High Rate of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV) Infections in Wild Chimpanzees in Northeastern Gabon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
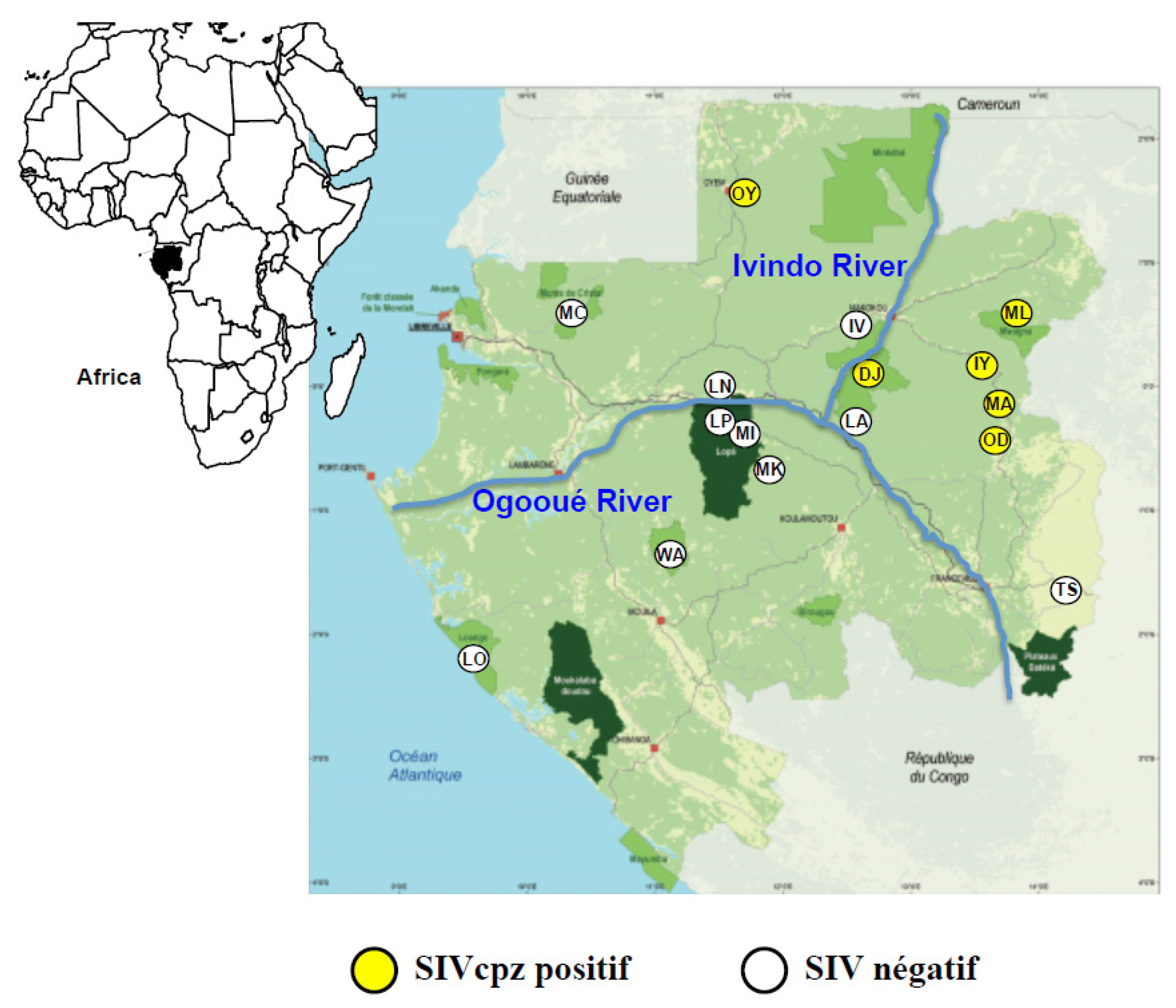
2.1. Study Sites and Chimpanzee Faecal Samples Collection
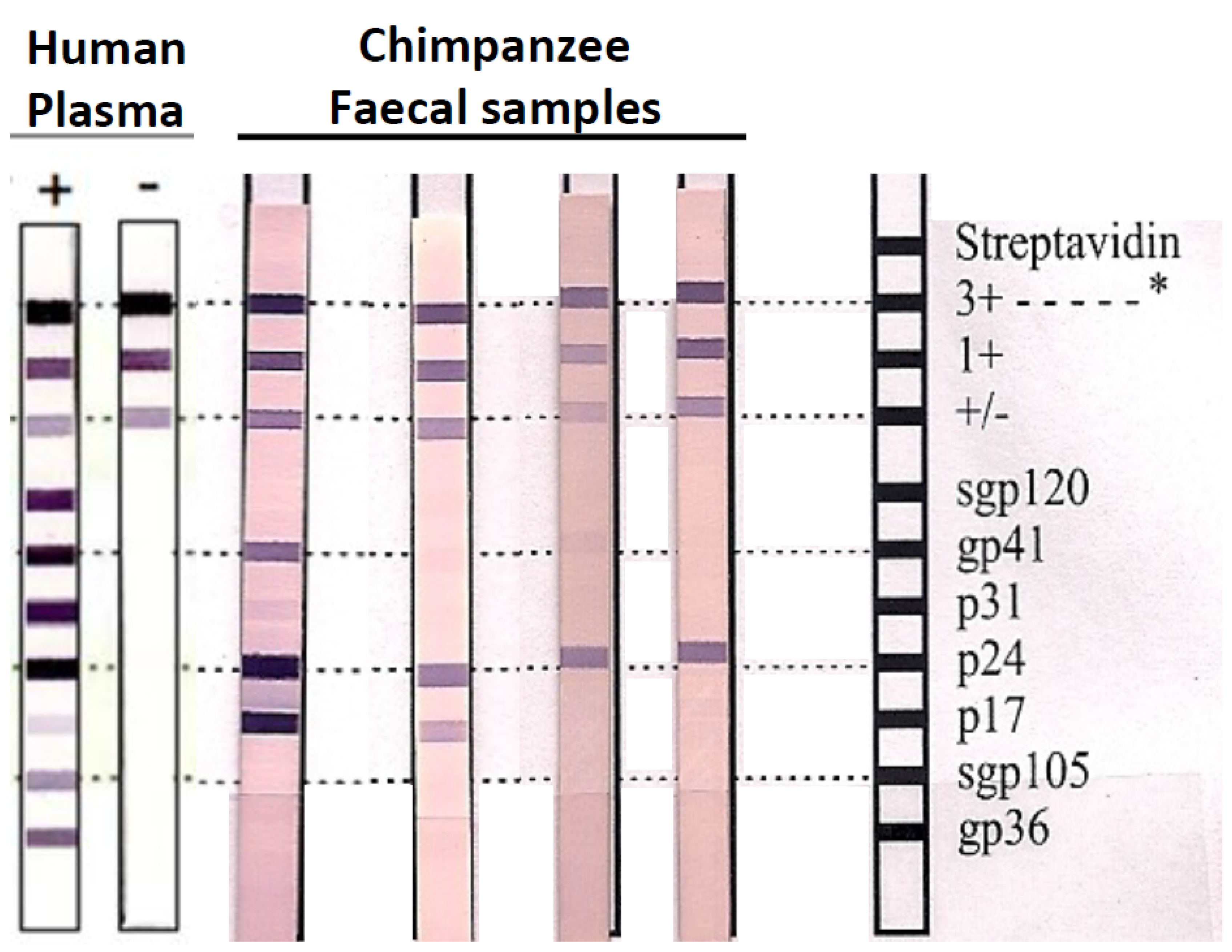
2.2. Detection of SIVcpz Antibodies in Chimpanzee Faecal Samples
2.3. DNA and RNA Extraction from Chimpanzee Faecal Samples
2.4. Species Determinations
2.5. Number of Collected Individuals
| HIV Antibody Positive Profile | HIV Antibody Negative Profile | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collection Sites | Faecal Samples Collected | SIVcpz Antibody Positive Samples | Estimated Number Of Individuals Collected | Samples Successfully Genotyped/not Genotyped | Prevalence Of SIVcpz Antibody Positive (%) Genotyped Animals (Individuals) | vRNA Positive Genotyped Animals pol / envA | SIVcpz Antibody Positive Samples | Number Of vRNA Positive Samples pol / envB | Antibody Negative Samples Tested By PCR | Number Of Individuals Tested By PCR | Number Of vRNA Positive Individuals pol / envC | Samples Tested By PCR | Number Of vRNA Positive Samples pol / envD |
| LP | 54 | 0 | |||||||||||
| MI | 194 | 0 | |||||||||||
| TS | 13 | 0 | |||||||||||
| MK | 11 | 0 | |||||||||||
| LA | 16 | 0 | |||||||||||
| MA | 608 | 263 (44%) | 224 | 504/104 | 103 (46%) | 23/18 | 44 | 6/4 | 146 | 50 | 5/6 | 23 | 2/1 |
| MC | 33 | 0 | |||||||||||
| IV | 19 | 0 | |||||||||||
| DJ | 40 | 8 (20%) | |||||||||||
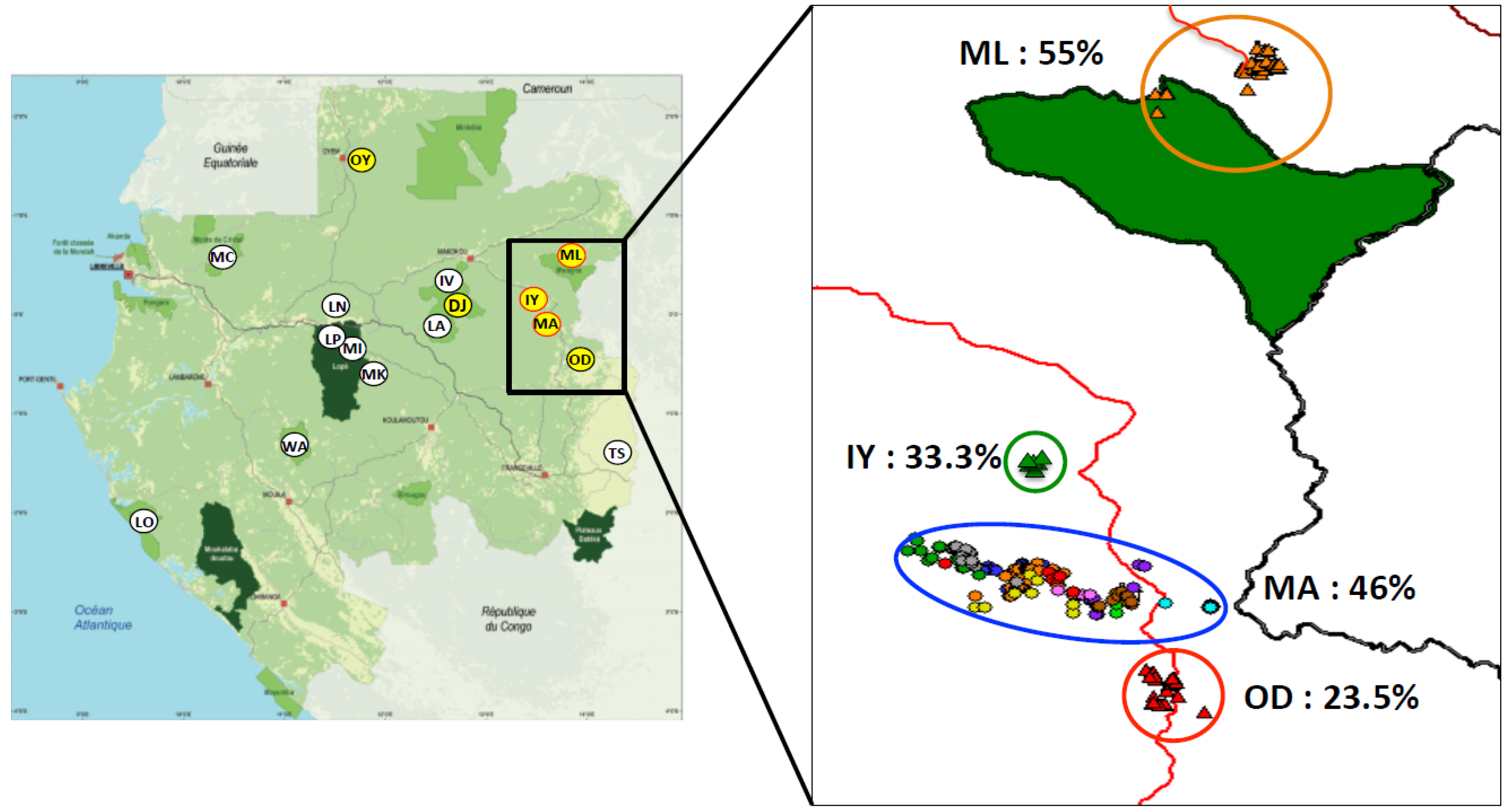
| ML | 181 | 85 (47%) | 19 | 85/96 | 12 (63.5%) | 5/1 | 47 | 5/2 | |||||
| WA | 18 | 0 | |||||||||||
| LN | 12 | 0 | |||||||||||
| OY | 78 | 1 (1.3%) | |||||||||||
| IY | 31 | 18 (58%) | 12 | 25/6 | 4 (33.3%) | 1 / 0 | |||||||
| OD | 39 | 5 (12.8%) | 17 | 35/4 | 4 (23.5%) | 0 | |||||||
| LO | 111 | 0 | |||||||||||
