First Report of the Yezo Virus Isolates Detection in Russia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Processing of Ticks
2.2. RT-PCR Screening
2.3. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.4. NGS Data Analysis
2.5. Sequence Alignments and Phylogenetic Reconstruction
2.6. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
2.7. Statistical Analysis
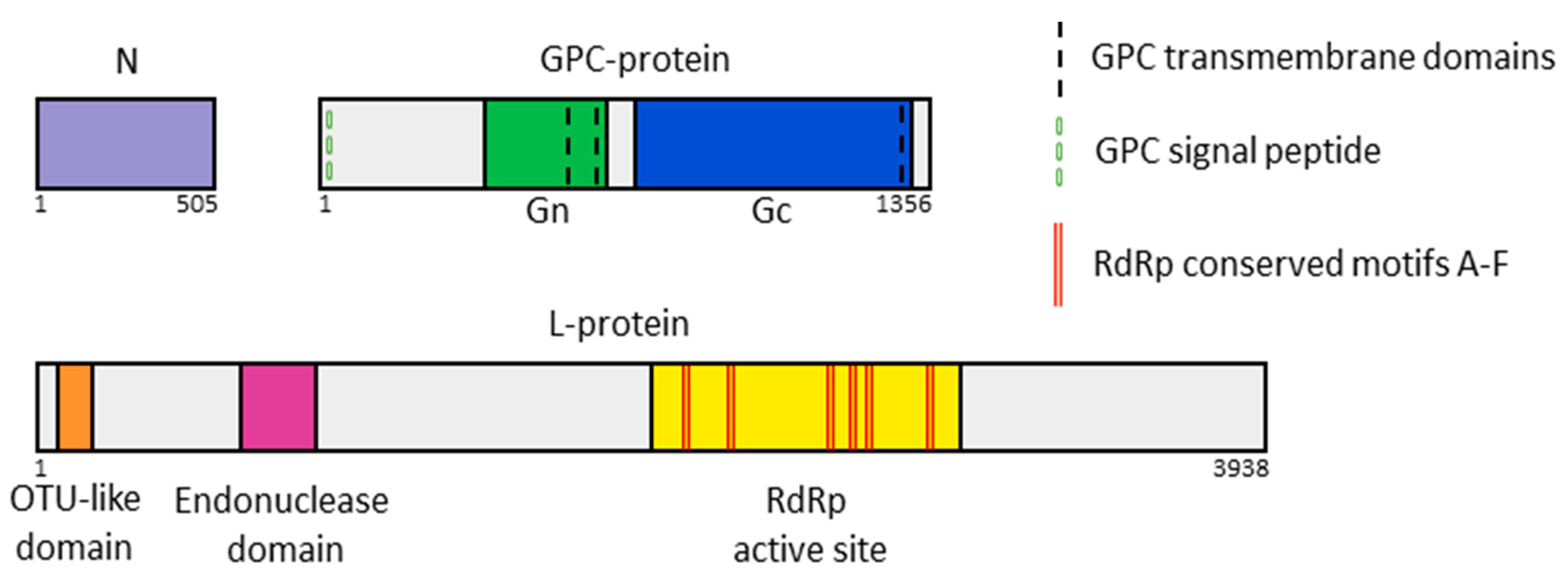
2.8. Functional Annotation of Viral Proteins
3. Results
3.1. Tick Identification and Yezo Virus Molecular Screening
3.2. Yezo Virus Genome
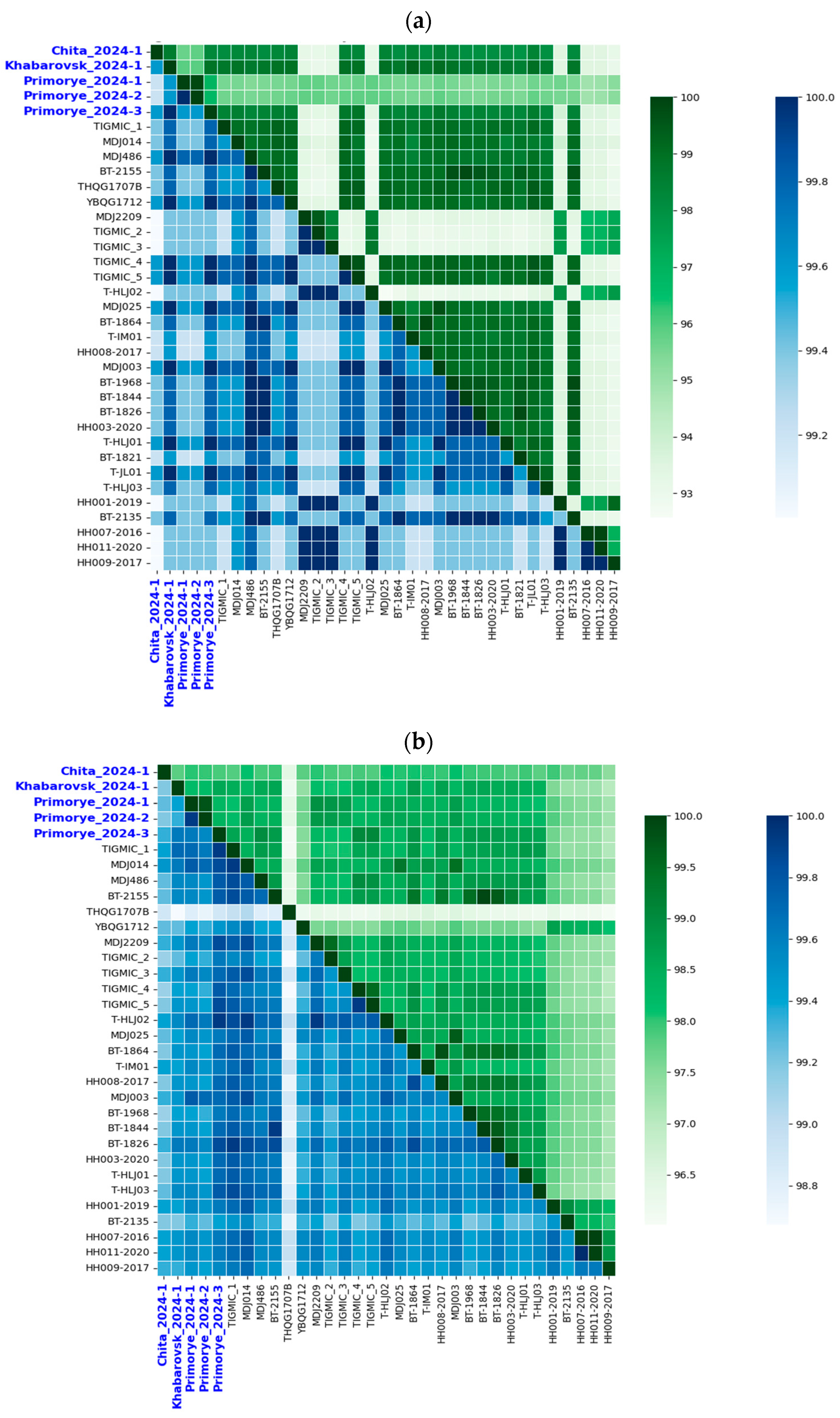
3.3. Homology Analysis of YEZV Nucleotide and Amino Acid Sequences
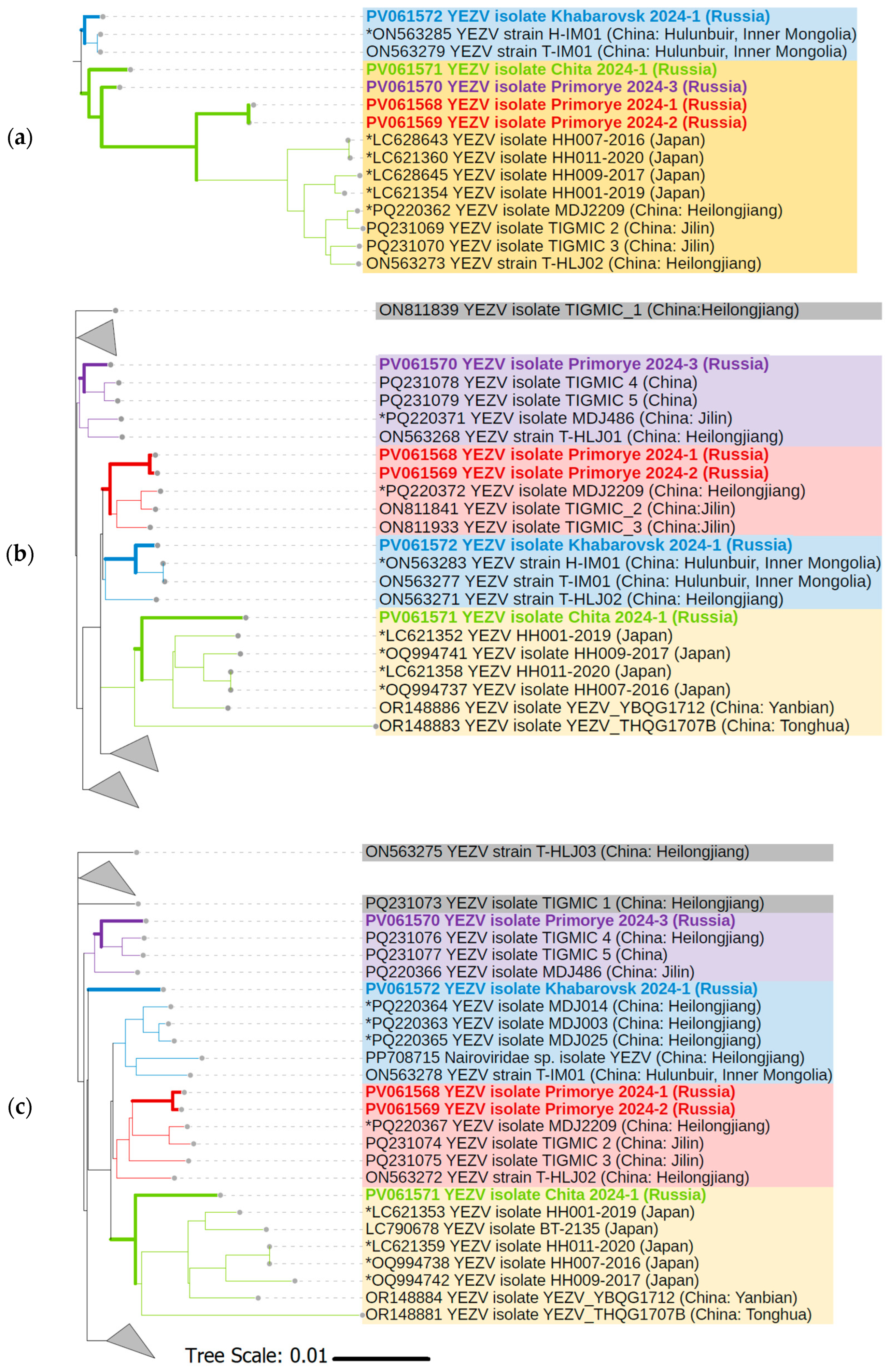
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of YEZV Genomic Segments
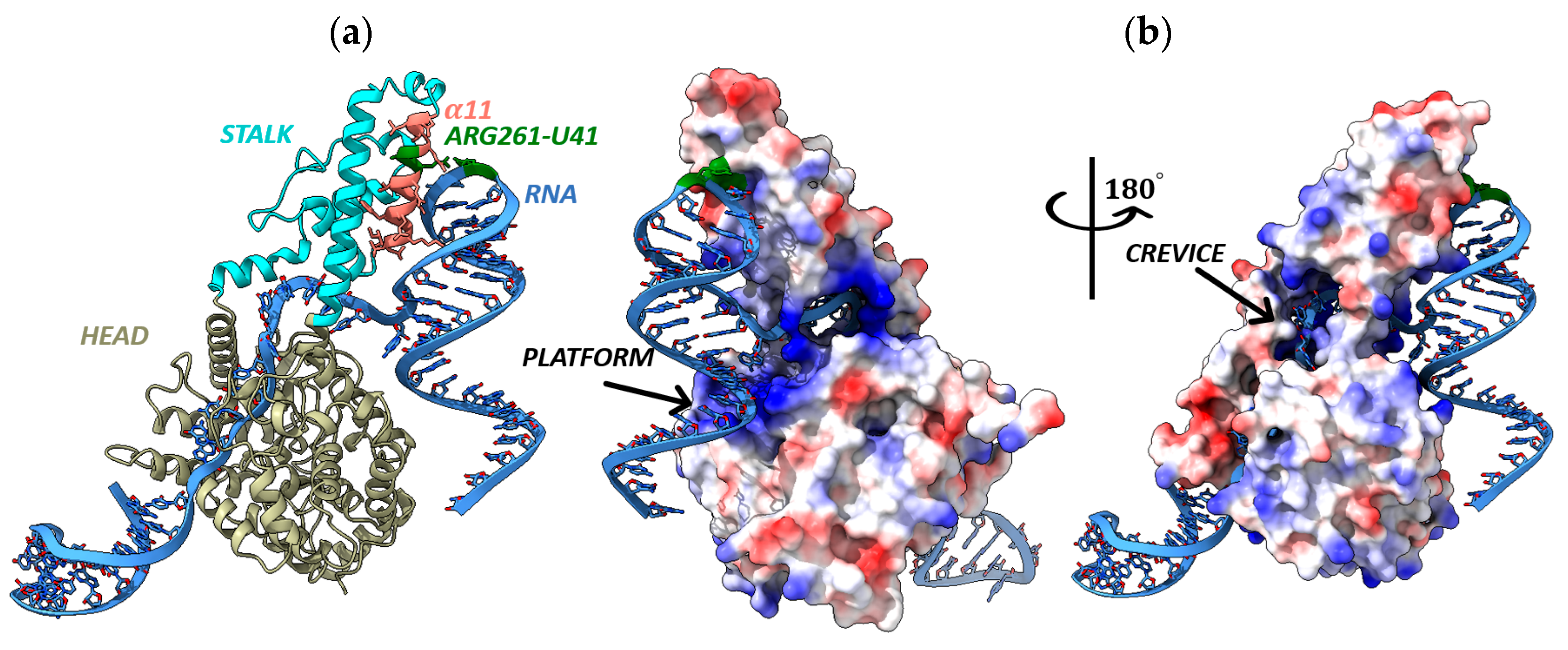
3.5. Nucleoprotein Structure Comparison of the Russian Yezo Virus Isolates
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| YEZV | Yezo virus |
| ssRNA(−) | Single-stranded negative-sense RNA |
| N | Nucleoprotein |
| I. persulcatus | Ixodes persulcatus |
| GPC | Glycoprotein precursor |
| RT-PCR | Real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| 95% CI | 95% confidence interval |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| RdRp | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| OTU-like domain | Viral homolog of the ovarian tumor protease domain |
| CCHFV | Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic virus |
| UTR | Untranslated regions |
References
- Lin, Y.; Pascall, D.J. Characterisation of putative novel tick viruses and zoonotic risk prediction. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e10814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, J.H.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Bergeron, É.; Burt, F.; Ergünay, K.; Garrison, A.R.; Marklewitz, M.; Mirazimi, A.; Papa, A.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Nairoviridae 2024. J. Gen. Virol. 