Performance of Ultrasensitive Polymerase Chain Reaction Testing for JC Polyomavirus in Cerebrospinal Fluid Compared with Pathological Diagnosis of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Clinical Data
2.2. PCR Testing for JCPyV DNA in CSF
2.3. Pathological Examination of Brain Tissues
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Detection Performance of Real-Time PCR Testing for JCPyV in CSF
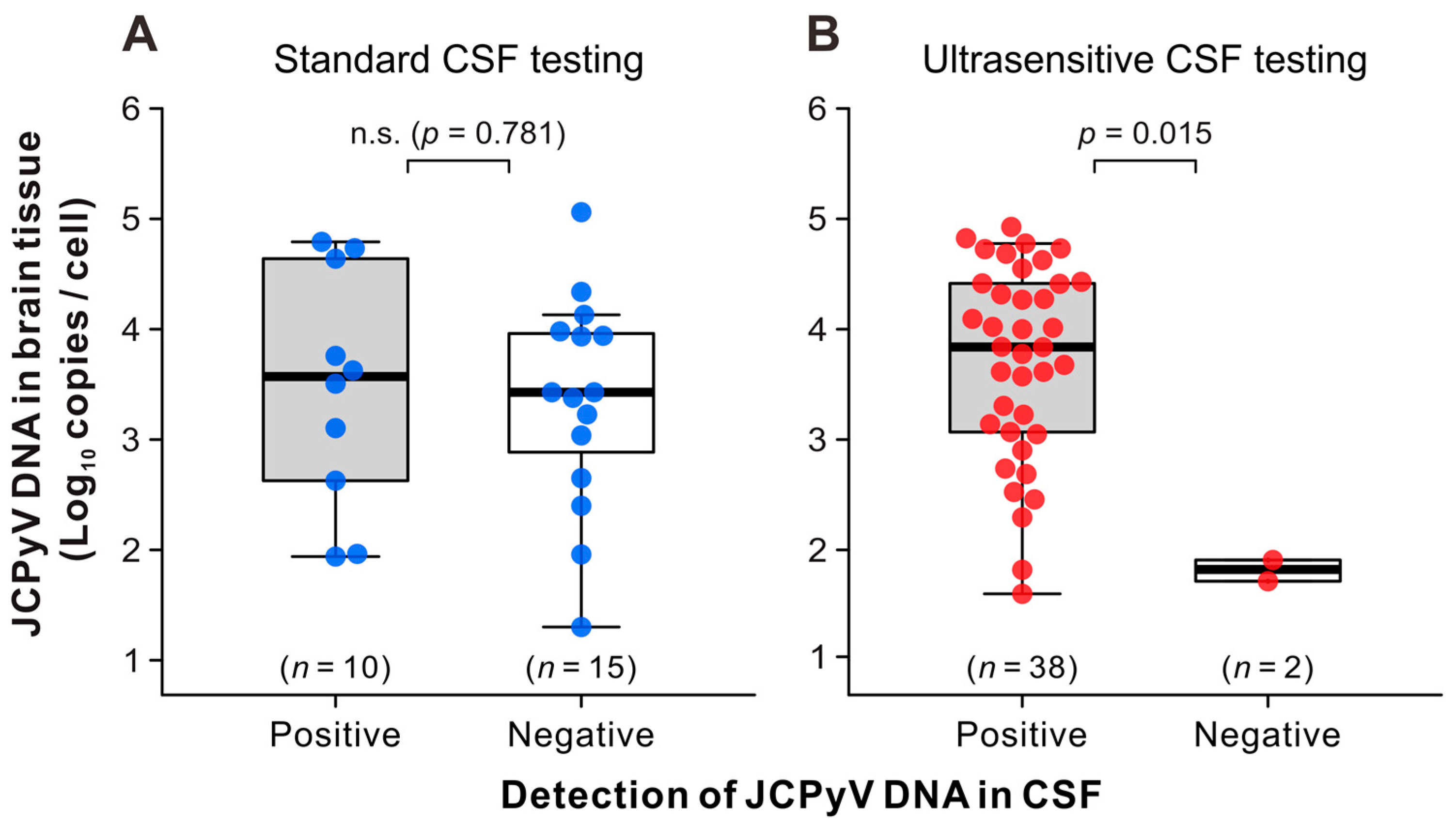
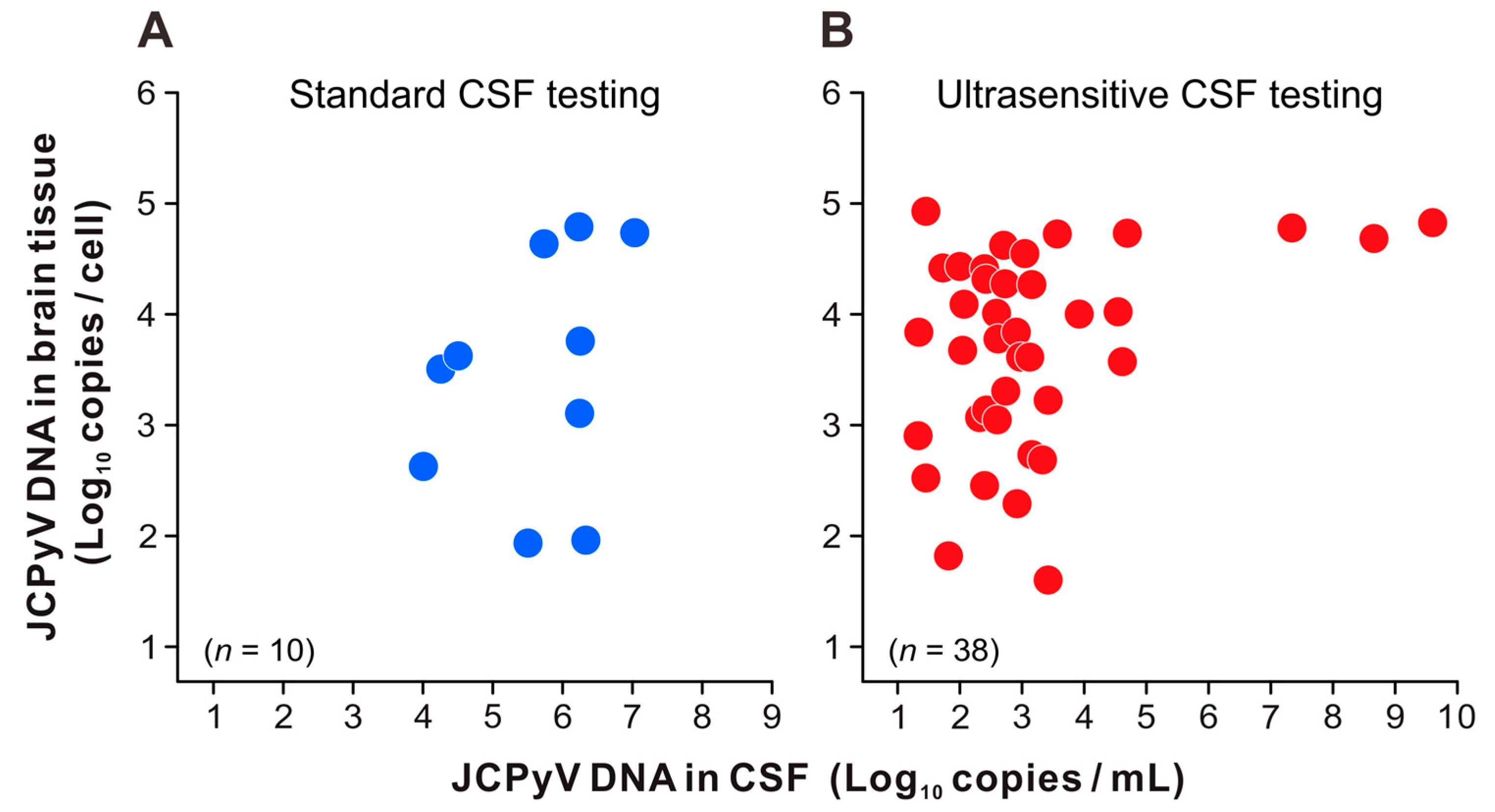
3.3. JCPyV Copy Levels in the CSF and Brain Tissue of Patients with PML
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, C.S.; Koralnik, I.J. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy and Other Disorders Caused by JC Virus: Clinical Features and Pathogenesis. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenczy, M.W.; Marshall, L.J.; Nelson, C.D.S.; Atwood, W.J.; Nath, A.; Khalili, K.; Major, E.O. Molecular Biology, Epidemiology, and Pathogenesis of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy, the JC Virus-Induced Demyelinating Disease of the Human Brain. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 471–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Kardas, P.; Kranz, D.; Leboeuf, C. The Human JC Polyomavirus (JCPyV): Virological Background and Clinical Implications. APMIS 2013, 121, 685–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamichi, K.; Miura, Y.; Shimokawa, T.; Takahashi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Funata, N.; Harada, M.; Mori, K.; Sanjo, N.; Yukitake, M.; et al. Nationwide Laboratory Surveillance of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in Japan: Fiscal Years 2011–2020. Viruses 2023, 15, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Assche, G.; Van Ranst, M.; Sciot, R.; Dubois, B.; Vermeire, S.; Noman, M.; Verbeeck, J.; Geboes, K.; Robberecht, W.; Rutgeerts, P. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy after Natalizumab Therapy for Crohn’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K.; Tyler, K.L. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Complicating Treatment with Natalizumab and Interferon Beta-1a for Multiple Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer-Gould, A.; Atlas, S.W.; Green, A.J.; Bollen, A.W.; Pelletier, D. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in a Patient Treated with Natalizumab. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, K.R.; Evens, A.M.; Richey, E.A.; Habermann, T.M.; Focosi, D.; Seymour, J.F.; Laubach, J.; Bawn, S.D.; Gordon, L.I.; Winter, J.N.; et al. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy after Rituximab Therapy in HIV-Negative Patients: A Report of 57 Cases from the Research on Adverse Drug Events and Reports Project. Blood 2009, 113, 4834–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyang, T.V.; Hamel, J.; Goodman, A.D.; Gross, R.A.; Samkoff, L. Fingolimod-Associated PML in a Patient with Prior Immunosuppression. Neurology 2016, 86, 1843–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yasui, K.; Ogiwara, H. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Neuropathology and Virus Isolation. Acta Pathol. Jpn. 1981, 31, 953–961. [Google Scholar]
