Identification of a Common Epitope between Enterovirus 71 and Human MED25 Proteins Which May Explain Virus-Associated Neurological Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Peptide Scanning for Common Epitope
2.3. Determination of Location of Common Epitope
2.4. Preparation of 2H2 mAb and EV71 Neutralization Assay
2.5. Expression of MED25 in 293T Cells
2.6. Immunizations
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay
2.9. ELISA
2.10. Determination of Affinity of 2H2 to MED25
2.11. Immunohistochemistry
2.12. Live Small Animal in Vivo Imaging
3. Results
3.1. Alignment of EV71 Proteome Fragments to MED25 of Various Species
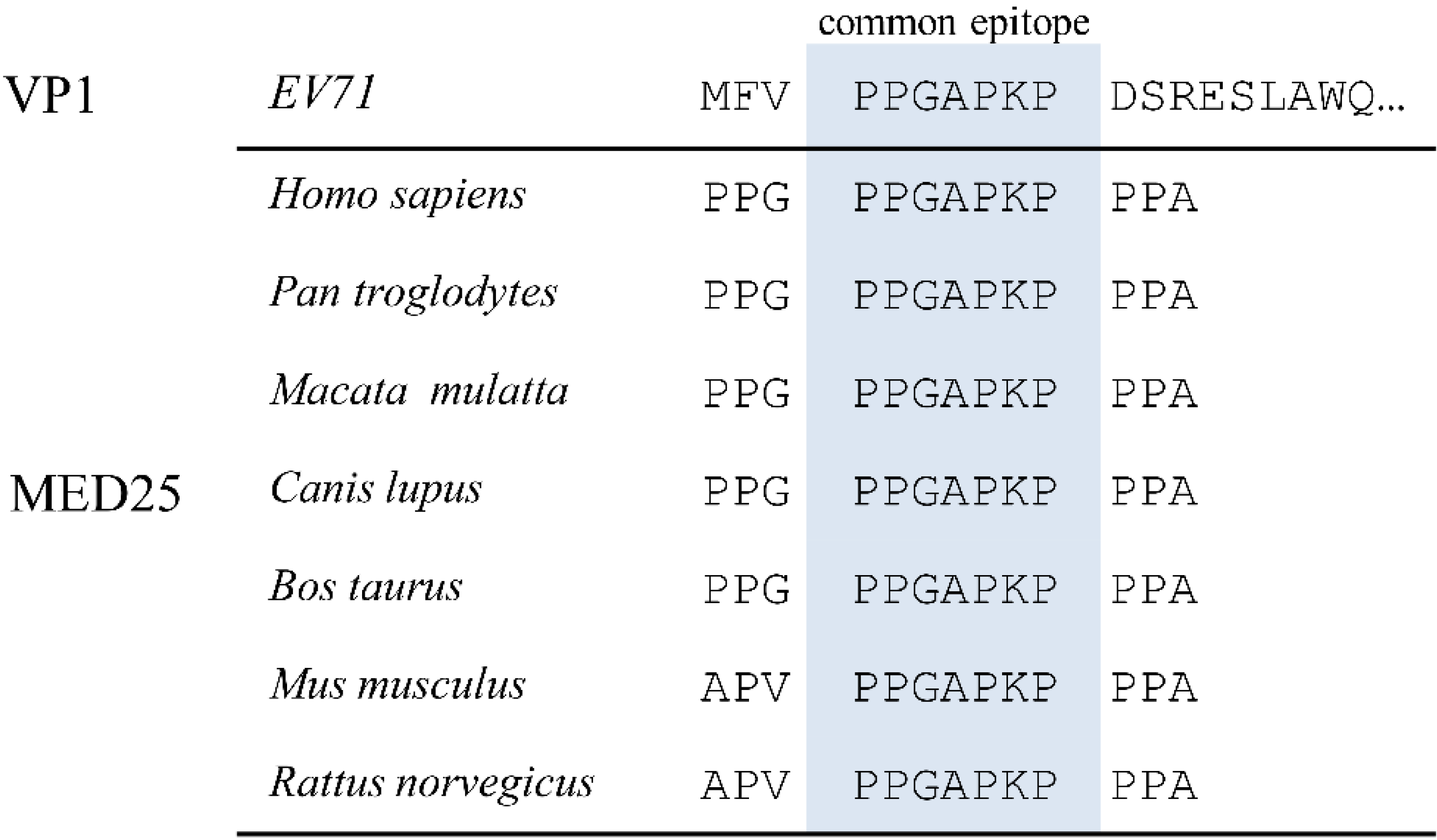
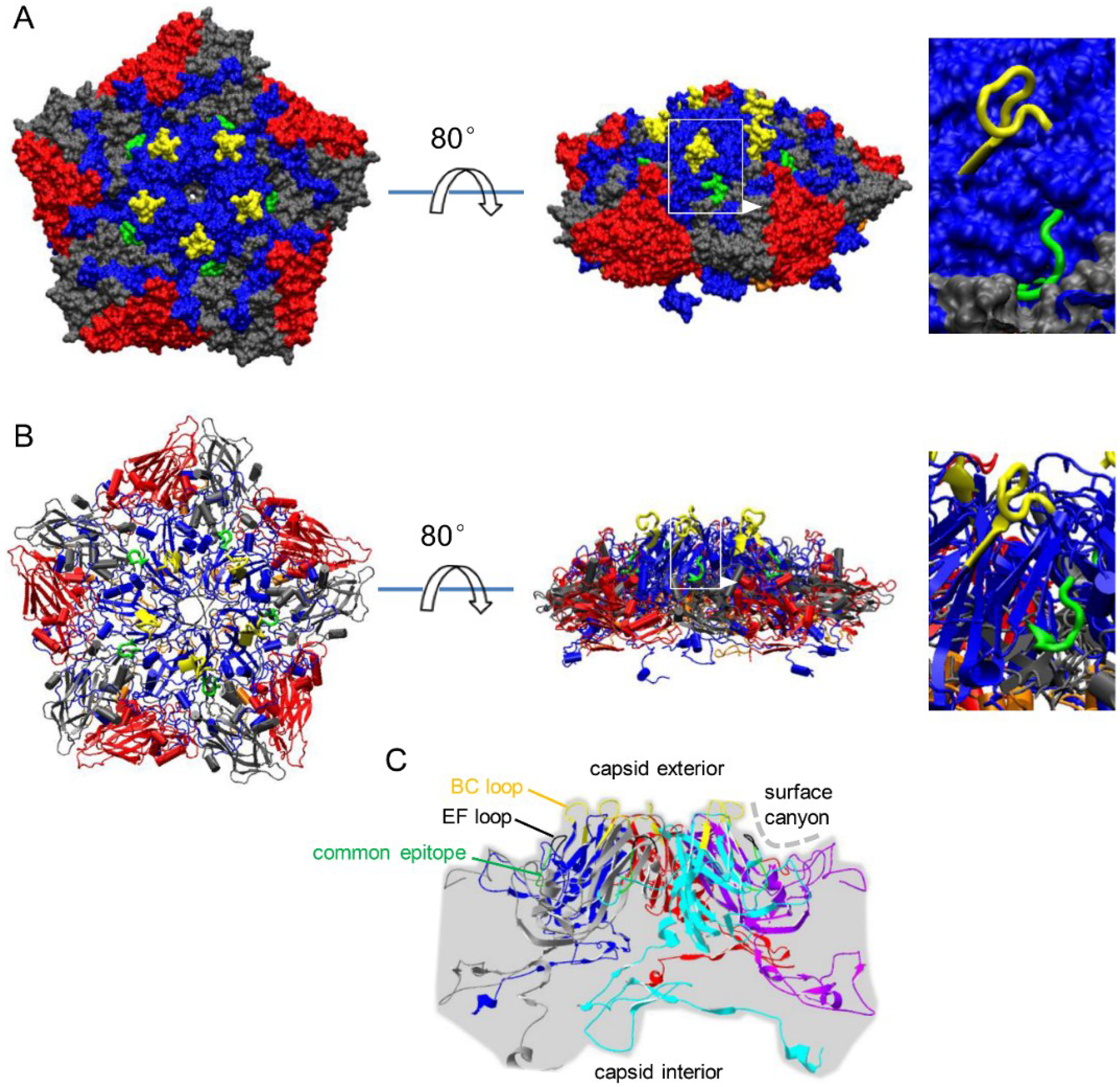
