DExD/H Box Helicases DDX24 and DDX49 Inhibit Reactivation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma Associated Herpesvirus by Interacting with Viral mRNAs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Helicase siRNA Screen
2.3. Real-Time qPCR
2.4. Transfection by Electroporation for BCBL-1 Overexpression
2.5. Antibodies and Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Lentiviral Stable Transduction for BCBL-1 Knockdown
2.7. Lentiviral Transduction for TREx BCBL1-Rta Overexpression
2.8. RNA Immunoprecipitation
2.9. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.10. Statistical Analyses
2.11. Type I Interferon Detection by SEAP Assay and Transcript Measurement by RT-qPCR
3. Results
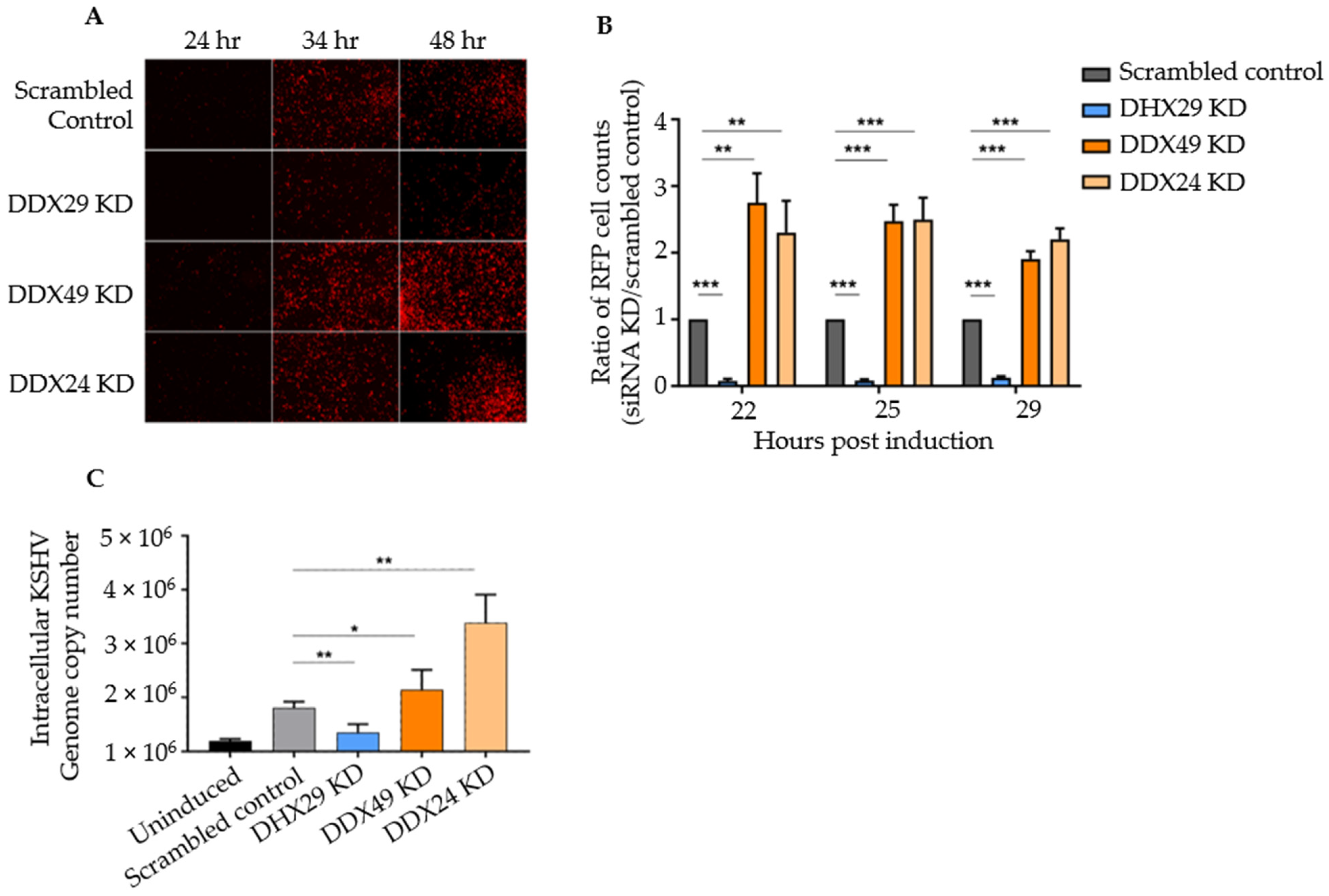
3.1. Knockdown of DexD/H Box Helicases to Screen for Effects on KSHV Reactivation
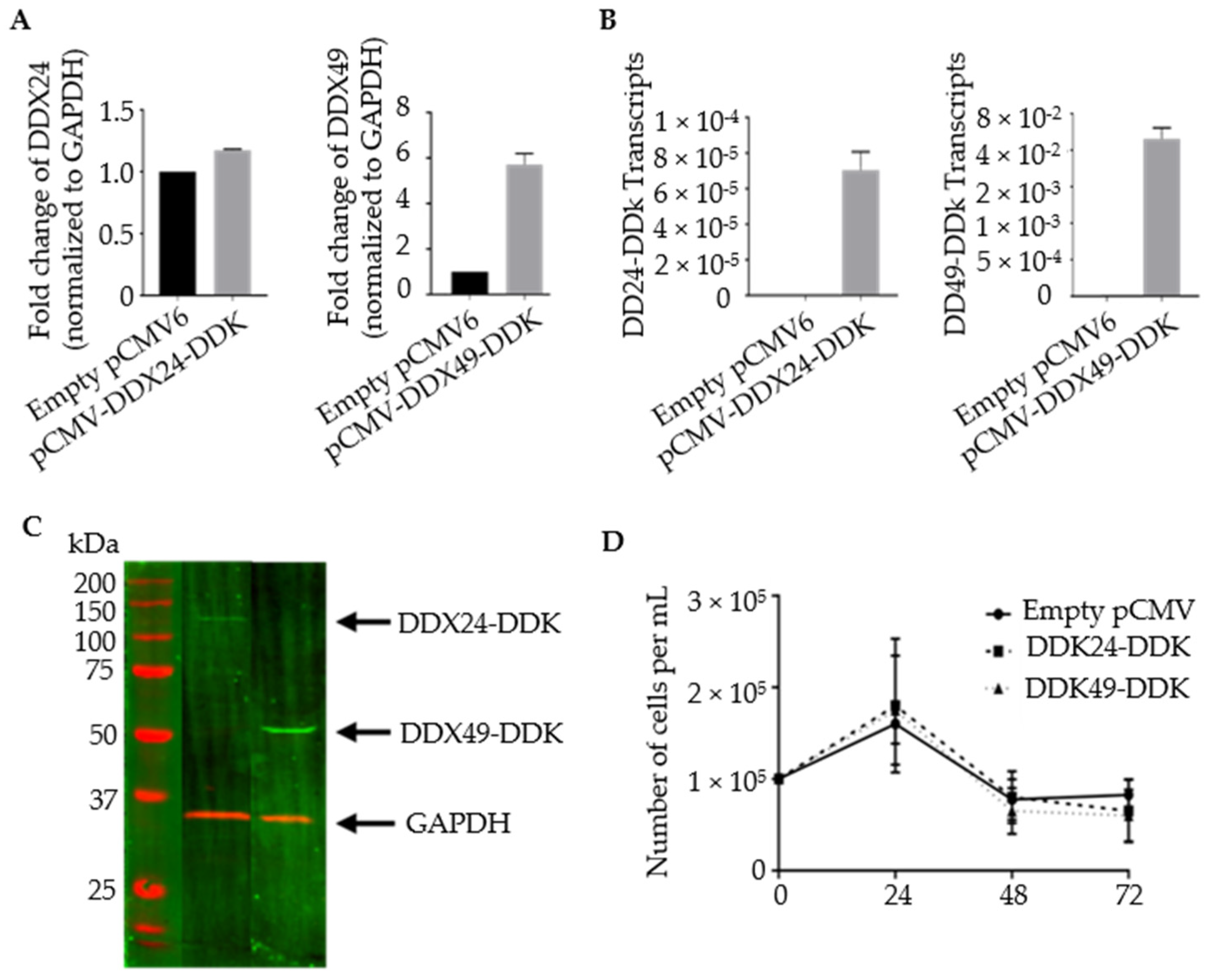
3.2. Construction of Stably Transfected BCBL-1 Cells Expressing DDX24-DDK and DDX49-DDK
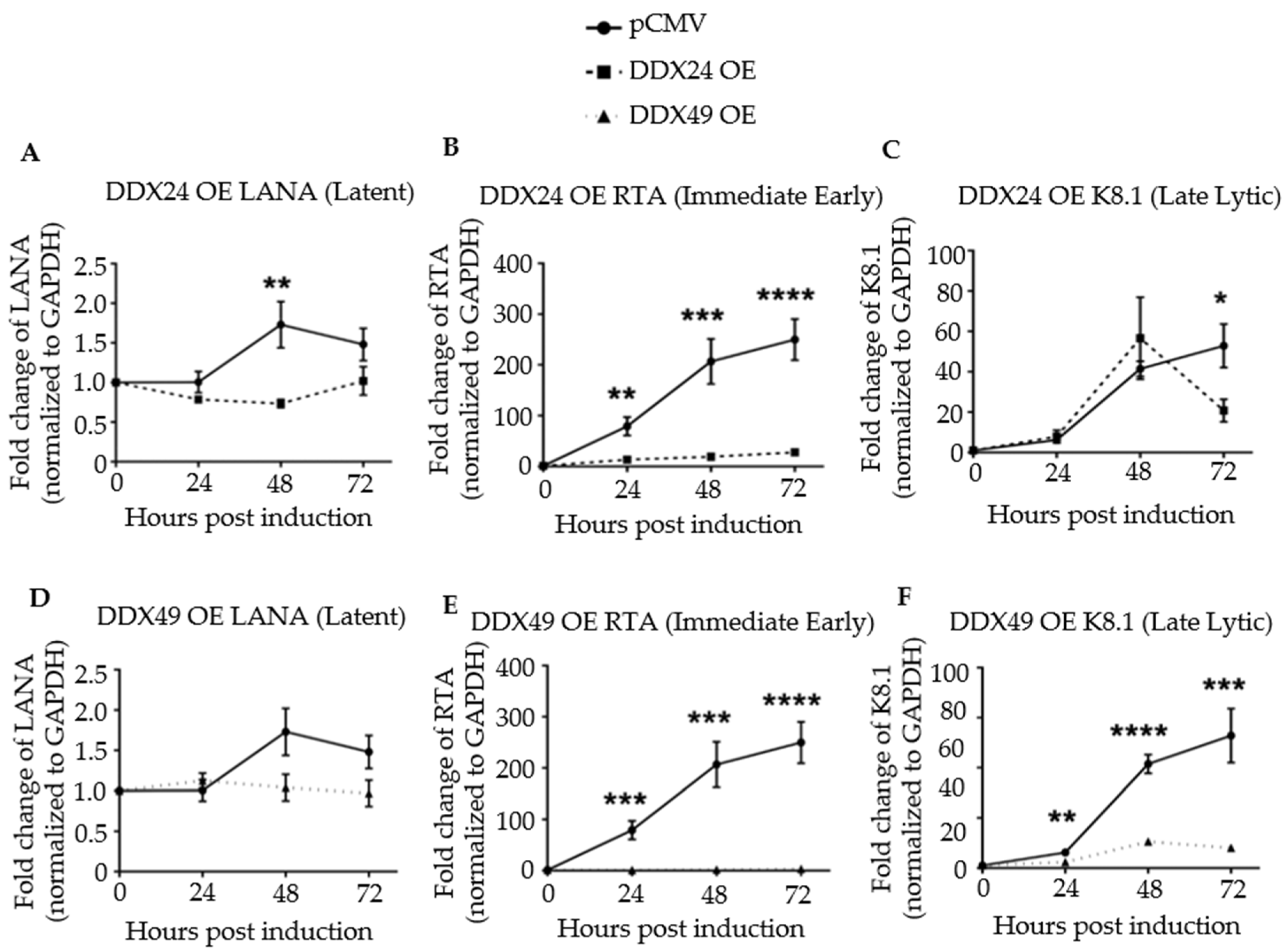
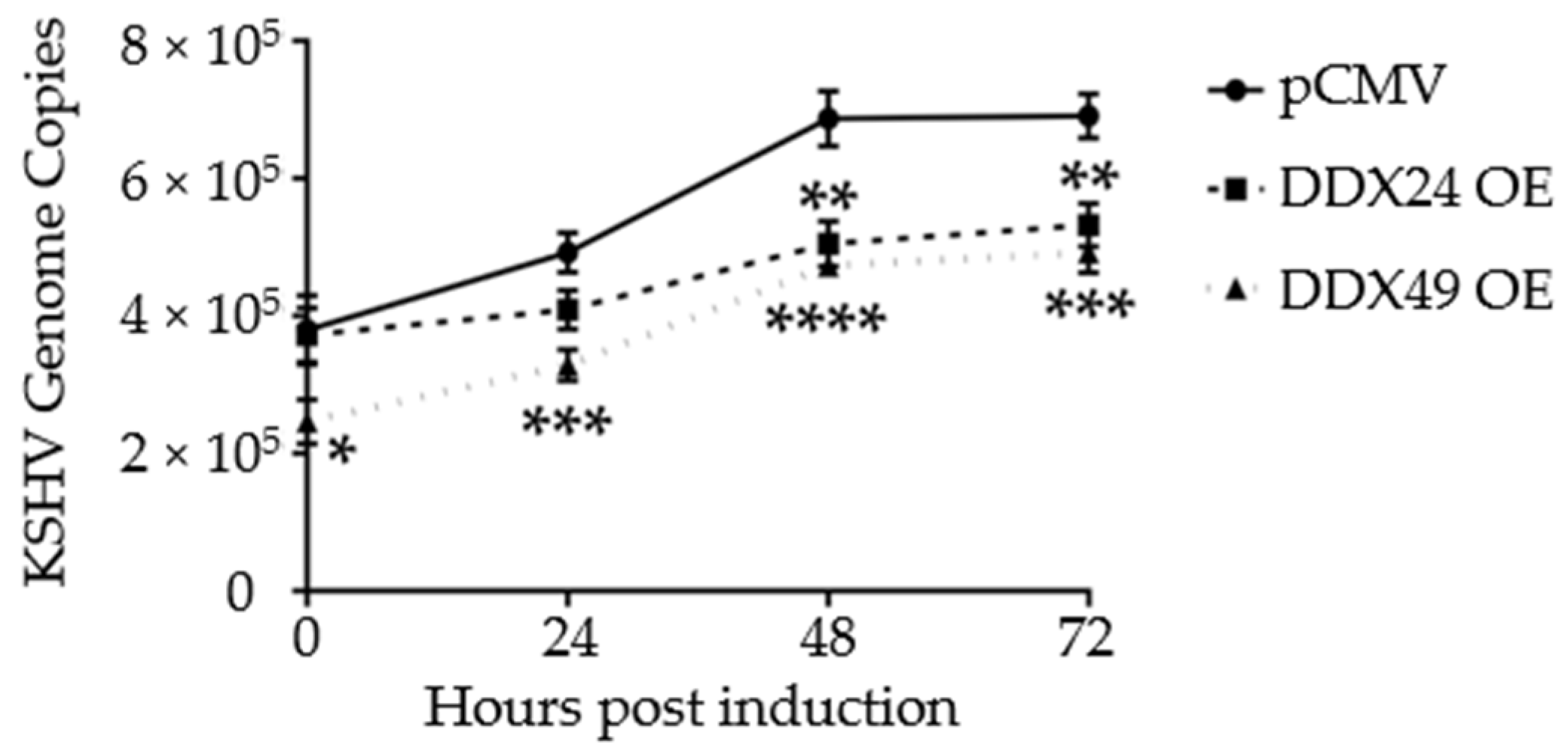
3.3. Effects of DDX24-DDK and DDX49-DDK on KSHV Gene Expression following Induction
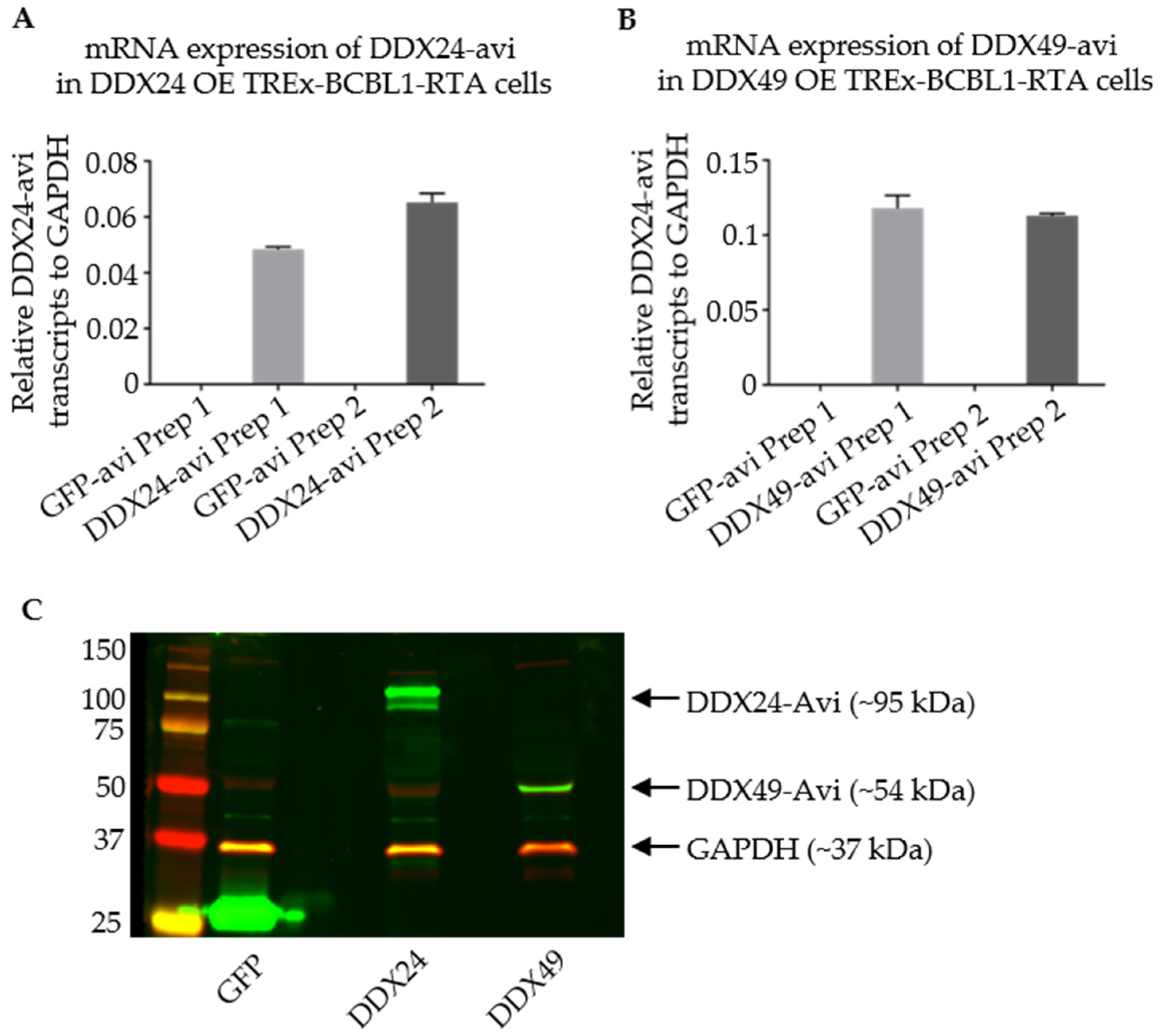
3.4. Stably Transduced TREx BCBL1-Rta Cells Expressing DDX24-Avi and DDX49-Avi
3.5. RNA Immunoprecipitation of TREx BCBL1-Rta Cells
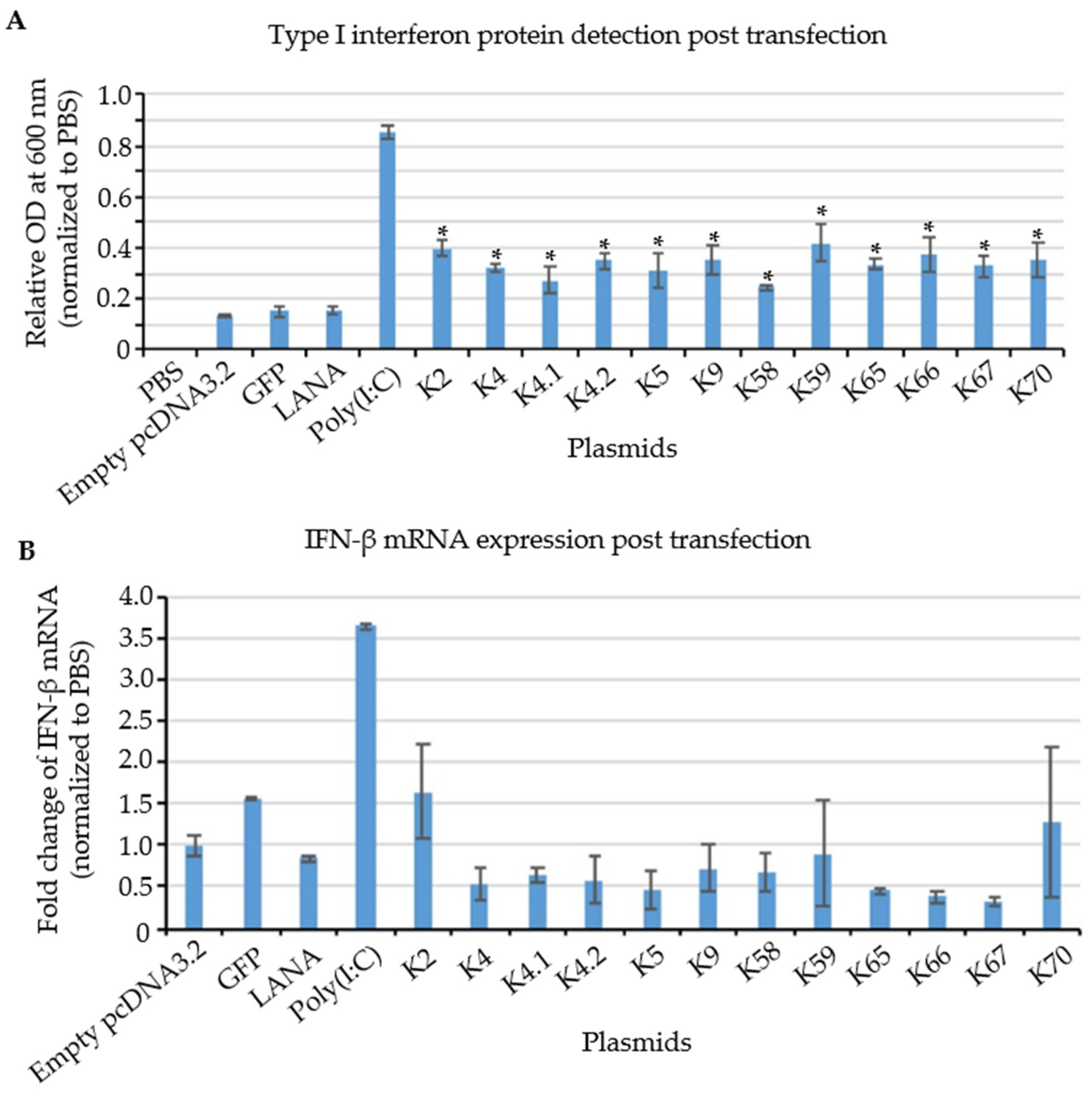
3.6. Testing of Cloned KSHV Genes for Their Ability to Induce a Type I Interferon Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harley, J.B.; Chen, X.; Pujato, M.; Miller, D.; Maddox, A.; Forney, C.; Magnusen, A.F.; de la Cruz-Lynch, A.; Chetal, K.; Yukawa, M.; et al. Transcription factors operate across disease loci, with EBNA2 implicated in autoimmunity. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesri, E.A.; Cesarman, E.; Boshoff, C. Kaposi’s sarcoma and its associated herpesvirus. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute DoEA. Investigation of the Transmission of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus 2017. Available online: https://deainfo.nci.nih.gov/advisory/joint/1117/07-Huppi.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- The American Cancer Society. Kaposi Sarcoma, Atlanta, GA, USA. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/kaposi-sarcoma/about/what-is-key-statistics.html (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Jha, H.C.; Banerjee, S.; Robertson, E.S. The Role of Gammaherpesviruses in Cancer Pathogenesis. Pathogens 2016, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Cesarman, E.; Pessin, M.S.; Lee, F.; Culpepper, J.; Knowles, D.M.; Moore, P.S. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Science 1994, 266, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renne, R.; Zhong, W.; Herndier, B.; Mcgrath, M.; Abbey, N.; Kedes, D.; Ganem, D. Lytic growth of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) in culture. Nat Med. 1996, 2, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukac, D.M.; Yuan, Y. Reactivation and lytic replication of KSHV. In Human Herpesviruses: Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis; Arvin, A., Campadelli-Fiume, G., Mocarski, E., Moore, P.S., Roizman, B., Whitley, R., Yamanishi, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Giffin, L.; West, J.A.; Damania, B. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Interleukin-6 Modulates Endothelial Cell Movement by Upregulating Cellular Genes Involved in Migration. MBio 2015, 6, e01499-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuconati, A.; White, E. Viral homologs of BCL-2: Role of apoptosis in the regulation of virus infection. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2465–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, S.M.; West, J.A.; Dillon, P.J.; Hilscher, C.; Dittmer, D.P.; Damania, B. Toll-like receptor signaling controls reactivation of KSHV from latency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11725–11730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.A.; Wicks, M.; Gregory, S.M.; Chugh, P.; Jacobs, S.R.; Zhang, Z.; Host, K.M.; Dittmer, D.P.; Damania, B. An important role for mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein in the Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus life cycle. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5778–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inn, K.S.; Lee, S.H.; Rathbun, J.Y.; Wong, L.Y.; Toth, Z.; Machida, K.; Ou, J.H.J.; Jung, J.U. Inhibition of RIG-I-mediated signaling by Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded deubiquitinase ORF64. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10899–10904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ye, X.; Dunker, W.; Song, Y.; Karijolich, J. RIG-I like receptor sensing of host RNAs facilitates the cell-intrinsic immune response to KSHV infection. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathish, N.; Yuan, Y. Evasion and subversion of interferon-mediated antiviral immunity by Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: An overview. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10934–10944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-R.; Choi, U.Y.; Hwang, S.-W.; Kim, S.; Jung, A.J.U. Viral Inhibition of PRR-Mediated Innate Immune Response: Learning from KSHV Evasion Strategies. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dittmer, D.P.; Mieczkowski, P.A.; Host, K.M.; Fusco, W.G.; Duncan, J.A.; Damania, B. RIG-I Detects Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Transcripts in a RNA Polymerase III-Independent Manner. mBio 2018, 9, e00823-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zevini, A.; Olagnier, D.; Hiscott, J. Crosstalk between Cytoplasmic RIG-I and STING Sensing Pathways. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-J.; Li, W.; Shao, Y.; Avey, D.; Fu, B.; Gillen, J.; Hand, T.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Miley, W.; et al. Inhibition of cGAS DNA Sensing by a Herpesvirus Virion Protein. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 18, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, C.; Mortreux, F.; Auboeuf, D. The multiple functions of RNA helicases as drivers and regulators of gene expression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.L.; Khoshnevis, S.; Karbstein, K. Cofactor-dependent specificity of a DEAD-box protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2668–E2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallam, A.L.; Del Campo, M.; Gilman, B.; Sidote, D.J.; Lambowitz, A.M. Structural basis for RNA-duplex recognition and unwinding by the DEAD-box helicase Mss116p. Nature 2012, 490, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowsky, E.; Bowers, H. Remodeling of ribonucleoprotein complexes with DExH/D RNA helicases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 4181–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, A.; Bowie, A.G. Innate immune recognition of DNA: A recent history. Virology 2015, 479–480, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullam, A.; Schroder, M. DExD/H-box RNA helicases as mediators of anti-viral innate immunity and essential host factors for viral replication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steimer, L.; Klostermeier, D. RNA helicases in infection and disease. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 751–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, C.M.; Bevilacqua, P.C. Discriminating Self and Non-Self by RNA: Roles for RNA Structure, Misfolding, and Modification in Regulating the Innate Immune Sensor PKR. Accounts Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, N.; Linder, P. DExD/H Box RNA Helicases: From Generic Motors to Specific Dissociation Functions. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmoskaite, I.; Russell, R. DEAD-box proteins as RNA helicases and chaperones. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2011, 2, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, P.; Jankowsky, E. From unwinding to clamping—The DEAD box RNA helicase family. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairman-Williams, M.E.; Guenther, U.-P.; Jankowsky, E. SF1 and SF2 helicases: Family matters. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010, 20, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, A.A.; Jankowsky, E. DEAD-box helicases as integrators of RNA, nucleotide and protein binding. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ge, L.-L.; Li, P.-P.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.-J.; Sun, M.-X.; Huang, L.; Shen, Z.-Q.; Hu, X.-C.; Ishag, H.; et al. Cellular DDX3 regulates Japanese encephalitis virus replication by interacting with viral un-translated regions. Virology 2014, 449, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Luo, M.; Li, C.; Wang, H.X.; Huan, C.C.; Qu, Y.R.; Liao, Y.; Mao, X. (DEAD)-box RNA helicase 3 modulates NF-kappaB signal pathway by controlling the phosphorylation of PP2A-C subunit. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33197–33213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiente-Echeverría, F.; Hermoso, M.A.; Rifo, R.S. RNA helicase DDX3: At the crossroad of viral replication and antiviral immunity. Rev. Med Virol. 2015, 25, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Z.-J.; Ouyang, S. The emerging roles of the DDX41 protein in immunity and diseases. Protein Cell 2017, 8, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Moore, R.; Xu, X.; Barber, G.N. DDX24 Negatively Regulates Cytosolic RNA-Mediated Innate Immune Signaling. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.; O’Hearn, P.M. Use of the red fluorescent protein as a marker of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic gene expression. Virology 2004, 325, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Lu, M.; Gwack, Y.; Souvlis, J.; Zeichner, S.L.; Jung, J.U. Global changes in Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated virus gene expression patterns following expression of a tetracycline-inducible Rta transactivator. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 4205–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Bagdassarian, E.; Ali, M.A.M.; McFadden, G. Identification of host DEAD-box RNA helicases that regulate cellular tropism of oncolytic Myxoma virus in human cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, A.M.; Gale, M., Jr. RIG-I in RNA virus recognition. Virology 2015, 479–480, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gack, M.U. Mechanisms of RIG-I-Like Receptor Activation and Manipulation by Viral Pathogens. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5213–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, D.; Kovaleva, E.; Schatz, P.J. A minimal peptide substrate in biotin holoenzyme synthetase-catalyzed biotinylation. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, P.; Uppal, T.; Verma, S.C. Molecular Biology of KSHV Lytic Reactivation. Viruses 2015, 7, 116–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brulois, K.; Toth, Z.; Wong, L.Y.; Feng, P.; Gao, S.J.; Ensser, A.; Jung, J.U. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K3 and K5 ubiquitin E3 ligases have stage-specific immune evasion roles during lytic replication. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9335–9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hideshima, T.; Chauhan, D.; Teoh, G.; Raje, N.; Treon, S.P.; Tai, Y.T.; Shima, Y.; Anderson, K.C. Characterization of signaling cascades triggered by human interleukin-6 versus Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpes virus-encoded viral interleukin 6. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Majerciak, V.; Yamanegi, K.; Zheng, Z.M. Gene structure and expression of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF56, ORF57, ORF58, and ORF59. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11968–11981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, S.R.; Gregory, S.M.; West, J.A.; Wollish, A.C.; Bennett, C.L.; Blackbourn, D.J.; Heise, M.T.; Damania, B. The viral interferon regulatory factors of kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus differ in their inhibition of interferon activation mediated by toll-like receptor 3. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burýsek, L.; Yeow, W.S.; Lubyová, B.; Kellum, M.; Schafer, S.L.; Huang, Y.Q.; Pitha, P.M. Functional analysis of human herpesvirus 8-encoded viral interferon regulatory factor 1 and its association with cellular interferon regulatory factors and p300. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7334–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Genin, P.; Mamane, Y.; Sgarbanti, M.; Battistini, A., Jr.; Harrington, W.J.; Barber, G.N.; Hiscott, J. HHV-8 encoded vIRF-1 represses the interferon antiviral response by blocking IRF-3 recruitment of the CBP/p300 coactivators. Oncogene 2001, 20, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yagi, S.; Yamanaka, T.; Fujimuro, M. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF34 is essential for late gene expression and virus production. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidle, U.H.; Weissmann, C. The 5′-flanking region of a human IFN-α gene mediates viral induction of transcription. Nature 1983, 303, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Rong, L.; Zhou, Y.; Roy, B.B.; Lu, J.; Abrahamyan, L.; Mouland, A.J.; Pan, Q.; Liang, C. The requirement of the DEAD-box protein DDX24 for the packaging of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA. Virology 2008, 375, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedavalli, V.S.; Neuveut, C.; Chi, Y.-H.; Kleiman, L.; Jeang, K.-T. Requirement of DDX3 DEAD Box RNA Helicase for HIV-1 Rev-RRE Export Function. Cell 2004, 119, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gringhuis, S.I.; Hertoghs, N.; Kaptein, T.M.; Zijlstra-Willems, E.M.; Sarrami-Forooshani, R.; Sprokholt, J.K.; van Teijlingen, N.H.; Kootstra, N.A.; Booiman, T.; van Dort, K.A.; et al. HIV-1 blocks the signaling adaptor MAVS to evade antiviral host defense after sensing of abortive HIV-1 RNA by the host helicase DDX3. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Nishiyama, M.; Moroishi, T.; Yumimoto, K.; Nakayama, K.I. MDM2 Mediates Nonproteolytic Polyubiquitylation of the DEAD-Box RNA Helicase DDX24. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 3321–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocarski, E.S.; Upton, J.; Kaiser, W.J. Viral infection and the evolution of caspase 8-regulated apoptotic and necrotic death pathways. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 12, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, L.A.; Sethuraman, S.; Thomas, M.; Turner, P.C.; Renne, R. Modified Cross-Linking, Ligation, and Sequencing of Hybrids (qCLASH) Identifies Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus MicroRNA Targets in Endothelial Cells. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02138-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, W.L.; Kara, M.; Gay, L.A.; Sethuraman, S.; Wang, Y.; Nirmalan, S.; Esemenli, A.; Feswick, A.; Hoffman, B.A.; Renne, R.; et al. Identification of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 miRNA-mRNA hybrids reveals miRNA target conservation among gammaherpesviruses including host translation and protein modification machinery. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungerleider, N.; Bullard, W.; Kara, M.; Wang, X.; Roberts, C.; Renne, R.; Tibbetts, S.; Flemington, E.K. EBV miRNAs are potent effectors of tumor cell transcriptome remodeling in promoting immune escape. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Verma, M.; Mahesh, A.; Khan, M.I.K.; Govindaraju, G.; Rajavelu, A.; Chavali, P.L.; Chavali, S.; Dhayalan, A. DDX49 is an RNA helicase that affects translation by regulating mRNA export and the levels of pre-ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 6304–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, S.; Jackson, B.R.; Baquero-Perez, B.; Whitehouse, A. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF57 Protein: Exploiting All Stages of Viral mRNA Processing. Viruses 2013, 5, 1901–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Kim, Y.H.; Xiao, Y.; Du, Y.; Xie, Y.; Lee, K.K.; Feng, J.; Farhat, N.; Zhao, D.; Shu, S.; et al. A Herpesvirus Protein Selectively Inhibits Cellular mRNA Nuclear Export. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haecker, I.; Gay, L.A.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Morse, A.M.; McIntyre, L.M.; Renne, R. Ago HITS-CLIP expands understanding of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus miRNA function in primary effusion lymphomas. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, Y.; Jung, J.U.; Lu, C.; Gao, S.J. Genomewide mapping and screening of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) 3’ untranslated regions identify bicistronic and polycistronic viral transcripts as frequent targets of KSHV microRNAs. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ni, G.; Damania, B. ADAR1 Facilitates KSHV Lytic Reactivation by Modulating the RLR-Dependent Signaling Pathway. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| KSHV Gene | Phase | Expressed from Spliced mRNAs | KSHV Protein | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K2 | Immediate-Early | Yes | viral interleukin-6 (v-IL6) | activates JAK/STAT, MAPK, and Akt signaling pathways to regulate B-cell proliferation and KSHV reactivation | [44,46] |
