Epstein–Barr Virus Load in the Saliva of Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer—Could It Have Prognostic Significance?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basic Description of the Studied Groups
2.2. Collecting Clinical Samples
2.2.1. Collecting Saliva Samples
2.2.2. Serum Collection
2.3. EBV DNA Detection in Saliva
2.4. Serological Methods Used in the Research
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Salivary EBV DNA Load in EBV-Positive and EBV-Negative OPSCC Patients
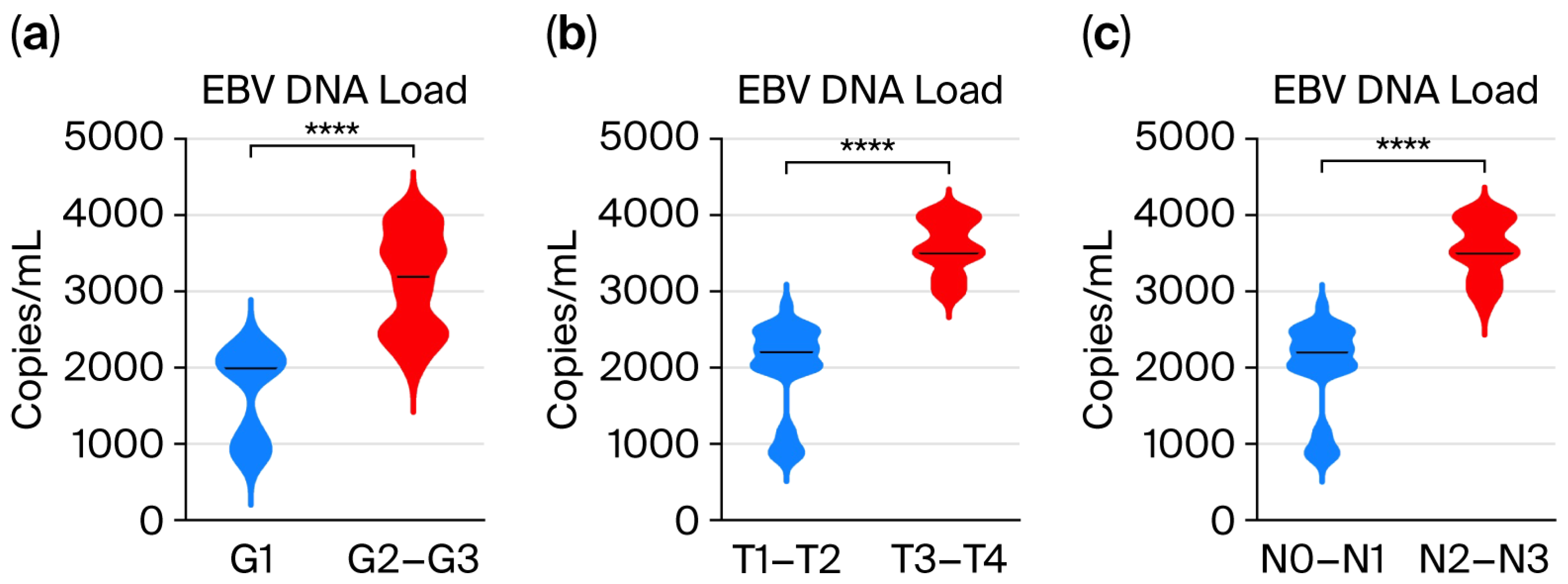
3.2. Assessment of EBV DNA Load in the Saliva of Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer Depending on the Grade (G1–G3) and TN Classification
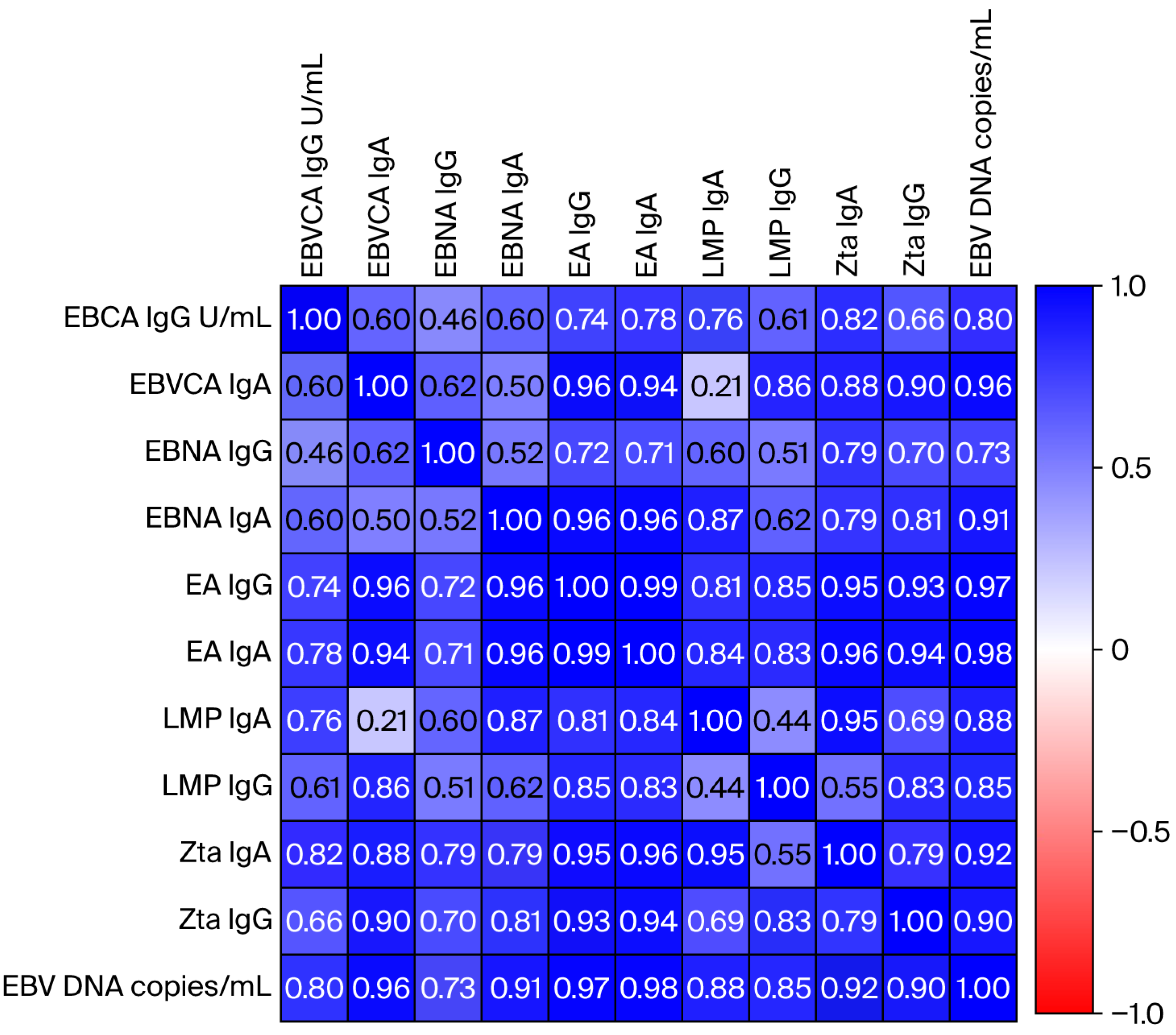
3.3. Correlation Analysis Between the EBV Load in Saliva and the Titer of Anti-EBV Antibodies in the Serum of Oropharyngeal Cancer Patients
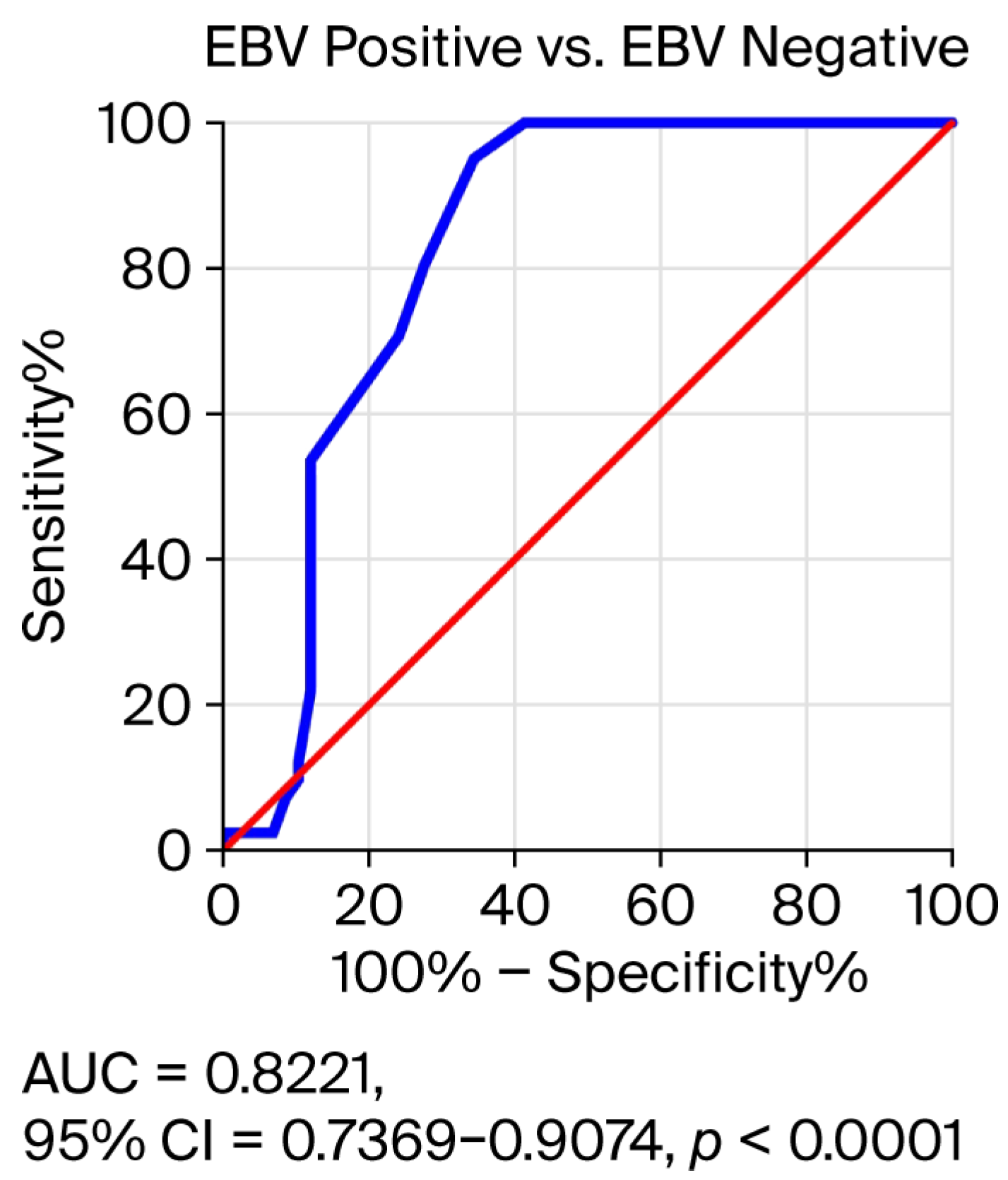
3.4. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Analysis to Determine the Diagnostic Accuracy of Salivary EBV DNA Load in EBV-Positive OPSCC Patients Compared to EBV-Negative Subjects
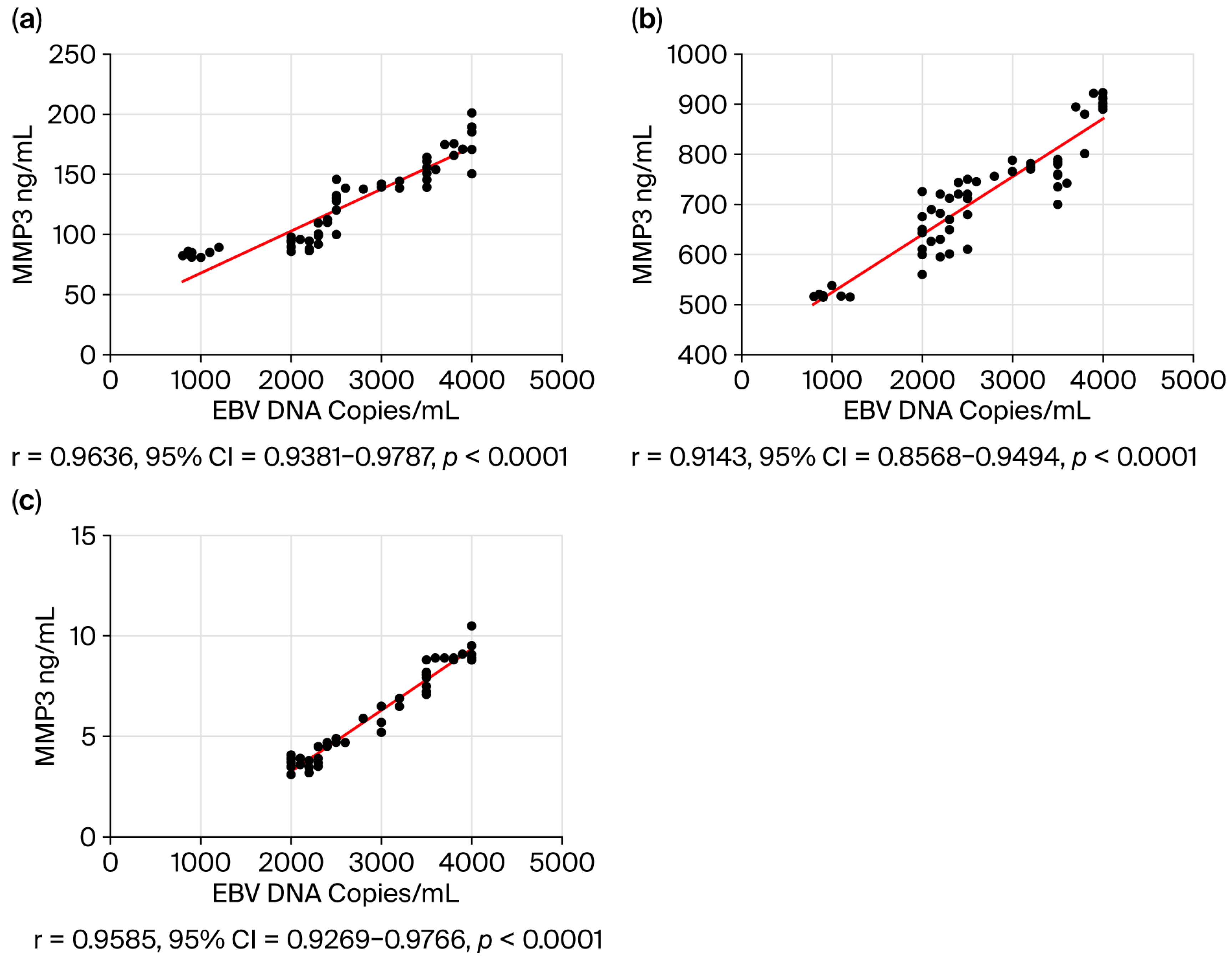
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between the EBV Load in Saliva and the Level of Selected Biomarkers in the Serum of Oropharyngeal Cancer Patients
4. Discussion
Limitations of Own Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HNC | Head and neck cancer |
| NPC | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| OPSCC | Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa |
| MMP3 | Metalloproteinase 3 |
| MMP9 | Metalloproteinase 9 |
| LMP | Latent membrane protein |
| VLPs | Virus-like particles |
References
- Globocan 2022. Global Cancer Observatory, IARC WHO. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Cancer Tomorrow. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Chen, C.J.; Hsu, W.L.; Yang, H.I.; Lee, M.H.; Chen, H.C.; Chien, Y.C.; You, S.L. Epidemiology of virus infection and human cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014, 193, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, Y.Q.; Xue, W.Q.; Xu, F.H.; Xu, Y.F.; Zhang, J.B.; Yu, H.L.; Feng, Q.S.; Chen, L.Z.; Cao, S.M.; Liu, Q.; et al. The Relationship Between Environmental Factors and the Profile of Epstein-Barr Virus Antibodies in the Lytic and Latent Infection Periods in Healthy Populations from Endemic and Non-Endemic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Areas in China. EBioMedicine 2018, 30, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpén, T.; Syrjanen, S.; Jouhi, L.; Randen-Brady, R.; Haglund, C.; Mäkitie, A.; Mattila, P.S.; Hagström, J. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) and Polyomaviruses Are Detectable in Oropharyngeal Cancer and EBV May Have Prognostic Impact. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svajdler, M.; Kaspirkova, J.; Mezencev, R.; Laco, J.; Torday, T.; Dubinsky, P.; Straka, L.; Ondic, O.; Michal, M.; Skalova, A. Human papillomavirus and Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a non-endemic eastern European population. Neoplasma 2016, 63, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ruuskanen, M.; Irjala, H.; Minn, H.; Vahlberg, T.; Randen-Brady, R.; Hagström, J.; Syrjänen, S.; Leivo, I. Epstein-Barr virus and human papillomaviruses as favorable prognostic factors in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A nationwide study in Finland. Head Neck 2019, 41, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damania, B.; Kenney, S.C.; Raab-Traub, N. Epstein-Barr virus: Biology and clinical disease. Cell 2022, 185, 3652–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, A. Why and How Epstein-Barr Virus Was Discovered 50 Years Ago. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 390 Pt 1, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman, P.M. Virology. Epstein-Barr virus turns 50. Science 2014, 343, 1323–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rickinson, A. The Global Landscape of EBV-Associated Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Han, L.; Liu, S.; Luo, B. Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Gastric Remnant Carcinoma and Recurrent Gastric Carcinoma in Qingdao of Northern China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Z.; Che, H.; Castro, F.H.; Hu, J.; Brenner, H. Epstein-Barr virus infection and gastric cancer: A systematic review. Medicine 2015, 94, e792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Dawson, C.W. Epstein-Barr virus and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, S.-W.; Tsang, C.M.; To, K.-F.; Lo, K.-W. The role of Epstein-Barr virus in epithelial malignancies. J. Pathol. 2014, 235, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, S.; Yan, B.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Quaid, J.T.; Lin, C.F.; Briggs, S.D.; Majumder, J.; Canaria, D.A.; Chauss, D.; et al. Integrated Pan-Cancer Map of EBV-Associated Neoplasms Reveals Functional Host–Virus Interactions. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 6010–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Yap, L.F.; Murray, P.G. Epstein–Barr virus: More than 50 years old and still providing surprises. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. In A Review of Human Carcinogens. Biological Agents; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2012; pp. 49–92.
