Iron Oxide Mesoporous Magnetic Nanostructures with High Surface Area for Enhanced and Selective Drug Delivery to Metastatic Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
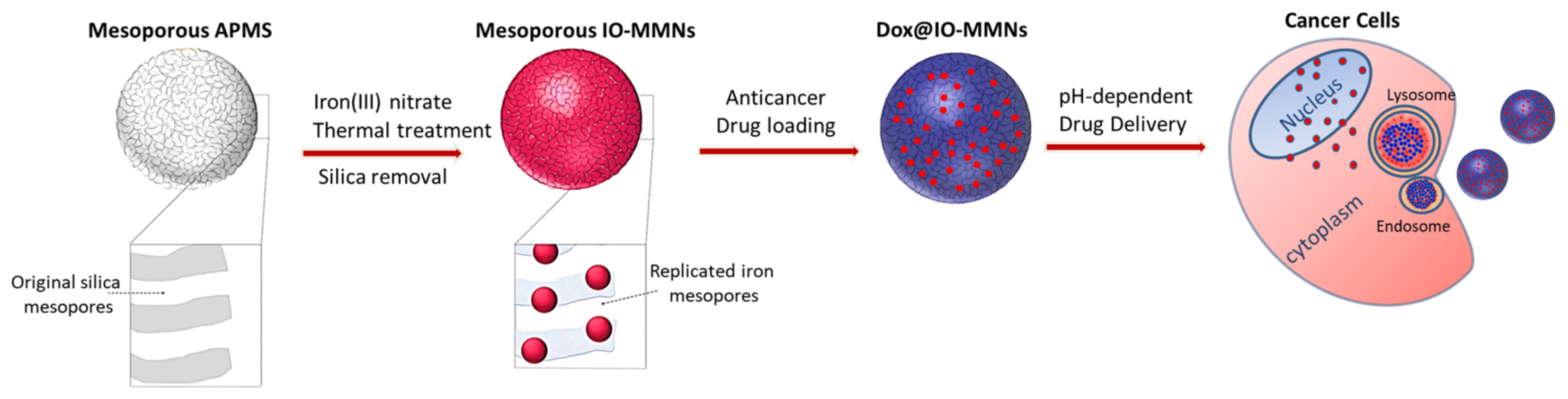
2.3. Preparation of IO-MMNs
2.4. Drug Loading and Release
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Live Confocal Imaging
2.7. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
3. Results and Discussion
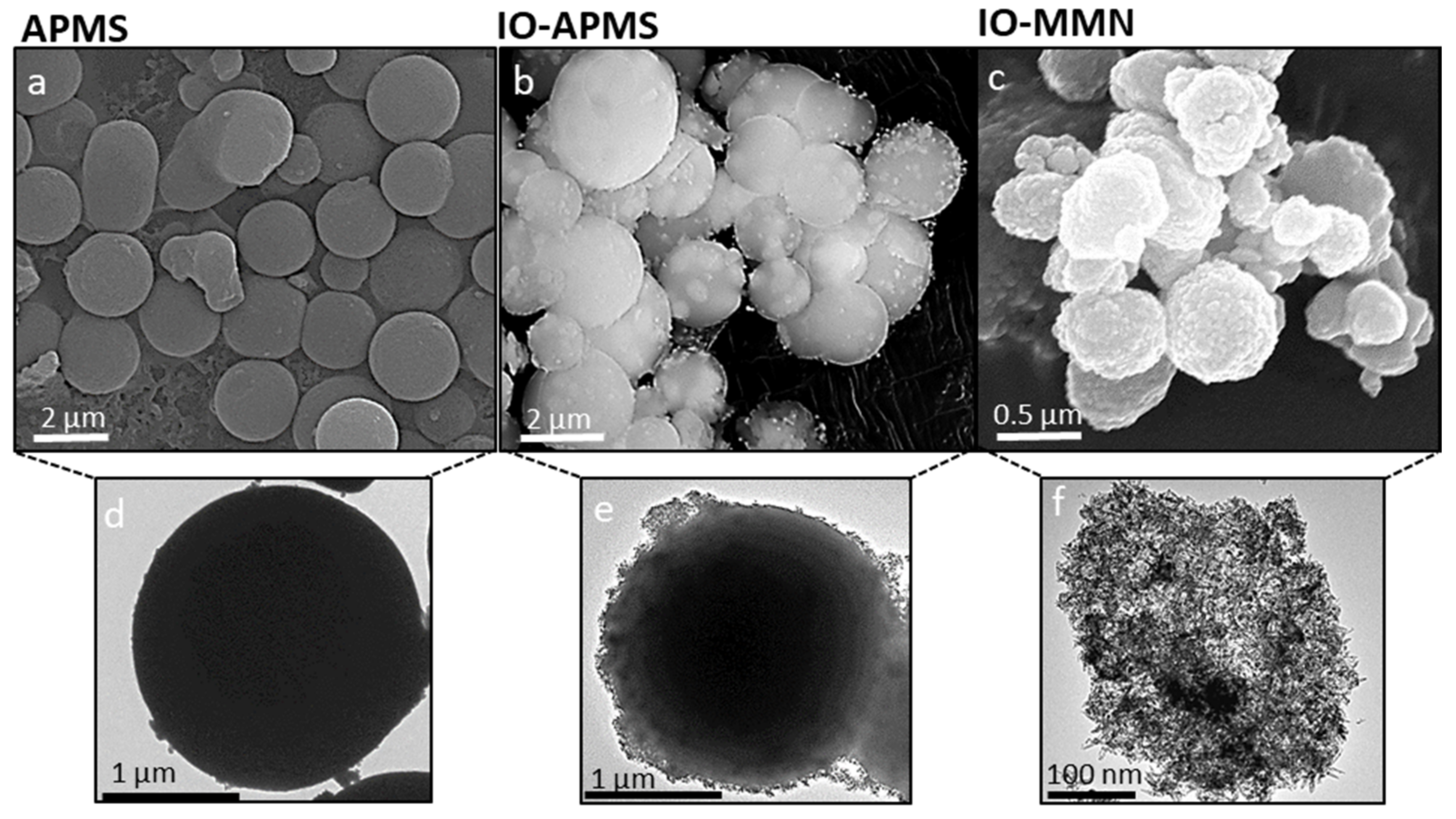
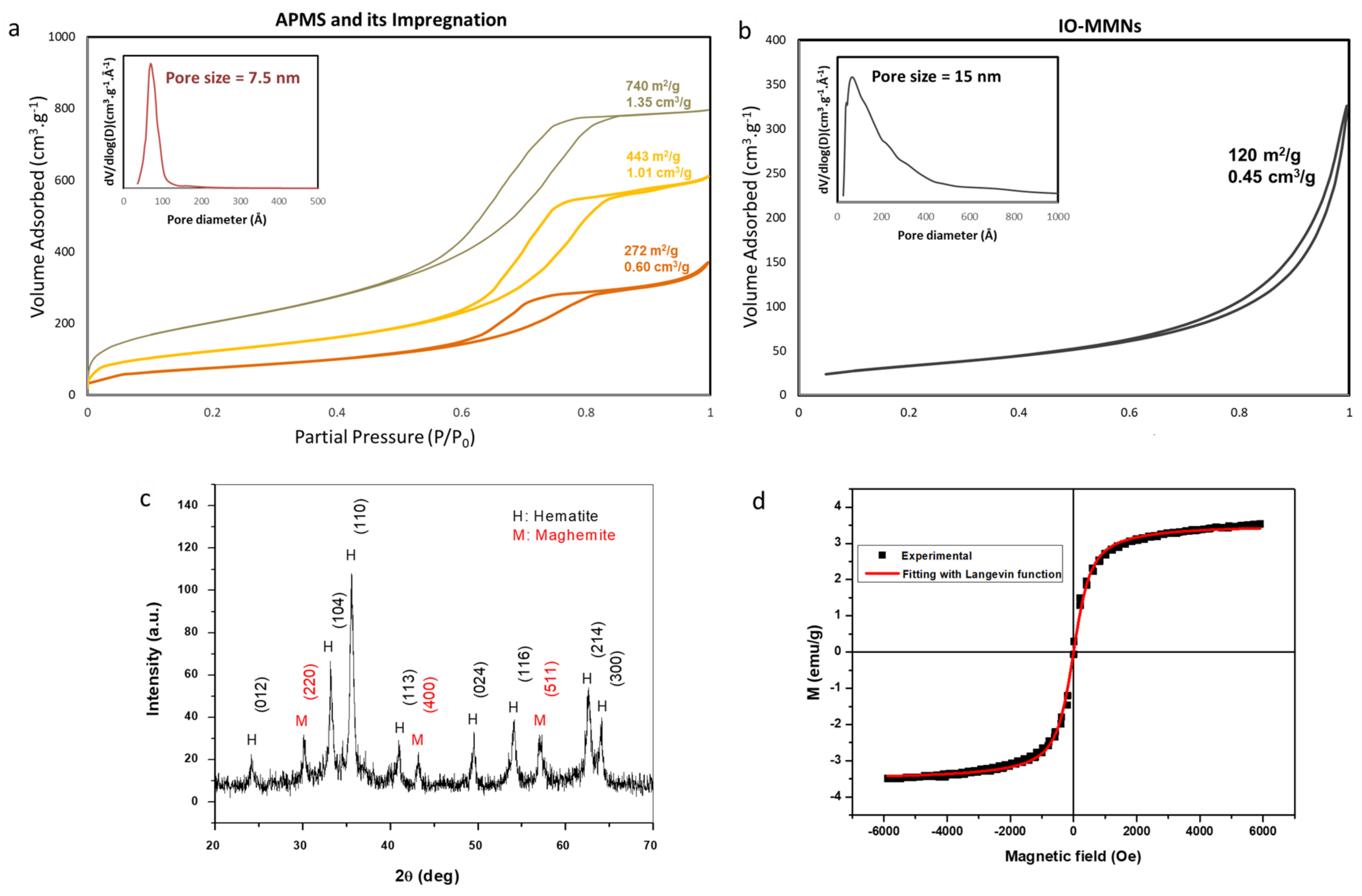
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of IO-MMNs
3.2. Drug Loading and Release
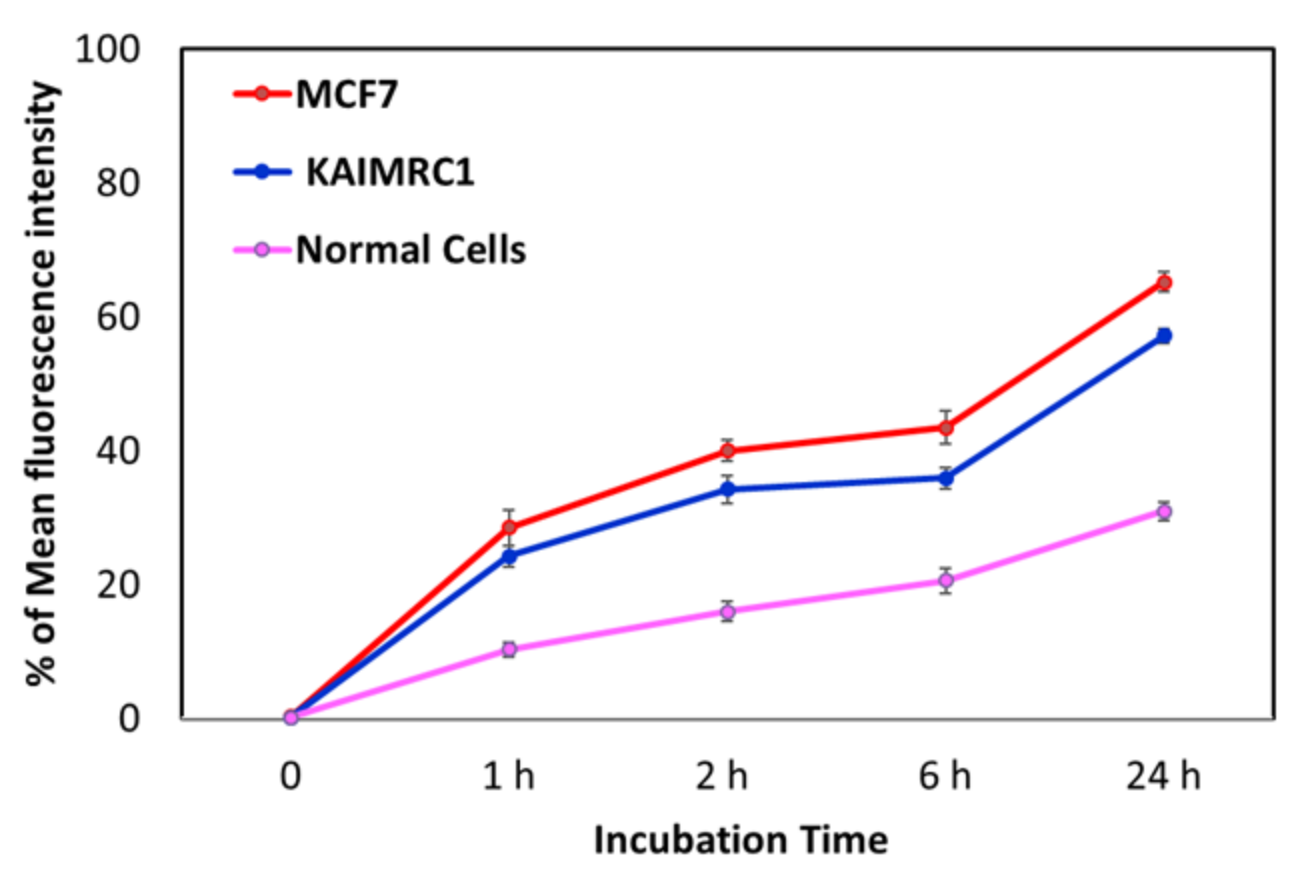
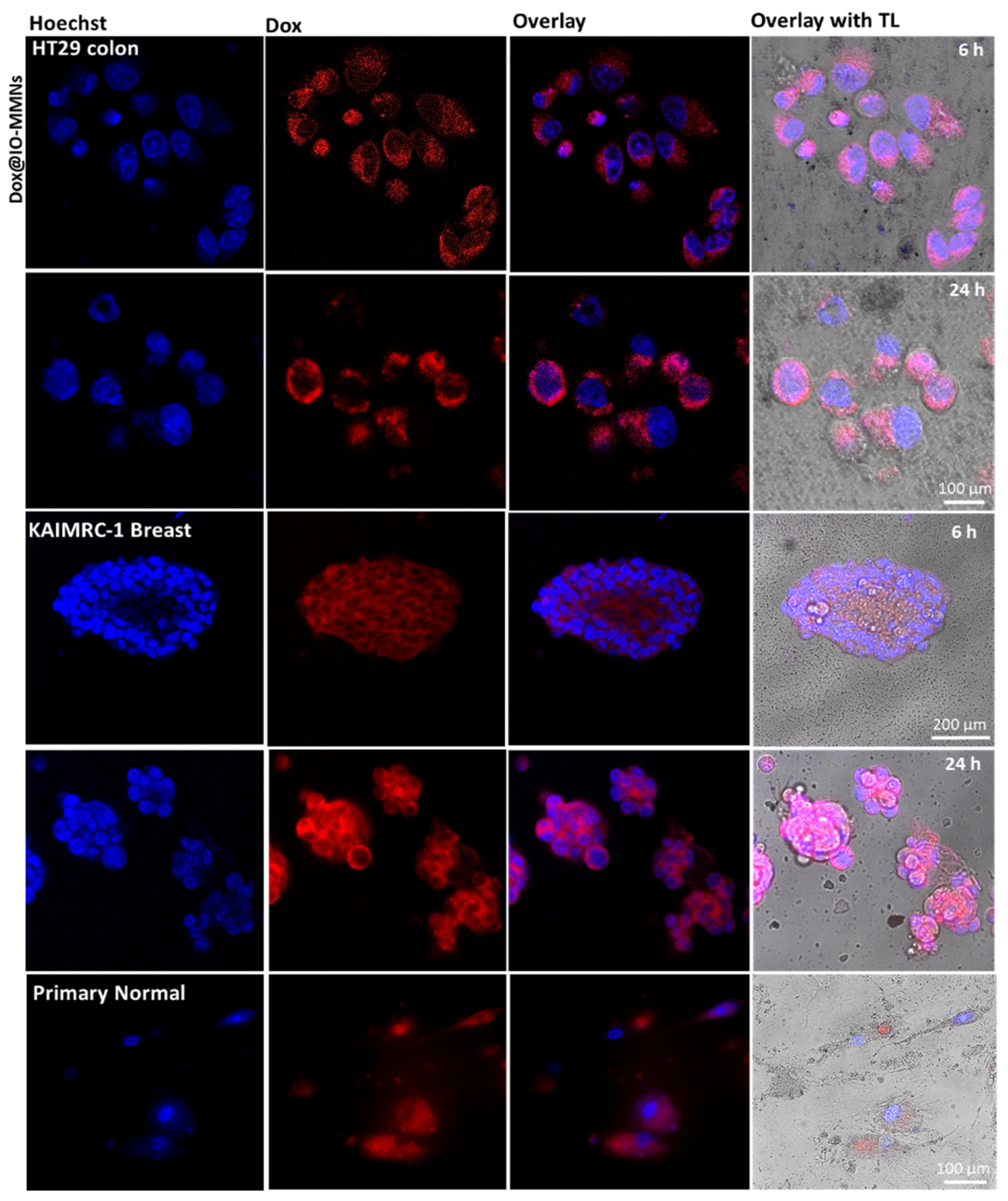
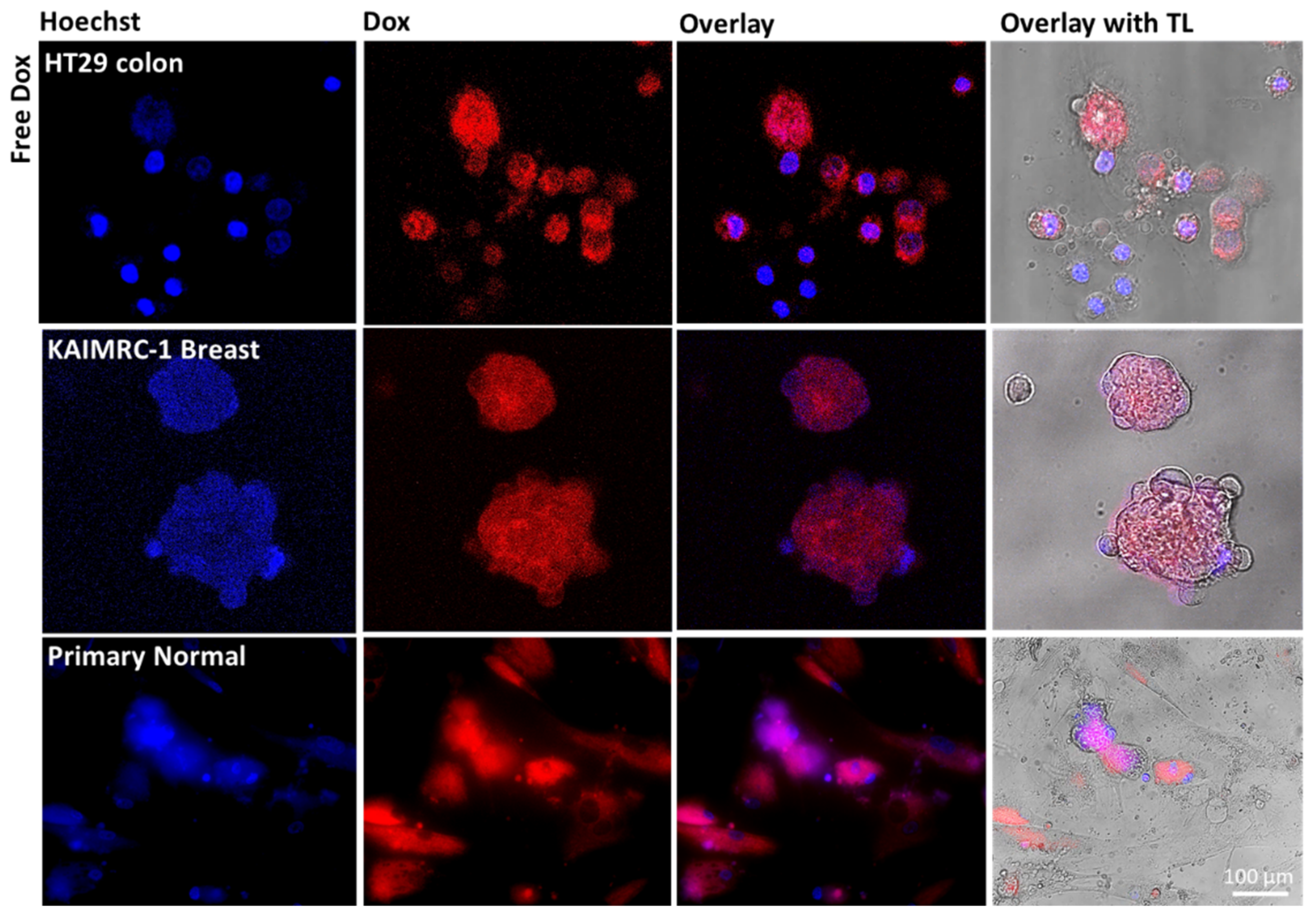
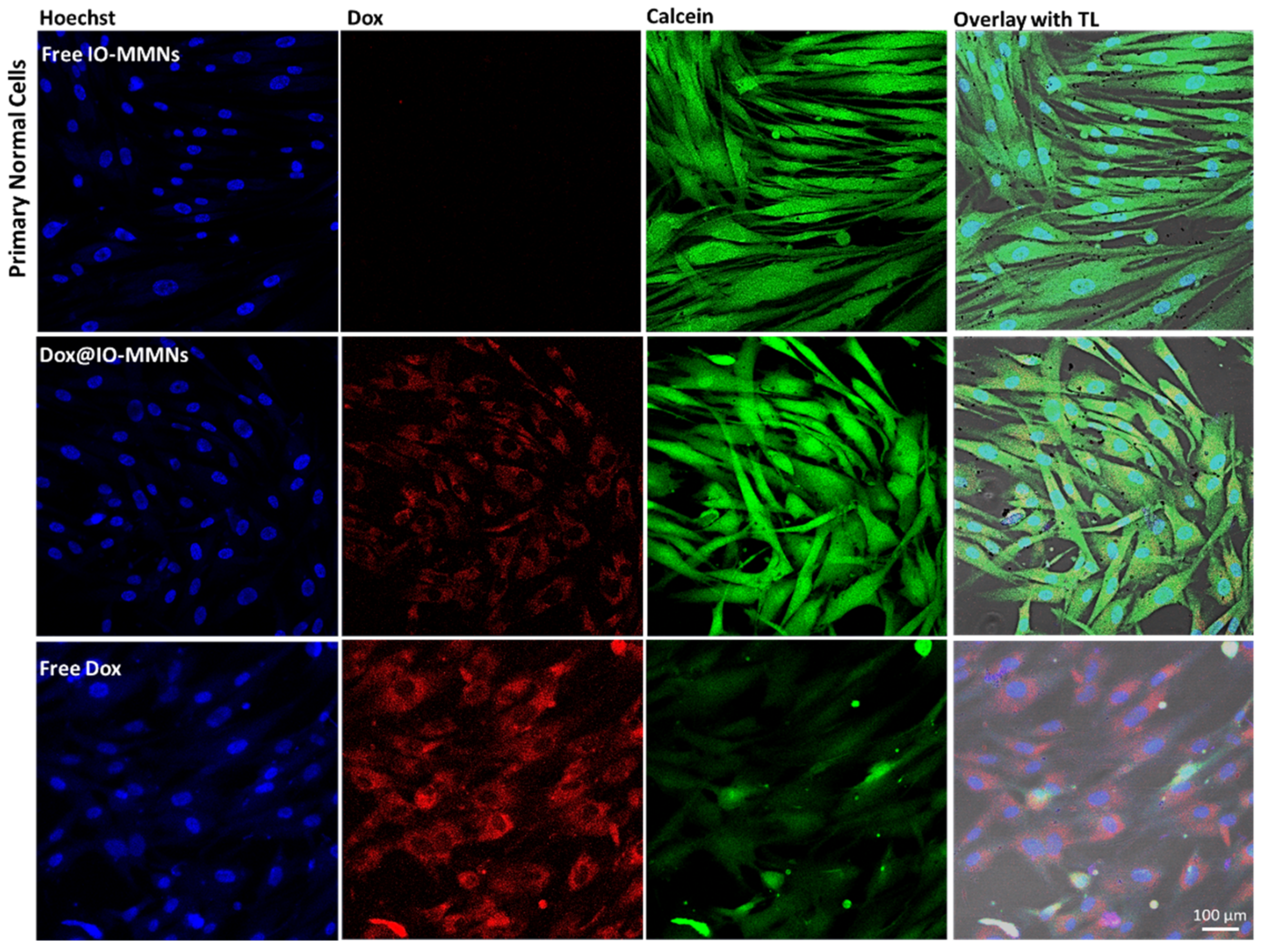
3.3. Biological Assays
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soler-Illia, G.J.d.A.A.; Sanchez, C.; Lebeau, B.; Patarin, J. Chemical Strategies To Design Textured Materials: From Microporous and Mesoporous Oxides to Nanonetworks and Hierarchical Structures. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4093–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, N.Ž.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Hennink, W.E.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetic mesoporous silica-based core/shell nanoparticles for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9584–9593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, N.; Kim, T.; Kim, J.; Hyeon, T. Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposite Nanoparticles for Theranostic Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.-C.; Zink, J.I. Probing the Local Nanoscale Heating Mechanism of a Magnetic Core in Mesoporous Silica Drug-Delivery Nanoparticles Using Fluorescence Depolarization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 5212–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-L.; Fang, J.-H.; Liao, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-T.; Li, Y.-T.; Hu, S.