Trimethoxylated Halogenated Chalcones as Dual Inhibitors of MAO-B and BACE-1 for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.1.1. (E)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (CH1)
2.1.2. (E)-3-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (CH2)
2.1.3. (E)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (CH3)
2.1.4. (E)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,3,4-trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (CH4)
2.1.5. (E)-3-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(2,3,4-trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (CH5)
2.1.6. (E)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(2,3,4-trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (CH6)
2.2. MAOs and BACE1 Inhibition Studies
2.3. Enzyme Inhibition and Kinetic Studies
2.4. Inhibitor Reversibility Analysis
2.5. Cytotoxicity and ROS Assay
2.6. Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) Permeability
2.7. Computational Studies
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. MAO-A, MAO-B, and BACE1 Inhibition Studies
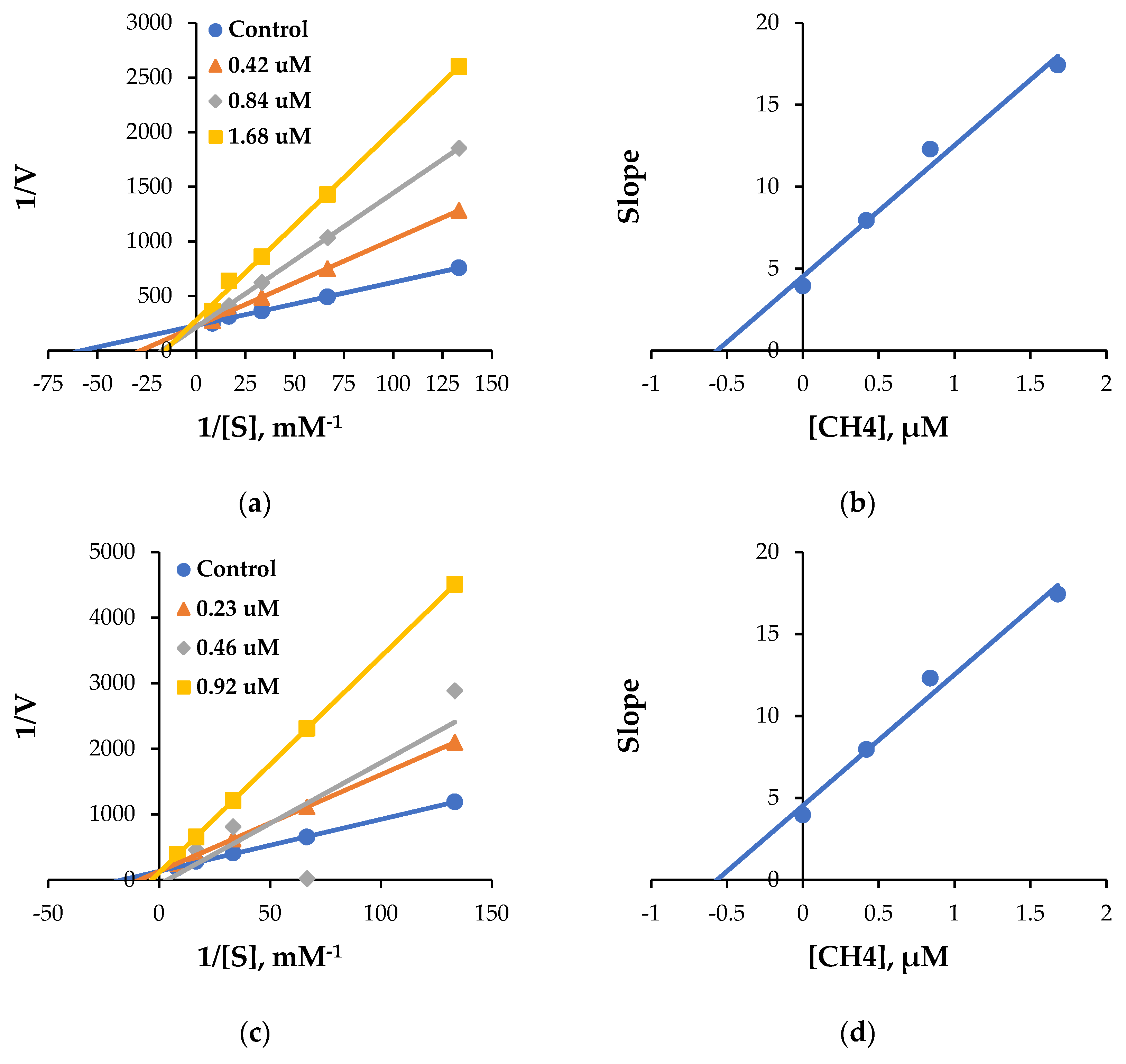
3.3. Kinetic Study
3.4. Reversibility Studies
3.5. Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) Permeation Studies
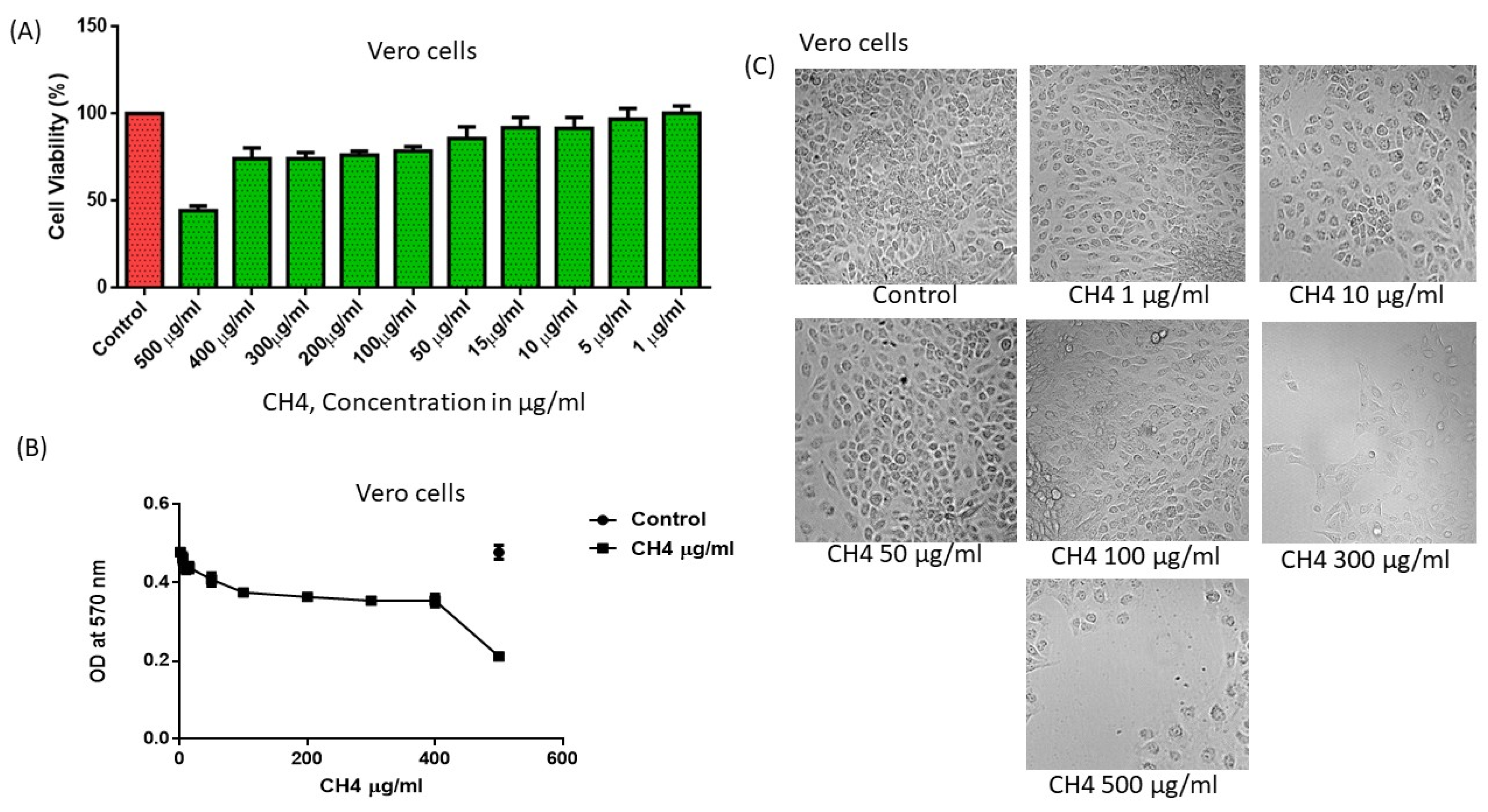
3.6. In Vitro Toxicity Evaluation
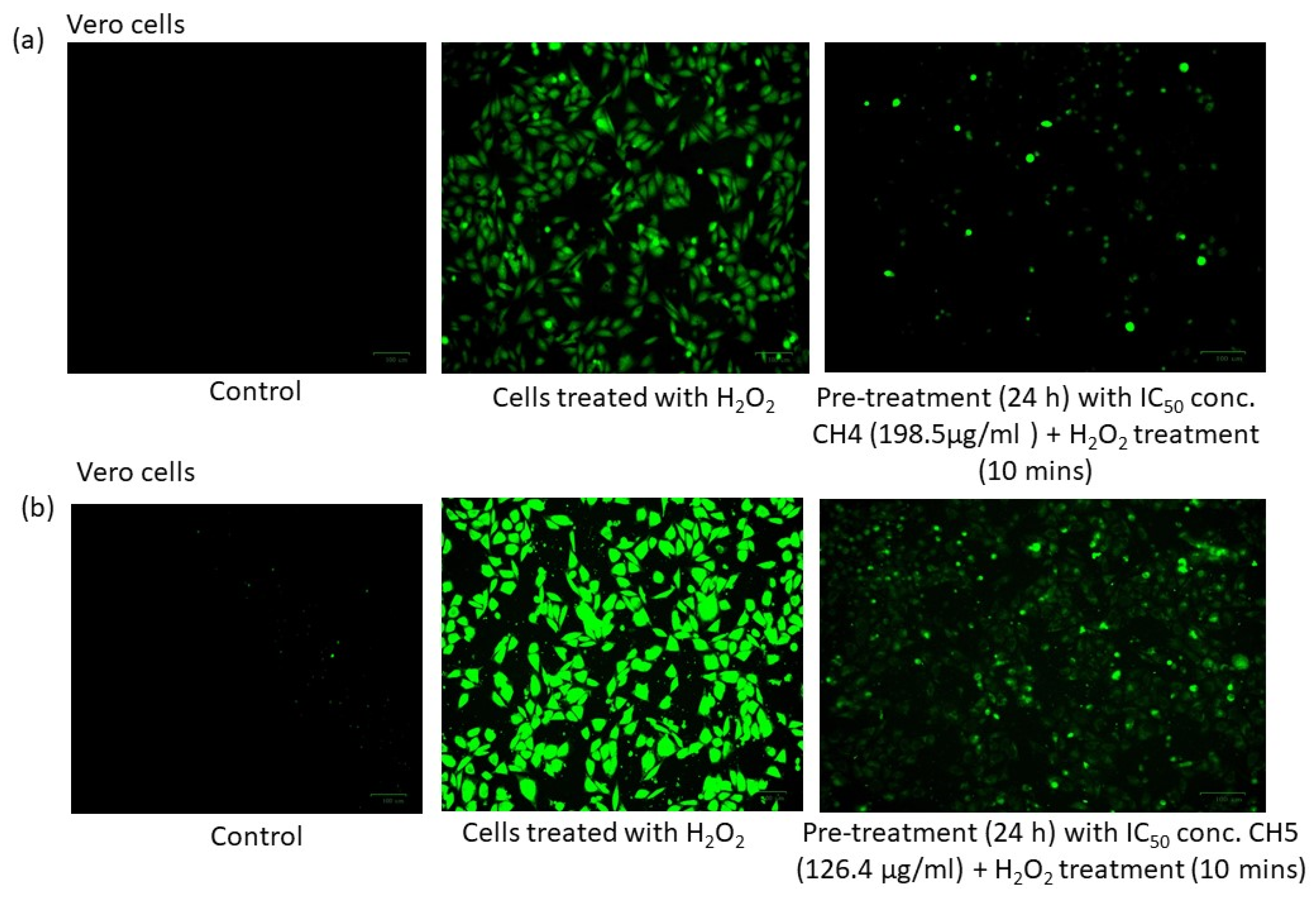
3.7. ROS Assay
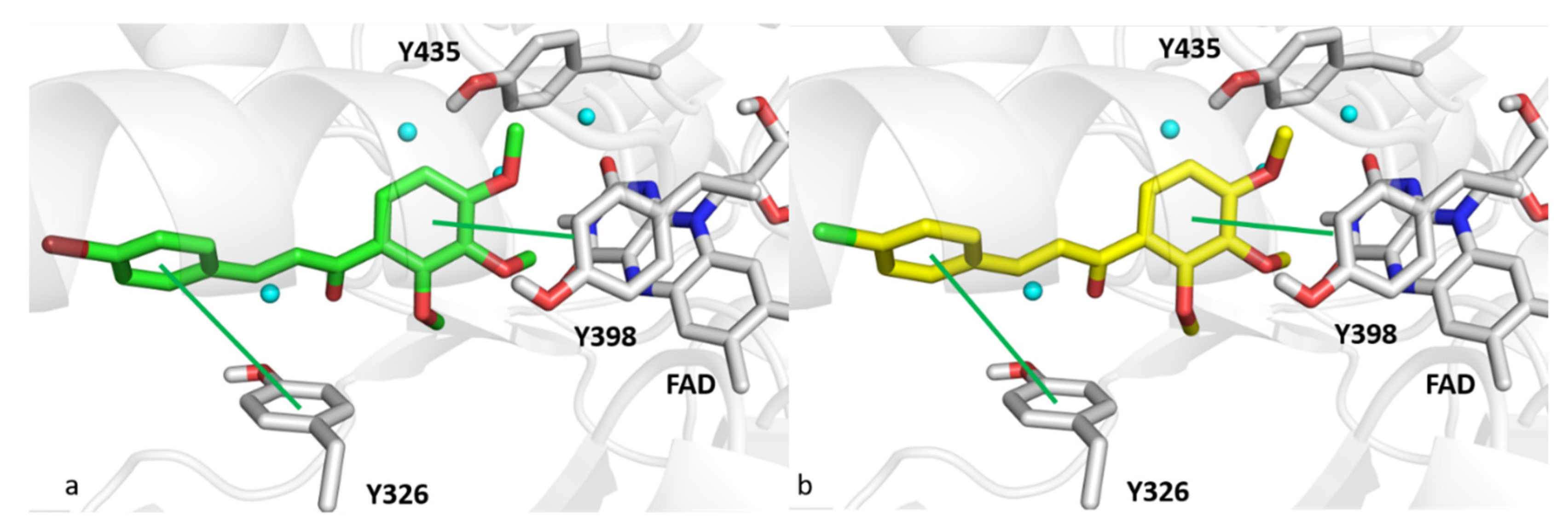
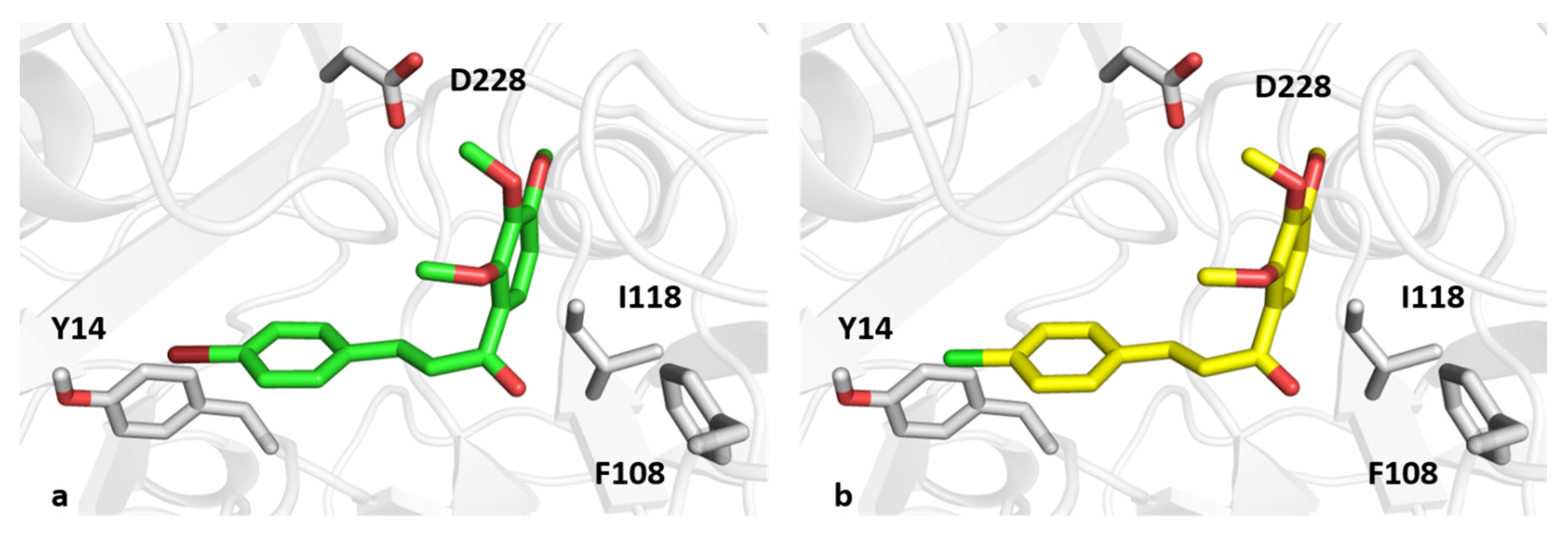
3.8. Computational Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Youdim, M.B.; Edmondson, D.; Tipton, K.F. The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carradori, S.; Secci, D.; Petzer, J.P. MAO inhibitors and their wider applications: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, S.; Hoda, N. A comprehensive review of monoamine oxidase inhibitors as Anti-Alzheimer’s disease agents: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 206, 112787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezsi, L.; Vecsei, L. Monoamine oxidase B inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riederer, P.; Müller, T. Use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in chronic neurodegeneration. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.K.P.; Ayyannan, S.R. Monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors as potential neurotherapeutic agents: An overview and update. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1603–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, P.; Carradori, S.; Ammazzalorso, A.; Secci, D. Novel approaches to the discovery of selective human monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors: Is there room for improvement? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 995–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, R.; Li, X. Discovery of monoamine oxidase inhibitors by medicinal chemistry approaches. Medchemcomm 2018, 10, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, M.B.; Bakhle, Y.S. Monoamine oxidase: Isoforms and inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease and depressive illness. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, S287–S296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, R.R.; Albreht, A. Kinetics, mechanism, and inhibition of monoamine oxidase. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1659–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Osswald, H.L. BACE1 (β-secretase) inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6765–6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Ganeshpurkar, A.; Kumar, D.; Modi, G.; Gupta, S.K.; Singh, S.K. Secretase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Long road ahead. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 148, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa-Pacha, N.M.; Abdin, S.M.; Omar, H.A.; Alniss, H.; Al-Tel, T.H. BACE1 inhibitors: Current status and future directions in treating Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 339–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, R.; Garcia, A.G.; Marco-Contelles, J. Recent advances in the multitarget-directed ligands approach for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Res. Rev. 2013, 33, 139–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaduangrat, N.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Choomwattana, S.; Wongchitrat, P.; Phopin, K.; Suwanjang, W.; Malik, A.A.; Vincent, B.; Nantasenamat, C. Multidisciplinary approaches for targeting the secretase protein family as a therapeutic route for Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1730–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Sheng, C.; Zhang, W.; Xing, C.; Miao, Z. Chalcone: A privileged structure in medicinal chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7762–7810. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, M.J.; Vazquez-Rodriguez, S.; Uriarte, E.; Santana, L. Potential pharmacological uses of chalcones: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Anand, A.; Kumar, V. Recent developments in biological activities of chalcones: A mini review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 758–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Kumar, R.; Kodwani, R.; Kapoor, S.; Khare, A.; Bansal, R.; Khurana, S.; Singh, S.; Thomas, J.; Roy, B.; et al. A review on mechanisms of anti tumor activity of chalcones. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 16, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowska, Z. A review of anti-infective and anti-inflammatory chalcones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 42, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.; Ribeiro, D.; Fernandes, E.; Freitas, M. A systematic review on anti-diabetic properties of chalcones. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 2257–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Sivasankarapillai, V.S.; Uddin, M.S.; Suresh, J.; Mathew, G.E.; Joy, M.; Marathakam, A.; Gupta, S.V. Perspective design of chalcones for the management of CNS disorders: A mini-review. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 18, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcken, R.; Zimmermann, M.O.; Lange, A.; Joerger, A.C.; Boeckler, F.M. Principles and applications of halogen bonding in medicinal chemistry and chemical biology. