Understanding the Complex Patterns Observed during Hepatitis B Virus Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mathematical Model
2.2. Monte Carlo Sampling
- MC.1
- The initial condition (2) exists and is stable, i.e., and .
- MC.2
- The components of initial condition (2) are bound by cells per ml, cells per mL, and virus per ml.
- MC.3
- The drug-dependent virus asymptotic removal condition (6) holds, i.e., . This condition guaranties that we are only examining drug therapy that is efficient in removing the hepatitis B virus.
- MC.4
- The total hepatocyte population is bound as follows cells per mL, for all t. This condition guarantees that the total liver cell population never decays below of the healthy hepatocyte concentration K [23].
3. Results
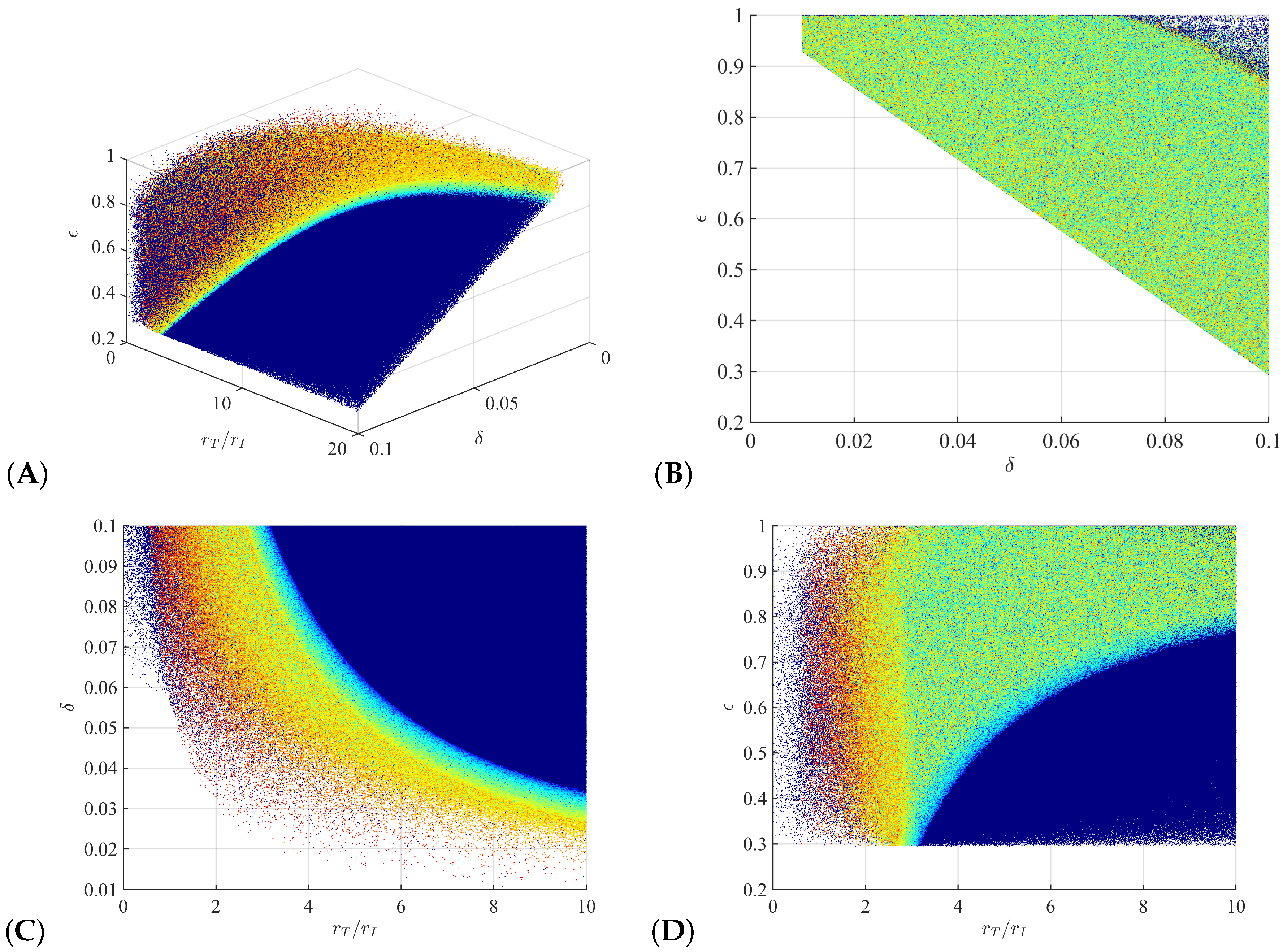
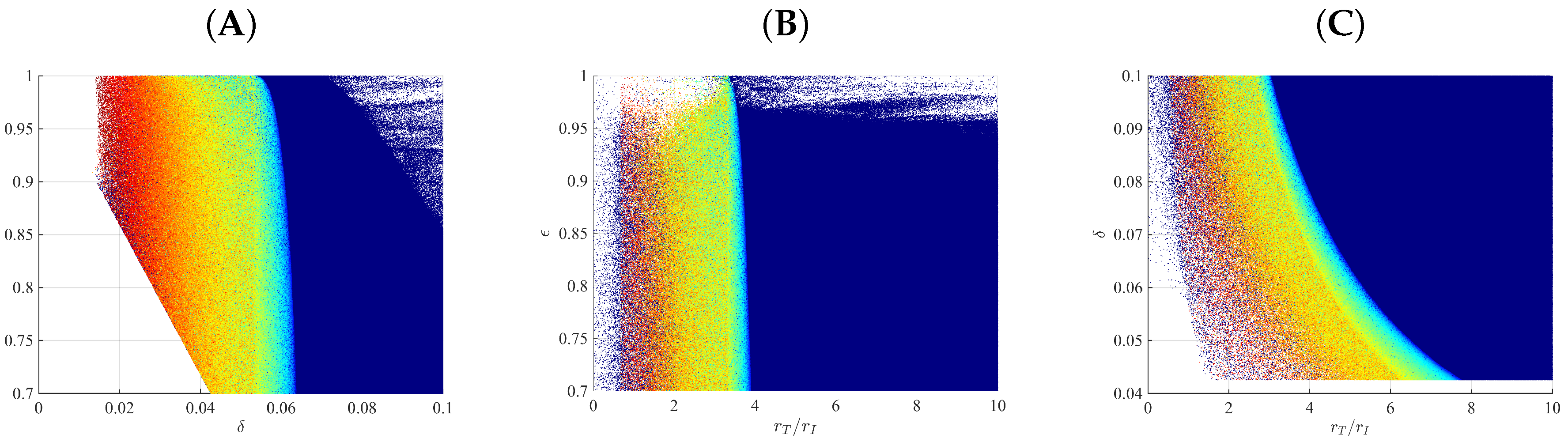
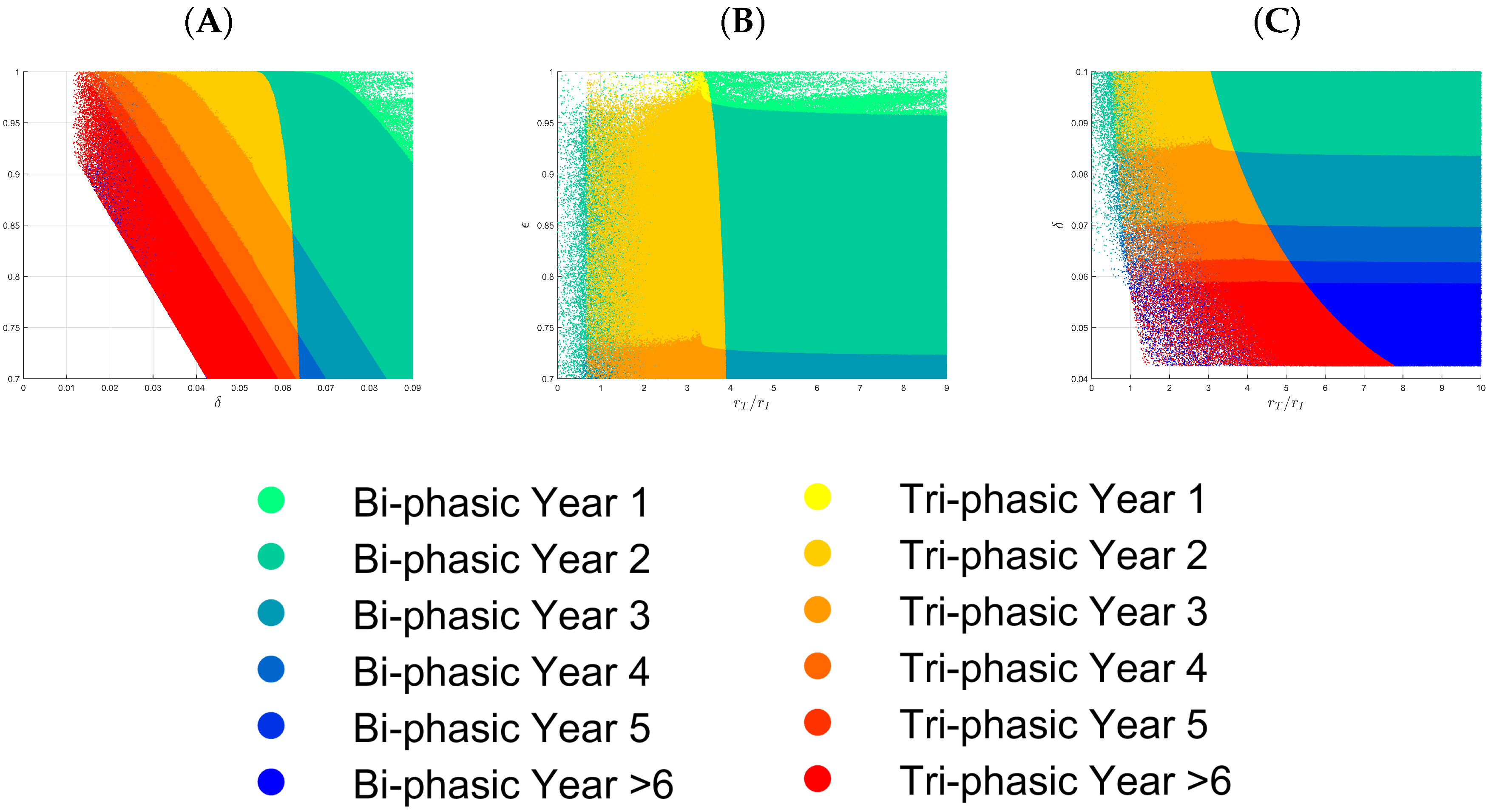
3.1. Parameter Regions for Bi-Phasic and Tri-Phasic Virus Dynamics
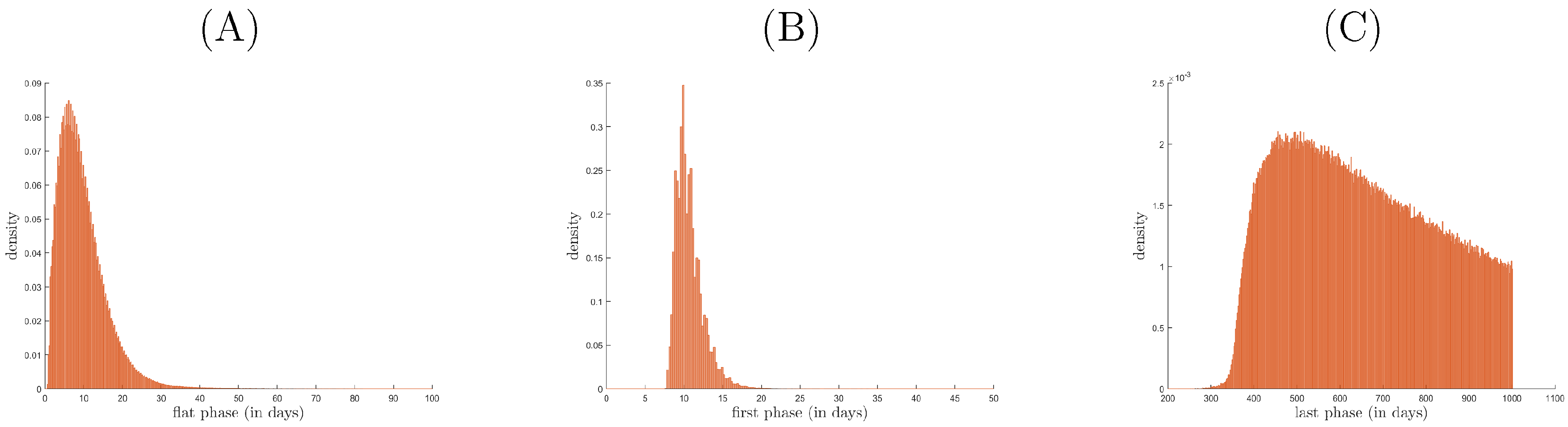
3.2. Relationship between Patterns and the Duration of Treatment
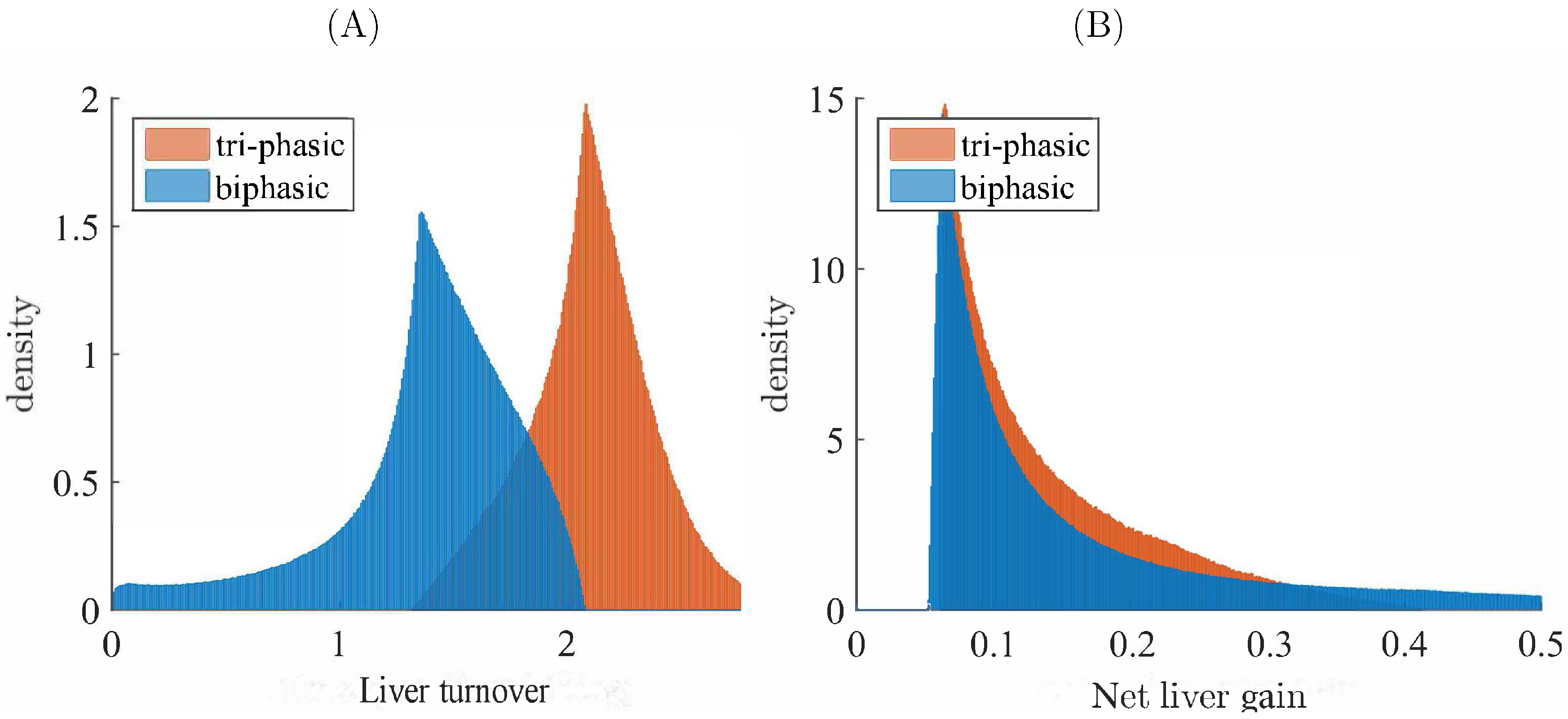
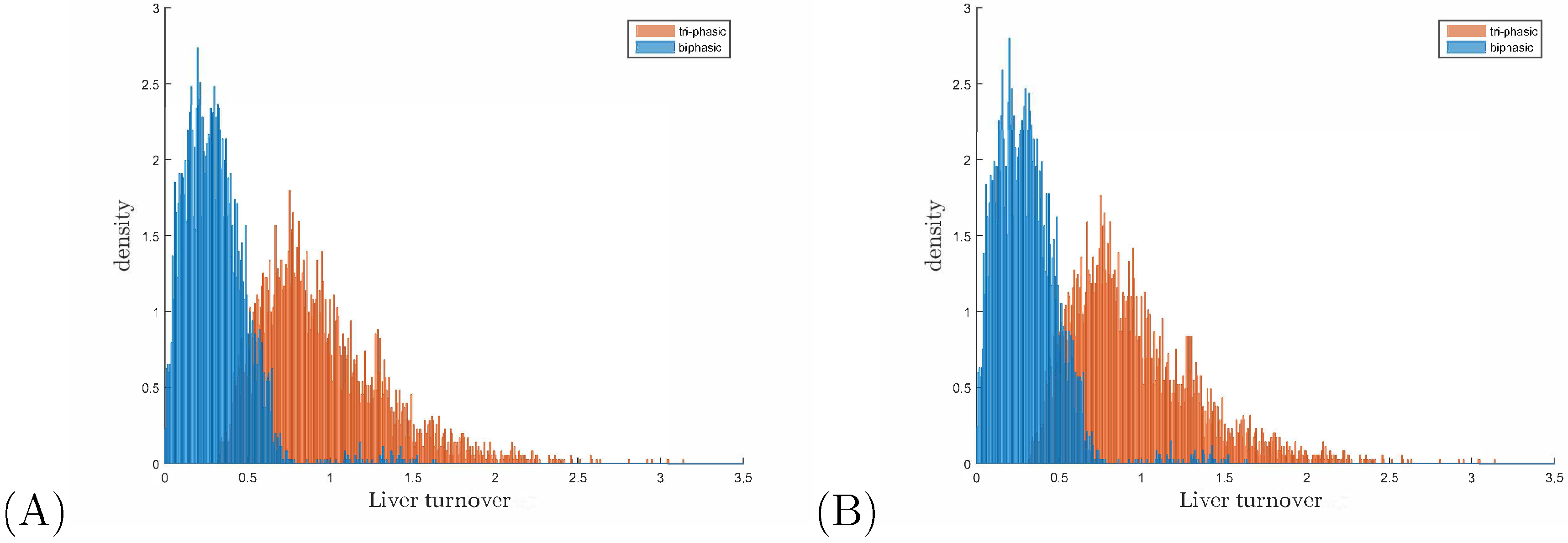
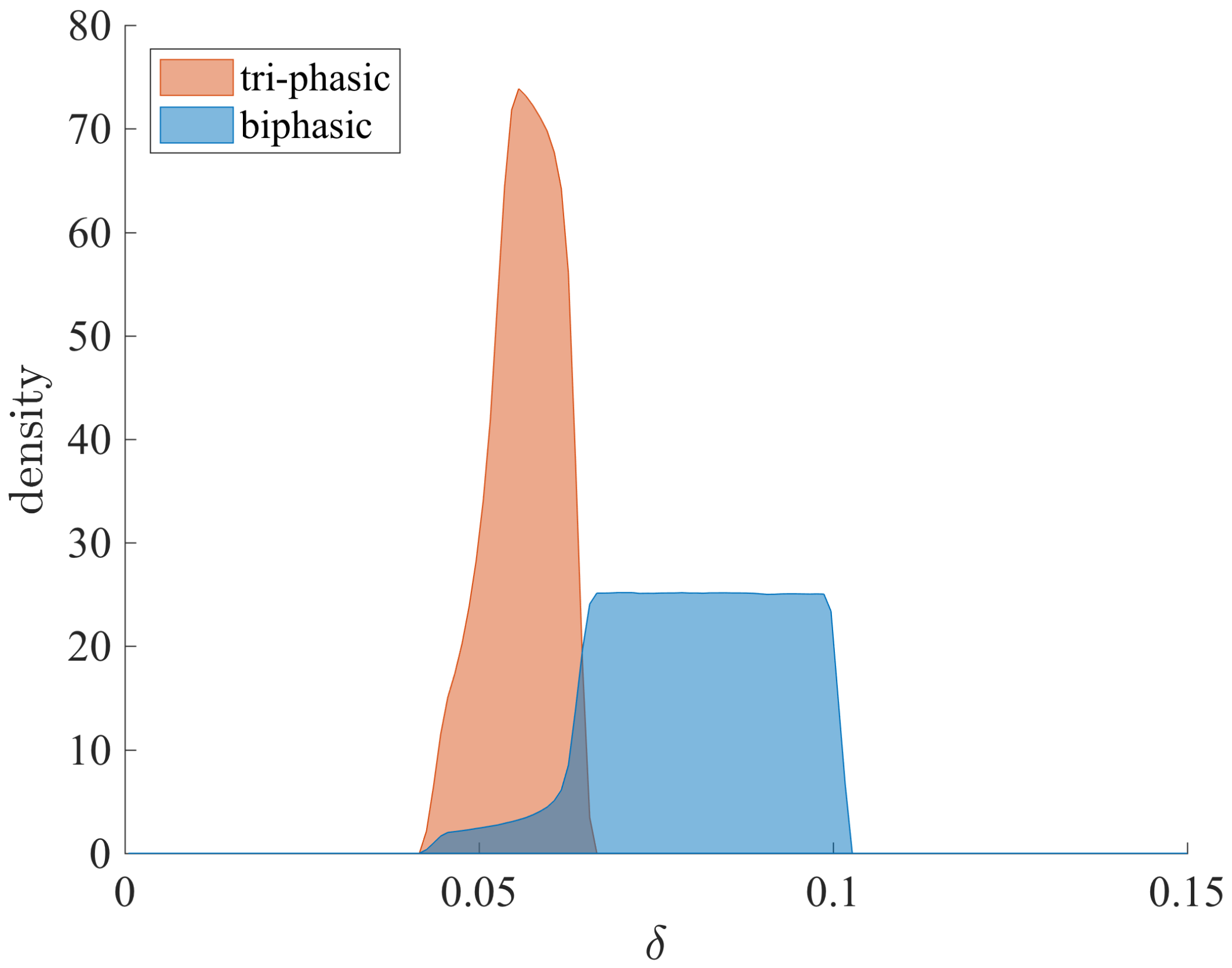
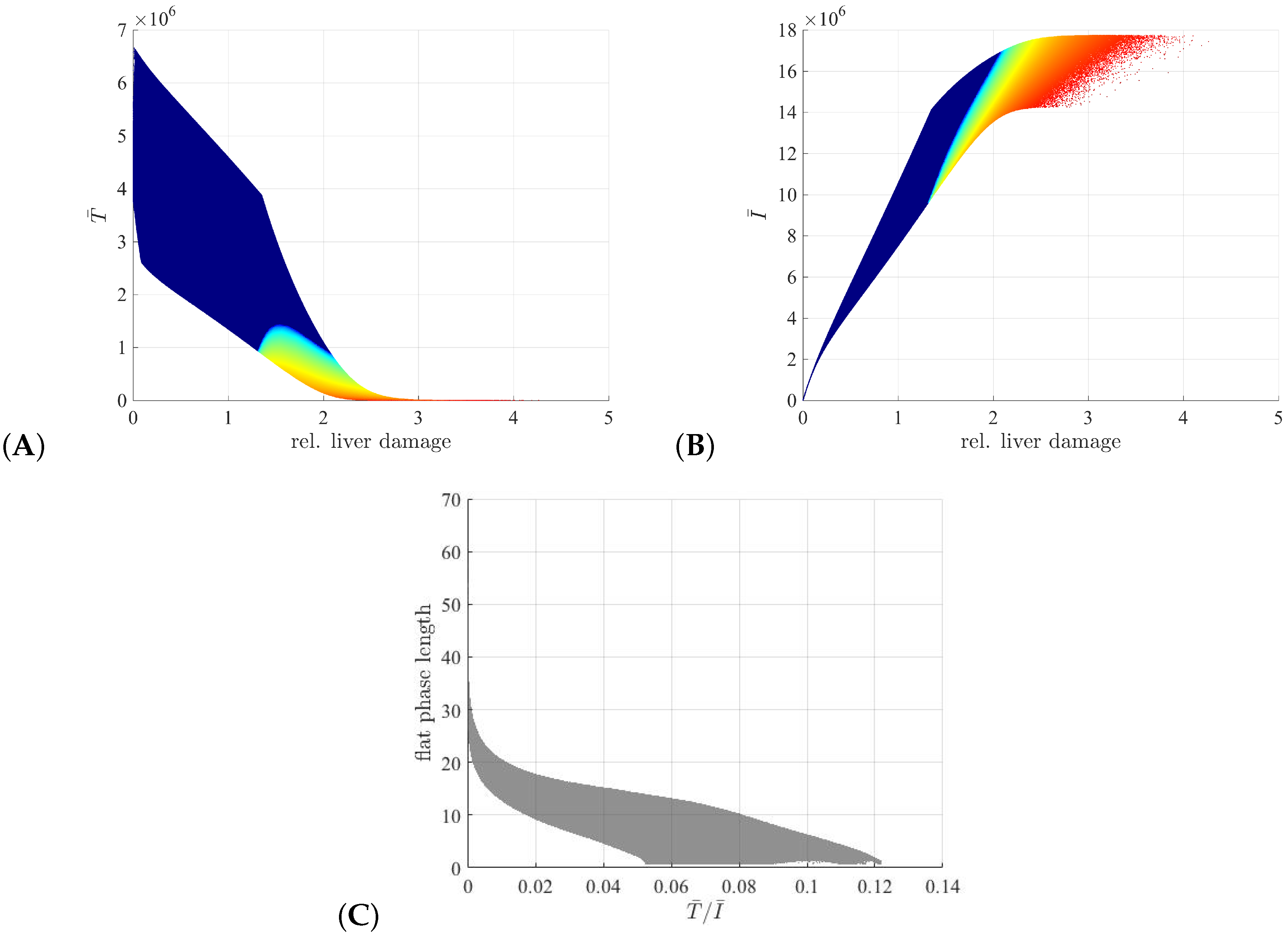