3.2. Localization of Common Epitope on Canyon Slope Surface of Viral Capsid Exterior
3.3. Preparation of mAb against the Common Epitope and the Reactivity of it with MED25
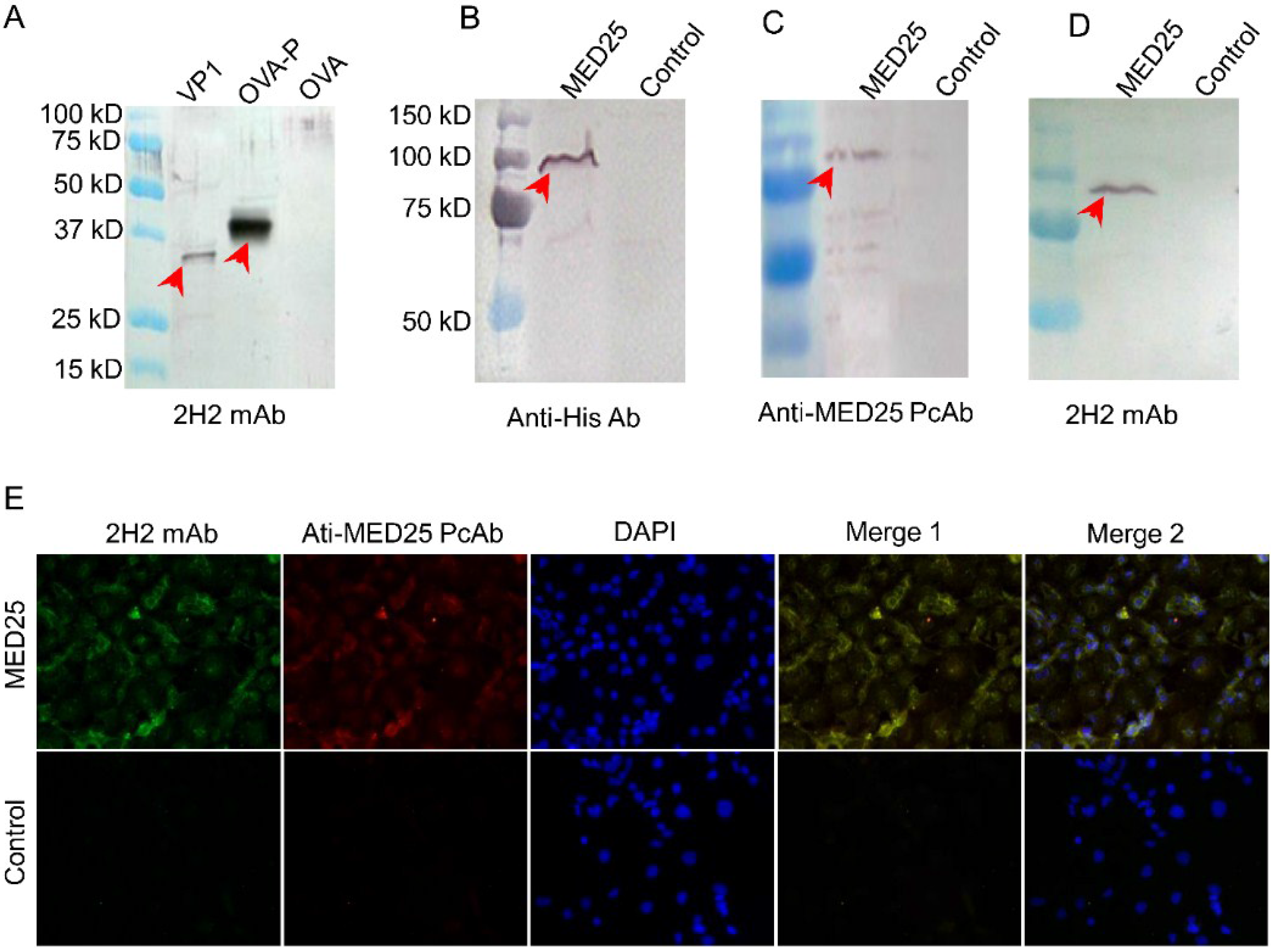
3.4. MED25 and VP1 Contain the Common Antigen Recognized by 2H2 mAb
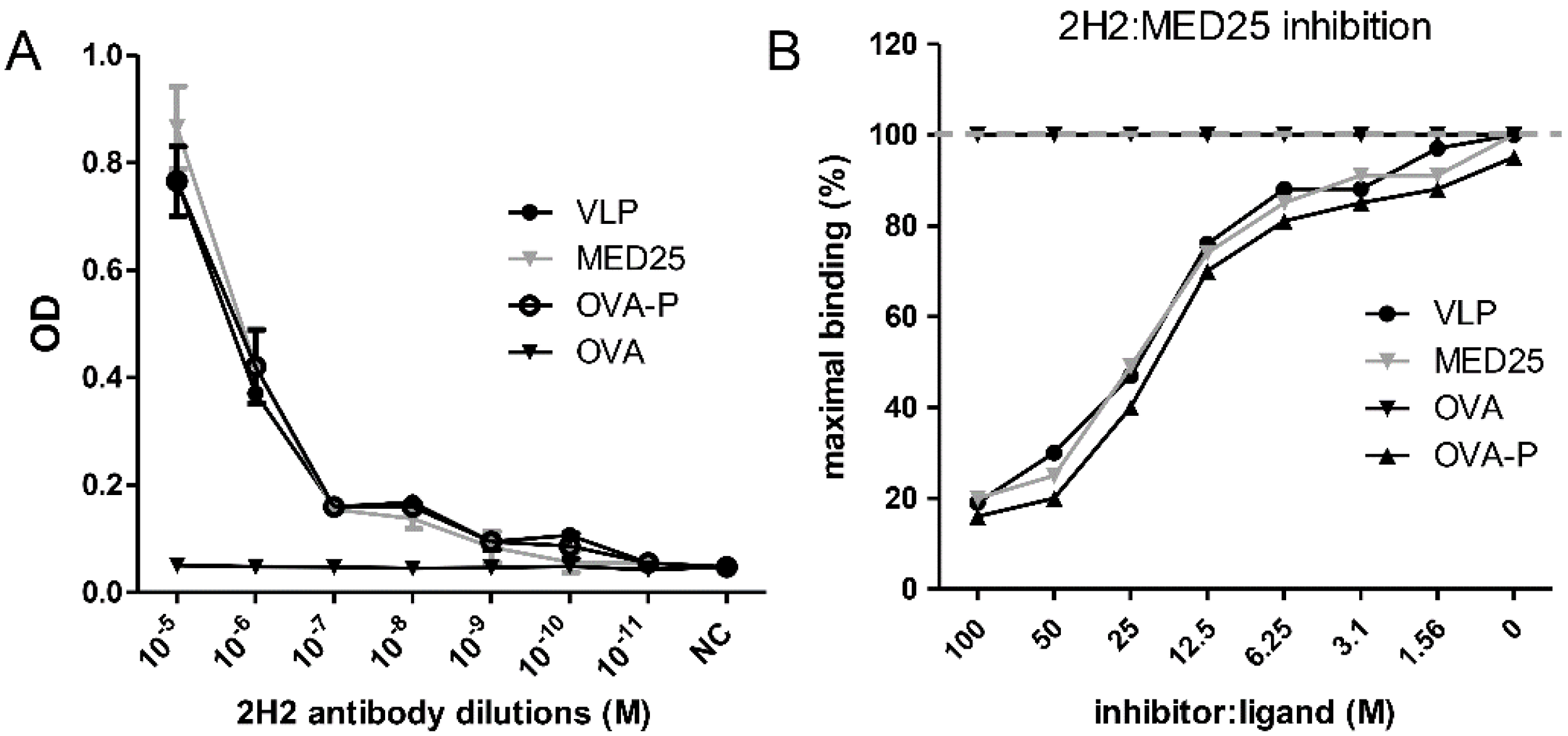
3.5. Determination of Binding Affinity of 2H2 to MED25
3.6. Detection of 2H2-Like Antibodies in Rabbit anti-VLP and anti-MED25 Sera and in EV71-Infected Patient Serum
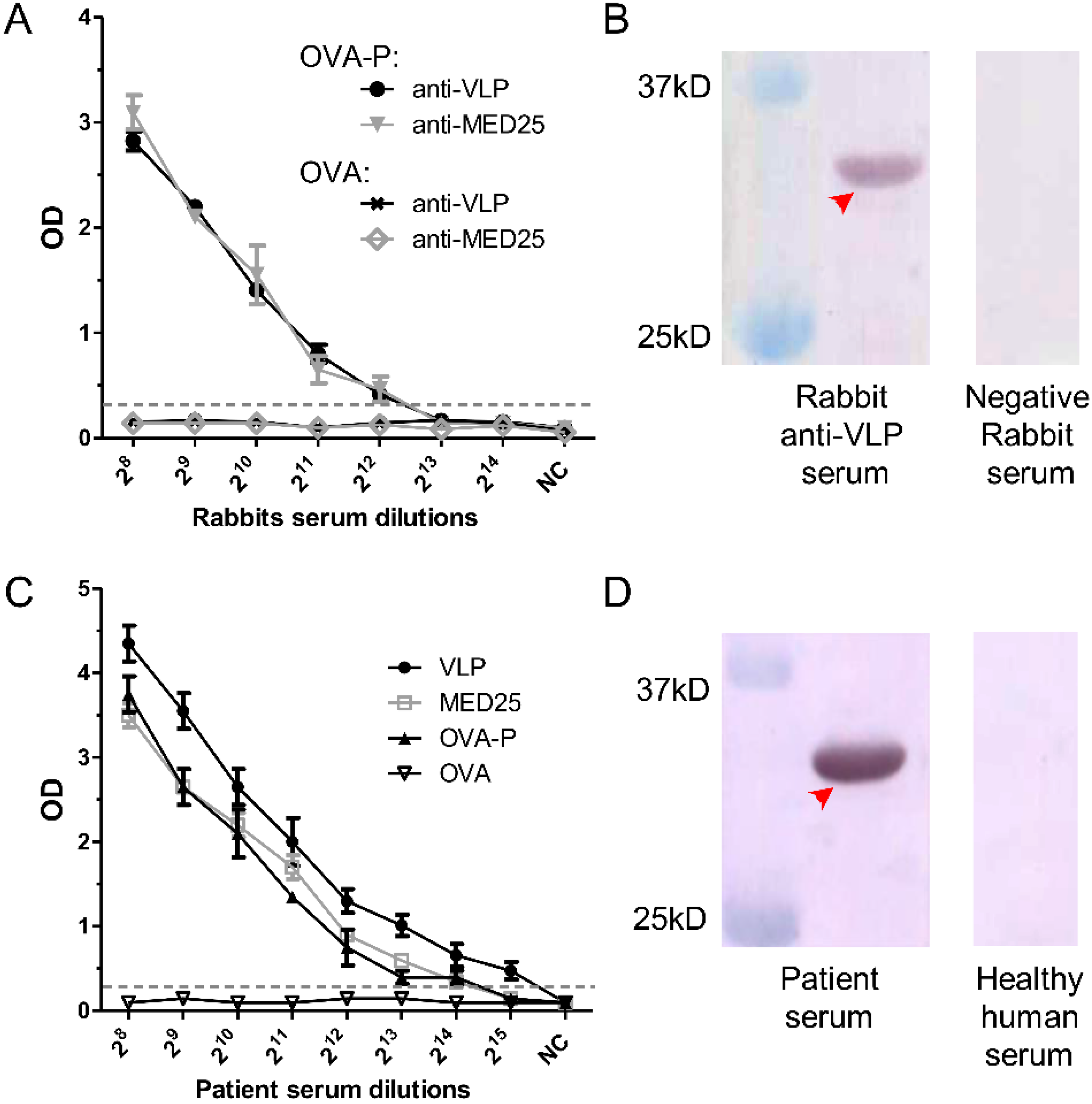
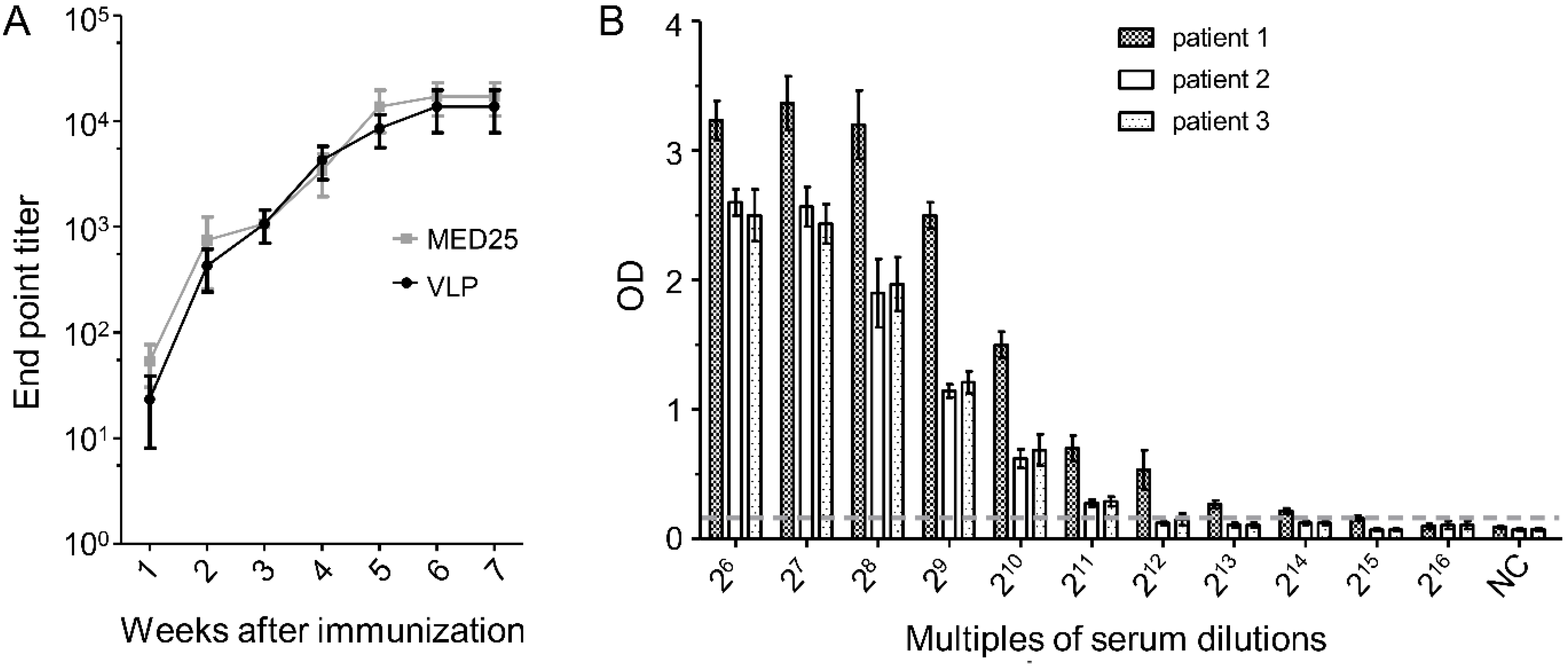
3.7. Dynamics of 2H2-Like Antibody Generation in Rabbit Immune Serum and Endpoint Titer in Patient Serum
3.8. Cross-Reactivity of 2H2, Rabbit anti-VLP Serum and EV71-Infected Patient Serum in Brain Tissue

