Doxorubicin–Loaded Human Serum Albumin Submicron Particles: Preparation, Characterization and In Vitro Cellular Uptake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
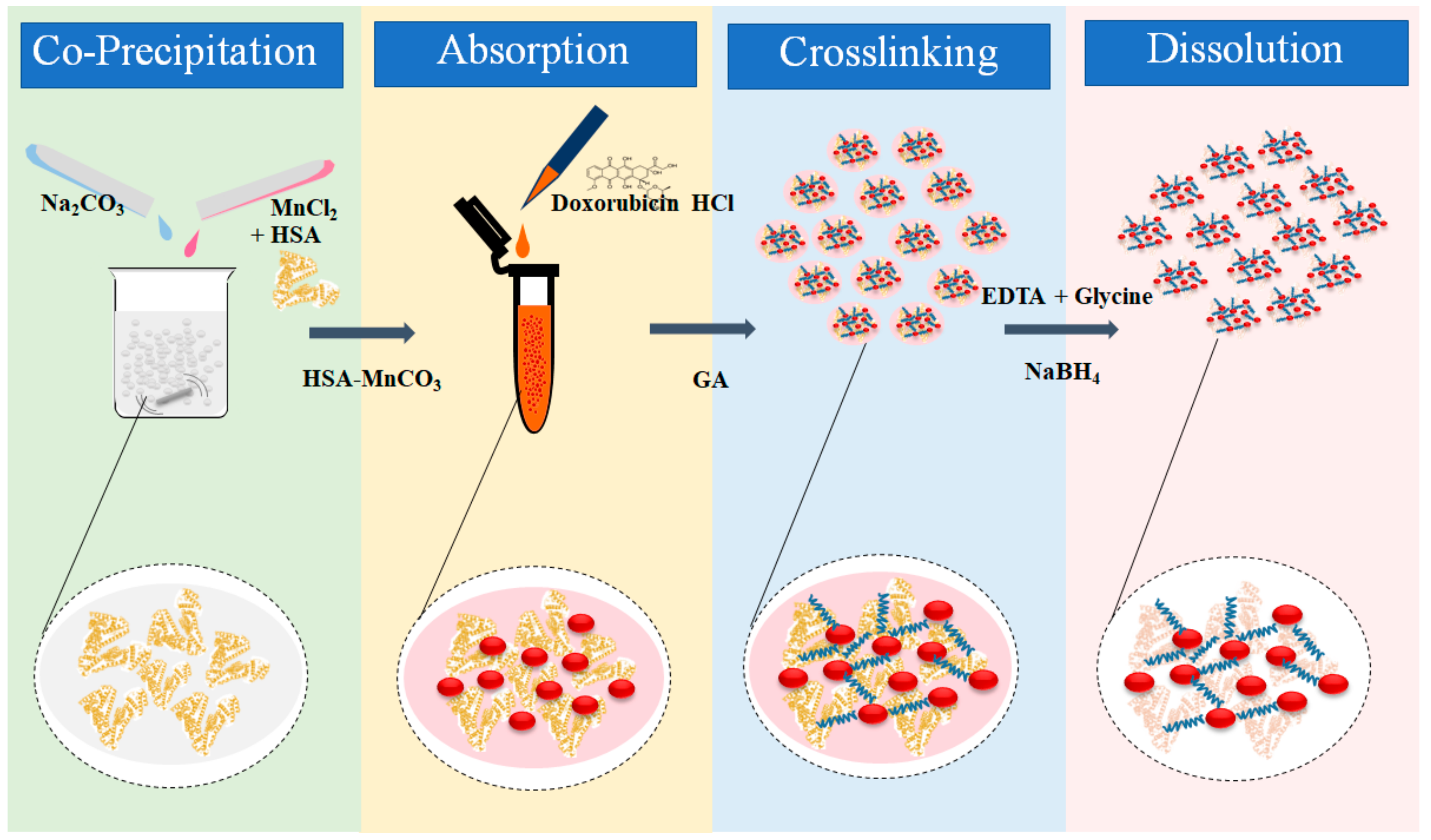
2.2. Particles Fabrication
2.3. Particle Characterization
2.3.1. Entrapment Efficiency of DOX
2.3.2. Particles Size and Zeta-Potential
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
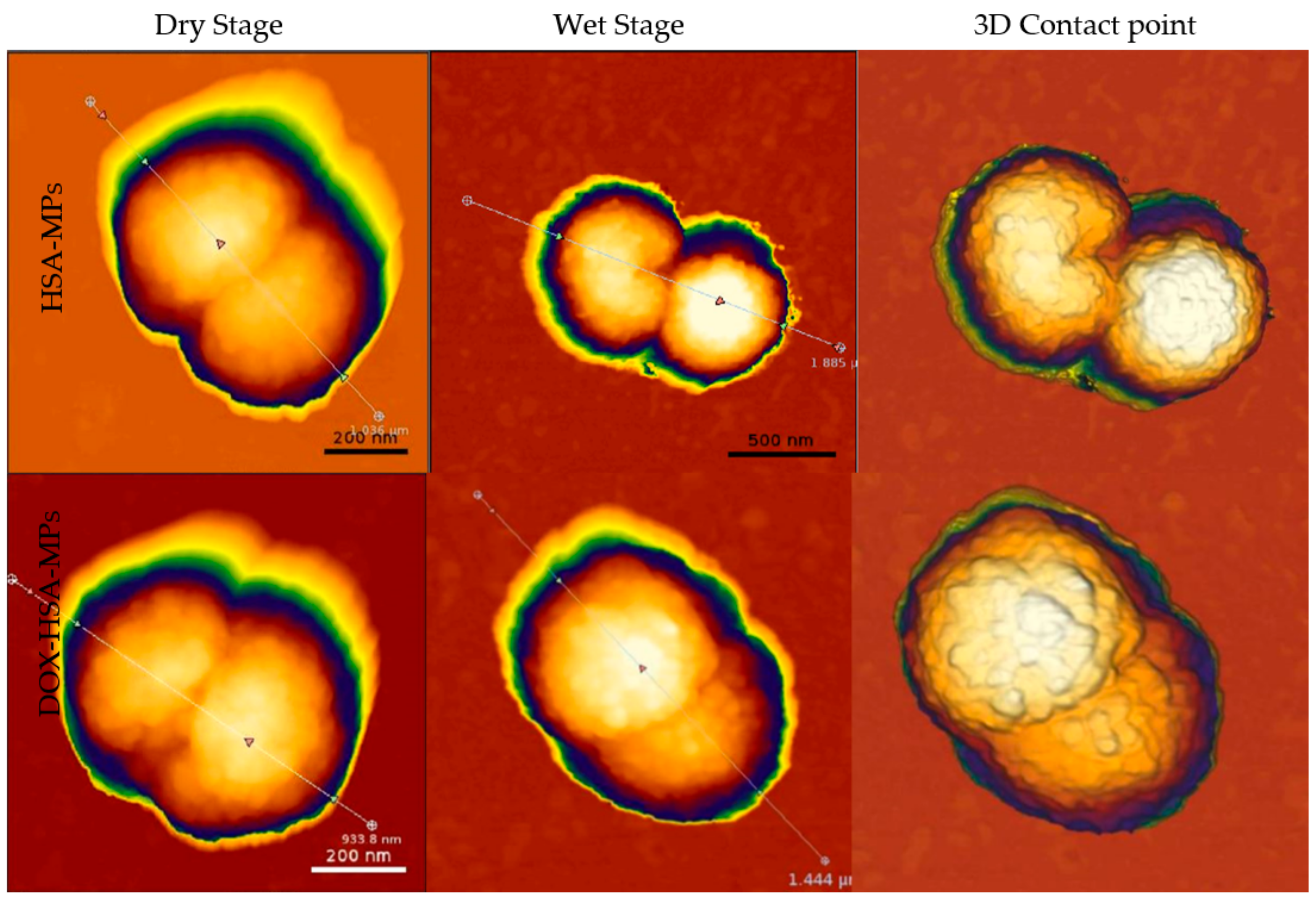
2.3.4. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
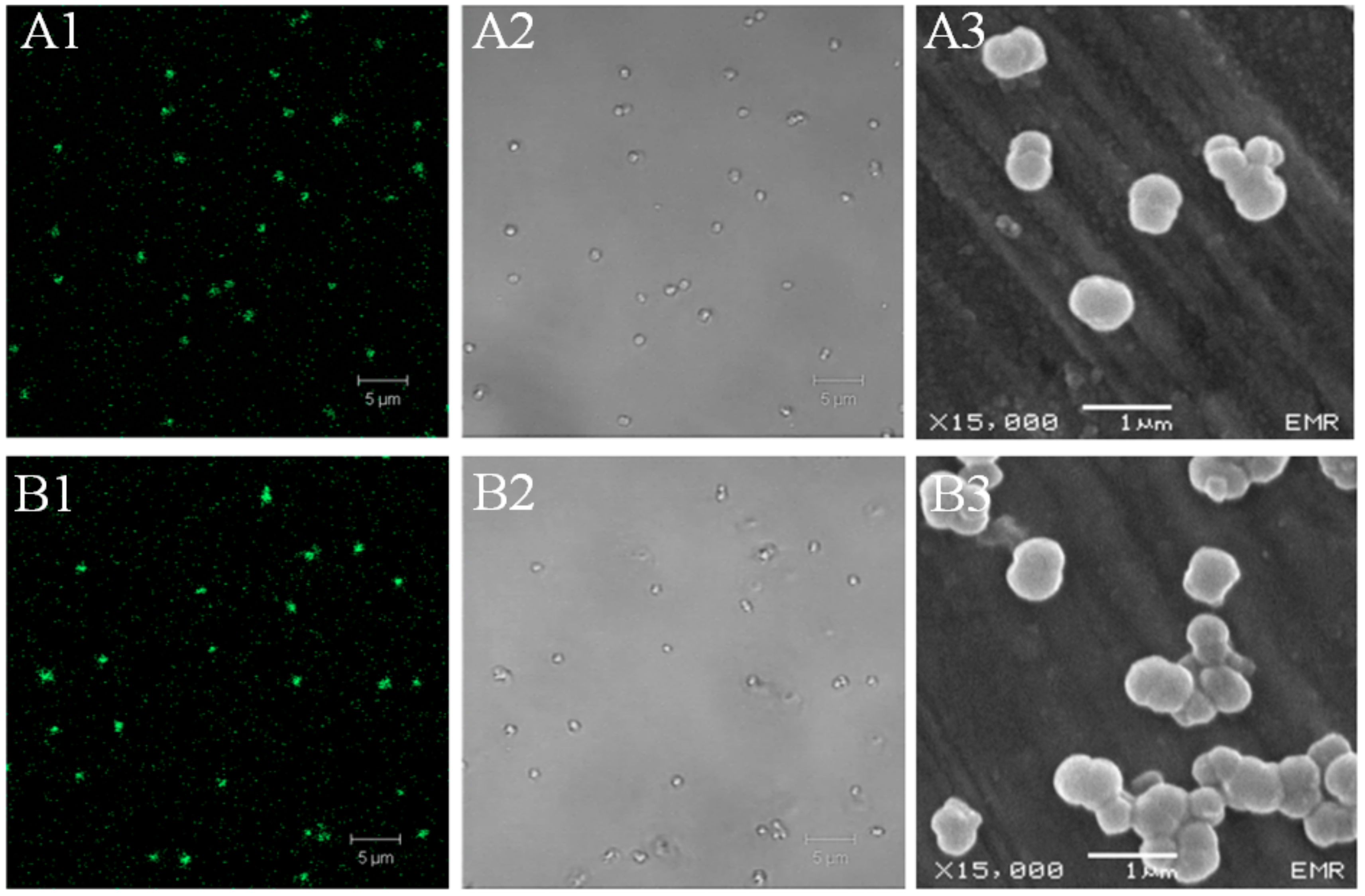
2.3.5. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
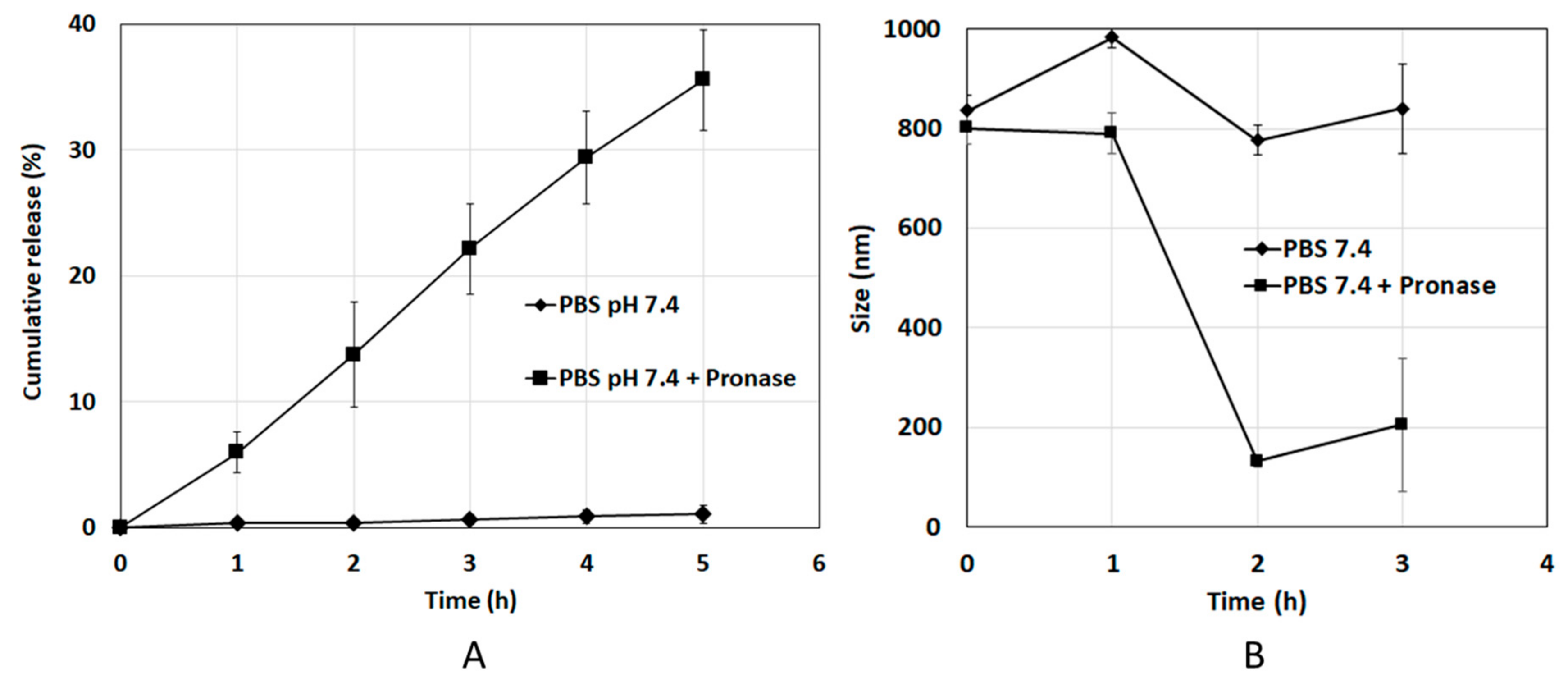
2.3.6. Release of DOX from DOX-HSA-MPs
2.4. Interaction of the Carriers with Cells
2.4.1. Cell Culture
2.4.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.4.3. Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Localization of HSA-MPs and DOX-HSA-MPs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of DOX HSA-MPs
3.2. Entrapment Efficiency and Release of Doxorubicin from DOX-HSA-MPs
3.3. Interaction of HSA-MPs and DOX-HSA-MPs with tumor cells
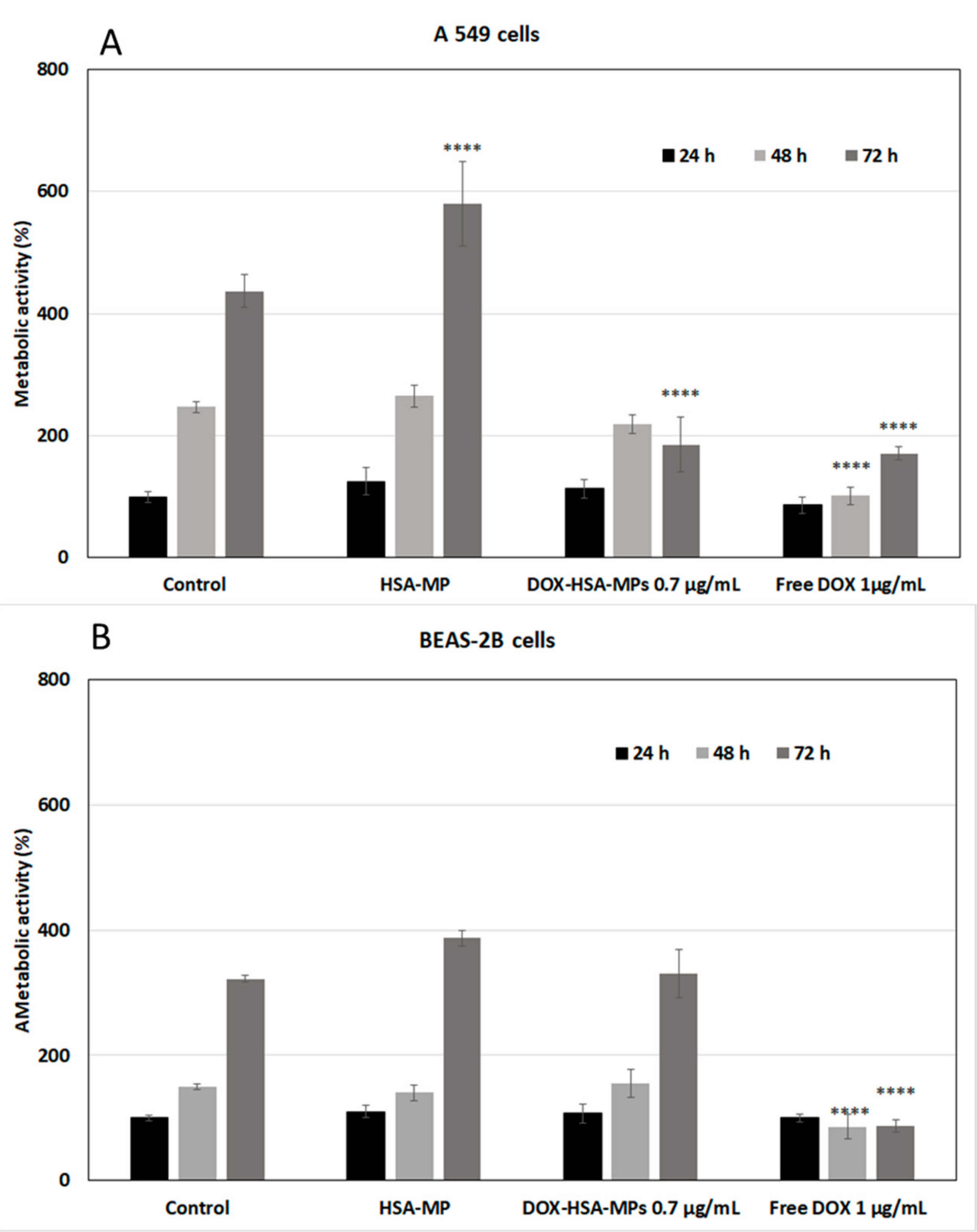
3.3.1. Cytotoxicity to Tumor Cells
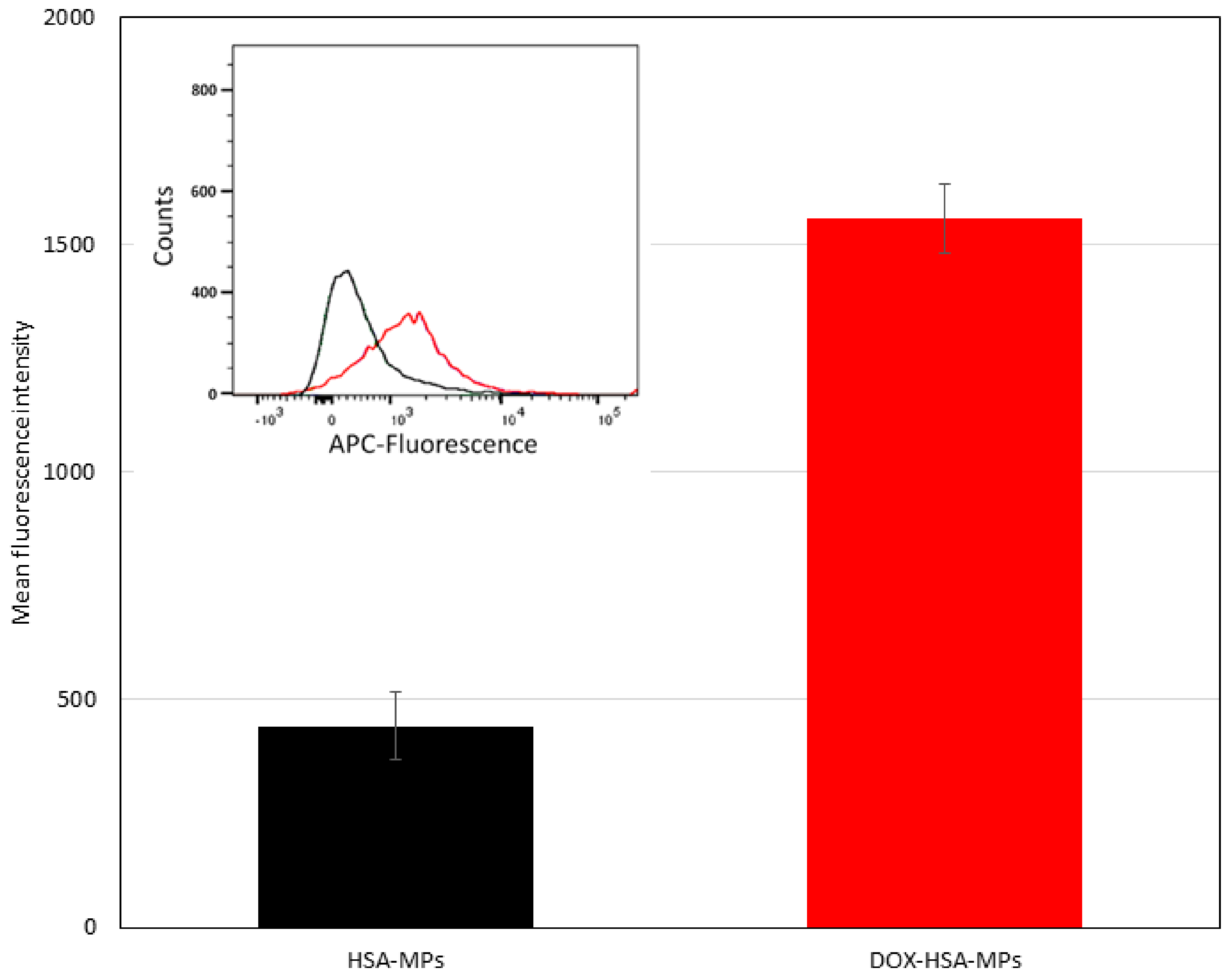
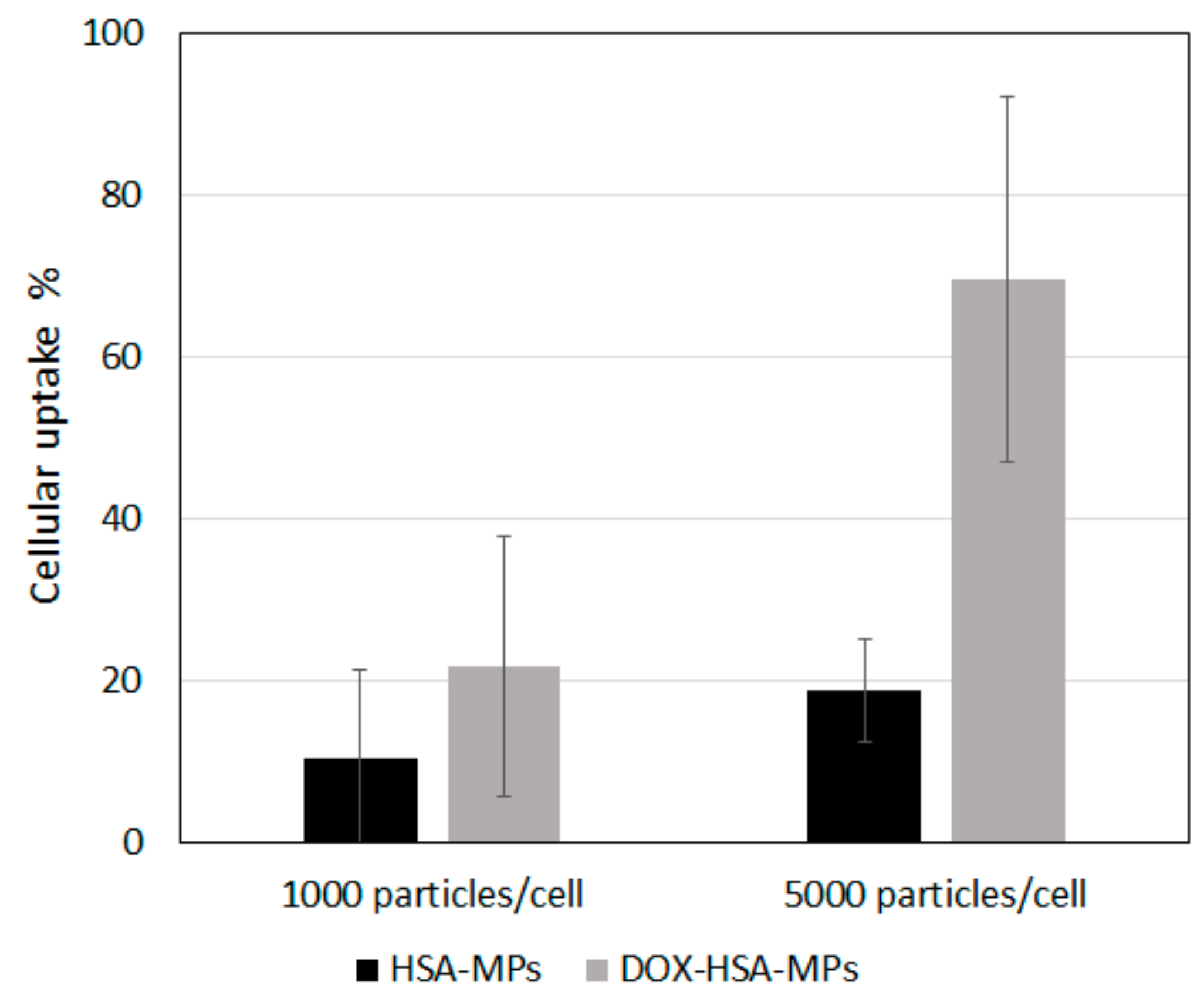
3.3.2. Cellular Uptake
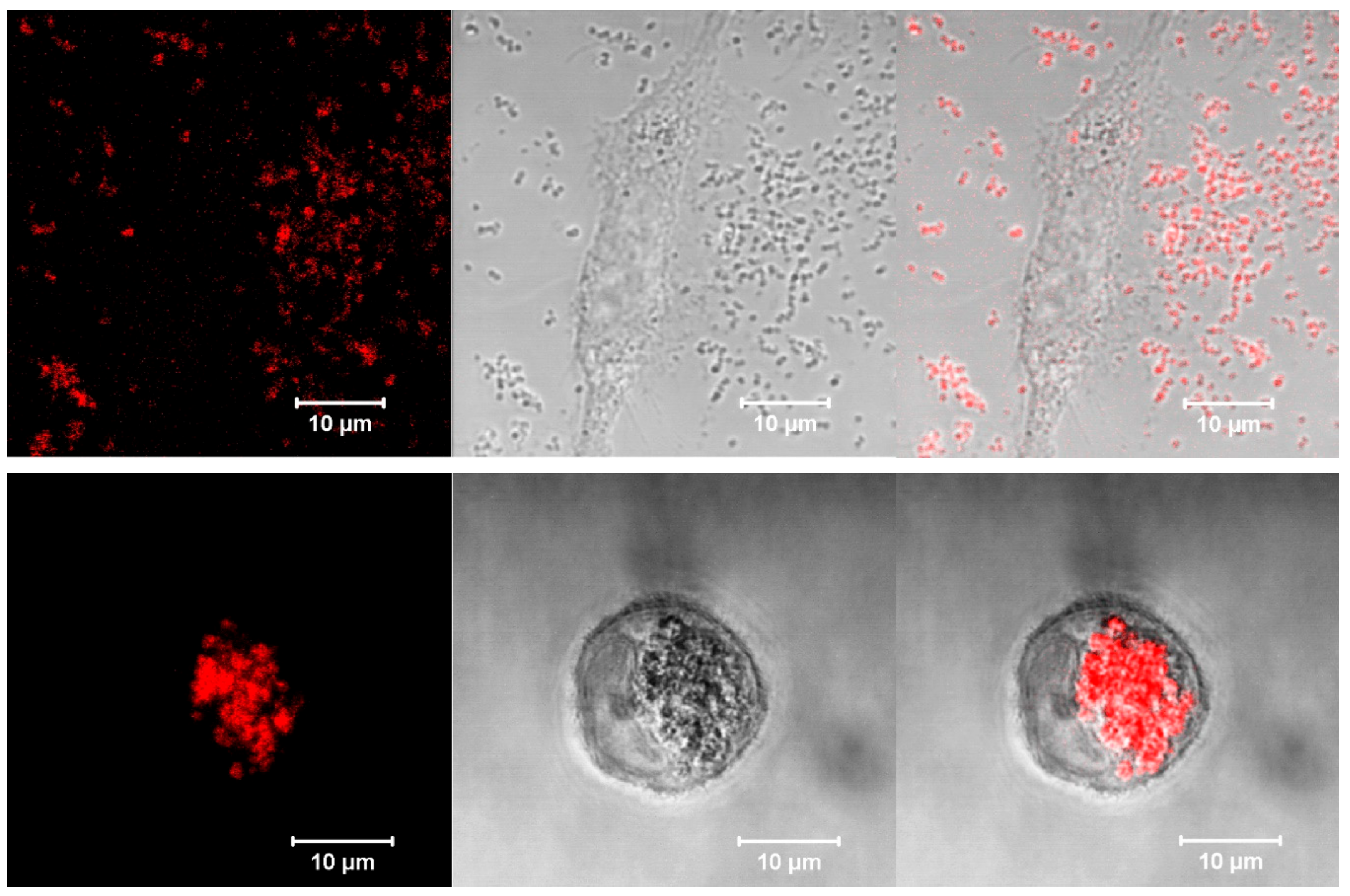
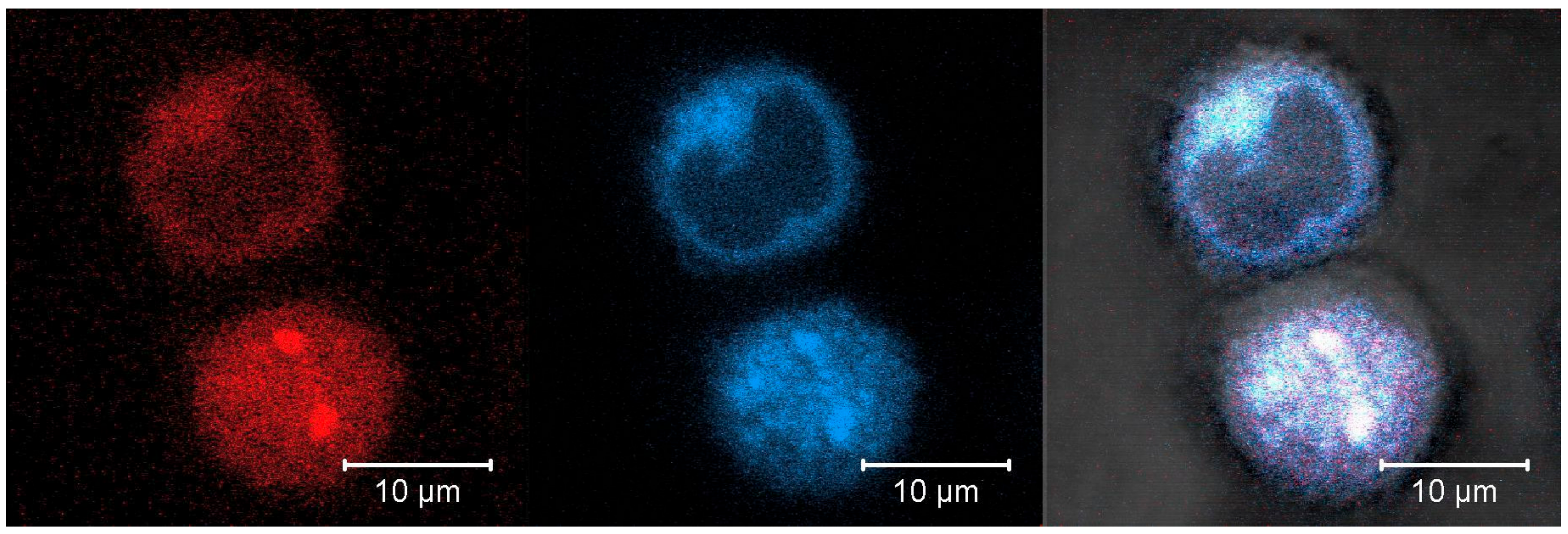
