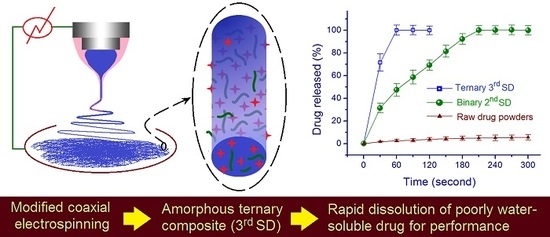
Fast Dissolving of Ferulic Acid via Electrospun Ternary Amorphous Composites Produced by a Coaxial Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
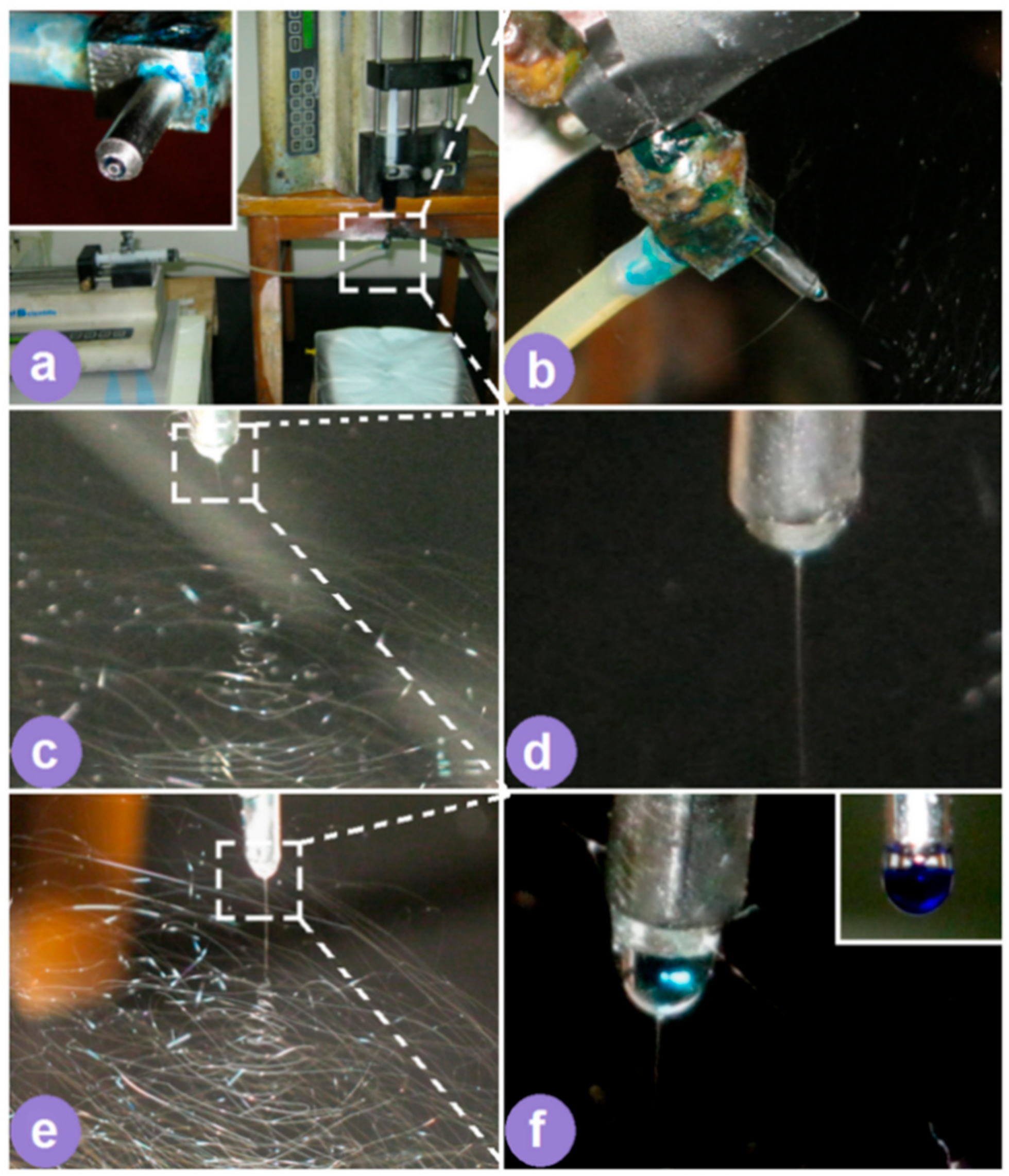
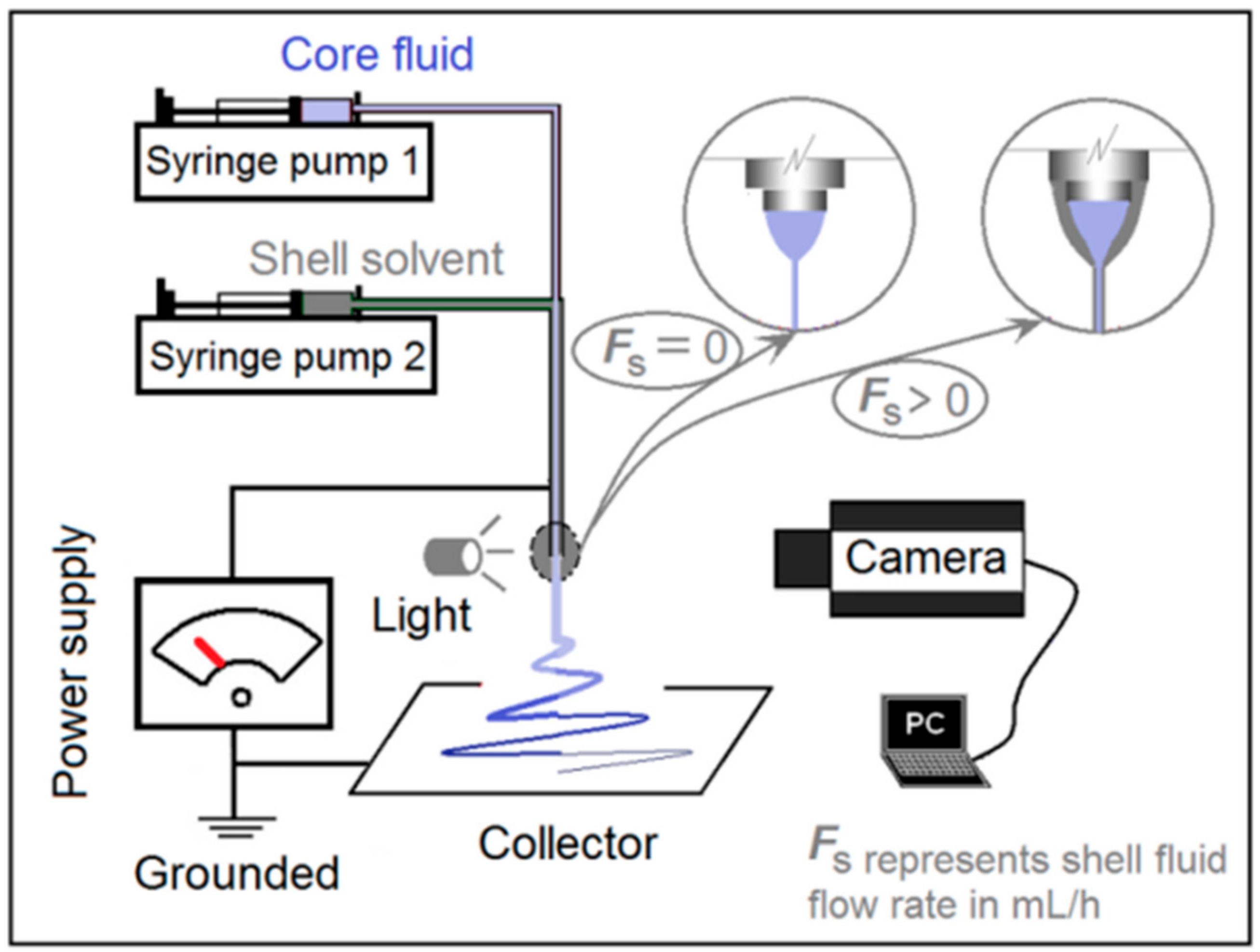
2.2. Electrospinning
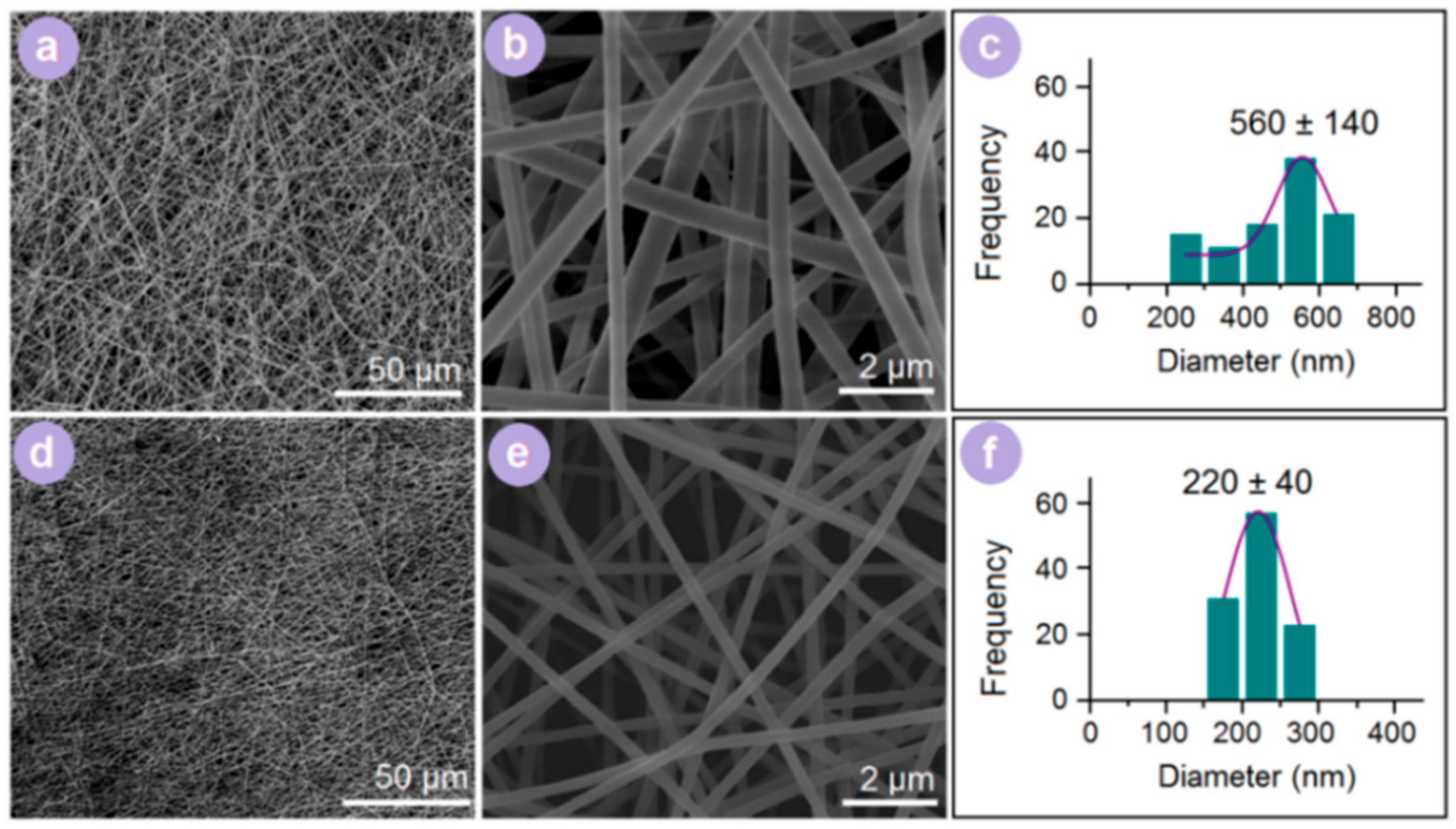
2.3. Morphology
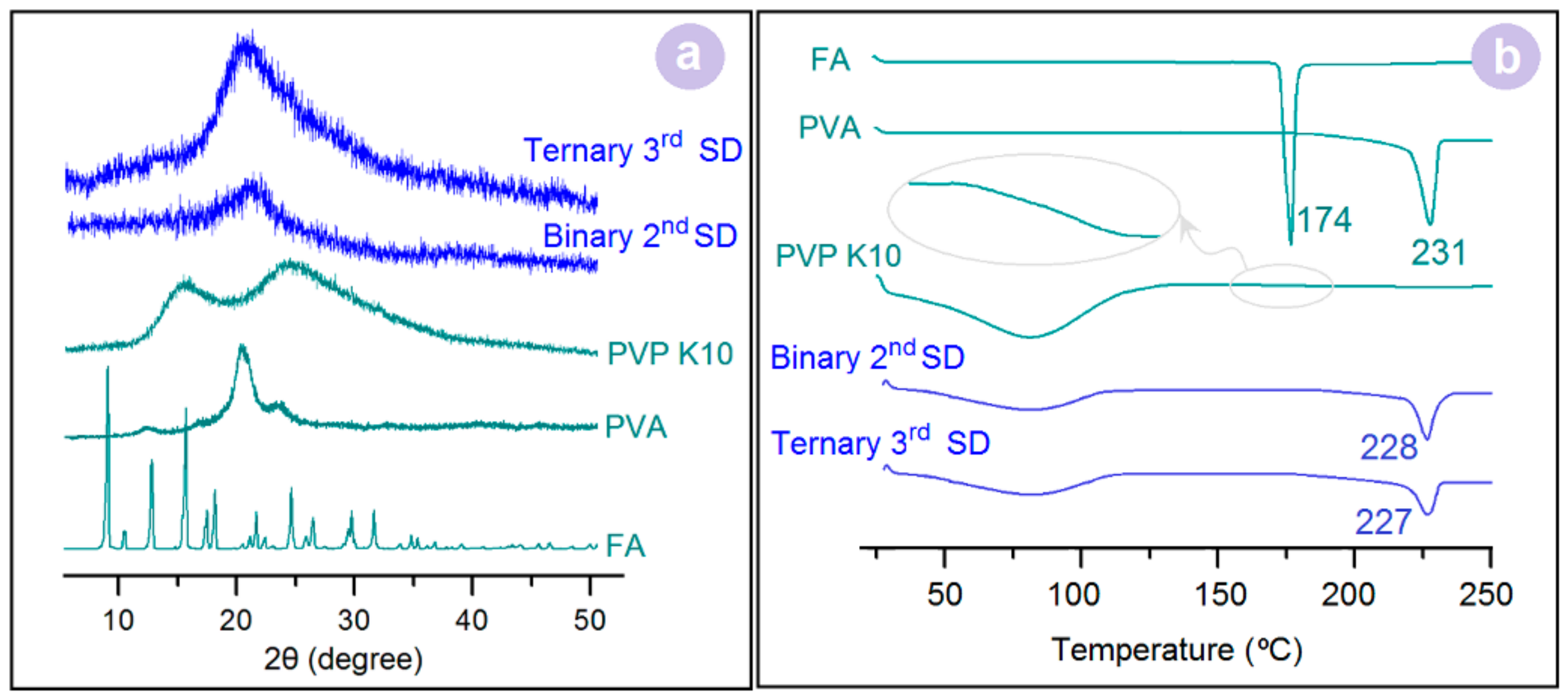
2.4. Physical Form and Compatibility
2.5. Property and Functional Performances
2.6. Statistical Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. One System but Two Different Electrospinning Processes
3.2. Morphology
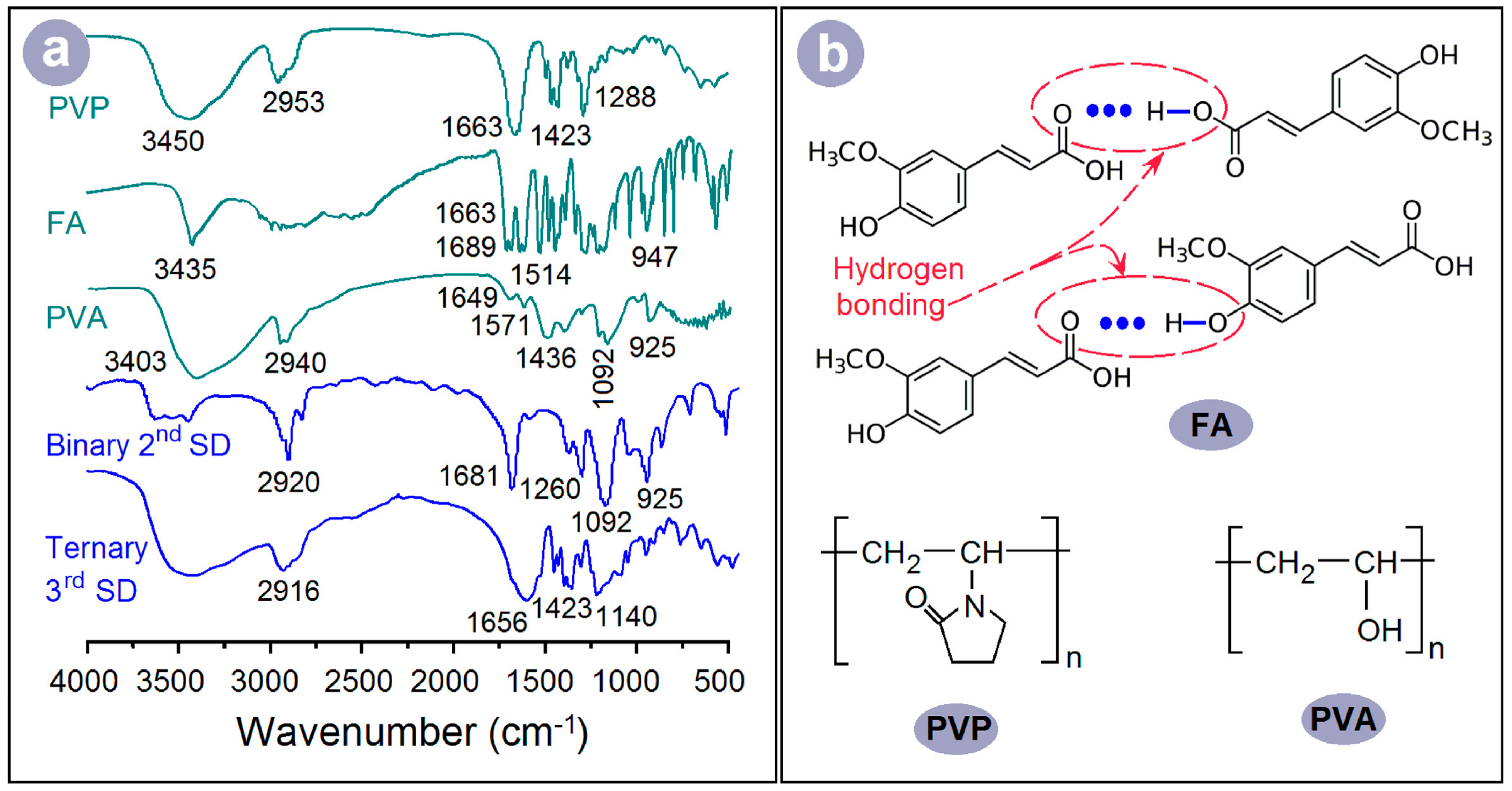
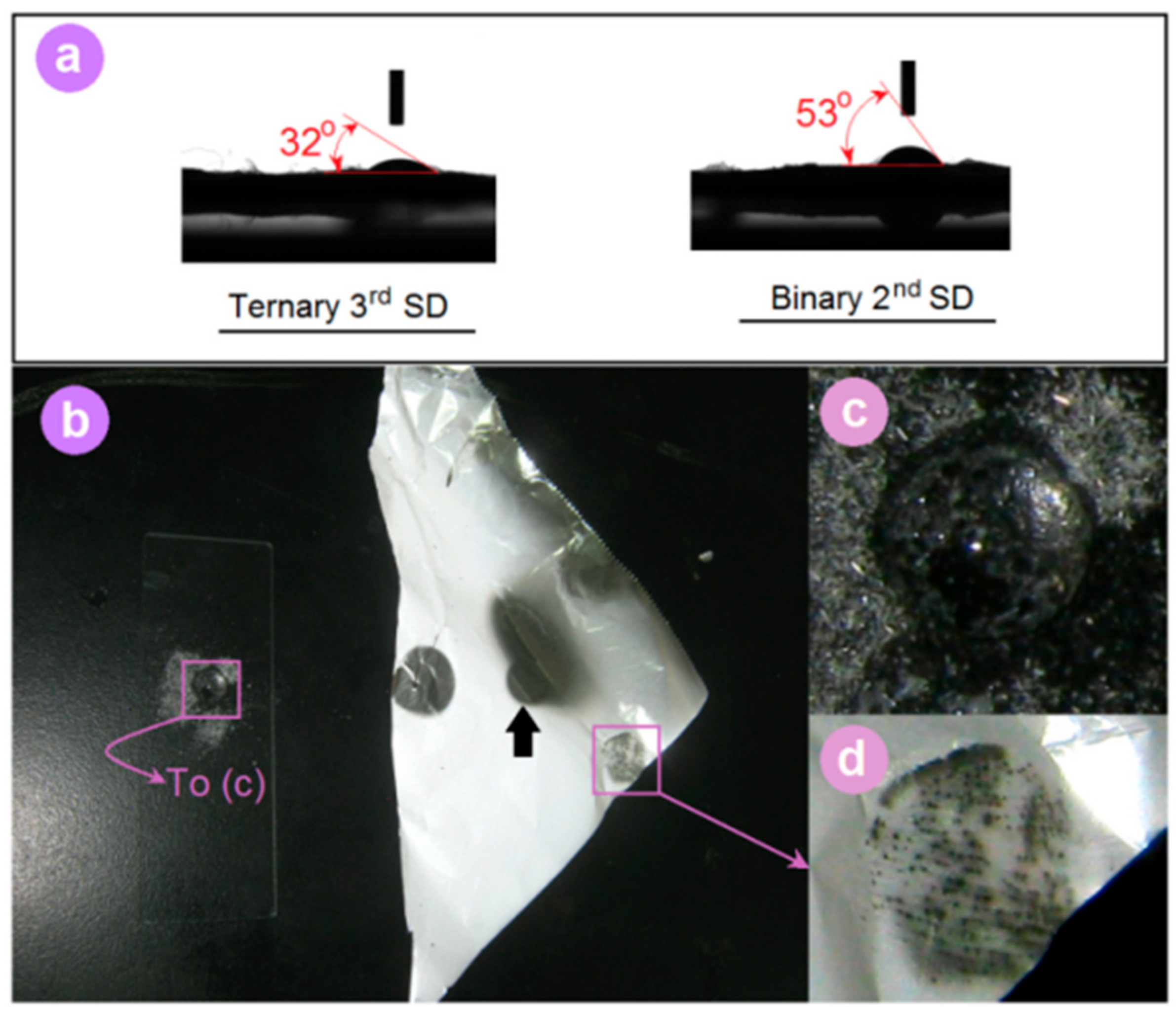
3.3. Physical Forms
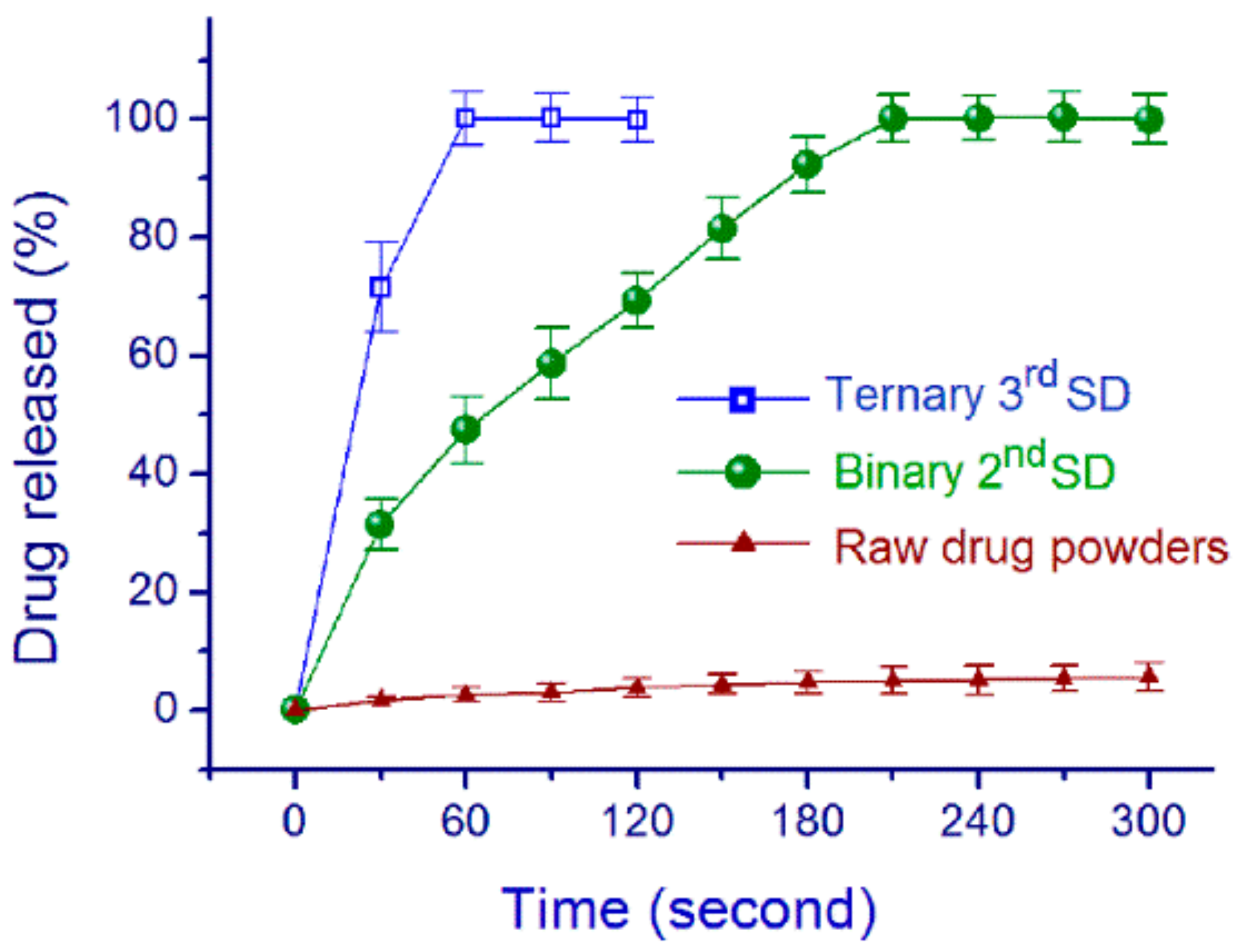
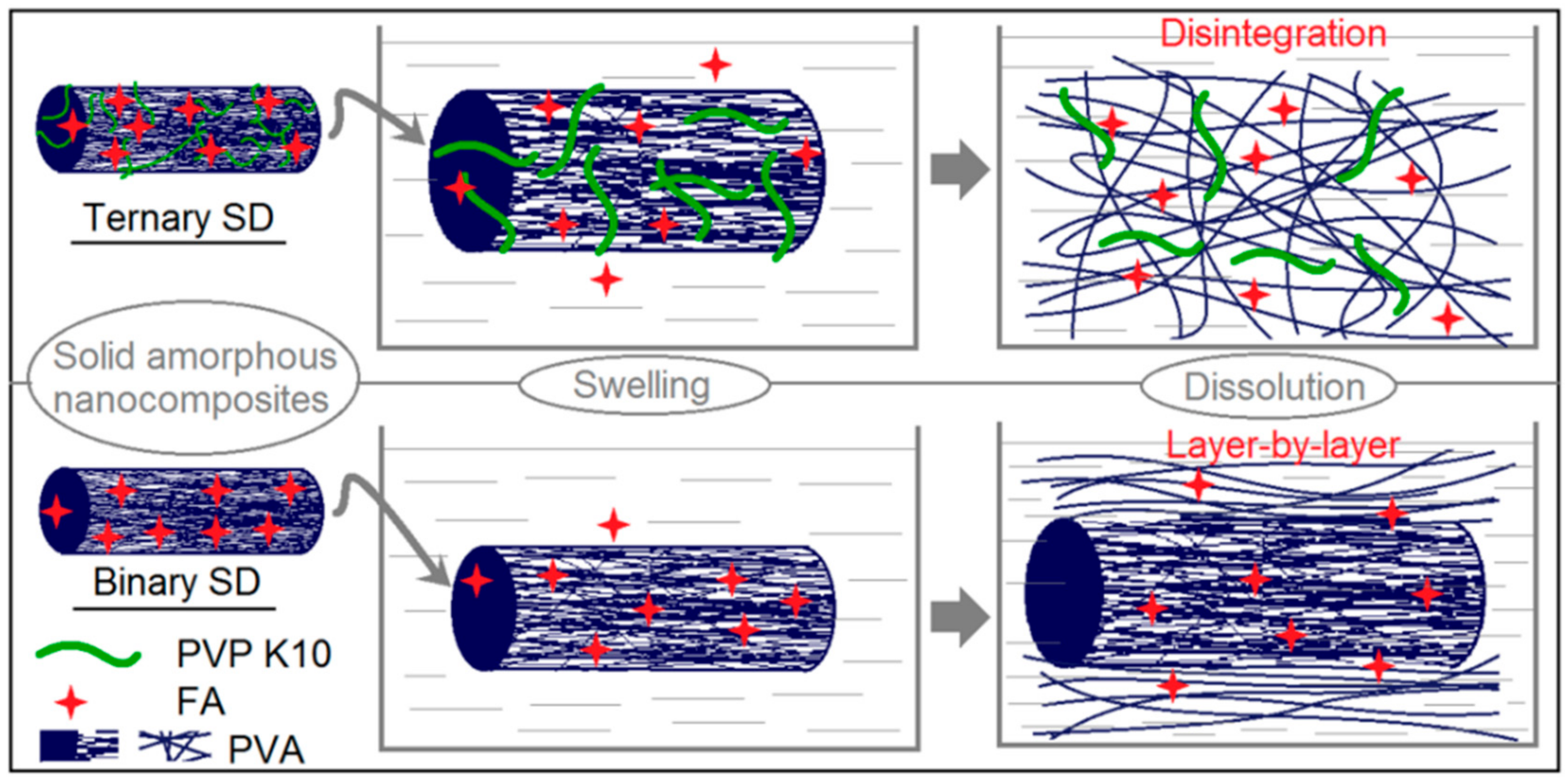
3.4. Property and Functional Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, A.; Van den Mooter, G. Spray drying formulation of amorphous solid dispersions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, M.E.; Maurer, R.; Paepe, A.T.; Stillhart, C.; Jacob, L.; James, R.; Kojima, Y.; Rietmann, R.; Kissling, T.; van den Ende, J.A.; et al. A miniaturized extruder to prototype amorphous solid dispersions: Selection of plasticizers for hot melt extrusion. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.; Peng, T.; Huang, Z.; Singh, V.; Shi, Y.; Wen, T.; Lu, M.; Quan, G.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Polymer-surfactant system based amorphous solid dispersion: Precipitation inhibition and bioavailability enhancement of itraconazole. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Okuda, T.; Lu, X.Y.; Chan, H.K. Amorphous powders for inhalation drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponnammal, P.; Kanaujia, P.; Yani, Y.; Ng, W.K.; Tan, R.B.H. Orally disintegrating tablets containing melt extruded amorphous solid dispersion of tacrolimus for dissolution enhancement. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ousset, A.; Chavez, P.F.; Meeus, J.; Robin, F.; Schubert, M.A.; Somville, P.; Dodou, K. Prediction of phase behavior of spray-dried amorphous solid dispersions: Assessment of thermodynamic models, standard screening methods and a novel atomization screening device with regard to prediction accuracy. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Mao, C.; Williams, R.O.; Yang, C.Y. Solubility advantage (and disadvantage) of pharmaceutical amorphous solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 3549–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Patel, D.; Wang, G. Use of spray-dried dispersions in early pharmaceutical development: Theoretical and practical challenges. AAPS J. 2016, 2016, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, W.L.; Riegelman, S. Pharmaceutical applications for solid dispersion systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1971, 60, 1281–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Rades, T.; Löbmann, K.; Grohganz, H. Influence of solvent composition on the performance of spray-dried co-amorphous formulations. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.; McGarry, K.; Chaw, C.S.; Elkordy, A.A. Feasibility of using gluconolactone, trehalose and hydroxy-propyl gamma cyclodextrin to enhance bendroflumethiazide dissolution using lyophilisation and physical mixing techniques. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogh, A.; Farkas, B.; Pálvölgyi, Á.; Domokos, A.; Démuth, B.