Abstract
While current therapies for chronic HBV infection work well to control viremia and stop the progression of liver disease, the preferred outcome of therapy is the restoration of immune control of HBV infection, allowing therapy to be removed while maintaining effective suppression of infection and reversal of liver damage. This “functional cure” of chronic HBV infection is characterized by the absence of detectable viremia (HBV DNA) and antigenemia (HBsAg) and normal liver function and is the goal of new therapies in development. Functional cure requires removal of the ability of infected cells in the liver to produce the hepatitis B surface antigen. The increased observation of transaminase elevations with new therapies makes understanding the safety and therapeutic impact of these flares an increasingly important issue. This review examines the factors driving the appearance of transaminase elevations during therapy of chronic HBV infection and the interplay of these factors in assessing the safety and beneficial nature of these flares.
1. Introduction
Exposure to the hepatitis B virus (HBV) causes a predominantly hepatotropic infection, which in its acute state commonly causes liver inflammation and dysfunction and in its chronic state fibrosis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [1,2,3]. While >80% of people infected with HBV achieve immune control and self-resolve their infection, reactivation of latent infection [4] in the livers of these individuals can still occur with immunosuppressive therapy [5,6]. Unfortunately, HBV infection remains chronic in more than 292 million people worldwide [7] and is responsible for 870,000 deaths annually [8]. This chronic infection results from (1) the inhibition of the immune response to HBV via the maintenance of abundant circulating HBsAg by the production of a large excess of non-infectious subviral particles (SVP) over virions [9], (2) the ability of the HBV genome to form a closed covalent circular DNA (cccDNA) “minichromosome” that can reside inside the nucleus of infected cells in an inactive “latent” state [10] and (3) the integration of HBV DNA into the chromosomes of liver cells [11,12], which progresses with continued chronic infection, becoming a significant source of SVP [9,13,14,15].
The current challenge in the treatment of chronic HBV infection is to restore immune control allowing suppression of viral infection to be maintained in the absence of therapy, thereby allowing liver damage to regress and the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma to decline. This “functional cure” of chronic HBV infection requires the reconstitution of immune control and is characterized by the absence of circulating HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) without therapy [16,17,18,19,20]. Since HBsAg is almost entirely derived from SVP [9], establishing a functional cure of HBV infection requires not only clearing SVP from the blood but removing the SVP producing capacity in the liver by the silencing of cccDNA and the removal of hepatocytes with integrated HBV DNA [14,15].
Since the clearance of hepatocytes with integrated HBV DNA from the liver is a critical milestone in achieving functional cure, the resulting damage in the liver is also expected to result in elevations in serum concentrations of liver enzymes. This creates a clinical challenge as liver enzyme flares are known to occur with a variety of other liver diseases where they are associated with hepatoxicity. Given the current focus on achieving a functional cure of HBV with new therapeutic agents, this review explores how liver enzyme flares during the treatment of chronic HBV infection affect liver function and the potential utility of these flares to predict positive therapeutic outcomes.
2. Distribution of HBV Infection in the Liver
During acute (initial) infection, HBV infection appears infrequently in individual hepatocytes where HBsAg is located primarily in the cytoplasm [21]. These cells presumably also contain replicating virus. Transition to chronic infection (Figure 1) appears to be accompanied by translocation of HBsAg to the cell margins [21]. The number of cells in an initially infected liver is unknown, as symptoms of acute infection are considered to occur weeks to months after the initial infection event. In chronic infection, the bulk of infected cells in the liver are hepatocytes, but infection is also present to a lesser extent in the bile duct epithelium as well as endothelial and smooth muscle cells of hepatic blood vessels [22]. Scattered HBsAg positive hepatocytes are accompanied by HBcAg positivity approximately 70% of the time, and HBsAg is found both in the cytoplasm and at the cell margin [21,23]. With the transition from HBeAg positive to HBeAg negative infection, HBsAg distribution becomes mainly distributed in clusters of hepatocytes predominantly in the cytoplasm [24], in which HBcAg is less frequently detected (Figure 1). This clustered HBsAg+, HBcAg- pattern persists in inactive HBV infection with mostly cytoplasmic HBsAg localization [21,23]. These patterns are consistent with the progressive establishment of HBV infection in the liver during the natural history of HBV infection, with transition from individual hepatocytes producing virus and SVP to clusters of infected cells, which include hepatocytes containing only integrated HBV DNA and producing only SVP.
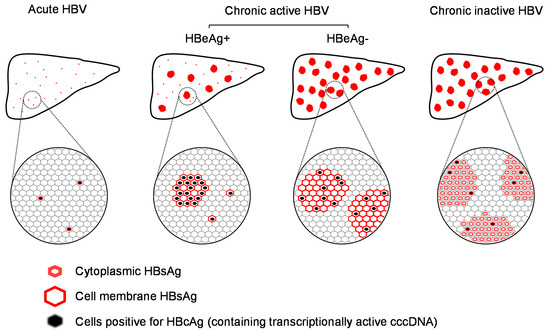
Figure 1.
Distribution of infection in the liver during the course of HBV infection.
In chronic HBV infection, numerous studies have confirmed the heterogenous pattern of infected hepatocytes in chronic HBV infection (Figure 1) where infection is spread intermittently throughout the liver in patches comprised entirely of infected cells [21,23,24,25,26,27,28] or in sparsely infected regions [21,24,25,27,29,30]. In many instances, HBsAg expression is detected in cells devoid of HBV DNA or HBcAg [26,28,31,32,33] (Figure 1), which signals the presence of cells containing integrated HBV DNA, producing HBsAg efficiently (as SVP) but not HBV pgRNA (and HBV DNA) or other viral antigens [11]. Based on the best available biopsy estimates, the extent of liver infection (cells containing either cccDNA or integrated HBV DNA) in chronic HBV infection varies from 35% [34] to 70% [21]. While these studies demonstrate the expansion of HBV infection throughout the liver, they also demonstrate the preservation of normal functioning hepatic tissue throughout the natural history of HBV infection.