2024, 105, 001974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Minamikawa, M.; Kovba, A.; Numata, H.; Itoh, T.; Ariizumi, T.; Shigeno, A.; Katada, Y.; Niwa, S.; Taya, Y.; et al. Environmental and host factors underlying tick-borne virus infection in wild animals: Investigation of the emerging Yezo virus in Hokkaido, Japan. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2024, 15, 102419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Xu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Z.; Sui, L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Yezo Virus Infection in Tick-Bitten Patient and Ticks, Northeastern China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Z.; Bian, C.; Ye, R.Z.; Cui, X.M.; Yao, N.N.; Yang, J.H.; Chu, Y.L.; Su, X.L.; Wu, Y.F.; Ye, J.L.; et al. A series of patients infected with the emerging tick-borne Yezo virus in China: An active surveillance and genomic analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Zhang, J.; He, P.-J.; Xiong, T.; Zhu, D.-Y.; Zhu, W.-J.; Ni, X.-B.; Du, L.-F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.-W.; et al. Characteristics of viral ovarian tumor domain protease from two emerging orthonairoviruses and identification of Yezo virus human infections in northeastern China as early as 2012. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0172724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, A.; Tatemoto, K.; Ishijima, K.; Inoue, Y.; Park, E.S.; Yamamoto, T.; Taira, M.; Kuroda, Y.; Virhuez-Mendoza, M.; Harada, M.; et al. Transboundary Movement of Yezo Virus via Ticks on Migratory Birds, Japan, 2020–2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 2674–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Priyanshu, P.; Sharma, R.K.; Sharma, D.; Arora, M.; Gaidhane, A.M.; Zahiruddin, Q.S.; Rustagi, S.; Mawejje, E.; Satapathy, P. Climate change and its role in the emergence of new tick-borne Yezo virus. New Microbes New Infect. 