Simian Foamy Virus Prevalence and Evolutionary Relationships in Two Free-Living Lion Tamarin Populations from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Processing and Analysis of Genomic DNA Integrity
2.3. Diagnostic qPCR
2.4. PCR of the Pol Region
2.5. Phylogenetic and Timescale Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
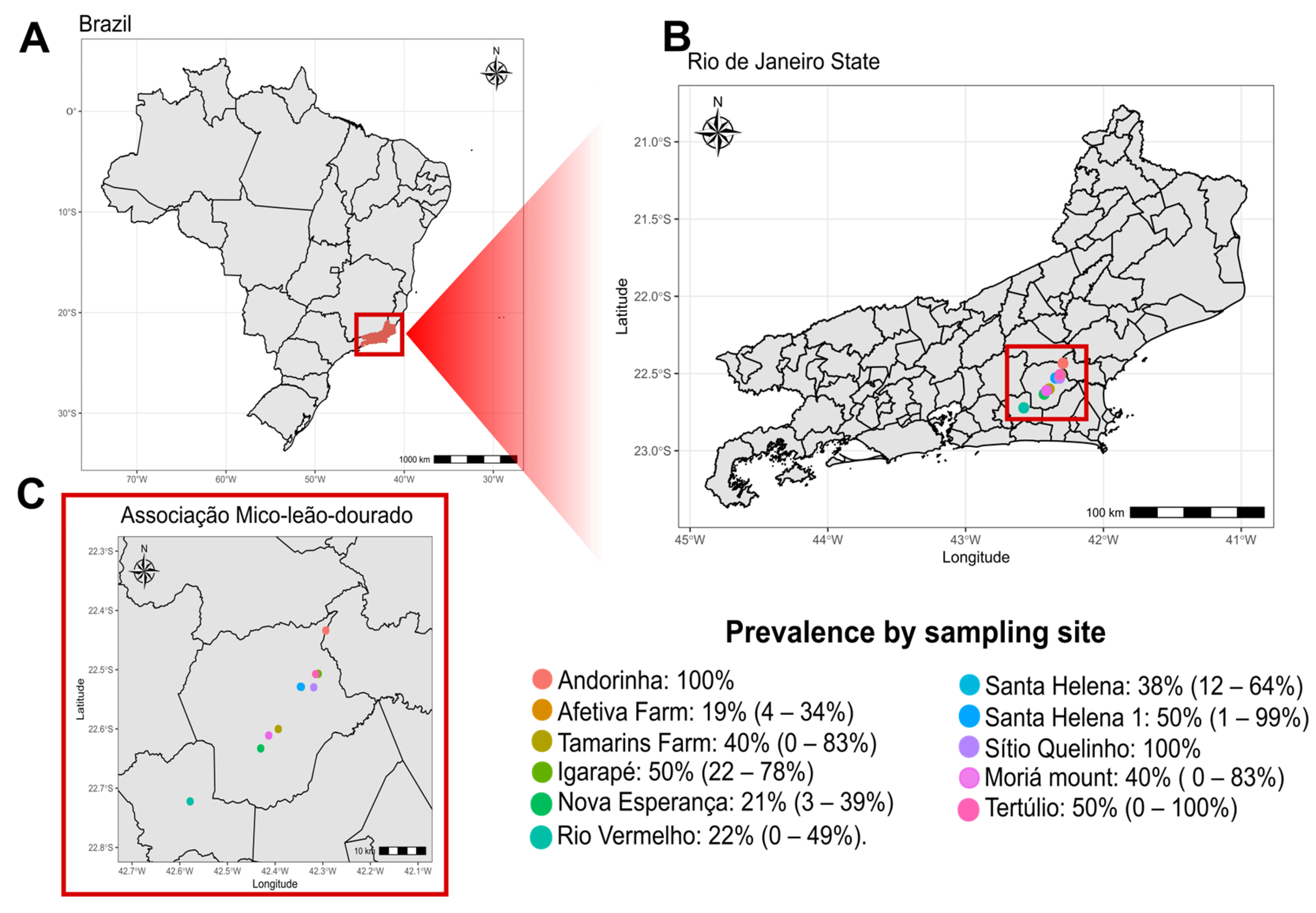
3.1. Study Population
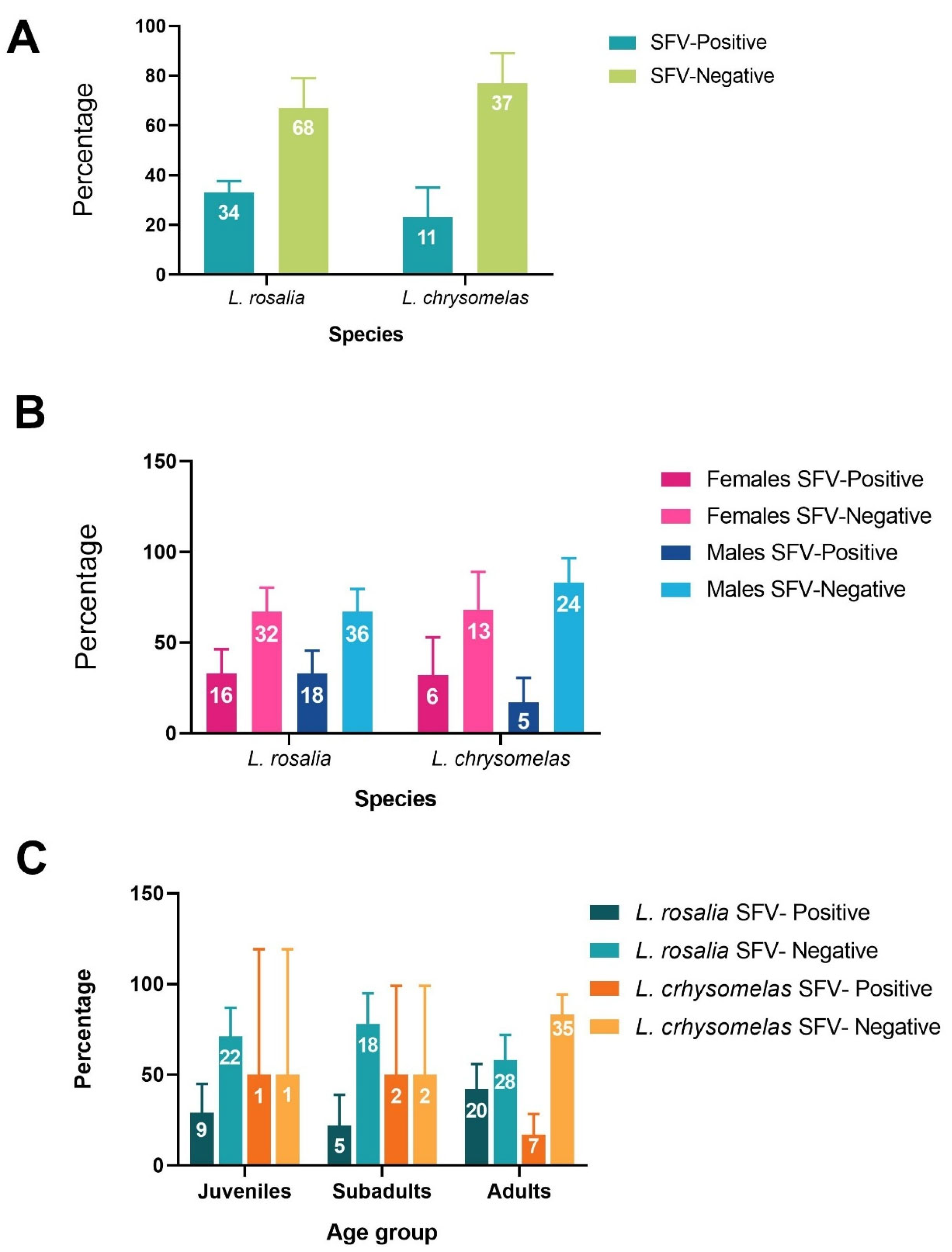
3.2. SFV Prevalence
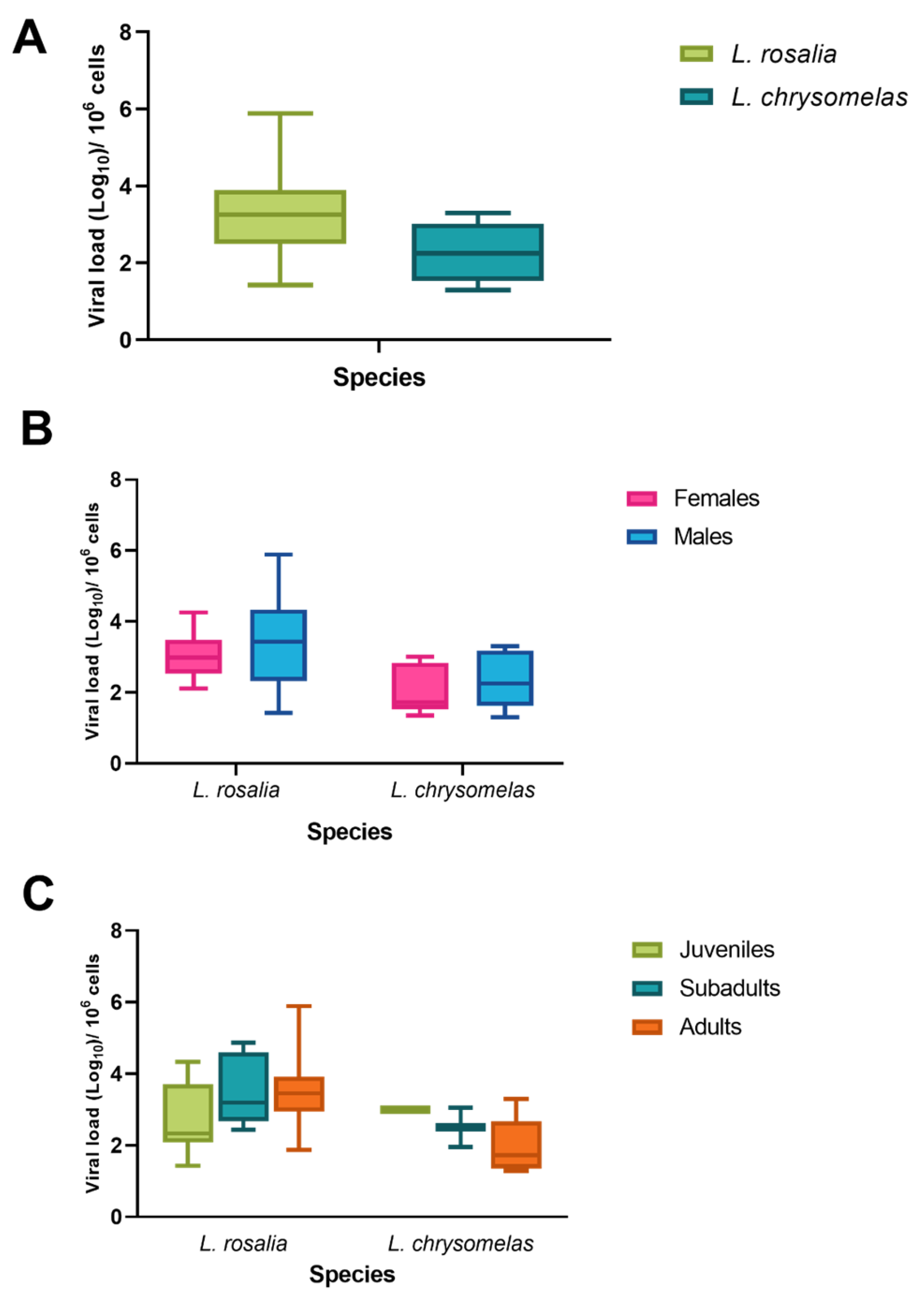
3.3. SFV Viral Load
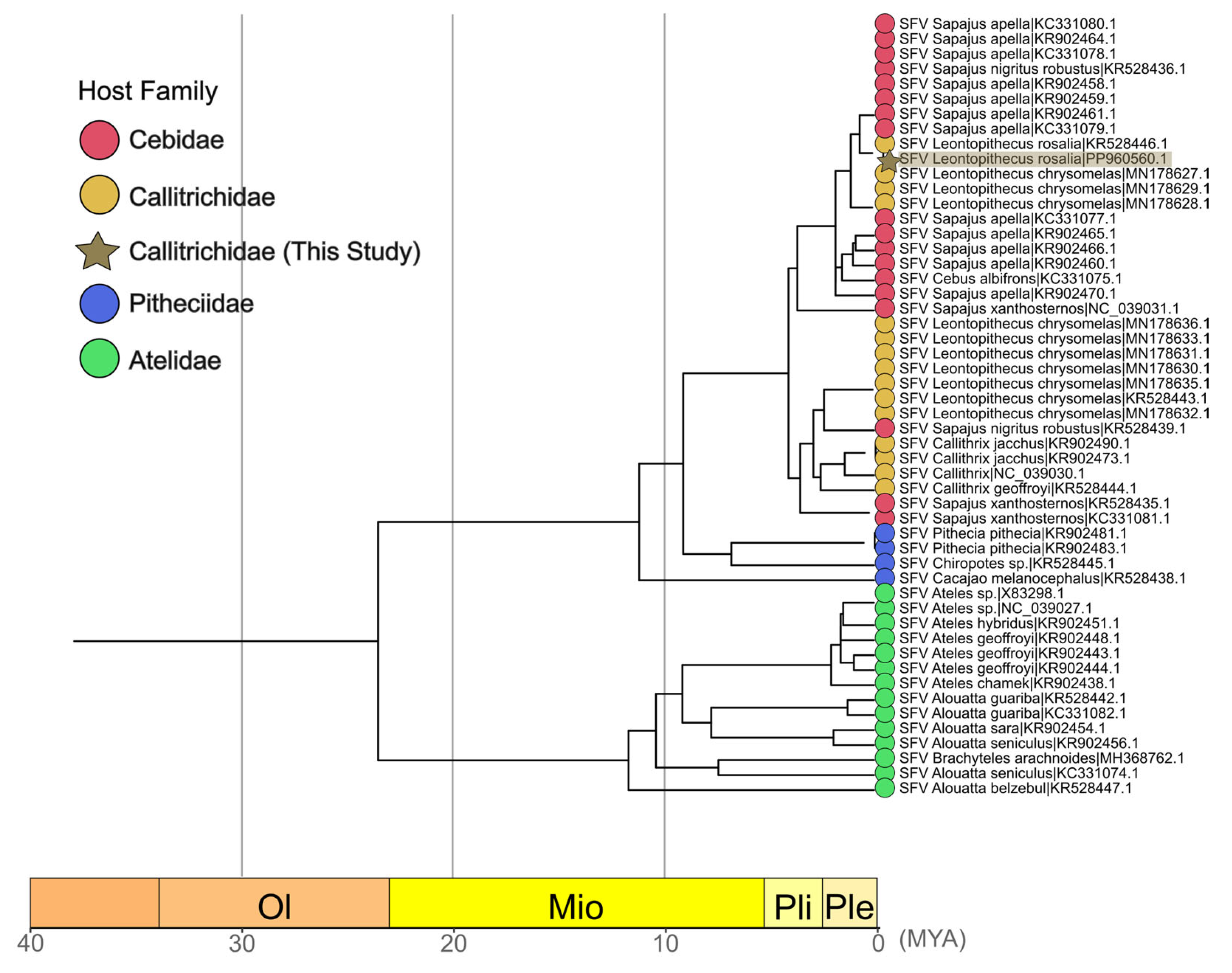
3.4. Phylogenetic and Timescale Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kehl, T.; Tan, J.; Materniak, M. Non-Simian Foamy Viruses: Molecular Virology, Tropism and prevalence and Zoonotic/Interspecies Transmission. Viruses 2013, 5, 2169–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Bodem, J.; Buseyne, F.; Gessain, A.; Johnson, W.; Kuhn, J.H.; Kuzmak, J.; Lindemann, D.; Linial, M.L.; Löchelt, M.; et al. Spumaretroviruses: Updated Taxonomy and Nomenclature. Virology 2018, 516, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, J.F.; Peebles, T.C. Propagation in Tissue Cultures of Cytopathogenic Agents from patients with Measles. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1954, 86, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustigian, R.; Johnston, P.; Reihart, H. Infection of Monkey Kidney Tissue Cultures with Virus-like Agents. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1955, 88, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto-Gotoh, A.; Yoshikawa, R.; Nakagawa So and Okamoto, M.; Miyazawa, T. Phylogenetic Analyses Reveal That Simian Foamy Virus isolated from Japanese Yakushima Macaques (Macaca fuscata yakui) Is from Most of Japanese Hondo Macaques (Macaca fuscata). Gene 2020, 734, 144382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, A.; Sibley, S.D.; Goldberg, T.L.; Switzer, W.M. Molecular Analysis of the Complete Genome of a Simian Foamy Virus Hylobates pileatus (Pileated Gibbon) Reveals Ancient-Evolution with Lesser Apes. Viruses 2019, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Switzer, W.M.; Salemi, M.; Shanmugam, V.; Gao, F.; Cong, M.E.; Kuiken, C.; Bhullar, V.; Beer, B.E.; Vallet, D.; Gautier-Hion, A.; et al. Ancient Co-Speciation of Simian Foamy Viruses and Primates. Nature 2005, 434, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz, C.P.; Troncoso, L.L.; Moreira, M.A.; Soares, E.A.; Pissinatti, A.; Bonvicino, C.R.; Seuánez, H.N.; Sharma, B.; Jia, H.; Shankar, A.