3.9. Reactivity of 2H2 to Brain Tissue and the Distribution in Vivo
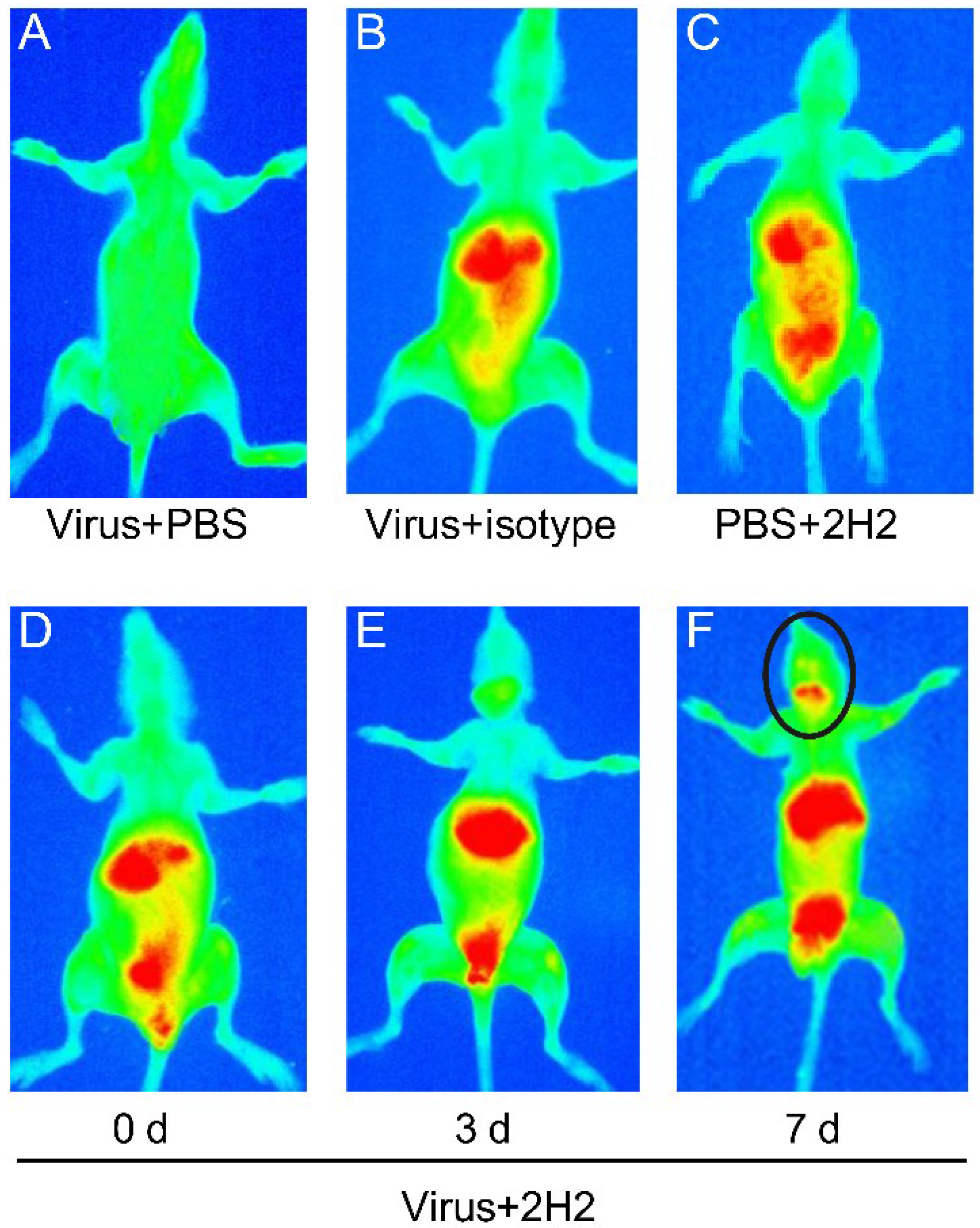
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McMinn, P.; Lindsay, K.; Perera, D.; Chan, H.M.; Chan, K.P.; Cardosa, M.J. Phylogenetic analysis of enterovirus 71 strains isolated during linked epidemics in Malaysia, Singapore, and Western Australia. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7732–7738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardosa, M.J.; Perera, D.; Brown, B.A.; Cheon, D.; Chan, H.M.; Chan, K.P.; Cho, H.; McMinn, P. Molecular epidemiology of human enterovirus 71 strains and recent outbreaks in the asia-pacific region: Comparative analysis of the vp1 and vp4 genes. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, M.; Wong, S.; Lewthwaite, P.; Cardosa, M.; Solomon, T. Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of enterovirus 71. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Shih, S.; Chen, T.; Li, M. The efficacy of viral capsid inhibitors in human enterovirus infection and associated diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Lin, Y.; Fann, C.; Liao, N.; Shih, S.; Ho, M. Protection against lethal enterovirus 71 infection in newborn mice by passive immunization with subunit vp1 vaccines and inactivated virus. Vaccine 2001, 20, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateu, M. Antibody recognition of picornaviruses and escape from neutralization: A structural view. Virus Res. 1995, 38, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minor, P. Antigenic structure of picornaviruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1990, 161, 121–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, N.J.; Lennette, E.H.; Ho, H.H. An apparently new enterovirus isolated from patients with disease of the central nervous system. J. Infect. Dis. 1974, 129, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, T.; Lewthwaite, P.; Perera, D.; Cardosa, M.J.; McMinn, P.; Ooi, M.H. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of enterovirus 71. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Tseng, F.; Wang, J.; Chi, C.; Chong, P.; Su, I. Challenges to licensure of enterovirus 71 vaccines. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Self, S.; Gao, Y.; Longini, I.M.; Wakefield, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; et al. Hand, foot, and mouth disease in China: Patterns of spread and transmissibility. Epidemiology 2011, 22, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Ren, L.; Xiong, Z.; Li, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, R.; He, Y.; Bu, G.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Enterovirus 71 outbreak in the peopleʼs republic of china in 2008. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2351–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) Situation Updates. Available online: http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/HFMD.situation.updates.archive/en/ (accessed on 15 January 2014).