3.3.3. Intracellular localization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thorn, C.F.; Oshiro, C.; Marsh, S.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; McLeod, H.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. Doxorubicin Pathways. Pharm. Genom. 2010, 21, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taymaz-Nikerel, H.; Karabekmez, M.E.; Eraslan, S.; Kırdar, B. Doxorubicin Induces an Extensive Transcriptional and Metabolic Rewiring in Yeast Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, B.M.; Anuszewska, E.L.; Priebe, W. The Effect of New Anthracycline Derivatives on the Induction of Apoptotic Processes in Human Neoplastic Cells. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2004, 42, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Octavia, Y.; Tocchetti, C.G.; Gabrielson, K.L.; Janssens, S.; Crijns, H.J.; Moens, A.L. Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 52, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, C.; Santos, R.; Cardoso, S.; Correia, S.; Oliveira, P.; Santos, M.; Moreira, P. Doxorubicin: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly Effect. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 3267–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangpong, J.; Miriyala, S.; Noel, T.; Sinthupibulyakit, C.; Jungsuwadee, P.; Clair, D.K.S. Doxorubicin-Induced Central Nervous System Toxicity and Protection by Xanthone Derivative of Garcinia Mangostana. Neuroscience 2011, 175, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, R.L.M.; de Klerk, G. An Illustrated Case of Doxorubicin-Induced Radiation Recall Dermatitis and