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1363–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yan, X.; Luo, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, W. C-X⋯H contacts in biomolecular systems: How they contribute to protein-ligand binding affinity. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2009, 113, 12615–12621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Carradori, S.; Guglielmi, P.; Uddin, M.S.; Kim, H. New aspects of monoamine oxidase b inhibitors: The key role of halogens to open the golden door. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 266–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Mathew, G.E.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Suresh, J.; Vilapurathu, J.K.; Prakasan, A.; Suresh, J.K.; Thomas, A. Development of fluorinated methoxylated chalcones as selective monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors: Synthesis, biochemistry and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2015, 62, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Camilo, N.; Salas, C.O.; Sanhueza, C.; Espinosa-Bustos, C.; Sepúlveda-Boza, S.; Reyes-Parada, M.; Gonzalez-Nilo, F.; Caroli-Rezende, M.; Fierro, A. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular simulation of chalcones and aurones as selective MAO-B inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 85, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Jang, B.K.; Cho, N.C.; Park, J.H.; Yeon, S.K.; Ju, E.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Han, G.; Pae, A.N.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Synthesis of a series of unsaturated ketone derivatives as selective and reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6486–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammuda, A.; Shalaby, R.; Rovida, S.; Edmondson, D.E.; Binda, C.; Khalil, A. Design and synthesis of novel chalcones as potent selective monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 114, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Uçar, G.; Mathew, G.E.; Mathew, S.; Purapurath, K.P.; Moolayil, F.; Mohan, S.; Gupta, S.V. Monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity: Methyl- versus Chloro chalcone derivatives. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016, 11, 2649–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Mathew, G.E.; Ucar, G.; Joy, M.; Nafna, E.K.; Lohidakshan, K.K.; Suresh, J. Monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity of methoxy-substituted chalcones. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimenti, F.; Fioravanti, R.; Bolasco, A.; Chimenti, P.; Secci, D.; Rossi, F.; Yáñez, M.; Orallo, F.; Ortuso, F.; Alcaro, S. Chalcones: A valid scaffold for monoamine oxidases inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minders, C.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A.; Lourens, A.C. Monoamine oxidase inhibitory activities of heterocyclic chalcones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5270–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, R.; Manju, S.L.