| Total | 1458 | 380 (26,1) | 272 | 649/210 | 123 (41.6%) | 29/19 | 91 | 11/6 | 146 | 50 | 5/6 | 23 | 2/1 |
2.6. SIVcpz Partial pol, env and gp41-nef PCR Amplifications
2.7. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.8. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. SIV Infection in Wild Chimpanzees in Gabon
3.1.1. Crude SIV Prevalence Rates in Wild Chimpanzee Faecal Samples
3.1.2. Adjusted SIV Prevalence Rates According to the Number of Collected Individuals
| IDa | Field Number | Date of Sampling | SIV Serological Testb | GPS Points | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples collected during different field missions | MA-ID-010 | Gab-0902 | 07/04/11 | neg | S00°08.276 | E013°38.105 |
| Gab-1001 | 17/05/11 | pos | 8 Km to the west from MA village | |||
| MA-ID-028 | Gab-1012 | 20/05/11 | pos | 8 Km to the west from MA village | ||
| Gab-2092 | 08/07/12 | neg | S00°08.170 | E013°37.466 | ||
| MA-ID-036 | Gab-1227 | 04/11/11 | pos | S00°07.707 | E013°31.226 | |
| Gab-1228 | 04/11/11 | pos | S00°07.707 | E013°31.226 | ||
| Gab-1229 | 04/11/11 | pos | S00°07.707 | E013°31.226 | ||
| Gab-1230 | 04/11/11 | pos | S00°07.707 | E013°31.226 | ||
| Gab-1510 | 11/03/12 | pos | S00°06.500 | E013°31.722 | ||
| Gab-1513 | 11/03/12 | pos | S00°06.397 | E013°31.777 | ||
| Gab-1515 | 11/03/12 | neg | S00°06.397 | E013°31.777 | ||
| Gab-1517 | 11/03/12 | pos | S00°06.335 | E013°31. 788 | ||
| Gab-1518 | 11/03/12 | pos | S00°06.264 | E013°31.792 | ||
| MA-ID-054 | Gab-0923 | 07/04/11 | neg | S00°08.093 | E013°36.047 | |
| Gab-0924 | 07/04/11 | neg | S00°08.093 | E013°36.047 | ||
| Gab-1283 | 01/12/11 | pos | S00°07.800 | E013°35.962 | ||
| Gab-1288 | 01/12/11 | pos | S00°07.890 | E013°36.116 | ||
| Gab-1289 | 01/12/11 | pos | S00°07.891 | E013°36.128 | ||
| Gab-1295 | 01/12/11 | pos | S00°08.002 | E013.36.262 | ||
| Gab-1321 | 03/12/11 | pos | S00°08.832 | E013°35.001 | ||
