Structures and Functions of the Envelope Glycoprotein in Flavivirus Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
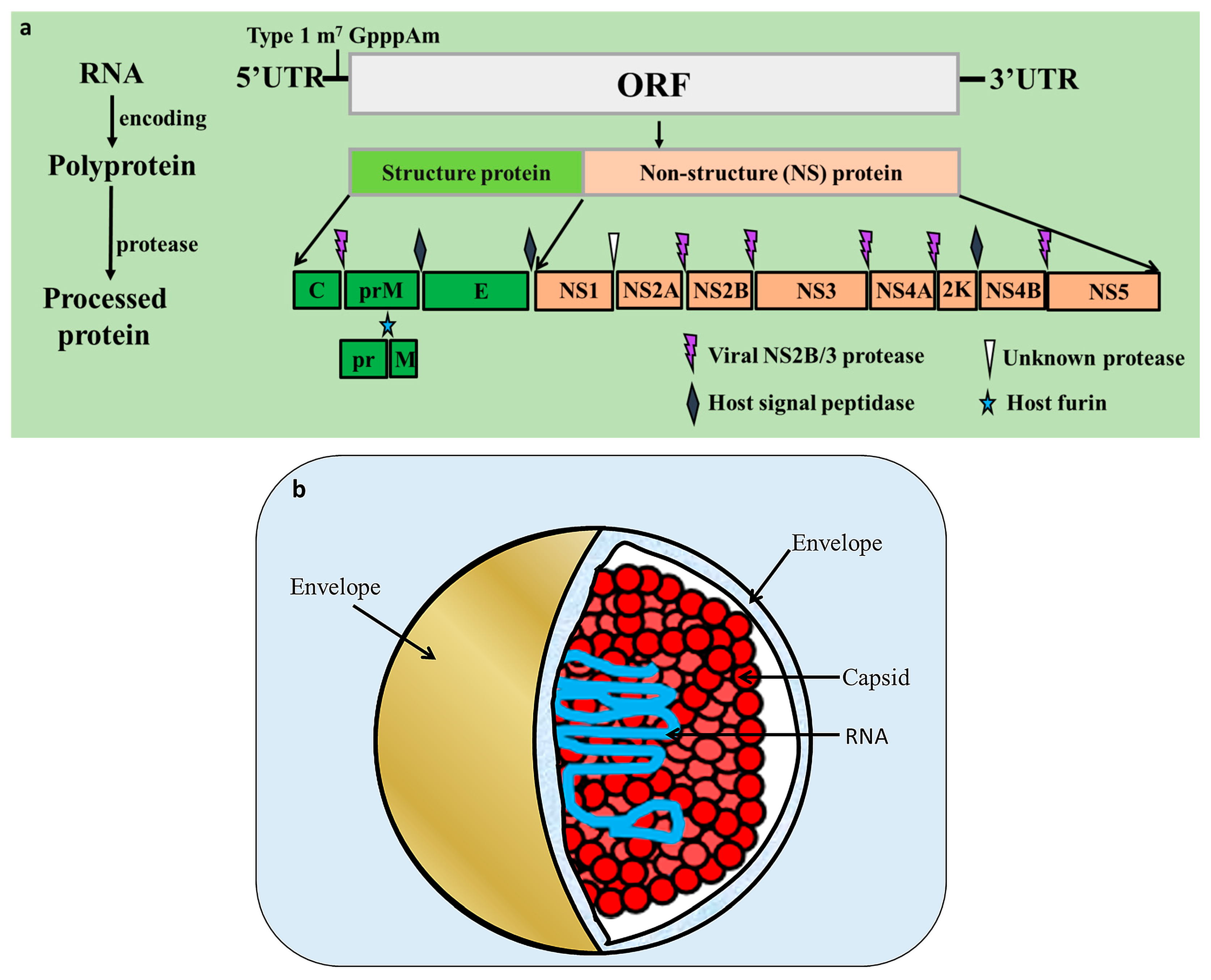
2. Flavivirus Genome and Encoded Proteins
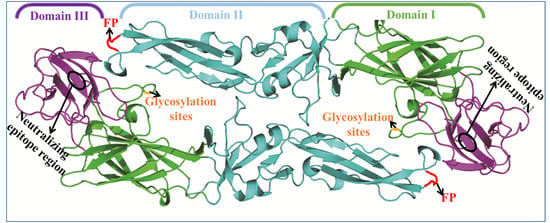
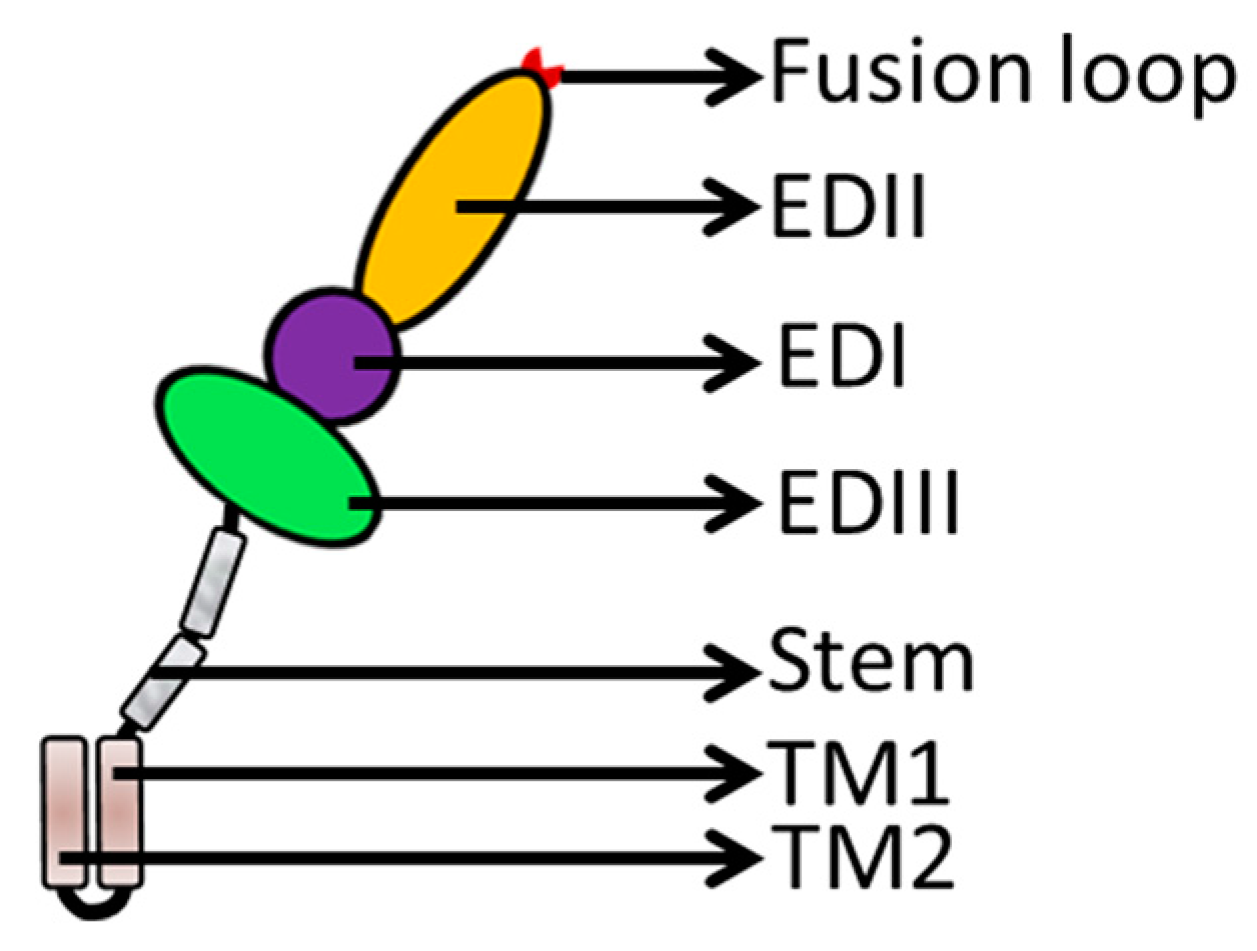
3. Flavivirus Envelope Glycoprotein Structure and its Role in Viral Infection
3.1. EDI Stabilizes the Overall Orientation of the Protein and Related to Virus Production, pH Sensitivity, and Neuroinvasiveness
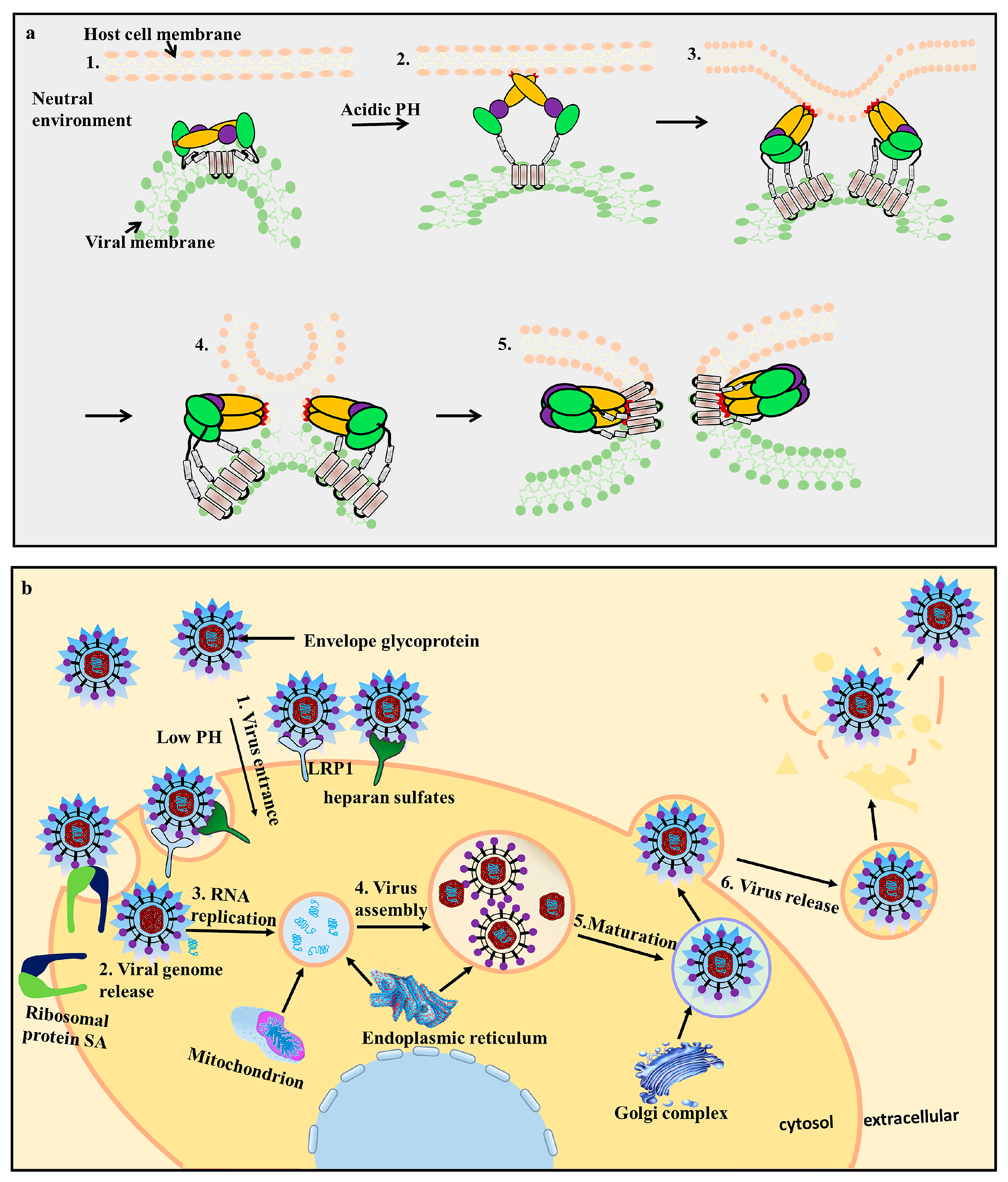
3.2. EDII Contributes to Virus-Mediated Membrane Fusion
3.3. EDIII Participates in Receptor Recognition and is Used as an Antigen
4. Envelope Proteins Applications
5. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathengtheng, L.; Burt, F.J. Use of envelope domain III protein for detection and differentiation of flaviviruses in the Free State Province, South Africa. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, C.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Yin, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Complete genomic sequence of duck flavivirus from China. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3398–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junglen, S.; Korries, M.; Grasse, W.; Wieseler, J.; Kopp, A.; Hermanns, K.; Leónjuárez, M.; Drosten, C.; Kümmerer, B.M. Host range restriction of insect-specific flaviviruses occurs at several levels of the viral life cycle. Msphere 2017, 2, e00375-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klema, V.J.; Padmanabhan, R.; Choi, K.H. Flaviviral replication complex: Coordination between RNA synthesis and 5′-RNA capping. Viruses 2015, 7, 4640–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S. Computational analysis of perturbations in the post-fusion Dengue virus envelope protein highlights known epitopes and conserved residues in the Zika virus. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, C.L.; Barrows, N.J.; Bradrick, S.S.; Pearson, J.L.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 promotes flaviviridae entry and replication. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Dowd, K.A.; Manhart, C.J.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; Durbin, A.P.; Whitehead, S.S.; Pierson, T.C. Mechanism and significance of cell type-dependent neutralization of flaviviruses. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pripuzova, N.S.; Gmyl, L.V.; Romanova, L.I.; Tereshkina, N.V.; Rogova, Y.V.; Terekhina, L.L.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Vorovitch, M.F.; Grishina, K.G.; Timofeev, A.V.; et al. Exploring of primate models of tick-borne flaviviruses infection for evaluation of vaccines and drugs efficacy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, L.; He, X.; Chen, H. The vaccine efficacy of recombinant duck enteritis virus expressing secreted E with or without PrM proteins of duck Tembusu virus. Vaccine 2014, 32, 5271–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, R.; Dejarnac, O.; Wichit, S.; Ekchariyawat, P.; Neyret, A.; Luplertlop, N.; Pereralecoin, M.; Surasombatpattana, P.; Talignani, L.; Thomas, F.; et al. Biology of Zika virus infection in human skin cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8880–8896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladner, J.T.; Wiley, M.R.; Prieto, K.; Yasuda, C.Y.; Nagle, E.; Kasper, M.R.; Reyes, D.; Vasilakis, N.; Heang, V.; Weaver, S.C.; et al. Complete genome sequences of five Zika virus isolates. Genome Announcements 2016, 4, e00377-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressanelli, S.; Stiasny, K.; Allison, S.L.; Stura, E.A.; Duquerroy, S.; Lescar, J.; Heinz, F.X.; Rey, F.A. Structure of a flavivirus envelope glycoprotein in its low-pH-induced membrane fusion conformation. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Nomaguchi, M.; Padmanabhan, R.; Markoff, L. Specific requirements for elements of the 5′ and 3′ terminal regions in flavivirus RNA synthesis and viral replication. Virology 2008, 374, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melian, E.B.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Du, F.; Owens, N.; Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Nagasaki, T.; Rudd, S.; Brault, A.C.; Bowen, R.A.; Hall, R.A.; et al. Programmed ribosomal frameshift alters expression of west nile virus genes and facilitates virus replication in birds and mosquitoes. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopezdenman, A.; Mackenzie, J. The IMPORTance of the nucleus during flavivirus replication. Viruses 2017, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aptesengupta, S.; Sirohi, D.; Kuhn, R.J. Coupling of replication and assembly in flaviviruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 9, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Jing, Y.; Ping, L.; Rong, J.; Yang, X.; Zhen, F.F.; Chen, H.; Cao, S. Induction of antigen-specific immune responses in mice by recombinant baculovirus expressing premembrane and envelope proteins of West Nile virus. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roby, J.A.; Setoh, Y.X.; Hall, R.A.; Khromykh, A.A. Post-translational regulation and modifications of flavivirus structural proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96 Pt 7, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.G.; Wu, S.C. Glutamic acid at residue 125 of the prM helix domain interacts with positively charged amino acids in E protein domain II for Japanese encephalitis virus-like-particle production. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8386–8396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiasny, K.; Fritz, R.; Pangerl, K.; Heinz, F.X. Molecular mechanisms of flavivirus membrane fusion. Amino Acids 2011, 41, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazevic, J.; Rouha, H.; Bradt, V.; Heinz, F.X.; Stiasny, K. Membrane anchors of the structural flavivirus proteins and their role in virus assembly. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6365–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagripanti, J.L.; Mazumder, R.; Wu, H.H. Amino acid sites in flavivirus e proteins useful for development of diagnostics and vaccines. U.S. Patent 7,943,148, 17 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chávez, J.H.; Silva, J.R.; Amarilla, A.A.; Figueiredo, L.T.M. Domain III peptides from flavivirus envelope protein are useful antigens for serologic diagnosis and targets for immunization. Biol. J. Int. Assoc. Biol. Stand. 2010, 38, 613–618. [Google Scholar]
- Fahimi, H.; Allahyari, H.; Hassan, Z.M.; Sadeghizadeh, M. Dengue virus type-3 envelope protein domain III; expression and immunogenicity. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2014, 17, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brecher, M.; Chen, H.; Liu, B.; Banavali, N.K.; Jones, S.A.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Kramer, L.D.; Li, H. Novel broad spectrum inhibitors targeting the flavivirus methyltransferase. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, B.; Shi, P.Y. Flavivirus methyltransferase: A novel antiviral target. Antivir. Res. 2008, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.P.; Wu, C.W.; Tsao, Y.P.; Kuo, T.W.; Lou, Y.C.; Lin, C.W.; Wu, S.C.; Cheng, J.W. Structural basis of a Flavivirus recognized by its neutralizing antibody: Solution structure of the domain III of the Japanese Encephalitis virus envelope protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46007–46013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.T.; Liao, M.Y.; Chiu, C.Y.; Shen, W.F.; Chiu, C.Y.; Cheng, P.C.; Chang, G.J.J.; Wu, H.C. Generation of monoclonal antibodies against Dengue virus type 4 and identification of enhancing epitopes on envelope protein. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.A.; Liu, D.; Holbrook, M.R.; Shope, R.E.; Barrett, A.D.T.; Fox, R.O. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of Langat virus envelope protein domain III. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 59, 1049–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherrier, M.V.; Kaufmann, B.; Nybakken, G.E.; Lok, S.M.; Warren, J.T.; Chen, B.R.; Nelson, C.A.; Kostyuchenko, V.A.; Holdaway, H.A.; Chipman, P.R. Structural basis for the preferential recognition of immature flaviviruses by a fusion-loop antibody. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 3269–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, D.E.; May, F.J.; Gandham, S.H.; Anderson, A.; Von Lindern, J.J.; Beasley, D.W.; Barrett, A.D.; Gorenstein, D.G. Structure of yellow fever virus envelope protein domain III. Virology 2011, 394, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modis, Y.; Ogata, S.; Clements, D.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of the Dengue virus envelope protein after membrane fusion. Nature 2004, 427, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goo, L.; Vanblargan, L.A.; Dowd, K.A.; Diamond, M.S.; Pierson, T.C. A single mutation in the envelope protein modulates flavivirus antigenicity, stability, and pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzinek, J.K.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Goh, E.; Huber, R.G.; Panzade, S.; Verma, C.; Bond, P.J. Characterizing the conformational landscape of flavivirus fusion peptides via simulation and experiment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, R.; Blazevic, J.; Taucher, C.; Pangerl, K.; Heinz, F.X.; Stiasny, K. The unique transmembrane hairpin of flavivirus fusion protein e is essential for membrane fusion. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4377–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langosch, D.; Hofmann, M.; Ungermann, C. The role of transmembrane domains in membrane fusion. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2007, 64, 850–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, F.X.; Stiasny, K. Flaviviruses and their antigenic structure. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 55, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostyuchenko, V.A.; Lim, E.X.Y.; Zhang, S.; Fibriansah, G.; Ng, T.S.; Ooi, J.S.G.; Jian, S.; Lok, S.M. Structure of the thermally stable Zika virus. Nature 2016, 533, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Sheng, Z.Z.; Huang, B.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Yuan, X.; Qin, Z.; Wang, D.; Chakravarty, S.; Li, F.; et al. Structural, antigenic, and evolutionary characterizations of the envelope protein of newly emerging duck Tembusu virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, V.C.; Abimansour, J.; Nelson, C.A.; Fremont, D.H. Crystal structure of the Japanese encephalitis virus envelope protein. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, R.; Stiasny, K.; Heinz, F.X. Identification of specific histidines as pH sensors in flavivirus membrane fusion. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fibriansah, G.; Ng, T.S.; Kostyuchenko, V.A.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Wang, J.; Lok, S.M. Structural changes in Dengue virus when exposed to a temperature of 37 C. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.C.; Chiu, H.C.; Chen, L.K.; Chang, G.J.; Chiou, S.S. Formalin inactivation of Japanese encephalitis virus vaccine alters the antigenicity and immunogenicity of a neutralization epitope in envelope protein domain III. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.C. Viral membrane fusion. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossenta, M.; Marchese, S.; Poggianella, M.; Slon Campos, J.L.; Burrone, O.R. Role of N-glycosylation on Zika virus E protein secretion, viral assembly and infectivity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 492, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Shaozhou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Qiu, N.; Meng, R.