- Major, E.O.; Amemiya, K.; Tornatore, C.S.; Houff, S.A.; Berger, J.R. Pathogenesis and Molecular Biology of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy, the JC Virus-Induced Demyelinating Disease of the Human Brain. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 5, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson-Burns, S.M.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K.; DeBiasi, R.L.; Tyler, K.L. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy and Apoptosis of Infected Oligodendrocytes in the Central Nervous System of Patients with and without AIDS. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.R.; Aksamit, A.J.; Clifford, D.B.; Davis, L.; Koralnik, I.J.; Sejvar, J.J.; Bartt, R.; Major, E.O.; Nath, A. PML Diagnostic Criteria: Consensus Statement from the AAN Neuroinfectious Disease Section. Neurology 2013, 80, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, R.M.; Russell, E.; Yungbluth, M.; Hidvegi, D.F.; Brody, B.A.; Dal Canto, M.C. The Efficacy of Image-Guided Stereotactic Brain Biopsy in Neurologically Symptomatic Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome Patients. Neurosurgery 1992, 30, 186–189; discussion 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antinori, A.; Ammassari, A.; De Luca, A.; Cingolani, A.; Murri, R.; Scoppettuolo, G.; Fortini, M.; Tartaglione, T.; Larocca, L.M.; Zannoni, G.; et al. Diagnosis of AIDS-Related Focal Brain Lesions: A Decision-Making Analysis Based on Clinical and Neuroradiologic Characteristics Combined with Polymerase Chain Reaction Assays in CSF. Neurology 1997, 48, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinque, P.; Scarpellini, P.; Vago, L.; Linde, A.; Lazzarin, A. Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Complications in HIV-Infected Patients: Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis by the Polymerase Chain Reaction. AIDS 1997, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinque, P.; Koralnik, I.J.; Gerevini, S.; Miro, J.M.; Price, R.W. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in HIV-1 Infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, I.W.; Britton, C.B.; Luinstra, K.E.; Toma, E.; Mahony, J.B. Diagnostic Value of Detecting JC Virus DNA in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnke, C.; von Geldern, G.; Markwerth, P.; Dehmel, T.; Hoepner, R.; Gold, R.; Pawlita, M.; Kümpfel, T.; Mäurer, M.; Stangel, M.