Extracellular Vesicle-Based Hybrid Systems for Advanced Drug Delivery
Abstract
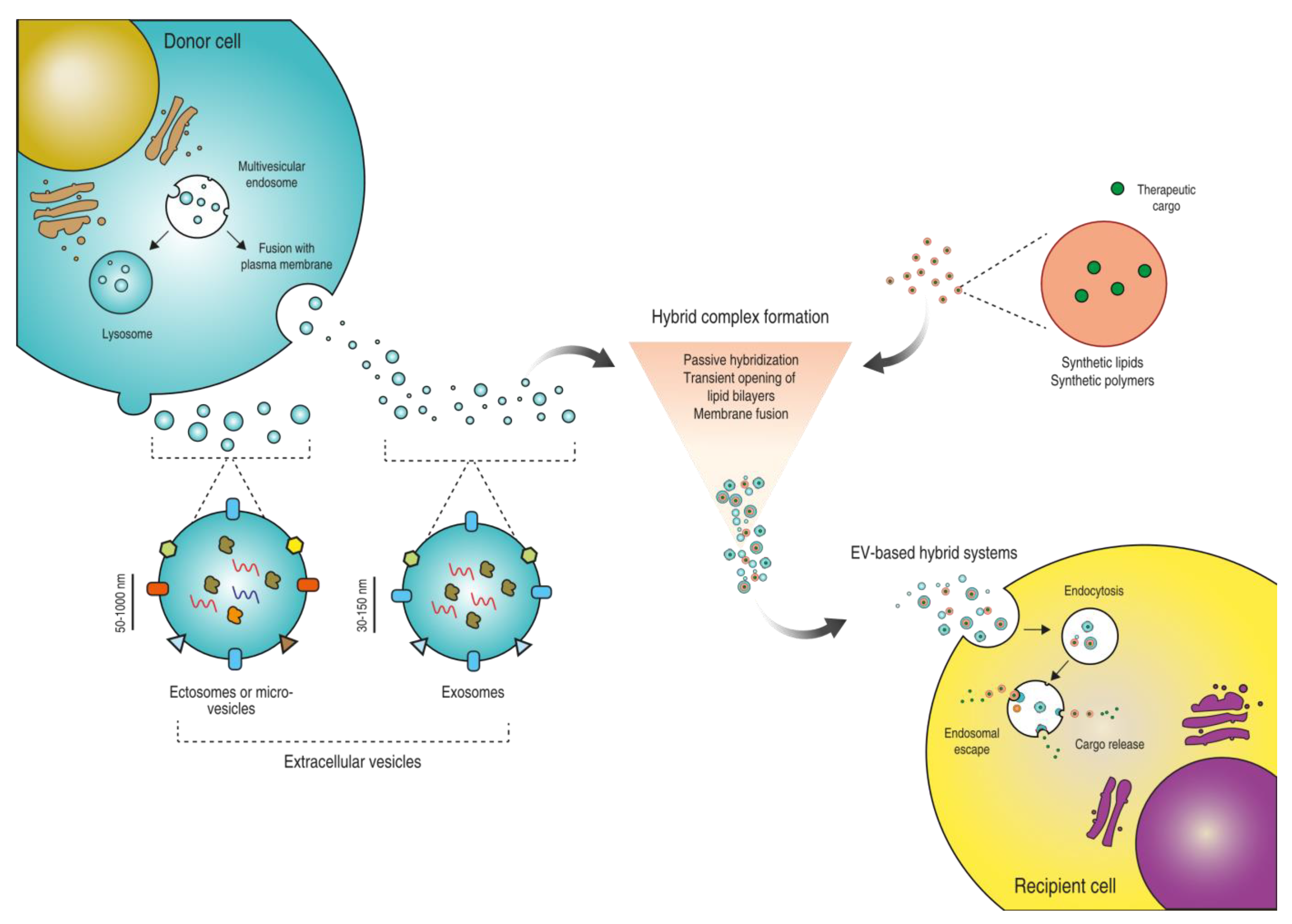
:1. Introduction
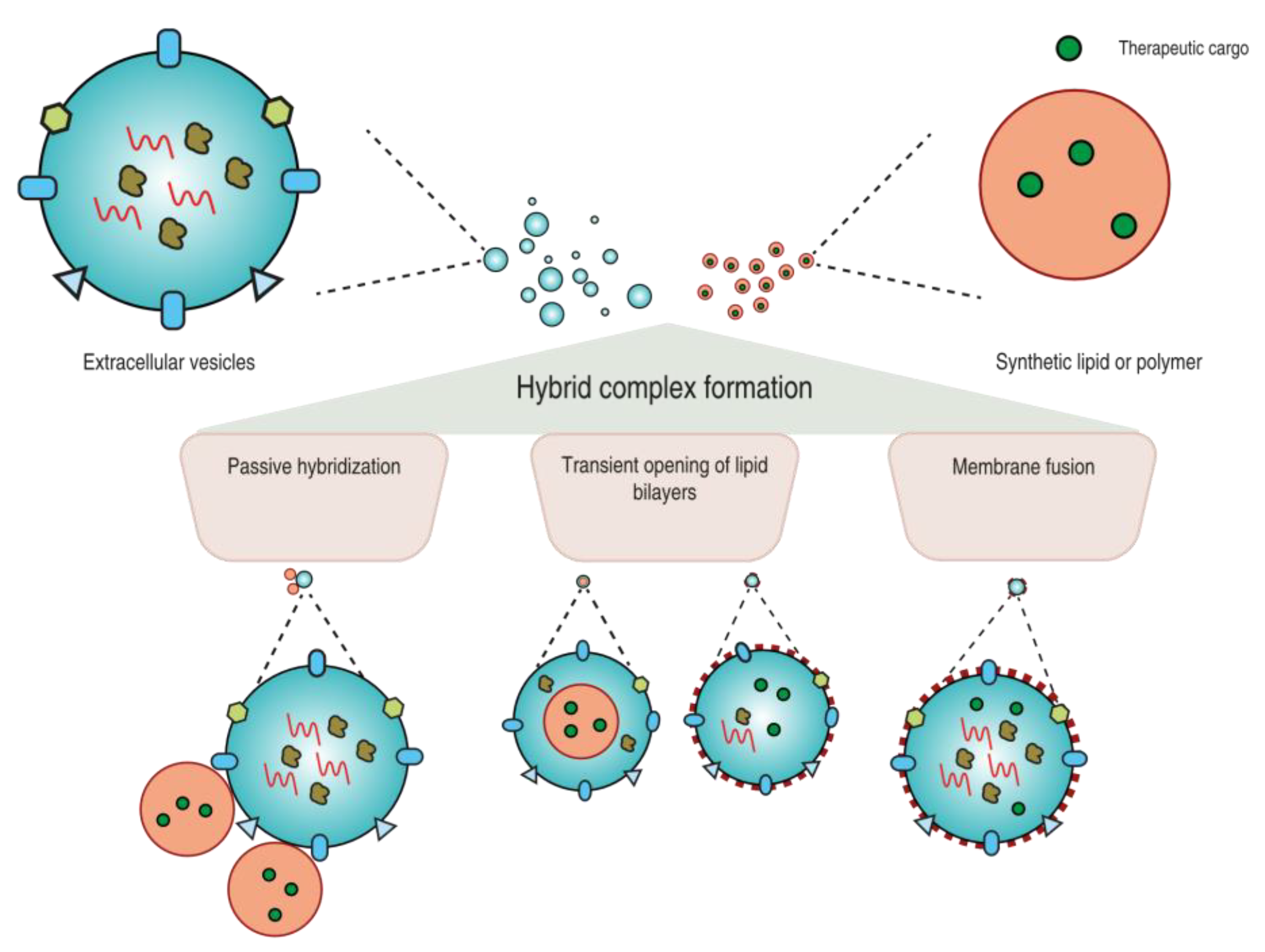
2. Strategies to Prepare EV-Based Hybrid Systems
2.1. Passive Hybridization
2.2. Transient Opening of Lipid Bilayers
2.3. Fusion of Lipid Bilayers
3. Advantages of EV-Based Hybrids in Comparison to Synthetic Drug Delivery Systems
3.1. Immuno-Evasive Benefits
3.2. Overcoming Biological Barriers
3.3. Enhanced Cellular Uptake and Cargo Delivery
3.4. Homing Properties
4. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Extracellular vesicles | EVs |
| Synthetic nanoparticles | sNPs |
| Drug delivery system | DDS |
| International Society for Extracellular Vesicles | ISEV |
| Polyethyleneimine | PEI |
| Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) | PLGA |
| Poly(ethylene glycol) | PEG |
| Signal regulatory protein alpha | SIRPα |
| Mesenchymal stem cells | MSCs |
References
- Nayak, A.K.; Ahmad, S.A.; Beg, S.; Ara, T.J.; Hasnain, M.S. Drug delivery: Present, past, and future of medicine. In Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Drug Delivery; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 255–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydbring, P.; Du, J. Nanoparticle interaction with immune cells for Nanoparticle-MEDIATED (Anticancer) immunotherapy. In Theranostic Bionanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wagner, E. Polymeric Carriers for Nucleic Acid Delivery: Current Designs and Future Directions. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 3613–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Su, Y.; Zhong, S.; Cong, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Tao, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y. Exosomes: Key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Large, D.E.; Abdelmessih, R.G.; Fink, E.A.; Auguste, D.T. Liposome composition in drug delivery design, synthesis, characterization, and clinical application. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-J.; Ju, R.-J.; Zeng, F.; Qi, X.-R.; Lu, W.-L. Liposomes in Drug Delivery: Status and Advances. In Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems; Biomaterial Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, D.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Nogueira, E. Design of liposomes as drug delivery system for therapeutic applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.S.; Pun, S.H. Extracellular Barriers to in Vivo PEI and PEGylated PEI Polyplex-Mediated Gene Delivery to the Liver. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoori, S.; Leroux, J.-C. Twenty-five years of polymersomes: Lost in translation? Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sercombe, L.; Veerati, T.; Moheimani, F.; Wu, S.Y.; Sood, A.K.; Hua, S. Advances and Challenges of Liposome Assisted Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antimisiaris, S.G.; Marazioti, A.; Kannavou, M.; Natsaridis, E.; Gkartziou, F.; Kogkos, G.; Mourtas, S. Overcoming barriers by local drug delivery with liposomes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 53–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kooijmans, S.A.A.; de Jong, O.G.; Schiffelers, R.M. Exploring interactions between extracellular vesicles and cells for innovative drug delivery system design. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 173, 252–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, K.; Robatzek, S. Functions of Extracellular Vesicles in Immunity and Virulence. Plant Physiol. 2019, 179, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, M.; Wu, D.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.S. Exosomes targeted towards applications in regenerative medicine. Nano Sel. 2021, 2, 880–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y. Extracellular vesicles in cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wu, C.; Yu, F.; Han, B.; Li, B.; Li, L. Therapeutic roles of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, O.G.; Kooijmans, S.A.; Murphy, D.E.; Jiang, L.; Evers, M.J.; Sluijter, J.P.; Vader, P.; Schiffelers, R.M. Drug Delivery with Extracellular Vesicles: From Imagination to Innovation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamerkar, S.; LeBleu, V.S.; Sugimoto, H.; Yang, S.; Ruivo, C.F.; Melo, S.A.; Lee, J.J.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2017, 546, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Haney, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Mahajan, V.; Deygen, I.; Klyachko, N.L.; Inskoe, E.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Okolie, O.; et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Graf, I.; Kuang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Haupt, M.; Majid, A.; Kilic, E.; Hermann, D.M.; Psychogios, M.-N.; Weber, M.S.; et al. Neural Progenitor Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity by NF-κB (Nuclear Factor-κB)-Dependent Regulation of ABCB1 (ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter B1) in Stroke Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1127–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morad, G.; Carman, C.V.; Hagedorn, E.J.; Perlin, J.R.; Zon, L.I.; Mustafaoglu, N.; Park, T.-E.; Ingber, D.E.; Daisy, C.C.; Moses, M.A. Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Breach the Intact Blood–Brain Barrier via Transcytosis. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13853–13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, L.A.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R.F. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oldenborg, P.A.; Zheleznyak, A.; Fang, Y.F.; Lagenaur, C.F.; Gresham, H.D.; Lindberg, F.P. Role of CD47 as a marker of self on red blood cells. Science 2000, 288, 2051–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Stremersch, S.; Braeckmans, K.; De Smedt, S.C.; Hendrix, A.; Wood, M.J.A.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Raemdonck, K.; Vader, P. Electroporation-induced siRNA precipitation obscures the efficiency of siRNA loading into extracellular vesicles. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin-Turner, S.; Vader, P.; O’Driscoll, L.; Giebel, B.; Heaney, L.M.; Davies, O.G. A call for the standardised reporting of factors affecting the exogenous loading of extracellular vesicles with therapeutic cargos. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 173, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagala, R.; Aqil, F.; Jeyabalan, J.; Kandimalla, R.; Wallen, M.; Tyagi, N.; Wilcher, S.; Yan, J.; Schultz, D.J.; Spencer, W.; et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of RNA and DNA for gene therapy. Cancer Lett. 2021, 505, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wu, J.; Gu, W.; Huang, Y.; Tong, Z.; Huang, L.; Tan, J. Exosome–Liposome Hybrid Nanoparticles Deliver CRISPR/Cas9 System in MSCs. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, R.; Sasaki, Y.; Kawasaki, R.; Katagiri, K.; Sawada, S.I.; Mukai, S.A.; Akiyoshi, K. Magnetically Navigated Intracellular Delivery of Extracellular Vesicles Using Amphiphilic Nanogels. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019, 30, 2150–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, S.I.; Sato, Y.T.; Kawasaki, R.; Yasuoka, J.I.; Mizuta, R.; Sasaki, Y.; Akiyoshi, K. Nanogel hybrid assembly for exosome intracellular delivery: Effects on endocytosis and fusion by exosome surface polymer engineering. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhupanyn, P.; Ewe, A.; Büch, T.; Malek, A.; Rademacher, P.; Müller, C.; Reinert, A.; Jaimes, Y.; Aigner, A. Extracellular vesicle (ECV)-modified polyethylenimine (PEI) complexes for enhanced siRNA delivery in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2020, 319, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewe, A.; Panchal, O.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Bakowsky, U.; Przybylski, S.; Temme, A.; Aigner, A. Liposome-polyethylenimine complexes (DPPC-PEI lipopolyplexes) for therapeutic siRNA delivery in vivo. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinaro, R.; Evangelopoulos, M.; Hoffman, J.R.; Corbo, C.; Taraballi, F.; Martinez, J.O.; Hartman, K.A.; Cosco, D.; Costa, G.; Romeo, I.; et al. Design and Development of Biomimetic Nanovesicles Using a Microfluidic Approach. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1702749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Cito, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Sikanen, T.M.; Santos, H.A. A versatile and robust microfluidic platform toward high throughput synthesis of homogeneous nanoparticles with tunable properties. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capretto, L.; Carugo, D.; Mazzitelli, S.; Nastruzzi, C.; Zhang, X. Microfluidic and lab-on-a-chip preparation routes for organic nanoparticles and vesicular systems for nanomedicine applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1496–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Hu, G.; Sun, J.; Jiang, X. Microfluidic based high throughput synthesis of lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles with tunable diameters. Biomicrofluidics 2015, 9, 052604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, L.; Cai, B.; Bu, L.-L.; Liao, Q.-Q.; Guo, S.-S.; Zhao, X.-Z.; Dong, W.-F.; Liu, W. Microfluidic Electroporation-Facilitated Synthesis of Erythrocyte Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Imaging-Guided Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3496–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Chang, J.; Tian, F.; Zhao, F.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J. Microfluidic Sonication to Assemble Exosome Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Immune Evasion-Mediated Targeting. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 7836–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Lv, W.; Li, Y.; Chang, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Sun, J. Improving Tumor Targeting of Exosomal Membrane-Coated Polymeric Nanoparticles by Conjugation with Aptamers. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 2666–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.P.; Xu, X.; Burgess, D.J. Freeze-Anneal-Thaw Cycling of Unilamellar Liposomes: Effect on Encapsulation Efficiency. Pharm. Res. 2013, 31, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.T.; Umezaki, K.; Sawada, S.; Mukai, S.A.; Sasaki, Y.; Harada, N.; Shiku, H.; Akiyoshi, K. Engineering hybrid exosomes by membrane fusion with liposomes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, Q.; Cheng, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, J. Thermosensitive Exosome–Liposome Hybrid Nanoparticle-Mediated Chemoimmunotherapy for Improved Treatment of Metastatic Peritoneal Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Tang, J.; Lv, Q.; Liu, J. Gene-engineered exosomes-thermosensitive liposomes hybrid nanovesicles by the blockade of CD47 signal for combined photothermal therapy and cancer immunotherapy. Biomaterials 2021, 275, 120964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhan, Y.Y.; Prasca-Chamorro, D.; Palou Zuniga, G.; Moore, D.M.; Arun Kumar, S.; Gaharwar, A.K.; Bishop, C.J. Engineered extracellular vesicles with synthetic lipids via membrane fusion to establish efficient gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 573, 118802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Deun, J.; Roux, Q.; Deville, S.; van Acker, T.; Rappu, P.; Miinalainen, I.; Heino, J.; Vanhaecke, F.; de Geest, B.G.; de Wever, O.; et al. Feasibility of Mechanical Extrusion to Coat Nanoparticles with Extracellular Vesicle Membranes. Cells 2020, 9, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evers, M.J.W.; van de Wakker, S.I.; de Groot, E.M.; de Jong, O.G.; Gitz-François, J.J.J.; Seinen, C.S.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Vader, P. Functional siRNA Delivery by Extracellular Vesicle–Liposome Hybrid Nanoparticles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 2101202, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Jing, Y.; Chen, X.; Su, J. Exosome-guided bone targeted delivery of Antagomir-188 as an anabolic therapy for bone loss. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2905–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Fan, M.; Huang, D.; Li, B.; Xu, R.; Gao, F.; Chen, Y. Clodronate-loaded liposomal and fibroblast-derived exosomal hybrid system for enhanced drug delivery to pulmonary fibrosis. Biomaterials 2021, 271, 120761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, J.P.K.; Holme, M.N.; Stevens, M.M. Re-Engineering Extracellular Vesicles as Smart Nanoscale Therapeutics. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piffoux, M.; Silva, A.K.A.; Wilhelm, C.; Gazeau, F.; Tareste, D. Modification of Extracellular Vesicles by Fusion with Liposomes for the Design of Personalized Biogenic Drug Delivery Systems. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6830–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Z.; Tian, H.; Chen, X. Production and clinical development of nanoparticles for gene delivery. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2016, 3, 16023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Xing, H.; Xun, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhao, X.; Cai, C.; Wang, D.; Ding, P. Functionalized extracellular vesicles as advanced therapeutic nanodelivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 121, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willingham, S.B.; Volkmer, J.