-H. Targeted Mesoporous Iron Oxide Nanoparticles-Encapsulated Perfluorohexane and a Hydrophobic Drug for Deep Tumor Penetration and Therapy. Theranostics 2015, 5, 1233–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Sahlgren, C.; Linden, M. Towards multifunctional, targeted drug delivery systems using mesoporous silica nanoparticles—Opportunities & challenges. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1870–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Sriwastawa, B.; Bhati, L.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Bannerjee, S. Drug delivery systems: An updated review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boubbou, K. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as drug carriers: Clinical relevance. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beagan, A.M.; Alghamdi, A.A.; Lahmadi, S.S.; Halwani, M.A.; Almeataq, M.S.; Alhazaa, A.N.; Alotaibi, K.M.; Alswieleh, A.M. Folic Acid-Terminated Poly(2-Diethyl Amino Ethyl Methacrylate) Brush-Gated Magnetic Mesoporous Nanoparticles as a Smart Drug Delivery System. Polymers 2020, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Kumar Sahu, N. Folate encapsulation in PEG-diamine grafted mesoporous Fe3O4 nanoparticles for hyperthermia and in vitro assessment. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Shen, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, C. Core-shell structured magnetic mesoporous carbon nanospheres derived from metal-polyphenol coordination polymer-coated Fe3O4 and its application in the enrichment of phthalates from water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 3512–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, N.; Kim, T.; Kim, H.; Yu, T.; Song, I.C.; Moon, W.K.; Hyeon, T. Multifunctional uniform nanoparticles composed of a magnetite nanocrystal core and a mesoporous silica shell for magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging and for drug delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8438–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.D.; Zhao, D.Y.; Margolese, D.I.