Influenza B Virus Receptor Specificity: Closing the Gap between Binding and Tropism
Abstract
1. Introduction
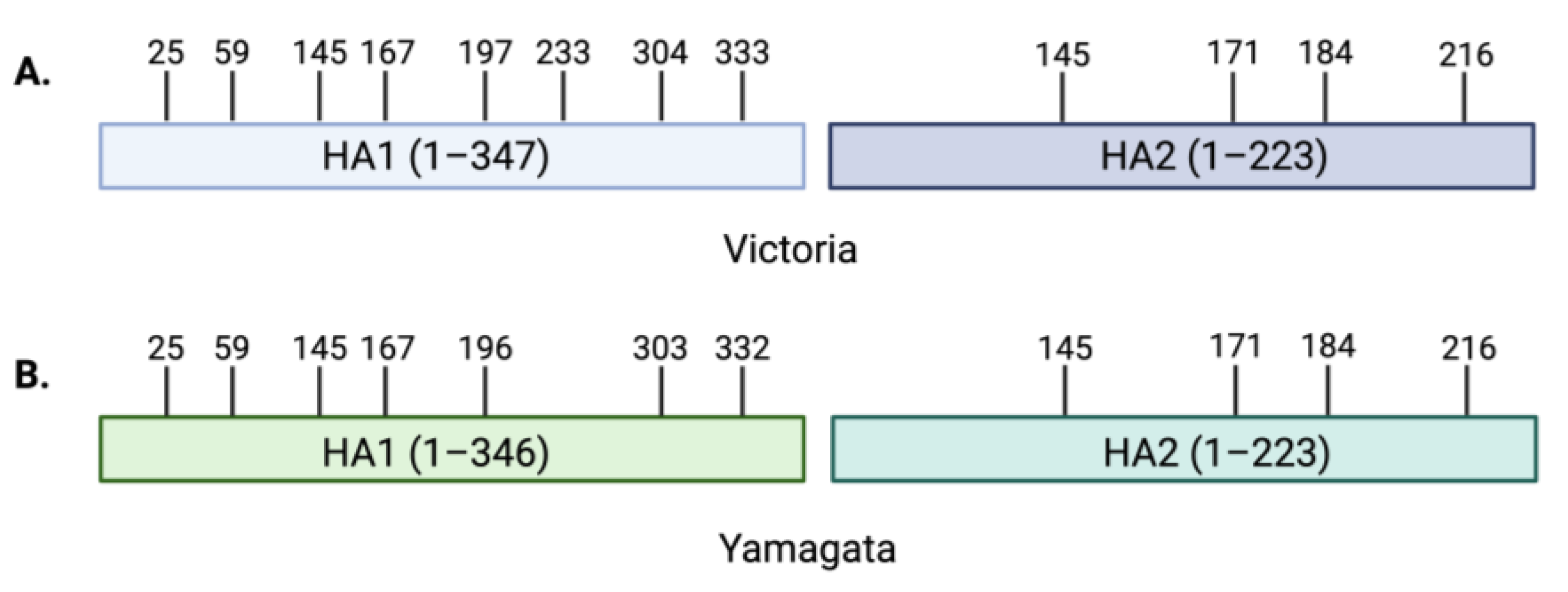
2. Influenza B Virus Receptor Specificity
3. Contribution of Viral Glycoproteins to Receptor Binding
4. Influenza B Glycosylation
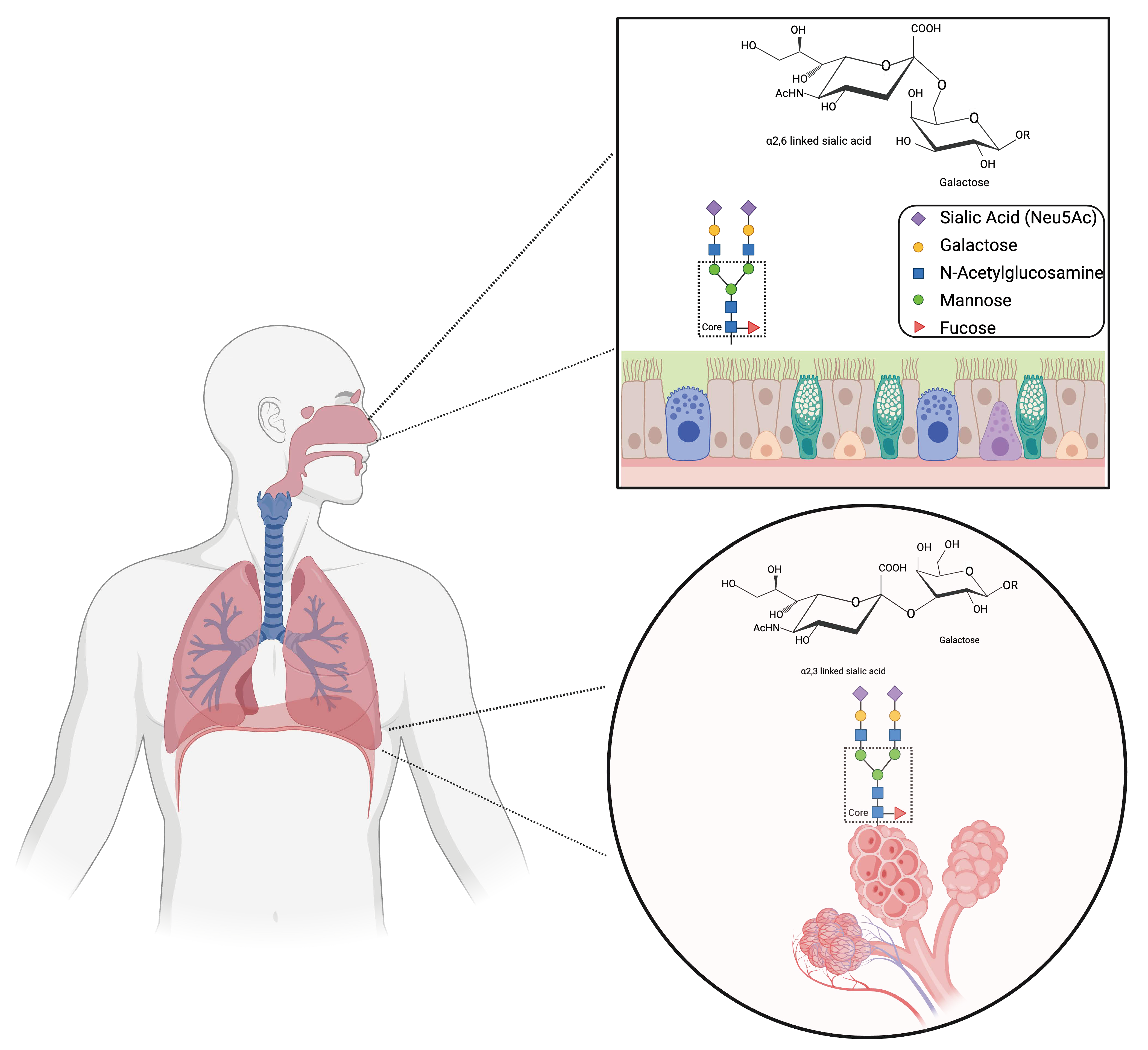
5. Host Cell Glycans and FLUBV Clinical Manifestations
5.1. Children vs. Adults
5.2. Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
5.3. Gastrointestinal Symptoms
5.4. Conjunctivitis
5.5. Neurotropism
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caini, S.; Kusznierz, G.; Garate, V.V.; Wangchuk, S.; Thapa, B.; de Paula Júnior, F.J.; de Almeida, W.A.F.; Njouom, R.; Fasce, R.A.; Bustos, P.; et al. The epidemiological signature of influenza B virus and its B/Victoria and B/Yamagata lineages in the 21st century. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, M.; Blanton, L.; Brammer, L.; Olsen, S.J.; Fry, A.M. Influenza-Associated Pediatric Deaths in the United States, 2010–2016. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20172918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerome, R.; Hiromoto, Y.; Sugita, S.; Tanabe, N.; Ishida, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Lindstrom, S.E.; Takahashi, T.; Nerome, K. Evolutionary characteristics of influenza B virus since its first isolation in 1940: Dynamic circulation of deletion and insertion mechanism. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 1569–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, D.G.; Taylor, A.R.; McLean, I.W.; Beard, D.; Beard, J.W.; Feller, A.E.; Dingle, J.H. Isolation and characterization of influenza virus B (Lee strain). J. Immunol. 1944, 48, 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, P.A.; Hemphill, M.L.; Whistler, T.; Regnery, H.L.; Kendal, A.P. Antigenic and genetic characterization of the haemagglutinins of recent cocirculating strains of influenza B virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 2737–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosu, M.E.; Lexmond, P.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Hauser, B.M.; Smith, D.J.; Herfst, S.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Substitutions near the HA receptor binding site explain the origin and major antigenic change of the B/Victoria and B/Yamagata lineages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2211616119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biere, B.; Bauer, B.; Schweiger, B. Differentiation of Influenza B Virus Lineages Yamagata and Victoria by Real-Time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1425–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanegae, Y.; Sugita, S.; Endo, A.; Ishida, M.; Senya, S.; Osako, K.; Nerome, K.; Oya, A. Evolutionary pattern of the hemagglutinin gene of influenza B viruses isolated in Japan: Cocirculating lineages in the same epidemic season. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2860–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, P.A.; Wallis, T.R.; Harmon, M.W.; Rota, J.S.; Kendal, A.P.; Nerome, K. Cocirculation of two distinct evolutionary lineages of influenza type B virus since 1983. Virology 1990, 175, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virk, R.K.; Jayakumar, J.; Mendenhall, I.H.; Moorthy, M.; Lam, P.; Linster, M.; Lim, J.; Lin, C.; Oon, L.L.E.; Lee, H.K.; et al. Divergent evolutionary trajectories of influenza B viruses underlie their contemporaneous epidemic activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotan, N.I.R. 100—Anti-Glycan Antibodies. In Autoantibodies, 2nd ed.; Shoenfeld, Y., Gershwin, M.E., Meroni, P.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, I.A.; Stevens, J.; Alymova, I.V. Influenza virus N-linked glycosylation and innate immunity. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20171505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullers, J.A.; Wang, G.C.; He, S.; Webster, R.G. Reassortment and Insertion-Deletion Are Strategies for the Evolution of Influenza B Viruses in Nature. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7343–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, B.; Kirby, M.K.; Warnes, C.; Sessions, W.M.; Davis, W.G.; Liu, J.; Wilson, M.M.; Lindstrom, S.; Wentworth, D.E.; Barnes, J.R. Detection and discrimination of influenza B Victoria lineage deletion variant viruses by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 1900652, Erratum in Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 201022e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Holmes, E.C. The evolutionary dynamics of human influenza B virus. J. Mol. Evol. 2008, 66, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyirenda, M.; Omori, R.; Tessmer, H.L.; Arimura, H.; Ito, K. Estimating the lineage dynamics of human influenza B viruses. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaykrishna, D.; Holmes, E.C.; Joseph, U.; Fourment, M.; Su, Y.C.F.; Halpin, R.; Lee, R.T.C.; Deng, Y.-M.; Gunalan, V.; Lin, X.; et al. The contrasting phylodynamics of human influenza B viruses. eLife 2015, 4, e05055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paget, J.; Caini, S.; Del Riccio, M.; van Waarden, W.; Meijer, A. Has influenza B/Yamagata become extinct and what implications might this have for quadrivalent influenza vaccines? Eurosurveillance 2022, 27, 2200753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caini, S.; Meijer, A.; Nunes, M.C.; Henaff, L.; Zounon, M.; Boudewijns, B.; Del Riccio, M.; Paget, J. Probable extinction of influenza B/Yamagata and its public health implications: A systematic literature review and assessment of global surveillance databases. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M. Influenza Virus Entry. In Viral Molecular Machines; Rossmann, M.G., Rao, V.B., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varki, A. Loss of N-glycolylneuraminic acid in humans: Mechanisms, consequences, and implications for hominid evolution. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2001, 116, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, J.M.; Bourne, A.J.; Chen, H.; Guan, Y.; Peiris, J.M. Sialic acid receptor detection in the human respiratory tract: Evidence for widespread distribution of potential binding sites for human and avian influenza viruses. Respir. Res. 2007, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Korteweg, C.; Hsueh, W.; Gu, J. Avian influenza receptor expression in H5N1-infected and noninfected human tissues. FASEB J. 2007, 22, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, T.; Karamanska, R.; Chan, R.W.Y.; Chan, M.C.W.; Jia, N.; Air, G.; Hopton, C.; Wong, M.P.; Dell, A.; Peiris, J.S.M.; et al. Glycomic Analysis of Human Respiratory Tract Tissues and Correlation with Influenza Virus Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Graaf, M.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Role of receptor binding specificity in influenza A virus transmission and pathogenesis. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 823–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Pu, J. Influence of Host Sialic Acid Receptors Structure on the Host Specificity of Influenza Viruses. Viruses 2022, 14, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, L.G.; Paulson, J.C. Sialyloligosaccharides of the respiratory epithelium in the selection of human influenza virus receptor specificity. Acta Histochem. Suppl. 1990, 40, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Shinya, K.; Ebina, M.; Yamada, S.; Ono, M.; Kasai, N.; Kawaoka, Y. Avian flu: Influenza virus receptors in the human airway. Nature 2006, 440, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varki, N.M.; Varki, A. Diversity in cell surface sialic acid presentations: Implications for biology and disease. Lab. Investig. 