3. Impact of HBV Infection on Hepatocyte Function
Although HBV infection is not directly cytopathic, HBV infection of hepatocytes is followed by extensive metabolic reprogramming. These effects are summarized in Table 1 and consist of alterations in lipid metabolism leading to intracellular lipid and cholesterol accumulation [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45], increased oxidative stress [39,46] and glucose metabolism [43,45], altered cell cycle regulation [44,47,48] and increased intracellular protein recycling [49,50,51]. HBV infection also sensitizes hepatocytes to apoptotic signaling [52,53]. These changes signal a reduction in the reservoir of normal liver infection driven by HBV replication in hepatocytes during acute and chronic HBV infection. These alterations may also be responsible in part for the reduced liver function observed with the expansion of HBV infection.

Table 1.
Impact of HBV infection on hepatocyte function.
4. The Molecular Basis of Liver Enzyme Elevations in the Blood
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), also known as glutamic–pyruvic transaminase (GPT), is a cytosolic enzyme involved in gluconeogenesis that catalyzes the amination of α-ketoglutarate from alanine to produce pyruvate and glutamate. In humans, two distinct ALT isozymes are produced from distinct but related genes, ALT1 and the more recently characterized ALT2 [54], which both contribute to ALT activity detected in standard blood testing [55]. These two ALT isozymes have different cellular and tissue distributions (Figure 2), with ALT1 most enriched in the liver (ER and cytoplasm) and ALT2 most enriched in skeletal muscle (ER and mitochondria) and absent in the liver [55,56,57]. Both ALT isozymes are present in human plasma [55,57], but most of the catalytic ALT activity detected in normal plasma appears to derived from ALT2 [55].
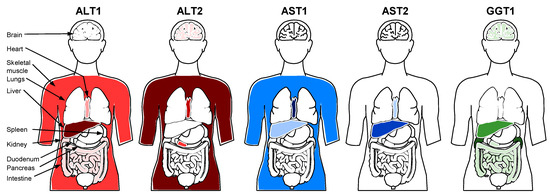
Figure 2.
Relative tissue expression of ALT, AST and GGT isozymes in humans.
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), also known as glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT), catalyzes the reversible transfer of an amino group between aspartate and glutamate. There are two AST isozymes dervied from distinct genes which produce the ALT forms found either in the cytoplasm (AST1) or mitochondria (AST2) [58]. These isozymes also have different tissue distributions (Figure 2): AST1 is found predominantly in the heart [59] and striated muscle [56], and AST2 is found predominantly in the liver [60].
γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT) cleaves the γ-glutamyl moiety from glutathione and transfers this moiety to a variety of acceptors (including water to form glutamate). There are two GGT genes (GGT 1 and GGT 2), each producing GGT precursor protein; however, only the GGT1 precursor undergoes autocleavage to become catalytically active [61]. GGT (GGT1) is membrane associated and primarily found in the kidneys (in proximal renal tubules) but also in significant levels in the liver in the biliary epithelial cells with lower levels present in the canicular and sinusoidal surfaces of hepatocytes [62,63,64] (Figure 2).
In subjects with previously characterized viral hepatitis, elevations of ALT, AST and GGT in the blood are driven by release of these enzymes from cells in the liver. This release can occur via rupture of plasma membrane blebs formed in response to cellular stress or inflammation [65], from cellular necrosis [66] or due to immune-mediated cellular damage [67,68]. Chronic HBV infection is accompanied by elevations of serum levels of ALT and AST [69], the latter of which is used to guide the initiation of antiviral therapy under current treatment guidelines for chronic HBV infection [70,71,72]. Elevations in GGT have also been linked to the progression of liver disease [73], mortality [74] and clinical outcomes from treatment of HBV infection [75]. Elevations in these enzymes during the natural course of HBV infection can be accompanied by alterations in the reservoir of liver synthetic and secretory function [76] reflected in increased serum bilirubin, decreased serum albumin, decreased platelet count and/or increased INR (biochemical flare). Although circulating ALT is not only derived from the liver, it is uniformly present in hepatocytes, and elevations observed during HBV infection are considered the most sensitive marker for cellular damage to hepatocytes.
5. Transaminase Flares and the Hepatic Reservoir during Natural History of HBV Infection
Definitions of clinically significant transaminase elevations including flares range from >2–5x the upper limit of normal (ULN) [77,78,79,80] or >3x higher than baseline levels [77,79]. All of these definitions have been shown to be associated with impacts on disease, indicating that all transaminase elevations should be regarded as clinically significant during the natural history or treatment of chronic HBV infection. ALT elevations can occur throughout the natural history of chronic HBV but are rarely accompanied by biochemical flare or by hepatic decompensation, which is characterized by severe biochemical flares accompanied by jaundice, ascites or encephalopathy, or signs of severe anticoagulation (easy bruising or bleeding) [81,82]. Elevations are more frequently observed in HBeAg positive infection [83,84], where they are preceded by increased viremia [85] and followed by increased immune activity [81,86,87,88,89,90,91], indicating that these flares are driven by immune-mediated damage/clearance of infected hepatocytes. Biochemical flare, hepatic decompensation and additional extrahepatic manifestations [92] accompanying ALT elevation (in up to 30% of cases) are mainly observed in acute HBV infection and HBeAg positive chronic infection [86] when HBV DNA exceeds 1.55 × 109 copies/mL (2.66 × 108 IU/mL) [93]. ALT elevations during the natural course of HBV infection are typically followed by declines in HBV DNA and/or HBeAg seroconversion [82,94] concomitant with a reduction in the activity and hepatic burden of covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA [95] and integrated HBV DNA [96].
From the initial establishment of HBV infection in the liver and its spread during the evolution of chronic HBV infection, elevations in liver enzymes are driven by hepatocyte damage and loss from: (1) the increased apoptotic sensitivity in hepatocytes resulting from HBV infection, (2) inflammation driven by the innate immune response to HBV infection and (3) specific targeting of infected hepatocytes by the HBV specific adaptive immune response, both B-cell [97] and T-cell mediated [91]. These effects drive reduction in the reservoir of normal hepatic function, fueling biochemical flare and decompensation. However, the liver has well-established regenerative properties [98,99,100,101] and clonal expansion of normal hepatocytes has been characterized throughout HBV infection [102,103], although the extent and rate of this clonal expansion has yet to be determined [12]. Thus, the available reservoir of normal liver function during the progression of HBV is governed by the balance of the loss of normally functioning hepatocytes due to HBV infection and the clearance of HBV infected hepatocytes with the restoration of normally functioning hepatocytes due to regeneration (Figure 3). In this context, ALT elevation accompanied by biochemical flare and/or hepatic decompensation likely reflects the expansion of viral infection and the accompanying hepatocyte loss from inflammation and immune-mediated clearance at a rate faster than can be compensated for by regeneration (Figure 4A). Host-mediated transaminase flares likely represent aspects of immune control of infection being established with the net removal of infected hepatocytes not impacting liver function (Figure 4B). However, without complete immunological control being established, even slow chronic HBV reinfection and hepatocyte turnover can lead to the development of fibrosis, which will eventually erode the reservoir of normally functioning hepatocytes, leading to biochemical flare and hepatic decompensation.