- Münz, C. Epstein-Barr virus pathogenesis and emerging control strategies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 23, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Robertson, E.S. Epstein-Barr Virus History and Pathogenesis. Viruses 2023, 15, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Q.; Zhou, T.; Yang, D.W.; Jia, Y.J.; Yuan, L.L.; Zhang, W.L.; Wang, T.M.; Liao, Y.; Xue, W.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; et al. Prognostic Value of Oral Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Load in Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 8, 757644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Feng, F.; Xu, M.; Liu, W.; Yao, Y.; Xie, S.; Li, X.; Ye, Z.; Feng, Q.; Chen, L.; et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk prediction via salivary detection of host and Epstein-Barr virus genetic variants. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 95066–95074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J.; Manzano-Moreno, F.J.; Ruiz, C.; Illescas-Montes, R. Salivary Biomarkers and Their Application in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of the Most Common Oral Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Dickey, B.L.; Coghill, A.E. Utility of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) antibodies as screening markers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A narrative review. Ann. Nasopharynx Cancer 2022, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paschale, M.; Clerici, P. Serological diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus infection: Problems and solutions. World J. Virol. 2012, 1, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A. Diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus-related diseases. Scand. J. Infect. Diseases Suppl. 1996, 100, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, Y.M.; Chan, L.Y.; Lo, K.W.; Leung, S.F.; Zhang, J.; Chan, A.T.; Lee, J.C.; Hjelm, N.M.; Johnson, P.J.; Huang, D.P. Quantitative analysis of cell-free Epstein-Barr virus DNA in plasma of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Baizig, N.M.; Morand, P.; Seigneurin, J.M.; Boussen, H.; Fourati, A.; Gritli, S.; Queslati, Z.; Touati, S.; Gamoudi, A.; Abdallah, M.; et al. Complementary determination of Epstein-Barr virus DNA load and serum markers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma screening and early detection in individuals at risk in Tunisia. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 269, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.K.; Siow, C.H.; Goh, H.L.; Lim, C.M.; Hsu, P.P.; Chan, S.H.; Loh, K.S. A comparison of EBV serology and serum cell-free DNA as screening tools for nasopharyngeal cancer: Results of the Singapore NPC screening cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 2923–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. (Eds.) AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machczyński, P.; Majchrzak, E.; Niewinski, P.; Marchlewska, J.; Golusiński, W. A review of the 8th edition of the AJCC staging system for oropharyngeal cancer according to HPV status. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 2407–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO classification of tumours series. In Head and Neck Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2022; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, P.; Chang, Y. Why do viruses cause cancer? Highlights of the first century of human tumour virology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Clifford, G.M. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, E180–E190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.A.; Forouzanfar, T.; Bloemena, E.; de Visscher, J.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Leemans, C.R.; Helder, M.N. A review of the most promising biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis prediction of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristaldi, M.; Mauceri, R.; Di Fede, O.; Giuliana, G.; Campisi, G.; Panzarella, V. Salivary Biomarkers for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis and Follow-Up: Current Status and Perspectives. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Sodnom-Ish, B.; Choi, S.W.; Jung, H.I.; Cho, J.; Hwang, I.; Kim, S.M. Salivary biomarkers in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 46, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roi, A.; Roi, C.I.; Negruțiu, M.L.; Riviș, M.; Sinescu, C.; Rusu, L.C. The Challenges of OSCC Diagnosis: Salivary Cytokines as Potential Biomarkers. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghizoni, J.S.; Nichele, R.; de Oliveira, M.T.; Pamato, S.; Pereira, J.R. The utilization of saliva as an early diagnostic tool for oral cancer: MicroRNA as a biomarker. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahran, F.; Ghalwash, D.; Shaker, O.; Al-Johani, K.; Scully, C. Salivary microRNAs in oral cancer. Oral Dis. 2015, 21, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.H.; Lu, L.X.; Li, X.Z.; Jia, W.H. Quantification of Epstein- Barr Virus DNA Load in Nasopharyngeal Brushing Samples in the Diagnosis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Southern China. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.-F.; Zheng, X.-H.; Li, X.-Z.; Tian, T.; Zhang, S.-D.; Hu, Y.-Z.; Jia, W.H. Nasopharyngeal Brushing: A Convenient and Feasible Sampling Method for Nucleic Acid-Based Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Research. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Lin, D.F.; Cai, Y.C.; Xie, S.H.; Lin, K.N.; Zhou, H.N.; Wu, Z.-C.; Ye, J.-P.; Peng, Y.-N.; Ma, Z.; et al. Diagnostic performance of EBV DNA load testing for nasopharyngeal carcinoma in nasopharyngeal swab outperforms the approach in other specimens. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtsevitch, V. EBV Serology and Plasma EBV DNA Load as a Combined Tool for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC). Diagnosis and Monitoring in Non-Endemic Regions. Virol. Immunol. J. 2021, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.H.; Li, X.Z.; Tang, C.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhou, T.; Yang, X.J.; Liao, Y.; He, Y.Q.; Wang, T.; Xue, W.Q.; et al. Detection of Epstein–Barr virus DNA methylation as tumor markers of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients in saliva, oropharyngeal swab, oral swab, and mouthwash. Med. Comm. 2024, 5, e673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.H.; Deng, C.M.; Zhou, T.; Tang, C.L.; Jiang, C.T.; Liao, Y.; Wang, T.-M.; He, Y.-Q.; Jia, W.-H. Saliva biopsy: Detecting the difference of EBV DNA methylation in the diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 153, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lee, C.H.-Y.; Delecluse, H.-J. Epstein–Barr virus lytic replication and cancer. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2025, 70, 101438. [Google Scholar]
- Abusalah, M.A.H.; Gan, S.H.; Al-Hatamleh, M.A.I.; Irekeola, A.A.; Shueb, R.H.; Yean Yean, C. Recent Advances in Diagnostic Approaches for Epstein–Barr Virus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Huang, L.; Luo, L.; Yu, Q.; Tian, J. Diagnostic value of serological and molecular biological tests for infectious mononucleosis by EBV in different age stages and course of the disease. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 3824–3834. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdulamir, A.S.; Hafidh, R.R.; Abu Bakar, F.; Abbas, K. Novel Epstein-Barr virus immunoglobulin G-based approach for the specific detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2010, 31, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, J.K.; Chan, S.H.; Lim, C.M.; Siow, C.H.; Goh, H.L.; Loh, K.S. The role of Epstein-Barr virus DNA load and serology as screening tools for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2016, 155, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.P.; Hsu, C.L.; Chang, Y.L.; Tsang, N.M.; Chen, C.K.; Lee, T.J.; Tsao, K.C.; Huang, C.G.; Chang, Y.S.; Yu, J.S.; et al. Complementary serum test of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1 and early antigen: A possible alternative for primary screening of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral. Oncol. 