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Mathew, B. Identification of indole-based chalcones: Discovery of a potent, selective, and reversible class of MAO-B inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. 2016, 349, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Haridas, A.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Joy, M.; Mathew, G.E.; Lakshmanan, B.; Jayaprakash, V. Synthesis, biochemistry, and computational studies of brominated thienyl chalcones: A new class of reversible MAO-B Inhibitors. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016, 11, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Li, Y.; Qiang, X.; Xu, R.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, Z.; Luo, L.; Yang, X.; Sang, Z.; Su, F.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 4′-aminochalcone-rivastigmine hybrids as multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yang, J.; Xu, R.; Song, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Qiang, X.; Li, Y.; Tan, Z.; Deng, Y. Design, synthesis and evaluation of 4′-OH-flurbiprofen-chalcone hybrids as potential multifunctional agents for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, R.; Baek, S.C.; Sreedharannair Leelabaiamma, M.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Imidazole bearing chalcones as a new class of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, J.; Baek, S.C.; Ramakrishnan, S.P.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Discovery of potent and reversible MAO-B inhibitors as furanochalcones. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeta; Baek, S.C.; Lee, J.P.; Rangarajan, T.M.; Ayushee; Singh, R.P.; Singh, M.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Nicolotti, O.; Kim, H.; et al. Ethyl acetohydroxamate incorporated chalcones: Unveiling a novel class of chalcones for multitarget monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors against Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 18, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Baek, S.C.; Thomas Parambi, D.G.; Lee, J.P.; Mathew, G.E.; Jayanthi, S.; Vinod, D.; Rapheal, C.; Devikrishna, V.; Kondarath, S.S.; et al. Potent and highly selective dual-targeting monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors: Fluorinated chalcones of morpholine versus imidazole. Arch. Pharm. 2019, 352, e1800309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parambi, D.G.T.; Oh, J.M.; Baek, S.C.; Lee, J.P.; Tondo, A.R.; Nicolotti, O.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of oxygenated chalcones as potent and selective MAO-B inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 103335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, P.; Shi, J.; Liu, W.; Tan, Z. Design, synthesis, in-silico and biological evaluation of novel chalcone derivatives as multi-function agents for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 180, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Q.; Cao, Z.; Li, Y.; Tian, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Y. Design, synthesis and evaluation of chalcone Mannich base derivatives as multifunctional agents for the potential treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, R.