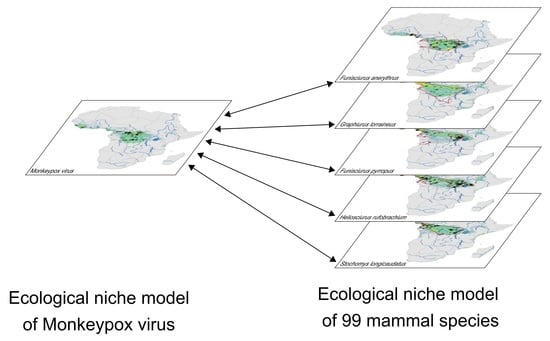
Identifying the Most Probable Mammal Reservoir Hosts for Monkeypox Virus Based on Ecological Niche Comparisons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mammal Species Identified as MPXV Hosts
2.2. Occurrence Records of Selected Mammal Species
2.3. Occurrence Records of MPXV Cases
2.4. Ecological Niche Modelling
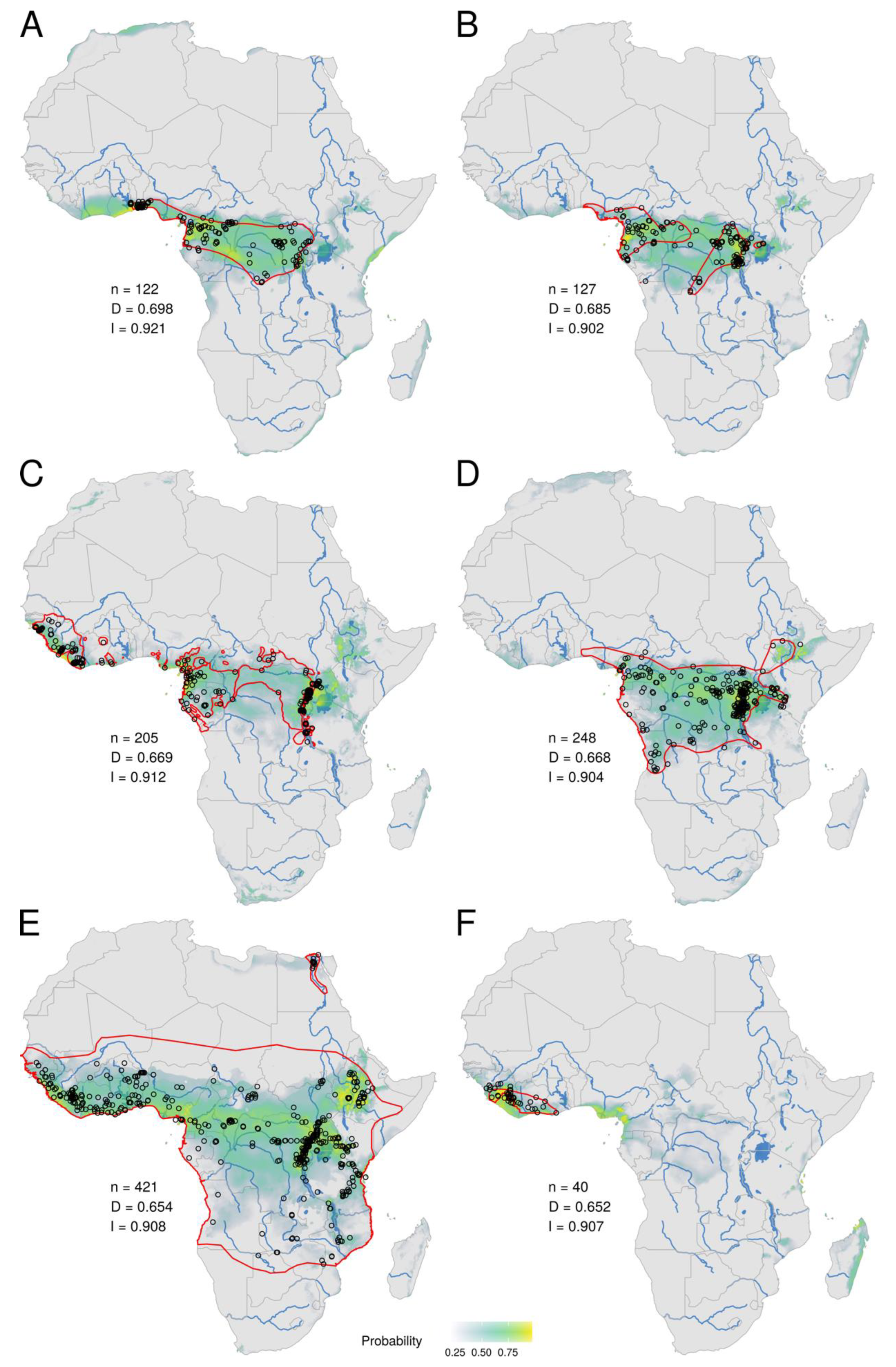
3. Results
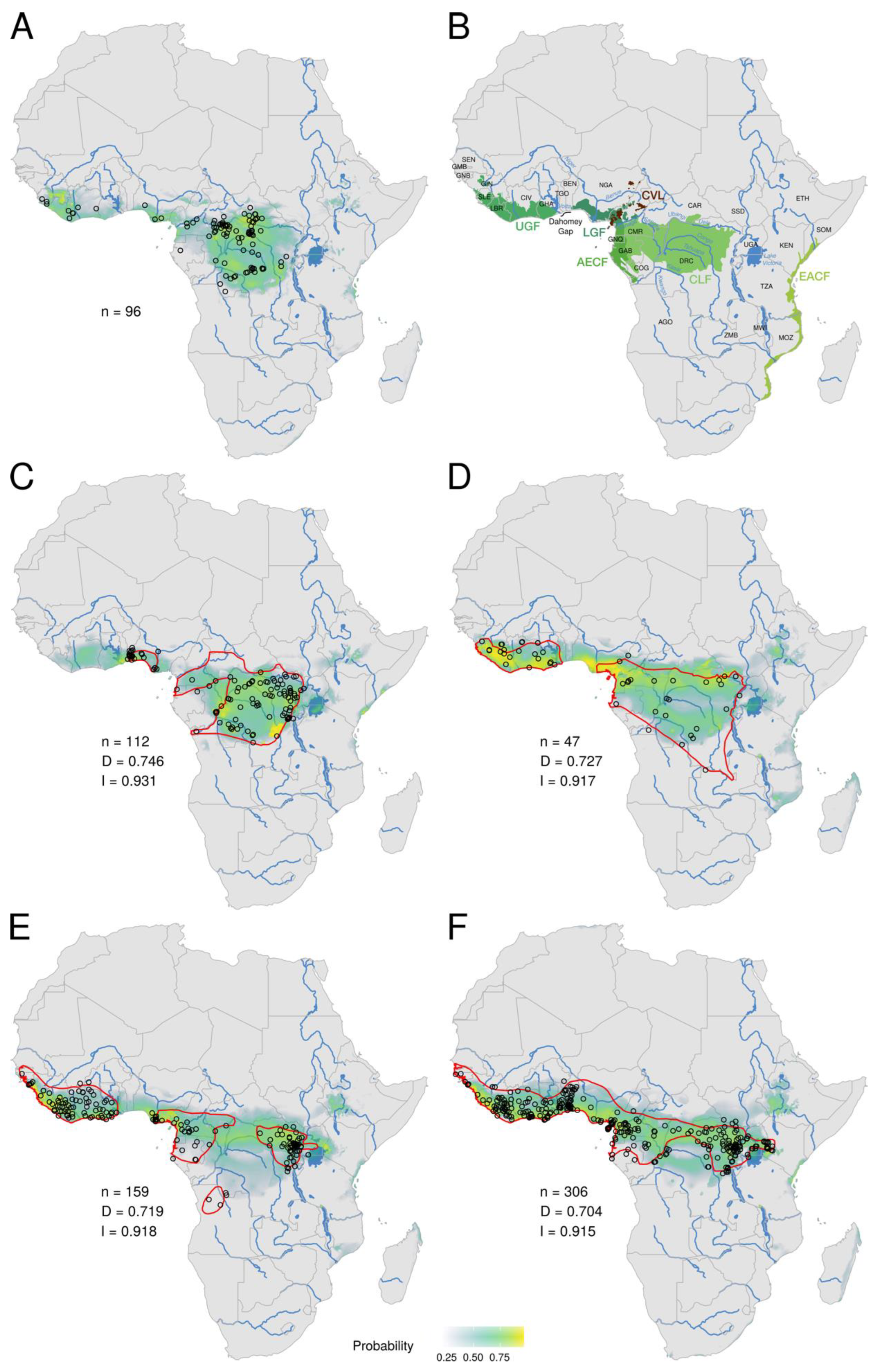
3.1. Ecological Niche of MPXV
3.2. Ecological Niches of Mammal Species and Overlap with the MPXV Niche
4. Discussion
4.1. Ecological Niche of MPXV Fragmented into Three Rainforests
4.2. Which Mammal Species Are the Most Probable Reservoir Hosts?
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Recommends New Name for Monkeypox Disease. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/28-11-2022-who-recommends-new-name-for-monkeypox-disease (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Damaso, C.R. Phasing out Monkeypox: Mpox Is the New Name for an Old Disease. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2023, 17, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.; Kantele, A.; Koopmans, M.; Asogun, D.; Yinka-Ogunleye, A.; Ihekweazu, C.; Zumla, A. Human Monkeypox: Epidemiologic and Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis, and Prevention. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 1027–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nylund, A.; Watanabe, K.; Nylund, S.; Karlsen, M.; Saether, P.A.; Arnesen, C.E.; Karlsbakk, E. Morphogenesis of Salmonid Gill Poxvirus Associated with Proliferative Gill Disease in Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar) in Norway. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, R.C.; Wang, C.; Hatcher, E.L.; Lefkowitz, E.J. Orthopoxvirus Genome Evolution: The Role of Gene Loss. Viruses 2010, 2, 1933–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelli, D.; Lavazza, A.; Prosperi, A.; Sozzi, E.; Faccin, F.; Baioni, L.; Trogu, T.; Cavallari, G.L.; Mauri, M.; Gibellini, A.M.; et al. Hypsugopoxvirus: A Novel Poxvirus Isolated from Hypsugo Savii in Italy. Viruses 2019, 11, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Gray, M.; Winter, L. Why Do Poxviruses Still Matter? Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, C.M.; Gao, J.; Tang, S.; McCollum, A.M.; Wilkins, K.; Reynolds, M.G.; Davidson, W.; McLaughlin, J.; Olson, V.A.; Li, Y. Genome of Alaskapox Virus, a Novel Orthopoxvirus Isolated from Alaska. Viruses 2019, 11, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Magnus, P.; Andersen, E.K.; Petersen, K.B.; Birch-Andersen, A. A Pox-like Disease in Cynomolgus Monkeys. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 1959, 46, 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, I.; Gispen, R.; Kalter, S.; Wah, L.T.; Marennikova, S.S.; Netter, R.; Tagaya, I. Outbreaks of Monkeypox and Serological Surveys in Nonhuman Primates. Bull. World Health Organ. 1972, 46, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ladnyj, I.D.; Ziegler, P.; Kima, E. A Human Infection Caused by Monkeypox Virus in Basankusu Territory, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Bull. World Health Organ. 1972, 46, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foster, S.O.; Brink, E.W.; Hutchins, D.L.; Pifer, J.M.; Lourie, B.; Moser, C.R.; Cummings, E.C.; Kuteyi, O.E.K.; Eke, R.E.A.; Titus, J.B.; et al. Human Monkeypox. Bull. World Health Organ. 1972, 46, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arita, I.; Henderson, D.A. Monkeypox and Whitepox Viruses in West and Central Africa. Bull. World Health Organ. 1976, 53, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Breman, J.G.; Steniowski, M.V.; Zanotto, E.; Gromyko, A.I.; Arita, I. Human Monkeypox, 1970–1979. Bull. World Health Organ. 1980, 58, 165–182. [Google Scholar]