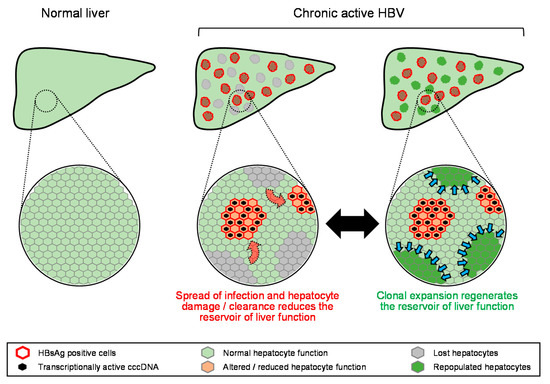
Figure 3.
Model for the equilibrium between loss and regeneration of the hepatic reservoir during chronic HBV infection. Red arrows indicate expansion of HBV infection, blue arrows indicate regeneration of normal hepatocytes.
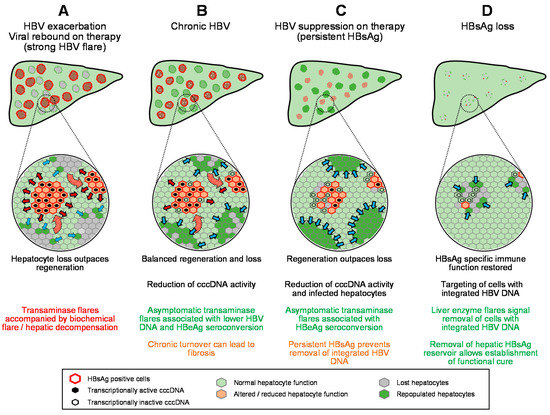
Figure 4.
Model for the impact of transaminase flares on the hepatic reservoir in the absence or presence of antiviral therapy (A–D). HB sAg loss. Red arrows indicate expansion of HBV infection, blue arrows indicate regeneration of normal hepatocytes.
6. Transaminase Flares during Therapy
The control of liver enzyme elevations is an important consideration during the management of chronic HBV infection as they can lead to hepatic decompensation, which is of special concern in patients with advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis who have only a fraction of the normal reservoir of hepatic function. As such, transaminase elevations, even if they may be beneficial, are generally recognized as an important indicator to initiate antiviral therapy to control liver dysfunction and the progression of liver disease. Current treatment guidelines with approved therapies [70,71,72] indicate the introduction of nucleos(t)ide analog inhibitors of the HBV reverse transcriptase (NUCs) only when chronic HBV infection is accompanied by HBV DNA > 2000 IU/mL and ALT elevation > ULN with the goal of providing long-term therapy for chronic suppression of infection. The use of pegylated interferon is also indicated for the treatment of chronic HBV infection with proper patient selection when the therapeutic goal is finite therapy leading to immunological control of infection (virologic response, as defined as normal ALT with HBV DNA < 2000 IU/mL).
6.1. Nucleos(t)ide Analogues
The guanine nucleoside analog entecavir (ETV), the adenosine nucleotide analog tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) and its more recent derivative tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) are the currently recommended NUC therapies [104] for the control of liver disease due to chronic HBV infection. These are bifunctional agents, having direct antiviral activity via inhibition of the HBV reverse transcriptase and indirect antiviral effect via the stimulation of innate immunity [105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112]. Transaminase flares observed during therapy with earlier generation NUCs such as lamivudine are typically associated with viral flare, and in some cases hepatic decompensation, as a result of the evolution of drug resistance to these early NUCs [113,114]. In these cases, a viral flare signals the expansion of infection in the liver and concomitant transaminase flares signal the removal of infected cells and/or cellular injury, resulting in net removal normal liver function at a pace greater than can be compensated for by regeneration (Figure 4A). The development of drug resistance to ETV and TDF/TAF is rare [115,116,117], and as a result, transaminase flares are less frequent with these NUCs but also not accompanied by biochemical flare or hepatic decompensation [79,114,118,119]. Flares during therapy with these later-generation NUCs are frequently associated with declines in HBV DNA, HBeAg seroconversion [79,119] and, in rarer instances, HBsAg loss [80,120], indicating an immunological basis for these flares. In these cases of transaminase flares during NUC-mediated HBV suppression, liver regeneration can match or outpace hepatocyte injury/infected hepatocyte loss (Figure 4C), preventing progression of fibrosis and hepatic decompensation.
6.2. Removal of NUC Therapy
Transaminase elevations often accompany removal of NUC therapy in HBeAg negative patients [121,122]. With older-generation NUCs such as lamivudine, these off-therapy flares were accompanied by biochemical flare and hepatic decompensation when HBV DNA levels were elevated [123,124]. Transaminase flares following withdrawal of TDF appear to occur earlier than withdrawal from ETV [125], but withdrawal from ETV or TDF is rarely accompanied by biochemical flare or hepatic decompensation [121,122,126,127]. Notwithstanding this, these host-mediated flares are not associated with sustained control of viremia, and re-treatment with NUCs is usually required [128].
6.3. Pegylated Interferon
Pegylated interferon (pegIFN) is a multifunctional immunotherapy that stimulates both innate [129,130] and adaptive immune responses [131,132] but also erodes T-cell function [131] as exposure increases. Transaminase flares are more frequently observed during pegIFN therapy than with NUCs and are driven either by viral flares which are more likely to be accompanied by biochemical flares and/or hepatic decompensation, or the host-mediated clearance of infected cells from the liver, which is followed by declines in HBV DNA [133,134] and has similar effects on the overall reservoir of liver function as observed with NUCs. Stronger host-mediated flares during pegIFN are associated with increased likelihood of HBV DNA decline, HBeAg seroconversion and increased rates of HBsAg loss and are not accompanied by biochemical flare or hepatic decompensation in non-cirrhotic patients [133,134,135,136,137,138,139].
