Emerging Themes from EBV and KSHV microRNA Targets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
 |
 |
3. Regulation of apoptosis by KSHV and EBV miRNAs
7. Similarities between miR-155 and miR-K12-11 in the context of KSHV/ EBV infection
8. Other targets of KSHV and EBV encoded miRNAs
9. Overlap of targets from KSHV and EBV high-throughput miRNA studies
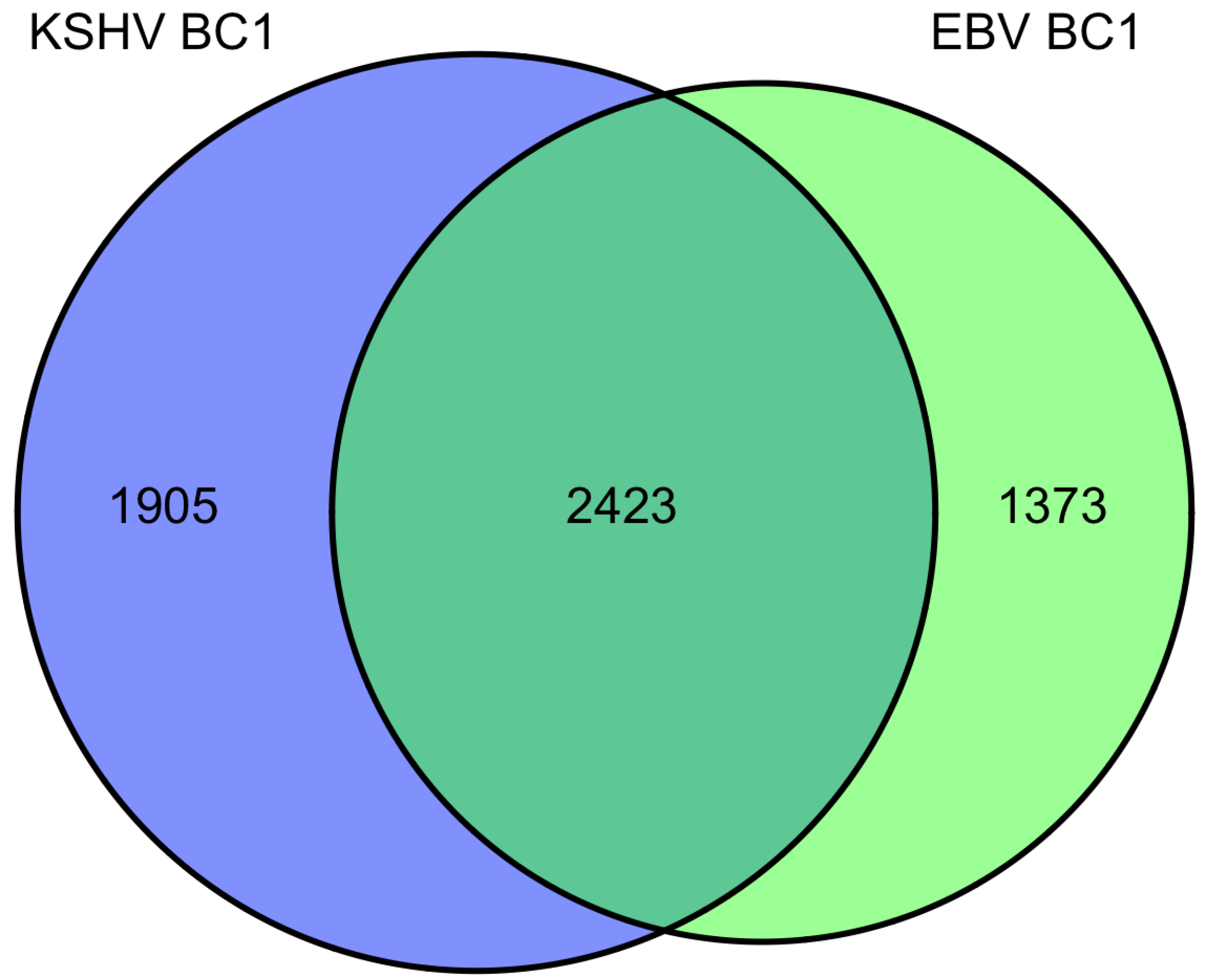
 |
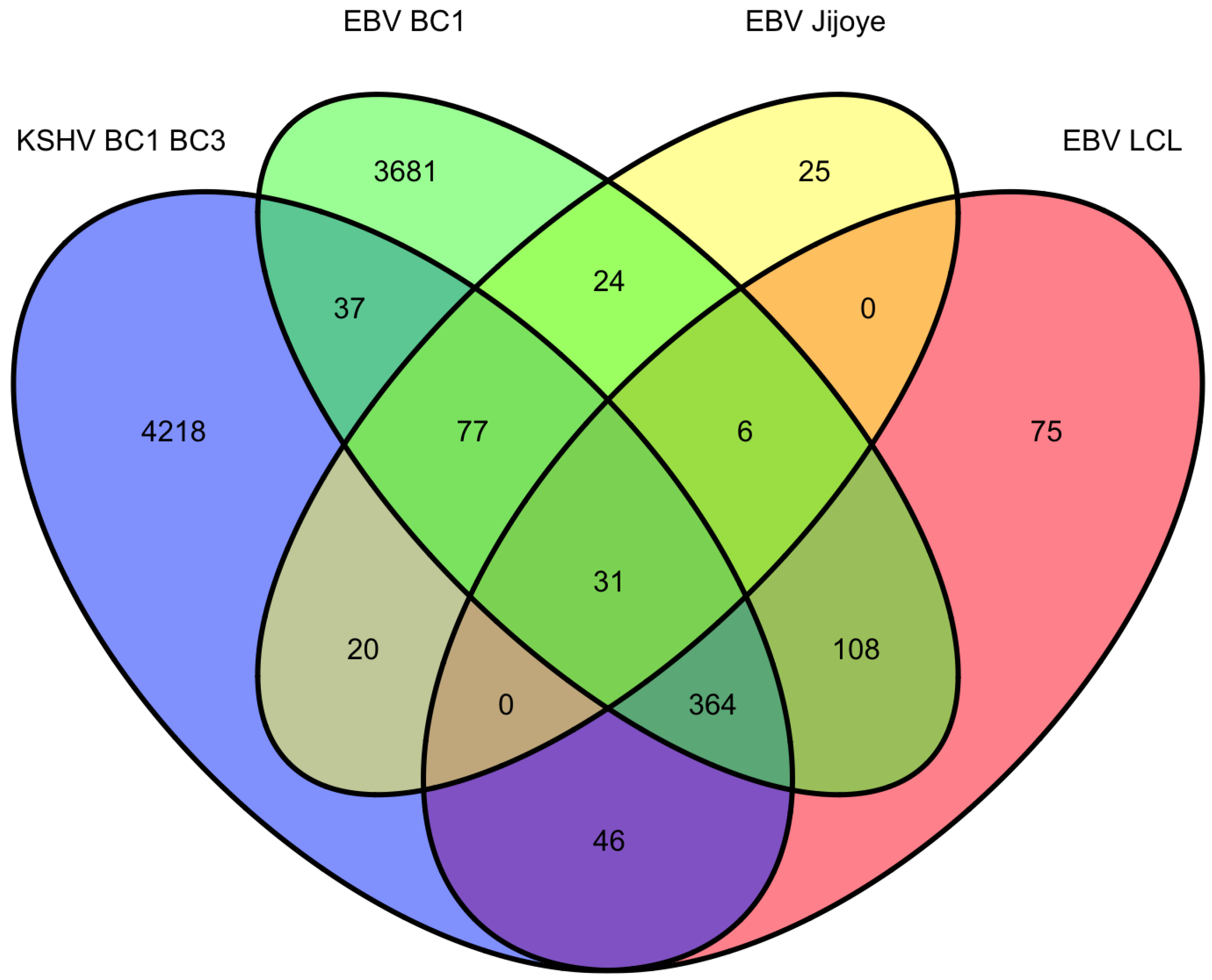
 |

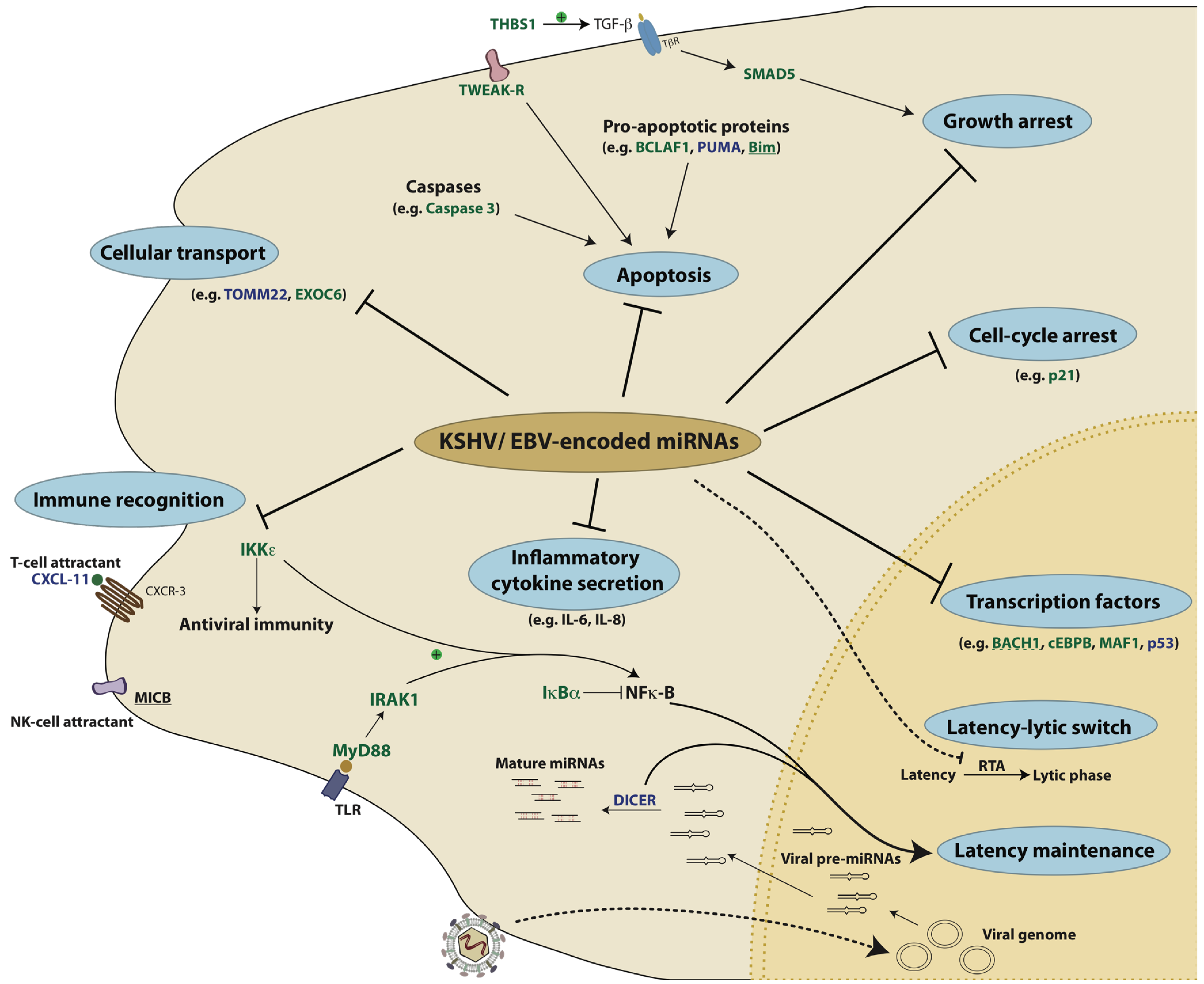
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References and Notes
- Zur Hausen, H. The search for infectious causes of human cancers: where and why. Virology 2009, 392, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab-Traub, N. EBV-induced oncogenesis. In Human Herpesviruses: Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis; Arvin, A, Campadelli-Fiume, G, Mocarski, E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2007; Chapter 55. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer, S.; Zavolan, M.; Grasser, F.A.; Chien, M.; Russo, J.J.; Ju, J.; John, B.; Enright, A.J.; Marks, D.; Sander, C.; Tuschl, T. Identification of virus-encoded microRNAs. Science 2004, 304, 734–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, S.; Sewer, A.; Lagos-Quintana, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sander, C.; Grasser, F.A.; van Dyk, L.F.; Ho, C.K.; Shuman, S.; Chien, M.; Russo, J.J.; et al. Identification of microRNAs of the herpesvirus family. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincaid, R.P.; Burke, J.M.; Sullivan, C.S. RNA virus microRNA that mimics a B-cell oncomiR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3077–3082. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Stedman, W.; Yousef, M.; Renne, R.; Lieberman, P.M. Epigenetic regulation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency by virus-encoded microRNAs that target Rta and the cellular Rbl2-DNMT pathway. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Bai, Z.; Ye, F.; Xie, J.; Kim, C.G.; Huang, Y.; Gao, S.J. Regulation of NF-kappaB inhibitor IkappaBalpha and viral replication by a KSHV microRNA. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquitz, A.R.; Raab-Traub, N. The role of miRNAs and EBV BARTs in NPC. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 22, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, B.R. Viruses and microRNAs: RISCy interactions with serious consequences. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundhoff, A.; Sullivan, C.S. Virus-encoded microRNAs. Virology 2011, 411, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaisance-Bonstaff, K.; Renne, R. Viral miRNAs. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 721, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwein, E.; Cullen, B.R. Viral and cellular microRNAs as determinants of viral pathogenesis and immunity. Cell Host Microbe. 2008, 3, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, N.; Christalla, T.; Tessmer, U.; Grundhoff, A. A global analysis of evolutionary conservation among known and predicted gammaherpesvirus microRNAs. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 716–728. [Google Scholar]