| MA-ID-055 | Gab-0926 | 07/04/11 | neg | S00°08.193 | E013°34.907 | |
| Gab-1293 | 01/12/11 | pos | S00°07.992 | E013°36.273 | ||
| Gab-1294 | 01/12/11 | pos | S00°07.986 | E013°36.264 | ||
| MA-ID-056 | Gab-0922 | 07/04/11 | neg | S00°08.093 | E013°36.047 | |
| Gab-1297 | 01/12/11 | pos | S00°08.086 | E013°36.337 | ||
| MA-ID-058 | Gab-0915 | 13/04/11 | neg | S00°07.276 | E013°35.538 | |
| Gab-0929 | 08/04/11 | neg | S00°08.552 | E013°34.845 | ||
| Gab-1314 | 02/12/11 | pos | S00°08.821 | E013°36.022 | ||
| Gab-2488 | 06/05/13 | pos | S00°08.790 | E013°38.036 | ||
| Gab-2489 | 06/05/13 | pos | S00°08.790 | E013°38.036 | ||
| MA-ID-077 | Gab-0919 | 07/04/11 | neg | S00°08.046 | E013°36.073 | |
| Gab-1301 | 02/12/11 | pos | S00°07.910 | E013°36.707 | ||
| Samples collected during the same field missions | MA-ID-081 | Gab-0905 | 08/04/11 | pos | S00°08.276 | E013°38.105 |
| Gab-0989 | 04/05/11 | neg | 8 Km to the west from MA village | |||
| Gab-1010 | 20/05/11 | neg | 8 Km to the west from MA village | |||
| Gab-1011 | 20/05/11 | neg | 8 Km to the west from MA village | |||
| Gab-1016 | 20/05/11 | pos | 8 Km to the west from MA village | |||
| Gab-1018 | 20/05/11 | neg | 8 Km to the west from MA village | |||
| Gab-2486 | 06/05/13 | neg | S00°08.790 | E013°38.036 | ||
| MA-ID-199 | Gab-2294 | 19/02/13 | pos | S00°11.355 | E013°48.664 | |
| Gab-2305 | 04/03/13 | neg | S00°11.352 | E013°40.754 | ||
| Gab-2334 | 04/03/13 | pos | S00°11.239 | E013°40.902 | ||
| MA-ID-025 | Gab-0977 | 02/05/11 | pos | 3 Km to the southwest from MA village | ||
| Gab-0978 | 02/05/11 | pos | 3 Km to the southwest from MA village | |||
| Gab-0981 | 02/05/11 | neg | 3 Km to the southwest from MA village | |||
| MA-ID-044 | Gab-1275 | 01/12/11 | pos | S00°07.720 | E013°35.734 | |
| Gab-1303 | 02/12/11 | neg | S00°08.021 | E013°35.394 | ||
| MA-ID-071 | Gab-1350 | 03/12/11 | pos | S00°10.331 | E013°34.642 | |
| Gab-1357 | 03/12/11 | neg | S00°10.323 | E013°34.658 | ||
