Efficient Intravenous Tumor Targeting Using the αvβ6 Integrin-Selective Precision Virotherapy Ad5NULL-A20
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. In Vitro Assays
2.4. In Vivo Studies
2.5. Statistical Analyses
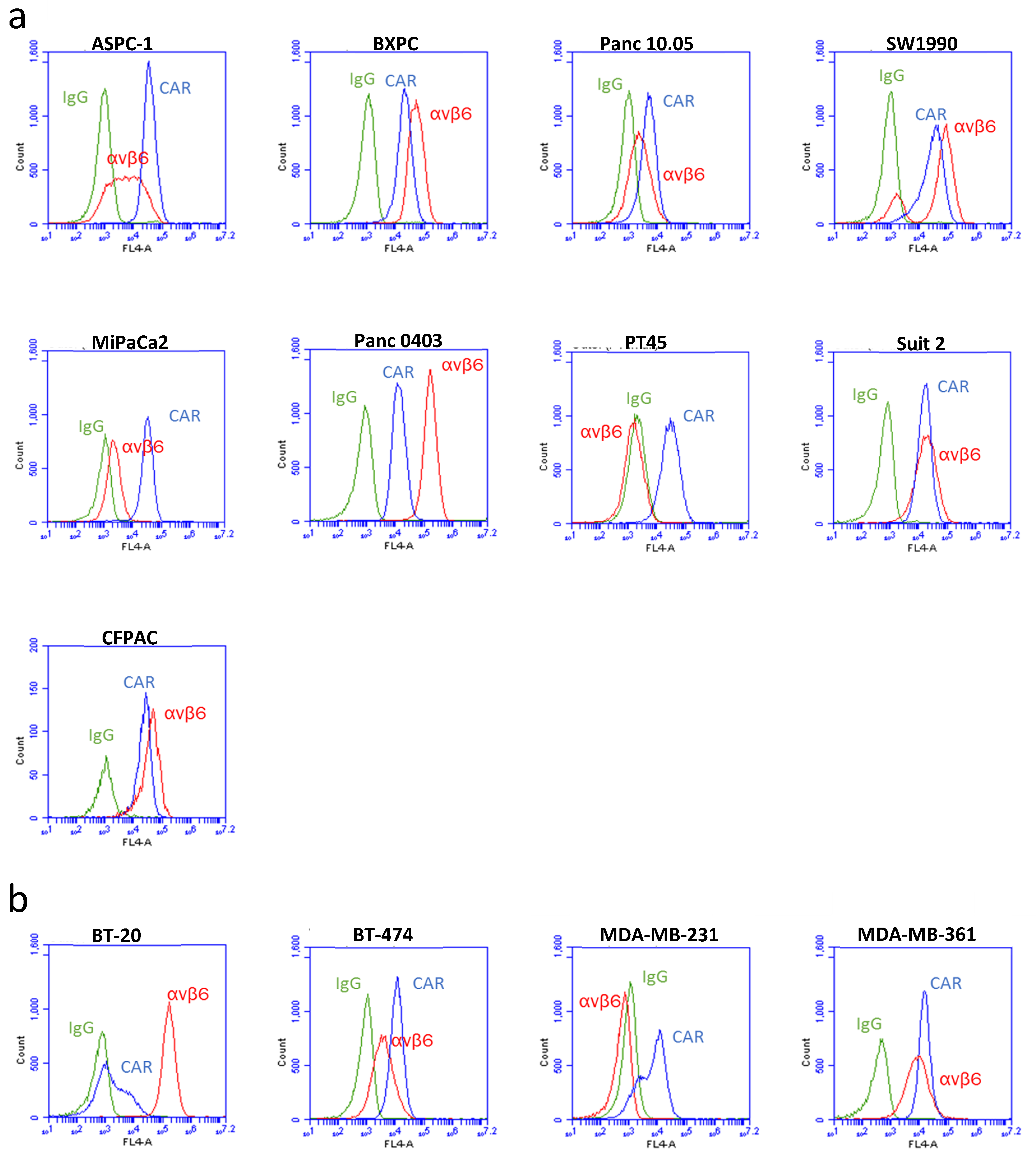
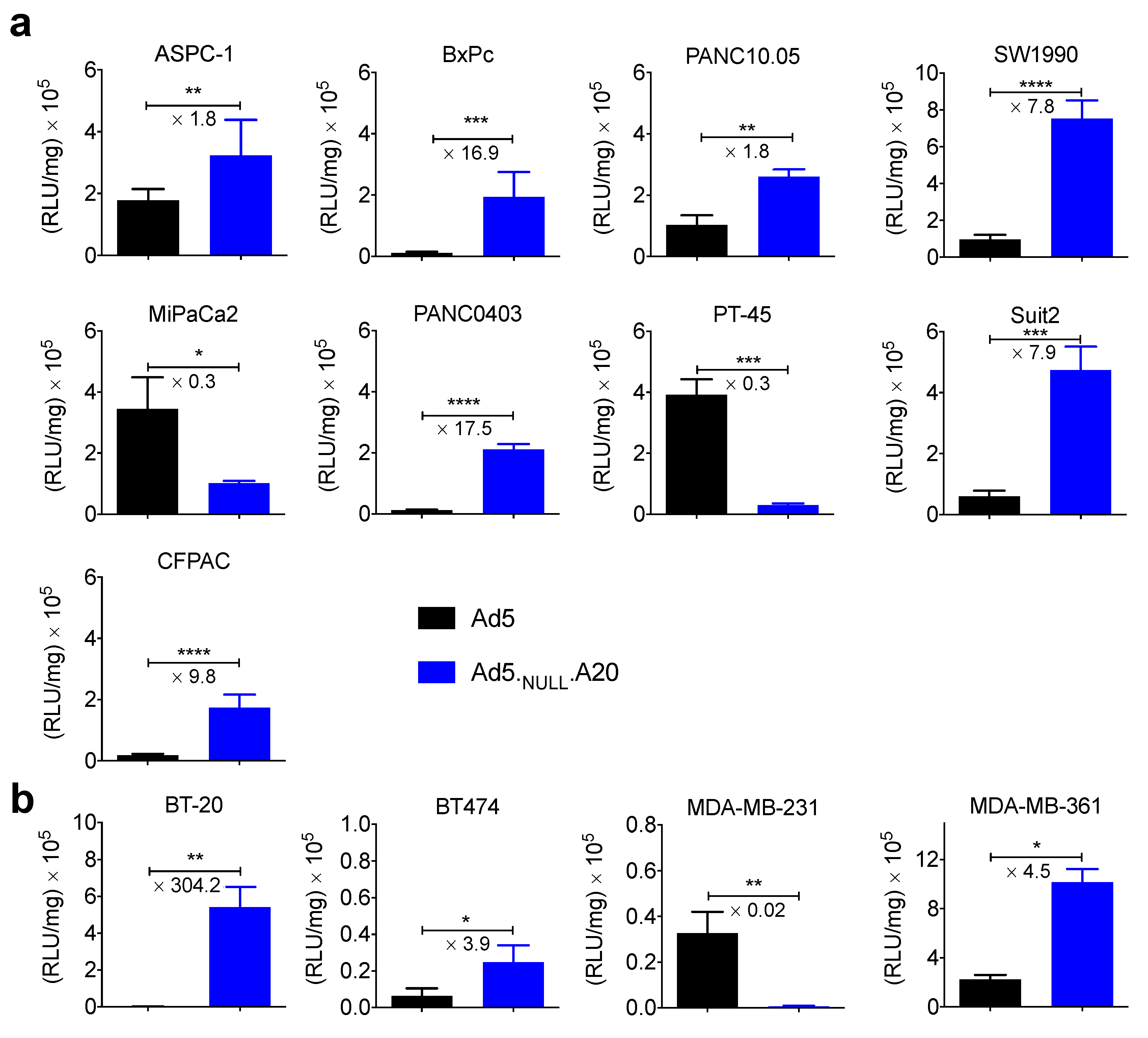
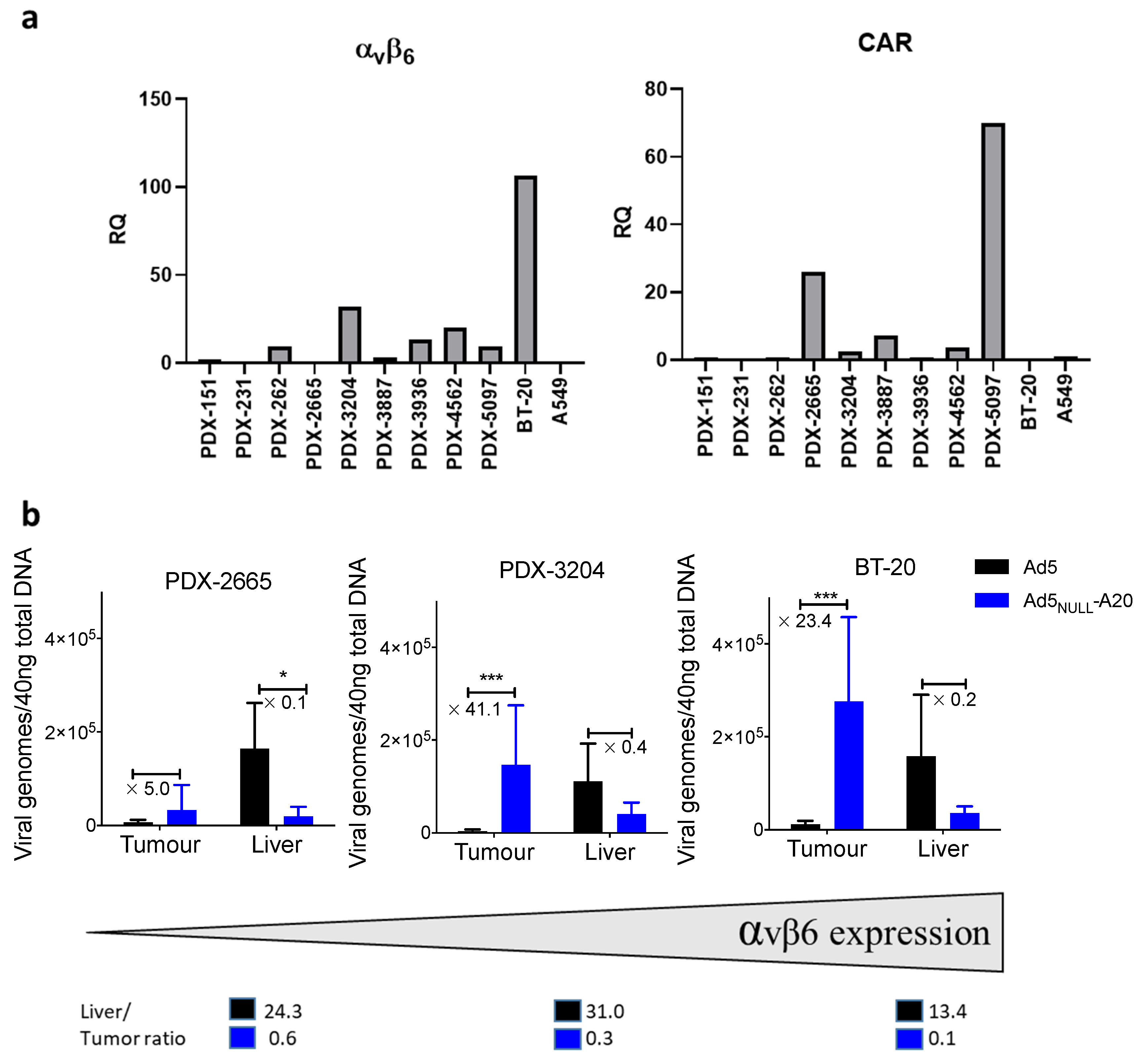
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rehman, H.; Silk, A.W.; Kane, M.P.; Kaufman, H.L. Into the clinic: Talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC), a first-in-class intratumoral oncolytic viral therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2016, 4, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, A.; Scott, K.J.; Taggart, D. Intravenous delivery of oncolytic reovirus to brain tumor patients immunologically primes for subsequent checkpoint blockade. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa, I.R.; Bustos-Villalobos, I.; Ichinose, T.; Matsumura, S.; Naoe, Y.; Miyajima, N.; Morimoto, D.; Mukoyama, N.; Zhiwen, W.; Tanaka, M.; et al. The Current Status and Future Prospects of Oncolytic Viruses in Clinical Trials against Melanoma, Glioma, Pancreatic, and Breast Cancers. Cancers 2018, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Carlisle, R. Achieving systemic delivery of oncolytic viruses. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Ernst, P.; Honegger, A.; Suomalainen, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Braun, L.; Stauffer, S.; Thom, C.; Dreier, B.; Eibauer, M.; et al. Adenoviral vector with shield and adapter increases tumor specificity and escapes liver and immune control. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemany, R. Cancer selective adenoviruses. Mol. Asp. Med. 2007, 28, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghi, M.; Martuza, R.L. Oncolytic viral therapies—The clinical experience. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7802–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganly, I.; Kirn, D.; Eckhardt, S.G.; Rodriguez, G.I.; Soutar, D.S.; Otto, R.; Kaye, S.B. A Phase I Study of Onyx-015, an E1B Attenuated Adenovirus, Administered Intratumorally to Patients with Recurrent Head and Neck Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 798–806. [Google Scholar]
