SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.1 Variant Infection of Human Colon Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
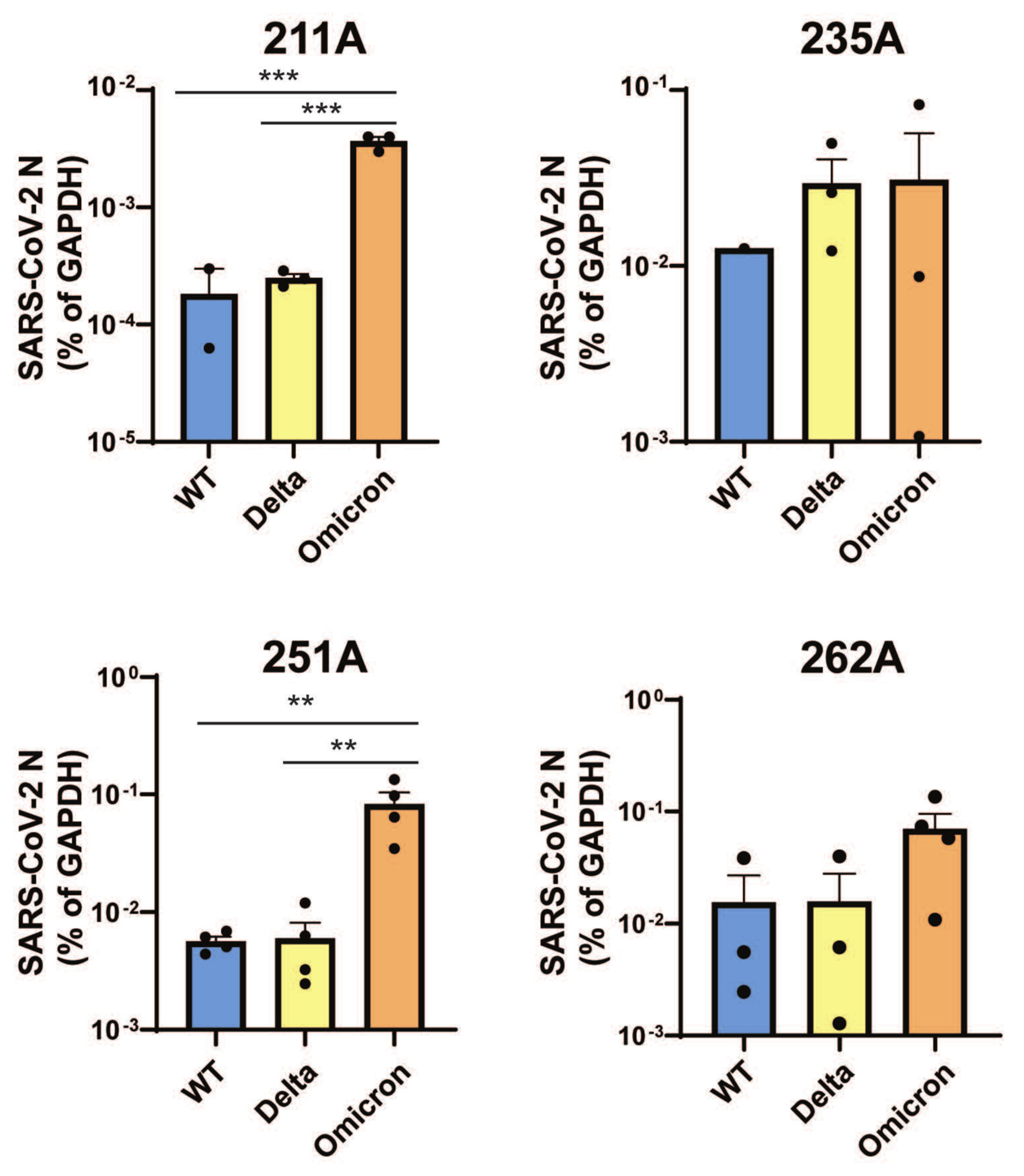
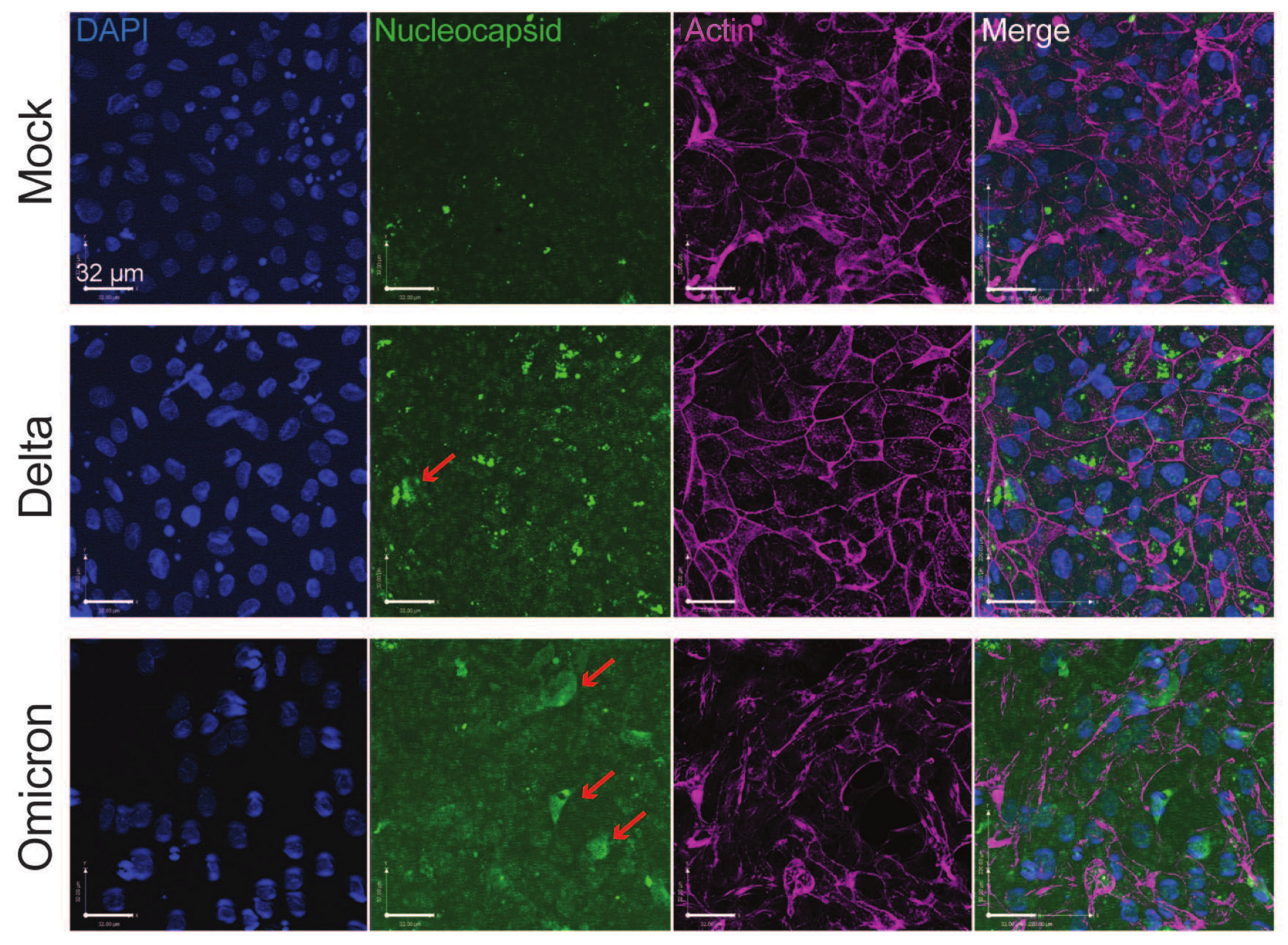
3.1. Omicron Variant SARS-CoV-2 Infects Human Colon-Derived Organoids
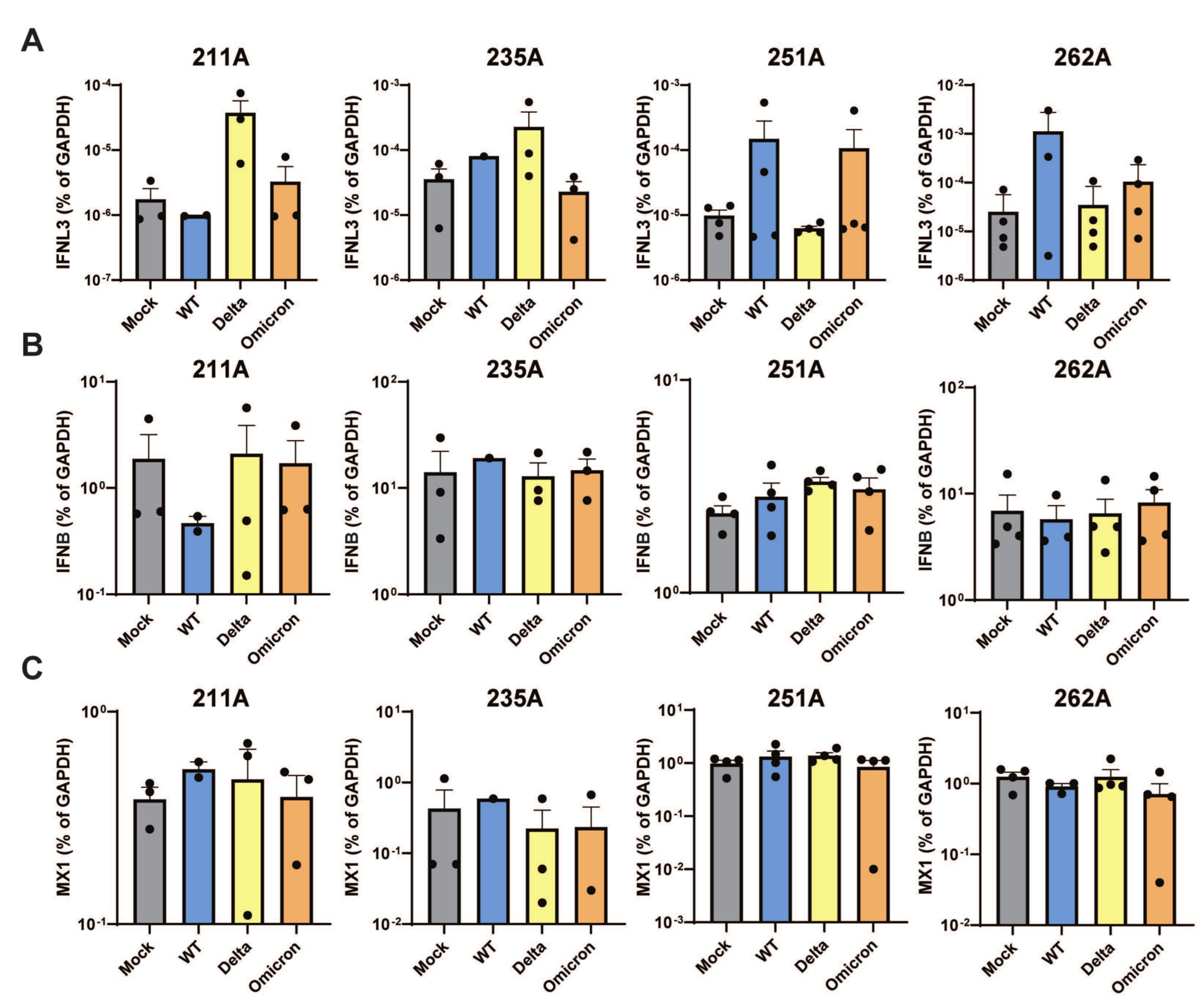
3.2. Interferon Responses in Human Colonoids to SARS-CoV-2 Variants
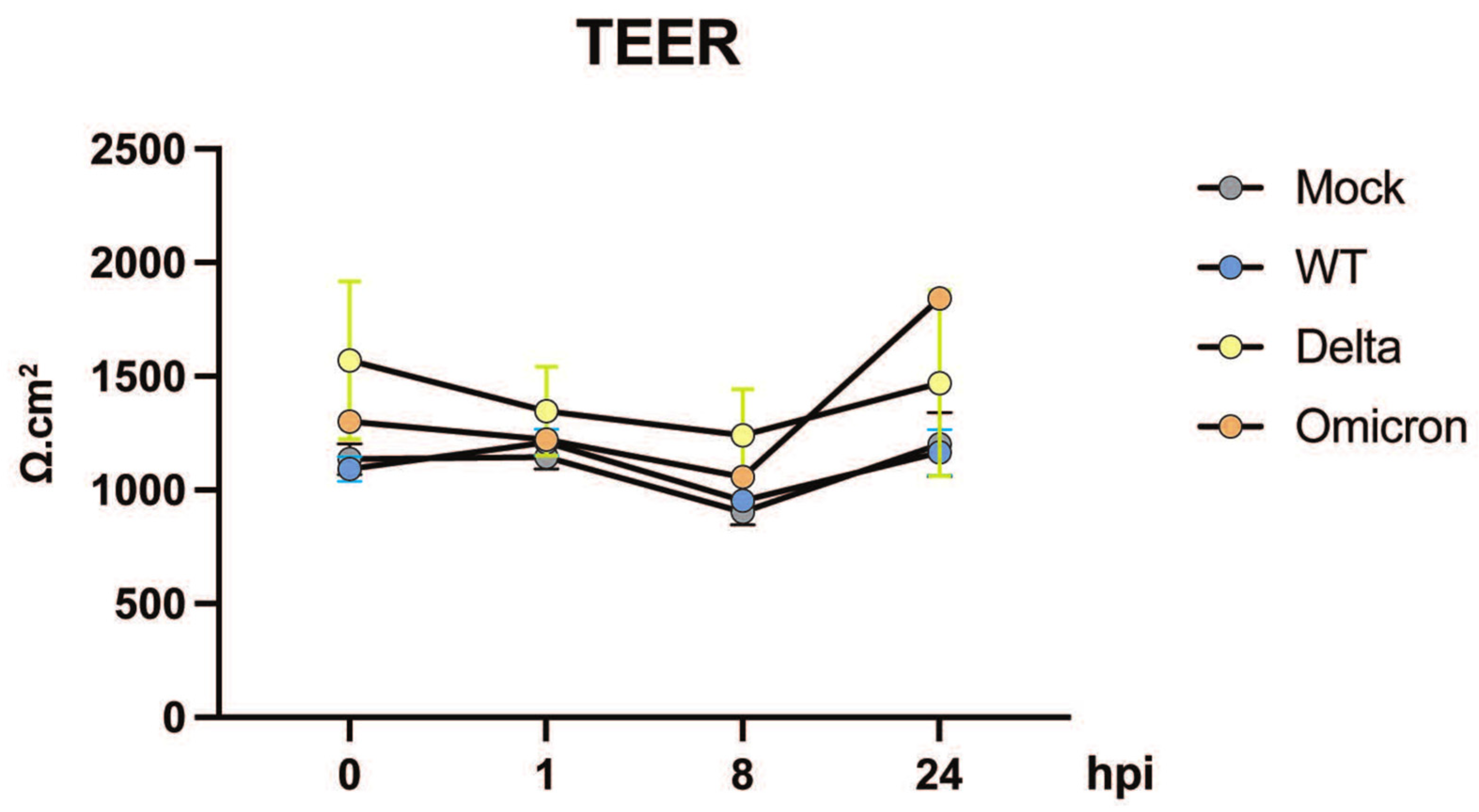
3.3. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Does Not Compromise the Integrity of Primary Human Intestinal Colonoids
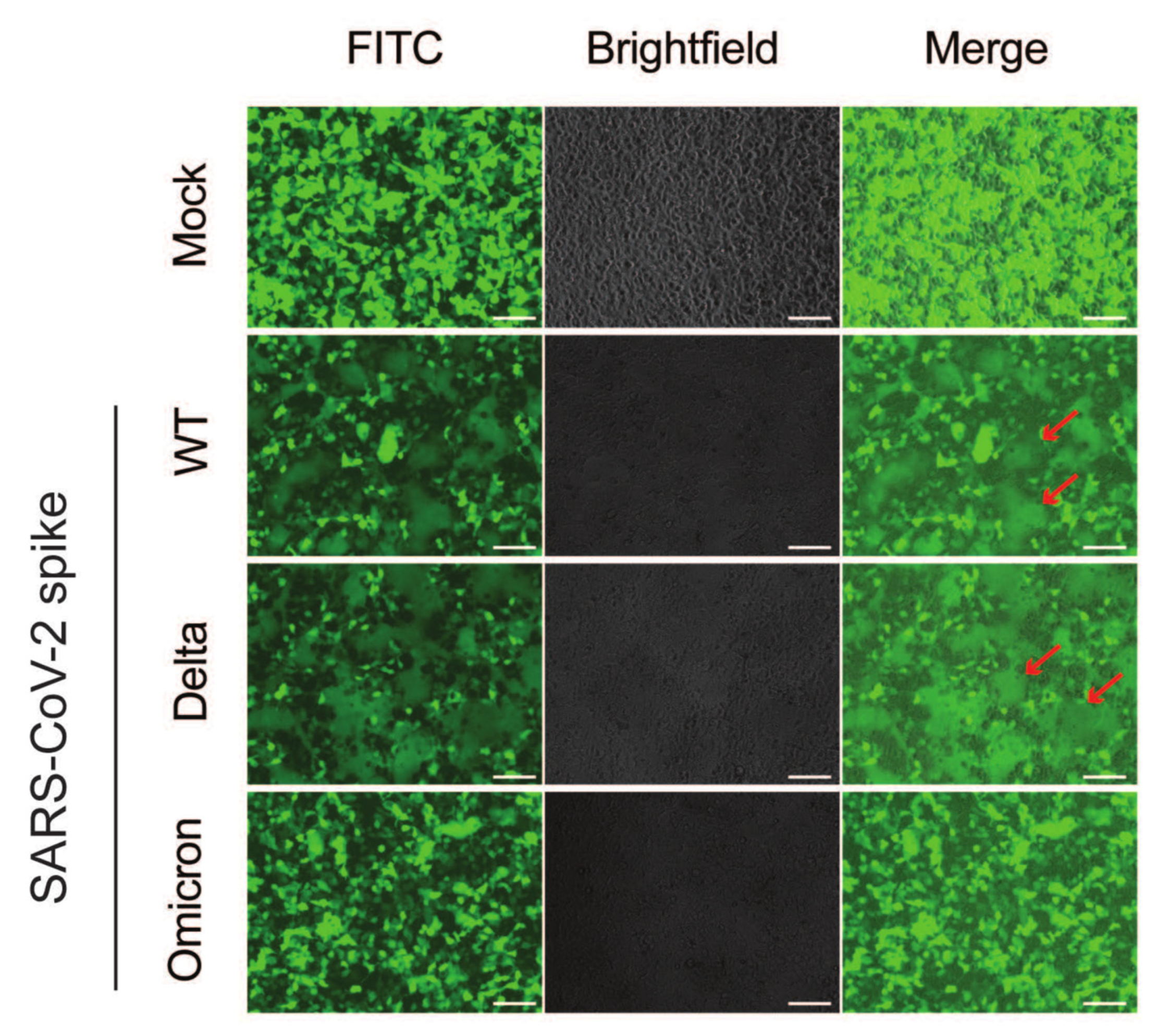
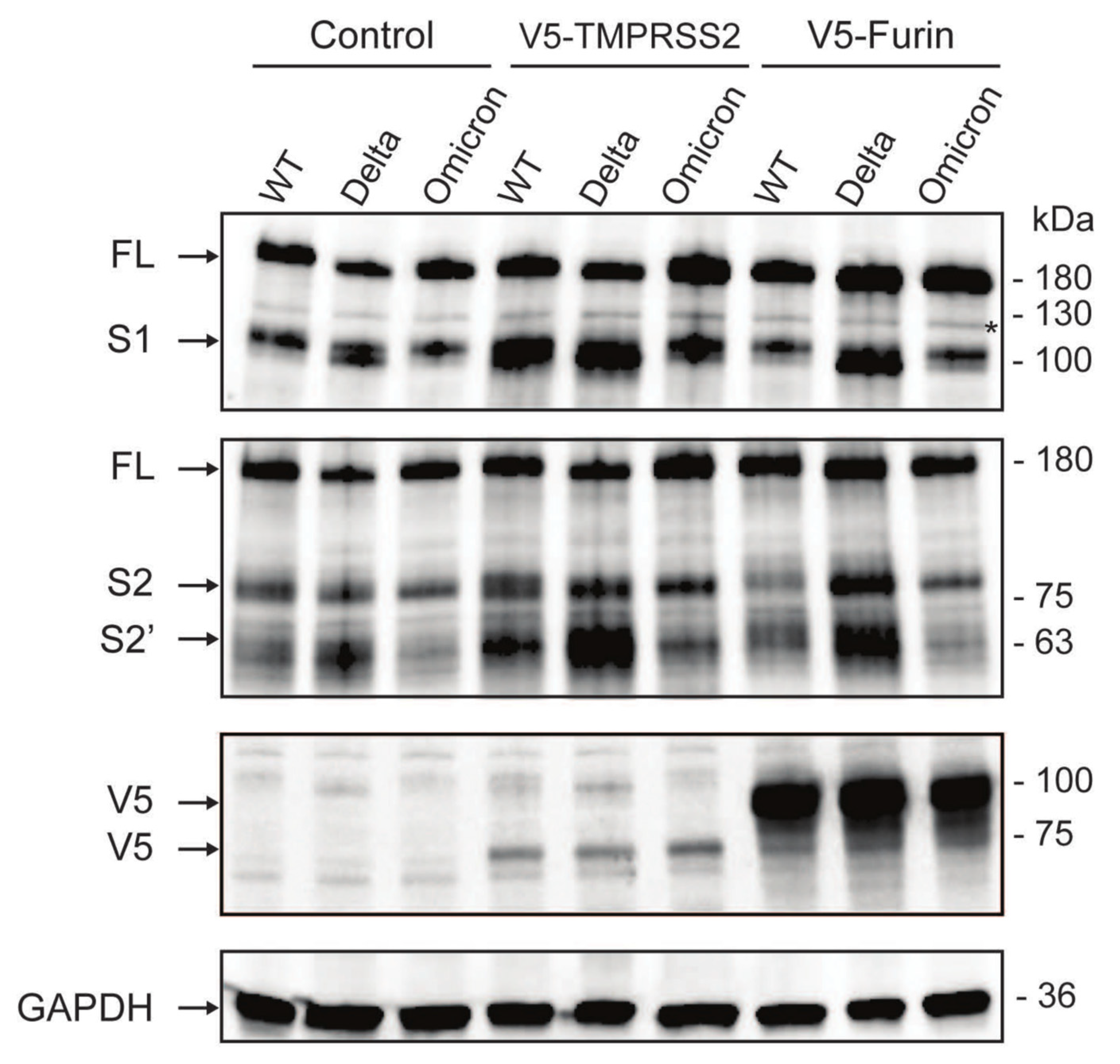
3.4. The Omicron Variant Exhibits Lower Syncytia Formation and Impaired Spike Processing in Human Colonoids
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 13 January 2024).
- Halfmann, P.J.; Iida, S.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Maemura, T.; Kiso, M.; Scheaffer, S.M.; Darling, T.L.; Joshi, A.; Loeber, S.; Singh, G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron virus causes attenuated disease in mice and hamsters. Nature 2022, 603, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanBlargan, L.A.; Errico, J.M.; Halfmann, P.J.; Zost, S.J.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; Purcell, L.A.; Kawaoka, Y.; Corti, D.; Fremont, D.H.; Diamond, M.S. An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekliz, M.; Adea, K.; Vetter, P.; Eberhardt, C.S.; Hosszu-Fellous, K.; Vu, D.L.; Puhach, O.; Essaidi-Laziosi, M.; Waldvogel-Abramowski, S.; Stephan, C.; et