High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Three Rhabdoviruses Persisting in the IRE/CTVM19 Cell Line
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. IRE/CTVM19 Cell Line Maintenance
2.2. High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Virus Genome Assembly
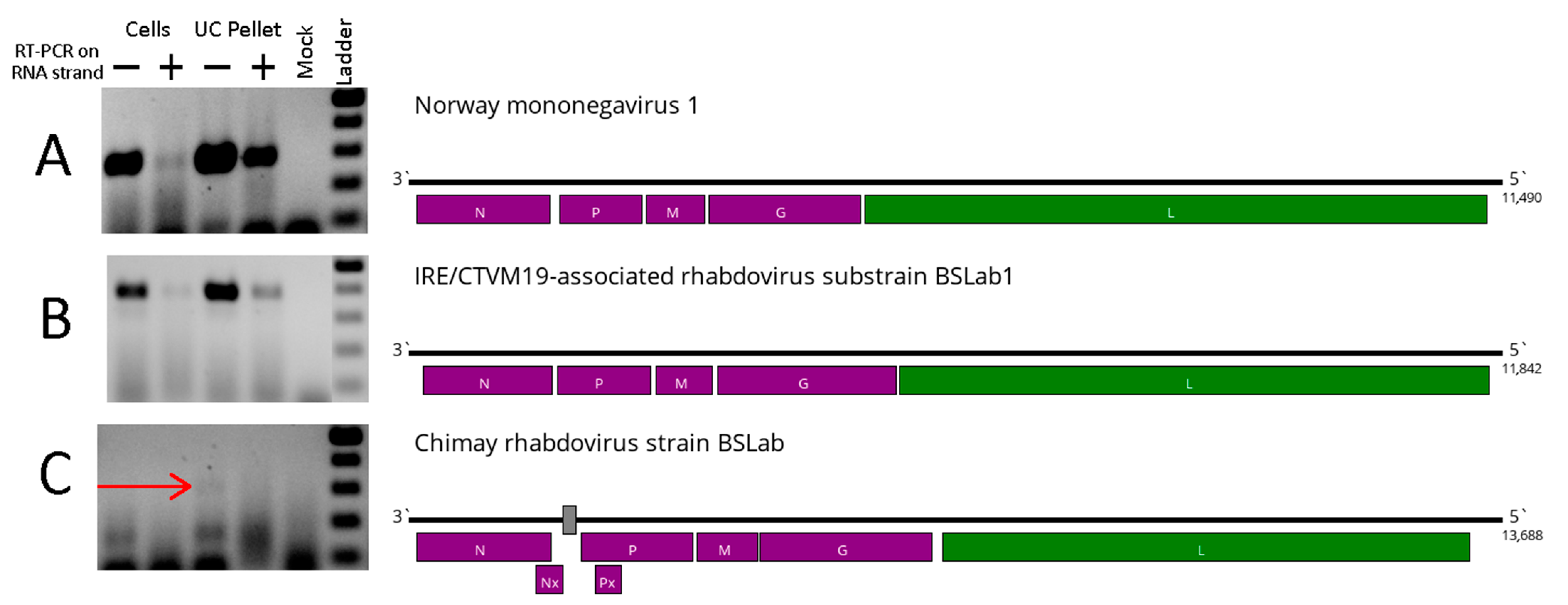
2.4. RNA Isolation and Virus Detection
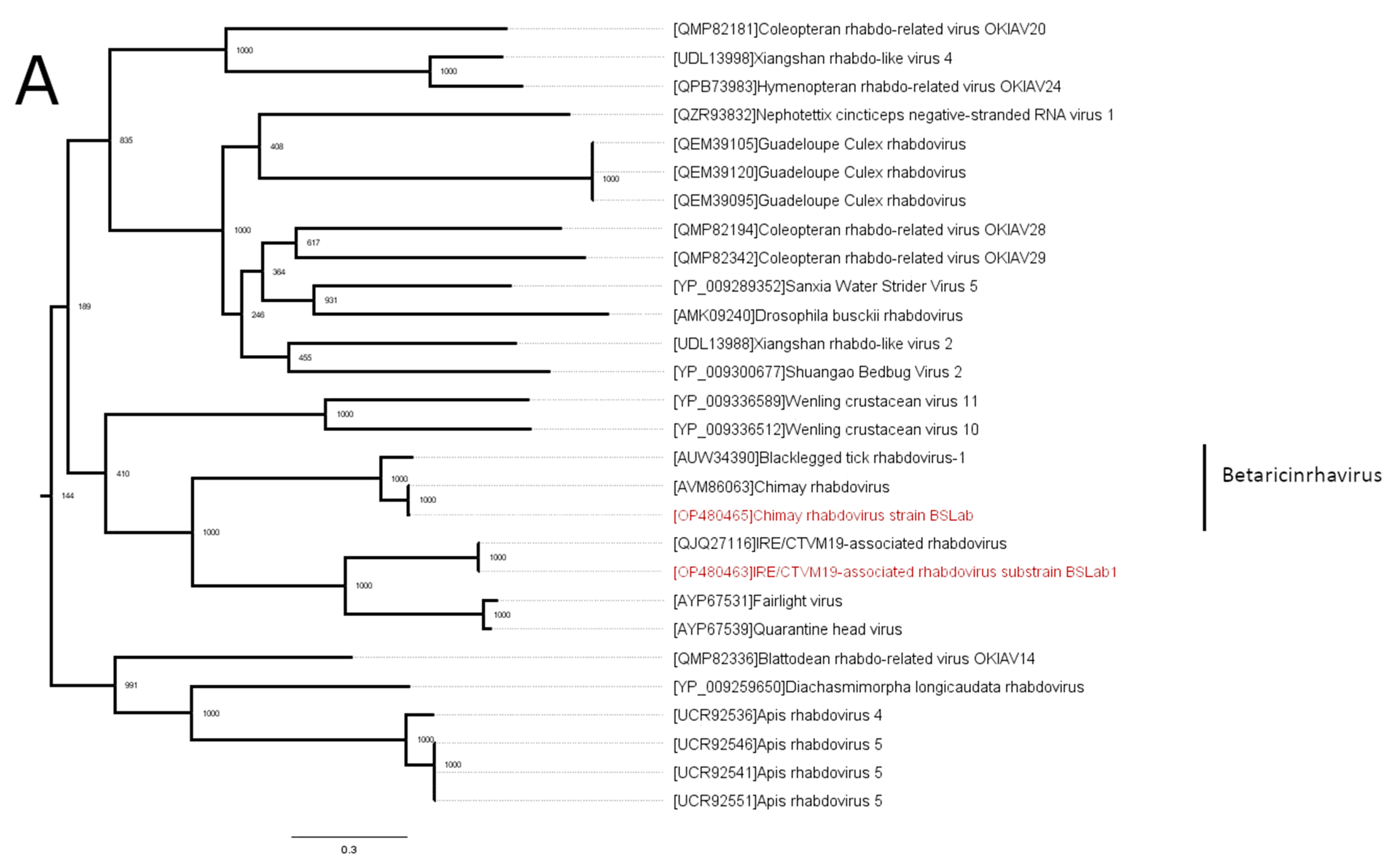
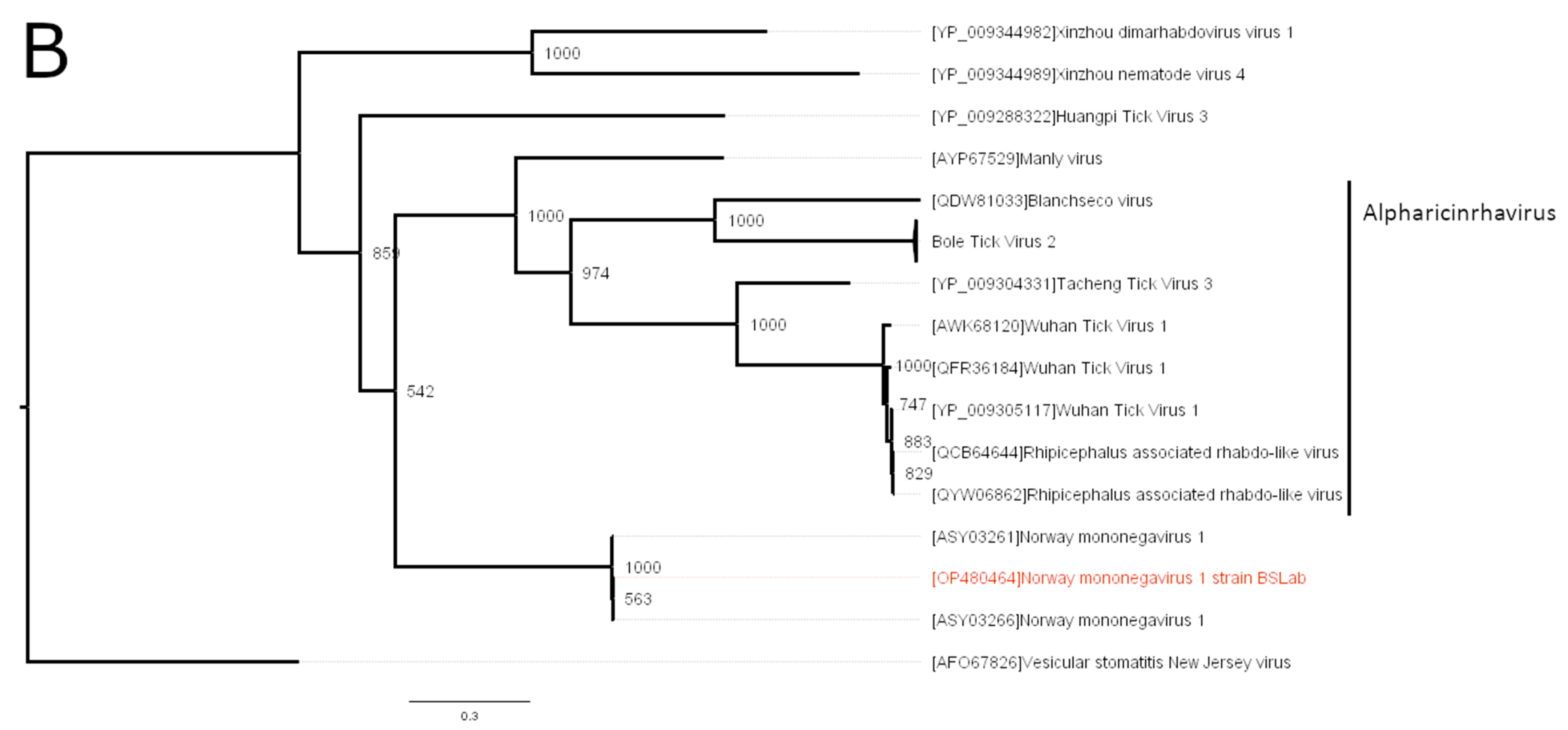
2.5. Phylogenetic Tree Construction
2.6. Virus Passages
3. Results
3.1. Viruses Found in the IRE/CTVM19 Cell Line
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. Passaging Experiment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonnet, S.I.; Pollet, T. Update on the intricate tango between tick microbiomes and tick-borne pathogens. Parasite Immunol. 2020, 43, e12813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.; Kahl, O.; Zintl, A. What do we still need to know about Ixodes ricinus? Ticks Tick. Borne. Dis. 2021, 12, 101682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogovic, P.; Strle, F. Tick-borne encephalitis: A review of epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and management. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.R.; Strle, F.; Wormser, G.P. Comparison of lyme disease in the United States and Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzek, D.; Av, T.; Borde, J.; Chrdle, A.; Eyer, L.; Karganova, G.; Kholodilov, I.; Kozlovskaya, L.; Matveev, A.; Miller, A.D.; et al. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe and Russia: Review of pathogenesis, clinical features, therapy, and vaccines. Antivir. Res. 2019, 164, 23–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell-Sakyi, L.; Zweygarth, E.; Blouin, E.F.; Gould, E.A.; Jongejan, F. Tick cell lines: Tools for tick and tick-borne disease research. Trends Parasitol. 2007, 23, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Uzcátegui, N.Y.; Armesto, M.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Gould, E.A. Susceptibility of mosquito and tick cell lines to infection with various flaviviruses. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2004, 18, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazelier, M.; Rouxel, N.; Zumstein, M.; Mancini, R.