Rhabdomyolysis after COVID-19 Infection: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
3. Background History and Previous Presentations of Rhabdomyolysis
4. Investigations
5. Treatment
6. Outcome and Follow-Up
7. Discussion
7.1. Risk Factors for Rhabdomyolysis in COVID-19 Illness
7.2. Viral-Induced Rhabdomyolysis
7.3. Rhabdomyolysis and COVID-19 Vaccination
7.4. “Long COVID” and Musculoskeletal Involvement
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gavriatopoulou, M.; Korompoki, E.; Fotiou, D.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Kastritis, E.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Organ-specific manifestations of COVID-19 infection. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaim, S.; Chong, J.H.; Sankaranarayanan, V.; Harky, A. COVID-19 and multiorgan response. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2020, 45, 100618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.A.; Helmstetter, J.A.; Kaye, A.M.; Kaye, A.D. Rhabdomyolysis: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Ochsner J. 2015, 15, 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- Huerta-Alardín, A.L.; Varon, J.; Marik, P.E. Bench-to-bedside review: Rhabdomyolysis—An overview for clinicians. Crit. Care 2005, 9, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.Y. Rhabdomyolysis: A review of the literature. Neth. J. Med. 2009, 67, 272–283. [Google Scholar]
- Valente-Acosta, B.; Moreno-Sanchez, F.; Fueyo-Rodriguez, O.; Palomar-Lever, A. Rhabdomyolysis as an initial presentation in a patient diagnosed with COVID-19. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e236719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxbro, K.; Kahlow, H.; Wulcan, H.; Fornarve, A. Rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury in severe COVID-19 infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e237616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Kanai, O.; Nanba, K.; Esaka, N.; Hata, H.; Seta, K.; Odagaki, T. Acute rhabdomyolysis in a young woman with moderate COVID-19. IDCases 2021, 25, e01212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Tong, Q. Rhabdomyolysis as potential late complication associated with COVID-19. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanwongse, K.; Shabarek, N. Rhabdomyolysis as a presentation of 2019 novel coronavirus disease. Cureus 2020, 12, e7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, B.B.; Ikitimur, H.; Yavuzer, S.; Islamoglu, M.S.; Cengiz, M. Case report: A COVID-19 patient presenting with mild rhabdomyolysis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kaur, P.; Mechineni, A.; Maroules, M. Rhabdomyolysis in COVID-19: Report of four cases. Cureus 2020, 12, e10686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosla, S.G.; Nylen, E.S.; Khosla, R. Rhabdomyolysis in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Infection: Five Case Series. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2020, 8, 2324709620984603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas-García, S.; Bernal, J.; Bachiller-Corral, J. Rhabdomyolysis as the main manifestation of coronavirus disease 2019. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2174–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, R.; Corcuera-Solano, I.; Dayan, E.; Jacobi, A.H.; Huang, M. Rhabdomyolysis as a manifestation of a severe case of COVID-19: A case report. Radiol. Case Rep. 2020, 15, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrubaye, R.; Choudhary, H. Severe rhabdomyolysis in a 35-year-old woman with COVID-19 due to SARS-CoV-2 infection: A case report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e926733-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckholz, A.P.; Kaplan, A.; Rosenblatt, R.E.; Wan, D. Clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and outcomes of 6 patients with COVID-19 infection and rhabdomyolysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 2557–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, J.G.; Pineda, A.E.; Minutti, P.A.; Sánchez, A.A. Case report: Rhabdomyolysis in a patient with COVID-19: A proposed diagnostic-therapeutic algorithm. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedid, N.R.; Udit, S.; Solhjou, Z.; Patanwala, M.Y.; Sheridan, A.M.; Barkoudah, E. COVID-19 and rhabdomyolysis. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 3087–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byler, J.; Harrison, R.; Fell, L.L. Rhabdomyolysis following recovery from severe COVID-19: A case report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2021, 22, e931616-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kaur, P.; Reid, R.-J.R. Case Reports: Rhabdomyolysis associated with COVID-19. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 102, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shanbhag, A.; Manaktala, P.S.; Rizvi, H.; Frey, K.; Narayanan, R. COVID-19 presenting as severe rhabdomyolysis with normal renal function. Cureus 2020, 12, e9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Ma, Q.; Du, Y.-S.; Peng, N.; Yang, T.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Wu, F.-F.; Lin, H.-L.; Su, L. Rhabdomyolysis is associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19. Shock 2021, 56, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, A.; Verrengia, E.P.; Merlo, I.; Rea, F.; Siciliano, G.; Corrao, G.; Prelle, A. Muscle manifestations and CK levels in COVID infection: Results of a large cohort of patients inside a Pandemic COVID-19 Area. Acta Myol. 2021, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, A.K.; Maurer, L.R.; Christensen, M.A.; El Moheb, M.; Naar, L.; Alser, O.; Gaitanidis, A.; Langeveld, K.; Kapoen, C.; Breen, K. Rhabdomyolysis in Severe COVID-19: Male Sex, High Body Mass Index, and Prone Positioning Confer High Risk. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 266, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroun, M.W.; Dieiev, V.; Kang, J.; Barbi, M.; Nia, S.F.M.; Gabr, M.; Eman, G.; Kajita, G.; Swedish, K. Rhabdomyolysis in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective observational study. Cureus 2021, 13, e12552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, M.; Nichols, L.; Guerrero, D.M. Rhabdomyolysis Secondary to COVID-19 Vaccination. Cureus 2021, 13, e15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M.; Chung, H.; Dhayaparan, Y.; Nyein, A.; Acevedo, B.J.; Chicos, C.; Zheng, D.; Barras, M.; Mohamed, M.; Alfishawy, M.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine induced rhabdomyolysis: Case report with literature review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 102170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, E.; Esposito, C.; Giardino, G.; Azan, G.; Fecarotta, S.; Pittaluga, S.; Ruggiero, L.; Barretta, F.; Frisso, G.; Notarangelo, L.D.; et al. Case Report: Severe Rhabdomyolysis and Multiorgan Failure after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 845496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmera, K.M. Fatal case of rhabdomyolysis post-COVID-19 vaccine. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, K.; Ponte, C.D.; Anderson, D. A Possible Case of COVID-19 Booster Vaccine–Associated Rhabdomyolysis and Acute Kidney Injury. J. Pharm. Technol. 2022, 38, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salter, B.; Jessome, M.; Tarnopolsky, M.; Yousuf, H. Possible association between rhabdomyolysis and mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in a patient with RYR1 gene mutation. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2022, 194, E252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandava, K.; Jaffry, M.; Rosario, S.; Jedidi, K.; Souayah, N. Association between COVID-19 Vaccination and Rhabdomyolysis in Adults: A Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) Study (S18.006). Neurology 2022, 98 (Suppl. 18), 1265. [Google Scholar]
- Callado, R.B.; Carneiro, T.G.P.; da Cunha Parahyba, C.C.; de Alcantara Lima, N.; da Silva Junior, G.B.; de Francesco Daher, E. Rhabdomyolysis secondary to influenza A H1N1 vaccine resulting in acute kidney injury. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2013, 11, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, K.S.; Chandrasekar, T.; Reeve, R.; Roberts, M.; Kalra, P. Influenza vaccine-induced rhabdomyolysis leading to acute renal transplant dysfunction. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 530–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, E.; Bernheim, J.; Ben-Chetrit, S.; Mor, A.; Korzets, Z.E. Influenza vaccine—A possible trigger of rhabdomyolysis induced acute renal failure due to the combined use of cerivastatin and bezafibrate. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2000, 15, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, L.G.; Gourna Paleoudis, E.; Lesky-Di Bari, D.; Nyirenda, T.; Friedman, T.; Gupta, A.; Rasouli, L.; Zetkulic, M.; Balani, B.; Ogedegbe, C. Persistence of symptoms and quality of life at 35 days after hospitalization for COVID-19 infection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagarra-Romero, L.; Viñas-Barros, A. COVID-19: Short and long-term effects of hospitalization on muscular weakness in the elderly. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, P.K.; Sigoli, E.; Bragança, L.J.; Cornachione, A.S. The Musculoskeletal Involvement after Mild to Moderate COVID-19 Infection. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 813924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, B.; Nansoz, S.; Cameron, D.R.; Z’Graggen, W.J. Is myopathy part of Long-COVID? Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 1241–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
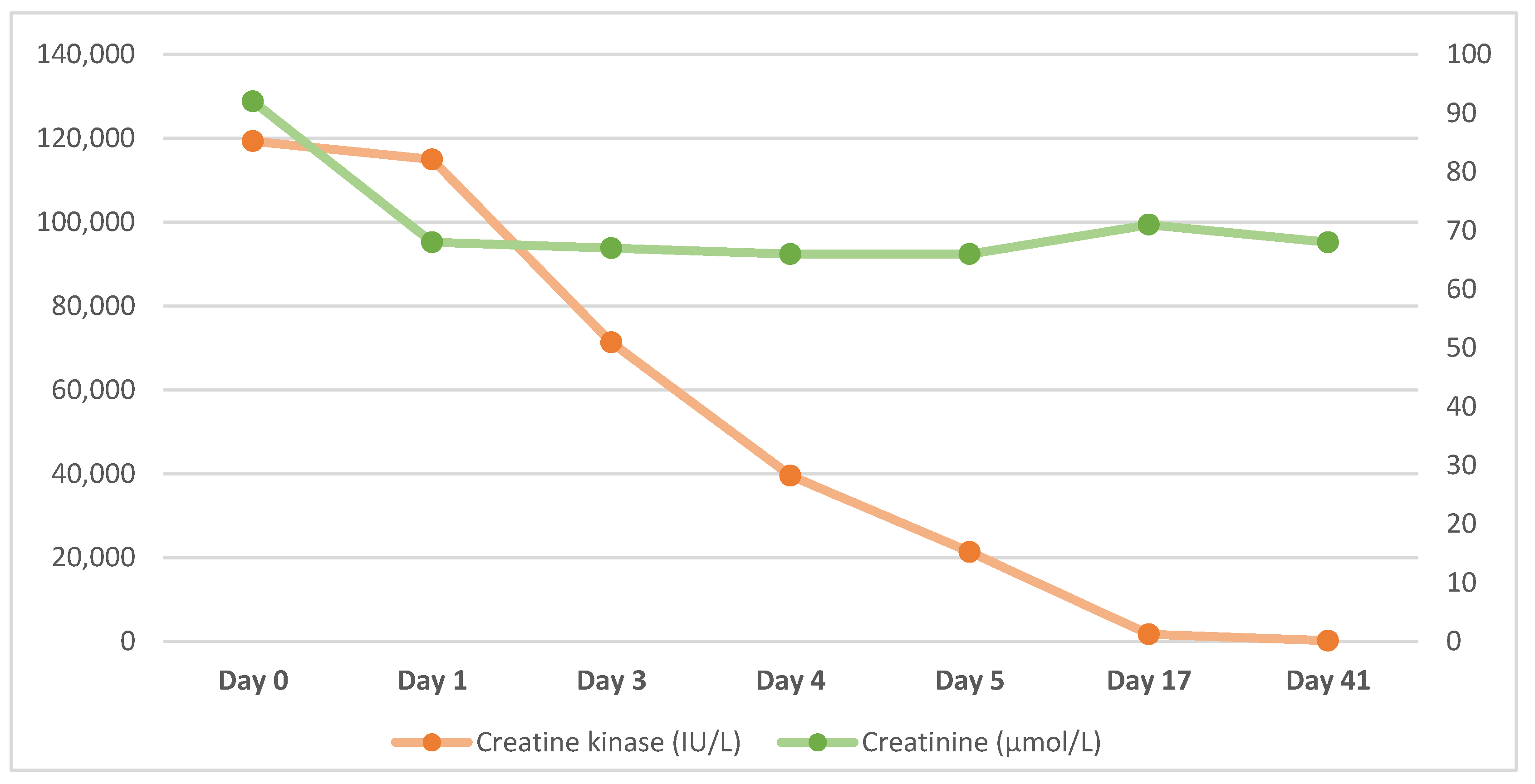
| Date | Hb (g/L) | WCC (×109/L) | Creatinine (µmol/L) | eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | CRP (mg/L) | Platelets (×109/L) | Creatine Kinase (IU/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | 137 | 4.6 | 92 | 57 | - | 114 | 119,301 |
| Day 1 | 123 | 3.2 | 68 | 82 | 11.9 | 72 | 114,965 |
| Day 2 | 125 | 3.5 | 67 | 83 | 8.4 | 68 | 71,303 |
| Day 3 | 128 | 4.2 | 66 | 85 | 10.3 | 79 | 39,540 |
| Day 4 | 116 | 3.8 | 66 | 85 | 8.7 | 106 | 21,344 |
| Day 10 | 126 | 5.4 | 71 | 78 | - | 314 | 1709 |
| Day 41 | - | - | 68 | 82 | - | - | 195 |
| Age (Years) | Gender | Ethnicity | Background | Level of Care | Peak CK Level (IU/L) | AKI | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valente-Acosta 2020 [6] | 71 | Male | Unknown | BPH, smoker | Ward | 8720 | Yes | Discharged |
| Taxbro 2020 [7] | 38 | Male | Unknown | T2DM, gout, mild obesity | ICU | N/A | Yes | Discharged |
| Fujita 2021 [8] | 19 | Female | Unknown | None | Ward | 55,613 | No | Discharged |
| Jin & Tong 2020 [9] | 60 | Male | Unknown | Unknown | Ward | 11,842 | No | Discharged |
| Suwanwongse & Shabarek 2020 [10] | 88 | Male | Unknown | HTN, CKD, HF, BPH, OA, Cognitive impairment | Ward | 13,581 | Yes | Discharged |
| Uysal 2020 [11] | 60 | Male | Unknown | None | Ward | 4267 | No | Discharged |
| Singh 2020 [12]—Case 1 | 67 | Male | Unknown | HTN | ICU | 19,773 | Yes | Died |
| Singh 2020 [12]—Case 2 | 39 | Male | Unknown | HTN | ICU | 4330 | Yes | Died |
| Singh 2020 [12]—Case 3 | 43 | Male | Unknown | ESRF | Ward | 9793 | Unknown | Died |
| Singh 2020 [12]—Case 4 | 70 | Male | Unknown | None | ICU | 5008 | Unknown | Died |
| Khosla 2020 [13]—Case 1 | 65 | Male | Black | HTN, OSA hyperlipidaemia, | ICU | 7854 | Yes | Died |
| Khosla 2020 [13]—Case 2 | 78 | Male | White | T2DM, HTN, hyperlipidaemia, HF, MVR, CABG | ICU | >22,000 | Yes | Died |
| Khosla 2020 [13]—Case 3 | 67 | Male | Black | T2DM, HTN, hyperlipidaemia CKD, hemicolectomy | Dialysis | 6164 | Yes | Discharged |
| Khosla 2020 [13]—Case 4 | 58 | Male | Black | T2DM, HTN, hyperlipidaemia | Ward | 4625 | Yes | Discharged |
| Khosla 2020 [13]—Case 5 | 64 | Male | Black | T2DM, HTN, HIV | Ward | 3135 | No | Discharged |
| Rivas-Garcia 2020 [14] | 78 | Male | White | HTN, T2DM | Ward | 22,511 | Yes | Discharged |
| Hussein 2020 [15] | 38 | Male | Unknown | Obesity | ICU | 33,000 | Yes | Discharged |
| Alrubaye & Choudhury 2020 [16] | 35 | Female | Unknown | None | Ward | 71,000 | Unknown | Discharged |