-P.; Gentles, A.J.; Sahoo, D.; Dalerba, P.; Mitra, S.S.; Wang, J.; Contreras-Trujillo, H.; Martin, R.; Cohen, J.D.; et al. The CD47-signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPa) interaction is a therapeutic target for human solid tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6662–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clayton, A.; Harris, C.L.; Court, J.; Mason, M.D.; Morgan, B.P. Antigen-presenting cell exosomes are protected from complement-mediated lysis by expression of CD55 and CD59. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Pi, J.; Xu, H.; Zhao, H.; Xu, J.; Evans, C.E.; Jin, H. Advances in Anti-Tumor Treatments Targeting the CD47/SIRPα Axis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elliott, R.O.; He, M. Unlocking the Power of Exosomes for Crossing Biological Barriers in Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, C.; Cavalli, R.; Panciani, P.P.; Battaglia, L. Overcoming the Blood–Brain Barrier: Successes and Challenges in Developing Nanoparticle-Mediated Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Brain Tumours. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A.; Selby, L.I.; Johnston, A.P.R.; Such, G.K. The Endosomal Escape of Nanoparticles: Toward More Efficient Cellular Delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 30, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J.A. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, B.S.; de Beer, M.A.; Giepmans, B.N.G.; Zuhorn, I.S. Endocytosis of Extracellular Vesicles and Release of Their Cargo from Endosomes. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 4444–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andaloussi, S.E.L.; Mäger, I.; Breakefield, X.O.; Wood, M.J.A. Extracellular vesicles: Biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockman, P.R.; Mittapalli, R.K.; Taskar, K.S.; Rudraraju, V.; Gril, B.; Bohn, K.A.; Adkins, C.E.; Roberts, A.; Thorsheim, H.R.; Gaasch, J.A.; et al. Heterogeneous Blood–Tumor Barrier Permeability Determines Drug Efficacy in Experimental Brain Metastases of Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5664–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muldoon, L.L.; Soussain, C.; Janhke, K.; Johanson, C.; Siegal, T.; Smith, Q.R.; Hall, W.A.; Hynynen, K.; Senter, P.D.; Peerboom, D.M.; et al. Chemotherapy delivery issues in central nervous system malignancy: A reality check. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sathornsumetee, S.; Rich, J.N. New approaches to primary brain tumor treatment. Anticancer Drugs 2006, 17, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Martin, P.; Fogarty, B.; Brown, A.; Schurman, K.; Phipps, R.; Yin, V.P.; Lockman, P.; Bai, S. Exosome delivered anticancer drugs across the blood-brain barrier for brain cancer therapy in Danio Rerio. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemler, M.E. Tetraspanin Proteins Mediate Cellular Penetration, Invasion, and Fusion Events and Define a Novel Type of Membrane Microdomain. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2003, 19, 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ding, X.; Jiang, C. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes for penetrating and targeted chemotherapy of pancreatic cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklander, O.P.B.; Nordin, J.Z.; O’Loughlin, A.; Gustafsson, Y.; Corso, G.; Mäger, I.; Vader, P.; Lee, Y.; Sork, H.; Seow, Y.; et al. Extracellular vesicle in vivo biodistribution is determined by cell source, route of administration and targeting. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soininen, S.K.; Vellonen, K.S.; Heikkinen, A.T.; Auriola, S.; Ranta, V.P.; Urtti, A.; Ruponen, M. Intracellular PK/PD Relationships of Free and Liposomal Doxorubicin: Quantitative Analyses and PK/PD Modeling. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, C.; Collinson, A.; Matthews, C.; Pointon, A.; Jenkinson, L.; Minter, R.R.; Vaughan, T.J.; Tigue, N.J. Exosomal delivery of doxorubicin enables rapid cell entry and enhanced in vitro potency. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Théry, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Brigstock, D.R. Integrins and heparan sulfate proteoglycans on hepatic stellate cells (HSC) are novel receptors for HSC-derived exosomes. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 4263–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D.E.; de Jong, O.G.; Evers, M.J.W.; Nurazizah, M.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Vader, P. Natural or Synthetic RNA Delivery: A Stoichiometric Comparison of Extracellular Vesicles and Synthetic Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1888–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, T.J.; Redzic, J.S.; Graner, M.W.; Anchordoquy, T.J. Examination of the specificity of tumor cell derived exosomes with tumor cells in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 2954–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Koog, L.; Gandek, T.B.; Nagelkerke, A. Liposomes and Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery Systems: A Comparison of Composition, Pharmacokinetics, and Functionalization. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 2100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, H.H.; Holt-Casper, D.; Grainger, D.W.; Ghandehari, H. Nanoparticle Uptake: The Phagocyte Problem. Nano Today 2015, 10, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, L.; Hu, S.; Huang, K.; Su, T.; Li, Z.; Vandergriff, A.; Cores, J.; Dinh, P.-U.; Allen, T.; Shen, D.; et al. Tumor cell-derived exosomes home to their cells of origin and can be used as Trojan horses to deliver cancer drugs. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrmann, I.K.; Wood, M.J.A.; Fuhrmann, G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geminder, H.; Sagi-Assif, O.; Goldberg, L.; Meshel, T.; Rechavi, G.; Witz, I.P.; Ben-Baruch, A. A Possible Role for CXCR4 and Its Ligand, the CXC Chemokine Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1, in the Development of Bone Marrow Metastases in Neuroblastoma. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 4747–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zehentmeier, S.; Pereira, J.P. Cell circuits and niches controlling B cell development. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 289, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| EV Source | Isolation Method | Nanoparticle | Hybrid Formation Strategy | Therapeutic Cargo | Benefits upon Hybridization with EVs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-929 | Ultracentrifugation | Liposomes | Sonication and extrusion | Nintedanib | Enhanced cellular uptake Reduced accumulation in liver and enhanced penetration inside pulmonary fibrotic tissue | [51] |