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A.; Ashraf, U.M.; Atari, E.; Alasmari, F.; Kumarasamy, S.; Sari, Y.; Khalil, A. SAR and molecular mechanism studies of monoamine oxidase inhibition by selected chalcone analogs. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Wang, K.; Zhang, P.; Shi, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, C.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.; et al. Development of chalcone-O-alkylamine derivatives as multifunctional agents against Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 183, 111737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.M.; Rangarajan, T.M.; Chaudhary, R.; Singh, R.P.; Singh, M.; Singh, R.P.; Tondo, A.R.; Gambacorta, N.; Nicolotti, O.; Mathew, B.; et al. Novel class of chalcone oxime ethers as potent monoamine oxidase-B and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Molecules 2020, 25, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.S.; Kaipakasseri, S.; Lee, S.R.; Marraiki, N.; Batiha, G.E.; Dev, S.; Palakkathondi, A.; Kavully, F.S.; Gambacorta, N.; Nicolotti, O.; et al. Selected 1,3-benzodioxine-containing chalcones as multipotent oxidase and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 2257–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Z.; Sun, D.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Y. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of 1, 4-benzodioxan-substituted chalcones as selective and reversible inhibitors of human monoamine oxidase B. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasidharan, R.; Eom, B.H.; Heo, J.H.; Park, J.E.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Musa, A.; Gambacorta, N.; Nicolotti, O.; Manju, S.L.; Mathew, B.; et al. Morpholine-based chalcones as dual-acting monoamine oxidase-B and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Synthesis and biochemical investigations. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Rakesh, K.P.; Bukhari, S.N.A.; Balakrishna, M.; Manukumar, H.M.; Qin, H.L. Multi-targetable chalcone analogs to treat deadly Alzheimer’s disease: Current view and upcoming advice. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 80, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmi, P.; Mathew, B.; Secci, D.; Carradori, S. Chalcones: Unearthing their therapeutic possibility as monoamine oxidase B inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 205, 112650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B. Privileged pharmacophore of FDA approved drugs in combination with chalcone framework: A new hope for alzheimer’s treatment. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2020, 23, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmaoglu, S.; Kazancioglu, E.A.; Kaya, R.; Kazancioglu, M.; Karaman, M.; Algul, O.; Gulcin, I. Synthesis of novel organohalogen chalcone derivatives and screening of their molecular docking study and some enzymes inhibition effects. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1208, 127868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Baek, S.C.; Grace Thomas Parambi, D.; Pil Lee, J.; Joy, M.; Annie Rilda, P.R.; Randev, R.V.; Nithyamol, P.; Vijayan, V.; Inasu, S.T.; et al. Selected aryl thiosemicarbazones as a new class of multi-targeted monoamine oxidase inhibitors. MedChemComm 2018, 9, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Oh, J.M.; Baty, R.S.; Batiha, G.E.