Detection of Feline Coronavirus RNA in Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis and Their Housemates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment of Study Cats and Housemates
2.2. Feline Sample Processing
2.3. Extraction of Feline Coronavirus RNA and Synthesis of cDNA
2.4. Taqman-Probe RT-qPCR
3. Results
3.1. Assessing Specificity of the RT-qPCR Assay
3.2. Sites and Levels of FCoV RNA Do Not Distinguish Clinical FIP
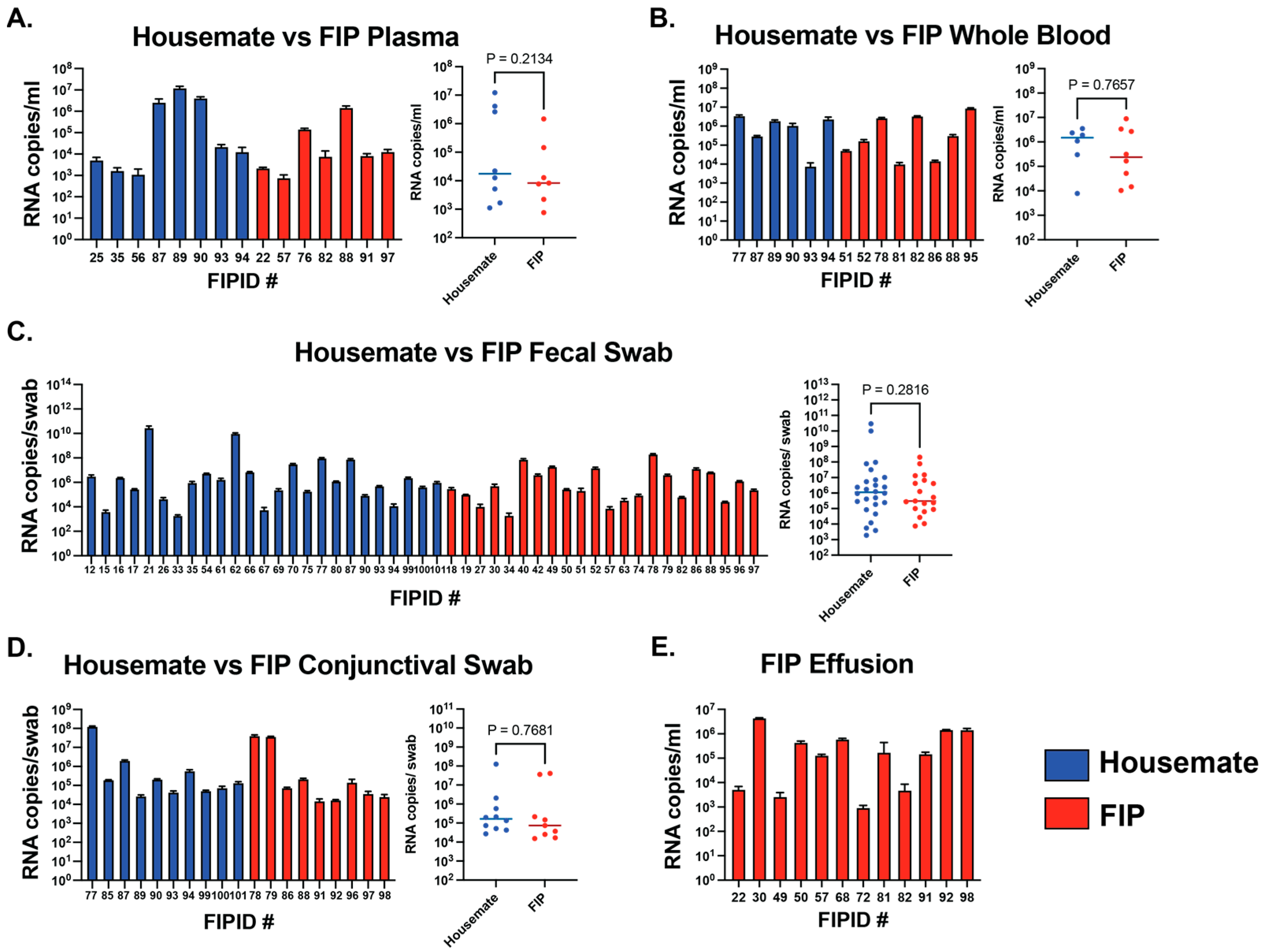
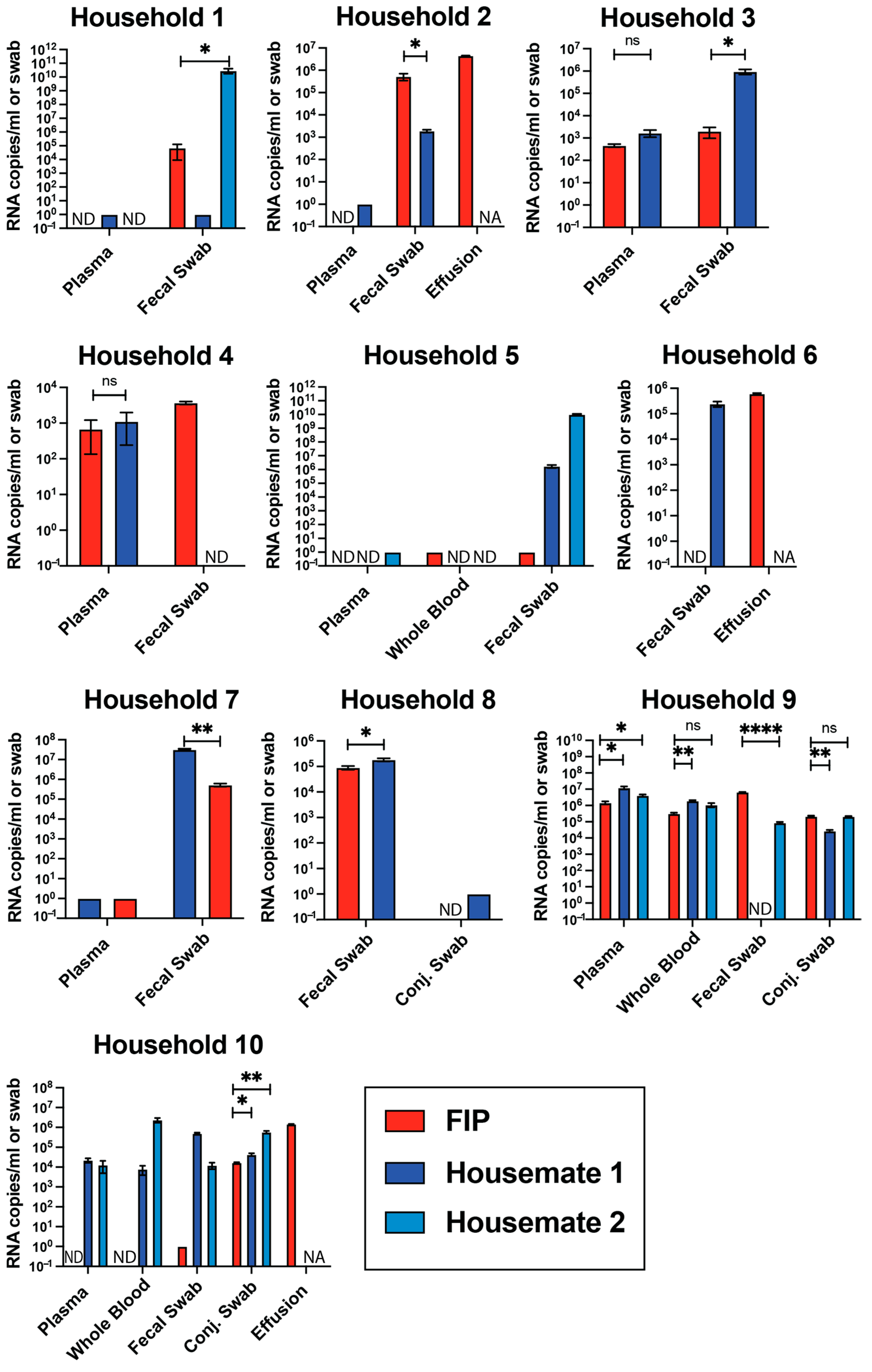
3.3. Viral RNA Levels Are Not Different Between FIP Cats and Their Housemates
3.4. RNA Copies Do Not Differ Between Sexes and Cluster in Young Cats
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Woolhouse, M.E.; Haydon, D.T.; Antia, R. Emerging pathogens: The epidemiology and evolution of species jumps. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Widagdo, W.; Okba, N.M.A.; Stalin Raj, V.; Haagmans, B.L. MERS-coronavirus: From discovery to intervention. One Health 2016, 3, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Du, L.; Jiang, S.; Shi, Z.; Baric, R.S.; Li, F. Two mutations were critical for bat-to-human transmission of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9119–9123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.F.; To, K.K.; Tse, H.; Jin, D.Y.; Yuen, K.Y. Interspecies transmission and emergence of novel viruses: Lessons from bats and birds. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Domingo, E.; García-Crespo, C.; Lobo-Vega, R.; Perales, C. Mutation Rates, Mutation Frequencies, and Proofreading-Repair Activities in RNA Virus Genetics. Viruses 2021, 13, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Flores-Vega, V.R.; Monroy-Molina, J.V.; Jiménez-Hernández, L.E.; Torres, A.G.; Santos-Preciado, J.I.; Rosales-Reyes, R. SARS-CoV-2: Evolution and Emergence of New Viral Variants. Viruses 2022, 14, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- ARohaim, M.; FEl Naggar, R.; MHelal, A.; MBayoumi, M.; AEl-Saied, M.; AAhmed, K.; ZShabbir, M.; Munir, M. Genetic Diversity and Phylodynamics of Avian Coronaviruses in Egyptian Wild Birds. Viruses 2019, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.; Lau, S.K.; To, K.K.; Cheng, V.C.; Woo, P.C.; Yuen, K.Y. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: Another zoonotic betacoronavirus causing SARS-like disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 465–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Benetka, V.; Kübber-Heiss, A.; Kolodziejek, J.; Nowotny, N.; Hofmann-Parisot, M.; Möstl, K. Prevalence of feline coronavirus types I and II in cats with histopathologically verified feline infectious peritonitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 99, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Addie, D.D.; Schaap, I.A.T.; Nicolson, L.; Jarrett, O. Persistence and transmission of natural type I feline coronavirus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84 Pt 10, 2735–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummrow, M.; Meli, M.L.; Haessig, M.; Goenczi, E.; Poland, A.; Pedersen, N.C.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Lutz, H. Feline coronavirus serotypes 1 and 2: Seroprevalence and association with disease in Switzerland. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Kong, F.; Guo, D.; Zhai, J.; Su, M.; Sun, D. Circulation and genetic diversity of Feline coronavirus type I and II from clinically healthy and FIP-suspected cats in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.; Liang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.; Bao, D.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.B.; Wang, K.; Hu, G.X.; Gao, F.S. An updated review of feline coronavirus: Mind the two biotypes. Virus Res. 2023, 326, 199059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pedersen, N.C. An update on feline infectious peritonitis: Virology and immunopathogenesis. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kipar, A.; Meli, M.L.; Baptiste, K.E.; Bowker, L.J.; Lutz, H. Sites of feline coronavirus persistence in healthy cats. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91 Pt 7, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, L.; Van der Lubben, M.; te Lintelo, E.G.; Bekker, C.P.; Geerts, T.; Schuijff, L.S.; Grinwis, G.C.; Egberink, H.F.; Rottier, P.J. Pathogenic characteristics of persistent feline enteric coronavirus infection in cats. Vet. Res. 2010, 41, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Doenges, S.J.; Weber, K.; Dorsch, R.; Fux, R.; Fischer, A.; Matiasek, L.A.; Matiasek, K.; Hartmann, K. Detection of feline coronavirus in cerebrospinal fluid for diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis in cats with and without neurological signs. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2016, 18, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Boyle, J.F.; Floyd, K.; Fudge, A.; Barker, J. An enteric coronavirus infection of cats and its relationship to feline infectious peritonitis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1981, 42, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Liu, H.; Scarlett, J.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Golovko, L.; Kennedy, H.; Kamal, F.M. Feline infectious peritonitis: Role of the feline coronavirus 3c gene in intestinal tropism and pathogenicity based upon isolates from resident and adopted shelter cats. Virus Res. 2012, 165, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rottier, P.J.; Nakamura, K.; Schellen, P.; Volders, H.; Haijema, B.J. Acquisition of macrophage tropism during the pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis is determined by mutations in the feline coronavirus spike protein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14122–14130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Felten, S.; Hartmann, K. Diagnosis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis: A Review of the Current Literature. Viruses 2019, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jaimes, J.A.; Whittaker, G.R. Feline coronavirus: Insights into viral pathogenesis based on the spike protein structure and function. Virology 2018, 517, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Licitra, B.N.; Millet, J.K.; Regan, A.D.; Hamilton, B.S.; Rinaldi, V.D.; Duhamel, G.E.; Whittaker, G.R. Mutation in spike protein cleavage site and pathogenesis of feline coronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martinez, A.; Lavergne, E.; Brauge, C.; Laveran, E.; Bertagnoli, S.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Bessière, P. Feline coronavirus-associated uveitis: The eye as a gateway to systemic spread and feline infectious peritonitis? Vet. Microbiol. 