| ORF70/K4/K4.1/K4.2 | Immediate-Early/Early | No | v-CCL3 (v-MIP-III), v-CCL3 (v-MIP-II) | ORF70: Govern the transition of the KSHV genome from latent to lytic phase. K4/K4.1: Homologs of cellular chemokines | [44] |
| K5 | Immediate-Early | Yes | Modulator of Immune Recognition (MIR2) | encodes for a ubiquitin E3 ligase that can degrade MHC-I molecules | [45] |
| ORF58 | Early | No | EBV BMRF2 homologue | A component of the tegument that interacts with the envelope | [47] |
| ORF59 | Early | Yes | DNA polymerase processivity factor, Cytomegalovirus (CMV) and EBV homolog | A viral DNA polymerase processivity factor required for lytic DNA replication | [47] |
| K9 (only in DDX49) | Early | No | vIRF1 | Homolog of cellular interferon regulatory factor | [48,49,50] |
| ORF65/66/67 (only in DDX49) | Early/Late | No | EBV BFRF2 | Required for virion production | [51] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serfecz, J.C.; Hong, Y.; Gay, L.A.; Shekhar, R.; Turner, P.C.; Renne, R. DExD/H Box Helicases DDX24 and DDX49 Inhibit Reactivation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma Associated Herpesvirus by Interacting with Viral mRNAs. Viruses 2022, 14, 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102083
Serfecz JC, Hong Y, Gay LA, Shekhar R, Turner PC, Renne R. DExD/H Box Helicases DDX24 and DDX49 Inhibit Reactivation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma Associated Herpesvirus by Interacting with Viral mRNAs. Viruses. 2022; 14(10):2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerfecz, Jacquelyn C., Yuan Hong, Lauren A. Gay, Ritu Shekhar, Peter C. Turner, and Rolf Renne. 2022. "DExD/H Box Helicases DDX24 and DDX49 Inhibit Reactivation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma Associated Herpesvirus by Interacting with Viral mRNAs" Viruses 14, no. 10: 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102083
APA StyleSerfecz, J. C., Hong, Y., Gay, L. A., Shekhar, R., Turner, P. C., & Renne, R. (2022). DExD/H Box Helicases DDX24 and DDX49 Inhibit Reactivation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma Associated Herpesvirus by Interacting with Viral mRNAs. Viruses, 14(10), 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102083