| Gab-1358 | 03/12/11 | neg | S00°10.328 | E013°34.660 | ||
| Gab-1359 | 03/12/11 | neg | S00°10.329 | E013°34.653 | ||
| Gab-1360 | 03/12/11 | neg | S00°10.334 | E013°34.656 | ||
| Gab-1361 | 03/12/11 | neg | S00°10.326 | E013°34.658 | ||
| Gab-1362 | 03/12/11 | neg | S00°10.330 | E013°34.656 | ||
| Gab-1363 | 03/12/11 | neg | S00°10.327 | E013°34.656 | ||
| Gab-1364 | 03/12/11 | neg | S00°09.555 | E013°34.728 | ||
| MA-ID-150 | Gab-2522 | 09/05/13 | pos | S00°07.265 | E013°30.113 | |
| Gab-2523 | 09/05/13 | neg | S00°07.265 | E013°30.113 | ||
| MA-ID-171 | Gab-2499 | 07/05/13 | neg | S00°08.040 | E013°37.291 | |
| Gab-2505 | 07/05/13 | pos | S00°08.040 | E013°37.291 | ||
| Gab-2506 | 07/05/13 | pos | S00°08.040 | E013°37.291 | ||
| Gab-2511 | 08/05/13 | pos | S00°08.040 | E013°37.291 | ||
| Gab-2515 | 08/05/13 | pos | S00°08.040 | E013°37.291 | ||
| Gab-2517 | 08/05/13 | pos | S00°08.040 | E013°37.291 | ||
| Gab-2519 | 08/05/13 | neg | S00°08.040 | E013°37.291 | ||
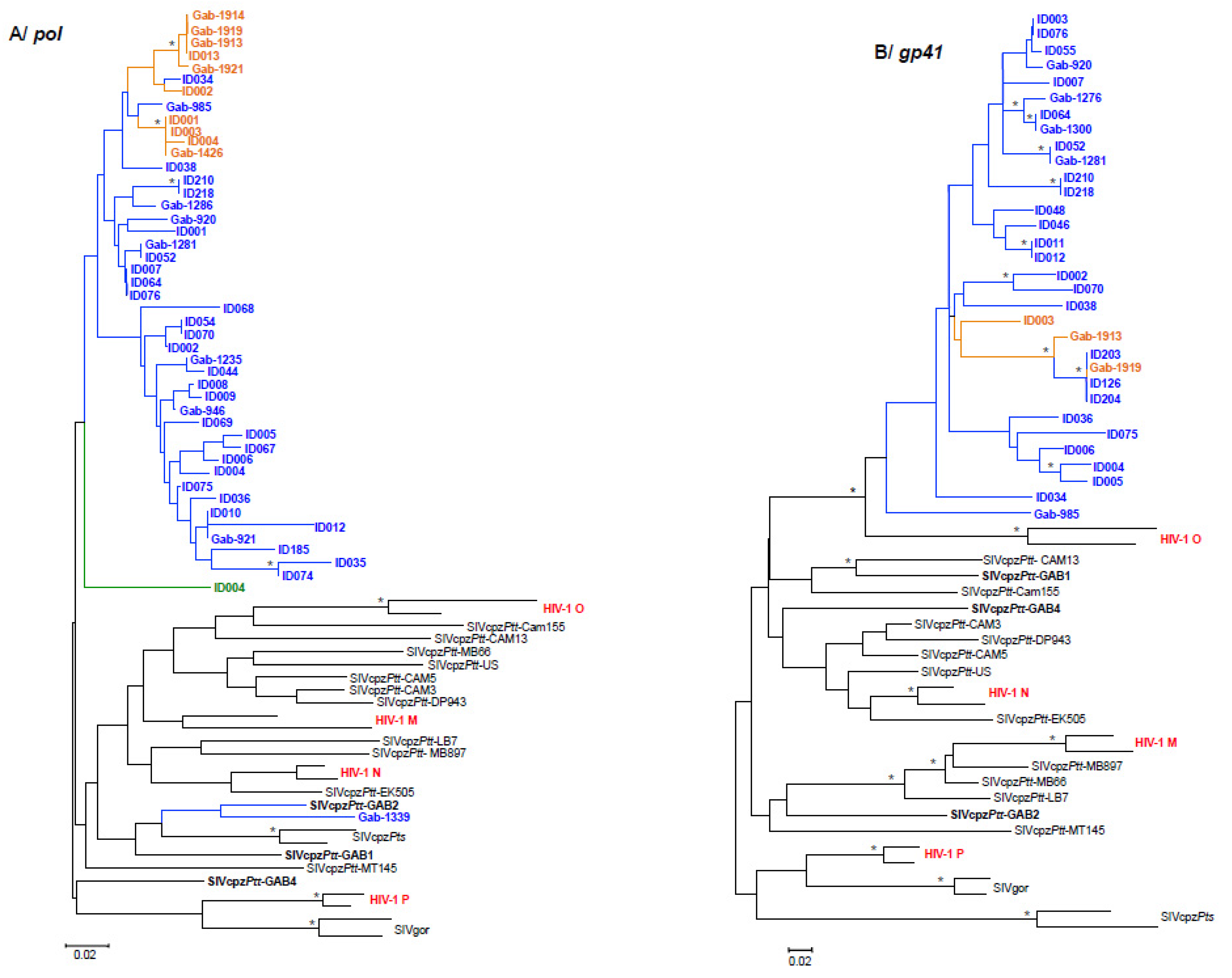
3.2. Partial SIV pol, env and gp41-nef PCR Amplifications and Phylogenetic Analyses
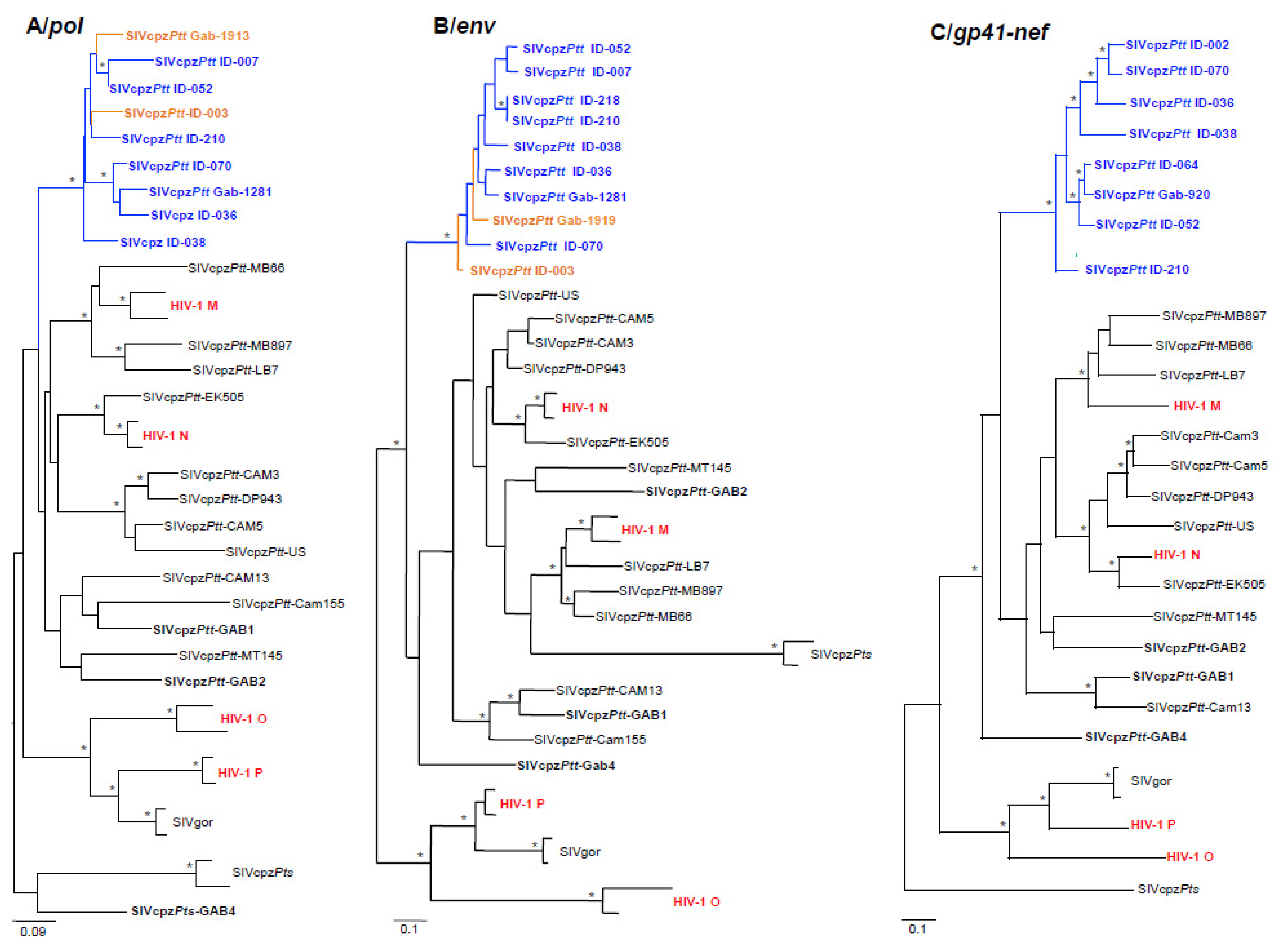
3.3. Vertical and Horizontal Transmission of SIV within and between Chimpanzee Communities
3.3.1. Allele Frequency Analysis
3.3.2. Simulation of Parentage Analysis
3.3.3. Parentage Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Supplementary Materials
References
- Keele, B.F.; Van Heuverswyn, F.; Li, Y.; Bailes, E.; Takehisa, J.; Santiago, M.L.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Chen, Y.; Wain, L.V.; Liegeois, F.; et al. Chimpanzee reservoirs of pandemic and nonpandemic HIV-1. Science 2006, 313, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Heuverswyn, F.; Li, Y.; Neel, C.; Bailes, E.; Keele, B.F.; Liu, W.; Loul, S.; Butel, C.; Liegeois, F.; Bienvenue, Y.; et al. Human immunodeficiency viruses: SIV infection