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid JC Virus Antibody Index for Diagnosis of Natalizumab-Associated Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzocchetti, A.; Di Giambenedetto, S.; Cingolani, A.; Ammassari, A.; Cauda, R.; De Luca, A. Reduced Rate of Diagnostic Positive Detection of JC Virus DNA in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Cases of Suspected Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in the Era of Potent Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4175–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, M.L.; Eid, T.; Bannykh, S.; Major, E. False Negative PCR despite High Levels of JC Virus DNA in Spinal Fluid: Implications for Diagnostic Testing. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 43, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhle, J.; Gosert, R.; Bühler, R.; Derfuss, T.; Sutter, R.; Yaldizli, O.; Radue, E.-W.; Ryschkewitsch, C.; Major, E.O.; Kappos, L.; et al. Management and Outcome of CSF-JC Virus PCR-Negative PML in a Natalizumab-Treated Patient with MS. Neurology 2011, 77, 2010–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagayama, S.; Gondo, Y.; Araya, S.; Minato, N.; Fujita-Nakata, M.; Kaito, M.; Nakanishi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Yamaya, H.; Yokoyama, H.; et al. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Developed 26 Years after Renal Transplantation. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 115, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, J.; Matsushima, A.; Ishii, W.; Goto, T.; Takahashi, K.; Nakamichi, K.; Saijo, M.; Sekijima, Y.; Ikeda, S.-I. Brain Biopsy Is More Reliable than the DNA Test for JC Virus in Cerebrospinal Fluid for the Diagnosis of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 1231–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ryschkewitsch, C.; Jensen, P.; Hou, J.; Fahle, G.; Fischer, S.; Major, E.O. Comparison of PCR-Southern Hybridization and Quantitative Real-Time PCR for the Detection of JC and BK Viral Nucleotide Sequences in Urine and Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 121, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryschkewitsch, C.F.; Jensen, P.N.; Major, E.O. Multiplex qPCR Assay for Ultra Sensitive Detection of JCV DNA with Simultaneous Identification of Genotypes That Discriminates Non-Virulent from Virulent Variants. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 57, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamichi, K.; Kawamoto, M.; Ishii, J.; Saijo, M. Improving Detection of JC Virus by Ultrafiltration of Cerebrospinal Fluid before Polymerase Chain Reaction for the Diagnosis of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentzer, D.; Prestel, J.; Adams, O.; Gold, R.; Hartung, H.-P.; Hengel, H.; Kieseier, B.C.; Ludwig, W.-D.; Keller-Stanislawski, B. Case Definition for Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Following Treatment with Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamichi, K.; Mizusawa, H.; Yamada, M.; Kishida, S.; Miura, Y.; Shimokawa, T.; Takasaki, T.; Lim, C.-K.; Kurane, I.; Saijo, M. Characteristics of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Clarified through Internet-Assisted Laboratory Surveillance in Japan. BMC Neurol. 