al. Neutralization capacity of antibodies elicited through homologous or heterologous infection or vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 VOCs. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, D.J.; Franchini, M.; Joyner, M.J.; Casadevall, A.; Focosi, D. Analysis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-neutralizing antibody titers in different vaccinated and unvaccinated convalescent plasma sources. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liao, H.; Meng, Y.; Li, W.; Han, P.; Liu, K.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Structural basis of human ACE2 higher binding affinity to currently circulating Omicron SARS-CoV-2 sub-variants BA.2 and BA.1.1. Cell 2022, 185, 2952–2960.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Yamasoba, D.; Kimura, I.; Wang, L.; Kishimoto, M.; Ito, J.; Morioka, Y.; Nao, N.; Nasser, H.; Uriu, K.; et al. Attenuated fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Nature 2022, 603, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Ferreira, I.A.T.M.; Abdullahi, A.; Saito, A.; Kimura, I.; Yamasoba, D.; Kemp, S.A.; Goonawardane, N.; Papa, G.; Fatihi, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron spike mediated immune escape, infectivity and cell-cell fusion. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, A.; Zlitni, S.; Brooks, E.F.; Vance, S.E.; Dahlen, A.; Hedlin, H.; Park, R.M.; Han, A.; Schmidtke, D.T.; Verma, R.; et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms and fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 RNA suggest prolonged gastrointestinal infection. Med 2022, 3, 371–387.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.K.; Kaczmarek, M.E.; Dallari, S.; Chen, Y.-H.; Tada, T.; Axelrad, J.; Landau, N.R.; Stapleford, K.A.; Cadwell, K. Variable susceptibility of intestinal organoid–derived monolayers to SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, R.; Gomez Castro, M.F.; McCune, B.T.; Zeng, Q.; Rothlauf, P.W.; Sonnek, N.M.; Liu, Z.; Brulois, K.F.; Wang, X.; Greenberg, H.B.; et al. TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human small intestinal enterocytes. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabc3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, M.M.; Beumer, J.; van der Vaart, J.; Knoops, K.; Puschhof, J.; Breugem, T.I.; Ravelli, R.B.G.; Paul van Schayck, J.; Mykytyn, A.Z.; Duimel, H.Q.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 productively infects human gut enterocytes. Science 2020, 369, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Chu, M.; Zhong, F.; Tan, X.; Tang, G.; Mai, J.; Lai, N.; Guan, C.; Liang, Y.; Liao, G. Digestive symptoms of COVID-19 and expression of ACE2 in digestive tract organs. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes Sousa, S.; Kleiton de Sousa, A.; Maria Carvalho Pereira, C.; Sofia Miranda Loiola Araujo, A.; de Aguiar Magalhaes, D.; Vieira de Brito, T.; Barbosa, A. SARS-CoV-2 infection causes intestinal cell damage: Role of interferon’s imbalance. Cytokine 2022, 152, 155826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.R.; Leibowitz, J.L. Coronavirus pathogenesis. Adv. Virus Res. 2011, 81, 85–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfel, R.; Corman, V.M.; Guggemos, W.; Seilmaier, M.; Zange, S.; Muller, M.A.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Vollmar, P.; Rothe, C.; et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 2020, 581, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhu, S.; Shu, C.; Wang, D.; Song, J.; Song, Y.; Zhen, W.; Feng, Z.; Wu, G.; et al. Isolation of 2019-nCoV from a Stool Specimen of a Laboratory-Confirmed Case of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). China CDC Wkly. 2020, 2, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, E.; Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Long-term gastrointestinal outcomes of COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Aly, Z.; Xie, Y.; Bowe, B. High-dimensional characterization of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19. Nature 2021, 594, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.C.; Devason, A.S.; Umana, I.C.; Cox, T.O.; Dohnalova, L.; Litichevskiy, L.; Perla, J.; Lundgren, P.; Etwebi, Z.; Izzo, L.T.; et al. Serotonin reduction in post-acute sequelae of viral infection. Cell 2023, 186, 4851–4867.