2008, 44, 784–792. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Q. Utility of Serum EB Virus Zta Antibody in the Diagnostic of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Evidences from 2126 Cases and 15,644 Controls. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardari, R.; Khyatti, M.; Benider, A.; Jouhadi, H.; Kahlain, A.; Cochet, C.; Mansouri, A.; El Gueddari, B.; Benslimane, A.; Joab, I. Antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus transactivator protein (ZEBRA) as a valuable biomarker in young patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 86, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.; Cheng, H.M.; Sam, C.K.; Joab, I.; Prasad, U.; Cochet, C. A high incidence of serum IgG antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus replication activator protein in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1994, 38, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germini, D.; Sall, F.B.; Shmakova, A.; Wiels, J.; Dokudovskaya, S.; Drouet, E.; Vassetzky, Y. Oncogenic properties of the EBV ZEBRA protein. Cancers 2020, 12, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.; Mojares, E.; del Río Hernández, A. Role of Extracellular Matrix in Development and Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.K.; Baishya, N.; Sarma, A.; Kataki, A.C.; Rai, A.K.; Kalita, C.R. Assessment and clinicopathological correlation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Carcinog. 2019, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Wang, J.; Su, Q.; Luan, M.; Chen, X.; Xu, X. The role of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in the metastasis and development of hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 87, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Yang, Z.; Luo, W.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Yao, K.; Wu, B.; Fang, W. Increased expression of MMP9 is correlated with poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, Z.; Xing, S.; Liu, W.; Zhang, G. Combination of serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 activity and EBV antibodies improves the diagnostic performance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 6009–6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.-Y.; Yeh, T.-H.; Lin, W.-H.; Wu, S.-Y.; Lai, H.