3.3. Liver Toxicity and the Role of Initial Conditions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Locarnini, S.; Hatzakis, A.; Chen, D.S.; Lok, A. Strategies to control hepatitis B: Public policy, epidemiology, vaccine and drugs. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S76–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S. Hepatitis B vaccination: The key towards elimination and eradication of hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, S.; Saalim, M.; Imran, M.; Resham, S.; Ashraf, J. Hepatitis B virus therapy: What’s the future holding for us? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12558–12575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis B Fact sheet 204; Technical report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lampertico, P.; Aghemo, A.; Viganò, M.; Colombo, M. HBV and HCV therapy. Viruses 2009, 1, 484–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneveld, M.; Wong, V.; Woltman, A.; Wong, G.; Cakaloglu, Y.; Zeuzem, S.; Buster, E.; Uitterlinden, A.; Hansen, B.; Chan, H.; et al. Polymorphisms Near IL28B and Serologic Response to Peginterferon in HBeAg-Positive Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadziyannis, S.; Tassopoulos, N.; Heathcote, E.; Chang, T.T.; Kitis, G.; Rizzetto, M.; Marcellin, P.; Lim, S.; Goodman, Z.; Wulfsohn, M.; et al. Adefovir Dipivoxil for the Treatment of Hepatitis B e Antigen–Negative Chronic Hepatitis