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadlier, C.; Albrich, W.C.; Neogi, U.; Lunjani, N.; Horgan, M.; O’Toole, P.W.; O’Mahony, L. Metabolic rewiring and serotonin depletion in patients with postacute sequelae of COVID-19. Allergy 2022, 77, 1623–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado, D.M.; Son, J.; Thackray, L.B.; Gomez Castro, M.F.; Prasad, S.; Cui, X.; Sonnek, N.M.; Diamond, M.S.; Ding, S.; Ciorba, M.A. Mesalamine Reduces Intestinal ACE2 Expression Without Modifying SARS-CoV-2 Infection or Disease Severity in Mice. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 28, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanDussen, K.L.; Marinshaw, J.M.; Shaikh, N.; Miyoshi, H.; Moon, C.; Tarr, P.I.; Ciorba, M.A.; Stappenbeck, T.S. Development of an enhanced human gastrointestinal epithelial culture system to facilitate patient-based assays. Gut 2015, 64, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, J.B.; Bailey, A.L.; Kim, A.S.; Chen, R.E.; Diamond, M.S. Growth, detection, quantification, and inactivation of SARS-CoV-2. Virology 2020, 548, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood, K.I.; Yameen, M.; Ashraf, J.; Shahid, S.; Mahmood, S.F.; Nasir, A.; Nasir, N.; Jamil, B.; Ghanchi, N.K.; Khanum, I.; et al. Upregulated type I interferon responses in asymptomatic COVID-19 infection are associated with improved clinical outcome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santer, D.M.; Li, D.; Ghosheh, Y.; Zahoor, M.A.; Prajapati, D.; Hansen, B.E.; Tyrrell, D.L.J.; Feld, J.J.; Gehring, A.J. Interferon-lambda