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Lozach, P. Uukuniemi virus as a tick-borne virus model. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6784–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell-Sakyi, L.; Kohl, A.; Bente, D.A.; Fazakerley, J.K. Tick cell lines for study of crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever virus and other arboviruses. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husin, N.A.; Khoo, J.J.; Mustika, M.; Zulkifli, S.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Abubakar, S. Replication kinetics of Rickettsia raoultii in tick cell lines. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomar, A.M.; Premchand-Branker, S.; Alberdi, P.; Belova, O.A.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A.; Kahl, O.; Bell-Sakyi, L. Isolation of known and potentially pathogenic tick-borne microorganisms from European ixodid ticks using tick cell lines. Ticks Tick. Borne. Dis. 2019, 10, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangia, C.; Vismarra, A.; Kramer, L.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Porretta, D.; Otranto, D.; Epis, S.; Grandi, G. Evaluation of the in vitro expression of ATP binding-cassette (ABC) proteins in an Ixodes ricinus cell line exposed to ivermectin. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belova, O.A.; Litov, A.G.; Kholodilov, I.S.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Romanova, L.I.; Karganova, G.G. Properties of the tick-borne encephalitis virus population during persistent infection of ixodid ticks and tick cell lines. Ticks Tick. Borne. Dis. 2017, 8, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodilov, I.S.; Belova, O.A.; Morozkin, E.S.; Litov, A.G.; Ivannikova, A.Y.; Makenov, M.T.; Shchetinin, A.M.; Aibulatov, S.V.; Bazarova, G.K.; Bell-sakyi, L.; et al. Geographical and tick-dependent distribution of flavi-like Alongshan and Yanggou tick viruses in Russia. Viruses 2021, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attoui, H.; Stirling, J.M.; Munderloh, U.G.; Burroughs, F.; Brookes, S.M.; Burroughs, J.N.; Micco, P.; Mertens, P.P.C.; Lamballerie, X. Complete sequence characterization of the genome of the St Croix River virus, a new orbivirus isolated from cells of Ixodes scapularis. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberdi, M.P.; Dalby, M.J.; Rodriguez-Andres, J.; Fazakerley, J.K.; Kohl, A.; Bell-Sakyi, L. Detection and identification of putative bacterial endosymbionts and endogenous viruses in tick cell lines. Ticks Tick. Borne. Dis. 2012, 3, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell-Sakyi, L.; Attoui, H. Virus discovery using tick cell lines. Evol. Bioinforma. 2016, 12, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodilov, I.S.; Litov, A.G.; Klimentov, A.S.; Belova, O.A.; Polienko, A.E.; Nikitin, N.A.; Shchetinin, A.M.; Ivannikova, A.Y.; Bell-sakyi, L.; Yakovlev, A.S.; et al. Isolation and characterisation of Alongshan virus in Russia. Viruses 2020, 12, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.; Lin, X.; Kang, Y.; Chen, L.; Qin, X.; Xu, J.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y. Unprecedented genomic diversity of RNA viruses in arthropods reveals the ancestry of negative-sense RNA viruses. Elife 2015, 4, e05378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.; Tian, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Qin, X.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Eden, J.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, E.; Rose, K.; Eden, J.; Lo, N.; Abeyasuriya, T.; Shi, M.; Doggett, S.L.; Holmes, E.C. Extensive diversity of RNA viruses in Australian ticks. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01358-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, J.H.; Shi, M.; Bohlin, J.; Eldhol, V.; Brynildsrud, O.B.; Paulsen, K.M.; Andreassen, Å.; Holmes, E.C. Characterizing the virome of Ixodes ricinus ticks from northern Europe. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.C.; Chain, P.S.G. Rapid evaluation and quality control of next generation sequencing data with FaQCs. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonechnikov, K.; Golosova, O.; Fursov, M.; UGENE team. Unipro UGENE: A unified bioinformatics toolkit. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2013, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; Mcginnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: A better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Silla-Martinez, J.M.; Gabaldon, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanmechelen, B.; Merino, M.; Vergote, V.; Laenen, L.; Thijssen, M.; Martí-carreras, J.; Claerebout, E.; Maes, P. Exploration of the Ixodes ricinus virosphere unveils an extensive virus diversity including novel coltiviruses and other reoviruses. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, P.; Freitas-Astúa, J.; Walker, P.J.; Astúa, J.F.-; Bejerman, N.; Blasdell, K.R.; Breyta, R.; Dietzgen, R.G. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Rhabdoviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, E.C. The evolution of endogenous viral elements. CHOM 2011, 10, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzourakis, A.; Gifford, R.J. Endogenous viral elements in animal genomes. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrao, E.P.; Lopes da Fonseca, B. Infection of mosquito cells (C6/36) by Dengue-2 virus interferes with subsequent infection by Yellow Fever Virus. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwata, R.; Isawa, H.; Hoshino, K.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Maeda, K.; Sawabe, K. Analysis of mosquito-borne flavivirus superinfection in Culex tritaeniorhynchus (Diptera: Culicidae) cells persistently infected with culex flavivirus (Flaviviridae). J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, E.I.; Kautz, T.F.; Contreras-gutierrez, M.A.; Guzman, H.; Tesh, R.B.; Hughes, G.L.; Forrester, N.L. Negeviruses reduce replication of alphaviruses during coinfection. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e00433-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Virus | Percent of the Virus-Containing Reads | Closest Sequence | Nucleotide Identity in Polymerase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chimay rhabdovirus strain BSLab | 0.12% | [MF975531] | 99.21% |
| IRE/CTVM19-associated rhabdovirus substrain BSLab1 | 3.78% | [MT181988] | 99.92% |
| Norway mononegavirus 1 strain BSLab | 5.55% | [MF141072] | 98.30% |
