Roles of Human Endogenous Retrovirus-K-Encoded Np9 in Human Diseases: A Small Protein with Big Functions
Abstract
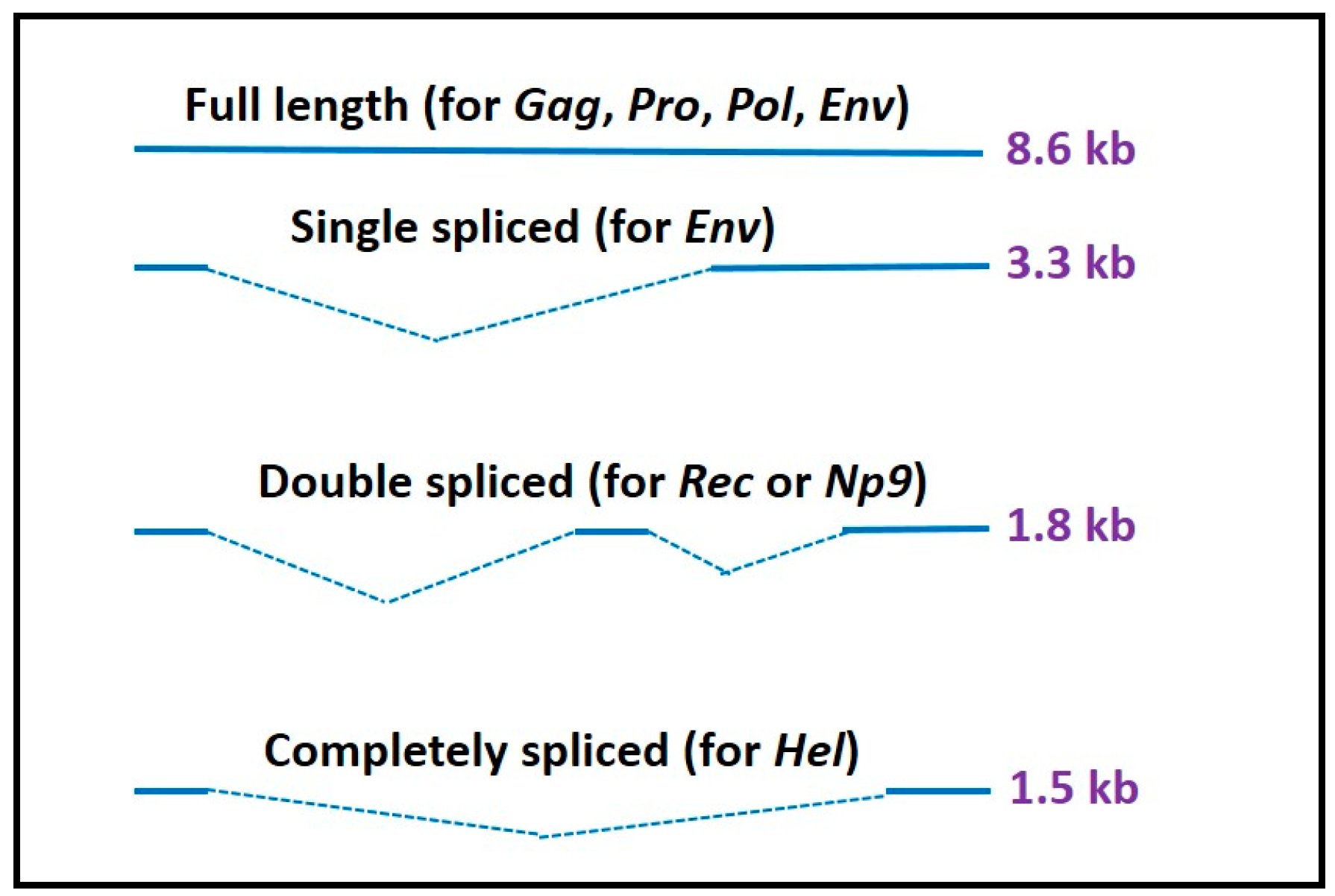
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Relevance of Np9 in Human Diseases
3. The Molecular Mechanisms of Np9-Mediated Pathogenesis and Oncogenesis
4. Development of Np9-Targeted Therapies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Markovitz, D.M. “Reverse genomics” and human endogenous retroviruses. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2014, 125, 57–62, discussion 62–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Galindo, R.; Kaplan, M.H.; Dube, D.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M.J.; Chan, S.; Meng, F.; Dai, M.; Omenn, G.S.; Gitlin, S.D.; Markovitz, D.M. Human Endogenous Retrovirus Type K (HERV-K) Particles Package and Transmit HERV-K-Related Sequences. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7187–7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tristem, M. Identification and characterization of novel human endogenous retrovirus families by phylogenetic screening of the human genome mapping project database. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3715–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, W.; Mun, S.; Han, K. Human Endogenous Retrovirus-K (HML-2)-Related Genetic Variation: Human Genome Diversity and Disease. Genes 2023, 14, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Sechi, L.A.; Kelvin, D.J. Human Endogenous Retrovirus K (HML-2) in Health and Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.J. Endogenous retroviruses in the human genome sequence. Genome Biol. 2001, 2, reviews1017.1–reviews1017.5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downey, R.F.; Sullivan, F.J.; Wang-Johanning, F.; Ambs, S.; Giles, F.J.; Glynn, S.A. Human endogenous retrovirus K and cancer: Innocent bystander or tumorigenic accomplice? Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, R.P.; Wildschutte, J.H.; Russo, C.; Coffin, J.M. Identification, characterization, and comparative genomic distribution of the HERV-K (HML-2) group of human endogenous retroviruses. Retrovirology 2011, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakolian, S.; Goudarzi, H.; Faghihloo, E. Evaluating the expression level of HERV-K env, np9, rec and gag in breast tissue. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2019, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Echeverria, N.; Moratorio, G.; Landoni, A.I.; Dighiero, G.; Cristina, J.; Oppezzo, P.; Moreno, P. Human endogenous retrovirus np9 gene is over expressed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Leuk. Res. Rep. 2014, 3, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakolian, S.; Iranshahi, M.; Faghihloo, E. The Evaluation of HERV-K np9, rec, gag Expression in Isolated Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) of Gastric and Colon Cancer. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2023, 12, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Radvanyi, L.; Yin, B.; Rycaj, K.; Li, J.; Chivukula, R.; Lin, K.; Lu, Y.; Shen, J.; Chang, D.Z.; et al. Downregulation of Human Endogenous Retrovirus Type K (HERV-K) Viral env RNA in Pancreatic Cancer Cells Decreases Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5892–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscher, K.; Hahn, S.; Hofmann, M.; Trefzer, U.; Ozel, M.; Sterry, W.; Lower, J.; Lower, R.; Kurth, R.; Denner, J. Expression of the human endogenous retrovirus-K transmembrane envelope, Rec and Np9 proteins in melanomas and melanoma cell lines. Melanoma Res. 2006, 16, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, K.; Reichrath, J.; Roesch, A.; Meese, E.; Mayer, J. Transcriptional profiling of human endogenous retrovirus group HERV-K(HML-2) loci in melanoma. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Cesarman, E.; Pessin, M.S.; Lee, F.; Culpepper, J.; Knowles, D.M.; Moore, P.S. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Science 1994, 266, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarman, E.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S.; Said, J.W.; Knowles, D.M. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Del Valle, L.; Miley, W.; Whitby, D.; Ochoa, A.C.; Flemington, E.K.; Qin, Z. Transactivation of human endogenous retrovirus K (HERV-K) by KSHV promotes Kaposi’s sarcoma development. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4534–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denne, M.; Sauter, M.; Armbruester, V.; Licht, J.D.; Roemer, K.; Mueller-Lantzsch, N. Physical and functional interactions of human endogenous retrovirus proteins Np9 and rec with the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5607–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Meng, Z.; Gan, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, F.; Gu, Y.; Xu, X.; Tang, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. The viral oncogene Np9 acts as a critical molecular switch for co-activating beta-catenin, ERK, Akt and Notch1 and promoting the growth of human leukemia stem/progenitor cells. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruester, V.; Sauter, M.; Roemer, K.; Best, B.; Hahn, S.; Nty, A.; Schmid, A.; Philipp, S.; Mueller, A.; Mueller-Lantzsch, N. Np9 protein of human endogenous retrovirus K interacts with ligand of numb protein X. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 10310–10319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Heyne, K.; Kolsch, K.; Bruand, M.; Kremmer, E.; Grasser, F.A.; Mayer, J.; Roemer, K. Np9, a cellular protein of retroviral ancestry restricted to human, chimpanzee and gorilla, binds and regulates ubiquitin ligase MDM2. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2619–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.M.; Sapir, T.; Park, S.S.; Rual, J.F.; Contreras-Galindo, R.; Reiner, O.; Markovitz, D.M. The HERV-K accessory protein Np9 controls viability and migration of teratocarcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Trillo-Tinoco, J.; Chen, Y.; Bonstaff, K.; Del Valle, L.; Parsons, C.; Ochoa, A.C.; Zabaleta, J.; Toole, B.P.; Qin, Z. CD147 and downstream ADAMTSs promote the tumorigenicity of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infected endothelial cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3806–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Fan, J.; Lin, Z.; Dai, L.; Qin, Z. Human endogenous retrovirus type K encoded Np9 oncoprotein induces DNA damage response. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Qiao, J.; Nguyen, D.; Struckhoff, A.P.; Doyle, L.; Bonstaff, K.; Del Valle, L.; Parsons, C.; Toole, B.P.; Renne, R.; et al. Role of heme oxygenase-1 in the pathogenesis and tumorigenicity of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10459–10471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.; Barth, S.; Pfuhl, T.; Willnecker, V.; Spurk, A.; Gurtsevitch, V.; Sauter, M.; Hu, B.; Noessner, E.; Mueller-Lantzsch, N.; et al. The NP9 protein encoded by the human endogenous retrovirus HERV-K(HML-2) negatively regulates gene activation of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2). Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupchan, S.M.; Court, W.A.; Dailey, R.G., Jr.; Gilmore, C.J.; Bryan, R.F. Triptolide and tripdiolide, novel antileukemic diterpenoid triepoxides from Tripterygium wilfordii. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 7194–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.L.; Yang, Y.X.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.C.; Miao, Z.H. Triptolide: Structural modifications, structure-activity relationships, bioactivities, clinical development and mechanisms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zheng, W.; Jiang, X.; Lu, X.; Xu, R. Triptolide induces apoptosis of human acute T lymphocytic leukemia Jurkat cells via inhibiting transcription of human endogenous retrovirus HERV-K Np9 gene. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2015, 35, 702–706. [Google Scholar]
- Long, C.; Guo, W.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, X. Triptolide decreases expression of latency-associated nuclear antigen 1 and reduces viral titers in Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated and herpesvirus-related primary effusion lymphoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, S.L.; Crews, C.M. Targeted protein degradation: Elements of PROTAC design. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 50, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douville, R.; Liu, J.; Rothstein, J.; Nath, A. Identification of active loci of a human endogenous retrovirus in neurons of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freimanis, G.; Hooley, P.; Ejtehadi, H.D.; Ali, H.A.; Veitch, A.; Rylance, P.B.; Alawi, A.; Axford, J.; Nevill, A.; Murray, P.G.; et al. A role for human endogenous retrovirus-K (HML-2) in rheumatoid arthritis: Investigating mechanisms of pathogenesis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 160, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, J.; Qin, Z. Roles of Human Endogenous Retrovirus-K-Encoded Np9 in Human Diseases: A Small Protein with Big Functions. Viruses 2024, 16, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040581
Fan J, Qin Z. Roles of Human Endogenous Retrovirus-K-Encoded Np9 in Human Diseases: A Small Protein with Big Functions. Viruses. 2024; 16(4):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040581
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Jiaojiao, and Zhiqiang Qin. 2024. "Roles of Human Endogenous Retrovirus-K-Encoded Np9 in Human Diseases: A Small Protein with Big Functions" Viruses 16, no. 4: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040581
APA StyleFan, J., & Qin, Z. (2024). Roles of Human Endogenous Retrovirus-K-Encoded Np9 in Human Diseases: A Small Protein with Big Functions. Viruses, 16(4), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040581