2025, 301, 110355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phyu, E.M.; Charoenkul, K.; Nasamran, C.; Chamsai, E.; Thaw, Y.N.; Phyu, H.W.; Soe, H.W.; Chaiyawong, S.; Amonsin, A. Whole genome characterization of feline coronaviruses in Thailand: Evidence of genetic recombination and mutation M1058L in pathotype switch. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1451967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Krentz, D.; Zenger, K.; Alberer, M.; Felten, S.; Bergmann, M.; Dorsch, R.; Matiasek, K.; Kolberg, L.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Meli, M.L.; et al. Curing Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis with an Oral Multi-Component Drug Containing GS-441524. Viruses 2021, 13, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, Y.; Shivanna, V.; Narayanan, S.; Prior, A.M.; Weerasekara, S.; Hua, D.H.; Kankanamalage, A.C.; Groutas, W.C.; Chang, K.O. Broad-spectrum inhibitors against 3C-like proteases of feline coronaviruses and feline caliciviruses. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4942–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Eckstrand, C.; Liu, H.; Leutenegger, C.; Murphy, B. Levels of feline infectious peritonitis virus in blood, effusions, and various tissues and the role of lymphopenia in disease outcome following experimental infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 175, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Takano, T.; Yamada, S.; Doki, T.; Hohdatsu, T. Pathogenesis of oral type I feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV) infection: Antibody-dependent enhancement infection of cats with type I FIPV via the oral route. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hohdatsu, T.; Yamada, M.; Tominaga, R.; Makino, K.; Kida, K.; Koyama, H. Antibody-dependent enhancement of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection in feline alveolar macrophages and human monocyte cell line U937 by serum of cats experimentally or naturally infected with feline coronavirus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1998, 60, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, J.E.; Lapointe, J.M.; Koblik, P.; Poland, A.; Pedersen, N.C. Diagnostic features of clinical neurologic feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1998, 12, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stiles, J. Ocular manifestations of feline viral diseases. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kipar, A.; May, H.; Menger, S.; Weber, M.; Leukert, W.; Reinacher, M. Morphologic features and development of granulomatous vasculitis in feline infectious peritonitis. Vet. Pathol. 2005, 42, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, J.V.; Poma, R. Diagnosis and clinical signs of feline infectious peritonitis in the central nervous system. Can. Vet. J. 2009, 50, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Attipa, C.; Warr, A.S.; Epaminondas, D.; O’Shea, M.; Fletcher, S.; Malbon, A.; Lyraki, M.; Hammond, R.; Hardas, A.; Zanti, A.; et al. Emergence and spread of feline infectious peritonitis due to a highly pathogenic canine/feline recombinant coronavirus. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokic, G.; Hillen, H.S.; Tegunov, D.; Dienemann, C.; Seitz, F.; Schmitzova, J.; Farnung, L.; Siewert, A.; Höbartner, C.; Cramer, P. Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 polymerase stalling by remdesivir. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Green, J.; Syme, H.; Tayler, S. Thirty-two cats with effusive or non-effusive feline infectious peritonitis treated with a combination of remdesivir and GS-441524. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Meli, M.L.; Spiri, A.M.; Zwicklbauer, K.; Krentz, D.; Felten, S.; Bergmann, M.; Dorsch, R.; Matiasek, K.; Alberer, M.; Kolberg, L.; et al. Fecal Feline Coronavirus RNA Shedding and Spike Gene Mutations in Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis Treated with GS-441524. Viruses 2022, 14, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Kim, Y.; Liu, H.; Galasiti Kankanamalage, A.C.; Eckstrand, C.; Groutas, W.C.; Bannasch, M.; Meadows, J.M.; Chang, K.O. Efficacy of a 3C-like protease inhibitor in treating various forms of acquired feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 20, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, Y.; Liu, H.; Galasiti Kankanamalage, A.C.; Weerasekara, S.; Hua, D.H.; Groutas, W.C.; Chang, K.O.; Pedersen, N.C. Reversal of the Progression of Fatal Coronavirus Infection in Cats by a Broad-Spectrum Coronavirus Protease Inhibitor. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005531, Erratum in PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dong, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, X.; Hu, W.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Deng, H.; Lin, W. Prevalence of natural feline coronavirus infection in domestic cats in Fujian, China. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doenges, S.J.; Weber, K.; Dorsch, R.; Fux, R.; Hartmann, K. Comparison of real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of peripheral blood mononuclear cells, serum and cell-free body cavity effusion for the diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017, 19, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrewegh, A.A.; de Groot, R.J.; Cepica, A.; Egberink, H.F.; Horzinek, M.C.; Rottier, P.J. Detection of feline coronavirus RNA in feces, tissues, and body fluids of naturally infected cats by reverse transcriptase PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fish, E.J.; Diniz, P.P.V.; Juan, Y.C.; Bossong, F.; Collisson, E.W.; Drechsler, Y.; Kaltenboeck, B. Cross-sectional quantitative RT-PCR study of feline coronavirus viremia and replication in peripheral blood of healthy shelter cats in Southern California. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 20, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, E.; Mari, V.; Losurdo, M.; Lanave, G.; Trotta, A.; Dowgier, G.; Colaianni, M.L.; Zatelli, A.; Elia, G.; Buonavoglia, D.; et al. Discrepancies between feline coronavirus antibody and nucleic acid detection in effusions of cats with suspected feline infectious peritonitis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 125, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dye, C.; Helps, C.R.; Siddell, S.G. Evaluation of real-time RT-PCR for the quantification of FCoV shedding in the faeces of domestic cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2008, 10, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thayer, V.; Gogolski, S.; Felten, S.; Hartmann, K.; Kennedy, M.; Olah, G.A. 2022 AAFP/EveryCat Feline Infectious Peritonitis Diagnosis Guidelines. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, 905–933, Erratum in J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, e676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can-Sahna, K.; Soydal Ataseven, V.; Pinar, D.; Oğuzoğlu, T.C. The detection of feline coronaviruses in blood samples from cats by mRNA RT-PCR. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2007, 9, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nunes, B.T.D.; de Mendonça, M.H.R.; Simith, D.B.; Moraes, A.F.; Cardoso, C.C.; Prazeres, I.T.E.; de Aquino, A.A.; Santos, A.D.C.M.; Queiroz, A.L.N.; Rodrigues, D.S.G.; et al. Development of RT-qPCR and semi-nested RT-PCR assays for molecular diagnosis of hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hirotsu, Y.; Mochizuki, H.; Omata, M. Double-quencher probes improve detection sensitivity toward Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in a reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 284, 113926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bui, H.T.V.; Bui, H.T.; Chu, S.V.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, A.T.V.; Truong, P.T.; Dang, T.T.H.; Nguyen, A.T.V. Simultaneous real-time PCR detection of nine prevalent sexually transmitted infections using a predesigned double-quenched TaqMan probe panel. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gunn-Moore, D.A.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.J.; Harbour, D.A. Detection of feline coronaviruses by culture and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction of blood samples from healthy cats and cats with clinical feline infectious peritonitis. Vet. Microbiol. 1998, 62, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Addie, D.D.; Toth, S.; Herrewegh, A.A.; Jarrett, O. Feline coronavirus in the intestinal contents of cats with feline infectious peritonitis. Vet. Rec. 1996, 139, 522–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meli, M.; Kipar, A.; Müller, C.; Jenal, K.; Gönczi, E.; Borel, N.; Gunn-Moore, D.; Chalmers, S.; Lin, F.; Reinacher, M.; et al. High viral loads despite absence of clinical and pathological findings in cats experimentally infected with feline coronavirus (FCoV) type I and in naturally FCoV-infected cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2004, 6, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Felten, S.; Klein-Richers, U.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Bergmann, M.; Unterer, S.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Hartmann, K. Correlation of Feline Coronavirus Shedding in Feces with Coronavirus Antibody Titer. Pathogens 2020, 9, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Černá, P.; Lobová, D.; Bubeníková, J.; Vrábelová, J.; Molínková, D.; Hořín, P. Shedding persistency and intensity patterns of feline coronavirus (FCoV) in feces of cats living in breeding catteries in the Czech Republic. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 152, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Poder, S. Feline and canine coronaviruses: Common genetic and pathobiological features. Adv. Virol. 2011, 2011, 609465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tresnan, D.B.; Levis, R.; Holmes, K.V. Feline aminopeptidase N serves as a receptor for feline, canine, porcine, and human coronaviruses in serogroup I. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 8669–8674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barlough, J.E.; Stoddart, C.A.; Sorresso, G.P.; Jacobson, R.H.; Scott, F.W. Experimental inoculation of cats with canine coronavirus and subsequent challenge with feline infectious peritonitis virus. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1984, 34, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McArdle, F.; Bennett, M.; Gaskell, R.M.; Tennant, B.; Kelly, D.F.; Gaskell, C.J. Canine coronavirus infection in cats; a possible role in feline infectious peritonitis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1990, 276, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, Y.; Matsui, N.; Noguchi, K.; Kuwata, R.; Shimoda, H.; Soma, T.; Mochizuki, M.; Maeda, K. Emergence of pathogenic coronaviruses in cats by homologous recombination between feline and canine coronaviruses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jähne, S.; Felten, S.; Bergmann, M.; Erber, K.; Matiasek, K.; Meli, M.L.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Hartmann, K. Detection of Feline Coronavirus Variants in Cats Without Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Viruses 2022, 14, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Raya, S.; Malla, B.; Thakali, O.; Angga, M.S.; Haramoto, E. Development of highly sensitive one-step reverse transcription-quantitative PCR for SARS-CoV-2 detection in wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Franco, D.; Orschler, L.; Lackner, S.; Agrawal, S.; Weissbrodt, D.G. Monitoring SARS-CoV-2 in sewage: Toward sentinels with analytical accuracy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wacker, M.J.; Godard, M.P. Analysis of one-step and two-step real-time RT-PCR using SuperScript III. J. Biomol. Tech. 2005, 16, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Plasma (68) | Whole Blood (40) | Fecal Swab (65) | Conjunctival Swab (28) | Effusion (16) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Quantifiable (n) | 22.06% (15) | 35.00% (14) | 72.58% (48) | 67.86% (19) | 75.00% (12) |
| % Detected (n) | 19.12% (13) | 15.00% (6) | 8.06% (5) | 10.71% (3) | 0.00% (0) |
| % Below the LoD (n) | 58.82% (40) | 50.00% (20) | 19.36% (12) | 21.43% (6) | 25.00% (4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shepherd, P.M.; Elbe, A.; Lynch, B.M.; Lashnits, E.; Kirchdoerfer, R.N. Detection of Feline Coronavirus RNA in Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis and Their Housemates. Viruses 2025, 17, 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070948
Shepherd PM, Elbe A, Lynch BM, Lashnits E, Kirchdoerfer RN. Detection of Feline Coronavirus RNA in Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis and Their Housemates. Viruses. 2025; 17(7):948. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070948
Chicago/Turabian StyleShepherd, Phoenix M., Amy Elbe, Brianna M. Lynch, Erin Lashnits, and Robert N. Kirchdoerfer. 2025. "Detection of Feline Coronavirus RNA in Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis and Their Housemates" Viruses 17, no. 7: 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070948
APA StyleShepherd, P. M., Elbe, A., Lynch, B. M., Lashnits, E., & Kirchdoerfer, R. N. (2025). Detection of Feline Coronavirus RNA in Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis and Their Housemates. Viruses, 17(7), 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070948