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Gambacorta, N.; Nicolotti, O.; Kim, H. Piperazine-substituted chalcones: A new class of MAO-B, AChE, and BACE-1 inhibitors for the treatment of neurological disorders. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.S.; Oh, J.-M.; Koyiparambath, V.P.; Kumar, S.; Sudevan, S.T.; Soremekun, O.; Soliman, M.E.; Khames, A.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Pappachen, L.K.; et al. Development of halogenated pyrazolines as selective monoamine oxidase-B Inhibitors: Deciphering via molecular dynamics approach. Molecules 2021, 26, 3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.M.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, W.J.; Kang, M.G.; Baek, S.C.; Lee, J.P.; Park, D.; Oh, S.R.; Kim, H. Calycosin and 9-O-methylretusin isolated from Maackia amurensis as potent and selective reversible inhibitors of human monoamine oxidase-B. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotakis, G.; Timbrell, J.A. In vitro cytotoxicity assays: Comparison of LDH, neutral red, MTT and protein assay in hepatoma cell lines following exposure to cadmium chloride. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 160, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambunathan, N. Determination and detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS), lipid peroxidation, and electrolyte leakage in plants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 639, 292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Di, L.; Kerns, E.H.; Fan, K.; McConnell, O.J.; Carter, G.T. High throughput artificial membrane permeability assay for blood-brain barrier. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.Y.; Ma, J.; Kondou, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamashita, E.; Tsukihara, T. Structure of human monoamine oxidase A at 2.2-A resolution: The control of opening the entry for substrates/inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5739–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, C.; Wang, J.; Pisani, L.; Caccia, C.; Carotti, A.; Salvati, P.; Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, A. Structures of human monoamine oxidase B complexes with selective noncovalent inhibitors: Safinamide and coumarin analogs. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5848–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Greenblatt, H.; Chen, W.; Paz, A.; Dym, O.; Peleg, Y.; Chen, T.; Shen, X.; He, J.; et al. Flexibility of the flap in the active site of BACE1 as revealed by crystal structures and molecular dynamics simulations. Acta Cryst. D 2012, 68, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2020-4: Protein Preparation Wizard; Epik, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016.
- Madhavi Sastry, G.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and Ligand Preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2020-4: LigPrep; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020.