6.4. Thymosin Alpha 1
Thymosin alpha 1 is synthetic form of a naturally occurring thymic peptide hormone that acts primarily as a T-cell agonist [140,141,142]. Treatment of chronic HBV infection with thymosin alpha 1 is also accompanied by transaminase flares, which either resolve during therapy [143] or appear and self-resolve after therapy [144] with no biochemical flare or hepatic decompensation and are associated with HBeAg seroconversion [143,144].
6.5. RNAi/Antisense
These oligonucleotide-based compounds are designed to target the cleavage of HBV mRNA via the RISC complex (in the case of RNAi) or via RNAse H (in the case of antisense). The specificity and activity of both these classes of oligonucleotides is strictly dependent on the perfect homology between the single-stranded (antisense) or double-stranded (RNAi) oligonucleotide and the target region of the mRNA. While in vivo data have been consistent with this mechanism, clinical studies with a variety of these compounds have indicated that off-target stimulation of innate immunity is playing a role in the clinical responses observed [9,145]. Limited data are available from ongoing trials with these compounds. However, the lipid-nanoparticle-formulated ARC-520 RNAi therapy was associated with mild transaminase flares during or after therapy, which self-resolved without biochemical flare or hepatic decompensation and in some cases were associated with declines in HBsAg [146]. Therapy with the GalNAc conjugated RNAi RG6346 (DCR-HBVS) was associated with transaminase flares in 3/6 participants at the 3 mg/kg dose in NUC-suppressed participants and accompanied by declines in HBV DNA and weaker declines in HBsAg [147].
6.6. Nucleic Acid Polymers
Nucleic acid polymers are broad spectrum antiviral agents [148] that selectively inhibit the assembly and secretion of HBV subviral particles without affecting secretion of HBeAg or virus [149,150]. Rapid and multilog HbsAg declines following NAP monotherapy in HBeAg positive infection are accompanied by strong, asymptomatic host-mediated transaminase flares, which are in turn accompanied by declines in HBV DNA, HBeAg seroconversion and HBsAg loss and seroconversion [151]. These flares are likely driven by rapid reduction in intrahepatic HBsAg, which restores innate immune function resulting in the clearance of infected cells and/or clearance of circulating HBsAg, which removes the exhaustion of the HBsAg-specific immune response, allowing the targeting of cells in the liver harboring both cccDNA and integrated HBV DNA [9]. In HBeAg negative co-infection with HDV, similar HBsAg declines are associated with much weaker host-mediated flares [152]. Introduction of pegIFN or thymosin alpha 1 greatly increases the strength and frequency of these host-mediated flares [151]. In the latest study of TDF, pegIFN and REP 2139 or REP 2165, 95% of participants experienced transaminase flares (ALT and AST) as well as GGT flares, all of which were host-mediated [153]. Recent analysis of the effects of these high rates of flares on therapeutic outcomes in this latest study indicated that transaminase flares occurring during HBsAg clearance were associated with partial or functional cure, while transaminase flares occurring in the presence of HBsAg were associated with viral rebound after removal of therapy [154]. In cases of transaminase flares with HBsAg loss, HBsAg-specific exhaustion is absent, suggesting that these transaminase flares are associated with removal of all HBsAg reactive hepatocytes, those with active cccDNA or with integrated HBV DNA (Figure 4D). Recent compassionate use of REP 2165 and TDF in a cirrhotic patient with HBV/HDV co-infection was accompanied by an early, host-mediated transaminase (ALT/AST) and GGT flare with no biochemical flare or hepatic decompensation [155].
6.7. Transaminase Flares during Therapy with Cirrhosis
The benefit/risk of transaminase flares in the presence of cirrhosis is an important consideration as cirrhotic patients represent a small but significant proportion of patients of HBV monoinfection [156], with faster onset and greater prevalence in HBV/HDV co-infection [157,158]. Flares are beneficial in cirrhotic patients with antiviral response to non-pegylated INF, but in the absence of an antiviral response, flares are frequently accompanied by severe hepatic decompensation leading to death or liver transplantation [29,159]. With pegIFN, transaminase flares associated with hepatic decompensation were less frequent but still more commonly found in cirrhotic patients [133]. In these cases, additional depletion of the already diminished hepatic reservoir by reduction in functional hepatocytes from expansion of infection or increased hepatocyte loss drives severe hepatic decompensation (Figure 5A).
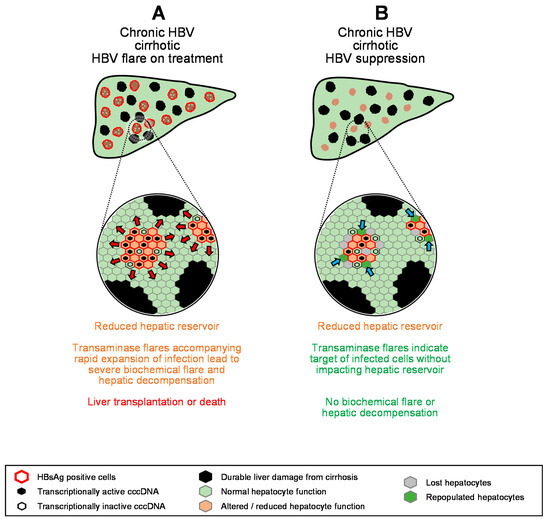
Figure 5.
Model for the impact of transaminase flares on the hepatic reservoir in cirrhotic patients (A,B). Red arrows indicate expansion of HBV infection, blue arrows indicate regeneration of normal hepatocytes.
However, recent data have demonstrated that transaminase flares are beneficial in cirrhotic patients who achieved HBV suppression on NUC therapy, with increased HBeAg seroconversion, reduced incidence of ascites, esophageal varices, splenomegaly and death or liver transplantation and were not accompanied by biochemical flare or hepatic decompensation [160]. Moreover, combination therapy with TDF + pegIFN in patients with advanced cirrhosis with chronic HBV/HDV co-infection was also accompanied by host-derived transaminase flares, none of which were accompanied by biochemical flare or hepatic decompensation [161]. These more recent observations suggest that with the maintenance of effective HBV suppression, host-mediated transaminase flares do not impact the limited hepatic reservoir in cirrhotic patients (Figure 5B) and can be a means to safely achieve functional cure in cirrhotic patients.