| 3T3 and A549 | Ultracentrifugation | Liposomes | Sonication and extrusion | siRNA loading via electroporation | - | [47] |
| Bovine colostrum powder | Ultracentrifugation | Folic acid-coated EV + polyethyleneimine | Passive hybridization | siRNA and pDNA | Enhanced cellular uptake, gene silencing ability, and pDNA delivery in vitro | [30] |
| NIH-3T3 (overexpressing CXCR4) | Ultracentrifugation | Liposomes | Extrusion | antagomiR | Selective accumulation in bone marrow Increased miRNA silencing in vitro and in vivo | [50] |
| 4T1 | Density gradient, size exclusion chromatography | Gold nanoparticles | Extrusion | - | Reduced uptake by macrophages | [48] |
| PC3, SKOV3, HCT-116, Saos-2 | Ultracentrifugation | Polyethyleneimine | Sonication | siRNA, anti-miRNA | Increased gene delivery efficacy and storage stability in vitro | [34] |
| CT26 (overexpressing CD47) | Ultracentrifugation | Thermosensitive-liposome | Freeze–thaw | ICG and R837 | Enhanced cellular uptake and targeting capability Prolonged circulation time | [46] |
| BALB/c 3T3 (overexpressing CD47) | Ultracentrifugation | Thermosensitive-liposome | Freeze–thaw | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and/or docetaxel | Preferential accumulation in tumor and inhibition of tumor progression Enhanced cellular uptake | [45] |
| A549 | Ultracentrifugation | PLGA | Microfluidics + sonication | - | Reduced uptake by macrophages Enhanced cellular uptake Homotypic targeting in vivo | [41] |
| MDA-MB-231 | Ultracentrifugation | PLGA/Cholesterol-AS1411 aptamer | Microfluidics + sonication | - | Reduced uptake by macrophages Prolonged circulation time Increased accumulation in tumor sites | [42] |
| HUVEC, murine MSC | Ultracentrifugation | Liposomes | Membrane fusion | mTHPC | - | [53] |
| Raw264.7, CMS7-wt, CMS7-HE (overexpressing HER2 receptor) | Differential centrifugation and microfiltration | Liposomes | Freeze–thaw | - | - | [44] |
| SKOV3, CPC | Tangential flow filtration, size exclusion chromatography | Liposomes | Extrusion | siRNA | Reduced toxicity Intrinsic regenerative properties | [49] |
| HEK293FT | PEG 6000 precipitation method | Liposomes | Passive hybridization | pDNA | Functional delivery of large plasmids into MSCs | [31] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez, D.A.; Vader, P. Extracellular Vesicle-Based Hybrid Systems for Advanced Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020267
Rodríguez DA, Vader P. Extracellular Vesicle-Based Hybrid Systems for Advanced Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(2):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020267
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez, Diego A., and Pieter Vader. 2022. "Extracellular Vesicle-Based Hybrid Systems for Advanced Drug Delivery" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 2: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020267
APA StyleRodríguez, D. A., & Vader, P. (2022). Extracellular Vesicle-Based Hybrid Systems for Advanced Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 14(2), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020267