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z.K. Novel alternating current electrospinning of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS) nanofibers for dissolution enhancement: The importance of solution conductivity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogh, A.; Farkas, B.; Domokos, A.; Farkas, A.; Démuth, B.; Borbás, E.; Nagy, B.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z.K. Controlled-release solid dispersions of Eudragit® FS 100 and poorly soluble spironolactone prepared by electrospinning and melt extrusion. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 95, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbás, E.; Nagy, Z.K.; Nagy, B.; Balogh, A.; Farkas, B.; Tsinman, O.; Tsinman, K.; Sinkó, B. The effect of formulation additives on in vitro dissolution-absorption profile and in vivo bioavailability of telmisartan from brand and generic formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 114, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Duong, T.; Van den Mooter, G. The role of the carrier in the formulation of pharmaceutical solid dispersions. Part II: Amorphous carriers. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Sarmento, B.; Costa, P. Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water soluble drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenawy, E.R.; Abdel-Hay, F.I.; El-Newehy, M.H.; Wnek, G.E. Controlled release of ketoprofen from electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 459, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Ngoc Vo, C.; Park, C.; Lee, B.J. Current trends and future perspectives of solid dispersions containing poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 799–813. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, G.; Qu, Y.; Yu, D.G. Electrospun 4th generation solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drug utilizing two different processes. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 2012140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallouard, F.; Mehenni, L.; Lahiani-Skiba, M.; Anouar, Y.; Skiba, M. Solid dispersions for oral administration: An overview of the methods for their preparation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 4942–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wen, H.F.; Yu, D.G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D.F. Electrosprayed hydrophilic nanocomposites coated with shellac for colon-specific delayed drug delivery. Mater. Des. 2018, 143, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, K.; Yu, D.G. pH-sensitive polymer nanocoating on hydrophilic composites fabricated using modified coaxial electrospraying. Mater. Lett. 2018, 227, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.P.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wu, D.; Jiang, G.; Yu, D.G. Preparing composite nanoparticles for immediate drug release by modifying electrohydrodynamic interfaces during electrospraying. Powder Technol. 2018, 327, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.P.; Wang, K.; Yu, D.G. Meletin sustained-release gliadin nanoparticles prepared via solvent surface modification on blending electrospray. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 434, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.K.; Shao, W.Y.; Luo, M.Y.; Bian, J.Y.; Yu, D.G. Electrospun blank nanocoating for improved sustained release profiles from medicated gliadin nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 184. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.J.; Yu, D.G.; Williams, G.R.; Yang, J.H.; Wang, X. Influence of the drug distribution in electrospun gliadin fibers on drug-release behavior. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Zheng, Z.B.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, X.K.; Qu, Y.L.; Li, H.L. Electrosprayed sperical ethylcellulose nanoparticles for an improved sustained-release profile of anticancer drug. Cellulose 2017, 24, 5551–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.P.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yu, D.G.; Wu, D.; Li, H.L. Fabrication of sustained-release zein nanoparticles via modified coaxial electrospraying. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.H.; Annie Bligh, S.W.; Williams, G.R. Nanofibers fabricated using triaxial electrospinning as zero order drug delivery systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18891–18897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.G.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, M.; Williams, G.R. High-quality janus nanofibers prepared using three-fluid electrospinning. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 4542–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, D.G.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, X.K.; Deng, Y.C.; Zhao, M. Electrospun hypromellose-based hydrophilic composites for rapid dissolution of poorly water-soluble drug. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.P.; Yu, D.G.; Wang, K.; Liu, P.; Chen, X.H. Colon-specific pulsatile drug release provided by electrospun shellac nanocoating on hydrophilic amorphous composites. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Liu, X.K.; Chen, X.H.; Yu, D.G.; Yang, Y.Y.; Liu, P. Electrospun hydrophilic janus nanocomposites for the rapid onset of therapeutic action of helicid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2859–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Functional materials by electrospinning of polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 963–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, D.G.; Zhou, S.Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, M. Fabrication of amorphous electrospun medicated-nanocomposites using a Teflon-based concentric spinneret. e-Polymer 2018, 18, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Saquing, C.D.; Harding, J.R.; Khan, S.A. In situ cross-linking of electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers. Macromolecules 2009, 43, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kanjwal, M.A.; Lin, L.; Chronakis, I.S. Electrospun polyvinyl-alcohol nanofibers as oral fast-dissolving delivery system of caffeine and riboflavin. Colloid Surf. B 2013, 103, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Démuth, B.; Galata, D.L.; Szabó, E.; Nagy, B.; Farkas, A.; Balogh, A.; Hirsch, E.; Pataki, H.; Rapi, Z.; Bezúr, L.; et al. Investigation of deteriorated dissolution of amorphous itraconazole: Description of incompatibility with magnesium stearate and possible solutions. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 3927–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gately, N.M.; Kennedy, J.E. The development of a melt-extruded shellac carrier for the targeted delivery of probiotics to the colon. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, E.; Calabrese, V.; Mancuso, C. Ferulic acid and its therapeutic potential as a hormetin for age-related diseases. Biogerontology 2009, 10, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.G.; Yang, J.M.; Branford-White, C.; Lu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, L.M. Third generation solid dispersions of ferulic acid in electrospun composite nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 400, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.G.; Zhu, L.M.; Branford-White, C.; Yang, J.H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Qian, W. Solid dispersions in the form of electrospun core-sheath nanofibers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 3271–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, E.; Démuth, B.; Nagy, B.; Molnár, K.; Farkas, A.; Szabó, B.; Balogh, A.; Hirsch, E.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z.K. Scaled-up preparation of drug-loaded electrospun polymer fibres and investigation of their continuous processing to tablet form. Express Polym. Lett. 2018, 12, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Ito, S.; Sakagami, S.; Asada, H.; Saito, M.; Quan, Y.S.; Kamiyama, F.; Hirobe, S.; Okada, N. Development of novel faster-dissolving microneedle patches for transcutaneous vaccine delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Démuth, B.; Nagy, Z.K.; Balogh, A.; Vigh, T.; Marosi, G.; Verreck, G.; Van Assche, I.; Brewster, M.E. Downstream processing of polymer-based amorphous solid dispersions to generate tablet formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 486, 268–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| No. | Electrospinning | Sheath Fluid | Core Fluid | Flow Rate (mL/h) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sheath | Core | ||||