B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.; Wang, H.; Niu, J.; Chim, A.; Sung, J. Two-year lamivudine treatment for hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Antivir. Ther. 2007, 12, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lok, A.; McMahon, B.; Brown, R.; Wong, J.; Ahmed, A.; Farah, W.; Almasri, J.; Alahdab, F.; Benkhadra, K.; Mouchli, M.; et al. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B viral infection in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2016, 63, 284–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, S.R.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Walters, T.; Lau, G.K.; Bowden, S.; Locarnini, S.; Perelson, A.S. Analysis of hepatitis B viral load decline under potent therapy: complex decay profiles observed. Hepatology 2001, 34, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiang, M.; Rooney, J.F.; Toole, J.J.; Gibbs, C.S. Biphasic clearance kinetics of hepatitis B virus from patients during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Hepatology 1999, 29, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahari, H.; Shudo, E.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Perelson, A.S. Modeling complex decay profiles of Hepatitis B virus during antiviral therapy. Hepatology 2009, 49, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, C.; Mason, W. HBV replication, pathobiology and therapy: Unanswered questions. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S1–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.; Goyal, A. In silico single cell dynamics of hepatitis B virus infection and clearance. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 366, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.; Rochford, R.; Chung, J.; Shapiro, M.; Purcell, R.; Chisari, F. Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection. Science 1999, 284, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, R.; Germanidis, G.; Powers, K.; Pellegrin, B.; Nikolaidis, P.; Perelson, A.; Pawlotsky, J.M. Hepatitis B Virus Kinetics under Antiviral Therapy Sheds Light on Differences in Hepatitis B e Antigen Positive and Negative Infections. J. Inf. Dis. 2010, 202, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, G.; Tsiang, M.; Hou, J.; Yuen, S.; Carman, W.; Zhang, L.; Gibbs, C. Combination therapy with lamivudine and famciclovir for chronic hepatitis B-infected Chinese patients: A viral dynamics study. Hepatology 2000, 32, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombatto, P.; Civitano, L.; Bizzarri, R.; Oliveri, F.; Choudhury, S.; Gieschke, R. A multiphase model of the dynamics of HBV infection in HBeAg-negative patients during pegylated interferon-alpha2a, lamivudine and