Arctiin Inhibits Cervical Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through Suppression of S100A4 Expression via PI3K/Akt Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture
2.2. Cell Cytotoxicity
2.3. Migration and Invasion Assay
2.4. CS2-Empty Vector and CS2-S100A4 Transfection
2.5. Western Blot Assay
2.6. Real-Time RT-PCR
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Arctiin on the Viability of Cervical Cancer Cells
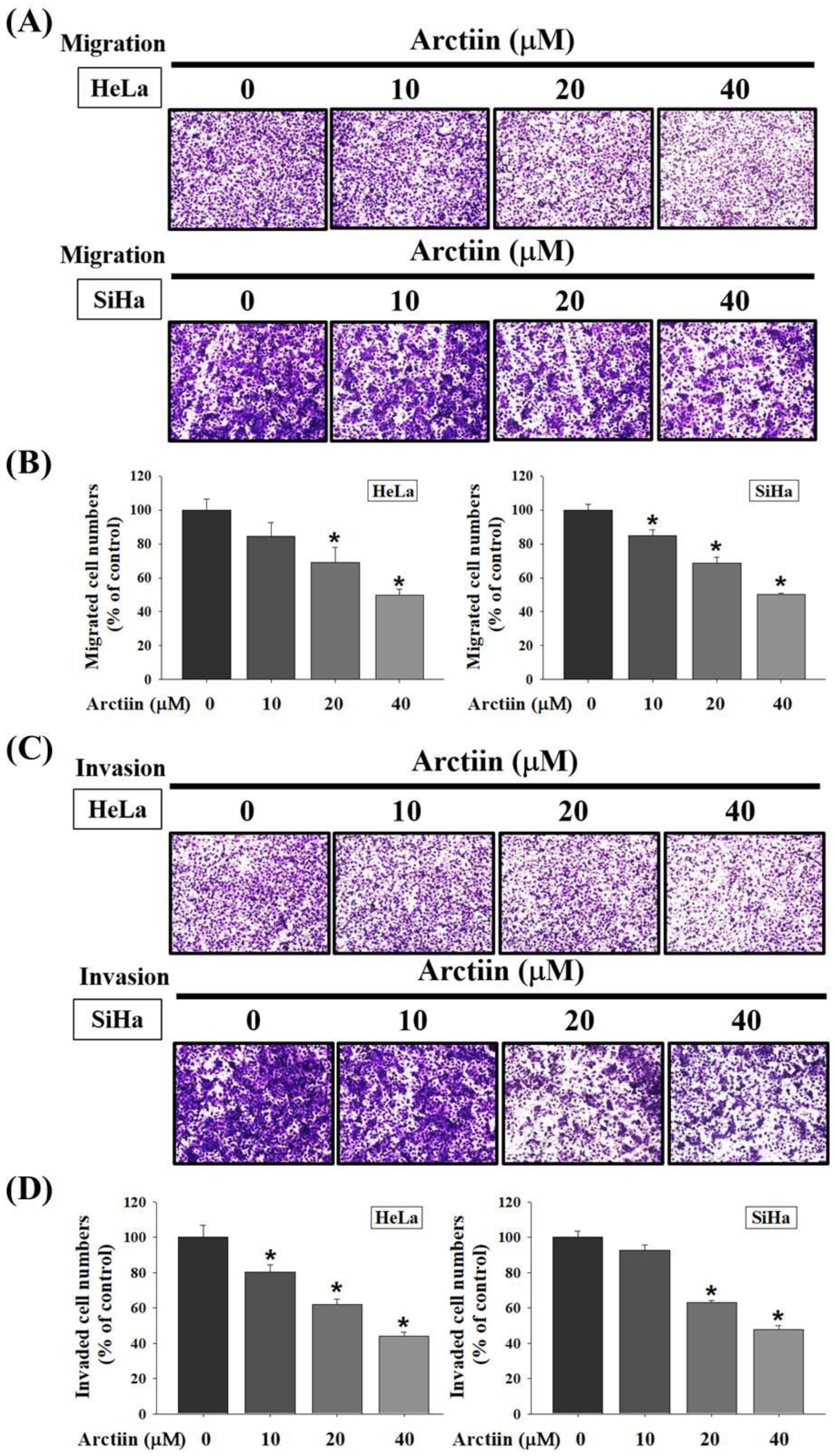
3.2. Inhibitory Effects of Arctiin on Cell Migration and Invasion in Cervical Cancer Cells
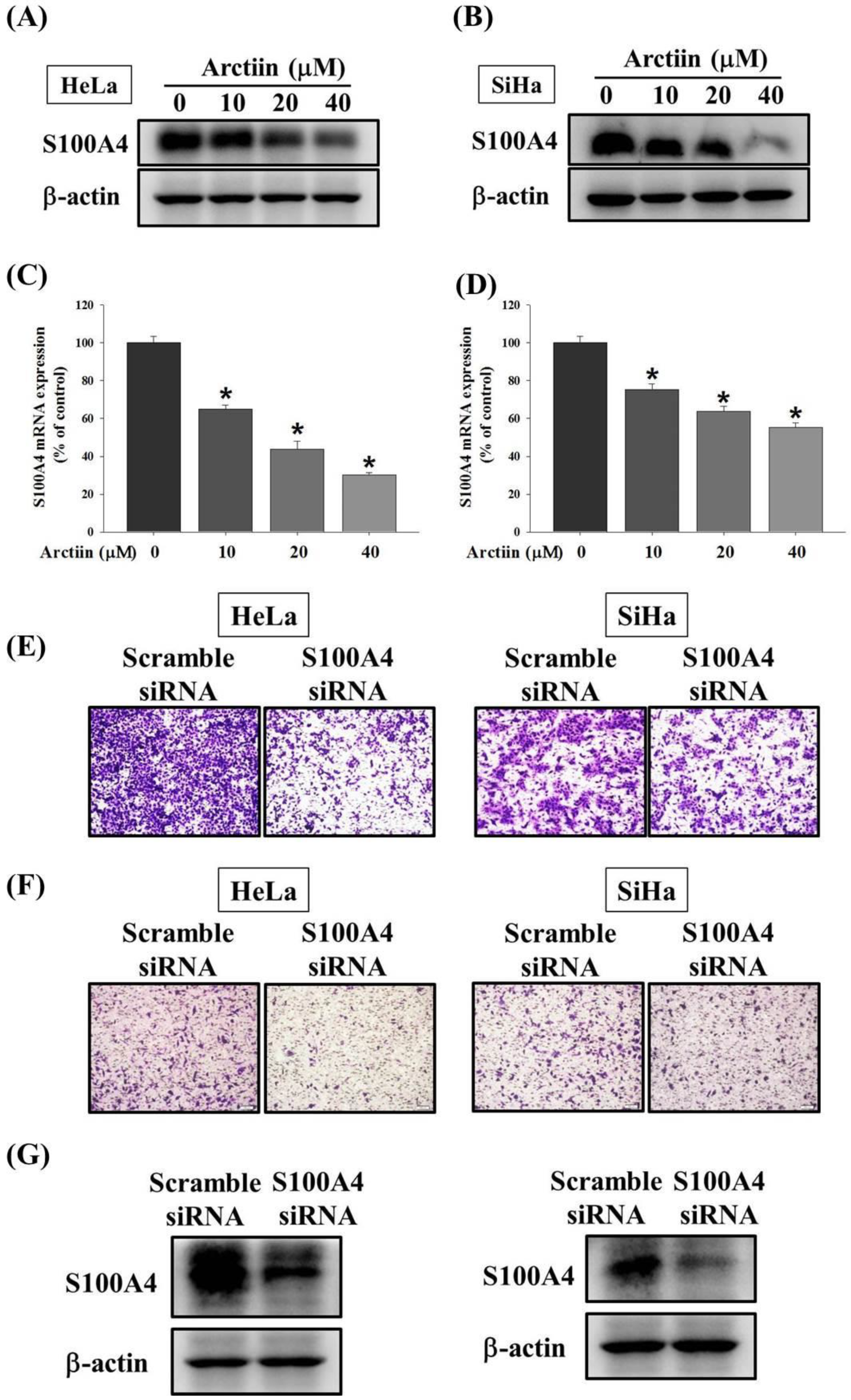
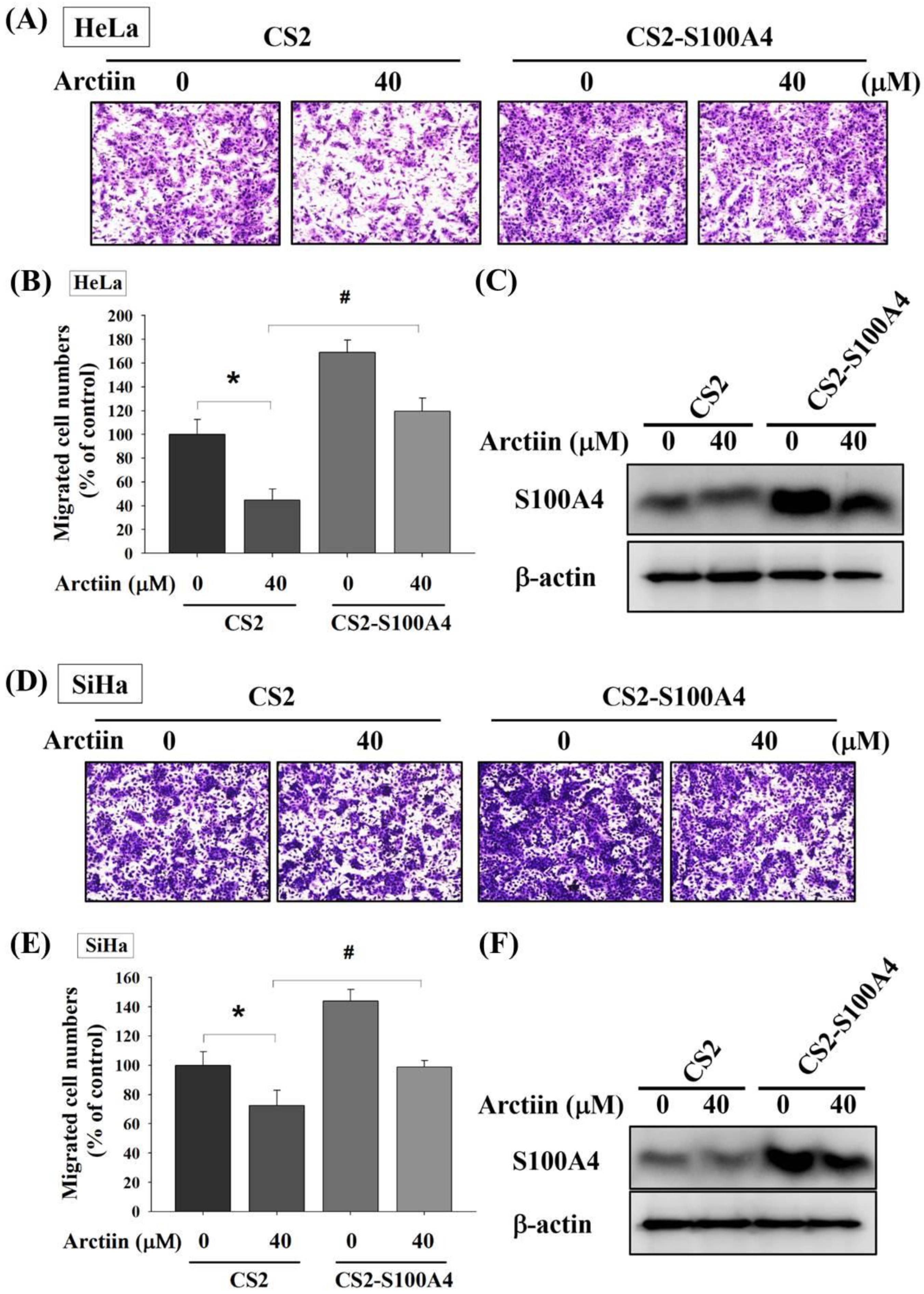
3.3. Effects of Arctiin on the S100A4 Protein and Mrna Level
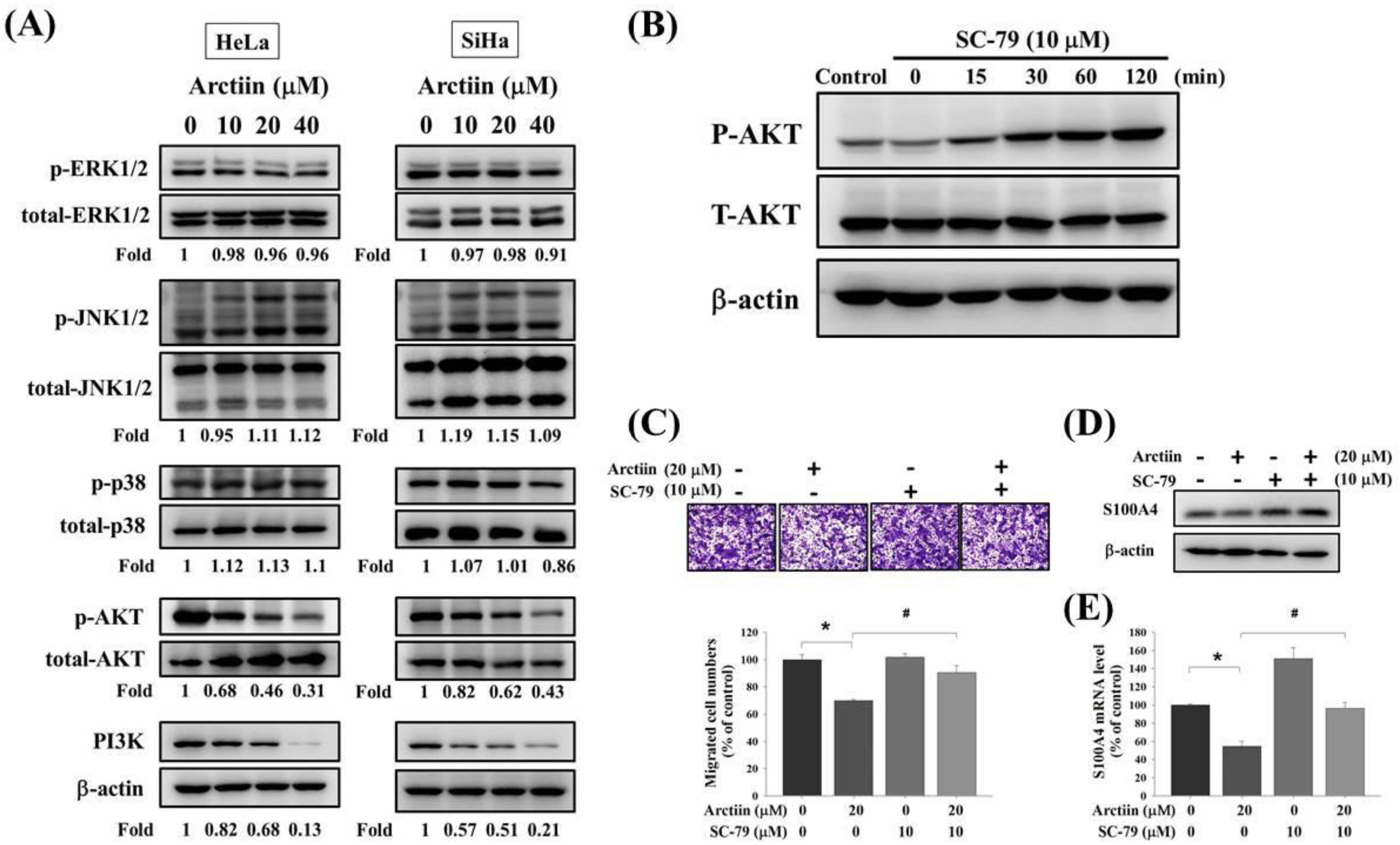
3.4. Effects of Arctiin on PI3K/Akt Pathway in Cervical Cancer Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Small, W., Jr.; Bacon, M.A.; Bajaj, A.; Chuang, L.T.; Fisher, B.J.; Harkenrider, M.M.; Jhingran, A.; Kitchener, H.C.; Mileshkin, L.R.; Viswanathan, A.N.; et al. Cervical cancer: A global health crisis. Cancer 2017, 123, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meir, H.; Kenter, G.G.; Burggraaf, J.; Kroep, J.R.; Welters, M.J.; Melief, C.J.; van der Burg, S.H.; van Poelgeest, M.I. The need for improvement of the treatment of advanced and metastatic cervical cancer, the rationale for combined chemo-immunotherapy. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wu, X. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of metastatic cervical cancer. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 27, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsin, M.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Wang, P.H.; Ko, J.L.; Hsin, I.L.; Yang, S.F. Hispolon suppresses metastasis via autophagic degradation of cathepsin S in cervical cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Siddique, H.R.; Saleem, M. S100A4 calcium-binding protein is key player in tumor progression and metastasis: Preclinical and clinical evidence. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, P.; Yang, Y.; Han, X.; Hu, M.; Sellers, J.C.; Londono-Joshi, A.I.; Cai, G.Q.; Buchsbaum, D.J.; Christein, J.D.; Tang, Q.; et al. S100A4 promotes pancreatic cancer progression through a dual signaling pathway mediated by Src and focal adhesion kinase. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, K.; Maelandsmo, G.M. S100A4 and metastasis: A small actor playing many roles. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, S.C.; Varney, K.M.; Weber, D.J.; Bresnick, A.R. S100A4, a mediator of metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfman, D.M.; Kim, E.J.; Lukanidin, E.; Grigorian, M. The metastasis associated protein S100A4: Role in tumour progression and metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 1955–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, N.; Horiuchi, A.; Osada, R.; Imai, T.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Konishi, I. Nuclear expression of S100A4 is associated with aggressive behavior of epithelial ovarian carcinoma: An important autocrine/paracrine factor in tumor progression. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Kweon, M.H.; Johnson, J.J.; Adhami, V.M.; Elcheva, I.; Khan, N.; Bin Hafeez, B.; Bhat, K.M.; Sarfaraz, S.; Reagan-Shaw, S.; et al. S100A4 accelerates tumorigenesis and invasion of human prostate cancer through the transcriptional regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14825–14830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.Y.; Su, W.C.; Lin, P.W.; Guo, H.R.; Chang, T.W.; Chen, H.H. Expression of S100A4 and Met: Potential predictors for metastasis and survival in early-stage breast cancer. Oncology 2004, 66, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, K.X.; Lu, L.Y.; Huang, X.Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.Z. Prognostic significance of S100A4 and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1931–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Tian, T.; Qi, D.; Sun, K.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Qin, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J. S100A4 promotes lung tumor development through β-catenin pathway-mediated autophagy inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, B.; Gao, X.; Gao, L.L.; Kong, Q.Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, H. Inversed Expression Patterns of S100A4 and E-Cadherin in Cervical Cancers: Implication in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Anat. Rec. 2017, 300, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Yang, M.; Zuo, Z. Overview of the anti-inflammatory effects, pharmacokinetic properties and clinical efficacies of arctigenin and arctiin from Arctium lappa L. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.; Um, J.Y.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Arctiin is a pharmacological inhibitor of STAT3 phosphorylation at tyrosine 705 residue and potentiates bortezomib-induced apoptotic and anti-angiogenic effects in human multiple myeloma cells. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2019, 55, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.M.; Guh, J.H.; Chueh, S.C.; Teng, C.M. Modulation of anti-adhesion molecule MUC-1 is associated with arctiin-induced growth inhibition in PC-3 cells. Prostate 2004, 59, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, Y.; Koyama, M.; Hitomi, T.; Yokota, T.; Kawanaka, M.; Nishikawa, A.; Germain, D.; Sakai, T. Arctiin induces cell growth inhibition through the down-regulation of cyclin D1 expression. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 19, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Su, S.C.; Yeh, C.M.; Lin, C.W.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Chuang, C.Y.; Tang, C.