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Highly Divergent Simian Viruses in a Wide Range of New World Primates from Brazil. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghersi, B.M.; Jia, H.; Aiewsakun, P.; Katzourakis, A.; Mendoza, P.; Bausch, D.G.; Kasper, M.R.; Montgomery, J.M.; Switzer, W.M. Wide Distribution and Ancient Evolutionary History of Simian Viruses in New World Primates. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.; Cavalcante, L.T.F.; Muniz, C.P.; Switzer, W.M.; Soares, M.A. Simian Foamy Viruses in Central and South America: A New World of Discovery. Viruses 2019, 11, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, T.S.; Muniz, C.P.; Moreira, S.B.; Bueno, M.G.; Kierulff, M.C.M.; Molina, C.V.; Catão-Dias, J.L.; Pissinatti, A.; Soares, M.A.; Santos, A.F. Eco-Epidemiological Profile and Molecular Characterization of simian Foamy Virus in a Recently-Captured Invasive Population of Leontopithecus chrysomelas (Golden-Headed Lion Tamarin) in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Viruses 2019, 11, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrago, C.G.; Menezes, A.N.; Furtado, C.; Bonvicino, C.R.; Seuanez, H.N. Multispecies Coalescent Analysis of the Early Diversification of neotropical Primates: Phylogenetic Inference under Strong Gene/Species Tree Conflict. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 3105–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUCN/SSC Primates-Specialist Group. Available online: http://www.primate-sg.org/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Hooks, J.J.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Chou, S.; Howk, R.; Lewis, M.; Gajdusek, D.C. Isolation of a New Simian Foamy Virus from a Spider Monkey Brain. Infect. Immun. 1973, 8, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troncoso, L.L.; Muniz, C.P.; Siqueira, J.D.; Curty, G.; Schrago, C.G.; Augusto, A.; Fedullo, L.; Soares, M.A.; Santos, A.F. Characterization and Comparative Analysis of a Simian Foamy Virus Genome Isolated from Brazilian Capuchin Monkeys. Virus Res. 2015, 208, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, C.P.; Cavalcante, L.T.F.; Dudley Dawn, M.; Pissinatti, A.; O’Connor, D.H.; Santos André, F.; Soares, M.A. First Complete Genome Sequence of a Simian Foamy Virus Infecting the Neotropical Primate Brachyteles arachnoides. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7, e00839-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thümer, L.; Rethwilm, A.; Holmes, E.C.; Bodem, J. The Complete Nucleotide Sequence of a New World Simian Foamy Virus. Virology 2007, 369, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, B.; Finzi, A.; McGee-Estrada, K.; Sodroski, J. Species-Specific Inhibition of Foamy Viruses from South American by New World Monkey TRIM5α Proteins. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4095–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczynska, B.; Jones, C.J.; Wolfe, L.G. Syncytium-Forming Virus of Common Marmosets (Callithrix jacchus). Infect. Immun. 1981, 31, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, C.P.; Jia, H.; Shankar, A.; Troncoso, L.L.; Augusto, A.M.; Farias, E.; Pissinatti, A.; Fedullo, L.P.; Santos, A.F.; Soares, M.A.; et al. An Expanded Search for Simian Foamy Viruses (SFV) in Brazilian World Primates Identifies Novel SFV Lineages and Host-Related Infections. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuderna, L.F.K.; Gao, H.; Janiak, M.C.; Kuhlwilm, M.; Orkin, J.D.; Bataillon, T.; Manu, S.; Valenzuela, A.; Bergman, J.; Rousselle, M.; et al. A Global Catalog of Whole-Genome Diversity from 233 Primate. Science 2023, 380, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzourakis, A.; Aiewsakun, P.; Jia, H.; Wolfe, N.D.; LeBreton, M.; Yoder, A.D.; Switzer, W.M. Discovery of Prosimian and Afrotherian Foamy Viruses and Potential Species Transmissions amidst Stable and Ancient Mammalian-Evolution. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wei, X.; Cui, J. Multiple Infiltration and Cross-Species Transmission of Foamy across the Paleozoic to the Cenozoic Era. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0048421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUCN/SSC Primates-Specialist Group. Global Non-Human Primate Diversity. 2023. Available online: http://www.primate-sg.org/primate_diversity_by_region/ (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Meyer, A.L.S.; Pie, M.R.; Passos, F.C. Assessing the Exposure of Lion Tamarins (Leontopithecus spp.) to future Climate Change. Am. J. Primatol. 