Drug Solubility Enhancement through the Preparation of Multicomponent Organic Materials: Eutectics of Lovastatin with Carboxylic Acids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
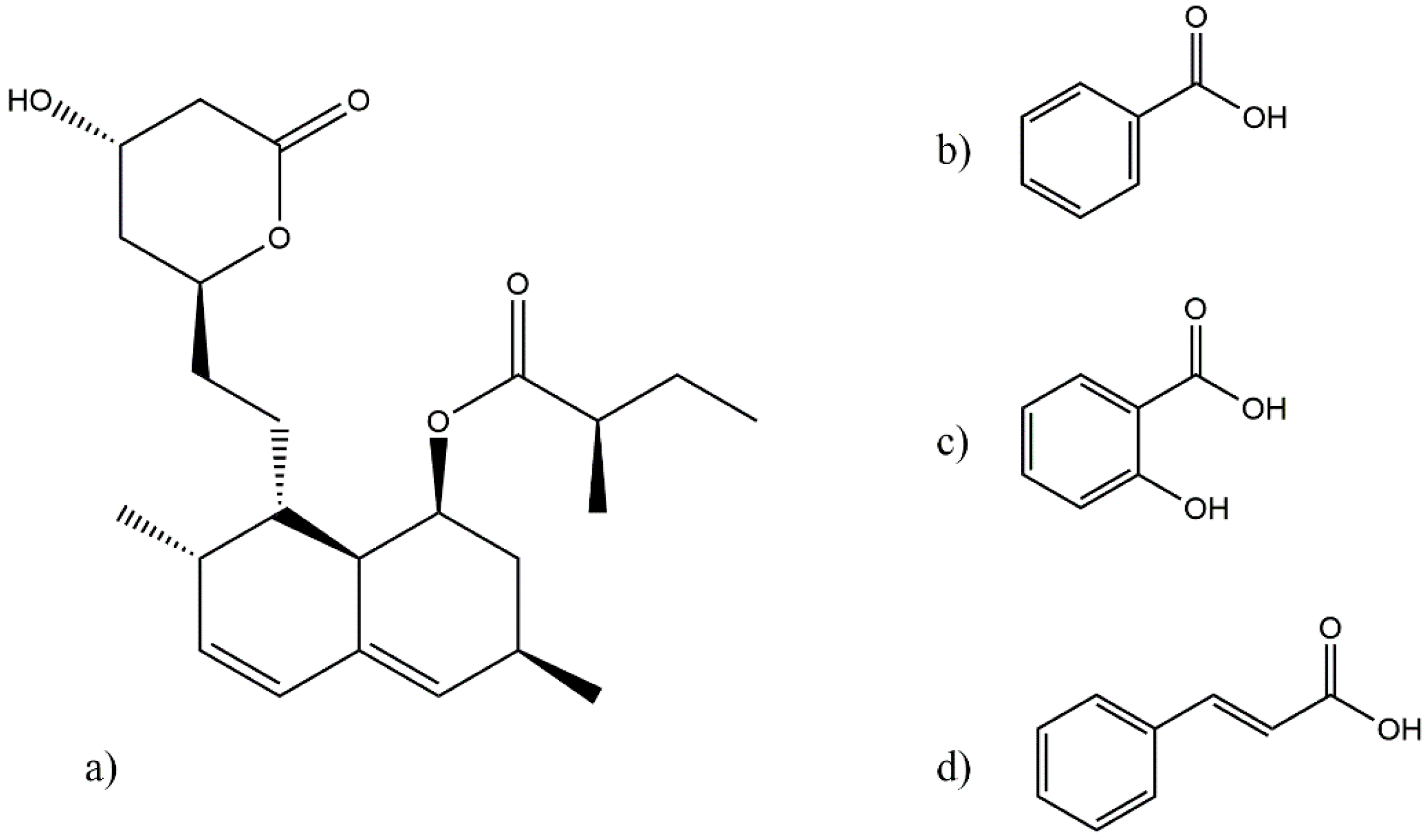
2.1. Materials
2.2. Lovastatin Eutectic Mixture Screening
2.3. LOV-BEN, LOV-SAL and LOV-CIN Eutectic Systems
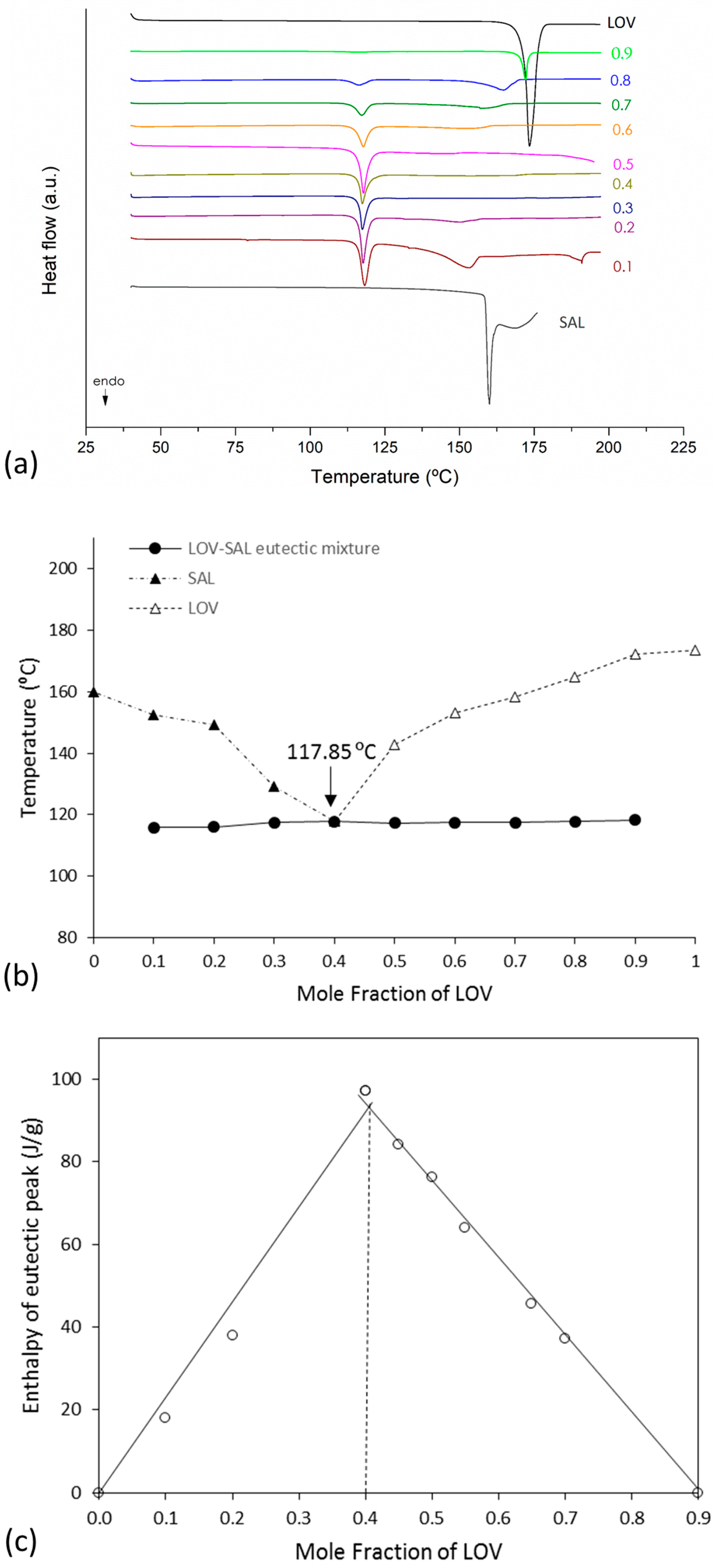
2.3.1. Determination of Mixture Composition at the Eutectic Point
2.3.2. Preparation of Bulk Mixtures at the Eutectic Composition
2.4. Characterization of the Eutectic Mixtures
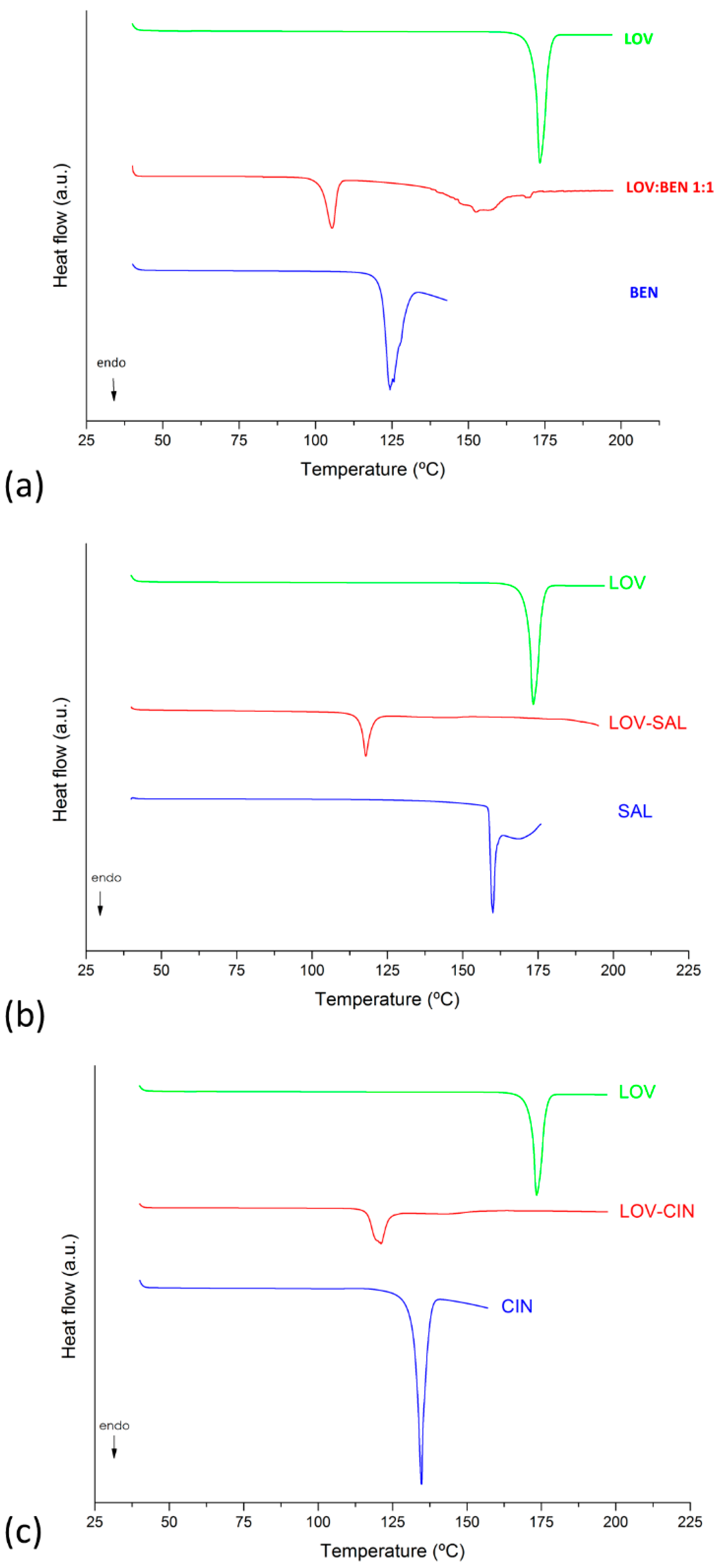
2.4.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
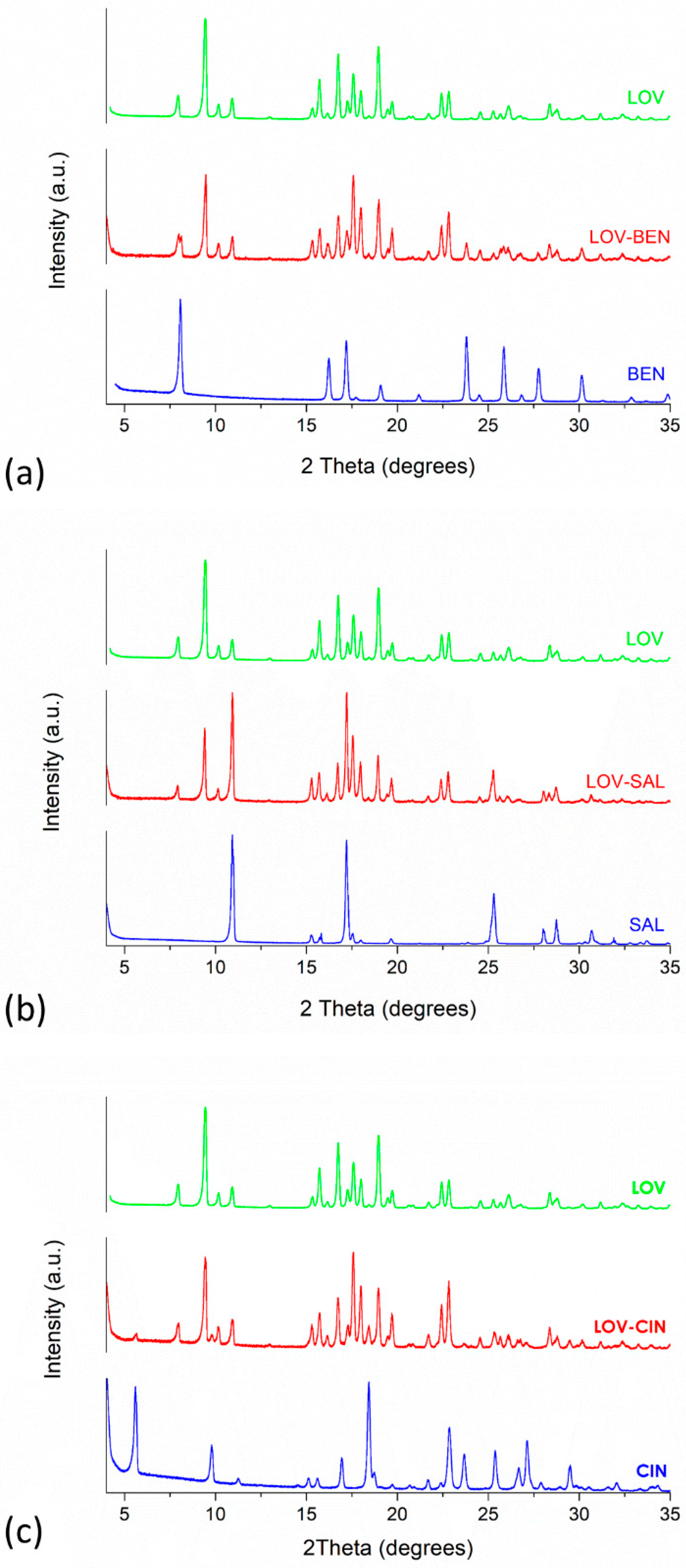
2.4.2. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD) Study