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.caesar-project.eu (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Available online: http://predherg.labmol.com.br/ (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Mathew, B.; Adeniyi, A.A.; Joy, M.; Mathew, G.E.; Ashona Singh-Pillay, A.S.; Sudarsanakumar, C.; Soliman, M.E.S.; Suresh, J. Anti-oxidant behavior of functionalized chalcone-a combined quantum chemical and crystallographic structural investigation. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1146, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, N.; Maitra, S.S. In vitro and in vivo toxicity assessment of nanoparticles. Int. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Zhou, T.; Pannell, B.K.; Ziegler, A.C.; Best, T.M. Biological and physiological role of reactive oxygen species—The good, the bad and the ugly. Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 2015, 214, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Cha, H.J.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, B.W.; Jeon, Y.J.; Choi, Y.H. Protective effect of phloroglucinol on oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and apoptosis through activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in HaCaT human keratinocytes. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberga, D.; Trisciuzzi, D.; Montaruli, M.; Leonetti, F.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Nicolotti, O. A new approach for drug target and bioactivity prediction: The multifingerprint similarity search algorithm (MuSSeL). J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaruli, M.; Alberga, D.; Ciriaco, F.; Trisciuzzi, D.; Tondo, A.R.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Nicolotti, O. Accelerating drug discovery by early protein drug target prediction based on a multi-fingerprint similarity search. Molecules 2019, 24, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolotti, O.; Benfenati, E.; Carotti, A.; Gadaleta, D.; Gissi, A.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Novellino, E. REACH and in silico methods: An attractive opportunity for medicinal chemists. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalluzzi, M.M.; Imbrici, P.; Gualdani, R.; Stefanachi, A.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Lentini, G.; Nicolotti, O. Human ether-à-go-go-related potassium channel: Exploring SAR to improve drug design. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 344–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangiatordi, G.F.; Alberga, D.; Altomare, C.D.; Carotti, A.; Catto, M.; Cellamare, S.; Gadaleta, D.; Lattanzi, G.; Leonetti, F.; Pisani, L.; et al. Mind the gap! A journey towards computational toxicology. Mol. Inform. 2016, 35, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, T.; Gini, G. An open source multistep model to predict mutagenicity from statistical analysis and relevant structural alerts. Chem Cent. J. 2010, 4, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, R.C.; Alves, V.M.; Silva, M.F.; Muratov, E.; Fourches, D.; Lião, L.M.; Tropsha, A.; Andrade, C.H. Pred-hERG: A novel web-accessible computational tool for predicting cardiac toxicity. Mol. Inform. 2015, 34, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Compounds | Residual Activity (%) | IC50 (µM) | SI b | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAO-A | MAO-B | AChE | BChE | BACE-1 | MAO-A | MAO-B | BACE-1 | ||