| 2nd | Blending | -- | 13% (w/v) PVA and 2% (w/v) FA in 50% (v/v) aqueous ethanol | -- | 1.0 |
| 3rd | Modified coaxial process | 50% (v/v) aqueous ethanol | 13% (w/v) PVA, 2% (w/v) PVP K10 and 2% (w/v) FA in 50% (v/v) aqueous ethanol | 0.2 | 1.0 |
| Electrospinning Working Fluid | Viscosity | Surface Tension | Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| (cp) | (N·m−1 × 10−3) | (μS·cm−1) | |
| Fluid for the blending process | 212.4 ± 4.5 | 87.6 ± 1.2 | 57.4 ± 0.5 |
| Core fluid of the coaxial process | 343.7 ± 6.8 | 93.3 ± 0.7 | 57.8 ± 0.5 |
| Sheath fluid of the coaxial process | 2.87 ± 0.04 | 27.5 ± 0.4 | 0.87 ± 0.02 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Liang, G.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.-L.; Yu, D.-G. Fast Dissolving of Ferulic Acid via Electrospun Ternary Amorphous Composites Produced by a Coaxial Process. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030115
Huang W, Yang Y, Zhao B, Liang G, Liu S, Liu X-L, Yu D-G. Fast Dissolving of Ferulic Acid via Electrospun Ternary Amorphous Composites Produced by a Coaxial Process. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030115
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Weidong, Yaoyao Yang, Biwei Zhao, Gangqiang Liang, Shiwei Liu, Xian-Li Liu, and Deng-Guang Yu. 2018. "Fast Dissolving of Ferulic Acid via Electrospun Ternary Amorphous Composites Produced by a Coaxial Process" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030115
APA StyleHuang, W., Yang, Y., Zhao, B., Liang, G., Liu, S., Liu, X.-L., & Yu, D.-G. (2018). Fast Dissolving of Ferulic Acid via Electrospun Ternary Amorphous Composites Produced by a Coaxial Process. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030115