7. Perspectives
With the overall goal of functional cure requiring the removal of hepatocytes with integrated HBV DNA and active cccDNA, transaminase flares are likely an essential milestone in this process and will be required for the achievement of HBsAg loss with currently approved therapies and therapies in development. The current clinical data indicate that with maintenance of viral suppression, transaminase flares appear to be universally host-mediated, do not negatively impact liver function and are associated with both improvement in virologic status and liver function and correlated with increased rates of functional cure of HBV, even with cirrhosis. As such, viral suppression during experimental therapies (such as NAPs) which yield both high rates of transaminase flares and functional cure should be accompanied by NUCs such as ETV, TDF or TAF to ensure safety during therapy.
However, higher-frequency monitoring of transaminases, GGT as well as markers of liver function should continue to be both essential data gathered during clinical trials for agents in HBV and be reported in detail to increase the available clinical database, especially during treatment of cirrhotic patients. Of important note here is GGT; although it is not considered as hepato-specific as ALT and AST, its elevation in the blood can signal effective targeting of infected cells in the bile duct epithelium and endothelial and smooth muscle cells of hepatic blood vessels. The reporting of changes in this liver enzyme should be included not only to indicate the targeting of non-hepatocyte reservoirs of HBV infection in the liver but also to better exclude a link between GGT elevations and other potential safety concerns.
In the interim, the current clinical experience with transaminase flares indicates a common approach for interpreting these events with all antiviral agents (Figure 6). Transaminase flares driven by reduction of normal functioning hepatocytes due to increased viral activity in the liver or drug-induced liver injury outpace the regenerative capacity of the liver and lead to biochemical flare and/or hepatic decompensation. These flares are grounds for the introduction of HBV suppressive NUC (ETV/TDF/TAF) therapy or for dose reduction of immunotherapies or experimental antiviral agents. On the other hand, host-mediated flares are easily identified by the presence of an antiviral response and lack of biochemical flare or hepatic decompensation. These fares are highly correlated with HBV DNA reduction, HBeAg seroconversion and silencing/reduction of cccDNA and should not be grounds for halting therapy or dose reduction of experimental therapies in development. Strong flares with HBsAg loss may signal more efficient targeting of integrated HBV DNA and appear to be a marker for the establishment of functional cure with pegIFN and/or NAPs. This event may be required to establish high rates of functional cure in all patient populations, regardless of therapeutic approach. In the case of cirrhotic patients, the current clinical data suggest that transaminase flares are safe and well tolerated (even pegIFN-mediated) when effective HBV suppression (NUC therapy) is in place and that these flares are associated with improved virologic status. However, additional clinical data will be required to reinforce the observations of these recent studies.
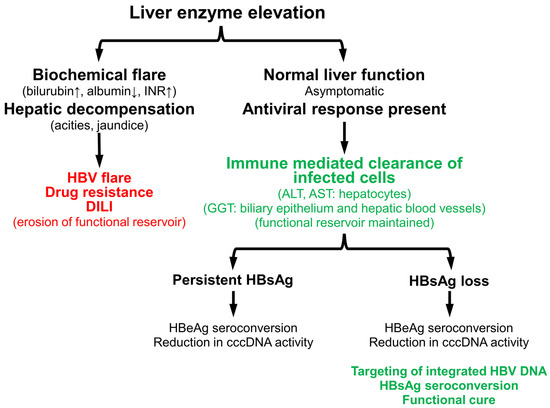
Figure 6.
Identification and impact of detrimental and beneficial transaminase flares during the natural history or treatment of chronic HBV infection.
Funding
The research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
A.V. is a shareholder and employee of Replicor Inc. and is an inventor on all patents assigned to Replicor Inc.
References
- Ganem, D.; Prince, A.M. Hepatitis B virus infection--natural history and clinical consequences. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.S.; Coffin, C.S. Hepatitis B virus lymphotropism: Emerging details and challenges. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2018, 34, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Q.; Huang, J.; Su, E.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, K. Infection of hepatitis B virus in extrahepatic endothelial tissues mediated by endothelial progenitor cells. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehermann, B.; Ferrari, C.; Pasquinelli, C.; Chisari, F.V. The hepatitis B virus persists for decades after patients’ recovery from acute viral hepatitis despite active maintenance of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B Reactivation Associated With Immune Suppressive and Biological Modifier Therapies: Current Concepts, Management Strategies, and Future Directions. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bath, R.M.; Doering, B.E.; Nailor, M.D.; Goodlet, K.J. Pharmacotherapy-Induced Hepatitis B Reactivation Among Patients With Prior Functional Cure: A Systematic Review. Ann. Pharmacother. 2019, 53, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polaris Observatory, C. Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Hepatitis B Fact Sheet; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vaillant, A. HBsAg, Subviral Particles, and Their Clearance in Establishing a Functional Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levrero, M.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Belloni, L.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M. Control of cccDNA function in hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. HBV DNA Integration: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Viruses 2017, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.S.; Jilbert, A.R.; Litwin, S. Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration and Clonal Expansion of Hepatocytes in the Chronically Infected Liver. Viruses 2021, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, N.; Lukash, T.; Gunewardena, S.; Chappell, B.; Slagle, B.L.; Gudima, S.O. Relative Abundance of Integrant-Derived Viral. RNAs in Infected Tissues Harvested from Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Carriers. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindh, M.; Rydell, G.E.; Larsson, S.B. Impact of integrated viral DNA on the goal to clear hepatitis B surface antigen with different therapeutic strategies. Curr. Opin Virol. 2018, 30, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornberg, M.; Manns, M.P. Hepatitis: No cure for hepatitis B and D without targeting integrated viral DNA? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moucari, R.; Lada, O.; Marcellin, P. Chronic hepatitis B: Back to the future with HBsAg. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2009, 7, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kim, W.R. Emerging Therapies Toward a Functional Cure for Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. (N. Y.) 2018, 14, 439–442. [Google Scholar]
