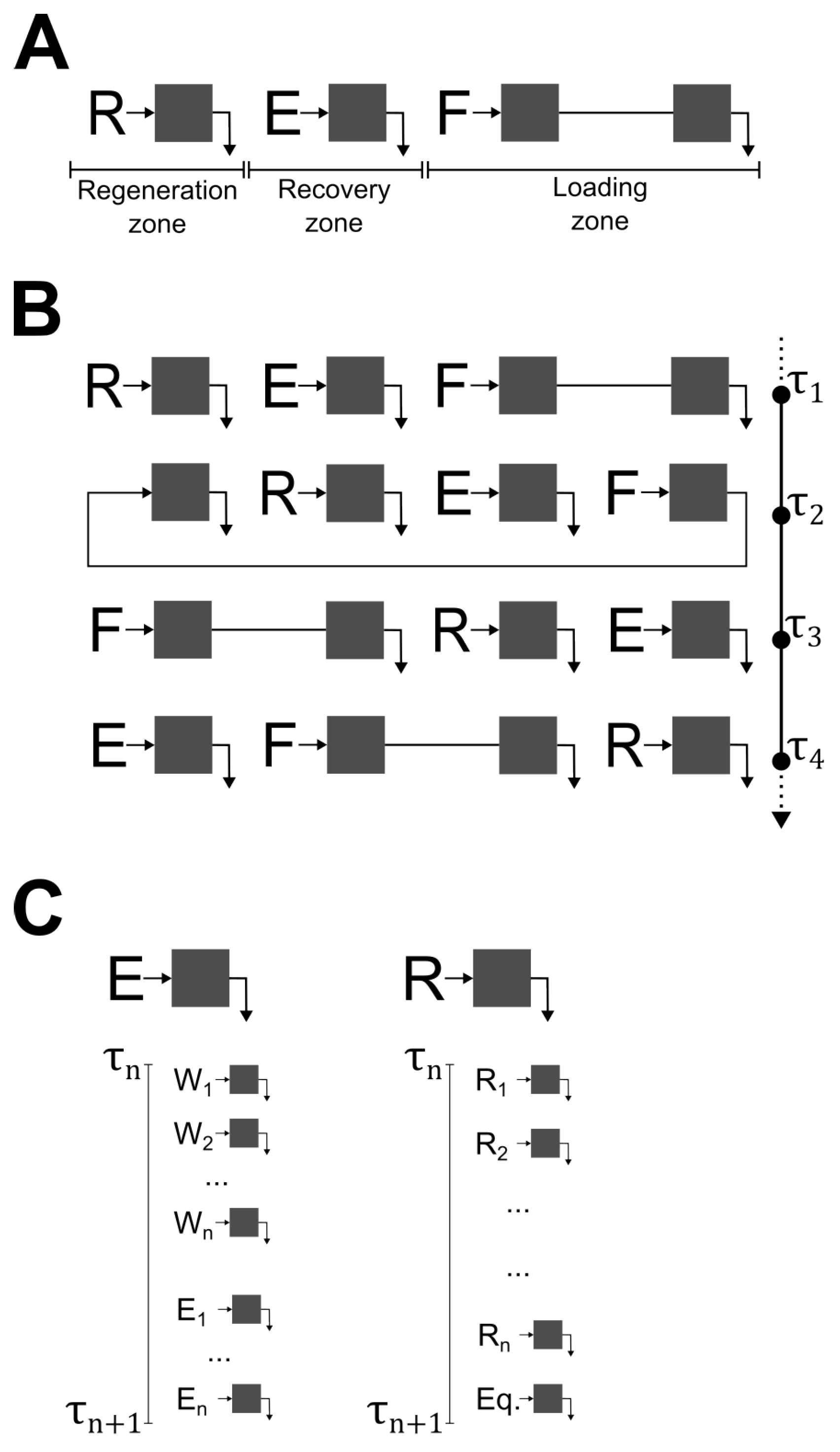
2.4. 4C-PCC Experiments
2.5. Analytical Quantification Methods
2.5.1. Total Particle Quantification
2.5.2. Genome Copies Quantification
2.5.3. Total Protein and ds-DNA
2.5.4. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
2.5.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.6. Chromatography Model
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of Elution Buffer
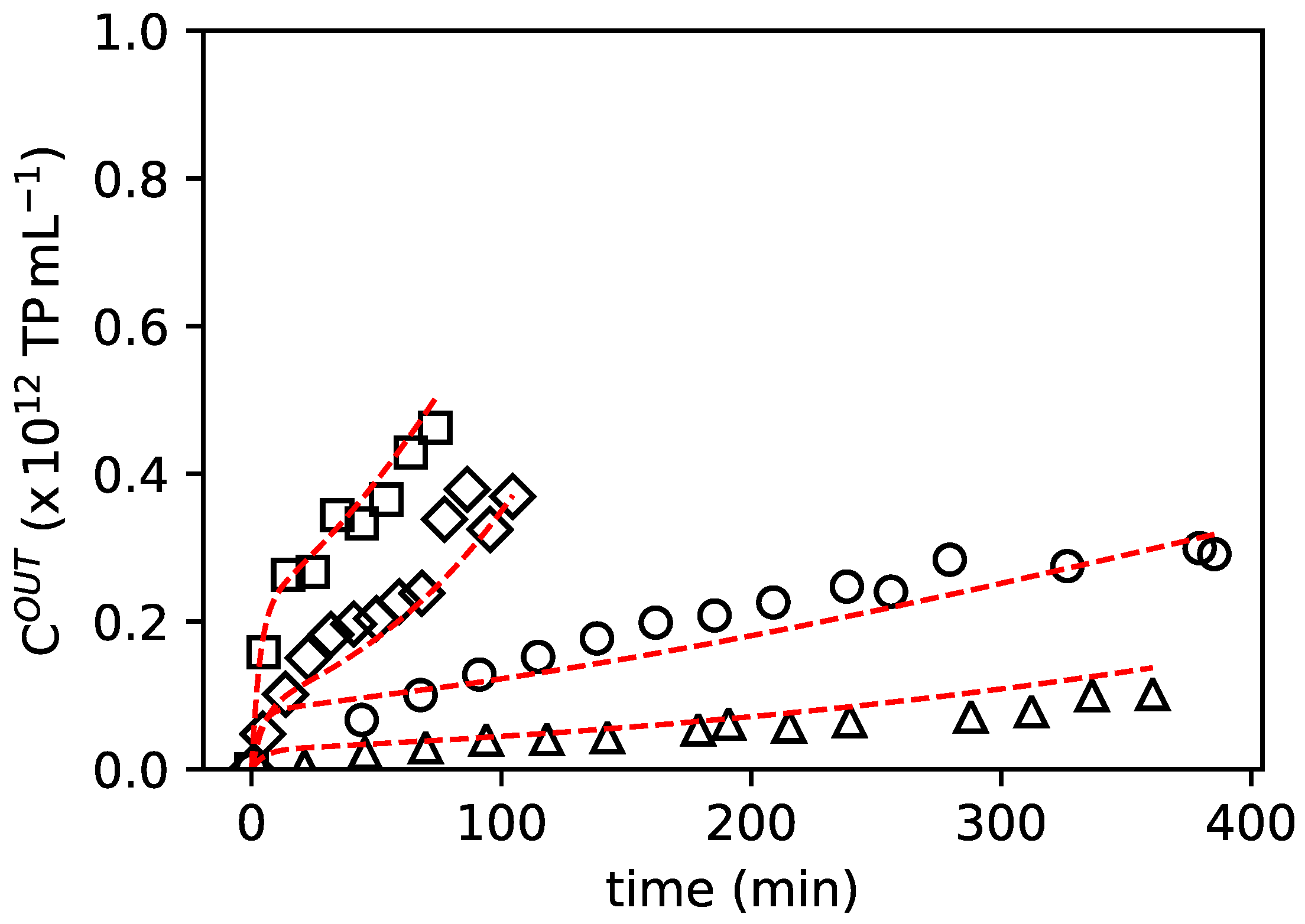
3.2. Breakthrough Curves
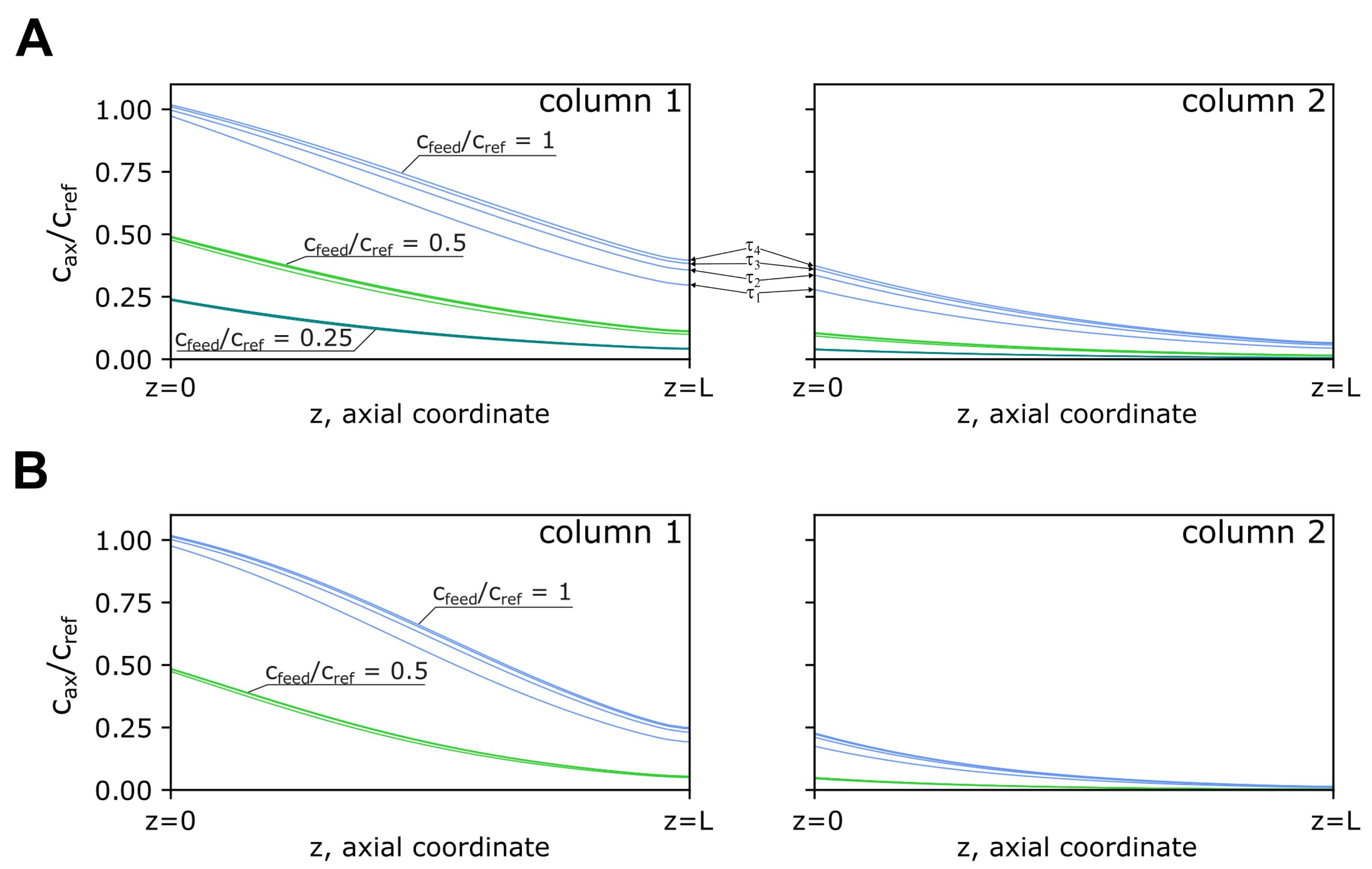
3.3. Chromatography Model of 4C-PCC Loading Zone
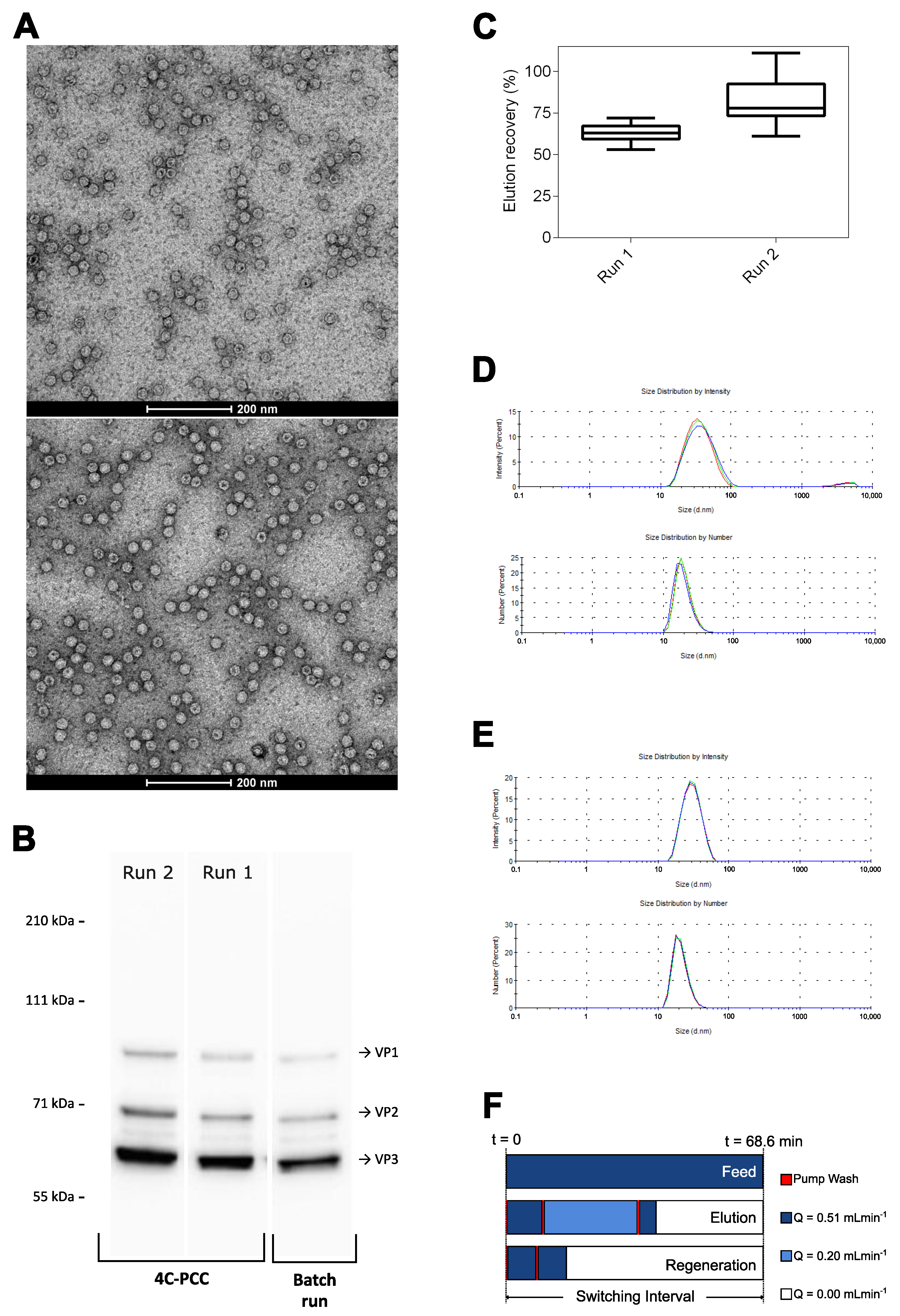
3.4. 4C-PCC Affinity Capture Process
4. Discussion
4.1. High Elution Recovery Yield Obtained after Buffer Screening
4.2. Modelling of the Breakthrough Curves Improves PCC Process Development
4.3. Continuous Affinity Capture Using 4C-PCC
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pang, J.; Lauramore, A.; Deng, W.; Li, Q.; Doyle, T.J.; Chiodo, V.; Li, J.; Hauswirth, W.W. Comparative analysis of in vivo and in vitro AAV vector transduction in the neonatal mouse retina: Effects of serotype and site of administration. Vis. Res. 2008, 48, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penaud-Budloo, M.; François, A.; Clément, N.; Ayuso, E. Pharmacology of recombinant adeno-associated virus production. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2018, 8, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, D. Systemic AAV micro-dystrophin gene therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 2337–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moleirinho, M.G.; Silva, R.J.; Alves, P.M.; Carrondo, M.J.; Peixoto, C. Current challenges in biotherapeutic particles manufacturing. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, W.; Wang, M.; Wu, Y.; Xu, R. Scalable downstream strategies for purification of recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors in light of the properties. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adams, B.; Bak, H.; Tustian, A.D. Moving from the bench towards a large scale, industrial platform process for adeno-associated viral vector purification. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 3199–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nass, S.A.; Mattingly, M.A.; Woodcock, D.A.; Burnham, B.L.; Ardinger, J.A.; Osmond, S.E.; Frederick, A.M.; Scaria, A.; Cheng, S.H.; O’Riordan, C.R. Universal method for the purification of recombinant AAV vectors of differing serotypes. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2018, 9, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaludov, N.; Handelman, B.; Chiorini, J.A. Scalable purification of adeno-associated virus type 2, 4, or 5 using ion-exchange chromatography. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomono, T.; Hirai, Y.; Okada, H.; Miyagawa, Y.; Adachi, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Kawano, Y.; Chono, H.; Mineno, J.; Ishii, A.; et al. Highly efficient ultracentrifugation-free chromatographic purification of recombinant AAV serotype 9. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2018, 11, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Mun, S.; Kim, J.; Wang, N.H.L. Standing wave design and experimental validation of a tandem simulated moving bed process for insulin purification. Biotechnol. Prog. 2002, 18, 1332–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.J.