2012, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamichi, K.; Kurane, I.; Saijo, M. Evaluation of a Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay for the Detection of JC Polyomavirus DNA in Cerebrospinal Fluid without Nucleic Acid Extraction. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 64, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamichi, K.; Lim, C.-K.; Saijo, M. Stability of JC Virus DNA in Cerebrospinal Fluid Specimens Preserved with Guanidine Lysis Buffer for Quantitative PCR Testing. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 67, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nakamichi, K.; Shimokawa, T. Database and Statistical Analyses of Transcription Factor Binding Sites in the Non-Coding Control Region of JC Virus. Viruses 2021, 13, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamichi, K.; Kishida, S.; Tanaka, K.; Suganuma, A.; Sano, Y.; Sano, H.; Kanda, T.; Maeda, N.; Kira, J.-I.; Itoh, A.; et al. Sequential Changes in the Non-Coding Control Region Sequences of JC Polyomaviruses from the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamichi, K.; Tajima, S.; Lim, C.-K.; Saijo, M. High-Resolution Melting Analysis for Mutation Scanning in the Non-Coding Control Region of JC Polyomavirus from Patients with Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwami, K.; Nakamichi, K.; Matsushima, M.; Nagai, A.; Shirai, S.; Nakakubo, S.; Takahashi-Iwata, I.; Yamada, M.; Yabe, I. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy with Mild Clinical Conditions and Detection of Archetype-like JC Virus in Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. NeuroVirology 2021, 27, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobaeus, E.; Ryschkewitsch, C.; Gravell, M.; Khademi, M.; Wallstrom, E.; Olsson, T.; Brundin, L.; Major, E. Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid and Cerebrospinal Fluid Cells from Patients with Multiple Sclerosis for Detection of JC Virus DNA. Mult. Scler. 2009, 15, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Sawa, H.; Komagome, R.; Orba, Y.; Yamada, M.; Okada, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Nishihara, H.; Tanaka, S.; Nagashima, K. Broad Distribution of the JC Virus Receptor Contrasts with a Marked Cellular Restriction of Virus Replication. Virology 2001, 286, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Sawa, H.; Endo, S.; Orba, Y.; Umemura, T.; Nishihara, H.; Stan, A.C.; Tanaka, S.; Takahashi, H.; Nagashima, K. Expression of JC Virus Agnoprotein in Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Brain. Acta Neuropathol. 2002, 104, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Sekizuka, T.; Fukumoto, H.; Nakamichi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Sato, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Kuroda, M.; Katano, H. Deep-Sequence Identification and Role in Virus Replication of a JC Virus Quasispecies in Patients with Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01335-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Sirota, L.; Maudru, T.; Peden, K.; Lewis, A.M. Real-Time, Quantitative PCR Assays for the Detection of Virus-Specific DNA in Samples with Mixed Populations of Polyomaviruses. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 135, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, H.; Hayashi, K.; Uchida, K.; Miyakura, S.; Shimizu, D.; Vallböhmer, D.; Park, S.; Danenberg, K.D.; Takasaki, K.; Danenberg, P.V. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Messenger RNA Expression Level Is Preserved in Liver Metastases Compared with Corresponding Primary Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahi-Ozaki, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kanno, T.; Sata, T.; Katano, H. Quantitative Analysis of Kaposi Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV) in KSHV-Associated Diseases. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijburg, M.T.; Kleerekooper, I.; Lissenberg-Witte, B.I.; de Vos, M.; Warnke, C.; Uitdehaag, B.M.J.; Barkhof, F.; Killestein, J.; Wattjes, M.P. Association of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Lesion Volume with JC Virus Polymerase Chain Reaction Results in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Natalizumab-Treated Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funatsu, A.; Nakamichi, K.; Araki, M.; Fukumoto, T.; Mine, H. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in a Patient with Multifocal Neurological Manifestations Caused by Solitary Brainstem Involvement. Intern. Med. 2023, 62, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Category | Subcategory | All | Definite PML | Not PML | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 110 | n = 65 | n = 45 | |||||
| Age | n.a. | 59.9 ± 14.1 | 60.3 ± 13.3 | 59.2 ± 15.3 | |||
| Sex | Male | 60 | (55) | 34 | (52) | 26 | (58) |
| Female | 50 | (45) | 31 | (48) | 19 | (42) | |
| Underlying diseases a | Hematopoietic malignancy | 30 | (27) | 20 | (31) | 10 | (22) |
| Autoimmune diseases | 24 | (22) | 18 | (28) | 6 | (13) | |
| AIDS | 14 | (13) | 9 | (14) | 5 | (11) | |
| Solid organ cancer | 10 | (9) | 5 | (8) | 5 | (11) | |
| Solid organ transplantation | 8 | (7) | 5 | (8) | 3 | (7) | |
| Renal dysfunction | 4 | (4) | 3 | (5) | 1 | (2) | |
| Sarcoidosis | 3 | (3) | 3 | (5) | 0 | (0) | |
| Congenital immunodeficiency | 2 | (2) | 2 | (3) | 0 | (0) | |
| Acquired immunodeficiency b | 2 | (2) | 2 | (3) | 0 | (0) | |
| Hepatic dysfunction | 2 | (2) | 2 | (3) | 0 | (0) | |
| Multiple sclerosis | 4 | (4) | 0 | (0) | 4 | (9) | |
| Not obvious | 15 | (14) | 4 | (6) | 11 | (24) | |
| Uncertain | 1 | (1) | 0 | (0) | 1 | (2) | |
| CSF sampling | Before brain tissue examination | 84 | (76) | 49 | (75) | 35 | (78) |
| After brain tissue examination | 26 | (24) | 16 | (25) | 10 | (22) | |
| Brain tissue sampling | Biopsy c | 99 | (90) | 56 | (86) | 43 | (96) |
