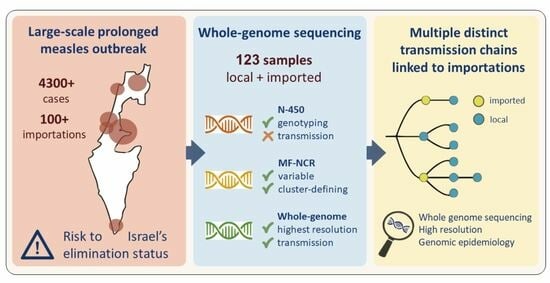
Measles Sequencing: Lessons Learned from a Large-Scale Outbreak
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Selection
2.2. MeV Whole Genome Sequencing
- Primer MeV-L19-1F, sequence: 5′-CTAACCGATCATATCAAGGCAGAG-3′
- Primer MeV-L19-1R, sequence: 5′-GTCCGCACAGATGATTCAATTATC-3′
- Primer MeV-L20-F1, sequence: 5′-CACGTGGGTAGGCAGTATAGATTG-3′
- Primer MeV-L20-R1, sequence: 5′-ACCTGACAAAGCTGGGAATAG-3′
- Primer MeV-L21-1F, sequence: 5′-CAAAGAAGTCAACAAGGGATGTTC-3′
2.3. Bioinformatic Analyses
3. Results
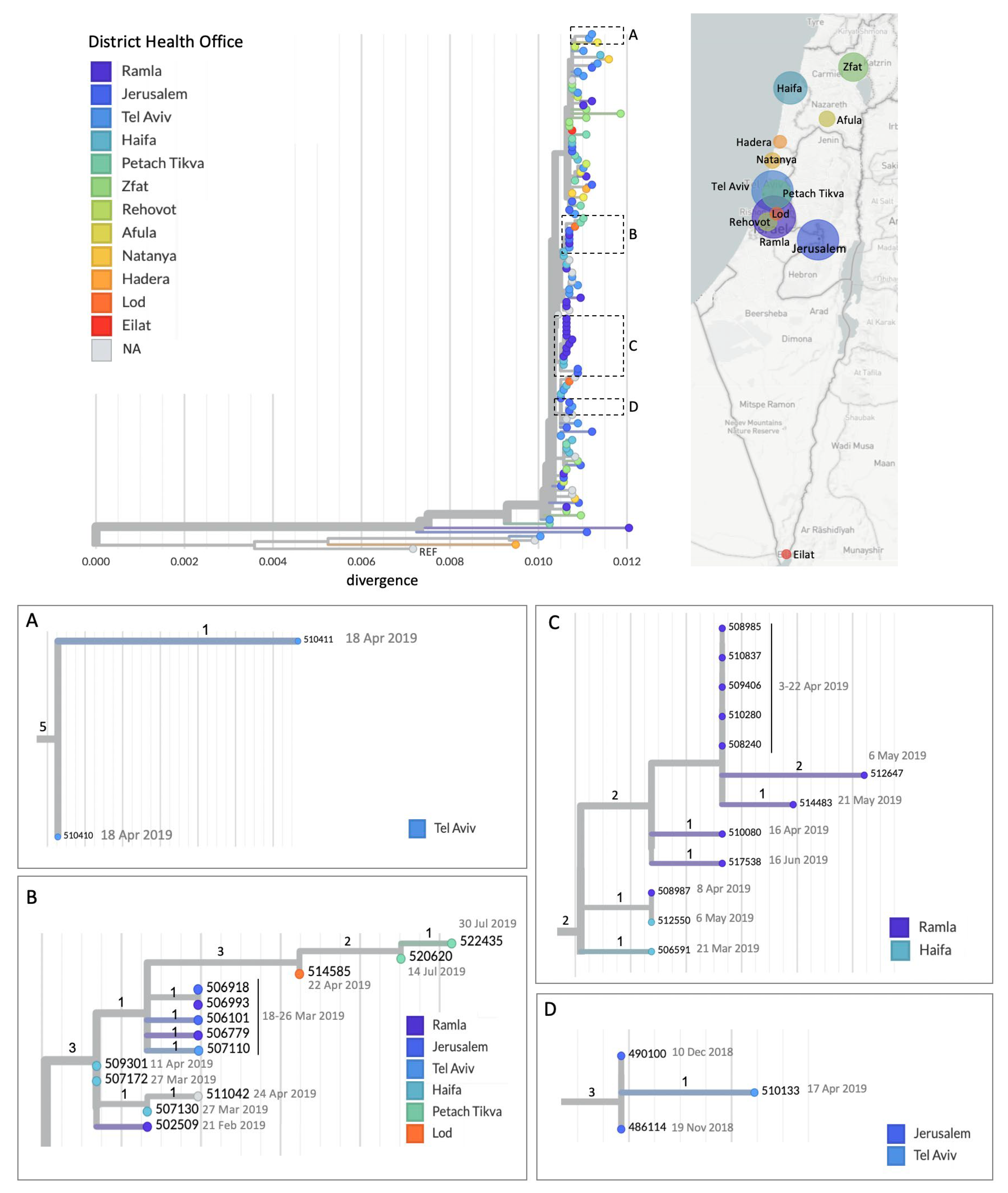
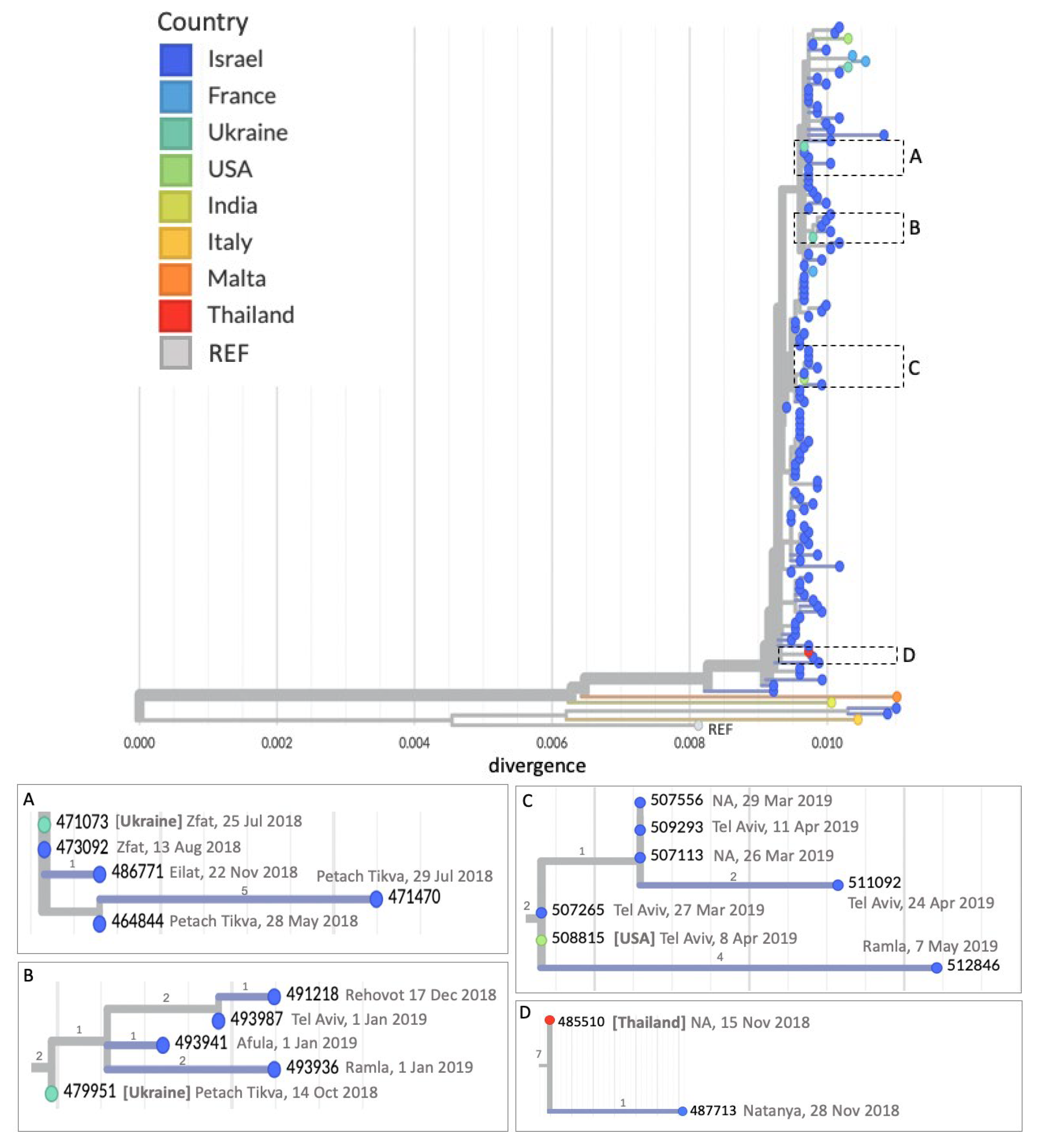
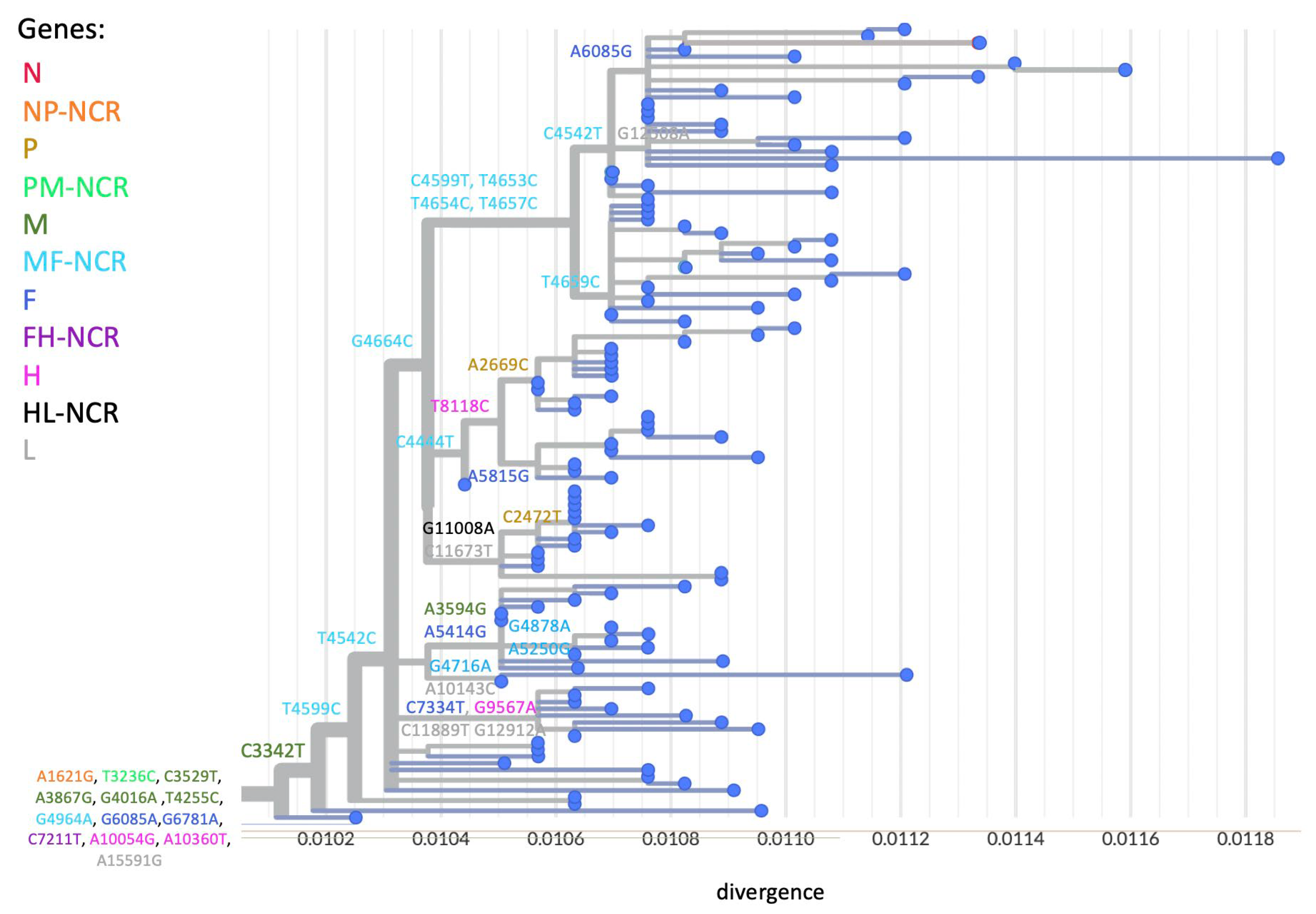
3.1. A Prolonged Outbreak with Multiple Transmission Chains
3.2. Imported Cases Initiating Transmission Clusters
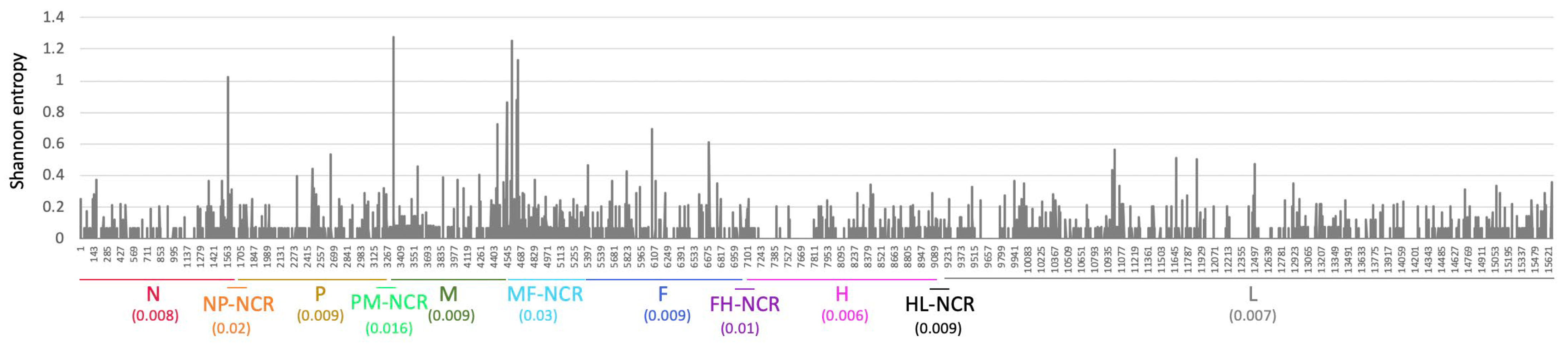
3.3. WGS Improves Resolution of Measles Transmission
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DHO | district health offices |
| MeV | measles virus |
| MF-NCR | MF non-coding region |
| WGS | whole genome sequencing |
| WHO | world health organization |
References
- World Health Organization. Worldwide Measles Deaths Climb 50% from 2016 to 2019 Claiming over 207500 Lives in 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/12-11-2020-worldwide-measles-deaths-climb-50-from-2016-to-2019-claiming-over-207-500-lives-in-2019 (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Feemster, K.A.; Szipszky, C. Resurgence of measles in the United States: How did we get here? Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2020, 32, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffmann, F.; Heffernan, C.; Meurice, F.; Ota, M.O.C.; Vetter, V.; Casabona, G. Measles, mumps, rubella prevention: How can we do better? Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwangilwa, K.; Sialubanje, C.; Chipoya, M.; Mulenga, C.; Mwale, M.; Chileshe, C.; Sinyange, D.; Banda, M.; Gardner, P.N.; Lamba, L.; et al. Attention to COVID 19 pandemic resulted in increased measles cases and deaths in Zambia. Trop. Med. Health 2025, 53, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melkonyan, N.; Ter-Stepanyan, M.; Badalyan, A.; Hovhannisyan, H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the measles elimination status in Armenia. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2025, 19, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Feasibility Assessment of Measles and Rubella Eradication. Available online: https://terrance.who.int/mediacentre/data/sage/SAGE_Docs_Ppt_Oct2019/4_session_measles_and_rubella_vaccines/Oct2019_session4_feasibility_assessment_Measles-Rubella_eradication.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- World Health Organization. WHO EpiBrief: A Report on the Epidemiology of Selected Vaccine-Preventable Diseases in the European Region. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/librariesprovider2/euro-health-topics/vaccines-and-immunization/epibrief_1_2020_en.pdf?sfvrsn=95f25520_10&utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Anis, E.; Haas, E.J.; Indenbaum, V.; Singer, S.R.; Warshavsky, B.; Rishpon, S.; Green, M.S.; Mendelson, E.; Grotto, I.; Kaliner, E.; et al. A prolonged, nationwide measles outbreak despite very high vaccination coverage in Israel, 2018–2019. J. Infect. 2021, 83, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penedos, A.R.; Myers, R.; Hadef, B.; Aladin, F.; Brown, K.E. Assessment of the Utility of Whole Genome Sequencing of Measles Virus in the Characterisation of Outbreaks. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardy, J.L.; Naus, M.; Amlani, A.; Chung, W.; Kim, H.; Tan, M.; Severini, A.; Krajden, M.; Puddicombe, D.; Sahni, V.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Measles Virus Genotypes H1 and D8 During Outbreaks of Infection Following the 2010 Olympic Winter Games Reveals Viral Transmission Routes. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1574–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, P.A.; Bankamp, B. Whole-Genome Sequencing During Measles Outbreaks. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1529–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulders, M.N. Annex C16: CDC Protocol for Amplification and Sequencing of Measles Virus MF-NCR from Patient Samples. Available online: https://www.technet-21.org/media/com_resources/trl/8421/multi_upload/RT-PCRsequencingformeaslesMFregion.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Aligning Sequence Reads, Clone Sequences and Assembly Contigs with BWA-MEM. 2013. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1303.3997 (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; Sagulenko, P.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A. Nextstrain: Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagulenko, P.; Puller, V.; Neher, R.A. TreeTime: Maximum-likelihood phylodynamic analysis. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vex042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, H.; Hu, M.; Xia, B.; Zhang, Y. M-F noncoding region sequences of H1 genotype measles virus provide higher resolution for virus transmission tracing. Virology 2024, 596, 110104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.-Y.; Chen, B.-S.; Wang, H.-C.; Liu, M.-T. Genetic Characteristics of Measles Viruses Isolated in Taiwan between 2015 and 2020. Viruses 2023, 15, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodewes, R.; Reijnen, L.; Zwagemaker, F.; Kohl, R.H.; Kerkhof, J.; Veldhuijzen, I.K.; van Binnendijk, R. An efficient molecular approach to distinguish chains of measles virus transmission in the elimination phase. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 91, 104794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucris, E.; Indenbaum, V.; Levin, T.; Kanaaneh, Y.; Friedman, K.; Kushnir, T.; Sheffer, R.; Savion, M.; Salama, M.; Di-Castro, N.; et al. Rapid molecular epidemiology investigations into two recent measles outbreaks in Israel detected from October 2023 to January 2024. Eurosurveillance 2024, 29, 2400202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiebert, J.; Zubach, V.; Schulz, H.; Severini, A. Genomic tools for post-elimination measles molecular epidemiology using Canadian surveillance data from 2018–2020. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1475144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohan, R.; Surleac, M.; Miron, V.D.; Tudor, A.; Tudor, A.-M.; Săndulescu, O.; Vlaicu, O.; Aramă, V.; Pițigoi, D.; Hristea, A.; et al. Ongoing measles outbreak in Romania: Clinical investigation and molecular epidemiology performed on whole genome sequences. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0317045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| District | DHO | # Cases | # Imported Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northern | Zfat | 9 | 1 (Ukraine) |