-C.; Chang, F.H.; Takada, K.; Chang, Y. Epstein-Barr Virus Zta Upregulates Matrix Metalloproteinases 3 and 9 That Synergistically Promote Cell Invasion In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zinatizadeh, M.R.; Schock, B.; Chalbatani, G.M.; Zarandi, P.K.; Jalali, S.A.; Miri, S.R. The Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-kB) signalling in cancer development and immune diseases. Genes Dis. 2021, 8, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lenardo, M.J.; Baltimore, D. Thirty years of NF-κB: A blossoming of relevance to human pathobiology. Cell 2017, 168, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, M.; Scheidereit, C. The IκB kinase complex in NF-κB regulation and beyond. EMBO Rep. 2013, 15, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, C.; Bucci, I.; Napolitano, G. The Role of the Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor-kappa B in Thyroid Autoimmunity and Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. NF-κB signalling in inflammation and cancer. Med. Comm. 2021, 2, 618–653. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Y.; Chung, G.T.; Lui, V.W.; To, K.F.; Ma, B.B.; Chow, C.; Woo, J.K.; Yip, K.Y.; Seo, J.; Hui, E.P.; et al. Exome and genome sequencing of nasopharynx cancer identifies NF-κB pathway activating mutations. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruce, J.P.; To, K.F.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Chung, G.T.Y.; Chan, Y.Y.; Tsang, C.M.; Yip, K.Y.; Ma, B.B.Y.; Woo, J.K.S.; Hui, E.P.; et al. Whole-genome profiling of nasopharyngeal carcinoma reveals viral-host co-operation in inflammatory NF-κB activation and immune escape. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, Y.P.; Tan, L.P.; Chai, S.J.; Abdul Aziz, N.; Choo, S.W.; Lim, P.V.H.; Pathmanathan, R.; Mohd Kornain, N.K.; Lum, C.L.; Pua, K.C.; et al. Exome Sequencing Identifies Potentially Druggable Mutations in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pian, L.; Meng, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Kang, M. Therapeutic vaccines for Epstein–Barr virus: A way forward. Lancet 2024, 403, 2779–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Krummenacher, C.; Zhang, W.; Hong, J.; Feng, O.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, O.; Zeng, M.-S.; Zeng, Y.-X.; Xu, M.; et al. Urgency and necessity of Epstein-Barr virus prophylactic vaccines. Npj Vaccines 2022, 7, 159. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, R.; Shaikh, M.H.; Gopinath, D.; Idris, A.; Johnson, N.W. Human papillomavirus and Epstein-Barr virus co-infection in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2023, 38, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, G.; Gong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liao, X.; Liao, W.; Song, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. The diagnostic value of EBV-DNA and EBV-related antibodies detection for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, R.; Carrillo-Beltrán, D.; Corvalán, A.H.; Aguayo, F. High-Risk Human Papillomavirus and Epstein–Barr Virus Coinfection: A Potential Role in Head and Neck Carcinogenesis. Biology 2021, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| EBV | p | Total Patients | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |||||||