2007, 87, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, C.; Chi, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Su, I. Characterization of glycan binding specificities of influenza B viruses with correlation with hemagglutinin genotypes and clinical features. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, X.; Chen, X.; Ma, J. Structural basis for receptor specificity of influenza B virus hemagglutinin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16874–16879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Watanabe, T.; Hatta, M.; Das, S.C.; Ozawa, M.; Shinya, K.; Zhong, G.; Hanson, A.; Katsura, H.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Experimental adaptation of an influenza H5 HA confers respiratory droplet transmission to a reassortant H5 HA/H1N1 virus in ferrets. Nature 2012, 486, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herfst, S.; Schrauwen, E.J.A.; Linster, M.; Chutinimitkul, S.; de Wit, E.; Munster, V.J.; Sorrell, E.M.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Burke, D.F.; Smith, D.J.; et al. Airborne transmission of influenza A/H5N1 virus between ferrets. Science 2012, 336, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.S.; Mistry, B.; Haslam, S.M.; Barclay, W.S. Host and viral determinants of influenza A virus species specificity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 17, 67–81, Erratum in Nat. Reviews. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodewes, R.; Morick, D.; de Mutsert, G.; Osinga, N.; Bestebroer, T.; van der Vliet, S.; Smits, S.L.; Kuiken, T.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Fouchier, R.A.; et al. Recurring influenza B virus infections in seals. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Martina, B.E.E.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Influenza B virus in seals. Science 2000, 288, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouchier, R.; Bestebroer, T.; Martina, B.; Rimmelzwaan, G.; Osterhaus, A. Infection of grey seals and harbour seals with influenza B virus. Int. Congr. Ser. 2001, 1219, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nakao, T.; Ito, T.; Watanabe, N.; Toda, Y.; Guiyun, X.; Suzuki, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kimura, Y.; Yamada, A.; et al. Structural determination of gangliosides that bind to influenza A, B, and C viruses by an improved binding assay: Strain-specific receptor epitopes in sialo-sugar chains. Virology 1992, 189, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaryan, A.; Robertson, J.; Matrosovich, M. Effects of Egg-Adaptation on the Receptor-Binding Properties of Human Influenza A and B Viruses. Virology 1999, 258, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaryan, A.S.; Tuzikov, A.B.; Piskarev, V.E.; Yamnikova, S.S.; Lvov, D.K.; Robertson, J.S.; Bovin, N.V.; Matrosovich, M.N. Specification of Receptor-Binding Phenotypes of Influenza Virus Isolates from Different Hosts Using Synthetic Sialylglycopolymers: Non-Egg-Adapted Human H1 and H3 Influenza A and Influenza B Viruses Share a Common High Binding Affinity for 6′-Sialyl(N-acetyllactosamine). Virology 1997, 232, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blixt, O.; Head, S.; Mondala, T.; Scanlan, C.; Huflejt, M.E.; Alvarez, R.; Bryan, M.C.; Fazio, F.; Calarese, D.; Stevens, J.; et al. Printed covalent glycan array for ligand profiling of diverse glycan binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17033–17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hyun, J.Y.; Shin, I. Glycan microarrays from construction to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 8276–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugovtsev, V.Y.; Smith, D.F.; Weir, J.P. Changes of the receptor-binding properties of influenza B virus B/Victoria/504/2000 during adaptation in chicken eggs. Virology 2009, 394, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, C.H.; Chan, R.W.; Ng, M.M.; Cheung, M.