In Vivo Investigation of (2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin-Based Formulation of Spironolactone in Aqueous Solution for Paediatric Use
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Phase Solubility Studies
2.2.1. UV/Vis Spectroscopy Method
2.2.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method
2.3. Job’s Plot
2.4. NMR Studies
2.5. Molecular Modelling
2.6. BATA Experiments
2.6.1. Test Solutions
2.6.2. Animals
2.6.3. Procedure
2.6.4. Data Analysis
2.7. Human Taste Panel
2.7.1. Taste Solutions
- One calibration sample (C): a saturated solution of SPL in water.
- Six test samples:
- ⋅
- Formulation 1 (F1): SPL 1 mg/mL in 1% (w/v) HP-β-CyD and corresponding placebo (P1).
- ⋅
- Formulation 2 (F2): SPL 1 mg/mL in 6% (w/v) HP-β-CyD and corresponding placebo (P2).
- ⋅
- Formulation 3 (F3): SPL 1 mg/mL in 18% (w/v) HP-β-CyD and corresponding placebo (P3).
2.7.2. Participants
2.7.3. Procedure
2.7.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
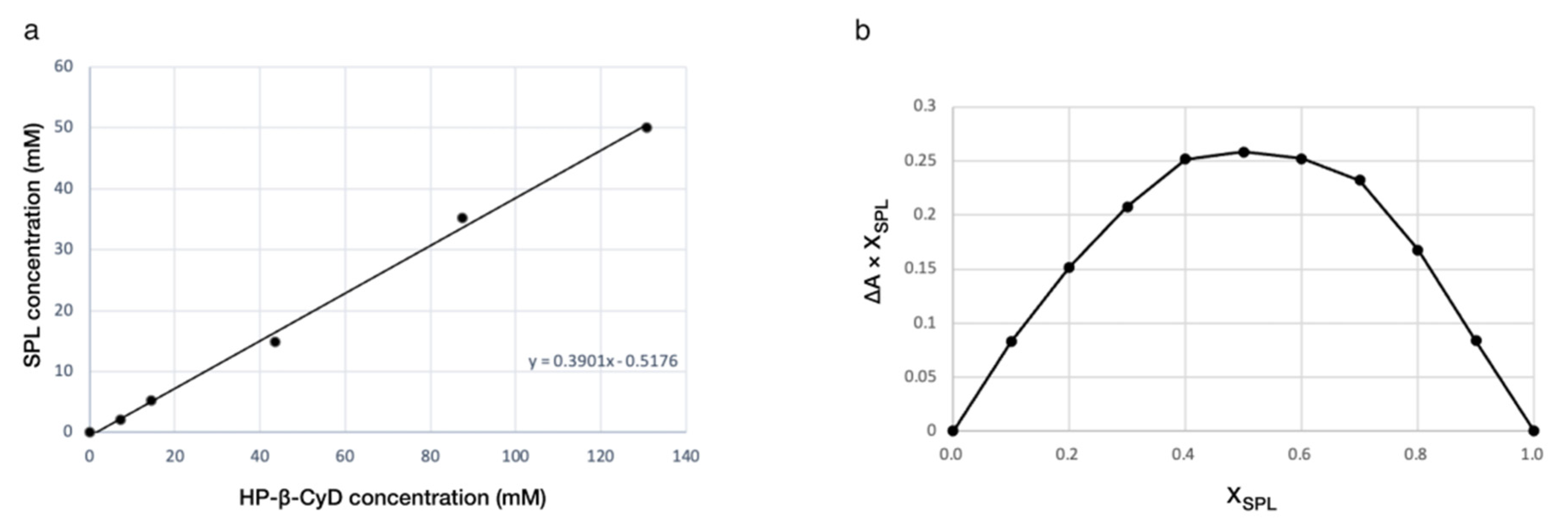
3.1. Phase Solubility Studies
UV/Vis Spectroscopic and HPLC Analyses
3.2. Job’s Plot
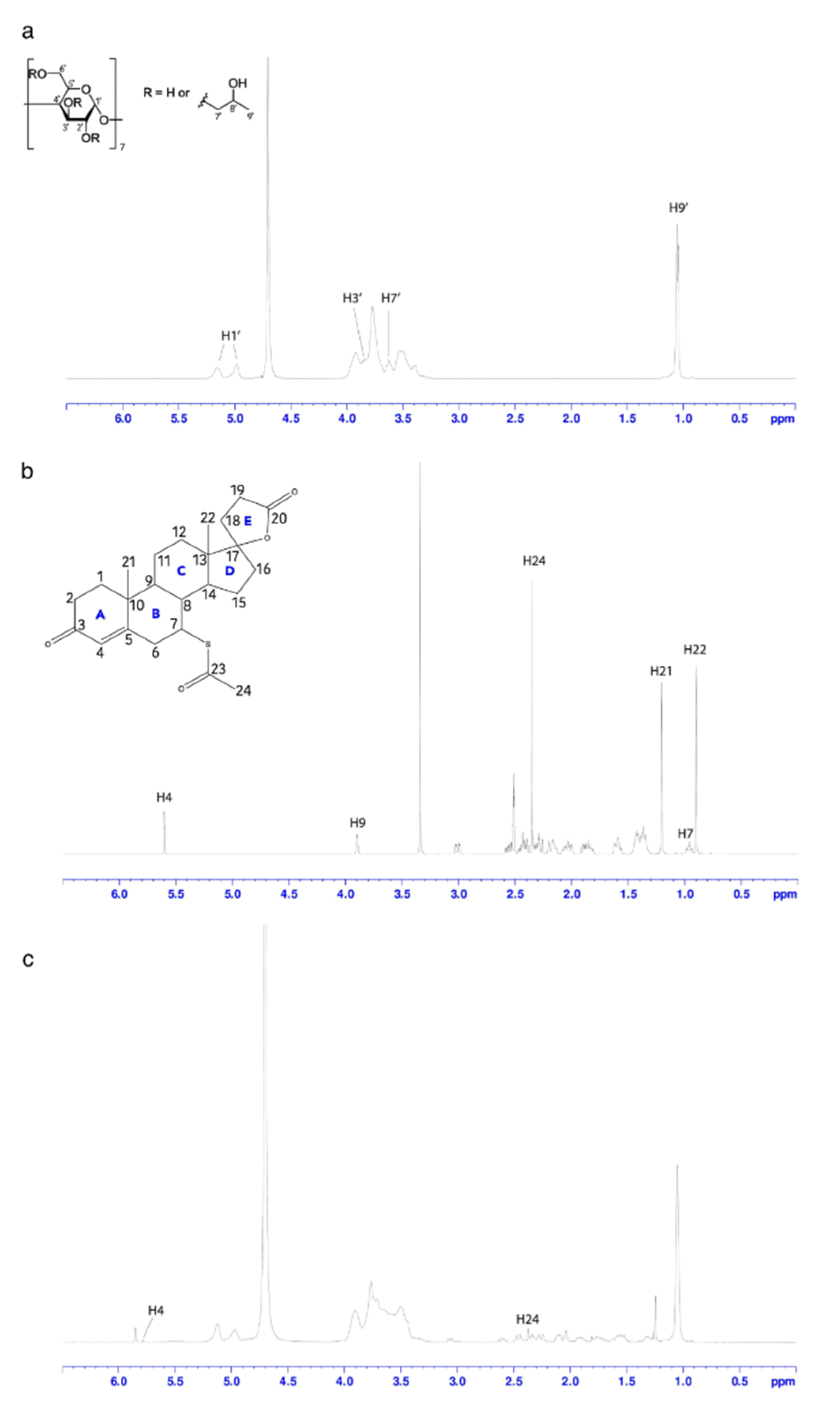
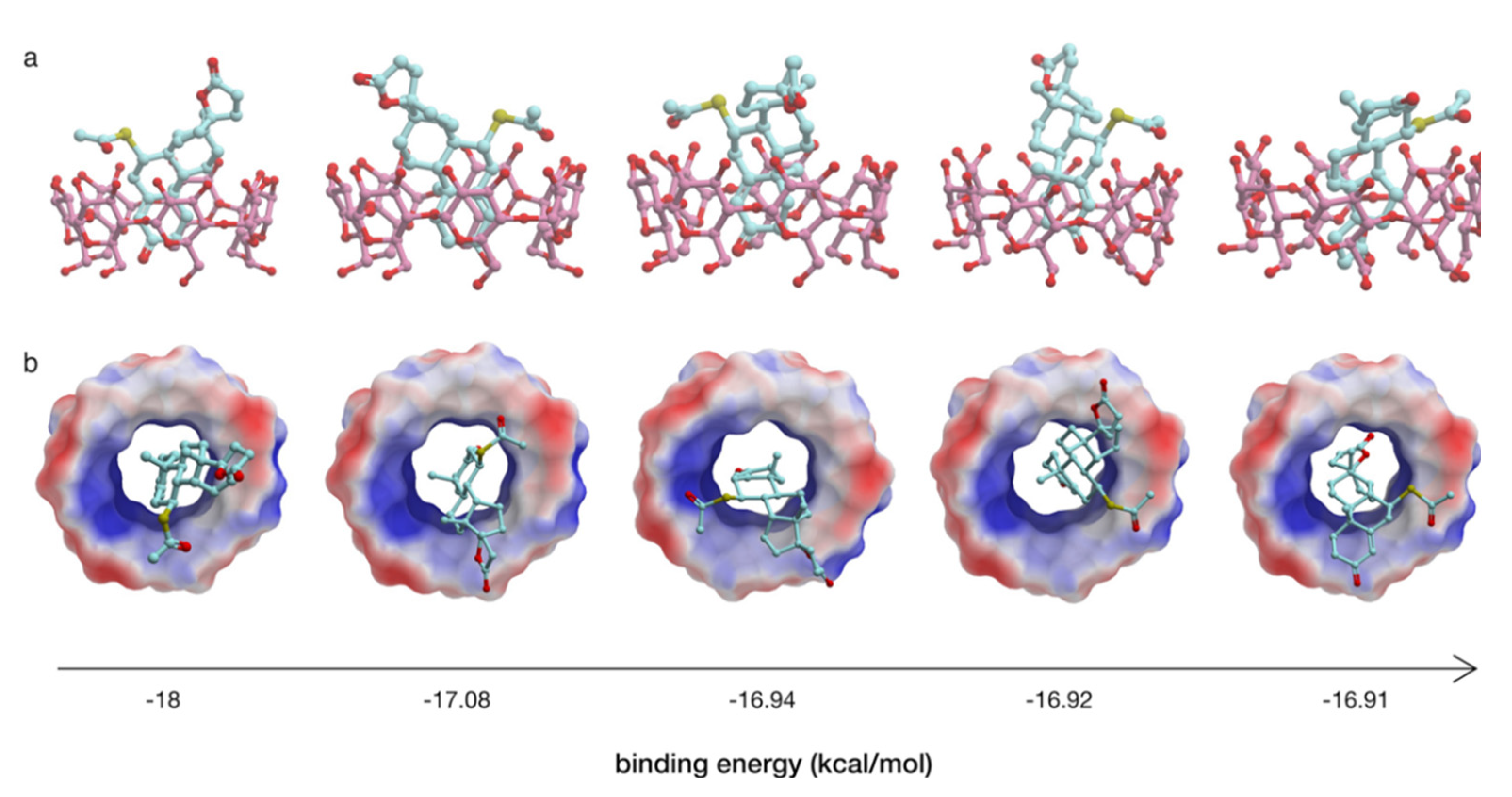
3.3. NMR and Molecular Modelling
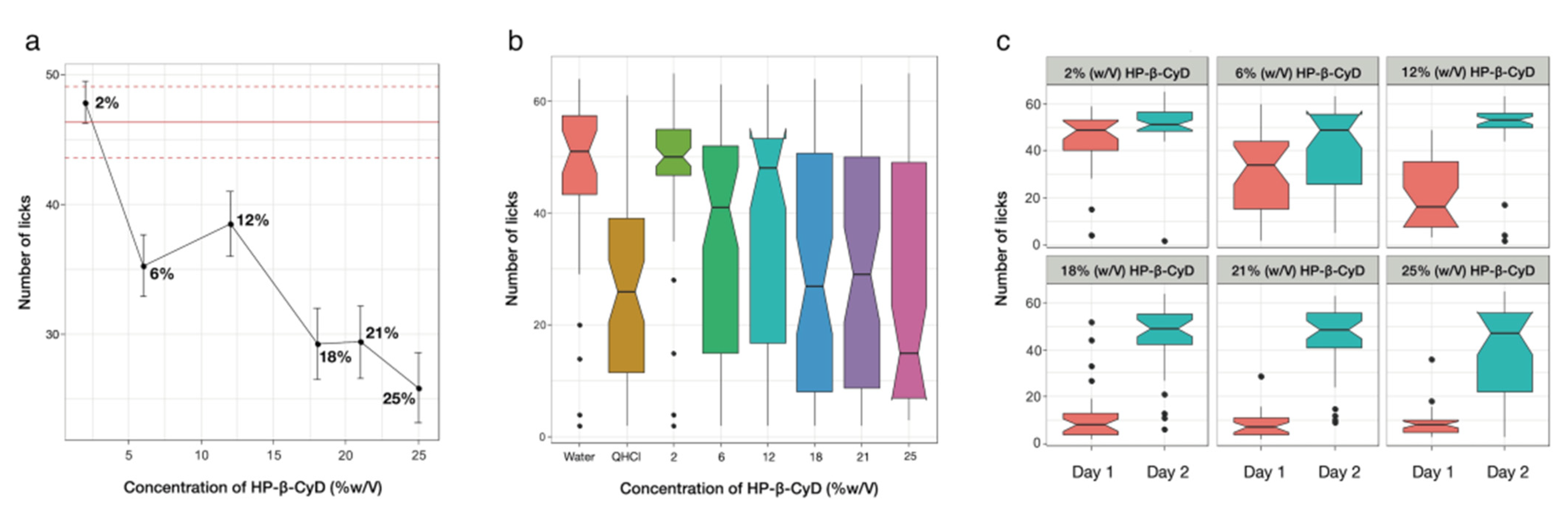
3.4. BATA Experiment
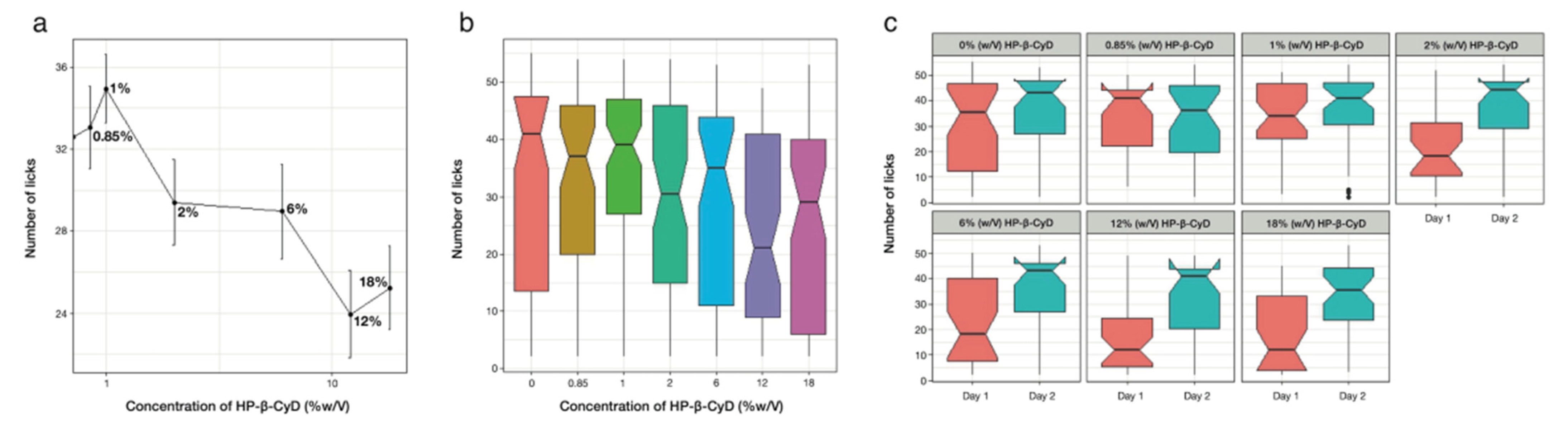
3.4.1. Taste Assessment of HP-β-CyD
3.4.2. Taste-Masking Assessment of SPL with HP-β-CyD
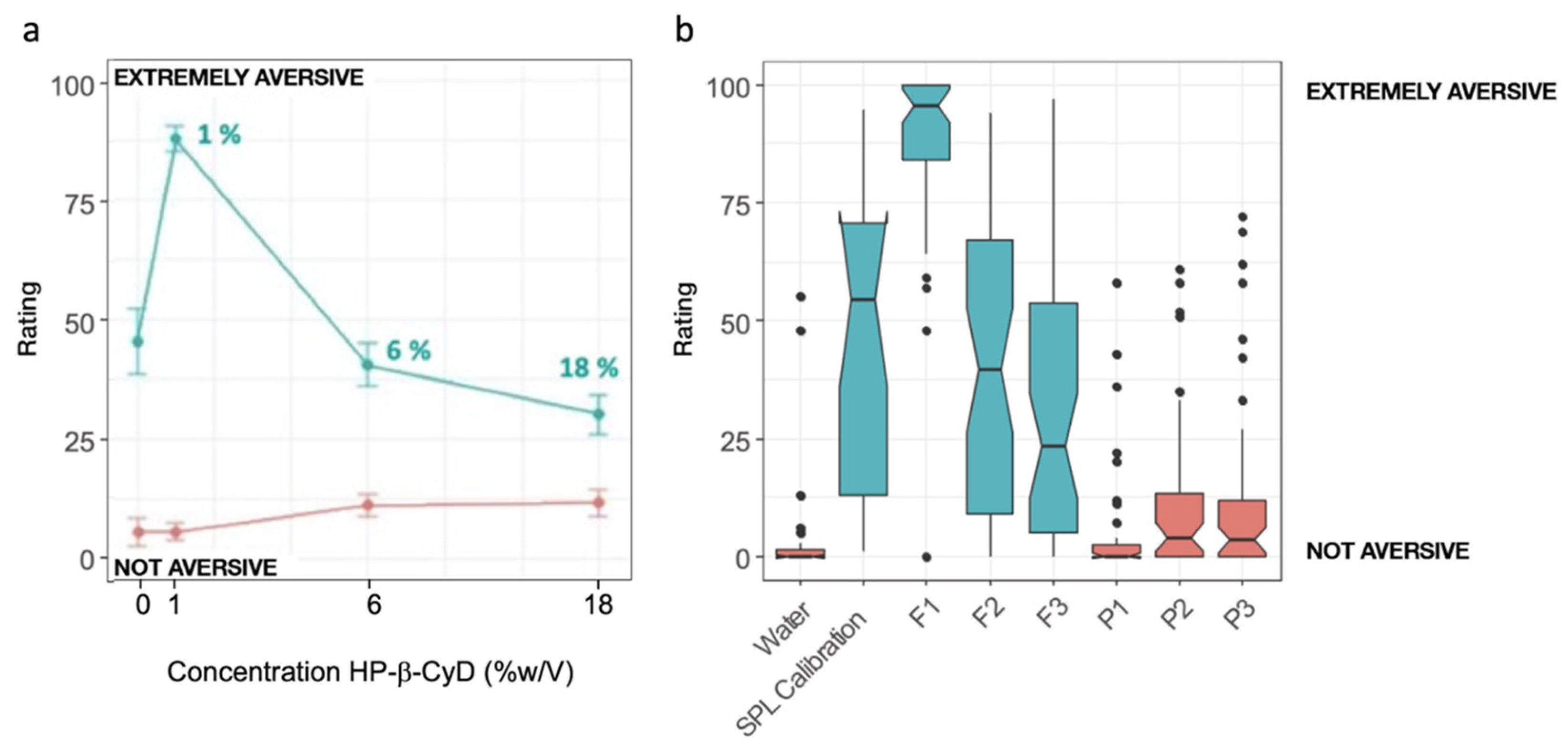
3.5. Human Taste Panel
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Segar, J.L. Neonatal Diuretic Therapy: Furosemide, Thiazides, and Spironolactone. Clin. Perinatol. 2012, 39, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seikaly, M.G. Hypertension in children: An update on treatment strategies. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2007, 19, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanaroff, J.M.; Fanaroff, A.A. Blood pressure disorders in the neonate: Hypotension and hypertension. Semin. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 2006, 11, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscaro, M.; Ronconi, V.; Turchi, F.; Giacchetti, G. Diagnosis and management of primary aldosteronism. Contemp. Endocrinol. 2018, 15, 245–260. [Google Scholar]