combination therapy. Antivir. Ther. 2006, 11, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kwon, H.D.; Jang, T.; Lim, J.; Lee, H.S. Mathematical Modeling of Triphasic Viral Dynamics in Patients with HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Showing Response to 24-Week Clevudine Therapy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciupe, S.; Ribeiro, R.; Nelson, P.; Perelson, A. Modeling the mechanisms of acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Theor. Biol. 2007, 247, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, M.A.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Hill, A.M.; Boehme, R.; Thomas, H.C.; McDade, H. Viral dynamics in Hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4398–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciupe, S.; Ribeiro, R.; Nelson, P.; Dusheiko, G.; Perelson, A. The role of cells refractory to productive infection in acute hepatitis B viral dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5050–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussinger, D. Liver Regeneration; De Gruyer: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, C.; Casella, G. Monte Carlo Statistical Methods, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chisari, L.G.F. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2006, 1, 23–61. [Google Scholar]
- van Thiel, D.H.; Gavaler, J.S.; Kam, I.; Francavilla, A.; Polimeno, L.; Schade, R.R.; Smith, J.; Diven, W.; Penkrot, R.J.; Starzl, T.E. Rapid Growth of an Intact Human Liver Transplanted Into a Recipient Larger Than the Donor. Gastroenterology 1987, 93, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Summers, J.; Jilbert, A.; Yang, W.; Aldrich, C.; Saputelli, J.; Litwin, S.; Toll, E.; Mason, W. Hepatocyte turnover during resolution of a transient hepadnaviral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11652–11659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.; Litwin, S.; Xu, C.; Jilbert, A. Hepatocyte turnover in transient and chronic hepadnavirus infections. J. Viral Hepat. 2007, 14, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.; Xu, C.; Low, H.; Saputelli, J.; Aldrich, C.; Scougall, C.; Grosse, A.; Colonno, R.; Litwin, S.; Jilbert, A. The amount of hepatocyte turnover that occurred during resolution of transient hepadnavirus infections was lower when virus replication was inhibited with entecavir. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1778–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeuzem, S.; de Man, R.; Honkoop, P.; Roth, W.; Schalm, S.; Schmidt, J. Dynamics of hepatitis B virus infection in vivo. J. Hepatol. 