2014, 76, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierulff, M.C.M.; Ruiz-Miranda, C.R.; de Oliveira, P.P.; Beck, B.B.; Martins, A.; Dietz, J.M.; Rambaldi, D.M.; Baker, A.J. The Golden Lion Tamarin Leontopithecus rosalia: A Success Story. Int. Zoo Yearbook 2012, 46, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Associação Mico-Leão-Dourado. Conectando Florestas Para Salvar a Espécie 2024. Available online: https://micoleao.org.br/ (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Associação Mico-Leão-Dourado. Publicações. Available online: https://micoleao.org.br/publicacoes/ (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Associação Mico-Leão-Dourado Manejo. Available online: https://micoleao.org.br/manejo/ (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Kleiman, D.G. Leontopithecus rosalia. Mamm. Species 1981, 148, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.C.; Neves, L.G.; Kierulff, M.C.M.; Jerusalinsky, L.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Rylands, A.B. Leontopithecus chrysomelas (Amended Version of 2020 Assessment). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. e.T40643A192327573, 2307-8235. 2021. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/40643/192327573 (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Raboy, B.E.; Christman, M.C.; Dietz, J.M. The Use of Degraded and Shade Cocoa Forests by Endangered Golden-Headed Lion Tamarins Leontopithecus chrysomelas. Oryx 2004, 38, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Miranda, C.R.; Affonso, A.G.; de Morais, M.M.; Verona, C.E.; Martins, A.; Beck, B.B. Behavioral and Ecological Interactions between Reintroduced Lion Tamarins (Leontopithecus rosalia Linnaeus, 1766) and introduced Marmosets (Callithrix spp, Linnaeus, 1758) in Brazil’s Coast Forest Fragments. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2006, 49, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, C.P.; Zheng, H.Q.; Jia, H.; Cavalcante, L.T.F.; Augusto, A.M.; Fedullo, L.P.; Pissinatti, A.; Soares, M.A.; Switzer, W.M.; Santos, A.F. A Non-Invasive Specimen Collection Method and a Novel Simian Virus (SFV) DNA Quantification Assay in New World Reveal Aspects of Tissue Tropism and Improved SFV. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Miranda, T.; Schiffler, F.B.; D’arc, M.; Moreira, F.R.R.; Cosentino, M.A.C.; Coimbra, A.; Mouta, R.; Medeiros, G.; Girardi, D.L.; Wanderkoke, V.; et al. Metagenomic Analysis Reveals Novel Dietary-Related Viruses in the gut Virome of Marmosets Hybrids (Callithrix jacchus x callithrix), Brazil. Virus Res. 2023, 325, 199017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Miranda, C.R.; Kleiman, D.G.; Dietz, J.M.; Moraes, E.; Grativol, A.D.; Baker, A.J.; Beck, B.B. Food Transfers in Wild and Reintroduced Golden Lion Tamarins, Leontopithecus rosalia. Am. J. Primatol. 