Vaccination with Prion Peptide-Displaying Polyomavirus-Like Particles Prolongs Incubation Time in Scrapie-Infected Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies and Prion Protein
2.2. Construction of Expression Plasmids
2.3. Generation, Purification and Electron Microscopy Analysis of Chimeric and Pseudotype Virus-Like Particles (VLPs)
2.4. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western Blot Analysis
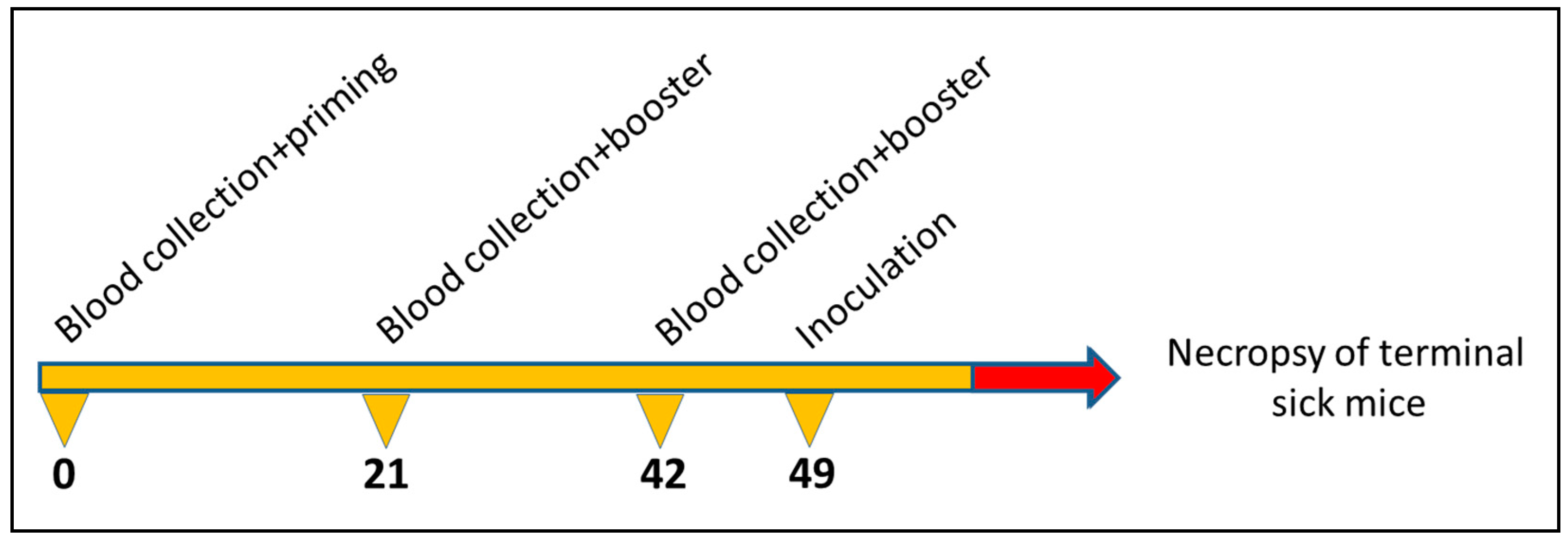
2.5. Propagation of Scrapie Strain and Immunisation Scheme
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biochemical and Electron-Microscopical Characterization of VLPs
3.2. Serological Analysis of VLP-Immunized Mice
3.3. In Vivo Efficacy of VLP Immunisation against Scrapie Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geschwind, M.D. Prion Diseases. Continuum (Minneap. Minn.) 2015, 21, 1612–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassmann, A.; Wolf, H.; Hofmann, J.; Graham, J.; Vorberg, I. Cellular aspects of prion replication in vitro. Viruses 2013, 5, 374–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, B.M.; Mabbott, N.A. Prion disease and the innate immune system. Viruses 2012, 4, 3389–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajj, G.N.M.; Lopes, M.H.; Mercadante, A.F.; Veiga, S.S.; Da Silveira, R.B.; Dos Santos, T.G.; Ribeiro, K.C.B.; Juliano, M.A.; Jacchieri, S.G.; Zanata, S.M.; et al. Cellular prion protein interaction with vitronectin supports axonal growth and is compensated by integrins. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, J.D.; Jackson, G.S.; Altmann, D.M. The role of the cellular prion protein in the immune system. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 146, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, L.; Nguyen, X.T.; Rolle, I.G.; D’Este, E.; Giachin, G.; Tran, T.H.; Šerbec, V.Č.; Cojoc, D.; Legname, G. Characterization of prion protein function by focal neurite stimulation. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 3878–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, N.; Herms, J. Cellular prion protein function in copper homeostasis and redox signalling at the synapse. J. Neurochem. 2003, 86, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.T.A.; Tran, T.H.; Cojoc, D.; Legname, G. Copper Binding Regulates Cellular Prion Protein Function. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 6121–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghetti, E.; Gasperini, L.; Virgilio, T.; Moda, F.; Tagliavini, F.; Benetti, F.; Legname, G. Prions Strongly Reduce NMDA Receptor S-Nitrosylation Levels at Pre-symptomatic and Terminal Stages of Prion Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 6035–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperini, L.; Meneghetti, E.; Pastore, B.; Benetti, F.; Legname, G. Prion protein and copper cooperatively protect neurons by modulating NMDA receptor through S-nitrosylation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caughey, B.; Ernst, D.; Race, R.E. Congo red inhibition of scrapie agent replication. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 6270–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caughey, B.; Raymond, G.J. Sulfated polyanion inhibition of scrapie-associated PrP accumulation in cultured cells. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangé, A.; Milhavet, O.; McMahon, H.E.; Casanova, D.; Lehmann, S. Effect of amphotericin B on wild-type and mutated prion proteins in cultured cells: Putative mechanism of action in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoungoure, V.L.; Schluesener, J.; Moundipa, P.F.; Schluesener, H. Natural polyphenols binding to amyloid: A broad class of compounds to treat different human amyloid diseases. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiden, M.; Leidel, F.; Strohmeier, B.; Fast, C.; Groschup, M.H. A Medicinal Herb Scutellaria lateriflora Inhibits PrP Replication in vitro and Delays the Onset of Prion Disease in Mice. Front. Psychiatry. 2012, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caughey, W.S.; Priola, S.A.; Kocisko, D.A.; Raymond, L.D.; Ward, A.; Caughey, B. Cyclic tetrapyrrole sulfonation, metals, and oligomerization in antiprion activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3887–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Gever, J.; Rao, S.; Widjaja, K.; Prusiner, S.B.; Silber, B.M. Discovery and Preliminary SAR of Arylpiperazines as Novel, Brainpenetrant Antiprion Compounds. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidel, F.; Eiden, M.; Geissen, M.; Hirschberger, T.; Tavan, P.; Giese, A.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Schätzl, H.; Groschup, M.H. Piperazine derivatives inhibit PrP/PrP(res) propagation in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 445, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korth, C.; May, B.C.; Cohen, F.E.; Prusiner, S.B. Acridine and phenothiazine derivatives as pharmacotherapeutics for prion disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9836–9841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Noor, A.; Zerr, I. Therapies for prion diseases. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 165, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski, M.J.; Pankiewicz, J.; Prelli, F.; Scholtzova, H.; Spinner, D.S.; Kascsak, R.B.; Kascsak, R.J.; Wisniewski, T. Anti-PrP Mab 6D11 suppresses PrP(Sc) replication in prion infected myeloid precursor line FDC-P1/22L and in the lymphoreticular system In Vivo. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 34, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdsson, E.M.; Sy, M.-S.; Li, R.; Scholtzova, H.; Kascsak, R.J.; Kascsak, R.; Carp, R.; Meeker, H.C.; Frangione, B.; Wisniewski, T. Anti-Prion antibodies for prophylaxis following prion exposure in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 336, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.R.; Enever, P.; Tayebi, M.; Mushens, R.; Linehan, J.; Brandner, S.; Anstee, D.; Collinge, J.; Hawke, S. Monoclonal antibodies inhibit prion replication and delay the development of prion disease. Nature 2003, 422, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, R.R.; Sonati, T.; Hornemann, S.; Herrmann, U.S.; Arand, M.; Hawke, S.; Aguzzi, A. Differential Toxicity of Antibodies to the Prion Protein. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, J. Immunotherapy against Prion Disease. Pathogens 2020, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, S. Prospects for preventative vaccines against prion diseases. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diederich, S.; Gedvilaite, A.; Zvirbliene, A.; Kazaks, A.; Sasnauskas, K.; Johnson, N.; Ulrich, R.G. Virus-like particles: A versatile tool for basic and applied research on emerging and reemerging viruses. In Viral Nanotechnology; Khudyakov, Y., Pumpens, P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sasnauskas, K.; Buzaite, O.; Vogel, F.; Jandrig, B.; Razanskas, R.; Staniulis, J.; Scherneck, S.; Krüger, D.H.; Ulrich, R. Yeast cells allow high-level expression and formation of polyomavirus-like particles. Biol. Chem. 1999, 380, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedvilaite, A.; Frömmel, C.; Sasnauskas, K.; Micheel, B.; Ozel, M.; Behrsing, O.; Staniulis, J.; Jandrig, B.; Scherneck, S.; Ulrich, R. Formation of immunogenic virus-like particles by inserting epitopes into surface-exposed regions of hamster polyomavirus major capsid protein. Virology 2000, 273, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandrig, B.; Krause, H.; Zimmermann, W.; Vasiliunaite, E.; Gedvilaite, A.; Ulrich, R.G. Hamster polyomavirus research: Past, present and future. Viruses 2021. under revision. [Google Scholar]
- Gedvilaite, A.; Zvirbliene, A.; Staniulis, J.; Sasnauskas, K.; Kruger, D.H.; Ulrich, R. Segments of Puumala hantavirus nucleocapsid protein inserted into chimeric polyomavirus-derived virus-like particles induce a strong immune response in mice. Viral Immunol. 2004, 17, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zvirbliene, A.; Samonskyte, L.; Gedvilaite, A.; Voronkova, T.; Ulrich, R.; Sasnauskas, K. Generation of monoclonal antibodies of desired specificity using chimeric polyomavirus-derived virus-like particles. J. Immunol. Methods 2006, 311, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zvirbliene, A.; Kucinskaite-Kodze, I.; Razanskiene, A.; Petraityte-Burneikiene, R.; Klempa, B.; Ulrich, R.G.; Gedvilaite, A. The use of chimeric virus-like particles harbouring a segment of hantavirus Gc glycoprotein to generate a broadly-reactive hantavirus-specific monoclonal antibody. Viruses 2014, 6, 640–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasickiene, R.; Gedvilaite, A.; Norkiene, M.; Simanaviciene, V.; Sezaite, I.; Dekaminaviciute, D.; Shikova, E.; Zvirbliene, A. The use of recombinant pseudotype virus-like particles harbouring inserted target antigen to generate antibodies against cellular marker p16INK4A. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 263737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleckaityte, M.; Zvirbliene, A.; Sezaite, I.; Gedvilaite, A. Production in yeast of pseudotype virus-like particles harboring functionally active antibody fragments neutralizing the cytolytic activity of vaginolysin. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleckaityte, M.; Bremer, C.M.; Gedvilaite, A.; Kucinskaite-Kodze, I.; Glebe, D.; Zvirbliene, A. Construction of polyomavirus-derived pseudotype virus-like particles displaying a functionally active neutralizing antibody against hepatitis B virus surface antigen. BMC Biotechnol. 2015, 15, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawatscheck, R.; Aleksaite, E.; Schenk, J.A.; Micheel, B.; Jandrig, B.; Holland, G.; Sasnauskas, K.; Gedvilaite, A.; Ulrich, R.G. Chimeric polyomavirus-derived virus-like particles: The immunogenicity of an inserted peptide applied without adjuvant to mice depends on its insertion site and its flanking linker sequence. Viral Immunol. 2007, 20, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazeike, E.; Gedvilaite, A.; Blohm, U. Induction of insert-specific immune response in mice by hamster polyomavirus VP1 derived virus-like particles carrying LCMV GP33 CTL epitope. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Norkiene, J.; Stonyte, D.; Ziogiene, E.; Mazeike, K.; Sasnauskas, A.; Gedvilaite, M. Production of recombinant VP1-derived virus-like particles from novel human polyomaviruses in yeast. BMC Biotechnol. 2015, 15, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gretzschel, A.; Buschmann, A.; Eiden, M.; Ziegler, U.; Luhken, G.; Erhardt, G.; Groschup, M.H. Strain typing of German transmissible spongiform encephalopathies field cases in small ruminants by biochemical methods. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2005, 52, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiden, M.; Palm, G.J.; Hinrichs, W.; Matthey, U.; Zahn, R.; Groschup, M.H. Synergistic and strain-specific effects of bovine spongiform encephalopathy and scrapie prions in the cell-free conversion of recombinant prion protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3753–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, R.L. Encephalopathy in mice produced by inoculation with scrapie brain material. Lancet 1961, 1, 1378–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepeda-Cervantes, J.; Ramírez-Jarquín, J.O.; Vaca, L. Interaction Between Virus-Like Particles (VLPs) and Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) from Dendritic Cells (DCs): Toward Better Engineering of VLPs. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabel, M.D.; Avery, A.C. Prions--not your immunologist’s pathogen. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczius, T.; Groschup, M.H. Differences in proteinase K resistance and neuronal deposition of abnormal prion proteins characterize bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) and scrapie strains. Mol. Med. 1999, 5, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatzel, M.; Heppner, F.L.; Albers, K.M.; Aguzzi, A. Sympathetic innervation of lymphoreticular organs is rate limiting for prion neuroinvasion. Neuron 2001, 31, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handisurya, A.; Gilch, S.; Winter, D.; Shafti-Keramat, S.; Maurer, D.; Schätzl, H.M.; Kirnbauer, R. Vaccination with prion peptide-displaying papillomavirus-like particles induces autoantibodies to normal prion protein that interfere with pathologic prion protein production in infected cells. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 1747–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikles, D.; Bach, P.; Boller, K.; Merten, C.A.; Montrasio, F.; Heppner, F.L.; Aguzzi, A.; Cichutek, K.; Kalinke, U.; Buchholz, C.J. Circumventing tolerance to the prion protein (PrP): Vaccination with PrP-displaying retrovirus particles induces humoral immune responses against the native form of cellular PrP. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 4033–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Kratke, O.; Burwinkel, M.; Riemer, C.; Schultz, J.; Henklein, P.; Bamme, T.; Baier, M. Immunisation with a synthetic prion protein-derived peptide prolongs survival times of mice orally exposed to the scrapie agent. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 350, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulos, K.; Lagoudaki, R.; Kontana, A.; Kyratsous, C.; Panagiotidis, C.; Grigoriadis, N.; Yiangou, M.; Sklaviadis, T. Immunisation with recombinant prion protein leads to partial protection in a murine model of TSEs through a novel mechanism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, G.; Clerici, M.; Dall’Ara, P.; Biasin, M.; Caramelli, M.; Casalone, C.; Giannino, M.L.; Longhi, R.; Piacentini, L.; Della Bella, S.; et al. Decrease in pathology and progression of scrapie after immunisation with synthetic prion protein peptides in hamsters. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2862–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachy, V.; Ballerini, C.; Gourdain, P.; Prignon, A.; Iken, S.; Antoine, N.; Rosset, M.; Carnaud, C. Mouse vaccination with dendritic cells loaded with prion protein peptides overcomes tolerance and delays scrapie. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilch, S.; Wopfner, F.; Renner-Muller, I.; Kremmer, E.; Bauer, C.; Wolf, E.; Brem, G.; Groschup, M.H.; Schatzl, H.M. Polyclonal anti-PrP auto-antibodies induced with dimeric PrP interfere efficiently with PrPSc propagation in prion-infected cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 18524–18531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser-Schulz, G.; Heit, A.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Hammerschmidt, F.; Hess, S.; Jennen, L.; Rezaei, H.; Wagner, H.; Schatzl, H.M. Polylactide-Coglycolide microspheres co-encapsulating recombinant tandem prion protein with CpG-oligonucleotide break self-tolerance to prion protein in wild-type mice and induce CD4 and CD8 T cell responses. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2797–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, D.H.; Thapa, S.; Abdulrahman, B.; Lu, L.; Jain, S.; Schatzl, H.M. Immunisation of cervidized transgenic mice with multimeric deer prion protein induces self-antibodies that antagonize chronic wasting disease infectivity in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, D.H.; Thapa, S.; Brandon, J.; Maybee, J.; Vankuppeveld, L.; McCorkell, R.; Schätzl, H.M. Recombinant prion protein vaccination of transgenic elk PrP mice and reindeer overcomes self-tolerance and protects mice against chronic wasting disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 19812–19822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wille, H.; Requena, J.R. The Structure of PrPSc Prions. Pathogens 2018, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretz, D.; Williamson, R.A.; Kaneko, K.; Vergara, J.; Leclerc, E.; Schmitt-Ulm, G.; Mehlhorn, I.R.; Legname, G.; Wormald, M.R.; Rudd, P.M.; et al. Antibodies inhibit prion propagation and clear cell cultures of prion infectivity. Nature 2001, 412, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrier, V.; Solassol, J.; Crozet, C.; Frobert, Y.; Mourton-Gilles, C.; Grassi, J.; Lehmann, S. Anti-PrP antibodies block PrPSc replication in prion-infected cell cultures by accelerating PrPC degradation. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
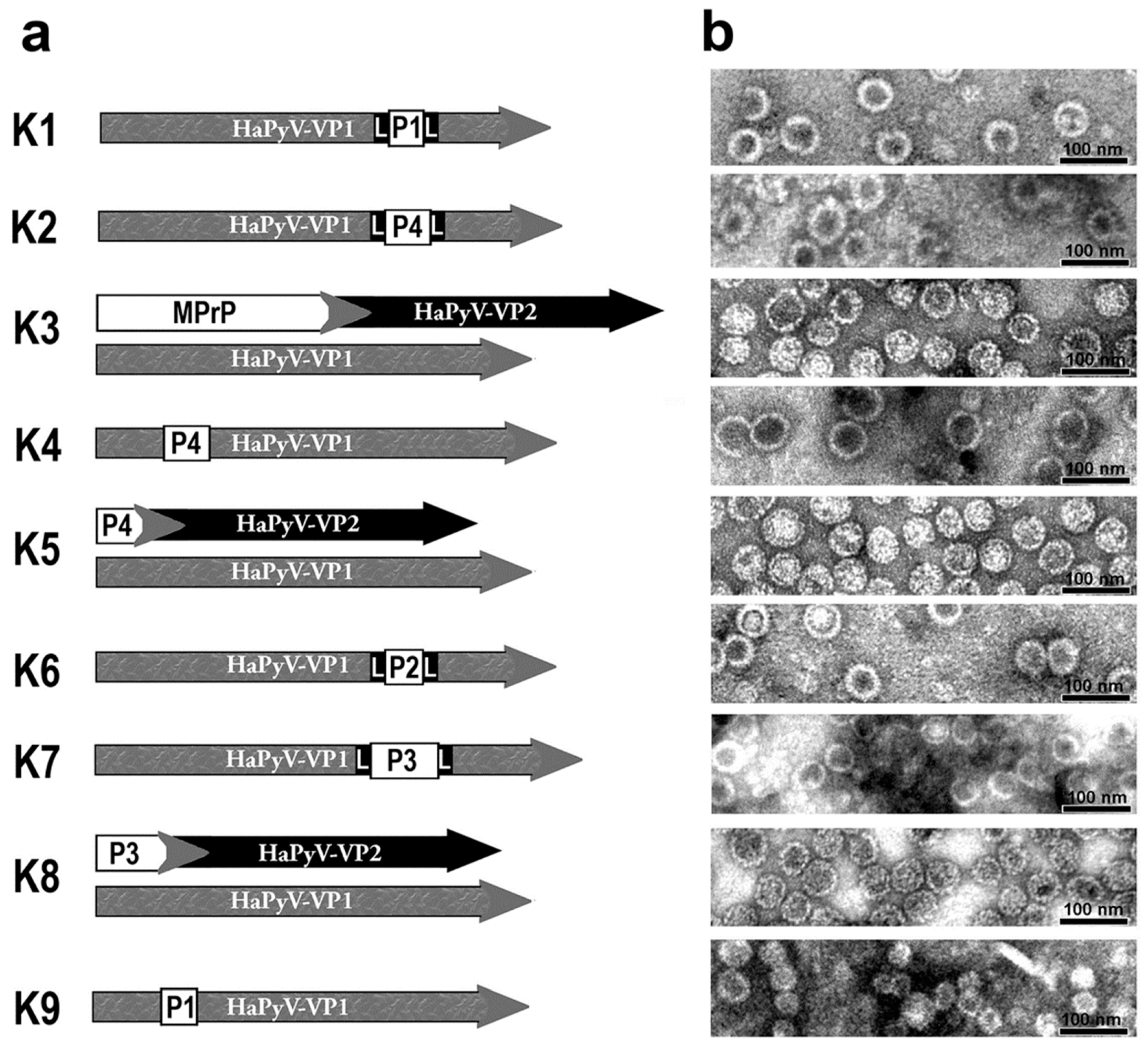
| Abbreviation | Plasmid | Expressed Protein | PrP Amino Acid Sequence * | Predicted Molecular Mass of Expressed Proteins [kDa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | pFX7-VP1-PrP1-4L | VP1-PrP1-4L | 128-164 | 47.5 |
| K2 | pFX7-VP1-PrP4-4L | VP1-PrP4-4L | 51-128 | 50.5 |
| K3 | pFGG3-VP1/VP2-MPrP | VP1 and VP2-MPrP | 23-231 | 42.55 and 52.5 |
| K4 | pFX7-VP1-PrP4-1 | VP1-PrP4-1 | 51-128 | 49.2 |
| K5 | pFGG3-VP1/VP2-PrP4 | VP1 and VP2-PrP4 | 51-128 | 42.5 and 37.0 |
| K6 | pFX7-VP1-PrP2-4L | VP1-PrP2-4L | 174-219 | 48.2 |
| K7 | pFX7-VP1-PrP3-4L | VP1-PrP3-4L | 128-219 | 64 |
| K8 | pFGG3-VP1/VP2-PrP3 | VP1 and VP2-PrP3 | 128-219 | 42.5 and 40.5 |
| K9 | pFX7-VP1-PrP1-1 | VP1-PrP1-1 | 128-164 | 46.3 |
| control | pFGG3-VP1/VP2 | VP1 and VP2 | - | 42.5 and 38.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eiden, M.; Gedvilaite, A.; Leidel, F.; Ulrich, R.G.; Groschup, M.H. Vaccination with Prion Peptide-Displaying Polyomavirus-Like Particles Prolongs Incubation Time in Scrapie-Infected Mice. Viruses 2021, 13, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050811
Eiden M, Gedvilaite A, Leidel F, Ulrich RG, Groschup MH. Vaccination with Prion Peptide-Displaying Polyomavirus-Like Particles Prolongs Incubation Time in Scrapie-Infected Mice. Viruses. 2021; 13(5):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050811
Chicago/Turabian StyleEiden, Martin, Alma Gedvilaite, Fabienne Leidel, Rainer G. Ulrich, and Martin H. Groschup. 2021. "Vaccination with Prion Peptide-Displaying Polyomavirus-Like Particles Prolongs Incubation Time in Scrapie-Infected Mice" Viruses 13, no. 5: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050811
APA StyleEiden, M., Gedvilaite, A., Leidel, F., Ulrich, R. G., & Groschup, M. H. (2021). Vaccination with Prion Peptide-Displaying Polyomavirus-Like Particles Prolongs Incubation Time in Scrapie-Infected Mice. Viruses, 13(5), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050811