- Khodakevich, L.; Widy-Wirski, R.; Arita, I.; Marennikova, S.S.; Nakano, J.; Meunier, D. Orthopoxvirose Simienne de l’Homme en République centrafricaine. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. Filiales 1985, 78, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Müller, G.; Meyer, A.; Gras, F.; Emmerich, P.; Kolakowski, T.; Esposito, J.J. Monekypox Virus in Liver and Spleen of Child in Gabon. Lancet 1988, 331, 769–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.; Esposito, J.J.; Gras, F.; Kolakowski, T.; Fatras, M.; Muller, G. Premiere apparition au Gabon de monkey-pox chez l’homme. Médecine Trop. 1991, 51, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Fenner, F.; Henderson, D.A.; Arita, I.; Jezek, Z.; Ladnyi, I.D. Human Monkeypox and Other Poxvirus Infections of Man; Smallpox and its Eradication; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1988; ISBN 92-4-156110-6.
- Heymann, D.L.; Szczeniowski, M.; Esteves, K. Re-Emergence of Monkeypox in Africa: A Review of the Past Six Years. Br. Med. Bull. 1998, 54, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklenovská, N.; Van Ranst, M. Emergence of Monkeypox as the Most Important Orthopoxvirus Infection in Humans. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinka-Ogunleye, A.; Aruna, O.; Ogoina, D.; Aworabhi, N.; Eteng, W.; Badaru, S.; Mohammed, A.; Agenyi, J.; Etebu, E.N.; Numbere, T.-W.; et al. Reemergence of Human Monkeypox in Nigeria, 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, J.; Tack, D.M.; McCollum, A.M.; Kabamba, J.; Pakuta, E.; Malekani, J.; Nguete, B.; Monroe, B.P.; Doty, J.B.; Karhemere, S.; et al. Enhancing Health Care Worker Ability to Detect and Care for Patients with Monkeypox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Int. Health 2013, 5, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edghill-Smith, Y.; Golding, H.; Manischewitz, J.; King, L.R.; Scott, D.; Bray, M.; Nalca, A.; Hooper, J.W.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Schmitz, J.E.; et al. Smallpox Vaccine–Induced Antibodies Are Necessary and Sufficient for Protection against Monkeypox Virus. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Multistate Outbreak of Monkeypox–Illinois, Indiana, and Wisconsin, 2003. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2003, 52, 537–540.