| Autopsy | 11 | (10) | 9 | (14) | 2 | (4) | |
| Immunohistochemistry | Positive | 59 | (54) | 59 | (91) | 0 | (0) |
| Negative | 38 | (35) | 5 | (8) | 33 | (73) | |
| Not performed | 13 | (12) | 1 | (2) | 12 | (27) | |
| Brain DNA extraction | FFPE sample d | 78 | (71) | 51 | (78) | 27 | (60) |
| Frozen sample | 32 | (29) | 14 | (22) | 18 | (40) | |
| JCPyV PCR of brain tissue | Positive | 65 | (59) | 65 | (100) | 0 | (0) |
| Negative | 45 | (41) | 0 | (0) | 45 | (100) | |
| Performance | CSF Sampling a | Number (%) of Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard PCR Assay | Ultrasensitive PCR Assay | ||||
| Sensitivity b | Initial | 10/25 | (40) | 34/40 | (85) |
| Initial and follow-up | n.a. | n.a. | 38/40 | (95) | |
| False-positive rate c | Initial | 0/11 | (0) | 0/34 | (0) |
| Initial and follow-up | n.a. | n.a. | 0/34 | (0) | |
| Positive predictive value d | Initial | 10/10 | (100) | 34/34 | (100) |
| Initial and follow-up | n.a. | n.a. | 38/38 | (100) | |
| Specificity e | Initial | 11/11 | (100) | 34/34 | (100) |
| Initial and follow-up | n.a. | n.a. | 34/34 | (100) | |
| False-negative rate f | Initial | 15/25 | (60) | 6/40 | (15) |
| Initial and follow-up | n.a. | n.a. | 2/40 | (5) | |
| Negative predictive value g | Initial | 11/26 | (42) | 34/40 | (85) |
| Initial and follow-up | n.a. | n.a. | 34/36 | (94) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi, K.; Nakamichi, K.; Sato, Y.; Katano, H.; Hasegawa, H.; Saijo, M.; Suzuki, T. Performance of Ultrasensitive Polymerase Chain Reaction Testing for JC Polyomavirus in Cerebrospinal Fluid Compared with Pathological Diagnosis of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Viruses 2024, 16, 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121950
Takahashi K, Nakamichi K, Sato Y, Katano H, Hasegawa H, Saijo M, Suzuki T. Performance of Ultrasensitive Polymerase Chain Reaction Testing for JC Polyomavirus in Cerebrospinal Fluid Compared with Pathological Diagnosis of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Viruses. 2024; 16(12):1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121950
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi, Kenta, Kazuo Nakamichi, Yuko Sato, Harutaka Katano, Hideki Hasegawa, Masayuki Saijo, and Tadaki Suzuki. 2024. "Performance of Ultrasensitive Polymerase Chain Reaction Testing for JC Polyomavirus in Cerebrospinal Fluid Compared with Pathological Diagnosis of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy" Viruses 16, no. 12: 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121950
APA StyleTakahashi, K., Nakamichi, K., Sato, Y., Katano, H., Hasegawa, H., Saijo, M., & Suzuki, T. (2024). Performance of Ultrasensitive Polymerase Chain Reaction Testing for JC Polyomavirus in Cerebrospinal Fluid Compared with Pathological Diagnosis of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Viruses, 16(12), 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121950