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against duck Tembusu virus E protein: An antigen-capture ELISA for the detection of Tembusu virus infection. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Bovshik, E.I.; Maillard, R.; Gromowski, G.D.; Volk, D.E.; Schein, C.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Gorenstein, D.G.; Lee, J.C.; Barrett, A.D.; et al. Role of BC loop residues in structure, function and antigenicity of the West Nile virus envelope protein receptor-binding domain III. Virology 2010, 403, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crill, W.D.; Chang, G.J. Localization and characterization of flavivirus envelope glycoprotein cross-reactive epitopes. J. Virol. 2005, 78, 13975–13986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, S.S.; Fan, Y.C.; Crill, W.D.; Chang, R.Y.; Chang, G.J. Mutation analysis of the cross-reactive epitopes of Japanese encephalitis virus envelope glycoprotein. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93 Pt 6, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modis, Y.; Ogata, S.; Clements, D.; Harrison, S.C. A ligand-binding pocket in the Dengue virus envelope glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6986–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Lobigs, M. E Protein domain III determinants of yellow fever virus 17D vaccine strain enhance binding to glycosaminoglycans, impede virus spread, and attenuate virulence. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6024–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, B.D.; Stanton, R.A.; Schinazi, R.F. Predicting Zika virus structural biology: Challenges and opportunities for intervention. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2016, 24, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariwa, H.; Murata, R.; Totani, M.; Yoshii, K.; Takashima, I. Increased pathogenicity of West Nile virus (WNV) by glycosylation of envelope protein and seroprevalence of wnv in wild birds in Far Eastern Russia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 7144–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, S.L.; Pierson, T.C.; Sanchez, M.D.; Ahmed, A.A.; Murtadha, M.M.; Doms, R.W. N-linked glycosylation of West Nile virus envelope proteins influences particle assembly and infectivity. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13262–13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.I.; Lee, Y.M. Zika virus: An emerging flavivirus. J. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, D.W.; Whiteman, M.C.; Zhang, S.; Huang, C.Y.; Schneider, B.S.; Smith, D.R.; Gromowski, G.D.; Higgs, S.; Kinney, R.M.; Barrett, A.D. Envelope protein glycosylation status influences mouse neuroinvasion phenotype of genetic lineage 1 West Nile virus strains. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8339–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fibriansah, G.; Tan, J.L.; Smith, S.A.; de, A.R.; Ng, T.S.; Kostyuchenko, V.A.; Jadi, R.S.; Kukkaro, P.; de Silva, A.M.; Crowe, J.E.; et al. A highly potent human antibody neutralizes Dengue virus serotype 3 by binding across three surface proteins. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.A.; de Alwis, A.R.; Kose, N.; Harris, E.; Ibarra, K.D.; Kahle, K.M.; Pfaff, J.M.; Xiang, X.; Doranz, B.J.; de Silva, A.M.; et al. The potent and broadly neutralizing human Dengue virus-specific monoclonal antibody 1C19 reveals a unique cross-reactive epitope on the bc loop of domain II of the envelope protein. mBio 2012, 4, 00873-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watterson, D.; Kobe, B.; Young, P.R. Residues in domain III of the Dengue virus envelope glycoprotein involved in cell-surface glycosaminoglycan binding. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93 Pt 1, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereralecoin, M.; Meertens, L.; Carnec, X.; Amara, A. Flavivirus Entry Receptors: An Update. Viruses 2014, 6, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messer, W.B.; de Alwis, R.; Yount, B.L.; Royal, S.R.; Huynh, J.P.; Smith, S.A.; Jr, C.J.; Doranz, B.J.; Kahle, K.M.; Pfaff, J.M.; et al. Dengue virus envelope protein domain I/II hinge determines long-lived serotype-specific dengue immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1939–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widman, D.G.; Baric, R.S. Dengue virus envelope protein domain I/II hinge: A key target for Dengue virus vaccine design? Expert Rev. Vaccines 2014, 14, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta, V.; Toledo, P.; Fleitas, N.; Martín, A.; Pupo, D.; Yero, A.; Sarría, M.; Sánchez, A.; Besada, V.; Ramos, Y.; et al. Receptor-activated human α2-macroglobulin interacts with the envelope protein of Dengue virus and protects virions from temperature-induced inactivation through multivalent binding. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, S.L.; Schalich, J.; Stiasny, K.; Mandl, C.W.; Heinz, F.X. Mutational evidence for an internal fusion peptide in flavivirus envelope protein E. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4268–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Song, J.; Lu, X.; Deng, Y.Q.; Musyoki, A.M.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Song, H.; Haywood, J.; et al. Structures of the Zika virus envelope protein and its complex with a flavivirus broadly protective antibody. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockstroh, A.; Barzon, L.; Pacenti, M.; Palù, G.; Niedrig, M.; Ulbert, S. Recombinant envelope-proteins with mutations in the conserved fusion loop allow specific serological diagnosis of dengue-infections. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, U.; Tyagi, P.; Swaminathan, S.; Khanna, N. Virus-like particles displaying envelope domain III of Dengue virus type 2 induce virus-specific antibody response in mice. Vaccine 2013, 31, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcauley, A.J.; Torres, M.; Plante, J.A.; Huang, C.Y.H.; Bente, D.A.; Beasley, D.W.C. Recovery of West Nile virus envelope protein domain III chimeras with altered antigenicity and mouse virulence. J. Virol. 2016, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, P.; Xin, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, G.; Wang, W. Antiviral activity of peptide inhibitors derived from the protein E stem against Japanese encephalitis and Zika viruses. Antivir. Res. 2017, 141, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, K.; Gromowski, G.D.; Li, L.; Barrett, A.D. Characterization of a dengue type-specific epitope on dengue 3 virus envelope protein domain III. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2249–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehrig, J.T.; Butrapet, S.; Liss, N.M.; Bennett, S.L.; Luy, B.E.; Childers, T.; Boroughs, K.L.; Stovall, J.L.; Calvert, A.E.; Blair, C.D.; et al. Mutation of the Dengue virus type 2 envelope protein heparan sulfate binding sites or the domain III lateral ridge blocks replication in Vero cells prior to membrane fusion. Virology 2013, 441, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta, V.; Chinea, G.; Fleitas, N.; Sarría, M.; Sánchez, J.; Toledo, P.; Padrón, G. Characterization of the interaction of domain III of the envelope protein of Dengue virus with putative receptors from CHO cells. Virus Res. 2008, 137, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Bai, X.; Meng, R.; Shaozhou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Hua, R.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y. Identification of a new broadly cross-reactive epitope within domain III of the duck Tembusu virus e protein. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, K.A.; Pierson, T.C. Antibody-mediated neutralization of flaviviruses: A reductionist view. Virology 2011, 411, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, M.G.; Hermida, L.; Bernardo, L.; Ramirez, R.; Guillén, G. Domain III of the envelope protein as a dengue vaccine target. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2014, 9, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.L.; Wahala, W.M.; Orozco, S.; de Silva, A.M.; Harris, E. Antibodies targeting Dengue virus envelope domain III are not required for serotype-specific protection or prevention of enhancement in vivo. Virology 2012, 429, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcíamachorro, J.; Lópezgonzález, M.; Barriosrojas, O.; Fernándezpomares, C.; Sandovalmontes, C.; Santosargumedo, L.; Villegassepúlveda, N.; Gutiérrezcastañeda, B.; Cedillobarrón, L. DENV-2 subunit proteins fused to CR2 receptor-binding domain (P28)-induces specific and neutralizing antibodies to the Dengue virus in mice. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2013, 9, 2326–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.J.; Rajamanonmani, R.; Li, J.; Bhuvanakantham, R.; Lescar, J.; Ng, M.L. Inhibition of West Nile virus entry by using a recombinant domain III from the envelope glycoprotein. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86 Pt 2, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, R.; Kar, K.; Anthony, K.; Gould, L.H.; Ledizet, M.; Fikrig, E.; Marasco, W.A.; Koski, R.A.; Modis, Y. Crystal structure of West Nile virus envelope glycoprotein reveals viral surface epitopes. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11000–11008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Wen, K.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, L.; Pan, Y.; Yu, L.; Di, B.; Chen, Y. Mapping of the B cell neutralizing epitopes on ED III of envelope protein from Dengue virus. Chin. J. Virol. 2015, 31, 665. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.L.; Guan, C.Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, X.M.; Feng, X.L.; Zhou, B.; Su, X.D.; Chen, P.Y. Fine mapping of a linear epitope on EDIII of Japanese encephalitis virus using a novel neutralizing monoclonal antibody. Virus Res. 2014, 179, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathengtheng, L.; Burt, F.J. Development of immunoassays for detection of flaviviruses in the Free State Province, South Africa. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 21, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.; Desprès, P.; Paulous, S.; Vanhomwegen, J.; Lowenski, S.; Nowotny, N.; Durand, B.; Garnier, A.; Blaiseboisseau, S.; Guitton, E.; et al. A High-performance multiplex immunoassay for serodiagnosis of flavivirus-associated neurological diseases in horses. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 678084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaycheva, L.; Nickells, M.; Droll, D.A.; Chambers, T.J. Neuroblastoma cell-adapted yellow fever virus: Mutagenesis of the E protein locus involved in persistent infection and its effects on virus penetration and spread. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86 Pt 2, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, G.; Teng, Q.; Yu, L.; Wu, X.; Li, Z. Development of a blocking ELISA for detection of serum neutralizing antibodies against newly emerged duck Tembusu virus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e53026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.C.; Lv, R.; Chen, X.D.; Liu, M.; Hua, R.H.; Zhang, Y. Detection of specific antibodies against tembusu virus in ducks by use of an e protein-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, Z.W. Immunogenicity and antigenicity of recombinant yellow fever virus envelope domain III as a subunit vaccine. Lett. Biotechnol. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.C.; Yu, C.H.; Lin, C.W.; Chu, I.M. The domain III fragment of Japanese encephalitis virus envelope protein: Mouse immunogenicity and liposome adjuvanticity. Vaccine 2003, 21, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershova, A.S.; Gra, O.A.; Lyaschuk, A.M.; Grunina, T.M.; Tkachuk, A.P.; Bartov, M.S.; Savina, D.M.; Sergienko, O.V.; Galushkina, Z.M.; Gudov, V.P.; et al. Recombinant domains III of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus envelope protein in combination with dextran and CpGs induce immune response and partial protectiveness against TBE virus infection in mice. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, M.S.; Pierson, T.C.; Fremont, D.H. The structural immunology of antibody protection against West Nile virus. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 225, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonsopadilla, J.; de Oya, N.J.; Blázquez, A.B.; Escribanoromero, E.; Escribano, J.M.; Saiz, J.C. Recombinant West Nile virus envelope protein E and domain III expressed in insect larvae protects mice against West Nile disease. Vaccine 2011, 29, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.D.; Pierson, T.C.; Mcallister, D.; Hanna, S.L.; Puffer, B.A.; Valentine, L.E.; Murtadha, M.M.; Hoxie, J.A.; Doms, R.W. Characterization of neutralizing antibodies to West Nile virus. Virology 2005, 336, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabierski, S.; Barzon, L.; Papa, A.; Niedrig, M.; Bramson, J.L.; Richner, J.M.; Palù, G.; Diamond, M.S.; Ulbert, S. Distinguishing West Nile virus infection using a recombinant envelope protein with mutations in the conserved fusion-loop. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.H.; Deng, Y.Q.; Yu, X.J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, H.J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, D.P.; Li, X.F.; Zhu, S.Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Characterization of a novel dengue serotype 4 virus-specific neutralizing epitope on the envelope protein domain III. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Q.; Qiu, L.W.; Chen, Y.; Wen, K.; Cai, J.P.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.X.; Li, J.; Hu, D.M.; Huang, Y.F.; et al. Dengue virus envelope domain III immunization elicits predominantly cross-reactive, poorly neutralizing antibodies localized to the AB loop: Implications for dengue vaccine design. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94 Pt 10, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanstrom, J.A.; Plante, J.A.; Plante, K.S.; Young, E.F.; Mcgowan, E.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Widman, D.G.; Heise, M.T.; de Silva, A.M.; Baric, R.S. Dengue virus envelope dimer epitope monoclonal antibodies isolated from dengue patients are protective against Zika virus. mBio 2016, 7, e01123-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, A.; Ali, S.; Ahamad, S.; Malik, M.Z.; Ishrat, R. From ZikV genome to vaccine: In silico approach for the epitopetopede peptide vaccine against Zika virus envelope glycoprotein. Immunology 2016, 149, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.M. In silico modeling and immunoinformatics probing disclose the epitope based peptide vaccine against Zika virus envelope glycoprotein. Indian J. Pharm. Biol. Res. 2014, 2, 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.J.; Bhattacharya, R.; Scheuermann, R.H.; Pickett, B.E. Identification of diagnostic peptide regions that distinguish Zika virus from related mosquito-borne Flaviviruses. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, B.; Rossmann, M.G. Molecular mechanisms involved in the early steps of flavivirus cell entry. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, L.H.; Klein, D.E.; Schmidt, A.G.; Peña, J.M.; Harrison, S.C. Sequential conformational rearrangements in flavivirus membrane fusion. eLife 2014, 3, e04389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brien, J.D. Genotype-specific neutralization and protection by antibodies against Dengue virus type 3. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10630–10643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouvinski, A.; Guardadocalvo, P.; Barbaspaeth, G.; Duquerroy, S.; Vaney, M.C.; Kikuti, C.M.; Sanchez, M.E.N.; Dejnirattisai, W.; Wongwiwat, W.; Haouz, A.; et al. Recognition determinants of broadly neutralizing human antibodies against Dengue viruses. Nature 2015, 520, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouvinski, A.; Dejnirattisai, W.; Guardadocalvo, P.; Vaney, M.C.; Sharma, A.; Duquerroy, S.; Supasa, P.; Wongwiwat, W.; Haouz, A.; Barbaspaeth, G.; et al. Covalently linked Dengue virus envelope glycoprotein dimers reduce exposure of the immunodominant fusion loop epitope. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejnirattisai, W.; Wongwiwat, W.; Supasa, S.; Zhang, X.; Dai, X.; Rouvinski, A.; Jumnainsong, A.; Edwards, C.; Quyen, N.T.H.; Duangchinda, T.; et al. A new class of highly potent, broadly neutralizing antibodies isolated from viremic patients infected with Dengue virus. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, M.R.; Dowd, K.A.; Engle, M.; Tesh, R.B.; Johnson, S.; Pierson, T.C.; Diamond, M.S. Poorly neutralizing cross-reactive antibodies against the fusion loop of West Nile virus envelope protein protect in vivo via Fcgamma receptor and complement-dependent effector mechanisms. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11567–11580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zidane, N.; Dussart, P.; Bremand, L.; Villani, M.E.; Bedouelle, H. Thermodynamic stability of domain III from the envelope protein of flaviviruses and its improvement by molecular design. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2013, 26, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejnirattisai, W.; Supasa, P.; Wongwiwat, W.; Rouvinski, A.; Barba-Spaeth, G.; Duangchinda, T.; Sakuntabhai, A.; Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; Malasit, P.; Rey, F.A.; et al. Dengue virus sero-cross-reactivity drives antibody-dependent enhancement of infection with Zika virus. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Structures | Viruses | Strains | Gen Bank Accession Numbers | Application Types | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDIII | YFV | 17D strain | JX949181.1 | vaccine | [87] |
| JEV | vaccine | [88] | |||
| TBEV | vaccine | [89] | |||
| TMUV | FX2010 | ELISA | [85] | ||
| WNV | therapeutic | [78,90] | |||
| E and EDIII | NY99-382 | AF196835 | vaccine | [91] | |
| E | mAb | [92] | |||
| New York 1999 strain | FJ151394 | diagnostic reagent | [93] | ||
| EDIII | DENV | B5/ H241 | AF289029/U18433 | neutralizing epitopes | [94] |
| Hawaii/New Guinea-C/Guanxi-80-2/H241 | vaccine | [95] | |||
| EDI/EDII hinge | rDENV-4 | 1683917 | vaccine | [61] | |
| E | DENV-1 WestPac74 | mAb | [96] | ||
| DENV-2 S-16803 | |||||
| DENV-3 CH-53489 | |||||
| DENV-4 TVP-376 | |||||
| ZIKV H/PF/2013 | |||||
| ZIKV PRVABC59 | |||||
| ZIKV | H/PF/2013 | KJ776791.2 | peptide drugs | [69] | |
| 50 strains | peptide vaccine | [97,98] | |||
| 5IRE | diagnostic sites | [99] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Jia, R.; Shen, H.; Wang, M.; Yin, Z.; Cheng, A. Structures and Functions of the Envelope Glycoprotein in Flavivirus Infections. Viruses 2017, 9, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110338
Zhang X, Jia R, Shen H, Wang M, Yin Z, Cheng A. Structures and Functions of the Envelope Glycoprotein in Flavivirus Infections. Viruses. 2017; 9(11):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110338
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xingcui, Renyong Jia, Haoyue Shen, Mingshu Wang, Zhongqiong Yin, and Anchun Cheng. 2017. "Structures and Functions of the Envelope Glycoprotein in Flavivirus Infections" Viruses 9, no. 11: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110338
APA StyleZhang, X., Jia, R., Shen, H., Wang, M., Yin, Z., & Cheng, A. (2017). Structures and Functions of the Envelope Glycoprotein in Flavivirus Infections. Viruses, 9(11), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110338