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Osuna-Sanchez, H.; Bailly, M.; Valéry, E.; Mota, J.P. A new multicolumn, open-loop process for center-cut separation by solvent-gradient chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 8257–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, V.; Hilbold, N.J.; Ng, C.K.; Pegon, L.; Chahim, W.; Rousset, F.; Monchois, V. Large-scale monoclonal antibody purification by continuous chromatography, from process design to scale-up. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 213, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Späth, T.; Aumann, L.; Melter, L.; Ströhlein, G.; Morbidelli, M. Chromatographic separation of three monoclonal antibody variants using multicolumn countercurrent solvent gradient purification (MCSGP). Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 100, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristancho, C.A.M.; Seidel-Morgenstern, A. Purification of single-chain antibody fragments exploiting pH-gradients in simulated moving bed chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1434, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kröber, T.; Wolff, M.W.; Hundt, B.; Seidel-Morgenstern, A.; Reichl, U. Continuous purification of influenza virus using simulated moving bed chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1307, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestola, P.; Silva, R.J.; Peixoto, C.; Alves, P.M.; Carrondo, M.J.; Mota, J.P. Robust design of adenovirus purification by two-column, simulated moving-bed, size-exclusion chromatography. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 213, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.M.; Wolff, M.W.; Reichl, U. Purification of cell culture-derived influenza A virus via continuous anion exchange chromatography on monoliths. Vaccine 2018, 36, 3153–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestola, P.; Silva, R.J.; Peixoto, C.; Alves, P.M.; Carrondo, M.J.; Mota, J.P. Adenovirus purification by two-column, size-exclusion, simulated countercurrent chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1347, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, J.P.; Silva, R.J.; Berg, M.; Mathiasson, L.; Peixoto, C.; Alves, P.M.; Carrondo, M.J. Oncolytic virus purification with periodic counter-current chromatography. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 3522–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleirinho, M.G.; Silva, R.J.; Carrondo, M.J.; Alves, P.M.; Peixoto, C. Exosome-based therapeutics: Purification using semi-continuous multi-column chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, H.; Fons, J.G.; Isaksson, M.; Scheffel, J.; Andersson, N.; Andersson, A.; Castan, A.; Solbrand, A.; Hober, S.; Nilsson, B.; et al. Integrated continuous biomanufacturing on pilot scale for acid-sensitive monoclonal antibodies. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coolbaugh, M.J.; Varner, C.T.; Vetter, T.A.; Davenport, E.K.; Bouchard, B.; Fiadeiro, M.; Tugcu, N.; Walther, J.; Patil, R.; Brower, K. Pilot-scale demonstration of an end-to-end integrated and continuous biomanufacturing process. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 3287–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffel, J.; Isaksson, M.; Gomis-Fons, J.; Schwarz, H.; Andersson, N.; Norén, B.; Solbrand, A.; Chotteau, V.; Hober, S.; Nilsson, B. Design of an integrated continuous downstream process for acid-sensitive monoclonal antibodies based on a calcium-dependent Protein A ligand. J. Chromatogr. 2022, 1664, 462806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiochon, G.; Felinger, A.; Shirazi, D.G. Fundamentals of Preparative and Nonlinear Chromatography; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.W.; Tan, D.; Yang, Y.S.; Zhang, W. Investigation of the effect of salt additives in Protein L affinity chromatography for the purification of tandem single-chain variable fragment bispecific antibodies. mAbs 2020, 12, 1718440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arakawa, T.; Ejima, D.; Tsumoto, K.; Obeyama, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Kita, Y.; Timasheff, S.N. Suppression of protein interactions by arginine: A proposed mechanism of the arginine effects. Biophys. Chem. 2007, 127, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielowski, R.A.; Mathiasson, L.; Blom, H.; Go, D.; Ehring, H.; Khan, H.; Li, H.; Cutler, C.; Lacki, K.; Tugcu, N.; et al. Definition and dynamic control of a continuous chromatography process independent of cell culture titer and impurities. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1526, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstweiler, L.; Billakanti, J.; Bi, J.; Middelberg, A.P. Control strategy for multi-column continuous periodic counter current chromatography subject to fluctuating inlet stream concentration. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1667, 462884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | |
|---|---|
| Pe | 26 |
| q (TP mL ) | |
| k (TP mL min) | |
| (TP mL min) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendes, J.P.; Bergman, M.; Solbrand, A.; Peixoto, C.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Silva, R.J.S. Continuous Affinity Purification of Adeno-Associated Virus Using Periodic Counter-Current Chromatography. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071346
Mendes JP, Bergman M, Solbrand A, Peixoto C, Carrondo MJT, Silva RJS. Continuous Affinity Purification of Adeno-Associated Virus Using Periodic Counter-Current Chromatography. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(7):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071346
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendes, João P., Magnus Bergman, Anita Solbrand, Cristina Peixoto, Manuel J. T. Carrondo, and Ricardo J. S. Silva. 2022. "Continuous Affinity Purification of Adeno-Associated Virus Using Periodic Counter-Current Chromatography" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 7: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071346
APA StyleMendes, J. P., Bergman, M., Solbrand, A., Peixoto, C., Carrondo, M. J. T., & Silva, R. J. S. (2022). Continuous Affinity Purification of Adeno-Associated Virus Using Periodic Counter-Current Chromatography. Pharmaceutics, 14(7), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071346