a Review of the Literature. Neth. J. Med. 2011, 69, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Kubicka-Wołkowska, J.; Kędzierska, M.; Lisik-Habib, M.; Potemski, P. Skin Toxicity in a Patient with Ovarian Cancer Treated with Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 5332–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Gaur, U.; Ghosh, P.C.; Maitra, A.N. Tumour Targeted Delivery of Encapsulated Dextran-Doxorubicin Conjugate Using Chitosan Nanoparticles as Carrier. J. Control. Release 2001, 74, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, R.; Sheng, L.; Wu, W.; Pan, G.; Feng, Q.; Cui, W. Doxorubicin-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Composite Nanofibers for Long-Term Adjustments of Tumor Apoptosis. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 245101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, P.; Rapoport, N. Doxorubicin as a Molecular Nanotheranostic Agent: Effect of Doxorubicin Encapsulation in Micelles or Nanoemulsions on the Ultrasound-Mediated Intracellular Delivery and Nuclear Trafficking. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 3921–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammers, T.; Storm, G. Nanomedicine Formulations for Combination Therapies. Nano Rev. 2010, 1, 5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantin, A.M.; Paquette, B.; Richter, M.; Larivée, P. Albumin-Mediated Regulation of Cellular Glutathione and Nuclear Factor Kappa B