- McMinn, P. An overview of the evolution of enterovirus 71 and its clinical and public health significance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 26, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahar, A.; Schupper, H.; Lustig, S.; Levin, R.; Friedmann, A.; Fuchs, P. Neuronal cell cultures as a model for assessing neurotoxicity induced by encephalitic viruses. Neurotoxicology 1992, 13, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.Y.; Chang, T.Y.; Chen, S.T.; Li, C.; Liu, H.S. Comparative study of enterovirus 71 infection of human cell lines. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 70, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordey, S.; Petty, T.J.; Schibler, M.; Martinez, Y.; Gerlach, D.; van Belle, S.; Turin, L.; Zdobnov, E.; Kaiser, L.; Tapparel, C. Identification of site-specific adaptations conferring increased neural cell tropism during human enterovirus 71 infection. PLOS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruu, A.L. Enteroviruses: Polioviruses, Coxsackieviruses, Echoviruses and Newer Enteroviruses. In A Practical Guide to Clinical Virology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson, N. The pathogenesis of poliomyelitis: What we donʼt know. Adv. Virus Res. 2008, 71, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Hsu, K.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Lin, K.L.; Hsueh, C.; Shih, S.R.; Ning, H.C.; Hwang, M.S.; Wang, H.S.; et al. Clinical features and risk factors of pulmonary oedema after enterovirus-71-related hand, foot, and mouth disease. Lancet 1999, 354, 1682–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Velez, C.M.; Anderson, M.S.; Robinson, C.C.; McFarland, E.J.; Nix, W.A.; Pallansch, M.A.; Oberste, M.S.; Glode, M.P. Outbreak of neurologic enterovirus type 71 disease: A diagnostic challenge. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C. Proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines as mediators in the pathogenesis of septic shock. Chest 1997, 112, 321S–329S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, S.; Hirasawa, H.; Shiga, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Matsuda, K.; Nakamua, M. Sequential measurement of IL-6 blood levels in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)/sepsis. Cytokine 2005, 29, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Chang, L.; Huang, Y.; Hsu, K.; Chiu, C.; Yang, K. Different proinflammatory reactions in fatal and non-fatal enterovirus 71 infections: Implications for early recognition and therapy. Acta Paediatr. 2002, 91, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Hsia, S.-H.; Huang, Y.-C.; Wu, C.-T.; Chang, L.-Y. Proinflammatory cytokine reactions in enterovirus 71 infections of the central nervous system. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.M.; Lei, H.Y.; Huang, K.J.; Wu, J.M.; Wang, J.R.; Yu, C.K.; Su, I.J.; Liu, C.C. Pathogenesis of enterovirus 71 brainstem encephalitis in pediatric patients: Roles of cytokines and cellular immune activation in patients with pulmonary edema. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.M.; Lei, H.Y.; Huang, M.C.; Su, L.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Yu, C.K.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, C.C. Modulation of cytokine production by intravenous immunoglobulin in patients with enterovirus 71-associated brainstem encephalitis. J. Clin. Virol. 2006, 37, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.M.; Lei, H.Y.; Liu, C.C. Cytokine immunopathogenesis of enterovirus 71 brain stem encephalitis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, e876241. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.S.; Liu, J.N.; Li, W.B.; Ma, C.M.; Lin, S.Z.; Hao, Y.; Gao, X.Z.; Liu, X.L.; Xu, Y.F.; Zhang, L.F.; et al. The cross-reactivity of the enterovirus 71 to human brain tissue and identification of the cross-reactivity related fragments. Virol. J. 2010, 7, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, G.; Stuhler, T.; Santolin, L.; Uhlmann, T.; Kremmer, E.; Lottspeich, F.; Berti, L.; Meisterernst, M. A novel docking site on mediator is critical for activation by vp16 in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 6494–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, Z.; Ansari, A.Z.; Gaudreau, L.; Nevado, J.; Ptashne, M. Gene transcription by recruitment. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1998, 63, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, L.C.; Kornberg, R.D. Mediator of transcriptional regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujisaki, M.; Imai, K.; Hishikawa, N.; Tokuchi, S.; Hinoda, Y.; Matsukawa, H.; Oikawa, S.; Nakazato, H.; Yachi, A. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific to synthetic peptide of carcinoembryonic antigen. Int. J. Cancer 1991, 47, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; An, D.; Liu, W.; Mao, Q.; Jin, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, S.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Shao, J.; et al. Analysis of cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies in human hfmd serum with an EV71 pseudovirus-based assay. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraoka, M.; Holl, T.M.; Liao, D.; Womble, M.; Cain, D.W.; Reynolds, A.E.; Kelsoe, G. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase mediates central tolerance in b cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11560–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Holl, T.M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Nicely, N.I.; Kepler, T.B.; Alam, S.M.; Liao, H.X.; Cain, D.W.; et al. Identification of autoantigens recognized by the 2f5 and 4e10 broadly neutralizing hiv-1 antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engvall, E.; Jonsson, K.; Perlmann, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. II. Quantitative assay of protein antigen, immunoglobulin g, by means of enzyme-labelled antigen and antibody-coated tubes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1971, 251, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoli, C.; Sessa, M.; Infante, T.; Casamassimi, A. Unraveling framework of the ancestral mediator complex in human diseases. Biochimie 2012, 94, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fan, P.; Jin, J.; Su, W.; An, D.; Xu, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Gao, F.; et al. Establishment of cell lines with increased susceptibility to ev71/ca16 by stable overexpression of scarb2. Virol. J. 2013, 10, e250. [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz, M.; Sarvetnick, N. Viruses, host responses, and autoimmunity. Immunol. Rev. 1999, 169, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldstone, M.; Nerenberg, M.; Southern, P.; Price, J.; Lewicki, H. Virus infection triggers insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in a transgenic model: Role of anti-self (virus) immune response. Cell 1991, 65, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aichele, P.; Bachmann, M.; Hengartner, H.; Zinkernagel, R. Immunopathology or organ-specific autoimmunity as a consequence of virus infection. Immunol. Rev. 1996, 152, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau, J.; Gleichman, A.; Hughes, E.; Rossi, J.; Peng, X.; Lai, M.; Dessain, S.; Rosenfeld, M.; Balice-Gordon, R.; Lynch, D. Anti-nmda-receptor encephalitis: Case series and analysis of the effects of antibodies. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.; Barber, P. Limbic encephalitis—A review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 15, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florance, N.; Davis, R.; Lam, C.; Szperka, C.; Zhou, L.; Ahmad, S.; Campen, C.; Moss, H.; Peter, N.; Gleichman, A.; et al. Anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis in children and adolescents. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khong, W.X.; Foo, D.G.; Trasti, S.L.; Tan, E.L.; Alonso, S. Sustained high levels of interleukin-6 contribute to the pathogenesis of enterovirus 71 in a neonate mouse model. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3067–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, O.; Karaki, T.; Imanishi, J. Protective effect of interferon on infections with hand, foot, and mouth disease virus in newborn mice. J. Infect. Dis. 1986, 153, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, K.C.; Badmanathan, M.; Devi, S.; Leong, K.L.; Cardosa, M.J.; Wong, K.T. Pathologic characterization of a murine model of human enterovirus 71 encephalomyelitis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Tsao, K.C.; Shih, S.R.; Kuo, M.L.; Ning, H.C.; Chung, P.W.; Kang, C.M. Comparison of enterovirus 71 and coxsackie-virus a16 clinical illnesses during the taiwan enterovirus epidemic, 1998. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1999, 18, 1092–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, C.; Wu, S.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A novel finding for enterovirus virulence from the capsid protein vp1 of EV71 circulating in mainland China. Virus Genes 2014, 48, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, P.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Su, W.; An, D.; Gao, F.; Kong, W.; Jiang, C. Identification of a Common Epitope between Enterovirus 71 and Human MED25 Proteins Which May Explain Virus-Associated Neurological Disease. Viruses 2015, 7, 1558-1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7041558
Fan P, Li X, Sun S, Su W, An D, Gao F, Kong W, Jiang C. Identification of a Common Epitope between Enterovirus 71 and Human MED25 Proteins Which May Explain Virus-Associated Neurological Disease. Viruses. 2015; 7(4):1558-1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7041558
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Peihu, Xiaojun Li, Shiyang Sun, Weiheng Su, Dong An, Feng Gao, Wei Kong, and Chunlai Jiang. 2015. "Identification of a Common Epitope between Enterovirus 71 and Human MED25 Proteins Which May Explain Virus-Associated Neurological Disease" Viruses 7, no. 4: 1558-1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7041558
APA StyleFan, P., Li, X., Sun, S., Su, W., An, D., Gao, F., Kong, W., & Jiang, C. (2015). Identification of a Common Epitope between Enterovirus 71 and Human MED25 Proteins Which May Explain Virus-Associated Neurological Disease. Viruses, 7(4), 1558-1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7041558