| CH1 | 90.1 ± 7.51 | 70.7 ± 2.16 | 89.2 ± 2.23 | 71.1 ± 0.68 | 61.3 ± 0.078 | ||||
| CH2 | 92.4 ± 1.10 | 84.3 ± 3.00 | 83.8 ± 7.96 | 74.5 ± 0.71 | 57.2 ± 0.46 | ||||
| CH3 | 94.9 ± 7.19 | 75.4 ± 0.27 | 75.2 ± 3.43 | 79.9 ± 0.76 | 59.7 ± 0.077 | ||||
| CH4 | 63.7 ± 1.02 | 0.93 ± 0.25 | 72.5 ± 7.22 | 73.8 ± 0.70 | 54.3 ± 2.20 | 12.7 ± 0.23 | 0.84 ± 0.025 | 13.6 ± 0.094 | 15.1 |
| CH5 | 66.7 ± 3.96 | 0.38 ± 0.53 | 81.5 ± 5.31 | 67.1 ± 0.64 | 64.3 ± 0.74 | 14.4 ± 1.10 | 0.46 ± 0.12 | 19.8 ± 0.12 | 31.3 |
| CH6 | 92.1 ± 0.75 | 19.6 ± 2.17 | 83.2 ± 1.23 | 84.6 ± 0.80 | 66.7 ± 0.45 | 4.17 ± 0.23 | |||
| Toloxatone | 1.08 ± 0.025 | - | - | ||||||
| Lazabemide | - | 0.11 ± 0.016 | - | ||||||
| Clorgyline | 0.007 ± 0.0007 | - | - | ||||||
| Pargyline | - | 0.14 ± 0.0059 | - | ||||||
| Quercetin | - | - | 13.4 ± 0.035 | ||||||
| Compounds | Bibliography Pe (×10−6 cm/s) a | Experimental Pe (×10−6 cm/s) | Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Progesterone | 9.3 | 9.02 ± 0.11 | CNS+ |
| Verapamil | 16.0 | 15.53 ± 0.24 | CNS+ |
| Piroxicam | 2.5 | 2.43 ± 0.30 | CNS+/− |
| Lomefloxacin | 1.1 | 1.12 ± 0.01 | CNS− |
| Dopamine | 0.2 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | CNS− |
| CH1 | 13.22 ± 0.33 | CNS+ | |
| CH2 | 14.06 ± 0.80 | CNS+ | |
| CH3 | 15.33 ± 0.71 | CNS+ | |
| CH4 | 14.56 ± 0.26 | CNS+ | |
| CH5 | 15.65 ± 0.22 | CNS+ | |
| CH6 | 15.22 ± 0.26 | CNS+ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vishal, P.K.; Oh, J.M.; Khames, A.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Nair, A.S.; Nath, L.R.; Gambacorta, N.; Ciriaco, F.; Nicolotti, O.; Kim, H.; et al. Trimethoxylated Halogenated Chalcones as Dual Inhibitors of MAO-B and BACE-1 for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060850
Vishal PK, Oh JM, Khames A, Abdelgawad MA, Nair AS, Nath LR, Gambacorta N, Ciriaco F, Nicolotti O, Kim H, et al. Trimethoxylated Halogenated Chalcones as Dual Inhibitors of MAO-B and BACE-1 for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(6):850. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060850
Chicago/Turabian StyleVishal, Payyalot Koyiparambath, Jong Min Oh, Ahmed Khames, Mohamed A. Abdelgawad, Aathira Sujathan Nair, Lekshmi R. Nath, Nicola Gambacorta, Fulvio Ciriaco, Orazio Nicolotti, Hoon Kim, and et al. 2021. "Trimethoxylated Halogenated Chalcones as Dual Inhibitors of MAO-B and BACE-1 for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 6: 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060850
APA StyleVishal, P. K., Oh, J. M., Khames, A., Abdelgawad, M. A., Nair, A. S., Nath, L. R., Gambacorta, N., Ciriaco, F., Nicolotti, O., Kim, H., & Mathew, B. (2021). Trimethoxylated Halogenated Chalcones as Dual Inhibitors of MAO-B and BACE-1 for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Pharmaceutics, 13(6), 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060850