2.4.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR)
2.4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5. Physicochemical Study
2.5.1. Apparent Solubility
2.5.2. Intrinsic Dissolution Rate (IDR) Determination
2.5.3. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Eutectic Mixture Screening
3.2. Binary Phase and Tammann Diagrams
3.3. Solid-State Characterization of LOV Eutectic Systems
3.3.1. PXRD and FT-IR Analyses
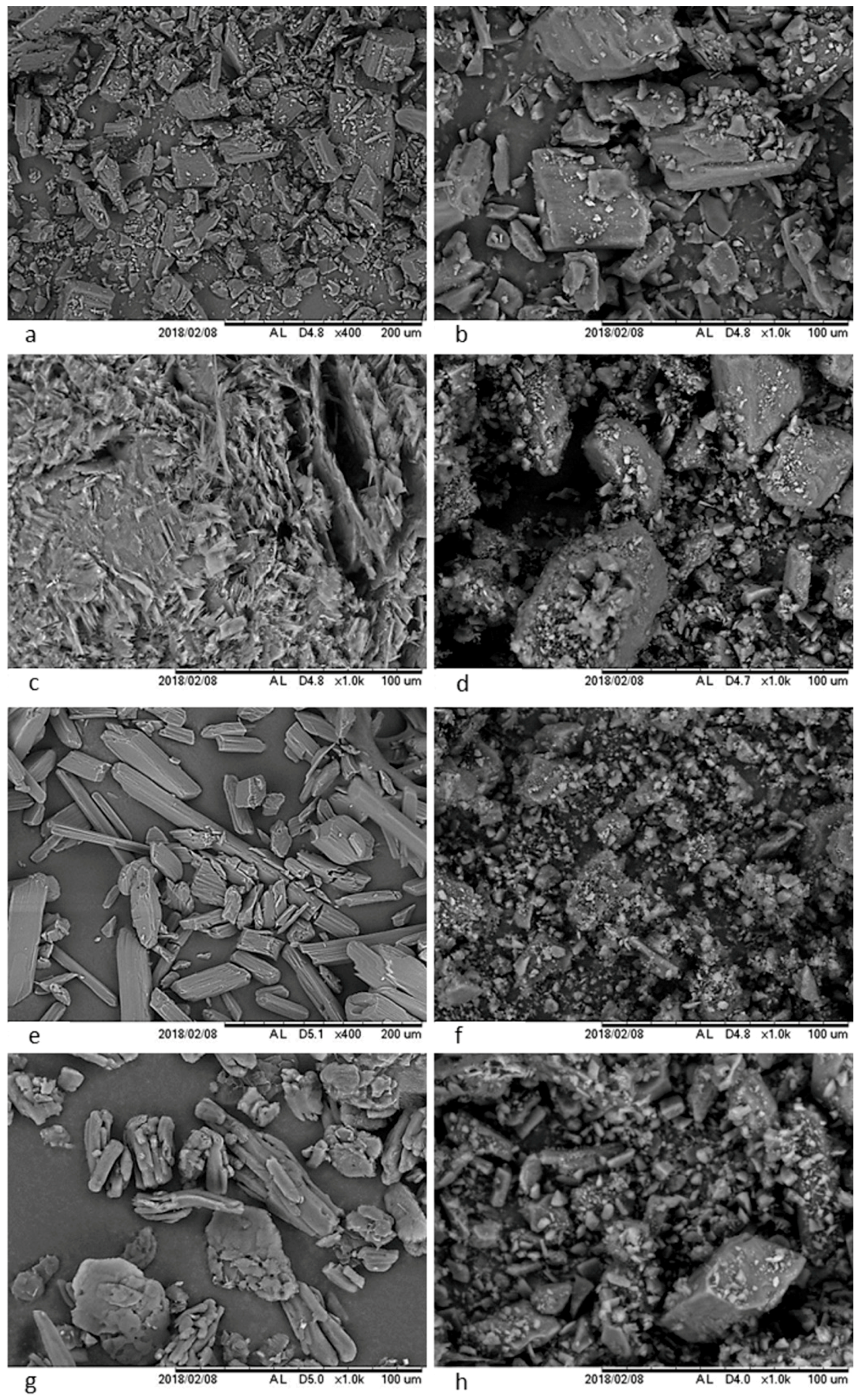
3.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
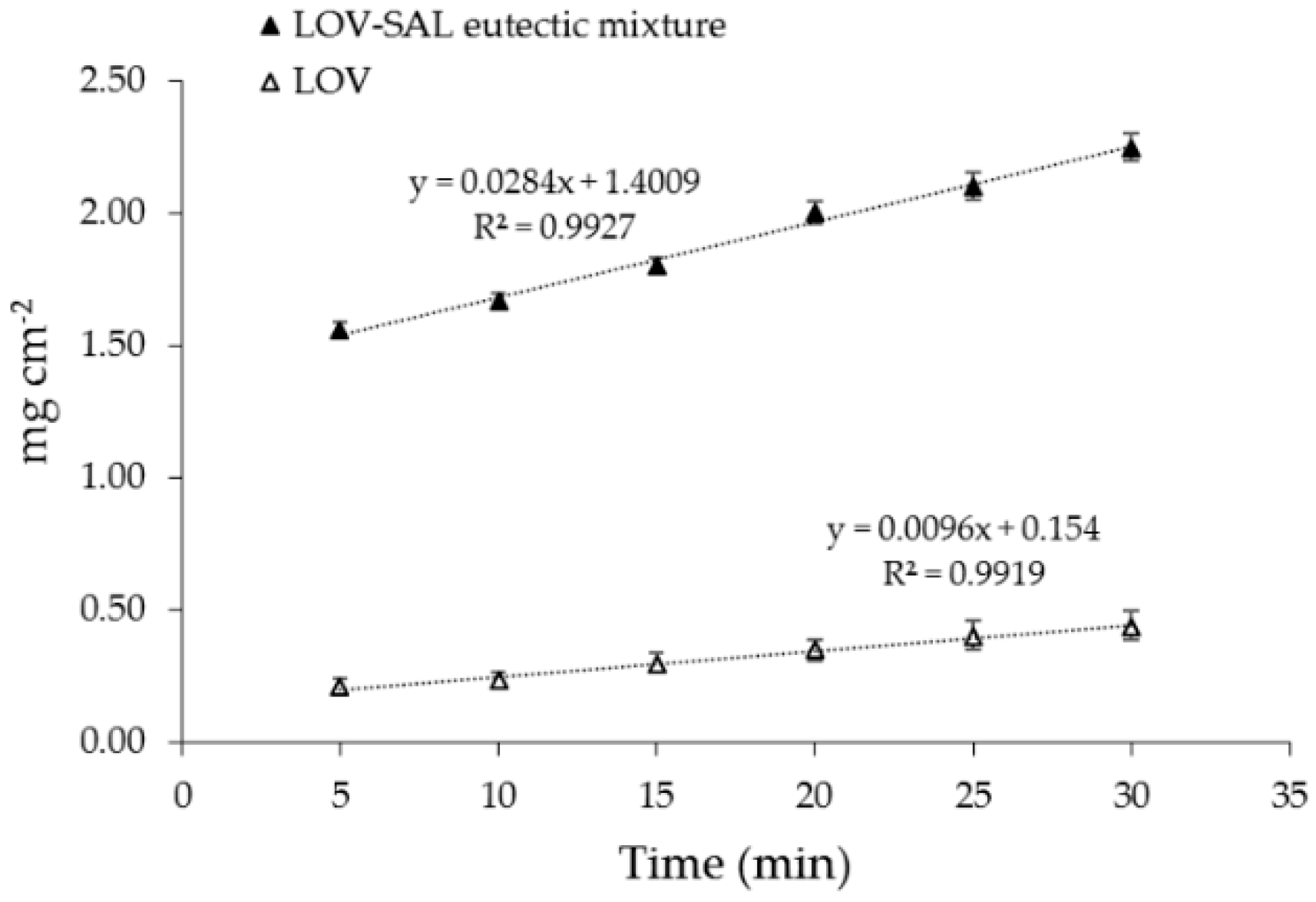
3.4. Solubility Determinations of the Eutectic Systems