1997, 27, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chu, C.; Liaw, Y. Age-Specific Prognosis Following Spontaneous Hepatitis B e Antigen Seroconversion in Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2010, 51, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetto, M.; Giarin, M.; Oliveri, F.; Chiaberge, E.; Baldi, M.; Alfarano, A.; Serra, A.; Saracco, G.; Verme, G.; Will, H. Wild-type and e antigen-minus hepatitis B viruses and course of chronic hepatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4186–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciupe, S.; Hews, S. Mathematical models of e-antigen mediated immune tolerance and activation following prenatal HBV infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
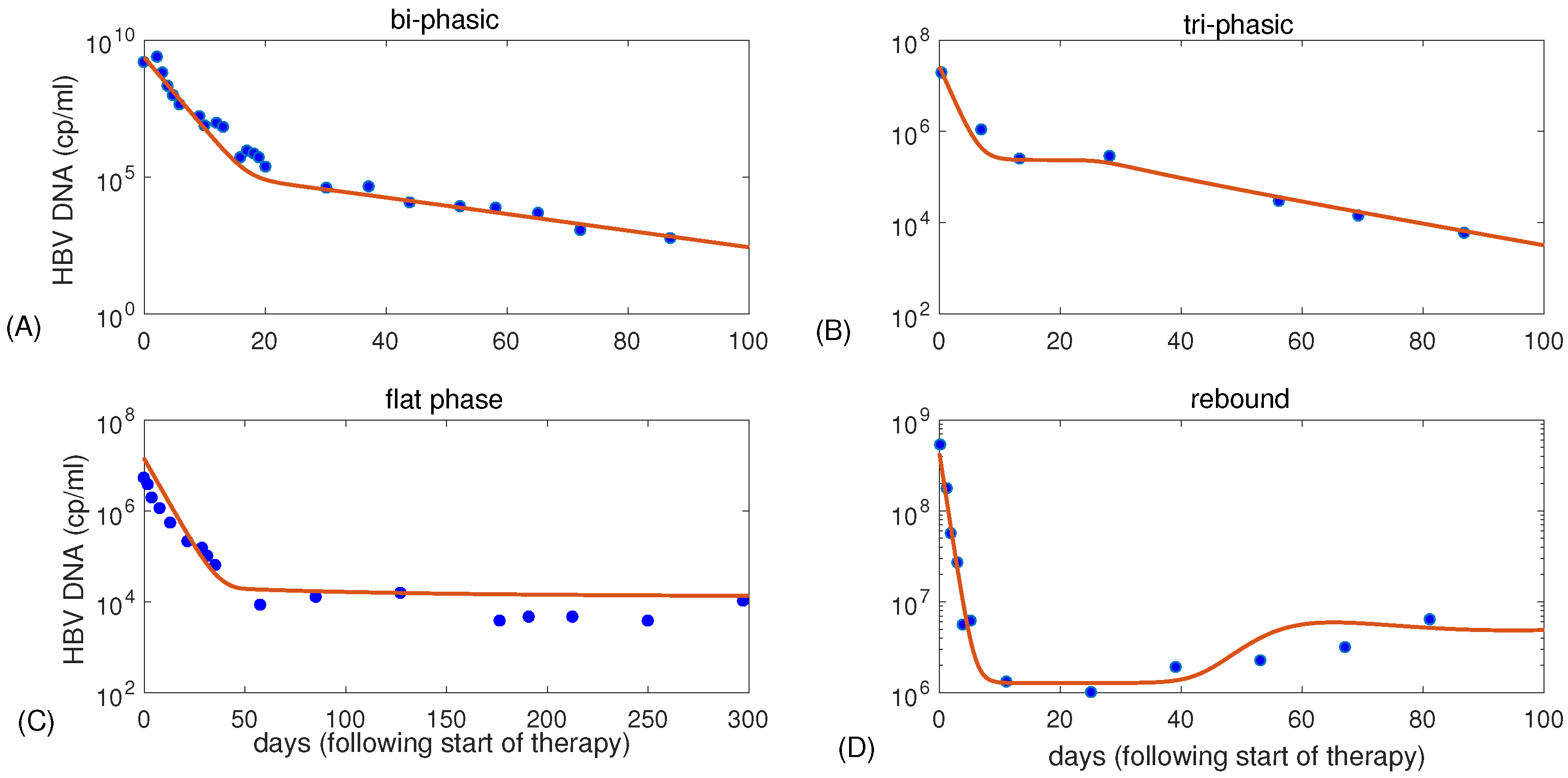
| Figure 1 | K | p | c | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | 3 | 5 | 0.07 | 100 | 0.67 | 0.5 | 0.99934 | ||
| (B) | 0.9 | 3.3 | 0.22 | 5 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.991 | ||
| (C) | 0.8 | 2.9 | 0.25 | 1.4 | 0.18 | 0.2 | 0.9988 | ||
| (D) | 0.5 | 7.2 | 0.06 | 164 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.997 |
| Parameter | Description | Value | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infectivity rate | mL/(virions × d) | [22] | |
| K | Hepatocyte-carrying capacity | cells/mL | [12] |
| p | Viral production | 100 virions/(cell × d) | [22] |
| c | Viral clearance | 0.67 | [21] |
| Efficacy of therapy in blocking infection | 0.5 | [10] | |
| Parameter | Description | Range | References |
| Uninfected cell division rate | (0,4] | [12,22] | |
| Infected cell division rate | (0,4] | [12] | |
| Infected cells killing rate | [0.01,0.1] | [10,11,12,22] | |
| Efficacy of therapy in blocking viral production | [0.2,1] | [10,12] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carracedo Rodriguez, A.; Chung, M.; Ciupe, S.M. Understanding the Complex Patterns Observed during Hepatitis B Virus Therapy. Viruses 2017, 9, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050117
Carracedo Rodriguez A, Chung M, Ciupe SM. Understanding the Complex Patterns Observed during Hepatitis B Virus Therapy. Viruses. 2017; 9(5):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050117
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarracedo Rodriguez, Andrea, Matthias Chung, and Stanca M. Ciupe. 2017. "Understanding the Complex Patterns Observed during Hepatitis B Virus Therapy" Viruses 9, no. 5: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050117
APA StyleCarracedo Rodriguez, A., Chung, M., & Ciupe, S. M. (2017). Understanding the Complex Patterns Observed during Hepatitis B Virus Therapy. Viruses, 9(5), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050117