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Yang, S.F. A novel melatonin-regulated lncRNA suppresses TPA-induced oral cancer cell motility through replenishing PRUNE2 expression. J. Pineal Res. 2021, 71, e12760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin, M.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Hsiao, Y.H.; Chen, P.N.; Wang, P.H.; Yang, S.F. Carbonic Anhydrase IX Promotes Human Cervical Cancer Cell Motility by Regulating PFKFB4 Expression. Cancers 2021, 13, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, Y.H.; Lin, C.W.; Wang, P.H.; Hsin, M.C.; Yang, S.F. The Potential of Chinese Herbal Medicines in the Treatment of Cervical Cancer. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1534735419861693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Hirose, M.; Takahashi, S.; Hasegawa, R.; Kohno, T.; Nishibe, S.; Kato, K.; Shirai, T. Effects of the lignan, arctiin, on 17-beta ethinyl estradiol promotion of preneoplastic liver cell foci development in rats. Anticancer Res. 1998, 18, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki, M.; Konoshima, T.; Komatsu, K.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H. Anti-tumor-promoting activity of lignans from the aerial part of Saussurea medusa. Cancer Lett. 2000, 158, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambartsumian, N.; Klingelhofer, J.; Grigorian, M. The Multifaceted S100A4 Protein in Cancer and Inflammation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1929, 339–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Liu, K.; Li, C.; Du, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. Molecular Mechanisms by Which S100A4 Regulates the Migration and Invasion of PGCCs With Their Daughter Cells in Human Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, K.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Ni, C.; Zhai, W.; Liang, J.; Qin, Z.; et al. S100A4 promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis by intensifying fibrosis-associated cancer cell stemness. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1725355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Mills, G.B. Targeting PI3K-AKT pathway for cancer therapy. Rev. Clin. Exp. Hematol. 2003, 7, 205–228. [Google Scholar]