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, S.; Kurup, N. Formulation of Irbesartan by Microcrystal Technology for Enhancing the Solubility and Dissolution Properties. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 6, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Janssens, S.; Van den Mooter, G. Review: Physical chemistry of solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 1571–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherukuvada, S.; Guru Row, T.N. Comprehending the Formation of Eutectics and Cocrystals in Terms of Design and Their Structural Interrelationships. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 4187–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gala, U.; Chuong, M.C.; Varanasi, R.; Chauhan, H. Characterization and Comparison of Lidocaine-Tetracaine and Lidocaine-Camphor Eutectic Mixtures Based on Their Crystallization and Hydrogen-Bonding Abilities. Aaps Pharmscitech 2015, 16, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, H.; Khomane, K.S.; Bansal, A.K. Implication of microstructure on the mechanical behaviour of an aspirin–paracetamol eutectic mixture. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 8471–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukuvada, S.; Nangia, A. Eutectics as improved pharmaceutical materials: Design, properties and characterization. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 906–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vippagunta, S.R.; Wang, Z.; Hornung, S.; Krill, S.L. Factors Affecting the Formation of Eutectic Solid Dispersions and Their Dissolution Behavior. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, S.-M.; Lee, B.J.; Abuzar, S.M.; Lee, S.; Joo, Y.; Hong, S.-H.; Kang, H.; Kwon, K.-A.; Velaga, S.; Hwang, S.-J. Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of celecoxib eutectic mixtures with adipic acid/saccharin for improvement of wettability and dissolution rate. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Sarmento, B.; Costa, P. Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water soluble drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoler, E.; Warner, J.C. Non-Covalent derivatives: Cocrystals and eutectics. Molecules 2015, 20, 14833–14848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, K.; Karan, M.; Chadha, R.; Bhalla, Y.; Vasisht, K. Is Failure of Cocrystallization Actually a Failure? Eutectic Formation in Cocrystal Screening of Hesperetin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 2026–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathisaran, I.; Dalvi, S. Engineering Cocrystals of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs to Enhance Dissolution in Aqueous Medium. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Conference on Harmonisation ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline Q6A. Test Procedures and Acceptance Criteria for New Drug Substance. Available online: https://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q6A/Step4/Q6Astep4.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2018).