Activation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziol, M.J.; Sievers, T.K.; Smuda, K.; Xiong, Y.; Müller, A.; Wojcik, F.; Steffen, A.; Dathe, M.; Georgieva, R.; Bäumler, H. Kinetics and Efficiency of a Methyl-Carboxylated 5-Fluorouracil-Bovine Serum Albumin Adduct for Targeted Delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, Q.Y.; Cai, Z.X.; Fang, Y.; Zheng, C.S.; Wang, L.L.; Lin, S.; Chen, D.X.; Peng, J. Interactions of Bovine Serum Albumin with Anti-Cancer Compounds Using a ProteOn XPR36 Array Biosensor and Molecular Docking. Molecules 2016, 21, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomis, N.; Westfall, S.; Farahdel, L.; Malhotra, M.; Shum-Tim, D.; Prakash, S. Human Serum Albumin Nanoparticles for Use in Cancer Drug Delivery: Process Optimization and In Vitro Characterization. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.E.; Tian, L.; Chang, Y.H. A Homogeneous Fluorescent Sensor for Human Serum Albumin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 63, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun’ko, V.M.; Turov, V.V.; Krupska, T.V.; Tsapko, M.D. Interactions of Human Serum Albumin with Doxorubicin in Different Media. Chem. Phys. 2017, 483, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svedberg, T.; Sjogren, B. The pH-Stability Regions of Serum Albumin and of Serum Globulin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1930, 52, 2855–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Ma, K.