- Osaki, M.; Oshimura, M.; Ito, H. PI3K-Akt pathway: Its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2004, 9, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, K.A.; Castillo, S.S.; Dennis, P.A. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and chemotherapeutic resistance. Drug Resist. Updates Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother. 2002, 5, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Hu, X.; Xu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Shao, Y.; Peng, Y. Effect of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway on the Process of Prostate Cancer Metastasis to Bone. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 72, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.; Bishayee, K.; Ghosh, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Sikdar, S.; Chakraborty, D.; Boujedaini, N.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A.R. Chelidonine isolated from ethanolic extract of Chelidonium majus promotes apoptosis in HeLa cells through p38-p53 and PI3K/AKT signalling pathways. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao J. Chin. Integr. Med. 2012, 10, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, G. Butein suppresses cervical cancer growth through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 3085–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.; Yang, X.; Zou, K.; He, H.; Wang, J.; Qin, H.; Yu, X.; Liu, C.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, F.; et al. Anti-proliferative effect of RCE-4 from Reineckia carnea on human cervical cancer HeLa cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and NF-κB activation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Duan, L.; Zou, Z.; Li, H.; Yuan, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Zha, H.; et al. Activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway is involved in S100A4-induced viability and migration in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Goldstein, L.D.; Durinck, S.; Chen, Y.J.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kljavin, N.M.; Sokol, E.S.; Stawiski, E.W.; Haley, B.; Ziai, J.; et al. S100a4 upregulation in Pik3caH1047R;Trp53R270H;MMTV-Cre-driven mammary tumors promotes metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.-Y.; Hsin, M.-C.; Chen, P.-N.; Lin, C.-W.; Wang, P.-H.; Yang, S.-F.; Hsiao, Y.-H. Arctiin Inhibits Cervical Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through Suppression of S100A4 Expression via PI3K/Akt Pathway. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020365
Lee C-Y, Hsin M-C, Chen P-N, Lin C-W, Wang P-H, Yang S-F, Hsiao Y-H. Arctiin Inhibits Cervical Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through Suppression of S100A4 Expression via PI3K/Akt Pathway. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(2):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020365
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Chung-Yuan, Min-Chieh Hsin, Pei-Ni Chen, Chiao-Wen Lin, Po-Hui Wang, Shun-Fa Yang, and Yi-Hsuan Hsiao. 2022. "Arctiin Inhibits Cervical Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through Suppression of S100A4 Expression via PI3K/Akt Pathway" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 2: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020365
APA StyleLee, C.-Y., Hsin, M.-C., Chen, P.-N., Lin, C.-W., Wang, P.-H., Yang, S.-F., & Hsiao, Y.-H. (2022). Arctiin Inhibits Cervical Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through Suppression of S100A4 Expression via PI3K/Akt Pathway. Pharmaceutics, 14(2), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020365