| N | % | N | % | N = 110 | % | |||
| Sex | Female | 8 | 13.8 | 7 | 13.5 | 0.9999 | 15 | 13.8 |
| Male | 50 | 86.2 | 45 | 86.5 | 95 | 86.2 | ||
| Age | 50–59 | 27 | 46.6 | 24 | 46.2 | 0.1116 | 59 | 53.4 |
| 60–79 | 31 | 53.4 | 28 | 53.8 | 51 | 46.6 | ||
| Place of residence | Urban | 41 | 70.7 | 36 | 69.2 | 0.1667 | 77 | 70.7 |
| Rural | 17 | 29.3 | 16 | 30.8 | 33 | 29.3 | ||
| Smoking | ≤10 * | 28 | 48.3 | 25 | 48.1 | 0.8427 | 53 | 48.3 |
| >10 | 10 | 17.2 | 10 | 19.2 | 20 | 18.2 | ||
| No | 20 | 34.5 | 17 | 32.7 | 37 | 34.5 | ||
| Alcohol abuse | ≤10 ** | 18 | 31.1 | 15 | 28.8 | 0.9834 | 53 | 48.3 |
| >10 | 10 | 17.2 | 10 | 19.3 | ||||
| No | 30 | 51.7 | 27 | 51.9 | 57 | 51.7 | ||
| G | G1 | 19 | 32.8 | 17 | 32.7 | 0.9997 | ||
| G2 | 30 | 51.7 | 27 | 51.9 | ||||
| G3 | 9 | 15.5 | 8 | 15.4 | ||||
| T | T1 | 7 | 12.1 | 8 | 15.4 | 0.9505 | ||
| T2 | 27 | 46.6 | 22 | 42.3 | ||||
| T3 | 16 | 27.6 | 15 | 28.8 | ||||
| T4 | 8 | 13.7 | 7 | 12.1 | ||||
| N0 | 23 | 39.7 | 22 | 42.3 | 0.9844 | |||
| N | N1 | 11 | 19.0 | 10 | 19.2 | |||
| N2 | 14 | 24.1 | 11 | 21.2 | ||||
| N3 | 10 | 17.2 | 9 | 17.3 | ||||
| M | M0 | 58 | 100.0 | 52 | 100.0 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paradowski, K.; Góralczyk, M.; Drop, B.; Jarosz, M.; Polz-Dacewicz, M. Epstein–Barr Virus Load in the Saliva of Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer—Could It Have Prognostic Significance? Viruses 2025, 17, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111523
Paradowski K, Góralczyk M, Drop B, Jarosz M, Polz-Dacewicz M. Epstein–Barr Virus Load in the Saliva of Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer—Could It Have Prognostic Significance? Viruses. 2025; 17(11):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111523
Chicago/Turabian StyleParadowski, Karol, Magdalena Góralczyk, Bartłomiej Drop, Mirosław Jarosz, and Małgorzata Polz-Dacewicz. 2025. "Epstein–Barr Virus Load in the Saliva of Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer—Could It Have Prognostic Significance?" Viruses 17, no. 11: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111523
APA StyleParadowski, K., Góralczyk, M., Drop, B., Jarosz, M., & Polz-Dacewicz, M. (2025). Epstein–Barr Virus Load in the Saliva of Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer—Could It Have Prognostic Significance? Viruses, 17(11), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111523