- Avula, S.G.C.; Alexander, K.; Riga, A. Thermal analytical characterization of mixtures of antipsychotic drugs with various excipients for improved drug delivery. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 123, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Yang, J.-C.; Uang, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-J. Improved dissolution rate and oral bioavailability of lovastatin in red yeast rice products. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 444, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffrin, E.L. Antioxidants in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Mol. Interv. 2010, 10, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellés, A.N. Terapia antioxidante, estrés oxidativo y productos antioxidantes: Retos y oportunidades. Rev. Cuba. Salud Pública 2011, 37, 644–660. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, G.M. Especies reactivas del oxígeno y balance redox, parte I: Aspectos básicos y principales especies reactivas del oxígeno. Rev. Cuba. Farm. 2005, 39. Available online: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S0034-75152005000300009&script=sci_arttext (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Kumar, S.; Srivastava, N.; Gomes, J. The effect of lovastatin on oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes in hydrogen peroxide intoxicated rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknejad, N.; Gorn-Hondermann, I.; Ma, L.; Zahr, S.; Johnson-Obeseki, S.; Corsten, M.; Dimitroulakos, J. Lovastatin-induced apoptosis is mediated by activating transcription factor 3 and enhanced in combination with salubrinal. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohestanimobarhan, S.; Salami, S.; Imeni, V.; Mohammadi, Z.; Bayat, O. Lipophilic statins antagonistically alter the major epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition signaling pathways in breast cancer stem–like cells via inhibition of the mevalonate pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 2515–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kang, W.; Lu, X.; Ma, S.; Dong, L.; Zou, B. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis and connectivity map identifies lovastatin as a treatment option of gastric cancer by inhibiting HDAC2. Gene 2019, 681, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; Woodard, A.; Okediji, E.J.; Toms, S.A.; Allen, G.S. Lovastatin is a potent inhibitor of meningioma cell proliferation: Evidence for inhibition of a mitogen associated protein kinase. J. Neurooncol. 2002, 56, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Tekade, A.; Gattani, S.; Surana, S. Solubility enhancement of lovastatin by modified locust bean gum using solid dispersion techniques. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, D. Improvement of oral bioavailability of lovastatin by using nanostructured lipid carriers. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Fu, Q.; Wu, C.; Guo, Z.; Li, M.; Sun, J.; He, Z.; Yang, L. Rod shaped nanocrystals exhibit superior in vitro dissolution and in vivo bioavailability over spherical like nanocrystals: A case study of lovastatin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Che, E.; Zhang, L.; Han, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C. Development of novel mesoporous nanomatrix-supported lipid bilayers for oral sustained delivery of the water-insoluble drug, lovastatin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Chen, W.; Hu, X. Development of lovastatin-loaded poly(lactic acid) microspheres for sustained oral delivery: In vitro and ex vivo evaluation. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, S.; Sandhu, P.S.; Batra, R.S.; Khurana, R.K.; Singh, B. QbD-based systematic development of novel optimized solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) of lovastatin with enhanced biopharmaceutical performance. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 765–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Tan, A.; Boyd, B.J.; Prestidge, C.A. Synergistic role of self-emulsifying lipids and nanostructured porous silica particles in optimizing the oral delivery of lovastatin. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 2745–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süle, A.; Szente, L.; Csempesz, F. Enhancement of Drug Solubility in Supramolecular and Colloidal Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, G.; Manjunath, K.; Venkateswarlu, V.; Satyanarayana, V. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of lovastatin solid lipid nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, E162–E170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górniak, A.; Gajda, M.; Pluta, J.; Czapor-Irzabek, H.; Karolewicz, B. Thermal, spectroscopic and dissolution studies of lovastatin solid dispersions with acetylsalicylic acid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 125, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem Benzoic Acid Water Solubility. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/benzoic_acid#section=Solubility (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- PubChem Salicylic Acid Water Solubility. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/salicylic_acid#section=Solubility (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- FDA Benzoic Acid. Available online: http://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20180124121624/https://www.fda.gov/Food/IngredientsPackagingLabeling/GRAS/SCOGS/ucm260036.htm (accessed on 5 October 2018).