- Amirlak, I.; Dawson, K.P. Bartter syndrome: An overview. QJM 2000, 93, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Cunha, T.S.; Heilberg, I.P. Bartter syndrome: Causes, diagnosis, and treatment. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2018, 11, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolis, A.A.; Manolis, T.A.; Melita, H.; Manolis, A.S. Spotlight on spironolactone oral suspension for the treatment of heart failure: Focus on patient selection and perspectives. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ranmal, S.; Batchelor, H.K.; Orlu-Gul, M.; Ernest, T.B.; Thomas, I.W.; Flanagan, T.; Kendall, R.; Tuleu, C. Formulation factors affecting acceptability of oral medicines in children. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 492, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneron, J. Stability Studies: A Scientific Mission of the Hospital Pharmacist. Pharm. Technol. Hosp. Pharm. 2018, 2, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipho, A.; De Hart, M.P. Spironolactone Aqueous Formulations. US Patent 9,757,394B2, 29 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman, S.S. Influence of medications on taste and smell. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 4, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuleu, C.; Solomonidou, D.; Breitkreutz, J. Paediatric Formulations. In Guide to Paediatric Drug Development and Clinical Research; Rose, K., van den Anker, J.N., Eds.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, J.; Cram, A.; Woertz, K.; Breitkreutz, J.; Winzenburg, G.; Turner, R.; Tuleu, C. Playing hide and seek with poorly tasting paediatric medicines: Do not forget the excipients. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 73, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozarewicz, P. Regulatory perspectives on acceptability testing of dosage forms in children. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 469, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchelor, H.K.; Marriott, J.F. Formulations for children: Problems and solutions. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohi, H.; Sultana, Y.; Khar, R.K. Taste masking technologies in oral pharmaceuticals: Recent developments and approaches. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2004, 30, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkov, D.; Tomasi, P.; Eichler, I.; Murphy, D.; Yao, L.P.; Temeck, J. Pediatric Medicine Development: An Overview and Comparison of Regulatory Processes in the European Union and United States. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2017, 51, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayenew, Z.; Puri, V.; Kumar, L.; Bansal, A.K. Trends in Pharmaceutical Taste Masking Technologies: A Patent Review. Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2009, 3, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirag, J.P.; Tyagi, P.S.; Dhruv, M.; Ishita, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Rageeb, M.; Usman, M. Pharmaceutical taste masking technologies of bitter drugs: A concise review. J. Drug Discov. Ther. 2013, 1, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lopalco, A.; Denora, N.; Laquintana, V.; Cutrignelli, A.; Franco, M.; Robota, M.; Hauschildt, N.; Mondelli, F.; Arduino, I.; Lopedota, A. Taste masking of propranolol hydrochloride by microbeads of EUDRAGIT® E PO obtained with prilling technique for paediatric oral administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 574, 118922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins: Basic science and product development. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basalious, E.B.; Abdullah, A.; Ibrahim, M. Utility of Mannitol and Citric Acid for Enhancing the Solubilizing and Taste Masking Properties of β-Cyclodextrin: Development of Fast-Dissolving Tablets Containing Extremely Bitter Drug. J. Pharm. Innov. 2014, 9, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.P.; Mashru, R.C. Palatable reconstitutable dry suspension of artemether for flexible pediatric dosing using cyclodextrin inclusion complexation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2010, 15, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, N.