treatment accelerates SARS-CoV-2 clearance despite age-related delays in the induction of T cell immunity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, K.; Simon, L.M.; Zeng, X.L.; Blutt, S.E.; Crawford, S.E.; Sastri, N.P.; Karandikar, U.C.; Ajami, N.J.; Zachos, N.C.; Kovbasnjuk, O.; et al. A paradox of transcriptional and functional innate interferon responses of human intestinal enteroids to enteric virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E570–E579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Roy, S.; Liu, H.; Roberts, R.M.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Ma, W. Tight junction protein occludin is an internalization factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection and mediates virus cell-to-cell transmission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2218623120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biering, S.B.; Gomes de Sousa, F.T.; Tjang, L.V.; Pahmeier, F.; Zhu, C.; Ruan, R.; Blanc, S.F.; Patel, T.S.; Worthington, C.M.; Glasner, D.R.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Spike triggers barrier dysfunction and vascular leak via integrins and TGF-beta signaling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volcic, M.; Nchioua, R.; Pastorio, C.; Zech, F.; Read, C.; Walther, P.; Kirchhoff, F. Attenuated replication and damaging effects of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants in an intestinal epithelial barrier model. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Tokuyama, M.; Wei, G.; Huang, R.; Livanos, A.; Jha, D.; Levescot, A.; Irizar, H.; Kosoy, R.; Cording, S.; et al. Intestinal Inflammation Modulates the Expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Potentially Overlaps With the Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2-related Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 160, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungaro, R.C.; Brenner, E.J.; Gearry, R.B.; Kaplan, G.G.; Kissous-Hunt, M.; Lewis, J.D.; Ng, S.C.; Rahier, J.F.; Reinisch, W.; Steinwurz, F.; et al. Effect of IBD medications on COVID-19 outcomes: Results from an international registry. Gut 2021, 70, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, S.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Shi, D.; Guo, J.; Wu, W.-R.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, K.-J.; et al. Six-month follow-up of gut microbiota richness in patients with COVID-19. Gut 2022, 71, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Mak, J.W.Y.; Su, Q.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Lui, G.C.; Ng, S.S.S.; Zhang, F.; Li, A.Y.L.; Lu, W.; Hui, D.S.; et al. Gut microbiota dynamics in a prospective cohort of patients with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Gut 2022, 71, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin Gimenez, V.M.; Modrego, J.; Gomez-Garre, D.; Manucha, W.; de Las Heras, N. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in COVID-19: Modulation and Approaches for Prevention and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antia, A.; Alvarado, D.M.; Zeng, Q.; Casorla-Perez, L.A.; Davis, D.L.; Sonnek, N.M.; Ciorba, M.A.; Ding, S. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.1 Variant Infection of Human Colon Epithelial Cells. Viruses 2024, 16, 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040634
Antia A, Alvarado DM, Zeng Q, Casorla-Perez LA, Davis DL, Sonnek NM, Ciorba MA, Ding S. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.1 Variant Infection of Human Colon Epithelial Cells. Viruses. 2024; 16(4):634. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040634
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntia, Avan, David M. Alvarado, Qiru Zeng, Luis A. Casorla-Perez, Deanna L. Davis, Naomi M. Sonnek, Matthew A. Ciorba, and Siyuan Ding. 2024. "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.1 Variant Infection of Human Colon Epithelial Cells" Viruses 16, no. 4: 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040634
APA StyleAntia, A., Alvarado, D. M., Zeng, Q., Casorla-Perez, L. A., Davis, D. L., Sonnek, N. M., Ciorba, M. A., & Ding, S. (2024). SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.1 Variant Infection of Human Colon Epithelial Cells. Viruses, 16(4), 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040634