- Lamont, J.P.; Nemunaitis, J.; Kuhn, J.A.; Landers, S.A.; McCarty, T.M. A prospective phase II trial of ONYX-015 adenovirus and chemotherapy in recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (the baylor experience). Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2000, 7, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.; Salama, H.; Abd El Latif Abu Median, A.; Isac Anis, I.; Abd Al Aziz, R.A.; Sarraf, C.; Mitry, R.; Havlik, R.; Seth, P.; Hartwigsen, J.; et al. Clinical trial of E1B-deleted adenovirus (dl1520) gene therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, O.; Varterasian, M.L.; Wadler, S.; Hecht, J.R.; Benson, A., 3rd; Galanis, E.; Uprichard, M.; Omer, C.; Bycott, P.; Hackman, R.C.; et al. Phase II trial of intravenous CI-1042 in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 1498–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, I.; Davison, E.; Beavil, A.J.; Soh, C.P.; Wickham, T.J.; Roelvink, P.W.; Kovesdi, I.; Sutton, B.J.; Santis, G. Identification of contact residues and definition of the CAR-binding site of adenovirus type 5 fiber protein. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2804–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, T.J.; Mathias, P.; Cheresh, D.A.; Nemerow, G.R. Integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5 promote adenovirus internalization but not virus attachment. Cell 1993, 73, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, K.; Koschel, A.; Rohwer, N.; Fischer, A.; Wiedenmann, B.; Anders, M. Downregulation of the coxsackie and adenovirus receptor in cancer cells by hypoxia depends on HIF-1alpha. Cancer Gene 2010, 17, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, R.C.; Di, Y.; Cerny, A.M.; Sonnen, A.F.; Sim, R.B.; Green, N.K.; Subr, V.; Ulbrich, K.; Gilbert, R.J.; Fisher, K.D.; et al. Human erythrocytes bind and inactivate type 5 adenovirus by presenting Coxsackie virus-adenovirus receptor and complement receptor 1. Blood 2009, 113, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiradake, E.; Henaff, D.; Wodrich, H.; Billet, O.; Perreau, M.; Hippert, C.; Mennechet, F.; Schoehn, G.; Lortat-Jacob, H.; Dreja, H.; et al. The Cell Adhesion Molecule “CAR” and Sialic Acid on Human Erythrocytes Influence Adenovirus In Vivo Biodistribution. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mast, T.C.; Kierstead, L.; Gupta, S.B.; Nikas, A.A.; Kallas, E.G.; Novitsky, V.; Mbewe, B.; Pitisuttithum, P.; Schechter, M.; Vardas, E.; et al. International epidemiology of human pre-existing adenovirus (Ad) type-5, type-6, type-26 and type-36 neutralizing antibodies: Correlates of high Ad5 titers and implications for potential HIV vaccine trials. Vaccine 2010, 28, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddington, S.N.; McVey, J.H.; Bhella, D.; Parker, A.L.; Barker, K.; Atoda, H.; Pink, R.; Buckley, S.M.K.; Greig, J.A.; Denby, L.; et al. Adenovirus Serotype 5 Hexon Mediates Liver Gene Transfer. Cell 2008, 132, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.L.; Waddington, S.N.; Nicol, C.G.; Shayakhmetov, D.M.; Buckley, S.M.; Denby, L.; Kemball-Cook, G.; Ni, S.; Lieber, A.; McVey, J.H.; et al. Multiple vitamin K-dependent coagulation zymogens promote adenovirus-mediated gene delivery to hepatocytes. Blood 2006, 108, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusi-Kerttula, H.; Davies, J.A.; Thompson, J.; Wongthida, P.; Evgin, L.; Shim, K.G.; Bradshaw, A.; Baker, A.T.; Rizkallah, P.J.; Jones, R.; et al. Ad5-NULL-A20—A tropism-modified, αvβ6 integrin-selective oncolytic adenovirus for epithelial ovarian cancer therapies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba, R.; Bradshaw, A.C.; Parker, A.L.; Bhella, D.; Waddington, S.N.; Nicklin, S.A.; van Rooijen, N.; Custers, J.; Goudsmit, J.; Barouch, D.H.; et al. Identification of coagulation factor (F)X binding sites on the adenovirus serotype 5 hexon: Effect of mutagenesis on FX interactions and gene transfer. Blood 2009, 114, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Idamakanti, N.; Kylefjord, H.; Rollence, M.; King, L.; Kaloss, M.; Kaleko, M.; Stevenson, S.C. In vivo hepatic adenoviral gene delivery occurs independently of the coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2002, 5, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusi-Kerttula, H.; Davies, J.; Coughlan, L.; Hulin-Curtis, S.; Jones, R.; Hanna, L.; Chester, J.D.; Parker, A.L. Pseudotyped alphavbeta6 integrin-targeted adenovirus vectors for ovarian cancer therapies. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27926–27937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiCara, D.; Burman, A.; Clark, S.; Berryman, S.; Howard, M.J.; Hart, I.R.; Marshall, J.F.; Jackson, T. Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Forms a Highly Stable, EDTA-Resistant Complex with Its Principal Receptor, Integrin αvβ6: Implications for Infectiousness. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, R.C. Colorectal cancer progression: Integrin alphavbeta6 and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tod, J.; Hanley, C.J.; Morgan, M.R.; Rucka, M.; Mellows, T.; Lopez, M.A.; Kiely, P.; Moutasim, K.A.; Frampton, S.J.; Sabnis, D.; et al. Pro-migratory and TGF-beta-activating functions of alphavbeta6 integrin in pancreatic cancer are differentially regulated via an Eps8-dependent GTPase switch. J. Pathol. 2017, 243, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.M.; Thomas, G.J.; Duffy, S.W.; Warwick, J.; Gabe, R.; Chou, P.; Ellis, I.O.; Green, A.R.; Haider, S.; Brouilette, K.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of integrin alphavbeta6 in breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, K.; Nair, M.G.; Prabhu, J.S.; Vinod, A.; Korlimarla, A.; Rajarajan, S.; Aiyappa, R.; Kaluve, R.S.; Alexander, A.; Hari, P.S.; et al. High expression of integrin beta6 in association with the Rho-Rac pathway identifies a poor prognostic subgroup within HER2 amplified breast cancers. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 2000–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, Y.K.S.; Davies, J.A.; Coughlan, L.; Pantelidou, C.; Blazquez-Moreno, A.; Marshall, J.F.; Parker, A.L.; Hallden, G. The Novel Oncolytic Adenoviral Mutant Ad5-3Delta-A20T Retargeted to alphavbeta6 Integrins Efficiently Eliminates Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberlein, C.; Kendrew, J.; McDaid, K.; Alfred, A.; Kang, J.S.; Jacobs, V.N.; Ross, S.J.; Rooney, C.; Smith, N.R.; Rinkenberger, J.; et al. A human monoclonal antibody 264RAD targeting alphavbeta6 integrin reduces tumour growth and metastasis, and modulates key biomarkers in vivo. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4406–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whilding, L.M.; Parente-Pereira, A.C.; Zabinski, T.; Davies, D.M.; Petrovic, R.M.G.; Kao, Y.V.; Saxena, S.A.; Romain, A.; Costa-Guerra, J.A.; Violette, S.; et al. Targeting of Aberrant alphavbeta6 Integrin Expression in Solid Tumors Using Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Engineered T Cells. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2017, 25, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, R.J.; McSharry, B.P.; Armstrong, M.; Tomasec, P.; Wilkinson, G.W. Re-engineering adenovirus vector systems to enable high-throughput analyses of gene function. BioTechniques 2008, 45, 659–662, 664–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fueyo, J.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Alemany, R.; Lee, P.S.; McDonnell, T.J.; Mitlianga, P.; Shi, Y.X.; Levin, V.A.; Yung, W.K.; Kyritsis, A.P. A mutant oncolytic adenovirus targeting the Rb pathway produces anti-glioma effect in vivo. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, A.; Martinez-Quintanilla, J.; Puig, C.; Guedan, S.; Mollevi, D.G.; Alemany, R.; Cascallo, M. Bioselection of a gain of function mutation that enhances adenovirus 5 release and improves its antitumoral potency. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8928–8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Claerhout, S.; Prat, A.; Dobrolecki, L.E.; Petrovic, I.; Lai, Q.; Landis, M.D.; Wiechmann, L.; Schiff, R.; Giuliano, M.; et al. A renewable tissue resource of phenotypically stable, biologically and ethnically diverse, patient-derived human breast cancer xenograft models. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4885–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worgall, S.; Wolff, G.; Falck-Pedersen, E.; Crystal, R.G. Innate immune mechanisms dominate elimination of adenoviral vectors following in vivo administration. Hum. Gene Ther. 1997, 8, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazan-Peregrino, M.; Carlisle, R.C.; Purdie, L.; Seymour, L.W. Factors influencing retention of adenovirus within tumours following direct intratumoural injection. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manickan, E.; Smith, J.S.; Tian, J.; Eggerman, T.L.; Lozier, J.N.; Muller, J.; Byrnes, A.P. Rapid Kupffer cell death after intravenous injection of adenovirus vectors. Mol. Ther. 2006, 13, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, K.; Schlitter, A.-M.; Weichert, W.; Esposito, I.; Wester, H.-J.; Notni, J. Perspective of αvβ6-Integrin Imaging for Clinical Management of Pancreatic Carcinoma and Its Precursor Lesions. Mol. Imaging 2017, 16, 1536012117709384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangi, A.; Zager, J.S. The safety of talimogene laherparepvec for the treatment of advanced melanoma. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2017, 16, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prill, J.