Anti-Schmallenberg Virus Activities of Type I/III Interferons-Induced Mx1 GTPases from Different Mammalian Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.1.1. Cells
2.1.2. Plasmids
2.1.3. Antibodies
2.1.4. Virus
2.2. Cell Expansion and Transfection
2.3. In Vitro Assay of Mx1 Anti-SBV Activity
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
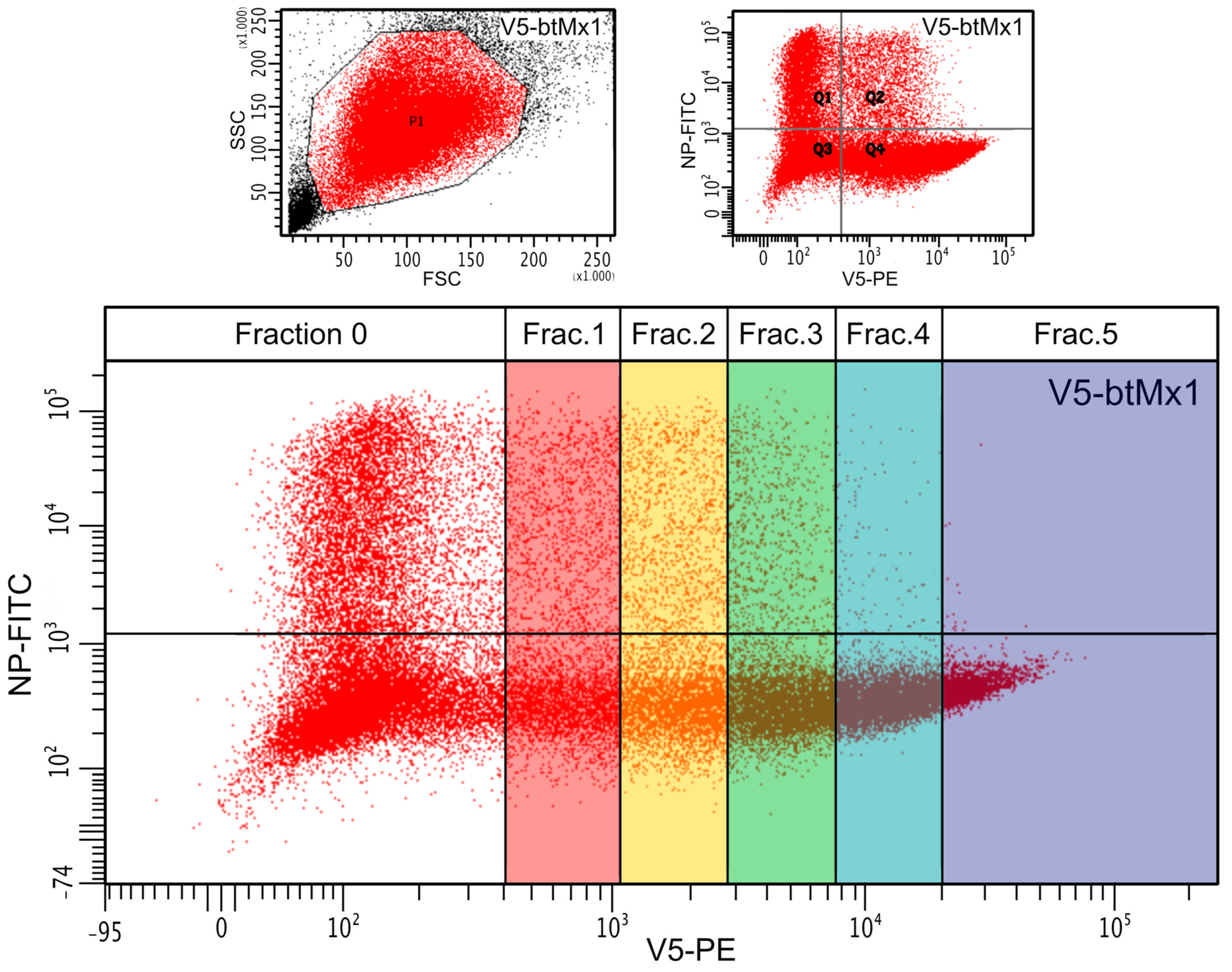
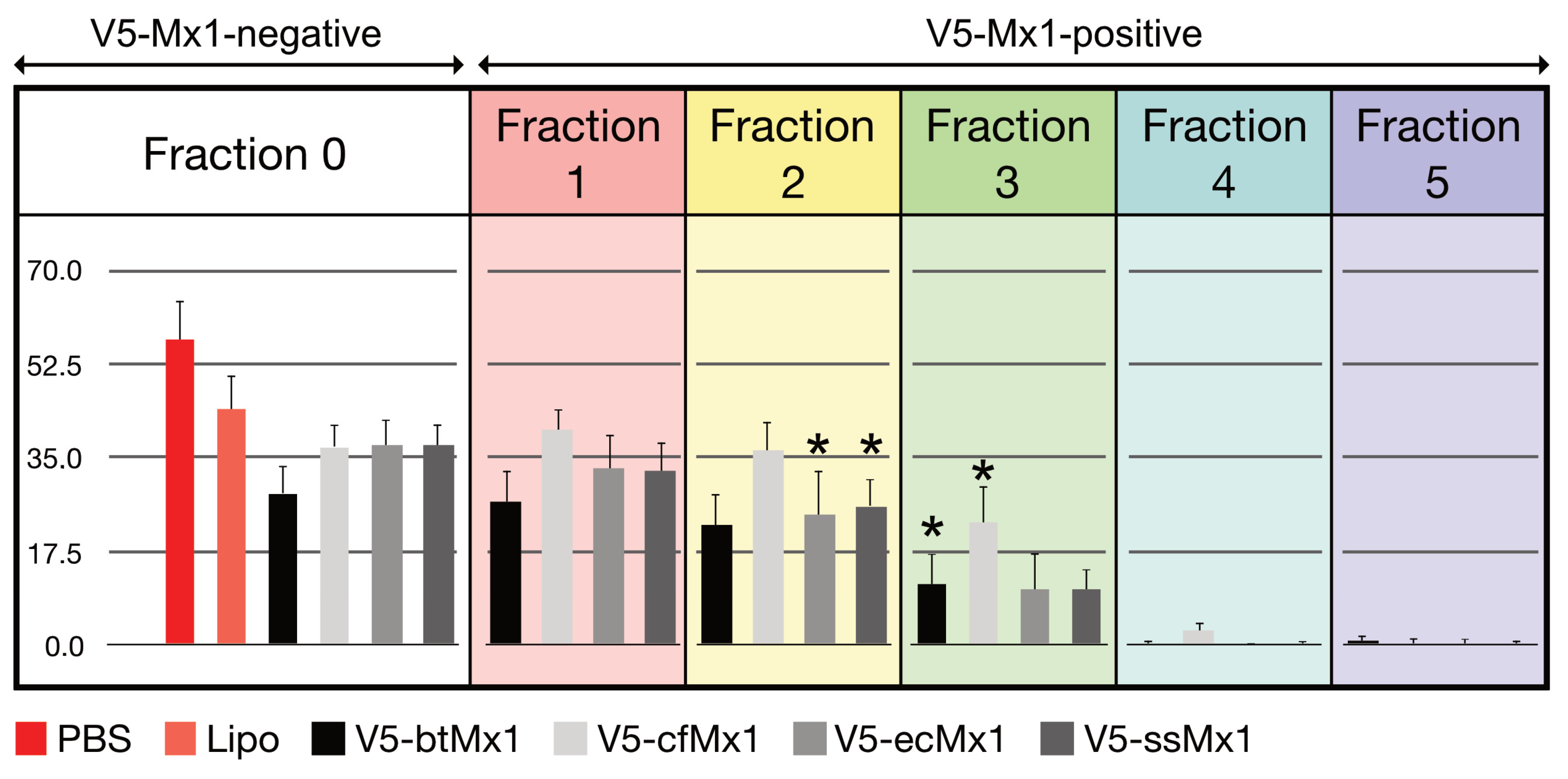
3.1. Effect of V5-Mx1 Proteins on Schmallenberg Virus NP Synthesis
3.2. Comparative Anti-SBV Activity among Different V5-Mx1 Proteins
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lazear, H.; Schoggins, J.; Diamond, M. Shared and Distinct Functions of Type I and Type III Interferons. Immunity 2019, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; von der Malsburg, A.; Dick, A.; Faelber, K.; Schröder, G.F.; Haller, O.; Kochs, G.; Daumke, O. Structure of myxovirus resistance protein a reveals intra- and intermolecular domain interactions required for the antiviral function. Immunity 2011, 35, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmann, J. Resistance of mice to mouse-adapted influenza A virus. Virology 1962, 16, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhelst, J.; Hulpiau, P.; Saelens, X. Mx proteins: Antiviral gatekeepers that restrain the uninvited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zav’yalov, V.; Hämäläinen-Laanaya, H.; Korpela, T.; Wahlroos, T. Interferon-Inducible Myxovirus Resistance Proteins: Potential Biomarkers for Differentiating Viral from Bacterial Infections. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisher, C.H. History, Classification, and Taxonomy of Viruses in the Family Bunyaviridae. In The Bunyaviridae. The Viruses; Elliott, R.M., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- King, A.; Adams, M.; Carstens, E.; Lefkowitz, E. Virus Taxonomy: Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; p. 651. [Google Scholar]
- Abudurexiti, A.; Adkins, S.; Alioto, D.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Avsic-Zupanc, T.; Ballinger, M.J.; Bente, D.A.; Beer, M.; Bergeron, É.; Blair, C.D.; et al. Taxonomy of the order Bunyavirales: Update 2019. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1949–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, S.; Sandhu, N.; Das, S.; Haque, S.; Koley, K. Global Comprehensive Outlook of Hantavirus Contagion on Humans: A Review. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2022, 22, e050122199975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odendaal, L.; Davis, S.; Venter, E. Insights into the Pathogenesis of Viral Haemorrhagic Fever Based on Virus Tropism and Tissue Lesions of Natural Rift Valley Fever. Viruses 2021, 13, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayhan, N.; Charrel, N. An update on Toscana virus distribution, genetics, medical and diagnostic aspects. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldan, S.S.; González-Scarano, F. Emerging infectious diseases: The Bunyaviridae. J. Neurovirol. 2005, 11, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawman, D.; Feldmann, H. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, I.; Bladh, L.; Mousavi-Jazi, M.; Magnusson, K.E.; Lundkvist, A.; Haller, O.; Mirazimi, A. Human MxA protein inhibits the replication of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4323–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgen, A.; Dalrymple, D.A.; Weber, F.; Elliott, R.M. Inhibition of Dugbe nairovirus replication by human MxA protein. Virus Res. 2004, 99, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frese, M.; Kochs, G.; Feldmann, H.; Hertkorn, C.; Haller, O. Inhibition of bunyaviruses, phleboviruses, and hantaviruses by human MxA protein. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanerva, M.; Melén, K.; Vaheri, A.; Julkunen, I. Inhibition of puumala and tula hantaviruses in Vero cells by MxA protein. Virology 1996, 224, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochs, G.; Janzen, C.; Hohenberg, H.; Haller, O. Antivirally active MxA protein sequesters La Crosse virus nucleocapsid protein into perinuclear complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3153–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefti, H.P.; Frese, M.; Landis, H.; Di Paolo, C.; Aguzzi, A.; Haller, O.; Pavlovic, J. Human MxA protein protects mice lacking a functional alpha/beta interferon system against La crosse virus and other lethal viral infections. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 6984–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.K.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Takada, A.; Ogino, M.; Asano, A.; Arikawa, J.; Watanabe, T. Mouse Mx2 protein inhibits hantavirus but not influenza virus replication. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrock, M.; Frese, M.; Haller, O.; Kochs, G. Interferon-induced rat Mx proteins confer resistance to Rift Valley fever virus and other arthropod-borne viruses. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2001, 21, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stertz, S.; Dittmann, J.; Blanco, J.C.G.; Pletneva, L.M.; Haller, O.; Kochs, G. The antiviral potential of interferon-induced cotton rat Mx proteins against orthomyxovirus (influenza), rhabdovirus, and bunyavirus. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2007, 27, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, J.; Hölzer, M.; Schilling, M.; Patzina, C.; Schoen, A.; Hoenen, T.; Zimmer, G.; Marz, M.; Weber, F.; Müller, M.A.; et al. Evolution and Antiviral Specificities of Interferon-Induced Mx Proteins of Bats against Ebola, Influenza, and Other RNA Viruses. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00361-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernike, K.; Aebischer, A.; Audonnet, J.C.; Beer, M. Vaccine development against Schmallenberg virus: From classical inactivated to modified-live to scaffold particle vaccines. One Health Outlook 2022, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasekh, M.; Sarani, A.; Jafari, A. First detection of Schmallenberg virus antibody in cattle population of eastern Iran. Vet. Res. Forum Int. Q. J. 2022, 13, 443–446. [Google Scholar]