-C.; Ng, K.-C.; Chan, M.P.; Chan, L.L.; Fong, J.H.; Nicholls, J.; Peiris, J.M.; et al. Tropism of influenza B viruses in human respiratory tract explants and airway organoids. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velkov, T. The specificity of the influenza B virus hemagglutinin receptor binding pocket: What does it bind to? J. Mol. Recognit. 2013, 26, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokin, E.; Tsareva, T.R.; Sominina, A.; Pisareva, M.M.; Komissarov, A.B.; Kosheleva, A.A. Influence of single amino acid substitutions in the hemagglutinin on antigenic and receptor-binding properties of influenza virus B/Florida/04/2006 of Yamagata-like evolutionary lineage. Microbiol. Indep. Res. J. 2016, 3, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, F.; Mbawuike, I.N.; Kondrashkina, E.; Wang, Q. The roles of hemagglutinin Phe-95 in receptor binding and pathogenicity of influenza B virus. Virology 2013, 450–451, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce-Staskal, P.J.; Woods, R.M.; Borisov, O.V.; Massare, M.J.; Hahn, T.J. Hemagglutinin from multiple divergent influenza A and B viruses bind to a distinct branched, sialylated poly-LacNAc glycan by surface plasmon resonance. Vaccine 2020, 38, 6757–6765, Erratum in Vaccine 2021, 39, 1544–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekarek, M.J.; Weaver, E.A. Existing Evidence for Influenza B Virus Adaptations to Drive Replication in Humans as the Primary Host. Viruses 2023, 15, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, M.; Stevaert, A.; Raeymaekers, V.; Boogaerts, T.; Nehlmeier, I.; Chiu, W.; Benkheil, M.; Vanaudenaerde, B.; Pöhlmann, S.; Naesens, L. Hemagglutinin Cleavability, Acid Stability, and Temperature Dependence Optimize Influenza B Virus for Replication in Human Airways. J. Virol. 2019, 94, e01430-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, F.; Kondrashkina, E.; Wang, Q. Structural basis for the divergent evolution of influenza B virus hemagglutinin. Virology 2013, 446, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cheng, F.; Lu, M.; Tian, X.; Ma, J. Crystal Structure of Unliganded Influenza B Virus Hemagglutinin. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3011–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suptawiwat, O.; Ninpan, K.; Boonarkart, C.; Ruangrung, K.; Auewarakul, P. Evolutionary dynamic of antigenic residues on influenza B hemagglutinin. Virology 2017, 502, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranaweera, A.; Ratnayake, P.U.; Weliky, D.P. The Stabilities of the Soluble Ectodomain and Fusion Peptide Hairpins of the Influenza Virus Hemagglutinin Subunit II Protein Are Positively Correlated with Membrane Fusion. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 5480–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosovich, M.; Gambaryan, A.; Tuzikov, A.; Byramova, N.; Mochalova, L.; Golbraikh, A.; Shenderovich, M.D.; Finne, J.; Bovin, N. Probing of the receptor-binding sites of the H1 and H3 influenza A and influenza B virus hemagglutinins by synthetic and natural sialosides. Virology 1993, 196, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Kirk, B.D.; Ma, J.; Wang, Q. Diversifying selective pressure on influenza B virus hemagglutinin. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 81, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtyrya, Y.A.; Mochalova, L.V.; Bovin, N.V. Influenza virus neuraminidase: Structure and function. Acta Naturae 2009, 1, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, W.; Ruigrok, R.; Cusack, S. The 2.2 A resolution crystal structure of influenza B neuraminidase and its complex with sialic acid. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janakiraman, M.N.; White, C.L.; Laver, W.G.; Air, G.M.; Luo, M. Structure of Influenza Virus Neuraminidase B/Lee/40 Complexed with Sialic Acid and a Dehydro Analog at 1.8-.ANG. Resolution: Implications for the Catalytic Mechanism. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 8172–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhail, N.M.; Tatyana, Y.M.; Gray, T.; Noel, A.R.; Klenk, H.-D. Neuraminidase Is Important for the Initiation of Influenza Virus Infection in Human Airway Epithelium. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12665–12667. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Steukers, L.; Forier, K.; Xiong, R.; Braeckmans, K.; Van Reeth, K.; Nauwynck, H. A beneficiary role for neuraminidase in influenza virus penetration through the respiratory mucus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, A.J.; Barrett, S.; Peat, T.S.; Newman, J.; Streltsov, V.A.; Waddington, L.; Saito, T.; Tashiro, M.; McKimm-Breschkin, J.L. Structural and functional basis of resistance to neuraminidase inhibitors of influenza B viruses. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 6421–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Nobusawa, E.; Nakajima, K. An analysis of the role of neuraminidase in the receptor-binding activity of influenza B virus: The inhibitory effect of Zanamivir on haemadsorption. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 2969–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, F.; Wan, X.-F. Influenza Neuraminidase: Underrated Role in Receptor Binding. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Huang, S.; Wen, F. Receptor Binding Properties of Neuraminidase for influenza A virus: An Overview of Recent Research Advances. Virulence 2023, 14, 2235459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.P.; Gregory, V.; Collins, P.; Kloess, J.; Wharton, S.; Cattle, N.; Lackenby, A.; Daniels, R.; Hay, A. Neuraminidase Receptor Binding Variants of Human Influenza A(H3N2) Viruses Resulting from Substitution of Aspartic Acid 151 in the Catalytic Site: A Role in Virus Attachment? J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6769–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Matrosovich, M.; Klenk, H. Functional balance between haemagglutinin and neuraminidase in influenza virus infections. Rev. Med. Virol. 2002, 12, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alymova, I.V.; Cipollo, J.F.; Parsons, L.M.; Music, N.; Kamal, R.P.; Tzeng, W.-P.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Contessa, J.N.; Hartshorn, K.L.; Wilson, J.R.; et al. Aberrant Cellular Glycosylation May Increase the Ability of Influenza Viruses to Escape Host Immune Responses through Modification of the Viral Glycome. mBio 2022, 13, e0298321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Östbye, H.; Gao, J.; Martinez, M.R.; Wang, H.; de Gier, J.-W.; Daniels, R. N-Linked Glycan Sites on the Influenza A Virus Neuraminidase Head Domain Are Required for Efficient Viral Incorporation and Replication. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00874-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P.C.; Garten, W.; Klenk, H.D. Role of conserved glycosylation sites in maturation and transport of influenza A virus hemagglutinin. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 3048–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchi, R.; Ohuchi, M.; Garten, W.; Klenk, H.D. Oligosaccharides in the stem region maintain the influenza virus hemagglutinin in the metastable form required for fusion activity. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 3719–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.S.; Naeve, C.W.; Webster, R.G.; Bootman, J.S.; Newman, R.; Schild, G.C. Alterations in the hemagglutinin associated with adaptation of influenza B virus to growth in eggs. Virology 1985, 143, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Aspelund, A.; Jin, H. Stabilizing the glycosylation pattern of influenza B hemagglutinin following adaptation to growth in eggs. Vaccine 2008, 26, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Nakaya, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Ito, R.; Saito, T.; Saito, H.; Takao, S.; Sahara, K.; Odagiri, T.; Murata, T.; et al. Antigenic alteration of influenza B virus associated with loss of a glycosylation site due to host-cell adaptation. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 74, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schild, G.C.; Oxford, J.S.; de Jong, J.C.; Webster, R.G. Evidence for host-cell selection of influenza virus antigenic variants. Nature 1983, 303, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubu, A.M.; Aryee, N.A.; Bonney, E.Y.; Kotey, E.N.; Bonney, J.H.K.; Wiley, M.R.; Pratt, C.B.; Ababio, G.K.; et al. Molecular characterization of haemagglutinin genes of influenza B viruses circulating in Ghana during 2016 and 2017. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271321. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Schulman, J.; Itamura, S.; Palese, P. Glycosylation of neuraminidase determines the neurovirulence of influenza A/WSN/33 virus. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 6667–6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, C.; Deveci, I.; McCammon, J.A. Glycosylation and Crowded Membrane Effects on Influenza Neuraminidase Stability and Dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 9926–9934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.; Blixt, O.; Tumpey, T.M.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Paulson, J.C.; Wilson, I.A. Structure and Receptor Specificity of the Hemagglutinin from an H5N1 Influenza Virus. Science 2006, 312, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumpey, T.M.; Maines, T.R.; Van Hoeven, N.; Glaser, L.; Solórzano, A.; Pappas, C.; Cox, N.J.; Swayne, D.E.; Palese, P.; Katz, J.M.; et al. A Two-Amino Acid Change in the Hemagglutinin of the 1918 Influenza Virus Abolishes Transmission. Science 2007, 315, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoeven, N.; Pappas, C.; Belser, J.A.; Maines, T.R.; Zeng, H.; García-Sastre, A.; Sasisekharan, R.; Katz, J.M.; Tumpey, T.M. Human HA and polymerase subunit PB2 proteins confer transmission of an avian influenza virus through the air. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3366–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Y.R. Influenza B infections in children: A review. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2020, 9, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Guan, W.; Lam, T.T.-Y.; Pan, S.; Wu, S.; Zhan, Y.; Viboud, C.; Holmes, E.C.; Yang, Z. Differing Epidemiological Dynamics of Influenza B Virus Lineages in Guangzhou, Southern China, 2009–2010. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12447–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sočan, M.; Prosenc, K.; Učakar, V.; Berginc, N. A comparison of the demographic and clinical characteristics of laboratory-confirmed influenza B Yamagata and Victoria lineage infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 61, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumlin, U.; Olofsson, S.; Dimock, K.; Arnberg, N. Sialic acid tissue distribution and influenza virus tropism. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2008, 2, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.; Severi, E.; Owen, C.D.; Latousakis, D.; Juge, N. Biochemical and structural basis of sialic acid utilization by gut microbes. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102989, Erratum in J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killingley, B.; Nguyen-Van-Tam, J. Routes of influenza transmission. Influenza Other Respir Viruses 2013, 7 (Suppl. S2), 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-M.; Lin, C.-C.; Wang, H.-C.; Wang, J.-R.; Su, I.-J.; Liu, C.-C. Clinical Features of Children Infected With Different Strains of Influenza B in Southern Taiwan. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, M.; Watanabe, A.; Aizawa, H. Differences in clinical features between influenza A H1N1, A H3N2, and B in adult patients. Respirology 2003, 8, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, T.M.; Benega, M.A.; Silva, D.B.B.; Santos, K.C.O.; Cruz, A.S.; Hortenci, M.F.; Barbieri, M.T.; Monteiro, M.M.; Barbosa, H.A.; Carvalhanas, T.R.M.P. Evolutionary pattern of reemerging influenza B/Victoria lineage viruses in São Paulo, Brazil, 1996–2012: Implications for vaccine composition strategy. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 1983–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Terao, K.; Nishimura, H.; Tamura, S. Conjuctivitis following Accidental Exposure to Influenza B virus/Shangdong/07/97. J. Infect. 2001, 42, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, A.; Nallusamy, R.; Isaacs, D. Comparison of influenza A and influenza B virus infection in hospitalized children. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2000, 36, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltola, V.; Ziegler, T.; Ruuskanen, O. Influenza A and B Virus Infections in Children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terraciano, A.J.; Wang, N.; Schuman, J.S.; Haffner, G.; Panjwani, N.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Z. Sialyl Lewis X, Lewis X, and N-acetyllactosamine expression on normal and glaucomatous eyes. Curr. Eye Res. 1999, 18, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creuzot-Garcher, C.; Guerzider, V.; Assem, M.; Bron, A.M.; Delannoy, P.; Bara, J. Alteration of Sialyl Lewis Epitope Expression in Pterygium. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999, 40, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Belser, J.A.; Rota, P.A.; Tumpey, T.M. Ocular tropism of respiratory viruses. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creager, H.M.; Kumar, A.; Zeng, H.; Maines, T.R.; Tumpey, T.M.; Belser, J.A. Infection and Replication of Influenza Virus at the Ocular Surface. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02192-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouchier, R.A.M.; Schneeberger, P.M.; Rozendaal, F.W.; Broekman, J.M.; Kemink, S.A.G.; Munster, V.; Kuiken, T.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Schutten, M.; van Doornum, G.J.J.; et al. Avian influenza A virus (H7N7) associated with human conjunctivitis and a fatal case of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.K.S. Outbreak of Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Infection in Hong Kong in 1997. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, S58–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belser, J.A.; Bridges, C.B.; Katz, J.M.; Tumpey, T.M. Past, present, and possible future human infection with influenza virus A subtype H7. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, M.; Wilbrink, B.; Conyn, M.; Natrop, G.; van der Nat, H.; Vennema, H.; Meijer, A.; van Steenbergen, J.; Fouchier, R.; Osterhaus, A.; et al. Transmission of H7N7 avian influenza A virus to human beings during a large outbreak in commercial poultry farms in the Netherlands. Lancet 2004, 363, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S. Outbreak of Highly Pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1) viruses in US dairy cattle and detection of two human cases—United States, 2024. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2024, 73, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Lai, L.; Li, R.; Lin, Q.; Chen, L.; Ren, T. The H5 subtype of avian influenza virus jumped across species to humans—A view from China. J. Infect. 2024, 89, 106193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyeki, T.M.; Milton, S.; Hamid, C.A.; Webb, C.R.; Presley, S.M.; Shetty, V.; Rollo, S.N.; Martinez, D.L.; Rai, S.; Gonzales, E.R.; et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1) virus infection in a dairy farm worker. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 2028–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, C.P.; Florescu, S.A.; Lupulescu, E.; Zaharia, M.; Tardei, G.; Lazar, M.; Ceausu, E.; Ruta, S.M. Neurologic Complications of Influenza B Virus Infection in Adults, Romania. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sazgar, M.; Robinson, J.L.; Chan, A.K.; Sinclair, D. Influenza B acute necrotizing encephalopathy: A case report and literature review. Pediatr. Neurol. 2003, 28, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamoto, M.; Okada, S.; Terashima, T. Encephalopathy Associated with Influenza B in a Healthy Young Man. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 1925–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McCullers, J.A.; Facchini, S.; Chesney, P.J.; Webster, R.G. Influenza B Virus Encephalitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 28, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, V.; Kim, H.; Huang, J.X.; Baker, M.A.; Ong, C.; Cooper, M.A.; Li, J.; Rockman, S.; Velkov, T. Molecular characterization of the receptor binding structure-activity relationships of influenza B virus hemagglutinin. Acta Virol. 2013, 57, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Suzuki, T.; Tahara, H.; Kiso, M.; Hasegawa, A.; Suzuki, Y. Specificity of Sialyl-Sugar Chain Mediated Recognition by the Hemagglutinin of Human Influenza B Virus Isolates1. J. Biochem. 1994, 115, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broszeit, F.; van Beek, R.J.; Unione, L.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Chapla, D.; Yang, J.-Y.; Moremen, K.W.; Herfst, S.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; de Vries, R.P.; et al. Glycan remodeled erythrocytes facilitate antigenic characterization of recent A/H3N2 influenza viruses. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Spruit, C.M.; Wei, N.; Liu, L.; Wolfert, M.A.; de Vries, R.P.; Boons, G.J. Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Tri-antennary N-Glycans Terminating in Sialyl-Lewisx Reveals the Importance of Glycan Complexity for Influenza A Virus Receptor Binding. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202401108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.; Rustandi, R.R.; Zheng, X.; Payne, A.; Shang, L. Applications of surface plasmon resonance and biolayer interferometry for virus–ligand binding. Viruses 2022, 14, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.; Wharton, S.A.; Lin, Y.P.; Takemoto, D.K.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C.; Steinhauer, D.A. Studies of the Binding Properties of Influenza Hemagglutinin Receptor-Site Mutants. Virology 1998, 241, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, R.; García-Sastre, A.; Swayne, D.E.; Palese, P. A Reassortment-Incompetent Live Attenuated Influenza Virus Vaccine for Protection against Pandemic Virus Strains. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6832–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Page, C.K.; Tompkins, S.M. Influenza B Virus Receptor Specificity: Closing the Gap between Binding and Tropism. Viruses 2024, 16, 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16091356
Page CK, Tompkins SM. Influenza B Virus Receptor Specificity: Closing the Gap between Binding and Tropism. Viruses. 2024; 16(9):1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16091356
Chicago/Turabian StylePage, Caroline K., and Stephen Mark Tompkins. 2024. "Influenza B Virus Receptor Specificity: Closing the Gap between Binding and Tropism" Viruses 16, no. 9: 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16091356
APA StylePage, C. K., & Tompkins, S. M. (2024). Influenza B Virus Receptor Specificity: Closing the Gap between Binding and Tropism. Viruses, 16(9), 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16091356