| Afula | 2 | 1 (USA) | |
| Haifa | Haifa | 12 | 1 (France) |
| Hadera | 1 | 1 (Italy) | |
| Natanya | 2 | 1 (France) | |
| Central | Lod | 2 | 0 |
| Petach Tikva | 9 | 1 (Ukraine) | |
| Ramla | 21 | 1 (Malta) | |
| Rehovot | 4 | 0 | |
| Tel Aviv | Tel Aviv | 17 | 3 (France, USA, Ukraine) |
| Jerusalem | Jerusalem | 20 | 0 |
| Southern | Eilat | 1 | 0 |
| unknown | 12 | 1 (Thailand) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Indenbaum, V.; Bucris, E.; Friedman, K.; Kushnir, T.; Eliyahu, H.; Azar, R.; Levin, T.; Kanaaneh, Y.; Haas, E.J.; Singer, S.R.; et al. Measles Sequencing: Lessons Learned from a Large-Scale Outbreak. Viruses 2025, 17, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070913
Indenbaum V, Bucris E, Friedman K, Kushnir T, Eliyahu H, Azar R, Levin T, Kanaaneh Y, Haas EJ, Singer SR, et al. Measles Sequencing: Lessons Learned from a Large-Scale Outbreak. Viruses. 2025; 17(7):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070913
Chicago/Turabian StyleIndenbaum, Victoria, Efrat Bucris, Keren Friedman, Tatyana Kushnir, Hagar Eliyahu, Roberto Azar, Tal Levin, Yara Kanaaneh, Eric J. Haas, Shepherd Roee Singer, and et al. 2025. "Measles Sequencing: Lessons Learned from a Large-Scale Outbreak" Viruses 17, no. 7: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070913
APA StyleIndenbaum, V., Bucris, E., Friedman, K., Kushnir, T., Eliyahu, H., Azar, R., Levin, T., Kanaaneh, Y., Haas, E. J., Singer, S. R., Lustig, Y., Mendelson, E., Erster, O., & Zuckerman, N. S. (2025). Measles Sequencing: Lessons Learned from a Large-Scale Outbreak. Viruses, 17(7), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070913