2024, 60–61, 101423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Shu, J.; Zhu, X.; Ren, Y.; Yu, J.; Ye, L.; Tan, Q.; Li, Q. Dual Fluorescent Quantitative RT-PCR Nucleic Acid Group, Kit and Method for Synchronously Detecting SGLV and YEZV. China Patent CN114438259A, 5 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Gangavarapu, K.; Quick, J.; Matteson, N.L.; De Jesus, J.G.; Main, B.J.; Tan, A.L.; Paul, L.M.; Brackney, D.E.; Grewal, S.; et al. An amplicon-based sequencing framework for accurately measuring intrahost virus diversity using PrimalSeq and iVar. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, S.C.; Luciani, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Park, Y.; Lopez, R.; Finn, R.D. HMMER web server: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W200–W204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, M.; Andreeva, A.; Florentino, L.C.; Chuguransky, S.R.; Grego, T.; Hobbs, E.; Pinto, B.L.; Orr, A.; Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Ponamareva, I.; et al. InterPro: The protein sequence classification resource in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D444–D456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devignot, S.; Bergeron, E.; Nichol, S.; Mirazimi, A.; Weber, F. A virus-like particle system identifies the endonuclease domain of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5957–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kempen, M.; Kim, S.S.; Tumescheit, C.; Mirdita, M.; Lee, J.; Gilchrist, C.L.M.; Söding, J.; Steinegger, M. Fast and accurate protein structure search with Foldseek. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhatt, R.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Biester, A.; Biswas, P.; Bittrich, S.; Blaumann, S.; Brown, R.; Chao, H.; et al. Updated resources for exploring experimentally-determined PDB structures and Computed Structure Models at the RCSB Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D564–D574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, W.; Ji, W.; Deng, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C.; Deng, F.