- Dusheiko, G.; Wang, B. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Loss: Too Little, Too Late and the Challenge for the Future. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, T.C.; Lok, A.S. How Do We Determine Whether a Functional Cure for HBV Infection Has Been Achieved? Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.T.; Choi, H.S.J.; Lenz, O.; Peters, M.G.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Mishra, P.; Donaldson, E.; Westman, G.; Buchholz, S.; Miller, V.; et al. Association Between Seroclearance of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and Long-term Clinical Outcomes of Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, M.B.; Desmet, V.J.; Fevery, J.; De Groote, J.; Bradburne, A.F.; Desmyter, J. Distribution patterns of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in the liver of hepatitis patients. J. Clin. Pathol. 1976, 29, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, H.E.; Stowring, L.; Figus, A.; Montgomery, C.K.; Haase, A.T.; Vyas, G.N. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in hepatocytes, bile duct epithelium, and vascular elements by in situ hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 6685–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakopoulou, L.; Adraskelas, N.; Stefanaki, K.; Zacharoulis, D.; Hadziyannis, S. Expression of HBsAg and HBcAg in liver tissue: Correlation with disease activity. Histol. Histopathol. 1992, 7, 493–499. [Google Scholar]
- Wee, A.; Yap, I.; Guan, R. Hepatocyte hepatitis B surface antigen expression in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers in Singapore: Correlation with viral replication and liver pathology. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1991, 6, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.C.; Lai, M.Y.; Su, I.J.; Chen, D.S.; Chang, M.H.; Yang, P.M.; Wu, C.Y.; Hsieh, H.C. Correlation of hepatocyte HBsAg expression with virus replication and liver pathology. Hepatology 1988, 8, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.H.; Hollinger, F.B.; Noonan, C.A.; Yoffe, B. Simultaneous detection of HBV-specific antigens and DNA in paraffin-embedded liver tissue by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization using a digoxigenin-labeled probe. J. Virol. Methods 1992, 37, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaie, P.; Poongkunran, M.; Kuang, P.P.; Javaid, A.; Jacobs, C.; Pohlmann, R.; Nasser, I.; Lau, D.T. Intrahepatic distribution of hepatitis B virus antigens in patients with and without hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3404–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Bai, L.; Chen, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Z. In situ analysis of intrahepatic virological events in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoumov, N.V.; Daniels, H.M.; Davison, F.; Eddleston, A.L.; Alexander, G.J.; Williams, R. Identification of hepatitis B virus-DNA in the liver by in situ hybridization using a biotinylated probe. Relation to HBcAg expression and histology. J. Hepatol. 1993, 19, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, S.R.; Schatzmayr, H.G.; Barth, O.M.; Simonetti, J.P. Detection of hepatitis B virus antigens in paraffin-embedded liver specimens from the Amazon region, Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2002, 97, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hirohashi, S.; Shimosato, Y.; Ino, Y.; Kishi, K. Distribution of hepatitis B surface and core antigens in human liver cell carcinoma and surrounding nontumorous liver. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1982, 69, 565–568. [Google Scholar]
- Gowans, E.J.; Burrell, C.J.; Jilbert, A.R.; Marmion, B.P. Patterns of single- and double-stranded hepatitis B virus DNA and viral antigen accumulation in infected liver cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1983, 64 Pt 6, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.Y.; Naoumov, N.V.; Alexander, G.J.; Williams, R. Rapid detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in liver tissue by in situ hybridisation and its combination with immunohistochemistry for simultaneous detection of HBV antigens. J. Clin. Pathol. 1991, 44, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Inigo, E.; Mariscal, L.; Bartolome, J.; Castillo, I.; Navacerrada, C.; Ortiz-Movilla, N.; Pardo, M.; Carreno, V. Distribution of hepatitis B virus in the liver of chronic hepatitis C patients with occult hepatitis B virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 70, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, P.A.; Gong, Q.; Mehta, A.S.; Lu, X.; Block, T.M. Hepatitis B virus-mediated changes of apolipoprotein mRNA abundance in cultured hepatoma cells. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 5503–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.B.; Zhu, C.L.; Liu, X.; Gao, G.S. HBV inhibits apoB production via the suppression of MTP expression. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hao, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Zeng, X.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Kuang, X.; Zhang, T. The mechanism of apoliprotein A1 down-regulated by Hepatitis B virus. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhu, H.; Song, H.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Liu, F.; Liu, X. Hepatitis B virus inhibits the in vivo and in vitro synthesis and secretion of apolipoprotein C3. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Yan, S.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Song, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yang, Y.; et al. Expression of hepatitis B virus proteins in transgenic mice alters lipid metabolism and induces oxidative stress in the liver. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehler, N.; Volz, T.; Bhadra, O.D.; Kah, J.; Allweiss, L.; Giersch, K.; Bierwolf, J.; Riecken, K.; Pollok, J.M.; Lohse, A.W.; et al. Binding of hepatitis B virus to its cellular receptor alters the expression profile of genes of bile acid metabolism. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, T.Y.; Shin, Y.K.; Roh, K.J.; Kang, S.A.; Hong, I.; Oh, S.J.; Seong, J.K.; Park, C.K.; Choi, Y.L.; Lee, M.O. Liver X receptor mediates hepatitis B virus X protein-induced lipogenesis in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Zhu, P.; Liang, Y.; Yin, W.G.; Xiao, J.H. Hepatitis B virus induces expression of cholesterol metabolism-related genes via TLR2 in HepG2 cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, L.; Lei, H.; Wu, X.; Guo, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. The metabolic responses to hepatitis B virus infection shed new light on pathogenesis and targets for treatment. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamontagne, J.; Mell, J.C.; Bouchard, M.J. Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus-Mediated Changes to Normal Hepatocyte Gene Expression. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamontagne, R.J.; Casciano, J.C.; Bouchard, M.J. A broad investigation of the HBV-mediated changes to primary hepatocyte physiology reveals HBV significantly alters metabolic pathways. Metabolism 2018, 83, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.I.; Hwang, J.M.; Im, J.H.; Lee, Y.I.; Kim, N.S.; Kim, D.G.; Yu, D.Y.; Moon, H.B.; Park, S.K. Human hepatitis B virus-X protein alters mitochondrial function and physiology in human liver cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 15460–15471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhart, T.L.; Bouchard, M.J. The hepatitis B virus X protein modulates hepatocyte proliferation pathways to stimulate viral replication. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2675–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearhart, T.L.; Bouchard, M.J. The hepatitis B virus HBx protein modulates cell cycle regulatory proteins in cultured primary human hepatocytes. Virus Res. 2011, 155, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sir, D.; Tian, Y.; Chen, W.L.; Ann, D.K.; Yen, T.S.; Ou, J.H. The early autophagic pathway is activated by hepatitis B virus and required for viral DNA replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4383–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.; Krueger, E.W.; Chen, J.; Cao, H.; Ninomiya, M.; McNiven, M.A. HBV secretion is regulated through the activation of endocytic and autophagic compartments mediated by Rab7 stimulation. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 1696–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, C.; Macovei, A.; Petrescu, S.; Branza-Nichita, N. Activation of ERAD pathway by human hepatitis B virus modulates viral and subviral particle production. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clippinger, A.J.; Gearhart, T.L.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B virus X protein modulates apoptosis in primary rat hepatocytes by regulating both NF-kappaB and the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4718–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.T.; Liu, W.; Wu, S.X.; He, Y.; Lin, Y.T.; Chen, W.N.; Lin, X.J.; Lin, X. Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Enhances the Sensitivity of Hepatocytes to Fas-Mediated Apoptosis via Suppression of AKT Phosphorylation. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.Z.; Blaileanu, G.; Hansen, B.C.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Gong, D.W. cDNA cloning, genomic structure, chromosomal mapping, and functional expression of a novel human alanine aminotransferase. Genomics 2002, 79, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindblom, P.; Rafter, I.; Copley, C.; Andersson, U.; Hedberg, J.J.; Berg, A.L.; Samuelsson, A.; Hellmold, H.; Cotgreave, I.; Glinghammar, B. Isoforms of alanine aminotransferases in human tissues and serum--differential tissue expression using novel antibodies. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 466, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindena, J.; Sommerfeld, U.; Hopfel, C.; Trautschold, I. Catalytic enzyme activity concentration in tissues of man, dog, rabbit, guinea pig, rat and mouse. Approach to a quantitative diagnostic enzymology, III. Communication. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1986, 24, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glinghammar, B.; Rafter, I.; Lindstrom, A.K.; Hedberg, J.J.; Andersson, H.B.; Lindblom, P.; Berg, A.L.; Cotgreave, I. Detection of the mitochondrial and catalytically active alanine aminotransferase in human tissues and plasma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 23, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteghini, M. Aspartate aminotransferase isoenzymes. Clin. Biochem. 1990, 23, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Laarse, A.; Dijkshoorn, N.J.; Hollaar, L.; Caspers, T. The (iso)enzyme activities of lactate dehydrogenase, alpha-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase and aspartate aminotransferase in human myocardial biopsies and autopsies. Clin. Chim. Acta 1980, 104, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rej, R. Aspartate aminotransferase activity and isoenzyme proportions in human liver tissues. Clin. Chem. 1978, 24, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, M.B.; Wickham, S.; Parks, E.E.; Sherry, D.M.; Hanigan, M.H. Human GGT2 does not autocleave into a functional enzyme: A cautionary tale for interpretation of microarray data on redox signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemesanszky, E.; Lott, J.A. Gamma-glutamyltransferase and its isoenzymes: Progress and problems. Clin. Chem. 1985, 31, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanigan, M.H.; Frierson, H.F., Jr. Immunohistochemical detection of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in normal human tissue. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1996, 44, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, M.; Suzuki, N.; Sohda, T.; Anan, A.; Iwata, K.; Takeyama, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Fischer, P.; Scherberich, J.E.; Sakisaka, S. Hepatic expression of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase in the human liver of patients with alcoholic liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gores, G.J.; Herman, B.; Lemasters, J.J. Plasma membrane bleb formation and rupture: A common feature of hepatocellular injury. Hepatology 1990, 11, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosser, B.G.; Gores, G.J. Liver cell necrosis: Cellular mechanisms and clinical implications. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Nandi, M.; Pal, S.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Chakraborty, B.C.; Khatun, M.; Bhowmick, D.; Mondal, R.K.; Das, S.; Das, K.; et al. Natural killer cells contribute to hepatic injury and help in viral persistence during progression of hepatitis B e-antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Clin. Microbiol Infect. 2016, 22, 733 e719–733 e739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, C.L.; Rinker, F.; Honer Zu Siederdissen, C.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H.; Cornberg, M.; Bjorkstrom, N.K. Increased NK Cell Function After Cessation of Long-Term Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Treatment in Chronic Hepatitis B Is Associated With Liver Damage and HBsAg Loss. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotman, Y.; Brown, T.A.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Evaluation of the patient with hepatitis B. Hepatology 2009, 49, S22–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Lau, G.K.; Abbas, Z.; Chan, H.L.; Chen, C.J.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chien, R.N.; et al. Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B: A 2015 update. Hepatol. Int. 2016, 10, 1–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eminler, A.T.; Irak, K.; Ayyildiz, T.; Keskin, M.; Kiyici, M.; Gurel, S.; Gulten, M.; Dolar, E.; Nak, S.G. The relation between liver histopathology and GGT levels in viral hepatitis: More important in hepatitis B. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 25, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manno, M.; Camma, C.; Schepis, F.; Bassi, F.; Gelmini, R.; Giannini, F.; Miselli, F.; Grottola, A.; Ferretti, I.; Vecchi, C.; et al. Natural history of chronic HBV carriers in northern Italy: Morbidity and mortality after 30 years. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Yang, C.C.; Liu, Y.; Xia, J.; Su, R.; Xiong, Y.L.; Wang, G.Y.; Sun, Z.H.; Yan, X.M.; Lu, S.; et al. Association of serum gamma-glutamyl transferase with treatment outcome in chronic hepatitis B patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 9957–9965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, E.G.; Testa, R.; Savarino, V. Liver enzyme alteration: A guide for clinicians. CMAJ 2005, 172, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Lai, C.L. Acute exacerbations in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Incidence, predisposing factors and etiology. J. Hepatol. 