- Reed, K.D.; Melski, J.W.; Graham, M.B.; Regnery, R.L.; Sotir, M.J.; Wegner, M.V.; Kazmierczak, J.J.; Stratman, E.J.; Li, Y.; Fairley, J.A.; et al. The Detection of Monkeypox in Humans in the Western Hemisphere. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erez, N.; Achdout, H.; Milrot, E.; Schwartz, Y.; Wiener-Well, Y.; Paran, N.; Politi, B.; Tamir, H.; Israely, T.; Weiss, S.; et al. Diagnosis of Imported Monkeypox, Israel, 2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 980–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, A.; Aarons, E.; Astbury, J.; Balasegaram, S.; Beadsworth, M.; Beck, C.R.; Chand, M.; O’Connor, C.; Dunning, J.; Ghebrehewet, S.; et al. Two Cases of Monkeypox Imported to the United Kingdom, September 2018. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 1800509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar, S.; Maskey, U.; Thada, P.K.; Mustansir, M.; Sarfraz, A.; Sarfraz, Z. Re-Emergence of Monkeypox amidst Delta Variant Concerns: A Point of Contention for Public Health Virology? J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, O.T.; Lee, V.; Marimuthu, K.; Vasoo, S.; Chan, G.; Lin, R.T.P.; Leo, Y.S. A Case of Imported Monkeypox in Singapore. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damon, I.K.; Roth, C.E.; Chowdhary, V. Discovery of Monkeypox in Sudan. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 962–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Emerson, G.L.; Carroll, D.S.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Reynolds, M.G.; Karem, K.L.; Olson, V.A.; Lash, R.R.; Davidson, W.B.; et al. Phylogenetic and Ecologic Perspectives of a Monkeypox Outbreak, Southern Sudan, 2005. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adalja, A.; Inglesby, T. A Novel International Monkeypox Outbreak. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, 1175–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessain, A.; Nakoune, E.; Yazdanpanah, Y. Monkeypox. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutombo, M.; Arita, I.; Ježek, Z. Human Monkeypox Transmitted by a Chimpanzee in a Tropical Rain-Forest Area of Zaire. Lancet 1983, 321, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezek, Z.; Arita, I.; Mutombo, M.; Dunn, C.; Nakano, J.H.; Szczeniowski, M. Four Generations of Probable Person-to-Person Transmission of Human Monkeypox. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986, 123, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Smallpox: Post-Eradication Surveillance: First Isolation of Monkeypox Virus from a Wild Animal Infected in Nature. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 1985, 60, 393–400.
- Khodakevich, L.; Jezek, Z.; Kinzanzka, K. Isolation of Monkeypox Virus from Wild Squirrel Infected in Nature. Lancet 1986, 327, 98–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Smallpox: Post-Eradication Surveillance: Squirrels Proved to Maintain Monkeypox Virus Transmission in Nature. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 1986, 61, 181–188.
- Radonić, A.; Metzger, S.; Dabrowski, P.W.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Schuenadel, L.; Kurth, A.; Mätz-Rensing, K.; Boesch, C.; Leendertz, F.H.; Nitsche, A. Fatal Monkeypox in Wild-Living Sooty Mangabey, Côte d’Ivoire, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1009–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrono, L.V.; Pléh, K.; Samuni, L.; Ulrich, M.; Röthemeier, C.; Sachse, A.; Muschter, S.; Nitsche, A.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Boesch, C.; et al. Monkeypox Virus Emergence in Wild Chimpanzees Reveals Distinct Clinical Outcomes and Viral Diversity. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariën, J.; Laudisoit, A.; Patrono, L.; Baelo, P.; van Vredendaal, R.; Musaba, P.; Gembu, G.; Mande, C.; Ngoy, S.; Mussaw, M.; et al. Monkeypox Viruses Circulate in Distantly-Related Small Mammal Species in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Res. Sq. 2021; preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Mauldin, M.R.; McCollum, A.M.; Nakazawa, Y.J.; Mandra, A.; Whitehouse, E.R.; Davidson, W.; Zhao, H.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Doty, J.; et al. Exportation of Monkeypox Virus from the African Continent. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 225, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.S.; Peterson, A.T.; Yorita, K.L.; Carroll, D.S.; Damon, I.K.; Reynolds, M.G. Ecological Niche and Geographic Distribution of Human Monkeypox in Africa. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lash, R.R.; Carroll, D.S.; Hughes, C.M.; Nakazawa, Y.; Karem, K.; Damon, I.K.; Peterson, A.T. Effects of Georeferencing Effort on Mapping Monkeypox Case Distributions and Transmission Risk. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2012, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Mauldin, M.R.; Emerson, G.L.; Reynolds, M.G.; Lash, R.R.; Gao, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Muyembe, J.-J.; Kingebeni, P.M.; et al. A Phylogeographic Investigation of African Monkeypox. Viruses 2015, 7, 2168–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likos, A.M.; Sammons, S.A.; Olson, V.A.; Frace, A.M.; Li, Y.; Olsen-Rasmussen, M.; Davidson, W.; Galloway, R.; Khristova, M.L.; Reynolds, M.G.; et al. A Tale of Two Clades: Monkeypox Viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, N.; Descorps-Declère, S.; Besombes, C.; Curaudeau, M.; Nkili Meyong, A.A.; Selekon, B.; Labouba, I.; Gonofio, E.C.; Ouilibona, R.S.; Simo Tchetgna, H.D.; et al. Genomic History of Human Monkey Pox Infections in the Central African Republic between 2001 and 2018. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happi, C.; Adetifa, I.; Mbala, P.; Njouom, R.; Nakoune, E.; Happi, A.; Ndodo, N.; Ayansola, O.; Mboowa, G.; Bedford, T.; et al. Urgent Need for a Non-Discriminatory and Non-Stigmatizing Nomenclature for Monkeypox Virus. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gispen, R.; Brand-Saathof, B.; Hekker, A.C. Monkeypox-Specific Antibodies in Human and Simian Sera from the Ivory Coast and Nigeria. Bull. World Health Organ. 1976, 53, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Breman, J.G.; Bernadou, J.; Nakano, J.H. Poxvirus in West African Nonhuman Primates: Serological Survey Results. Bull. World Health Organ. 1977, 55, 605–612. [Google Scholar]