in wild gorillas. Nature 2006, 444, 164–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arc, M.; Ayouba, A.; Esteban, A.; Learn, G.H.; Boue, V.; Liegeois, F.; Etienne, L.; Tagg, N.; Leendertz, F.H.; Boesch, C.; et al. Origin of the HIV-1 group O epidemic in western lowland gorillas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1343–E1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etienne, L.; Locatelli, S.; Ayouba, A.; Esteban, A.; Butel, C.; Liegeois, F.; Aghokeng, A.; Delaporte, E.; Mpoudi Ngole, E.; Peeters, M. Noninvasive follow-up of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus infection in wild-living nonhabituated western lowland gorillas in Cameroon. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 9760–9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Heuverswyn, F.; Li, Y.; Bailes, E.; Neel, C.; Lafay, B.; Keele, B.F.; Shaw, K.S.; Takehisa, J.; Kraus, M.H.; Loul, S.; et al. Genetic diversity and phylogeographic clustering of SIVcpzPtt in wild chimpanzees in Cameroon. Virology 2007, 368, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudicell, R.S.; Piel, A.K.; Stewart, F.; Moore, D.L.; Learn, G.H.; Li, Y.; Takehisa, J.; Pintea, L.; Shaw, G.M.; Moore, J.; et al. High prevalence of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus infection in a community of savanna chimpanzees. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9918–9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neel, C.; Etienne, L.; Li, Y.; Takehisa, J.; Rudicell, R.S.; Bass, I.N.; Moudindo, J.; Mebenga, A.; Esteban, A.; Van Heuverswyn, F.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus infection in wild-living gorillas. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudicell, R.S.; Holland Jones, J.; Wroblewski, E.E.; Learn, G.H.; Li, Y.; Robertson, J.D.; Greengrass, E.; Grossmann, F.; Kamenya, S.; Pintea, L.; et al. Impact of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus infection on chimpanzee population dynamics. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, S.; McKean, K.A.; Sesink Clee, P.R.; Gonder, M.K. The evolution of resistance to Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV): A review. Int. J. Primatol. 2014, 35, 349–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, S.; Peeters, M. Cross-species transmission of Simian Retroviruses: How and why they could lead to the emergence of new diseases in the human population. AIDS 2012, 26, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandrea, I.; Apetrei, C. Where the wild things are: Pathogenesis of SIV infection in African nonhuman primate hosts. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2010, 7, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keele, B.F.; Jones, J.H.; Terio, K.A.; Estes, J.D.; Rudicell, R.S.; Wilson, M.L.; Li, Y.; Learn, G.H.; Beasley, T.M.; Schumacher-Stankey, J.; et al. Increased mortality and AIDS-like immunopathology in wild chimpanzees infected with SIVcpz. Nature 2009, 460, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etienne, L.; Nerrienet, E.; LeBreton, M.; Bibila, G.T.; Foupouapouognigni, Y.; Rousset, D.; Nana, A.; Djoko, C.F.; Tamoufe, U.; Aghokeng, A.F.; et al. Characterization of a new Simian Immunodeficiency Virus strain in a naturally infected Pan troglodytes troglodytes chimpanzee with AIDS related symptoms. Retrovirology 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.; Greenwood, E.J.D.; Nagel, M.; Herbert, A.; Liégeois, F.; Mouinga-Ondémé, A.; Peeters, M.; Sica, J.; Oloussou, D.; Heeney, J.L.; et al. ARV treatment of a naturally SIVcpz infected and disease progressing Pan troglodytes troglodytes Chimpanzee shows clinical and immunovirological efficiency. In 38th Annual Meeting on Retroviruses, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, NY, USA, 20-25 May 2013.