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Generalized syntheses of large-pore mesoporous metal oxides with semicrystalline frameworks. Nature 1998, 396, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Schüth, F. Synthesis of non-siliceous mesoporous oxides. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 313–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Soler-Illia, G.; Ribot, F.; Lalot, T.; Mayer, C.R.; Cabuil, V. Designed hybrid organic-inorganic nanocomposites from functional nanobuilding blocks. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3061–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Illia, G.; Crepaldi, E.L.; Grosso, D.; Sanchez, C. Block copolymer-templated mesoporous oxides. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, M.Y.; Kou, H.Z. Mesoporous a-Fe2O3 nanospheres: Structural evolution and investigation of magnetic properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 4323–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Vázquez-Vázquez, C.; López-Quintela, M.A.; Paul, B.K.; Bhaumik, A. Soft-templating approach for the synthesis of high surface area and superparamagnetic mesoporous iron oxide materials. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2010, 131, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zhao. On the Controllable Soft-Templating Approach to Mesoporous Silicates. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2821–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahaye, E.; Escax, V.; El Hassan, N.; Davidson, A.; Aquino, R.; Dupuis, V.; Perzynski, R.; Raikher, Y.L. “Nanocasting”: Using SBA-15 silicas as hard templates to obtain ultrasmall monodispersed gamma-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 26001–26011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.G.; Ren, N.