1999, 48, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, J.M.; Baker, A.J.; Miglioretti, D. Seasonal Variation in Reproduction, Juvenile Growth, and Adult Mass in Golden Lion Tamarins (Leontopithecus rosalia). Am. J. Primatol. 1994, 34, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylands, A.B. Marmosets and Tamarins: Systematics, Behaviour, and Ecology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Muniz, C.P.; Cavalcante, L.T.F.; Jia, H.; Zheng, H.; Tang, S.; Augusto, A.M.; Pissinatti, A.; Fedullo, L.P.; Santos, A.F.; Soares, M.A.; et al. Zoonotic Infection of Brazilian Primate Workers with New World Foamy Virus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, R.; Cattori, V.; Gomes-Keller, M.A.; Meli, M.L.; Golder, M.C.; Lutz, H.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R. Quantitation of Feline Leukaemia Virus Viral and Proviral Loads by TaqMan Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 130, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. TrimAl: A Tool for Automated Alignment Trimming in Large-Scale Analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strimmer, K.; Von Haeseler, A. Likelihood-Mapping: A Simple Method to Visualize Phylogenetic Content of a Sequence Alignment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6815–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela, I.; Ashkenazy, H.; Katoh, K.; Pupko, T. GUIDANCE2: Accurate Detection of Unreliable Alignment Regions Accounting for the Uncertainty of Multiple Parameters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W7–W14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. DAMBE6: New Tools for Microbial Genomics, Phylogenetics, and Molecular Evolution. J. Hered. 2017, 108, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong Thomas, K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New Algorithms and Methods to Estimate Maximum-Likelihood: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast Approximation for Phylogenetic Bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Tao, Q.; Kumar, S. Theoretical Foundation of the RelTime Method for Estimating Times from Variable Evolutionary Rates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1770–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Battistuzzi, F.U.; Billing-Ross, P.; Murillo, O.