- Balinandi, S.; Hayer, J.; Cholleti, H.; Wille, M.; Lutwama, J.J.; Malmberg, M.; Mugisha, L. Identification and molecular characterization of highly divergent RNA viruses in cattle, Uganda. Virus Res. 2022, 313, 198739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrou, C.; Garigliany, M.-M.; Sarlet, M.; Sartelet, A.; Cassart, D.; Desmecht, D. Natural intrauterine infection with Schmallenberg virus in malformed newborn calves. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1327–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelle, L.; Dal Pozzo, F.; Gauthier, B.; Kirschvink, N.; Saegerman, C. Field veterinary survey on clinical and economic impact of Schmallenberg virus in Belgium. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2014, 61, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilston-Lunel, N.L.; Shi, X.; Elliott, R.M.; Acrani, G.O. The Potential for Reassortment between Oropouche and Schmallenberg Orthobunyaviruses. Viruses 2017, 9, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam Van, P.; Desmecht, D.; Garigliany, M.-M.; Bui Tran Anh, D.; Van Laere, A.-S. Anti-Influenza A Virus Activities of Type I/III Interferons-Induced Mx1 GTPases from Different Mammalian Species. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker, H.a.E.; Nakatsu, Y.; Yamada, K.; Yoneda, A.; Takada, A.; Ueda, J.; Hata, H.; Watanabe, T. Bovine and water buffalo Mx2 genes: Polymorphism and antiviral activity. Immunogenetics 2007, 59, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baise, E.; Pire, G.; Leroy, M.; Gérardin, J.; Goris, N.; De Clercq, K.; Kerkhofs, P.; Desmecht, D. Conditional expression of type I interferon-induced bovine Mx1 GTPase in a stable transgenic vero cell line interferes with replication of vesicular stomatitis virus. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2004, 24, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Nakatsu, Y.; Onogi, A.; Ueda, J.; Watanabe, T. Specific intracellular localization and antiviral property of genetic and splicing variants in bovine Mx1. Viral Immunol. 2009, 22, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, M.; Pire, G.; Baise, E.; Desmecht, D. Expression of the interferon- alpha/beta-inducible bovine Mx1 dynamin interferes with replication of rabies virus. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 21, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, M.; Baise, E.; Pire, G.; Gérardin, J.; Desmecht, D. Resistance of paramyxoviridae to type I interferon-induced Bos taurus Mx1 dynamin. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2005, 25, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermine, M.; Desmecht, D. In Vivo modulation of the innate response to pneumovirus by type-I and -III interferon-induced Bos taurus Mx1. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2012, 32, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, M.; Piras, I.M.; Mullan, C.; Shi, X.; Tilston-Lunel, N.L.; Pinto, R.M.; Taggart, A.; Welch, S.R.; Neil, S.J.D.; Kreher, F.; et al. Sensitivity to BST-2 restriction correlates with Orthobunyavirus host range. Virology 2017, 509, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lear, T.L.; Breen, M.; Ponce de Leon, F.A.; Coogle, L.; Ferguson, E.M.; Chambers, T.M.; Bailey, E. Cloning and chromosomal localization of MX1 and ETS2 to chromosome 26 of the horse (Equus caballus). Chromosome Res. 1998, 6, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, H.; Marquardt, J.; Schuberth, H.J.; Adolf, G.R.; Leibold, W. Proteins induced by recombinant equine interferon-beta 1 within equine peripheral blood mononuclear cells and polymorphonuclear neutrophilic granulocytes. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1994, 42, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, V.; Sabachvili, M.; Bendl, E.; Fuchs, J. The Antiviral Activity of Equine Mx1 against Thogoto Virus Is Determined by the Molecular Structure of Its Viral Specificity Region. J. Virol. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.V.; Palm, M.; Broers, A.D.; Zezafoun, H.; Desmecht, D. Genomic structure, promoter analysis, and expression of the porcine (Sus scrofa) Mx1 gene. Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, E.; Morozumi, T.; Tsukamoto, K.; Watanabe, T.; Plastow, G.; Mitsuhashi, T. A naturally occurring variant of porcine Mx1 associated with increased susceptibility to influenza virus in vitro. Biochem. Genet. 2007, 45, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, M.; Leroy, M.; Thomas, A.; Linden, A.; Desmecht, D. Differential anti-influenza activity among allelic variants at the Sus scrofa Mx1 locus. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2007, 27, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, M.; Garigliany, M.-M.; Cornet, F.; Desmecht, D. Interferon-induced Sus scrofa Mx1 blocks endocytic traffic of incoming influenza A virus particles. Vet. Res. 2010, 41, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, J.H.; Sun, R.C.; Li, X.H.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, B. Porcine Mx proteins inhibit pseudorabies virus replication through interfering with early gene synthesis. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 280, 109706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xiang, Z.; Ge, X.; Zhou, L.; Han, J.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Mx1 Inhibits Senecavirus A Replication in PK-15 Cells by Interacting with the Capsid Proteins VP1, VP2 and VP3. Viruses 2022, 14, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.M.; Gao, Z.C.; Liu, C.C.; Zhang, Y.N.; Hou, J.X.; Li, Z.Y.; Kan, L.; Li, W.L.; et al. Porcine Mx1 Protein Inhibits Classical Swine Fever Virus Replication by Targeting Nonstructural Protein NS5B. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02147-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Fu, Q.; Ren, Y.; Wang, D.; Qiao, J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C. Both foot-and-mouth disease virus and bovine viral diarrhea virus replication are inhibited by Mx1 protein originated from porcine. Anim. Biotechnol. 2015, 26, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Asano, A.; Okano, S.; Ko, J.-H.; Kon, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Agui, T. Intracellular localization and antiviral property of canine Mx proteins. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2005, 25, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frensing, T.; Seitz, C.; Heynisch, B.; Patzina, C.; Kochs, G.; Reichl, U. Efficient influenza B virus propagation due to deficient interferon-induced antiviral activity in MDCK cells. Vaccine 2011, 29, 7125–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, C.; Frensing, T.; Höper, D.; Kochs, G.; Reichl, U. High yields of influenza A virus in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells are promoted by an insufficient interferon-induced antiviral state. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frese, M.; Prins, M.; Ponten, A.; Goldbach, R.W.; Haller, O.; Zeltz, P. Constitutive expression of interferon-induced human MxA protein in transgenic tobacco plants does not confer resistance to a variety of RNA viruses. Transgenic Res. 2000, 9, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichelt, M.; Stertz, S.; Krijnse-Locker, J.; Haller, O.; Kochs, G. Missorting of LaCrosse virus nucleocapsid protein by the interferon-induced MxA GTPase involves smooth ER membranes: Membrane association of antivirally active MxA GTPase. Traffic 2004, 5, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, D.; Raju, R.; Kolakofsky, D. La Crosse virus nucleocapsid protein controls its own synthesis in mosquito cells by encapsidating its mRNA. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 5166–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmaljohn, C.; Nichol, S.T. Hantaviruses; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Habjan, M.; Penski, N.; Wagner, V.; Spiegel, M.; Overby, A.K.; Kochs, G.; Huiskonen, J.T.; Weber, F. Efficient production of Rift Valley fever virus-like particles: The antiviral protein MxA can inhibit primary transcription of bunyaviruses. Virology 2009, 385, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollidge, B.; Nedelsky, N.; Salzano, M.; Fraser, J.; González-Scarano, F.; Soldan, S. Orthobunyavirus entry into neurons and other mammalian cells occurs via clathrin-mediated endocytosis and requires trafficking into early endosomes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7988–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, J.E. Dynamin and its Role in Membrane Fission. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 16, 483–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bayrou, C.; Van Laere, A.-S.; Dam Van, P.; Moula, N.; Garigliany, M.-M.; Desmecht, D. Anti-Schmallenberg Virus Activities of Type I/III Interferons-Induced Mx1 GTPases from Different Mammalian Species. Viruses 2023, 15, 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051055
Bayrou C, Van Laere A-S, Dam Van P, Moula N, Garigliany M-M, Desmecht D. Anti-Schmallenberg Virus Activities of Type I/III Interferons-Induced Mx1 GTPases from Different Mammalian Species. Viruses. 2023; 15(5):1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051055
Chicago/Turabian StyleBayrou, Calixte, Anne-Sophie Van Laere, Phai Dam Van, Nassim Moula, Mutien-Marie Garigliany, and Daniel Desmecht. 2023. "Anti-Schmallenberg Virus Activities of Type I/III Interferons-Induced Mx1 GTPases from Different Mammalian Species" Viruses 15, no. 5: 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051055
APA StyleBayrou, C., Van Laere, A.-S., Dam Van, P., Moula, N., Garigliany, M.-M., & Desmecht, D. (2023). Anti-Schmallenberg Virus Activities of Type I/III Interferons-Induced Mx1 GTPases from Different Mammalian Species. Viruses, 15(5), 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051055





