Impact of Combined Antiretroviral Treatment (cART) on Latent Cytomegalovirus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. HIV Infection
2.3. CMV Infection
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. HIV+ Group Characteristics
3.2. Association of Antiretroviral Treatment with Protection Against CMV Reactivation
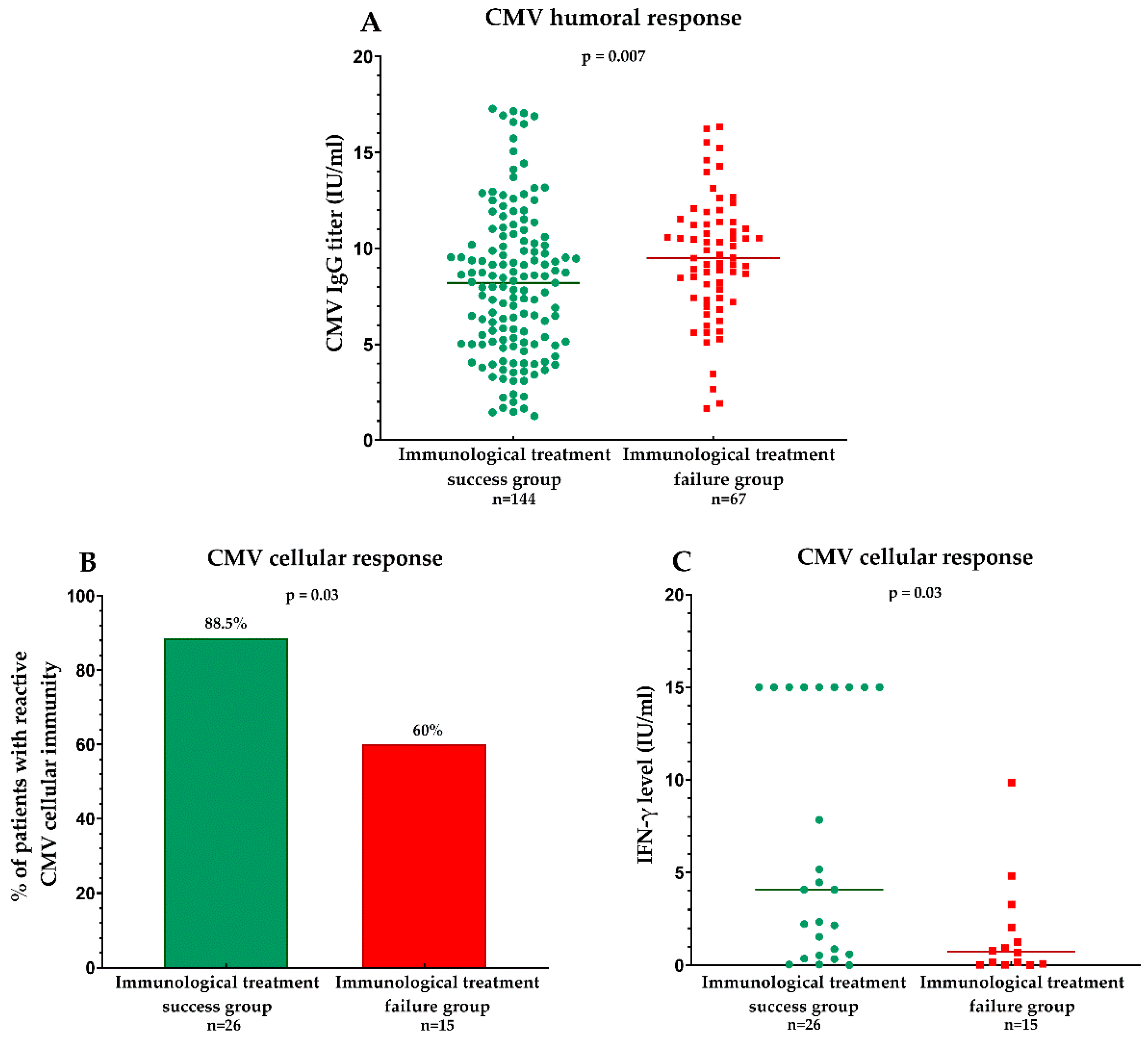
3.2.1. Humoral Response to CMV Measured by Specific IgG Levels
3.2.2. Cellular Response to CMV Measured by an Interferon Release Assay
3.3. Asymptomatic CMV Replication in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gianella, S.; Massanella, M.; Wertheim, J.O.; Smith, D.M. The Sordid Affair Between Human Herpesvirus and HIV. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, A.L.; O’Connor, C.M. Regulation of the MIE Locus During HCMV Latency and Reactivation. Pathogens 2020, 9, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, L.; Di Benedetto, S. Immunosenescence and Cytomegalovirus: Exploring Their Connection in the Context of Aging, Health, and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, W.; Rao, S. Mechanisms Underlying T Cell Immunosenescence: Aging and Cytomegalovirus Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.; Stern-Ginossar, N. Rethinking human cytomegalovirus latency reservoir. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2023, 1524, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurain, N.S.; Hanson, B.A.; Hotton, A.L.; Weber, K.M.; Cohen, M.H.; Landay, A.L. The Association of Human Cytomegalovirus with Biomarkers of Inflammation and Immune Activation in HIV-1-Infected Women. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2016, 32, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Z. Human cytomegalovirus infection and coronary heart disease: A systematic review. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshomo, T.; Molefe-Baikai, O.J.; Bennett, K.; Gaolathe, T.; Moyo, S.; Gaseitsewe, S.; Mohammed, T.; Lockman, S.; Mosepele, M. Cytomegalovirus Immunoglobulin G Levels and Subclinical Arterial Disease among People Living with HIV in Botswana: A Cross-Sectional Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, J.J.; Michael, D. The Immune Response Against Human Cytomegalovirus Links Cellular to Systemic Senescence. Cells 2020, 9, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadambari, S.; Klenerman, P.; Pollard, A.J. Why the elderly appear to be more severely affected by COVID-19: The potential role of immunosenescence and CMV. Rev. Med. Virol 2020, 30, e2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letendre, S.; Bharti, A.; Perez-Valero, I.; Hanson, B.; Franklin, D.; Woods, S.P.; Gianella, S.; de Oliveira, M.F.; Heaton, R.K.; Grant, I.; et al. Higher Anti-Cytomegalovirus Immunoglobulin G Concentrations Are Associated With Worse Neurocognitive Performance During Suppressive Antiretroviral Therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, E.U.; Gianella, S.; Newell, K.; Tobian, A.A.R.; Kirkpatrick, A.R.; Nalugoda, F.; Grabowski, M.K.; Gray, R.H.; Serwadda, D.; Quinn, T.C.; et al. Elevated Cytomegalovirus IgG Antibody Levels Are Associated with HIV-1 Disease Progression and Immune Activation. AIDS 2017, 31, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianella, S.; Morris, S.R.; Tatro, E.; Vargas, M.V.; Haubrich, R.H.; Daar, E.S.; Dube, M.P.; Richman, D.D.; Little, S.J.; Smith, D.M. Virologic Correlates of Anti-CMV IgG Levels in HIV-1–Infected Men. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlandson, K.M.; Allshouse, A.A.; Rapaport, E.; Palmer, B.E.; Wilson, C.C.; Weinberg, A.; MaWhinney, S.; Campbell, T.B. Physical Function Impairment of Older, HIV-Infected Adults Is Associated with Cytomegalovirus Immunoglobulin Response. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2015, 31, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nastri, B.M.; Pagliano, P.; Zannella, C.; Folliero, V.; Masullo, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Galdiero, M.; Franci, G. HIV and Drug-Resistant Subtypes. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, E.; Li, G. Approved Antiviral Drugs over the Past 50 Years. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 695–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deayton, J.; Mocroft, A.; Wilson, P.; Emery, V.C.; Johnson, M.A.; Griffiths, P.D. Loss of Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Viraemia Following Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy in the Absence of Specific Anti-CMV Therapy. AIDS 1999, 13, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L.; Stapleton, S.N.; Fudge, N.J.; Grant, M.D. Immune Resilience in HIV-Infected Individuals Seronegative for Cytomegalovirus. AIDS 2014, 28, 2045–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massanella, M.; Gianella, S.; Lada, S.M.; Richman, D.D.; Strain, M.C. Quantification of Total and 2-LTR (Long terminal repeat) HIV DNA, HIV RNA and Herpesvirus DNA in PBMCs. Bio-protocol 2015, 5, e1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Mora, E.; Massanella, M.; García, E.; Giles, D.; Bernadó, M.; Urrea, V.; Carrillo, J.; Ouchi, D.; Puig, J.; Negredo, E.; et al. Elevated Humoral Response to Cytomegalovirus in HIV-Infected Individuals with Poor CD4+ T-Cell Immune Recovery. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0184433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, M.; Pirillo, M.F.; Liotta, G.; Andreotti, M.; Jere, H.; Sagno, J.-B.; Ciccacci, F.; Amici, R.; Marazzi, M.C.; Vella, S.; et al. High CMV IgG Antibody Levels Are Associated to a Lower CD4+ RESPONSE to Antiretroviral Therapy in HIV-Infected Women. J. Clin. Virol. 2017, 96, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabs, D.A.; Ahuja, A.; Van Natta, M.; Dunn, J.P.; Yeh, S. Comparison of Treatment Regimens for Cytomegalovirus Retinitis in Patients with AIDS in the Era of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabs, D.A.; Ahuja, A.; Van Natta, M.L.; Lyon, A.T.; Yeh, S.; Danis, R. Studies of the Ocular Complications of AIDS Research Group. Long-term Outcomes of Cytomegalovirus Retinitis in the Era of Modern Antiretroviral Therapy: Results from a United States Cohort. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 1452–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, P.; Khan, N. CD8+ T-Cell Immunity to Cytomegalovirus. Hum. Immunol. 2004, 65, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronke, C.; Palmer, N.M.; Jansen, C.A.; Westerlaken, G.H.A.; Polstra, A.M.; Reiss, P.; Bakker, M.; Miedema, F.; Tesselaar, K.; van Baarle, D. Dynamics of Cytomegalovirus (CMV)–Specific T Cells in HIV-1–Infected Individuals Progressing to AIDS with CMV End-Organ Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeger, D.M.; Martin, J.N.; Sinclair, E.; Hunt, P.W.; Bangsberg, D.R.; Hecht, F.; Hsue, P.; McCune, J.M.; Deeks, S.G. Cytomegalovirus-Specific T Cells Persist at Very High Levels during Long-Term Antiretroviral Treatment of HIV Disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, S.F.; Price, P.; French, M.A. Cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific CD8+ T cells in individuals with HIV infection: Correlation with protection from CMV disease. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connick, E. Immune Reconstitution in HIV-1-Infected Individuals Treated with Potent Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2001, 6, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, D.C.; Kerr, S.J.; Iampornsin, T.; Pett, S.L.; Avihingsanon, A.; Thongpaeng, P.; Zaunders, J.J.; Ubolyam, S.; Ananworanich, J.; Kelleher, A.D.; et al. Restoration of CMV-specific-CD4 T cells with ART occurs early and is greater in those with more advanced immunodeficiency. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacre, K.; Carcelain, G.; Cassoux, N.; Fillet, A.-M.; Costagliola, D.; Vittecoq, D.; Salmon, D.; Amoura, Z.; Katlama, C.; Autran, B. Repertoire, Diversity, and Differentiation of Specific CD8 T Cells Are Associated with Immune Protection against Human Cytomegalovirus Disease. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1999–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics of the Patients | Total (n = 225) |
|---|---|
| Age, median (years) | 24 (23–25) |
| Sex, males (n; %) | 52% |
| Current CD4 count, median (cells/μL) | 476 (253–699) |
| Cumulative time spent with CD4 < 200 cells/μL, median (days) | 372 (28.5–983) |
| Current CD8 count, median (cells/μL) | 794 (571–1021) |
| CD4/CD8 Ratio, median | 0.6 (0.3–0.9) |
| Nadir CD4 count, median (cells/μL) | 92 (23–199) |
| HIV RNA | |
| HIV RNA, log10, median (copies/mL) | 2.1 (0–4.1) |
| HIV RNA detectable (n; %) | 94 (39.1%) |
| Cumulative time spent with detectable HIV RNA (days) | 1575 (538–2774) |
| Zenith HIV RNA, log10, median (copies/mL) | 5.1 (4.4–5.6) |
| Estimated duration of HIV, median (years) | 23.7 (22.8–24.6) |
| Antiretroviral treatment | |
| Total months of exposure to ARVs, median | 139.6 (96.4–172.6) |
| Months of exposure to current ARV regimen, median | 29.8 (13.1–51.4) |
| Any PI use (current) (n; %) | 70.1% |
| Any NRTI use (current) (n; %) | 83.8% |
| Any NNRTI use (current) (n; %) | 23.6% |
| Positive for CMV IgG antibodies (n; %) | 211 (93.7%) |
| QuantiFERON-CMV-reactive (n; %), n = 41 | 32 (78%) |
| CMV DNA detectable (n; %), n = 41 | 7 (17%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Temereanca, A.; Ene, L.; Tardei, G.; Grancea, C.; Achim, C.L.; Ruta, S. Impact of Combined Antiretroviral Treatment (cART) on Latent Cytomegalovirus Infection. Viruses 2025, 17, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010076
Temereanca A, Ene L, Tardei G, Grancea C, Achim CL, Ruta S. Impact of Combined Antiretroviral Treatment (cART) on Latent Cytomegalovirus Infection. Viruses. 2025; 17(1):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010076
Chicago/Turabian StyleTemereanca, Aura, Luminita Ene, Gratiela Tardei, Camelia Grancea, Cristian L. Achim, and Simona Ruta. 2025. "Impact of Combined Antiretroviral Treatment (cART) on Latent Cytomegalovirus Infection" Viruses 17, no. 1: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010076
APA StyleTemereanca, A., Ene, L., Tardei, G., Grancea, C., Achim, C. L., & Ruta, S. (2025). Impact of Combined Antiretroviral Treatment (cART) on Latent Cytomegalovirus Infection. Viruses, 17(1), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010076