- Sethupathy, P.; Megraw, M.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. A guide through present computational approaches for the identification of mammalian microRNA targets. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samols, M.A.; Skalsky, R.L.; Maldonado, A.M.; Riva, A.; Lopez, M.C.; Baker, H.V.; Renne, R. Identification of cellular genes targeted by KSHV-encoded microRNAs. PLoS. Pathog. 2007, 3, e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwein, E.; Mukherjee, N.; Sachse, C.; Frenzel, C.; Majoros, W.H.; Chi, J.T.; Braich, R.; Manoharan, M.; Soutschek, J.; Ohler, U.; et al. A viral microRNA functions as an orthologue of cellular miR-155. Nature 2007, 450, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegelbauer, J. M.; Sullivan, C.S.; Ganem, D. Tandem array-based expression screens identify host mRNA targets of virus-encoded microRNAs. Nat. Genet 2009, 41, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Dolken, L.; Malterer, G.; Erhard, F.; Kothe, S.; Friedel, C.C.; Suffert, G.; Marcinowski, L.; Motsch, N.; Barth, S.; Beitzinger, M.; et al. Systematic analysis of viral and cellular microRNA targets in cells latently infected with human gamma-herpesviruses by RISC immunoprecipitation assay. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwein, E.; Corcoran, D.L.; Mukherjee, N.; Skalsky, R.L.; Hafner, M.; Nusbaum, J.D.; Shamulailatpam, P.; Love, C.L.; Dave, S.S.; Tuschl, T.; et al. Viral MicroRNA Targetome of KSHV-Infected Primary Effusion Lymphoma Cell Lines. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalsky, R.L.; Corcoran, D.L.; Gottwein, E.; Frank, C.L.; Kang, D.; Hafner, M.; Nusbaum, J.D.; Feederle, R.; Delecluse, H.J.; Luftig, M.A.; et al. The viral and cellular microRNA targetome in lymphoblastoid cell lines. PLoS.Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002484. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, K.J.; Rabinowitz, G.S.; Yario, T. A.; Luna, JM.; Darnell, R.B.; Steitz, J.A. EBV and human microRNAs co-target oncogenic and apoptotic viral and human genes during latency. EMBO. J. 2012, 31, 2207–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dawson, C.W.; He, Z.; Huang, P. Immune evasion strategies of the human gamma-herpesviruses: implications for viral tumorigenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; O'Hara, A.; Araujo, I.; Barreto, J.; Carvalho, E.; Sapucaia, J.B.; Ramos, J. C.; Luz, E.; Pedroso, C.; Manrique, M.; et al. EBV microRNAs in primary lymphomas and targeting of CXCL-11 by ebv-mir-BHRF1-3. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Nachmani, D.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Sarid, R.; Mandelboim, O. Diverse herpesvirus microRNAs target the stress-induced immune ligand MICB to escape recognition by natural killer cells. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, C.; Meier, A.; Jensen, T.; Knapnougel, P.; Poupon, G.; Lazzari, A.; Neisig, A.; Hakansson, K.; Dong, T.; Wagtmann, N.; et al. Induction of lectin-like transcript 1 (LLT1) protein cell surface expression by pathogens and interferon-gamma contributes to modulate immune responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 37964–37975. [Google Scholar]
- Gurer, C.; Strowig, T.; Brilot, F.; Pack, M.; Trumpfheller, C.; Arrey, F.; Park, C.G.; Steinman, R.M.; Munz, C. Targeting the nuclear antigen 1 of Epstein-Barr virus to the human endocytic receptor DEC-205 stimulates protective T-cell responses. Blood 2008, 112, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, A.; Ogawa, K.; Sasaki, T.; Koyama, N.; Wada, K.; Kotera, J.; Kikkawa, H.; Omori, K.; Kaminuma, O. Potential role of phosphodiesterase 7 in human T cell function: comparative effects of two phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 128, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Murakawa, M.; Kadoshima-Yamaoka, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Inoue, H.; Murafuji, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Miura, K.; Nakatsuka, T.; et al. Phosphodiesterase 7A inhibitor ASB16165 suppresses proliferation and cytokine production of NKT cells. Cell Immunol. 2009, 258, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; McIntyre, K.W.; Townsend, R.M.; Shen, H.H.; Pitts, W.J.; Dodd, J.H.; Nadler, S.G.; McKinnon, M.; Watson, A.J. Phosphodiesterase 7A-deficient mice have functional T cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 6414–6420. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; Chang, M.; Sun, S.C. Peli: a family of signal-responsive E3 ubiquitin ligases mediating TLR signaling and T-cell tolerance. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2012, 9, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavalai, N.; Stamminger, T. Interplay between Herpesvirus Infection and Host Defense by PML Nuclear Bodies. Viruses 2009, 1, 1240–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Gao, Y.; Lin, X.; He, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Deng, Q.; Lan, K. A human herpesvirus miRNA attenuates interferon signaling and contributes to maintenance of viral latency by targeting IKKepsilon. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, B.; Sperisen, P.; Emery, P.; Barras, E.; Zufferey, M.; Mach, B.; Reith, W. RFXAP, a novel subunit of the RFX DNA binding complex is mutated in MHC class II deficiency. EMBO. J. 1997, 16, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keryer-Bibens, C.; Pioche-Durieu, C.; Villemant, C.; Souquere, S.; Nishi, N.; Hirashima, M.; Middeldorp, J.; Busson, P. Exosomes released by EBV-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells convey the viral latent membrane protein 1 and the immunomodulatory protein galectin 9. BMC. Cancer 2006, 6, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegtel, D. M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Wurdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar]
- Abend, J.R.; Uldrick, T.; Ziegelbauer, J.M. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis receptor protein (TWEAKR) expression by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus microRNA prevents TWEAK-induced apoptosis and inflammatory cytokine expression. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12139–12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffert, G.; Malterer, G.; Hausser, J.; Viiliainen, J.; Fender, A.; Contrant, M.; Ivacevic, T.; Benes, V.; Gros, F.; Voinnet, O.; et al. Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus microRNAs target caspase 3 and regulate apoptosis. PLoS. Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Ma, X.; Tang, M.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z.; Sun, L.; et al. EBV encoded miR-BHRF1-1 potentiates viral lytic replication by downregulating host p53 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalsky, R.L.; Samols, M.A.; Plaisance, K.B.; Boss, I.W.; Riva, A.; Lopez, M.C.; Baker, H.V.; Renne, R. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encodes an ortholog of miR-155. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12836–12845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwein, E.; Cullen, B.R. A human herpesvirus microRNA inhibits p21 expression and attenuates p21-mediated cell cycle arrest. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5229–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, E. Y.; Siu, K.L.; Kok, K.H.; Lung, R.W.; Tsang, C.M.; To, K.F.; Kwong, D.L.; Tsao, S.W.; Jin, D.Y. An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA targets PUMA to promote host cell survival. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquitz, A.R.; Mathur, A.; Nam, C.S.; Raab-Traub, N. The Epstein-Barr Virus BART microRNAs target the pro-apoptotic protein Bim. Virology 2011, 412, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, R.; Lin, X.; Liang, D.; Deng, Q.; Lan, K. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded microRNA miR-K12-11 attenuates transforming growth factor beta signaling through suppression of SMAD5. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bartolo, D.L.; Cannon, M.; Liu, Y.F.; Renne, R.; Chadburn, A.; Boshoff, C.; Cesarman, E. KSHV LANA inhibits TGF-beta signaling through epigenetic silencing of the TGF-beta type II receptor. Blood 2008, 111, 4731–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizasa, H.; Wulff, B.E.; Alla, N.R.; Maragkakis, M.; Megraw, M.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.; Iwakiri, D.; Takada, K.; Wiedmer, A.; Showe, L.; et al. Editing of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BART6 microRNAs controls their dicer targeting and consequently affects viral latency. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33358–33370. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.C.; Li, Z.; Chu, C.Y.; Feng, J.; Sun, R.; Rana, T.M. MicroRNAs encoded by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus regulate viral life cycle. EMBO. Rep. 2010, 11, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellare, P.; Ganem, D. Regulation of KSHV lytic switch protein expression by a virus-encoded microRNA: an evolutionary adaptation that fine-tunes lytic reactivation. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 6, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Liang, D.; He, Z.; Deng, Q.; Robertson, E.S.; Lan, K. miR-K12-7-5p encoded by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus stabilizes the latent state by targeting viral ORF50/RTA. PLoS. One. 2011, 6, e16224. [Google Scholar]
- Barth, S.; Pfuhl, T.; Mamiani, A.; Ehses, C.; Roemer, K.; Kremmer, E.; Jaker, C.; Hock, J.; Meister, G.; Grasser, F.A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA miR-BART2 down-regulates the viral DNA polymerase BALF5. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2008, 36, 666–675. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, M.; Wang, Y.Z.; Gout, P.W. The x(c)- cystine/glutamate antiporter: a potential target for therapy of cancer and other diseases. J.. Cell Physiol. 2008, 215, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleeba, J.A.; Berger, E.A. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus fusion-entry receptor: cystine transporter xCT. Science 2006, 311, 1921–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Freitas, E.; Sullivan, R.; Mohan, S.; Bacelieri, R.; Branch, D.; Romano, M.; Kearney, P.; Oates, J.; Plaisance, K.; et al. Upregulation of xCT by KSHV-encoded microRNAs facilitates KSHV dissemination and persistence in an environment of oxidative stress. PLoS. Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellot, G.; Cartron, P.F.; Er, E.; Oliver, L.; Juin, P.; Armstrong, L.C.; Bornstein, P.; Mihara, K.; Manon, S.; Vallette, F.M. TOM22, a core component of the mitochondria outer membrane protein translocation pore, is a mitochondrial receptor for the proapoptotic protein Bax. Cell Death Differ 2007, 14, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.V.; Wade, C.M.; Kang, H.M.; Alper, S.; Rutledge, H.; Lackford, B.; Eskin, E.; Daly, M. J.; Schwartz, D.A. Identification of novel genes that mediate innate immunity using inbred mice. Genetics 2009, 183, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Sultana, A.; Gandhi, P.; Franklin, E.; Hamamoto, S.; Khan, A.R.; Munson, M.; Schekman, R.; Weisman, L.S. Myosin V transports secretory vesicles via a Rab GTPase cascade and interaction with the exocyst complex. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 1156–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Kubo, K.; Waguri, S.; Yabashi, A.; Shin, H.W.; Katoh, Y.; Nakayama, K. Rab11 regulates exocytosis of recycling vesicles at the plasma membrane. J. Cell Sci. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnatz, H.J.; Schmidt, D.; Manke, T.; Piccini, I.; Sultan, M.; Borodina, T.; Balzereit, D.; Wruck, W.; Soldatov, A.; Vingron, M.; et al. The BTB and CNC homology 1 (BACH1) target genes are involved in the oxidative stress response and in control of the cell cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 23521–23532. [Google Scholar]
- Boss, I.W.; Nadeau, P.E.; Abbott, J.R.; Yang, Y.; Mergia, A.; Renne, R. A Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded ortholog of microRNA miR-155 induces human splenic B-cell expansion in NOD/LtSz-scid IL2Rgammanull mice. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9877–9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, D.; Kim, S.W.; McKeller, M.R.; Dahia, P.L.; Aguiar, R.C. Targeting of SMAD5 links microRNA-155 to the TGF-beta pathway and lymphomagenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3111–3116. [Google Scholar]
- Eis, P.S.; Tam, W.; Sun, L.; Chadburn, A.; Li, Z.; Gomez, M.F.; Lund, E.; Dahlberg, J.E. Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3627–3632. [Google Scholar]
- Kluiver, J.; Poppema, S.; de Jong, D.; Blokzijl, T.; Harms, G.; Jacobs, S.; Kroesen, B.J.; van den Berg, A. BIC and miR-155 are highly expressed in Hodgkin, primary mediastinal and diffuse large B cell lymphomas. J. Pathol. 2005, 207, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnstaedt, S.D.; Gottwein, E.; Skalsky, R.L.; Luftig, M.A.; Cullen, B.R. Virally induced cellular microRNA miR-155 plays a key role in B-cell immortalization by Epstein-Barr virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11670–11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Xu, H.; Lambeth, L.; Smith, L.P.; Kgosana, L.; Wang, X.; Nair, V. A functional MicroRNA-155 ortholog encoded by the oncogenic Marek's disease virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.W.; Trotter, M.W.; Lagos, D.; Bourboulia, D.; Henderson, S.; Makinen, T.; Elliman, S.; Flanagan, A.M.; Alitalo, K.; Boshoff, C. Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus-induced cellular reprogramming contributes to the lymphatic endothelial gene expression in Kaposi sarcoma. Nat. Genet 2004, 36, 687–693. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, A.; Henderson, S.; Lagos, D.; Nikitenko, L.; Coulter, E.; Roberts, S.; Gratrix, F.; Plaisance, K.; Renne, R.; Bower, M.; et al. KSHV-encoded miRNAs target MAF to induce endothelial cell reprogramming. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalsky, R.L.; Corcoran, D.L.; Gottwein, E.; Frank, C.L.; Kang, D.; Hafner, M.; Nusbaum, J.D.; Feederle, R.; Delecluse, H.J.; Luftig, M.A.; et al. The viral and cellular microRNA targetome in lymphoblastoid cell lines. PLoS. Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, K.J.; Rabinowitz, G. S.; Yario, T.A.; Luna, J.M.; Darnell, R.B.; Steitz, J.A. EBV and human microRNAs co-target oncogenic and apoptotic viral and human genes during latency. EMBO. J. 2012, 31, 2207–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolken, L.; Malterer, G.; Erhard, F.; Kothe, S.; Friedel, C.C.; Suffert, G.; Marcinowski, L.; Motsch, N.; Barth, S.; Beitzinger, M.; et al. Systematic analysis of viral and cellular microRNA targets in cells latently infected with human gamma-herpesviruses by RISC immunoprecipitation assay. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, J.O.; Alvarez, I.B.; Pasquinelli, V.; Martinez, G.J.; Quiroga, M.F.; Abbate, E.; Musella, R.M.; Chuluyan, H.E.; Garcia, V.E. Programmed death (PD)-1:PD-ligand 1/PD-ligand 2 pathway inhibits T cell effector functions during human tuberculosis. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 116–125. [Google Scholar]
- Scibetta, A.G.; Santangelo, S.; Coleman, J.; Hall, D.; Chaplin, T.; Copier, J.; Catchpole, S.; Burchell, J.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. Functional analysis of the transcription repressor PLU-1/JARID1B. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 7220–7235. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.A.; White, C.A.; Robb, L.; Alexander, W.S.; Tarlinton, D.M. SOCS3 deletion in B cells alters cytokine responses and germinal center output. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 6318–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, C.; Podgrabinska, S.; Skobe, M.; Ganem, D. Activation of NF-kappaB by the latent vFLIP gene of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is required for the spindle shape of virus-infected endothelial cells and contributes to their proinflammatory phenotype. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7179–7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, M.; Rose, P.P.; Moses, A.V.; Fruh, K. Remodeling of endothelial adherens junctions by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9615–9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, W.; Gao, S.J. Actin dynamics regulate multiple endosomal steps during Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus entry and trafficking in endothelial cells. PLoS. Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.; Robertson, E.S. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded latency-associated nuclear antigen induces chromosomal instability through inhibition of p53 function. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Z.; Lin, L.; Liang, J.; Li, J.L.; Chen, H.Y. Expression and prognosis of FOXO3a and HIF-1alpha in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.J.; Peterson, J.A. Nucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis during Poliovirus Infection of Human Cells. J. Mol. Biol. 1964, 8, 556–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malterer, G.; Dolken, L.; Haas, J. The miRNA-targetome of KSHV and EBV in human B-cells. RNA. Biol. 2011, 8, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abend, J.R.; Ramalingam, D.; Kieffer-Kwon, P.; Uldrick, T.S.; Yarchoan, R.; Ziegelbauer, J.M. KSHV microRNAs target two components of the TLR/IL-1R signaling cascade, IRAK1 and MYD88, to reduce inflammatory cytokine expression. J. Virol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, E.; Salinas, R.E.; Chang, C.; Zhou, T.; Linnstaedt, S.D.; Gottwein, E.; Jacobs, C.; Jima, D.; Li, Q.J.; Dave, S.S.; et al. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced tumor suppressor microRNA MiR-34a is growth promoting in EBV-infected B cells. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6889–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, E.; Luftig, M.A. The role of microRNAs in Epstein-Barr virus latency and lytic reactivation. Microbes Infect 2011, 13, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramalingam, D.; Kieffer-Kwon, P.; Ziegelbauer, J.M. Emerging Themes from EBV and KSHV microRNA Targets. Viruses 2012, 4, 1687-1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4091687
Ramalingam D, Kieffer-Kwon P, Ziegelbauer JM. Emerging Themes from EBV and KSHV microRNA Targets. Viruses. 2012; 4(9):1687-1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4091687
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamalingam, Dhivya, Philippe Kieffer-Kwon, and Joseph M. Ziegelbauer. 2012. "Emerging Themes from EBV and KSHV microRNA Targets" Viruses 4, no. 9: 1687-1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4091687
APA StyleRamalingam, D., Kieffer-Kwon, P., & Ziegelbauer, J. M. (2012). Emerging Themes from EBV and KSHV microRNA Targets. Viruses, 4(9), 1687-1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4091687