- Khodakevich, L.; Szczeniowski, M.; Jezek, Z.; Marennikova, S.; Nakano, J.; Messinger, D. The Role of Squirrels in Sustaining Monkeypox Virus Transmission. Trop. Geogr. Med. 1987, 39, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Ježek, Z.; Fenner, F. Human Monkeypox; Monographs in Virology; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 1988; Volume 17, ISBN 3-8055-4818-4. [Google Scholar]
- Khodakevich, L.; Ježek, Z.; Messinger, D. Monkeypox Virus: Ecology and Public Health Significance. Bull. World Health Organ. 1988, 66, 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Hutin, Y.; Williams, R.J.; Malfait, P.; Pebody, R.; Loparev, V.N.; Ropp, S.L.; Rodriguez, M.; Knight, J.C.; Tshioko, F.K.; Khan, A.S.; et al. Outbreak of Human Monkeypox, Democratic Republic of Congo, 1996 to 1997. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, C.L.; Lee, K.N.; Abel, J.; Carroll, D.S.; Montgomery, J.M.; Olson, V.A.; Li, Y.; Davidson, W.; Hughes, C.; Dillon, M.; et al. Monkeypox Zoonotic Associations: Insights from Laboratory Evaluation of Animals Associated with the Multi-State US Outbreak. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, M.G.; Carroll, D.S.; Olson, V.A.; Hughes, C.; Galley, J.; Likos, A.; Montgomery, J.M.; Suu-Ire, R.; Kwasi, M.O.; Root, J.J.; et al. A Silent Enzootic of an Orthopoxvirus in Ghana, West Africa: Evidence for Multi-Species Involvement in the Absence of Widespread Human Disease. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, J.B.; Malekani, J.M.; Kalemba, L.N.; Stanley, W.T.; Monroe, B.P.; Nakazawa, Y.U.; Mauldin, M.R.; Bakambana, T.L.; Liyandja Dja Liyandja, T.; Braden, Z.H.; et al. Assessing Monkeypox Virus Prevalence in Small Mammals at the Human–Animal Interface in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Viruses 2017, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiee, M.S.; Harrigan, R.J.; Thomassen, H.A.; Smith, T.B. Ghosts of Infections Past: Using Archival Samples to Understand a Century of Monkeypox Virus Prevalence among Host Communities across Space and Time. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.G.; Emerson, G.L.; Pukuta, E.; Karhemere, S.; Muyembe, J.J.; Bikindou, A.; McCollum, A.M.; Moses, C.; Wilkins, K.; Zhao, H.; et al. Detection of Human Monkeypox in the Republic of the Congo Following Intensive Community Education. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species Version 2022-1. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Boakes, E.H.; McGowan, P.J.; Fuller, R.A.; Chang-qing, D.; Clark, N.E.; O’Connor, K.; Mace, G.M. Distorted Views of Biodiversity: Spatial and Temporal Bias in Species Occurrence Data. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, D.E.; Callaghan, C.T.; Bhandari, N.; Henle, K.; Benjamin Barth, M.; Koppitz, C.; Klenke, R.; Winter, M.; Jansen, F.; Bruelheide, H.; et al. Temporal Trends in the Spatial Bias of Species Occurrence Records. Ecography 2022, 2022, e06219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, D.; Attfield, L.A.; Jones, K.E.; Watson-Jones, D.; Kock, R. Rodent Trapping Studies as an Overlooked Information Source for Understanding Endemic and Novel Zoonotic Spillover. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0010772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, S.; Ram, K.; Hart, T. Spocc: Interface to Species Occurrence Data Sources. R package version 1.2.0. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=spocc (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Nelson, G.; Paul, D.L. DiSSCo, IDigBio and the Future of Global Collaboration. Biodivers. Inf. Sci. Stand. 2019, 3, e37896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, H.; Guralnick, R.; Wieczorek, J.; Spencer, C.; Peterson, A.T. The VertNet Steering Committee VertNet: A New Model for Biodiversity Data Sharing. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizka, A.; Silvestro, D.; Andermann, T.; Azevedo, J.; Duarte Ritter, C.; Edler, D.; Farooq, H.; Herdean, A.; Ariza, M.; Scharn, R.; et al. CoordinateCleaner: Standardized Cleaning of Occurrence Records from Biological Collection Databases. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello-Lammens, M.E.; Boria, R.A.; Radosavljevic, A.; Vilela, B.; Anderson, R.P. SpThin: An R Package for Spatial Thinning of Species Occurrence Records for Use in Ecological Niche Models. Ecography 2015, 38, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.; Böller, M.; Erhardt, A.; Schwanghart, W. Spatial Bias in the GBIF Database and Its Effect on Modeling Species’ Geographic Distributions. Ecol. Inform. 2014, 19, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boria, R.A.; Olson, L.E.; Goodman, S.M.; Anderson, R.P. Spatial Filtering to Reduce Sampling Bias Can Improve the Performance of Ecological Niche Models. Ecol. Model. 2014, 275, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guagliardo, S.A.J.; Monroe, B.P.; Moundjoa, C.; Athanase, A.; Okpu, G.; Burgado, J.; Townsend, M.B.; Satheshkumar, P.S.; Epperson, S.; Doty, J.B.; et al. Asympto-matic Orthopoxvirus Circulation in Humans in the Wake of a Monkeypox Outbreak among Chimpanzees in Cameroon. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 102, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Human Monkeypox in West Africa. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 1979, 54, 121–128.