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). Unaids report on the global aids epidemic 2013, 2013.
- Simon, F.; Mauclere, P.; Roques, P.; Loussert-Ajaka, I.; Muller-Trutwin, M.C.; Saragosti, S.; Georges-Courbot, M.C.; Barre-Sinoussi, F.; Brun-Vezinet, F. Identification of a new Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 distinct from group M and group O. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plantier, J.C.; Leoz, M.; Dickerson, J.E.; De Oliveira, F.; Cordonnier, F.; Lemee, V.; Damond, F.; Robertson, D.L.; Simon, F. A new Human Immunodeficiency Virus derived from gorillas. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 871–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liegeois, F.; Boue, V.; Butel, C.; Mouinga-Ondeme, A.; Sica, J.; Zamba, C.; Peeters, M.; Delaporte, E.; Rouet, F. HIV type-1 group O infection in gabon: Low prevalence rate but circulation of genetically diverse and drug-resistant HIV type-1 group O strains. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2013, 29, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vessiere, A.; Rousset, D.; Kfutwah, A.; Leoz, M.; Depatureaux, A.; Simon, F.; Plantier, J.C. Diagnosis and monitoring of HIV-1 group O-infected patients in cameroun. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2010, 53, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemelaar, J. The origin and diversity of the HIV-1 pandemic. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, C. Smithsonian series in comparative evolutionary biology. In Primate taxonomy; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington D.C., WA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, P.M.; Shaw, G.M.; Hahn, B.H. Simian Immunodeficiency Virus infection of chimpanzees. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3891–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leendertz, S.A.; Locatelli, S.; Boesch, C.; Kucherer, C.; Formenty, P.; Liegeois, F.; Ayouba, A.; Peeters, M.; Leendertz, F.H. No evidence for transmission of SIVwrc from western red colobus monkeys (Piliocolobus badius badius) to wild west african chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) despite high exposure through hunting. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, A.M.; Brotman, B.; Lee, D.H.; Andrus, L.; Valinsky, J.; Marx, P. Lack of evidence for HIV type 1-related SIVcpz infection in captive and wild chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) in West Africa. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2002, 18, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oates, J.F.; Groves, C.P.; Jenkins, P.D. The type locality of Pan troglodytes vellerosus (gray, 1862), and implications for the nomenclature of West African chimpanzees. Primates 2009, 50, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ndjango, J.B.; Learn, G.H.; Ramirez, M.A.; Keele, B.F.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Liu, W.; Easlick, J.L.; Decker, J.M.; Rudicell, R.S.; et al. Eastern Chimpanzees, but not bonobos, represent a simian immunodeficiency virus reservoir. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10776–10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Honore, C.; Huet, T.; Bedjabaga, L.; Ossari, S.; Bussi, P.; Cooper, R.W.; Delaporte, E. Isolation and partial characterization of an HIV-related virus occurring naturally in chimpanzees in Gabon. AIDS 1989, 3, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huet, T.; Cheynier, R.; Meyerhans, A.; Roelants, G.; Wain-Hobson, S. Genetic organization of a chimpanzee lentivirus related to HIV. Nature 1990, 345, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souquiere, S.; Makuwa, M.; Salle, B.; Kazanji, M. New strain of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus identified in wild-born chimpanzees from Central Africa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liegeois, F.; Boue, V.; Mouacha, F.; Butel, C.; Ondo, B.M.; Pourrut, X.; Leroy, E.; Peeters, M.; Rouet, F. New STLV-3 strains and a divergent SIVmus strain identified in non-human primate bushmeat in Gabon. Retrovirology 2012, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liegeois, F.; Schmidt, F.; Boue, V.; Butel, C.; Mouacha, F.; Ngari, P.; Ondo, B.M.; Leroy, E.; Heeney, J.L.; Delaporte, E.; et al. Full-length genome analyses of two new Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV) strains from mustached monkeys (C. Cephus) in Gabon illustrate a complex evolutionary history among the SIVmus/mon/gsn lineage. Viruses 2014, 6, 2880–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouchet, D.; Verrier, D.; Ngoubangoye, B.; Souquiere, S.; Makuwa, M.; Kazanji, M.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Pontier, D. Natural Simian Immunodeficiency Virus transmission in mandrills: A family affair? Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 3426–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souquiere, S.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Robertson, D.L.; Makuwa, M.; Apetrei, C.; Onanga, R.; Kornfeld, C.; Plantier, J.C.; Gao, F.; Abernethy, K.; et al. Wild Mandrillus sphinx are carriers of two types of lentivirus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7086–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Courgnaud, V.; Abela, B.; Auzel, P.; Pourrut, X.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Loul, S.; Liegeois, F.; Butel, C.; Koulagna, D.; et al. Risk to human health from a plethora of Simian Immunodeficiency Viruses in primate bushmeat. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boom, R.; Sol, C.J.; Salimans, M.M.; Jansen, C.L.; Wertheim-van Dillen, P.M.; van der Noordaa, J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van der Kuyl, A.C.; Dekker, J.T.; Goudsmit, J. Primate genus Miopithecus: Evidence for the existence of species and subspecies of dwarf guenons based on cellular and endogenous viral sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2000, 14, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocher, T.D.; Thomas, W.K.; Meyer, A.; Edwards, S.V.; Paabo, S.; Villablanca, F.X.; Wilson, A.C. Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals: Amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6196–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Librairy of Medicine Basic local alignment search tools. Available online: http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 15 November 2014).