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; et al. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus nucleoprotein reveals endonuclease activity in bunyaviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5046–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasecka, L.; Baron, M.D. The molecular biology of nairoviruses, an emerging group of tick-borne arboviruses. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 1249–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergunay, K.; Bourke, B.P.; Reinbold-Wasson, D.D.; Caicedo-Quiroga, L.; Vaydayko, N.; Kirkitadze, G.; Chunashvili, T.; Tucker, C.L.; Linton, Y.M. Novel clades of tick-borne pathogenic nairoviruses in Europe. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2024, 121, 105593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter Horst, S.; Conceição-Neto, N.; Neyts, J.; Rocha-Pereira, J. Structural and functional similarities in bunyaviruses: Perspectives for pan-bunya antivirals. Rev. Med. Virol. 2019, 29, e2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Saka, N.; Nishio, M. Identification of critical residues for RNA binding of nairovirus nucleoprotein. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0144624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, A. Emerging Arboviruses in Europe. Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2024, 69, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xu, L.; Shi, W. The human-infection potential of emerging tick-borne viruses is a global public health concern. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartashov, M.Y.; Khankhareev, S.S.; Krivosheina, E.I.; Svirin, K.A.; Kurushina, V.Y.; Ternovoi, V.A. Detection and molecular genetic characterization of segmented flavi-like Yanggou virus in Dermacentor nuttalli Ol. (1929) ticks in Buryatia. Acta Biomed. Sci. 2024, 9, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartashov, M.Y.; Krivosheina, E.I.; Kurushina, V.Y.; Moshkin, A.B.; Khankhareev, S.S.; Biche-ool, C.R.; Pelevina, O.N.; Popov, N.V.; Bogomazova, O.L.; Ternovoi, V.A. Prevalence and genetic diversity of the Alongshan virus (Flaviviridae) circulating in ticks in the south of Eastern Siberia. Probl. Virol. (Vopr. Virusol.) 2024, 69, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, D.; Schulze-Niemand, E.; Stein, M.; Naumann, M. Ovarian tumor domain proteases in pathogen infection. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, A.; Tsergouli, K.; Tsioka, K.; Mirazimi, A. Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever: Tick-Host-Virus Interactions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukoaka, B.M.; Okesanya, O.J.; Daniel, F.M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Udam, N.G.; Wagwula, P.M.; Adigun, O.A.; Udoh, R.A.; Peter, I.G.; Lawal, H. Updated WHO list of emerging pathogens for a potential future pandemic: Implications for public health and global preparedness. Infez. Med. 2024, 32, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sabsay, K.R.; Te Velthuis, A.J.W. Negative and ambisense RNA virus ribonucleocapsids: More than protective armor. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2023, 87, e0008223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeeva, S.; Pador, S.; Voss, B.; Ganaie, S.S.; Mir, M.A. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus nucleocapsid protein has dual RNA binding modes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Chiou, C.C.; Almutairi, M.M.; Ajmal, A.; Batool, S.; Javed, B.; Tanaka, T.; Chen, C.C.; Alouffi, A.; Ali, A. Targeting Yezo Virus Structural Proteins for Multi-Epitope Vaccine Design Using Immunoinformatics Approach. Viruses 2024, 16, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. Region | Russia Region | Tick Species | No. Ticks Examined | No. Positive Ticks | Minimum YEZV Infection Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Primorsky Territory | I. persulcatus | 368 | 3 | 0.8% (95% CI: 0.3–2.4) |