- Merouze, F.; Lesoin, J. Monkeypox: Second Cas Humain Observé En Côte d’Ivoire (Secteur de Santé Rurale de Daloa). Médecine Trop. 1983, 43, 145–147. [Google Scholar]
- Janseghers, L.; Matamba, M.; Colaert, J.; Vandepitte, J.; Desmyter, J. Fatal Monkeypox in a Child in Kikwit, Zaire. Ann. Soc. Belg. Med. Trop. 1984, 64, 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Tchokoteu, P.; Kago, I.; Tetanye, E.; Ndoumbe, P.; Pignon, D.; Mbede, J. Variole Ou Varicelle Grave? Un Cas de Variole Humaine a Monkeypox Virus Chez Un Enfant Camerounais. Ann. Soc. Belg. Méd. Trop. 1991, 71, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization Human Monkeypox in Kasai Oriental, Democratic Republic of the Congo (Former Zaire). Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 1997, 72, 365–372.
- Meyer, H.; Perrichot, M.; Stemmler, M.; Emmerich, P.; Schmitz, H.; Varaine, F.; Shungu, R.; Tshioko, F.; Formenty, P. Outbreaks of Disease Suspected of Being Due to Human Monkeypox Virus Infection in the Democratic Republic of Congo in 2001. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2919–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learned, L.A.; Bolanda, J.D.; Li, Y.; Reynolds, M.G.; Moudzeo, H.; Wassa, D.W.; Libama, F.; Harvey, J.M.; Likos, A.; Formenty, P.; et al. Extended Interhuman Transmission of Monkeypox in a Hospital Community in the Republic of the Congo, 2003. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthet, N.; Nakouné, E.; Whist, E.; Selekon, B.; Burguière, A.-M.; Manuguerra, J.-C.; Gessain, A.; Kazanji, M. Maculopapular Lesions in the Central African Republic. Lancet 2011, 378, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolen, L.D.; Osadebe, L.; Katomba, J.; Likofata, J.; Mukadi, D.; Monroe, B.; Doty, J.; Kalemba, L.N.; Malekani, J.; Kabamba, J.; et al. Introduction of Monkeypox into a Community and Household: Risk Factors and Zoonotic Reservoirs in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCollum, A.M.; Reynolds, M.G.; Ndongala, G.M.; Pukuta, E.; Tamfum, J.-J.M.; Malekani, J.; Karhemere, S.; Lushima, R.S.; Wilkins, K.; Gao, J.; et al. Case Report: Human Monkeypox in the Kivus, a Conflict Region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalthan, E.; Dondo-Fongbia, J.; Yambele, S.; Dieu-Creer, L.; Zepio, R.; Pamatika, C. Epidémie de 12 Cas de Maladie à Virus Monkeypox Dans Le District de Bangassou En République Centrafricaine En Décembre 2015. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2016, 109, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudisoit, A.; Komba, M.; Akonda, I. Scientific Report Research Bushmeat and Monkeypox Yahuma Health Zone–Aketi Health Zone-Bombongolo Health Area. DRC. 2016. Available online: https://cd.chm-cbd.net/implementation/centre-de-sureveillance-de-la-biodiversite-csb/activites-du-csb/rapport-d-expedition-scientifique-expedition-biodiversite-en-ituri/research-bushmeat-and-monkeypox-yahuma-health-zone-aketi-health-zone-bombongolo/download/fr/1/Outbreak_Investigation_AKETI2016final.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Kalthan, E.; Tenguere, J.; Ndjapou, S.G.; Koyazengbe, T.A.; Mbomba, J.; Marada, R.M.; Rombebe, P.; Yangueme, P.; Babamingui, M.; Sambella, A.; et al. Investigation of an Outbreak of Monkeypox in an Area Occupied by Armed Groups, Central African Republic. Med. Mal. Infect. 2018, 48, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besombes, C.; Gonofio, E.; Konamna, X.; Selekon, B.; Gessain, A.; Berthet, N.; Manuguerra, J.-C.; Fontanet, A.; Nakouné, E. Intrafamily Transmission of Monkeypox Virus, Central African Republic, 2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, R.H.; Guagliardo, S.A.J.; Doty, J.B.; Babeaux, A.D.; Matheny, A.; Burgado, J.; Townsend, M.B.; Morgan, C.N.; Satheshkumar, P.S.; Ndakala, N.; et al. Epidemiologic and Ecologic Investigations of Monkeypox, Likouala Department, Republic of the Congo, 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.G.; Wauquier, N.; Li, Y.; Satheshkumar, P.S.; Kanneh, L.D.; Monroe, B.; Maikere, J.; Saffa, G.; Gonzalez, J.-P.; Fair, J.; et al. Human Monkeypox in Sierra Leone after 44-Year Absence of Reported Cases. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Song, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, L.; Zhu, L.; Kamara, I.L.; Ren, J.; Wang, W.; Tian, H.; et al. Molecular Evidence of Human Monkeypox Virus Infection, Sierra Leone. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gweh, D.D.; Adewuyi, P.; Amo-Addae, M.; Bulage, L.; Wilson, H.W.; Fulton Shannon, I.; Ilesanmi, O.S.; Nagbe, T.K.; Babalola, O.J. Monkeypox Outbreak, Harper District, Maryland County, Liberia, December 2017. J. Interv. Epidemiol. Public Health 2021, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besombes, C.; Mbrenga, F.; Schaeffer, L.; Malaka, C.; Gonofio, E.; Landier, J.; Vickos, U.; Konamna, X.; Selekon, B.; Dankpea, J.N.; et al. National Monkeypox Surveillance, Central African Republic, 2001-2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiner, C.A.; Moses, C.; Monroe, B.P.; Nakazawa, Y.; Doty, J.B.; Hughes, C.M.; McCollum, A.M.; Ibata, S.; Malekani, J.; Okitolonda, E.; et al. Presumptive Risk Factors for Monkeypox in Rural Communities in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boston, E.S.; Ian Montgomery, W.; Hynes, R.; Prodöhl, P.A. New Insights on Postglacial Colonization in Western Europe: The Phylogeography of the Leisler’s Bat (Nyctalus Leisleri). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20142605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, L.P.; Galetti, M.; Pires, M.M. Climate and Land-Use Change Will Lead to a Faunal “Savannization” on Tropical Rainforests. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 7036–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menchetti, M.; Guéguen, M.; Talavera, G. Spatio-Temporal Ecological Niche Modelling of Multigenerational Insect Migrations. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20191583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillero, N.; Huey, R.B.; Gilchrist, G.; Rissler, L.; Pascual, M. Distribution Modelling of an Introduced Species: Do Adaptive Genetic Markers Affect Potential Range? Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20201791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanin, A.; Tu, V.T.; Curaudeau, M.; Csorba, G. Inferring the Ecological Niche of Bat Viruses Closely Related to SARS-CoV-2 Using Phylogeographic Analyses of Rhinolophus Species. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, J.M.; Jetz, W.; Rogers, D.J. The Effects of Species’ Range Sizes on the Accuracy of Distribution Models: Ecological Phenomenon or Statistical Artefact? J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 41, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Proosdij, A.S.; Sosef, M.S.; Wieringa, J.J.; Raes, N. Minimum Required Number of Specimen Records to Develop Accurate Species Distribution Models. Ecography 2016, 39, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very High Resolution Interpolated Climate Surfaces for Global Land Areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-Km Spatial Resolution Climate Surfaces for Global Land Areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Title, P.O.; Bemmels, J.B. ENVIREM: An Expanded Set of Bioclimatic and Topographic Variables Increases Flexibility and Improves Performance of Ecological Niche Modeling. Ecography 2018, 41, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M. Building Predictive Models in R Using the Caret Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, C.F.; Elith, J.; Bacher, S.; Buchmann, C.; Carl, G.; Carré, G.; Marquéz, J.R.G.; Gruber, B.; Lafourcade, B.; Leitão, P.J.; et al. Collinearity: A Review of Methods to Deal with It and a Simulation Study Evaluating Their Performance. Ecography 2013, 36, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum Entropy Modeling of Species Geographic Distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Phillips, S.J.; Hastie, T.; Dudík, M.; Chee, Y.E.; Yates, C.J. A Statistical Explanation of MaxEnt for Ecologists. Divers. Distrib. 2011, 17, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, D.L.; Matzke, N.J.; Cardillo, M.; Baumgartner, J.B.; Beaumont, L.J.; Turelli, M.; Glor, R.E.; Huron, N.A.; Simões, M.; Iglesias, T.L.; et al. ENMTools 1.0: An R Package for Comparative Ecological Biogeography. Ecography 2021, 44, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillero, N.; Barbosa, A.M. Common Mistakes in Ecological Niche Models. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 35, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisz, M.S.; Hijmans, R.J.; Li, J.; Peterson, A.T.; Graham, C.H.; Guisan, A. NCEAS Predicting Species Distributions Working Group Effects of Sample Size on the Performance of Species Distribution Models. Divers. Distrib. 2008, 14, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, A.H.; Bell, J.F. A Review of Methods for the Assessment of Prediction Errors in Conservation Presence/Absence Models. Environ. Conserv. 1997, 24, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoener, T.W. The Anolis Lizards of Bimini: Resource Partitioning in a Complex Fauna. Ecology 1968, 49, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, D.L.; Glor, R.E.; Turelli, M. Environmental Niche Equivalency versus Conservatism: Quantitative Approaches to Niche Evolution. Evolution 2008, 62, 2868–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, A.H. The Niger, the Volta and the Dahomey Gap as Geographic Barriers. Evolution 1958, 12, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Martinez, J.; Sudmant, P.H.; Kidd, J.M.; Li, H.; Kelley, J.L.; Lorente-Galdos, B.; Veeramah, K.R.; Woerner, A.E.; O’Connor, T.D.; Santpere, G.; et al. Great Ape Genetic Diversity and Population History. Nature 2013, 499, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, V.; Missoup, A.D.; Denys, C.; Kerbis Peterhans, J.; Katuala, P.; Couloux, A.; Colyn, M. The Roles of Rivers and Pleistocene Refugia in Shaping Genetic Diversity in Praomys Misonnei in Tropical Africa. J. Biogeogr. 