- Sullivan, K.M.; Mannucci, A.; Kimpton, C.P.; Gill, P. A rapid and quantitative DNA sex test: Fluorescence-based PCR analysis of X-Y homologous gene amelogenin. Biotechniques 1993, 15, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonin, A.; Bellemain, E.; Bronken Eidesen, P.; Pompanon, F.; Brochmann, C.; Taberlet, P. How to track and assess genotyping errors in population genetics studies. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 3261–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinowski, S.T.; Taper, M.L.; Marshall, T.C. Revising how the computer program cervus accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigilant, L.; Guschanski, K. Using genetics to understand the dynamics of wild primate populations. Primates 2009, 50, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Mega5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of phyml 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, I.; Lindner, D.; Bayer, M.; Husmeier, D.; McGuire, G.; Marshall, D.F.; Wright, F. Topali v2: A rich graphical interface for evolutionary analyses of multiple alignments on hpc clusters and multi-core desktops. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 126–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.W.; Locatelli, S.; Sesink Clee, P.R.; Thomassen, H.A.; Gonder, M.K. Environmental variation and rivers govern the structure of chimpanzee genetic diversity in a biodiversity hotspot. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telfer, P.T.; Souquiere, S.; Clifford, S.L.; Abernethy, K.A.; Bruford, M.W.; Disotell, T.R.; Sterner, K.N.; Roques, P.; Marx, P.A.; Wickings, E.J. Molecular evidence for deep phylogenetic divergence in Mandrillus sphinx. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 2019–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, N.M.; Johnson-Bawe, M.; Jeffery, K.; Clifford, S.L.; Abernethy, K.A.; Tutin, C.E.; Lahm, S.A.; White, L.J.; Utley, J.F.; Wickings, E.J.; et al. The role of pleistocene refugia and rivers in shaping gorilla genetic diversity in Central Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20432–20436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, S.; Liegeois, F.; Lafay, B.; Roeder, A.D.; Bruford, M.W.; Formenty, P.; Noe, R.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus infection in wild-living red colobus monkeys (Piliocolobus badius badius) from the Taï forest, Côte d’Ivoire: SIVwrc in wild-living western red colobus monkeys. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2008, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutin, C.; Fernandez, M. Nationwide census of gorilla (Gorilla gorilla gorilla) and chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes troglodytes) populations in Gabon. Am. J. Primatol. 1984, 6, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. Red list of threatened species. Available online: http://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 30 March 2015).
- Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Gao, F.; Bailes, E.; Saragosti, S.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M.; Shaw, G.M.; Hahn, B.H.; Sharp, P.M. Complete genome analysis of one of the earliest SIVcpzPtt strains from Gabon (SIVcpzGab-2). AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2004, 20, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermejo, M.; Rodriguez-Teijeiro, J.D.; Illera, G.; Barroso, A.; Vila, C.; Walsh, P.D. Ebola outbreak killed 5000 gorillas. Science 2006, 314, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, P.D.; Abernethy, K.A.; Bermejo, M.; Beyers, R.; De Wachter, P.; Akou, M.E.; Huijbregts, B.; Mambounga, D.I.; Toham, A.K.; Kilbourn, A.M.; et al. Catastrophic ape decline in Western Equatorial Africa. Nature 2003, 422, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, E.M.; Rouquet, P.; Formenty, P.; Souquiere, S.; Kilbourne, A.; Froment, J.M.; Bermejo, M.; Smit, S.; Karesh, W.; Swanepoel, R.; et al. Multiple ebola virus transmission events and rapid decline of Central African wildlife. Science 2004, 303, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fa, J.E.; Ryan, S.F.; Bell, D.J. Hunting vulnerability, ecological charasteristics and harvest rates of buschmeat species in afrotropical forest. Biol. Conserv. 2005, 121, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boué, V.; Locatelli, S.; Boucher, F.; Ayouba, A.; Butel, C.; Esteban, A.; Okouga, A.-P.; Ndoungouet, A.; Motsch, P.; Flohic, G.L.; et al. High Rate of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV) Infections in Wild Chimpanzees in Northeastern Gabon. Viruses 2015, 7, 4997-5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092855
Boué V, Locatelli S, Boucher F, Ayouba A, Butel C, Esteban A, Okouga A-P, Ndoungouet A, Motsch P, Flohic GL, et al. High Rate of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV) Infections in Wild Chimpanzees in Northeastern Gabon. Viruses. 2015; 7(9):4997-5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092855
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoué, Vanina, Sabrina Locatelli, Floriane Boucher, Ahidjo Ayouba, Christelle Butel, Amandine Esteban, Alain-Prince Okouga, Alphonse Ndoungouet, Peggy Motsch, Guillaume Le Flohic, and et al. 2015. "High Rate of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV) Infections in Wild Chimpanzees in Northeastern Gabon" Viruses 7, no. 9: 4997-5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092855
APA StyleBoué, V., Locatelli, S., Boucher, F., Ayouba, A., Butel, C., Esteban, A., Okouga, A.-P., Ndoungouet, A., Motsch, P., Flohic, G. L., Ngari, P., Prugnolle, F., Ollomo, B., Rouet, F., & Liégeois, F. (2015). High Rate of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV) Infections in Wild Chimpanzees in Northeastern Gabon. Viruses, 7(9), 4997-5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092855