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Hua, W.M.; Gao, Z. General synthesis of mesoporous spheres of metal oxides and phosphates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4976–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Nitz, J.J.; Comotti, M.; Weidenthaler, C.; Schlichte, K.; Lehmann, C.W.; Terasaki, O.; Schuth, F. Spatially and Size Selective Synthesis of Fe-Based Nanoparticles on Ordered Mesoporous Supports as Highly Active and Stable Catalysts for Ammonia Decomposition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14152–14162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chen, K.; Tüysüz, H. Protocol for the Nanocasting Method: Preparation of Ordered Mesoporous Metal Oxides. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Jung, J.; Lee, C.W.; Cho, J. Synthesis of Mesoporous α-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles by Non-ionic Soft Template and Their Applications to Heavy Oil Upgrading. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, T.A.; Ziegler, K.J.; Lyons, D.M.; Erts, D.; Olin, H.; Morris, M.A.; Holmes, J.D. Synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanowire and nanotube arrays within a mesoporous silica template. Chem. Mat. 2003, 15, 3518–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.F.; Lu, Q.Y.; Gao, F.; Shi, Q.H.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, F.Q.; Xie, S.H.; Tu, B.; Zhao, D.Y. One-step synthesis of highly ordered mesoporous silica monoliths with metal oxide nanocrystals in their channels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, J.K.; Kong, S.S.; Kim, S.S.; Kang, M.S.; Kim, J.M.; So, B.G. Synthesis of Mesoporous Iron Oxide Nanoparticles from Mesoporous Silica Template Via Nano-Replication. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2008, 1, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, J.K.; Kong, S.S.; Kim, J.M.; Ko, C.H.; Jin, M.; Lee, Y.Y.; Hwang, S.H.; Yoona, J.A.; Kim, J.N. Facile synthesis of highly ordered mesoporous silver using cubic mesoporous silica template with controlled surface hydrophobicity. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shon, J.K.; Kong, S.