| Cell Line | Temperature | 1st Passage | 2nd Passage | 3rd Passage | 4th Passage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 Days | 14 Days | 7 Days | 14 Days | 7 Days | 14 Days | 7 Days | ||
| HEP-2 | 28 °C | I N C | N | I N | I N | I N | - | - |
| 32 °C | I N C | I N | - | - | - | - | nd | |
| BHK | 28 °C | I N | I N | I N | I N | I | - | - |
| 32 °C | I | I N | - | cd | nd | nd | nd | |
| NIH | 28 °C | I N C | I N C | - | - | - | - | nd |
| 32 °C | - | cd | - | - | - | - | nd | |
| HEK-293T | 28 °C | I N C | cd | - | cd | - | - | nd |
| 32 °C | I N | N | - | - | - | cd | nd | |
| PEK | 28 °C | - | I N C | I | - | nd | nd | nd |
| 32 °C | - | N | - | - | - | - | nd | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Litov, A.G.; Shchetinin, A.M.; Kholodilov, I.S.; Belova, O.A.; Gadzhikurbanov, M.N.; Ivannikova, A.Y.; Kovpak, A.A.; Gushchin, V.A.; Karganova, G.G. High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Three Rhabdoviruses Persisting in the IRE/CTVM19 Cell Line. Viruses 2024, 16, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040576
Litov AG, Shchetinin AM, Kholodilov IS, Belova OA, Gadzhikurbanov MN, Ivannikova AY, Kovpak AA, Gushchin VA, Karganova GG. High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Three Rhabdoviruses Persisting in the IRE/CTVM19 Cell Line. Viruses. 2024; 16(4):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040576
Chicago/Turabian StyleLitov, Alexander G., Alexey M. Shchetinin, Ivan S. Kholodilov, Oxana A. Belova, Magomed N. Gadzhikurbanov, Anna Y. Ivannikova, Anastasia A. Kovpak, Vladimir A. Gushchin, and Galina G. Karganova. 2024. "High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Three Rhabdoviruses Persisting in the IRE/CTVM19 Cell Line" Viruses 16, no. 4: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040576
APA StyleLitov, A. G., Shchetinin, A. M., Kholodilov, I. S., Belova, O. A., Gadzhikurbanov, M. N., Ivannikova, A. Y., Kovpak, A. A., Gushchin, V. A., & Karganova, G. G. (2024). High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Three Rhabdoviruses Persisting in the IRE/CTVM19 Cell Line. Viruses, 16(4), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040576