| Buckholz 2020 [17]—Case 1 | 43 | Male | Unknown | None | ICU | 75,240 | Yes | Discharged |
| Buckholz 2020 [17]—Case 2 | 37 | Male | Unknown | None | ICU | 82,960 | Yes | Discharged |
| Buckholz 2020 [17]—Case 3 | 75 | Male | Unknown | DVT | Ward | 3638 | Yes | Discharged |
| Buckholz 2020 [17]—Case 4 | 59 | Male | Unknown | None | ICU | 8310 | No | Died |
| Buckholz 2020 [17]—Case 5 | 66 | Male | Unknown | HTN | ICU | 10,100 | No | Discharged |
| Buckholz 2020 [17]—Case 6 | 70 | Female | Unknown | MM, CKD | ICU | 406,300 | Yes | Died |
| Solis 2020 [18] | 46 | Male | Unknown | CML | Unknown | 400,000 | Yes | Died |
| Chedid 2020 [19] | 51 | Male | Unknown | HTN, T2DM, CKD | Unknown | 464,000 | Yes | Discharged on HD |
| Byler 2021 [20] | 67 | Female | Unknown | HTN, T2DM, Hyperlipidaemia | ICU | 15,085 | Yes | Discharged on HD |
| Singh 2020 [21]—Case 1 | 54 | Male | Hispanic | Asthma, DM, HTN, obesity | Unknown | 7337 | Unknown | Died |
| Singh 2020 [21]—Case 2 | 54 | Male | White | None | Unknown | 3068 | Unknown | Discharged |
| Singh 2020 [21]—Case 3 | 34 | Male | White | Obesity, prediabetes | Unknown | 5454 | Unknown | Died |
| Singh 2020 [21]—Case 4 | 71 | Male | Black | HTN, seizures schizophrenia, | Unknown | 10,247 | Unknown | Died |
| Singh 2020 [21]—Case 5 | 88 | Male | White | Diabetes, HTN | Unknown | 2628 | Unknown | Died |
| Singh 2020 [21]—Case 6 | 56 | Male | Hispanic | HTN, prediabetes | Unknown | 5388 | Unknown | Discharged |
| Singh 2020 [21]—Case 7 | 57 | Male | Hispanic | None | Unknown | 37,524 | Unknown | Died |
| Singh 2020 [21]—Case 8 | 64 | Male | White | None | Unknown | 6435 | Unknown | Died |
| Singh 2020 [21]—Case 9 | 36 | Male | White | None | Unknown | 5531 | Unknown | Died |
| Singh 2020 [21]—Case 10 | 39 | Male | Black | HTN | Unknown | 4330 | Unknown | Died |
| Shanbhag 2020 [22] | 19 | Male | Black | Anxiety, previous influenza-associated rhabdomyolysis | Unknown | 694,200 | No | Discharged |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bawor, M.; Sairam, S.; Rozewicz, R.; Viegas, S.; Comninos, A.N.; Abbara, A. Rhabdomyolysis after COVID-19 Infection: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Viruses 2022, 14, 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102255
Bawor M, Sairam S, Rozewicz R, Viegas S, Comninos AN, Abbara A. Rhabdomyolysis after COVID-19 Infection: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Viruses. 2022; 14(10):2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102255
Chicago/Turabian StyleBawor, Monica, Shwetha Sairam, Rachel Rozewicz, Stuart Viegas, Alexander N. Comninos, and Ali Abbara. 2022. "Rhabdomyolysis after COVID-19 Infection: A Case Report and Review of the Literature" Viruses 14, no. 10: 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102255
APA StyleBawor, M., Sairam, S., Rozewicz, R., Viegas, S., Comninos, A. N., & Abbara, A. (2022). Rhabdomyolysis after COVID-19 Infection: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Viruses, 14(10), 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102255