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ishiguro, T.; Motoyama, K.; Hirayama, F.; Iohara, D.; Seo, H.; Tsuruta, S.; Arima, H.; Uekama, K. Reduction of bitterness of antihistaminic drugs by complexation with β-cyclodextrins. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.P.; Mashru, R.C. Formulation and Evaluation of Taste Masked Oral Reconstitutable Suspension of Primaquine Phosphate. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chay, S.K.; Keating, A.V.; James, C.; Aliev, A.E.; Haider, S.; Craig, D.Q.M. Evaluation of the taste-masking effects of (2-hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin on ranitidine hydrochloride; a combined biosensor, spectroscopic and molecular modelling assessment. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 3564–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birhade, S.T.; Bankar, V.H.; Gaikwad, P.D.; Pawar, S.P. Preparation and evaluation of cyclodextrin based binary systems for taste masking. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug Res. 2010, 2, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Binello, A.; Cravotto, G.; Nano, G.M.; Spagliardi, P. Synthesis of chitosan-cyclodextrin adducts and evaluation of their bitter-masking properties. Flavour Fragr. J. 2004, 19, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Kim, S.J.; Youn, Y.S.; Widjojokusumo, E.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.W.; Tjandrawinata, R.R. Preparation of bitter taste masked cetirizine dihydrochloride/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex by supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2010, 55, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Vavia, P.R. Preparation and Evaluation of Taste Masked Famotidine Formulation Using Drug/β-cyclodextrin/Polymer Ternary Complexation Approach. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, F.M.; Abou-taleb, A.E.; Khaled, K.A.; Yamasaki, K.; Iohara, D.; Taguchi, K.; Anraku, M.; Hirayama, F.; Uekama, K.; Otagiri, M. Evaluation of carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin with acid function: Improvement of chemical stability, oral bioavailability and bitter taste of famotidine. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 397, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaquias, L.F.B.; Sá-Barreto, L.C.L.; Freire, D.O.; Silva, I.C.R.; Karan, K.; Durig, T.; Lima, E.M.; Marreto, R.N.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Gratieri, T.; et al. Taste masking and rheology improvement of drug complexed with beta-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin by hot-melt extrusion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 185, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, A.; Shastri, N.; Sadanandam, M. Development of taste masked fast disintegrating films of levocetirizine dihydrochloride for oral use. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funasaki, N.; Uratsuji, I.; Okuno, T.; Hirota, S.; Neya, S. Masking mechanisms of bitter taste of drugs studied with ion selective electrodes. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binello, A.; Robaldo, B.; Barge, A.; Cavalli, R.; Cravotto, G. Synthesis of cyclodextrin-based polymers and their use as debittering agents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 2549–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.B.; Patel, J.K. Cyclodextrin inclusion complex to enhance solubility of poorly water soluble drugs: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Popielec, A.; Loftsson, T. Effects of cyclodextrins on the chemical stability of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewster, M.E.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kata, M.; Haragh, L. Spray embedding of spironolactone with β-cyclodextrin. Pharmazie 1981, 36, 784–785. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, H.; Tsuruoka, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Fujinaga, T.; Otagiri, M.; Uekama, K. Enhancement of oral bioavailability of spironolactone by beta- and gamma-cyclodextrin complexations. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukonen, A.M.; Lennernäs, H.; Mannermaa, J.P. Water-soluble beta-cyclodextrins in paediatric oral solutions of spironolactone: Preclinical evaluation of spironolactone bioavailability from solutions of beta-cyclodextrin derivatives in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1998, 50, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambhekar, S.S.; Breen, P. Cyclodextrins in pharmaceutical formulations I: Structure and physicochemical properties, formation of complexes, and types of complex. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, E.M.M. Cyclodextrins and their uses: A review. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekharsky, M.V.; Inoue, Y. Complexation Thermodynamics of Cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1875–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, J.; Mueller, K.L.; Hoon, M.A.; Adler, E.; Feng, L.; Guo, W.; Zuker, C.S.; Ryba, N.J.P.; Hughes, H.; Biosciences, A.; et al. T2Rs Function as Bitter Taste Receptors. Cell 2000, 100, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Ahmed, A.H.A.; Soto, J.; Ernest, T.; Tuleu, C. Non-human tools for the evaluation of bitter taste in the design and development of medicines: A systematic review. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, J.; Keeley, A.; Keating, A.V.; Mohamed-Ahmed, A.H.A.; Sheng, Y.; Winzenburg, G.; Turner, R.; Desset-Brèthes, S.; Orlu, M.; Tuleu, C. Rats can predict aversiveness of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 133, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, T.; Connors, K.A. Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 1965, 4, 117–212. [Google Scholar]
- Abagyan, R.A.; Totrov, M.M.; Kuznetsov, D.N. ICM—A new method for protein modeling and design. Applications to docking and structure prediction from the distorted native conformation. J. Comp. Chem. 1994, 15, 488–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, O.; Tayyari, F.; Salari, R.; Tayyari, S.F. Study of interaction of spironolactone with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in aqueous solution and in solid state. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 878, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, K.J.; Rubin, B.D.; Keene, J.C.; Katz, D.B. Licking Microstructure Reveals Rapid Attenuation of Neophobia. Chem. Senses 2014, 39, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kaukonen, A.M.; Kilpeläinen, I.; Mannermaa, J.P. Water-soluble β-cyclodextrins in paediatric oral solutions of spironolactone: Solubilization and stability of spironolactone in solutions of β-cyclodextrin derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 159, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitha, J.; Milecki, J.; Fales, H.; Pannell, L.; Uekema, K. Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin: Preparation and characterization; effects on solubility of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 29, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuff, N.; York, P. Spironolactone-cyclodextrin complexes: Phase solubility and ultrafiltration studies. Int. J. Pharm. 1991, 73, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Douroumis, D. An in-vitro-in-vivo taste assessment of bitter drug: Comparative electronic tongues study. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münster, M.; Mohamed-Ahmed, A.H.; Immohr, L.I.; Schoch, C.; Schmidt, C.; Tuleu, C.; Breitkreutz, J. Comparative in vitro and in vivo taste assessment of liquid praziquantel formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohapatraa, S.; Bosea, A.; Bindhania, S.; Karb, R.K.; Panic, N.R.; Nayakd, A.K. Effect of hydrophilic polymer on solubility and taste masking of linezolid in multi-component cyclodextrin inclusion complex: Physicochemical characterization and molecular docking. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, P.; De Marco, I. Preparation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes by supercritical antisolvent process. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 44, 101397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Ji, M.; Sun, Y.; Yan, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Preparation and characterization of baicalein/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex for enhancement of solubility, antioxidant activity and antibacterial activity using supercritical antisolvent technology. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2020, 96, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Header | First BATA Experiment | Second BATA Experiment | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| HP-β-CyD (w/v) | 2% | 6% | 12% | 18% | 21% | 25% | 0.85% | 1% | 2% | 6% | 12% | 18% |
| SPL (mg/mL) | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopalco, A.; Manni, A.; Keeley, A.; Haider, S.; Li, W.; Lopedota, A.; Altomare, C.D.; Denora, N.; Tuleu, C. In Vivo Investigation of (2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin-Based Formulation of Spironolactone in Aqueous Solution for Paediatric Use. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040780
Lopalco A, Manni A, Keeley A, Haider S, Li W, Lopedota A, Altomare CD, Denora N, Tuleu C. In Vivo Investigation of (2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin-Based Formulation of Spironolactone in Aqueous Solution for Paediatric Use. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(4):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040780
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopalco, Antonio, Annachiara Manni, Alexander Keeley, Shozeb Haider, Wenliang Li, Angela Lopedota, Cosimo Damiano Altomare, Nunzio Denora, and Catherine Tuleu. 2022. "In Vivo Investigation of (2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin-Based Formulation of Spironolactone in Aqueous Solution for Paediatric Use" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 4: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040780
APA StyleLopalco, A., Manni, A., Keeley, A., Haider, S., Li, W., Lopedota, A., Altomare, C. D., Denora, N., & Tuleu, C. (2022). In Vivo Investigation of (2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin-Based Formulation of Spironolactone in Aqueous Solution for Paediatric Use. Pharmaceutics, 14(4), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040780