| 2 | Khabarovsk Territory | I. persulcatus | 79 | 1 | 1.3% (95% CI: 0.2–6.8) |
| 3 | Transbaikal Territory | I. persulcatus | 150 | 1 | 0.7% (95% CI: 0.1–3.6) |
| 4 | Other regions | I. persulcatus | 3525 | 0 | 0 |
| I. ricinus | 1196 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total: | I. persulcatus | 4122 | 5 | 0.12% (95% CI: 0.05–0.28) | |
| 5318 | 5 | 0.1% (95% CI: 0.04–0.22) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kartashov, M.; Svirin, K.; Zheleznova, A.; Yanshin, A.; Radchenko, N.; Kurushina, V.; Tregubchak, T.; Maksimenko, L.; Sivay, M.; Ternovoi, V.; et al. First Report of the Yezo Virus Isolates Detection in Russia. Viruses 2025, 17, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081125
Kartashov M, Svirin K, Zheleznova A, Yanshin A, Radchenko N, Kurushina V, Tregubchak T, Maksimenko L, Sivay M, Ternovoi V, et al. First Report of the Yezo Virus Isolates Detection in Russia. Viruses. 2025; 17(8):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081125
Chicago/Turabian StyleKartashov, Mikhail, Kirill Svirin, Alina Zheleznova, Alexey Yanshin, Nikita Radchenko, Valentina Kurushina, Tatyana Tregubchak, Lada Maksimenko, Mariya Sivay, Vladimir Ternovoi, and et al. 2025. "First Report of the Yezo Virus Isolates Detection in Russia" Viruses 17, no. 8: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081125
APA StyleKartashov, M., Svirin, K., Zheleznova, A., Yanshin, A., Radchenko, N., Kurushina, V., Tregubchak, T., Maksimenko, L., Sivay, M., Ternovoi, V., Agafonov, A., & Gladysheva, A. (2025). First Report of the Yezo Virus Isolates Detection in Russia. Viruses, 17(8), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081125