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. Estimating Divergence Times in Large Molecular Phylogenies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19333–19338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, B.; Tao, Q.; Tamura, K.; Kumar, S. Fast and Accurate Estimates of Divergence Times from Big Data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.-Y. Ggtree: An r Package for Visualization and Annotation of phylogenetic Trees with Their Covariates and Other Associated. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, B.D. The R Project in Statistical Computing. MSOR Connect. 2001, 1, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S.; Christensen, R.H.B.; Singmann, H.; Dai, B.; Scheipl, F.; Grothendieck, G.; Green, P.; et al. Package “Lme4”. Convergence 2015, 12, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada, A.; Garber, P.A.; Rylands, A.B.; Roos, C.; Fernandez-Duque, E.; Di Fiore, A.; Nekaris, K.A.-I.; Nijman, V.; Heymann, E.W.; Lambert, J.E.; et al. Impending Extinction Crisis of the World’s Primates: Why Primates. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1600946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouinga-Ondémé, A.; Kazanji, M. Simian Foamy Virus in Non-Human Primates and Cross-Species to Humans in Gabon: An Emerging Zoonotic Disease in central Africa? Viruses 2013, 5, 1536–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, S.; Mitchell, J.L.; Sethi, M.; Almond, N.M.; Cutler, K.L.; Rose, N.J. Horizontal Acquisition and a Broad Biodistribution Typify Simian Foamy Virus Infection in a Cohort of Macaca fascicularis. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasse, A.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Merkel, K.; Goffe, A.S.; Boesch, C.; Mundry, R.; Leendertz, F.H. Mother-Offspring Transmission and Age-Dependent Accumulation of Simian Foamy Virus in Wild Chimpanzees. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5193–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Miranda, C.R.; de Morais, M.M., Jr.; Dietz, L.A.; Rocha Alexandre, B.; Martins, A.F.; Ferraz, L.P.; Mickelberg, J.; Hankerson, S.J.; Dietz, J.M. Estimating Population Sizes to Evaluate Progress in conservation of Endangered Golden Lion Tamarins (Leontopithecus rosalia). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, A.M.; Ruiz-Miranda, C.R.; Galetti Jr, P.M.; Niebuhr, B.B.; Alexandre, B.R.; Muylaert, R.L.; Grativol, A.D.; Ribeiro, J.W.; Ferreira, A.N.; Ribeiro, M.C. Landscape Resistance Influences Effective Dispersal of Endangered Lion Tamarins within the Atlantic Forest. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 224, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, V.; Martins, A.F.; Ruiz-Miranda, C.R. Unraveling the Dispersal Patterns and the Social Drivers of Natal of a Cooperative Breeding Mammal, the Golden Lion. Am. J. Primatol. 2019, 81, e22959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Round | Primer | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Direction | Size | Annealing Temperature (35 Cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 5960 | TACCACTTTGTAGGTCTTCC | Forward | 486 bp | 53.4 °C |
| 5878 | CTTTGGGGGTGGTAAGG | Reverse | |||
| 2nd | 5474 | GCCAAACATGAGAAAGGATG | Forward | 404 bp | 54 °C |
| 5878 | CTTTGGGGGTGGTAAGG | Reverse |
| Individuals | L. rosalia | L. chrysomelas |
|---|---|---|
| Total sample size | 102 | 48 |
| Males | 54 (53%) | 29 (60%) |
| Females | 48 (7%) | 19 (40%) |
| Adults | 48 (47%) | 42 (88%) |
| Subadults | 23 (23%) | 4 (8%) |
| Juveniles | 31 (30%) | 2 (4%) |
| Average weight (grams) | 521 (259–754) g | 603 (320–740) g |
| Average number of individuals sampled per site | 5 (2–26) | N/A * |
| Collection Point | Animals Sampled | Juveniles | Subadults | Adults | Prevalence (%) | Mean Viral Load * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afetiva | 26 | 12 | 9 | 5 | 19 (4–34) | 3.04 |
| Tamarins | 5 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 40 (0–83) | 3.81 |
| Igarapé | 12 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 50 (22–78) | 3.30 |
| Nova Esperança | 19 | 4 | 4 | 11 | 21 (3–39) | 3.14 |
| Rio Vermelho | 9 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 22 (0–49) | 2.74 |
| Ribeirão | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | N/A ** |
| Santa Helena | 14 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 36 (11–61) | 3.73 |
| Santa Helena I | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 50 (1–99) | 4.56 |
| Sítio Quelinho | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 3.91 |
| Tertúlio | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 50 (0–100) | 3.93 |