- FDA Salicylic Acid. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/?set=FoodSubstances&id=SALICYLICACID&sort=Sortterm&order=ASC&startrow=1&type=basic&search=salicylic acid (accessed on 5 October 2018).
- FDA Cinnamic Acid. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/index.cfm?set=FoodSubstances&id=CINNAMICACID&sort=Sortterm&order=ASC&startrow=1&type=basic&search=cinnamic acid (accessed on 5 October 2018).
- Rycerz, L. Practical remarks concerning phase diagrams determination on the basis of differential scanning calorimetry measurements. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 113, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USP 〈1087〉 Apparent intrinsic dissolution-dissolution testing procedures for rotating disk and stationary disk. In The United State Pharmacopeia; United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2012; pp. 609–612.
- USP. United State Pharmacopeia, 30th ed.; United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Figueirêdo, C.B.M.; Nadvorny, D.; de Medeiros Vieira, A.C.Q.; Soares Sobrinho, J.L.; Rolim Neto, P.J.; Lee, P.I.; de La Roca Soares, M.F. Enhancement of dissolution rate through eutectic mixture and solid solution of posaconazole and benznidazole. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 525, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugay, D.E. Characterization of the solid-state: Spectroscopic techniques. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanphui, P.; Goud, N.R.; Khandavilli, U.B.R.; Nangia, A. Fast Dissolving Curcumin Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 4135–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L. Feasibility studies of utilizing disk intrinsic dissolution rate to classify drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 270, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| System | Composition at the Eutectic Point a | Solubility (µg/mL) | Composition out of the Eutectic Point b | Solubility (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOV-BEN | 0.19:0.81 | 194 ± 8 | 0.70:0.30 | 147 ± 3 |
| LOV-SAL | 0.40:0.60 | 259 ± 4 | 0.60:0.40 | 186 ± 5 |
| LOV-CIN | 0.14:0.86 | 187 ± 5 | 0.30:0.70 | 163.7 ± 0.2 |
| Pure LOV | Solubility: 49 ± 4 ug/mL | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araya-Sibaja, A.M.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R.; Guillén-Girón, T.; Navarro-Hoyos, M.; Cuffini, S.L. Drug Solubility Enhancement through the Preparation of Multicomponent Organic Materials: Eutectics of Lovastatin with Carboxylic Acids. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11030112
Araya-Sibaja AM, Vega-Baudrit JR, Guillén-Girón T, Navarro-Hoyos M, Cuffini SL. Drug Solubility Enhancement through the Preparation of Multicomponent Organic Materials: Eutectics of Lovastatin with Carboxylic Acids. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(3):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11030112
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraya-Sibaja, Andrea Mariela, José Roberto Vega-Baudrit, Teodolito Guillén-Girón, Mirtha Navarro-Hoyos, and Silvia Lucia Cuffini. 2019. "Drug Solubility Enhancement through the Preparation of Multicomponent Organic Materials: Eutectics of Lovastatin with Carboxylic Acids" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 3: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11030112
APA StyleAraya-Sibaja, A. M., Vega-Baudrit, J. R., Guillén-Girón, T., Navarro-Hoyos, M., & Cuffini, S. L. (2019). Drug Solubility Enhancement through the Preparation of Multicomponent Organic Materials: Eutectics of Lovastatin with Carboxylic Acids. Pharmaceutics, 11(3), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11030112