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Park, W.K.; Park, S.C.; Kim, J.M. Solvent-free infiltration method for mesoporous SnO2 using mesoporous silica templates. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2009, 120, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröba, M.; Köhn, R.; Bouffaud, G.; Richard, O.; van Tendeloo, G. Fe2O3 Nanoparticles within Mesoporous MCM-48 Silica: In Situ Formation and Characterization. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 2858–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Giri, S.; Sastry, P.U.; Mal, N.K.; Manna, A.; Bhaumik, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Rich Highly Ordered Mesoporous Fe-MCM-41. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 3012–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Harrison, A.; Jumas, J.C.; Chadwick, A.V.; Kockelmann, W.; Bruce, P.G. Ordered mesoporous Fe2O3 with crystalline walls. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5468–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suteewong, T.; Sai, H.; Lee, J.; Bradbury, M.; Hyeon, T.; Gruner, S.M.; Wiesner, U. Ordered mesoporous silica nanoparticles with and without embedded iron oxide nanoparticles: Structure evolution during synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7807–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Jumas, J.C.; Womes, M.; Chadwick, A.V.; Harrison, A.; Bruce, P.G. Synthesis of ordered mesoporous Fe3O4 and g-Fe2O3 with crystalline walls using post-template reduction/oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12905–12909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoncheva, T.; Rosenholm, J.; Linden, M.; Kleitz, F.; Tiemann, M.; Ivanova, L.; Dimitrov, M.; Paneva, D.; Mitov, I.; Minchev, C. Critical evaluation of the state of iron oxide nanoparticles on different mesoporous silicas prepared by an impregnation method. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2008, 112, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, S.H.; Wang, F.; Lai, J.M.Y.; Sham, K.W.Y.; Wang, Y.X.J.; Lee, S.F.; Yu, J.C.; Cheng, C.H.K.; Leung, K.C.F. Synthesis of Biocompatible, Mesoporous Fe3O4 Nano/Microspheres with Large Surface Area for Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Therapeutic Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Tang, J.; Wei, C.; Guo, J.; Wang, S.; Chaudhary, D.; Wang, C. Doxorubicin-Conjugated Mesoporous Magnetic Colloidal Nanocrystal Clusters Stabilized by Polysaccharide as a Smart Anticancer Drug Vehicle. Small 2012, 8, 2690–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benyettou, F.; Ocadiz Flores, J.A.; Ravaux, F.; Rezgui, R.; Jouiad, M.; Nehme, S.I.; Parsapur, R.K.; Olsen, J.-C.; Selvam, P.; Trabolsi, A. Mesoporous γ-Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Magnetically Triggered Release of Doxorubicin and Hyperthermia Treatment. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 17020–17028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Boubbou, K.; Ali, R.; Al-Zahrani, H.; Trivilegio, T.; Alanazi, A.H.; Khan, A.L.; Boudjelal, M.; AlKushi, A. Preparation of iron oxide mesoporous magnetic microparticles as novel multidrug carriers for synergistic anticancer therapy and deep tumor penetration. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boubbou, K.; Schofield, D.A.; Landry, C.C. Enhanced Enzymatic Thermal Stability and Activity in Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Monitored by 31P NMR. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Boubbou, K.; Schofield, D.A.; Landry, C.C. Enhanced Enzymatic Activity of OPH in Ammonium-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica: Surface Modification and Pore Effects. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 17501–17506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boubbou, K.; Azar, D.; Bekdash, A.; Abi-Habib, R.J. Doxironide Magnetic Nanoparticles for Selective Drug Delivery to Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boubbou, K.; Ali, R.; Bahhari, H.M.; AlSaad, K.O.; Nehdi, A.; Boudjelal, M.; AlKushi, A. Magnetic Fluorescent Nanoformulation for Intracellular Drug Delivery to Human Breast Cancer, Primary Tumors, and Tumor Biopsies: Beyond Targeting Expectations. Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 27, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, F.N.; Polshettiwar, V. Facile and Sustainable Synthesis of Shaped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Effect of Iron Precursor Salts on the Shapes of Iron Oxides. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.M.; Zhou, Z.; Li, G. Structural evolution from mesoporous α-Fe2O3 to Fe3O4@C and γ-Fe2O3 nanospheres and their lithium storage performances. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 4709–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, A.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Shan, Y. Preparation of super paramagnetic crystalline mesoporous γ-Fe2O3 with high surface. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 943–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Liu, Y.; Ren, W. Structure switch between α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 during the large scale and low temperature sol–gel synthesis of nearly monodispersed iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja, A.S.; Koh, P.-Y. Synthesis, properties, and applications of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2009, 55, 22–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mao, K.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles conjugated with folic acid for dual target-specific drug delivery and MRI in cancer theranostics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Li, H.; Luo, Z.; Kong, J.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, H.; Vermorken, A.; Van de Ven, W.; et al. Dextran-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles as potential cancer drug carriers in vivo. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11155–11162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.; Samman, N.; Al Zahrani, H.; Nehdi, A.; Rahman, S.; Khan, A.L.; Al Balwi, M.; Alriyees, L.A.; Alzaid, M.; Al Askar, A.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a new naturally immortalized human breast carcinoma cell line, KAIMRC1. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghanem, B.; Ali, R.; Nehdi, A.; Al Zahrani, H.; Altolayyan, A.; Shaibah, H.; Baz, O.; Alhallaj, A.; Moresco, J.J.; Diedrich, J.K.; et al. Proteomics Profiling of KAIMRC1 in Comparison to MDA-MB231 and MCF-7. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Boubbou, K.; Ali, R.; Al-Humaid, S.; Alhallaj, A.; Lemine, O.M.; Boudjelal, M.; AlKushi, A. Iron Oxide Mesoporous Magnetic Nanostructures with High Surface Area for Enhanced and Selective Drug Delivery to Metastatic Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040553
El-Boubbou K, Ali R, Al-Humaid S, Alhallaj A, Lemine OM, Boudjelal M, AlKushi A. Iron Oxide Mesoporous Magnetic Nanostructures with High Surface Area for Enhanced and Selective Drug Delivery to Metastatic Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(4):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040553
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Boubbou, Kheireddine, Rizwan Ali, Sulaiman Al-Humaid, Alshaimaa Alhallaj, O. M. Lemine, Mohamed Boudjelal, and Abdulmohsen AlKushi. 2021. "Iron Oxide Mesoporous Magnetic Nanostructures with High Surface Area for Enhanced and Selective Drug Delivery to Metastatic Cancer Cells" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 4: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040553
APA StyleEl-Boubbou, K., Ali, R., Al-Humaid, S., Alhallaj, A., Lemine, O. M., Boudjelal, M., & AlKushi, A. (2021). Iron Oxide Mesoporous Magnetic Nanostructures with High Surface Area for Enhanced and Selective Drug Delivery to Metastatic Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics, 13(4), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040553