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, E.S.; Oh, K.T.; Park, E.S.; Lee, K.C.; Youn, Y.S. Doxorubicin-Loaded Human Serum Albumin Nanoparticles Surface-Modified with TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand and Transferrin for Targeting Multiple Tumor Types. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, D.M.; Judah, J.D.; Nicholls, M.R. Intracellular Distribution of Serum Albumin and Its Possible Precursors in Rat Liver. Biochem. J. 2015, 127, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäumler, H.; Georgieva, R. Coupled Enzyme Reactions in Multicompartment Microparticles. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Steffen, A.; Andreas, K.; Muller, S.; Sternberg, N.; Georgieva, R. Hemoglobin-Based Oxygen Carrier Microparticles: Synthesis, Properties, and In Vitro and In Vivo Investigations. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3292–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäumler, H.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Z.Z.; Patzak, A.; Georgieva, R. Novel Hemoglobin Particles-Promising New-Generation Hemoglobin-Based Oxygen Carriers. Artif. Organs 2014, 38, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Georgieva, R.; Steffen, A.; Smuda, K.; Bäumler, H. Structure and Properties of Hybrid Biopolymer Particles Fabricated by Co-Precipitation Cross-Linking Dissolution Procedure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 514, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannasom, N.; Smuda, K.; Kloypan, C.; Kaewprayoon, W.; Baisaeng, N.; Prapan, A.; Chaiwaree, S.; Georgieva, R.; Bäumler, H. Albumin Submicron Particles with Entrapped Riboflavin—Fabrication and Characterization. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumoto, R.; Suzuka, S.; Oda, K.; Nagai, J.; Takano, M. Endocytic Uptake of FITC-Albumin by Human Alveolar Epithelial Cell Line A549. Drug Metab. Pharm. 2012, 27, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.W.; Ko, W.H.; Yeh, M.K.; Chiang, C.H.; Chen, J.L. The Mechanism of High Transfection Efficiency of Human Serum Albumin Conjugated Polyethylenimine in A549 Cells. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 35, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlot, A.M.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Richardson, D.R. Unraveling the Mysteries of Serum Albumin-More than Just a Serum Protein. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiruppathi, C.; Naqvi, T.; Wu, Y.; Vogel, S.M.; Minshall, R.D.; Malik, A.B. Albumin Mediates the Transcytosis of Myeloperoxidase by Means of Caveolae in Endothelial Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7699–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, S.M.; Minshall, R.D.; Pilipović, M.; Tiruppathi, C.; Malik, A.B. Albumin Uptake and Transcytosis in Endothelial Cells in Vivo Induced by Albumin-Binding Protein. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 281, L1512–L1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yang, F.; Xiong, F.; Gu, N. The Smart Drug Delivery System and Its Clinical Potential. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1306–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.J.; Goldsmith, H.T. Spectral Properties of Fluorescence Induced by Glutaraldehyde Fixation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1981, 29, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, F.U.; Aman, W.; Ullah, I.; Qureshi, O.S.; Mustapha, O.; Shafique, S.Z.A. Effective Use of Nanocarriers as Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Selected Tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7291–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.L. Albumin and Mammalian Cell Culture: Implications for Biotechnology Applications. Cytotechnology 2010, 62, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, V.A.; García-Santisteban, I.; Warmerdam, D.O.; van den Broek, B.; Heck, A.J.R.; Mohammed, S.; Medema, R.H. Doxorubicin-Induced DNA Damage Causes Extensive Ubiquitination of Ribosomal Proteins Associated with a Decrease in Protein Translation*. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 2297–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.Z.; Li, H.Y.; Ma, Y.; Gong, H.; Yang, S.; Fang, Q.; Hu, Z.Y. Nanoparticle Abraxane Possesses Impaired Proliferation in A549 Cells Due to the Underexpression of Glucosamine 6-Phosphate N-Acetyltransferase 1 (GNPNAT1/GNA1). Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübke, T.; Lobel, P.; Sleat, D.E. Proteomics of the Lysosome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Mol. Cell Res. 2009, 1793, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaiwaree, S.; Prapan, A.; Suwannasom, N.; Laporte, T.; Neumann, T.; Pruß, A.; Georgieva, R.; Bäumler, H. Doxorubicin–Loaded Human Serum Albumin Submicron Particles: Preparation, Characterization and In Vitro Cellular Uptake. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030224
Chaiwaree S, Prapan A, Suwannasom N, Laporte T, Neumann T, Pruß A, Georgieva R, Bäumler H. Doxorubicin–Loaded Human Serum Albumin Submicron Particles: Preparation, Characterization and In Vitro Cellular Uptake. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(3):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030224
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaiwaree, Saranya, Ausanai Prapan, Nittiya Suwannasom, Tomás Laporte, Tanja Neumann, Axel Pruß, Radostina Georgieva, and Hans Bäumler. 2020. "Doxorubicin–Loaded Human Serum Albumin Submicron Particles: Preparation, Characterization and In Vitro Cellular Uptake" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 3: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030224
APA StyleChaiwaree, S., Prapan, A., Suwannasom, N., Laporte, T., Neumann, T., Pruß, A., Georgieva, R., & Bäumler, H. (2020). Doxorubicin–Loaded Human Serum Albumin Submicron Particles: Preparation, Characterization and In Vitro Cellular Uptake. Pharmaceutics, 12(3), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030224