-M.; Šubr, V.; Pasquarelli, N.; Engler, T.; Hoffmeister, A.; Kochanek, S.; Ulbrich, K.; Kreppel, F. Traceless Bioresponsive Shielding of Adenovirus Hexon with HPMA Copolymers Maintains Transduction Capacity In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e82716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Duffy, M.R.; Deng, L.; Dakin, R.S.; Uil, T.; Custers, J.; Kelly, S.M.; McVey, J.H.; Nicklin, S.A.; Baker, A.H. Manipulating Adenovirus Hexon Hypervariable Loops Dictates Immune Neutralisation and Coagulation Factor X-dependent Cell Interaction In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doronin, K.; Flatt, J.W.; Di Paolo, N.C.; Khare, R.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; Acchione, M.; Sumida, J.P.; Ohto, U.; Shimizu, T.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; et al. Coagulation factor X activates innate immunity to human species C adenovirus. Science 2012, 338, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davies, J.A.; Marlow, G.; Uusi-Kerttula, H.K.; Seaton, G.; Piggott, L.; Badder, L.M.; Clarkson, R.W.E.; Chester, J.D.; Parker, A.L. Efficient Intravenous Tumor Targeting Using the αvβ6 Integrin-Selective Precision Virotherapy Ad5NULL-A20. Viruses 2021, 13, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050864
Davies JA, Marlow G, Uusi-Kerttula HK, Seaton G, Piggott L, Badder LM, Clarkson RWE, Chester JD, Parker AL. Efficient Intravenous Tumor Targeting Using the αvβ6 Integrin-Selective Precision Virotherapy Ad5NULL-A20. Viruses. 2021; 13(5):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050864
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavies, James A., Gareth Marlow, Hanni K. Uusi-Kerttula, Gillian Seaton, Luke Piggott, Luned M. Badder, Richard W. E. Clarkson, John D. Chester, and Alan L. Parker. 2021. "Efficient Intravenous Tumor Targeting Using the αvβ6 Integrin-Selective Precision Virotherapy Ad5NULL-A20" Viruses 13, no. 5: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050864
APA StyleDavies, J. A., Marlow, G., Uusi-Kerttula, H. K., Seaton, G., Piggott, L., Badder, L. M., Clarkson, R. W. E., Chester, J. D., & Parker, A. L. (2021). Efficient Intravenous Tumor Targeting Using the αvβ6 Integrin-Selective Precision Virotherapy Ad5NULL-A20. Viruses, 13(5), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050864