2011, 38, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanin, A.; Khouider, S.; Gembu, G.-C.; Goodman, S.M.; Kadjo, B.; Nesi, N.; Pourrut, X.; Nakoune, E.; Bonillo, C. The Comparative Phylogeography of Fruit Bats of the Tribe Scotonycterini (Chiroptera, Pteropodidae) Reveals Cryptic Species Diversity Related to African Pleistocene Forest Refugia. C. R. Biol. 2015, 338, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingdon, J.; Happold, D.; Butynski, T.; Hoffmann, M.; Happold, M.; Kalina, J. Mammals of Africa; Bloomsbury Publishing: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4081-2253-2. [Google Scholar]
- Almécija, S.; Hammond, A.S.; Thompson, N.E.; Pugh, K.D.; Moyà-Solà, S.; Alba, D.M. Fossil Apes and Human Evolution. Science 2021, 372, eabb4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBrearty, S.; Jablonski, N.G. First Fossil Chimpanzee. Nature 2005, 437, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosevear, D.R. The Rodents of West Africa; Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History): London, UK, 1969. [Google Scholar]
| Order | Family | Genus | Virus Isolation | MPXV Fragment Amplified by PCR (Sequenced in Bold) | Anti-OPXV Antibodies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eulipotyphla | Erinaceidae | Atelerix | Atelerix spp. [55] | Atelerix spp. [55] | |
| Eulipotyphla | Soricidae | Crocidura | C. littoralis [41] | ||
| Macroscelidea | Macroscelididae | Petrodromus | P. tetradactylus [54,57] | ||
| Primates | Cercopithecidae | Allenopithecus | A. nigroviridis [52] | ||
| Primates | Cercopithecidae | Cercocebus | C. atys [39] | C. atys [39] | C. galeritus [52] |
| Primates | Cercopithecidae | Cercopithecus | C. ascanius [38,51,52,53] C. mona [52] C. nictitans [52] C. petaurista [49,50] C. pogonias [38,51,52] | ||
| Primates | Cercopithecidae | Chlorocebus | C. aethiops * [49] | ||
| Primates | Cercopithecidae | Piliocolobus | P. badius * [50] P. pennanti * [52] | ||
| Primates | Hominidae | Pan | P. troglodytes [40] | ||
| Primates | Lorisidae | Perodicticus | P. potto [52] | ||
| Rodentia | Dipodidae | Jaculus | Jaculus spp. [55] | ||
| Rodentia | Gliridae | Graphiurus | G. lorraineus [55] Graphiurus spp. [55,56] | G. lorraineus [57] Graphiurus spp. [55,56] | |
| Rodentia | Muridae | Malacomys | M. longipes (MT724769) | ||
| Rodentia | Muridae | Oenomys | O. hypoxanthus [57] | ||
| Rodentia | Muridae | Stochomys | S. longicaudatus [41] | ||
| Rodentia | Nesomyidae | Cricetomys | Cricetomys sp. [41] Cricetomys spp. [55,56] | C. emini [54,57] Cricetomys spp. [55,56] | |
| Rodentia | Sciuridae | Funisciurus | F. anerythrus [37] | F. anerythrus [37,41,55,56,58] F. bayonii [41] F. carruthersi [58] F. congicus [58] F. lemniscatus [58] F. pyrropus [58] Funisciurus. spp. [55,56] | F. anerythrus [38,51,52,54] F. isabella [52] F. lemniscatus [52] Funisciurus spp. [52,53,56,57,59] |
| Rodentia | Sciuridae | Heliosciurus | H. rufobrachium [51,52,53,54] H. gambianus [52,56] Heliosciurus spp. [39,53,57] | ||
| Rodentia | Sciuridae | Xerus | Xerus sp. [56] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Curaudeau, M.; Besombes, C.; Nakouné, E.; Fontanet, A.; Gessain, A.; Hassanin, A. Identifying the Most Probable Mammal Reservoir Hosts for Monkeypox Virus Based on Ecological Niche Comparisons. Viruses 2023, 15, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15030727
Curaudeau M, Besombes C, Nakouné E, Fontanet A, Gessain A, Hassanin A. Identifying the Most Probable Mammal Reservoir Hosts for Monkeypox Virus Based on Ecological Niche Comparisons. Viruses. 2023; 15(3):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15030727
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuraudeau, Manon, Camille Besombes, Emmanuel Nakouné, Arnaud Fontanet, Antoine Gessain, and Alexandre Hassanin. 2023. "Identifying the Most Probable Mammal Reservoir Hosts for Monkeypox Virus Based on Ecological Niche Comparisons" Viruses 15, no. 3: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15030727
APA StyleCuraudeau, M., Besombes, C., Nakouné, E., Fontanet, A., Gessain, A., & Hassanin, A. (2023). Identifying the Most Probable Mammal Reservoir Hosts for Monkeypox Virus Based on Ecological Niche Comparisons. Viruses, 15(3), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15030727