| Monte Moriá | 5 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 40 (0–83) | 3.63 |
| Andorinha | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 100 | 4.22 |
| Estimate | Standard Error | df | t Value | Pr (>|t|) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 4.41 | 1.67 | 29.12 | 2.65 | 0.01 |
| Age (Juvenile) | −1.16 | 0.69 | 38.11 | −1.68 | 0.10 |
| Age (Subadult) | −0.29 | 0.53 | 38.00 | −0.55 | 0.59 |
| Gender (Male) | 0.36 | 0.28 | 38.00 | 1.32 | 0.19 |
| Body Weight | −0.003 | 0.002 | 38.03 | −1.12 | 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Girardi, D.L.; Miranda, T.S.; Cosentino, M.A.C.; de Sá, C.C.; Francisco, T.M.; Afonso, B.C.; Soffiati, F.L.; Ferreira, S.S.; Moreira, S.B.; Pissinatti, A.; et al. Simian Foamy Virus Prevalence and Evolutionary Relationships in Two Free-Living Lion Tamarin Populations from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Viruses 2025, 17, 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081072
Girardi DL, Miranda TS, Cosentino MAC, de Sá CC, Francisco TM, Afonso BC, Soffiati FL, Ferreira SS, Moreira SB, Pissinatti A, et al. Simian Foamy Virus Prevalence and Evolutionary Relationships in Two Free-Living Lion Tamarin Populations from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Viruses. 2025; 17(8):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081072
Chicago/Turabian StyleGirardi, Déa Luiza, Thamiris Santos Miranda, Matheus Augusto Calvano Cosentino, Caroline Carvalho de Sá, Talitha Mayumi Francisco, Bianca Cardozo Afonso, Flávio Landim Soffiati, Suelen Sanches Ferreira, Silvia Bahadian Moreira, Alcides Pissinatti, and et al. 2025. "Simian Foamy Virus Prevalence and Evolutionary Relationships in Two Free-Living Lion Tamarin Populations from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil" Viruses 17, no. 8: 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081072
APA StyleGirardi, D. L., Miranda, T. S., Cosentino, M. A. C., de Sá, C. C., Francisco, T. M., Afonso, B. C., Soffiati, F. L., Ferreira, S. S., Moreira, S. B., Pissinatti, A., Ruiz-Miranda, C. R., Romano, V., Soares, M. A., D’arc, M., & Santos, A. F. (2025). Simian Foamy Virus Prevalence and Evolutionary Relationships in Two Free-Living Lion Tamarin Populations from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Viruses, 17(8), 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081072