1990, 10, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.C.; Lai, C.L.; Han, S.H.; Han, K.H.; Gordon, S.C.; Chao, Y.C.; Tan, C.K.; Sievert, W.; Tanwandee, T.; Xu, D.; et al. Efficacy of entecavir in chronic hepatitis B patients with mildly elevated alanine aminotransferase and biopsy-proven histological damage. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Arends, P.; Reijnders, J.G.; Carey, I.; Brown, A.; Fasano, M.; Mutimer, D.; Deterding, K.; Oo, Y.H.; Petersen, J.; et al. Flares during long-term entecavir therapy in chronic hepatitis B. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1882–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.; Littlejohn, M.; Edwards, R.; Jackson, K.; Revill, P.; Gaggar, A.; Kitrinos, K.; Subramanian, M.; Marcellin, P.; Buti-Ferret, M.; et al. ALT flares during nucleotide analogue therapy are associated with HBsAg loss in genotype A HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mels, G.C.; Bellati, G.; Leandro, G.; Brunetto, M.R.; Vicari, O.; Borzio, M.; Piantino, P.; Fornaciari, G.; Scudeller, G.; Angeli, G.; et al. Fluctuations in viremia, aminotransferases and IgM antibody to hepatitis B core antigen in chronic hepatitis B patients with disease exacerbations. Liver 1994, 14, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmania, M.; Lombardero, M.; Hansen, B.E.; Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.; Perrillo, R.P.; Belle, S.H.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Feld, J.J.; Lee, W.M.; et al. Association Between Severe Serum Alanine Aminotransferase Flares and Hepatitis B e Antigen Seroconversion and HBV DNA Decrease in Untreated Patients With Chronic HBV Infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrillo, R.; Campbell, C.; Wellinghoff, W.; Gelb, L. The relationship of hepatitis B e antigen, DNA polymerase activity, and titer of hepatitis B surface antigen with ongoing liver injury in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1982, 77, 445–449. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, Y.F.; Tai, D.I.; Chu, C.M.; Pao, C.C.; Chen, T.J. Acute exacerbation in chronic type B hepatitis: Comparison between HBeAg and antibody-positive patients. Hepatology 1987, 7, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Chauhan, R.; Gupta, N.; Hissar, S.; Sakhuja, P.; Sarin, S.K. Spontaneous increases in alanine aminotransferase levels in asymptomatic chronic hepatitis B virus-infected patients. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, Y.F.; Yang, S.S.; Chen, T.J.; Chu, C.M. Acute exacerbation in hepatitis B e antigen positive chronic type B hepatitis. A clinicopathological study. J. Hepatol. 1985, 1, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, Y.F.; Pao, C.C.; Chu, C.M.; Sheen, I.S.; Huang, M.J. Changes of serum hepatitis B virus DNA in two types of clinical events preceding spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic type B hepatitis. Hepatology 1987, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.M.; Su, I.J.; Lai, M.Y.; Huang, G.T.; Hsu, H.C.; Chen, D.S.; Sung, J.L. Immunohistochemical studies on intrahepatic lymphocyte infiltrates in chronic type B hepatitis, with special emphasis on the activation status of the lymphocytes. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1988, 83, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.L.; Chen, P.J.; Lai, M.Y.; Yang, P.M.; Sung, J.L.; Huang, J.H.; Hwang, L.H.; Chang, T.H.; Chen, D.S. Acute exacerbations of chronic type B hepatitis are accompanied by increased T cell responses to hepatitis B core and e antigens. Implications for hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 89, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Kuroda, M.J.; Terada, R.; Hakoda, T.; Shimomura, H.; Hata, H.; Nakayama, E.; Shiratori, Y. HBcAg-specific CD8 T cells play an important role in virus suppression, and acute flare-up is associated with the expansion of activated memory T cells. J. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 23, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogeveen, R.C.; Robidoux, M.P.; Schwarz, T.; Heydmann, L.; Cheney, J.A.; Kvistad, D.; Aneja, J.; Melgaco, J.G.; Fernandes, C.A.; Chung, R.T.; et al. Phenotype and function of HBV-specific T cells is determined by the targeted epitope in addition to the stage of infection. Gut 2019, 68, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappus, M.R.; Sterling, R.K. Extrahepatic manifestations of acute hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. (N. Y.) 2013, 9, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Jeng, W.J.; Sheen, I.S.; Liaw, Y.F. Hepatitis B virus DNA level predicts hepatic decompensation in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.F.; Yuan, H.J.; Hui, C.K.; Wong, D.K.; Wong, W.M.; Chan, A.O.; Wong, B.C.; Lai, C.L. A large population study of spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion and acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B infection: Implications for antiviral therapy. Gut 2003, 52, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslov, A.; Meier, M.A.; Ketterer, S.; Wang, X.; Wieland, S.; Heim, M.H. Transition to HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B virus infection is associated with reduced cccDNA transcriptional activity. J. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Huang, M.X.; Li, W.Y.; Gan, C.J.; Dong, W.X.; Peng, X.M. Liver damage favors the eliminations of HBV integration and clonal hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yin, W. The Multiple Functions of B Cells in Chronic HBV Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 582292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub, R. Liver regeneration: From myth to mechanism. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellous, T.G.; Islam, S.; Tadrous, P.J.; Elia, G.; Kocher, H.M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mears, L.; Turnbull, D.M.; Taylor, R.W.; Greaves, L.C.; et al. Locating the stem cell niche and tracing hepatocyte lineages in human liver. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fausto, N.; Campbell, J.S.; Riehle, K.J. Liver regeneration. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 692–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Miyajima, A. Liver regeneration and fibrosis after inflammation. Inflamm. Regen. 2016, 36, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, W.S.; Liu, C.; Aldrich, C.E.; Litwin, S.; Yeh, M.M. Clonal expansion of normal-appearing human hepatocytes during chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8308–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Mason, W.S.; Clouston, A.D.; Shackel, N.A.; McCaughan, G.W.; Yeh, M.M.; Schiff, E.R.; Ruszkiewicz, A.R.; Chen, J.W.; Harley, H.A.; et al. Clonal expansion of hepatocytes with a selective advantage occurs during all stages of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Viral. Hepat. 2015, 22, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigano, M.; Lampertico, P. Hepatitis B virus treatment: Which patients should be treated with nucleos(t)ide analogue? Clin. Liver Dis. (Hoboken) 2013, 2, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chuang, T.H.; Redecke, V.; She, L.; Pitha, P.M.; Carson, D.A.; Raz, E.; Cottam, H.B. Molecular basis for the immunostimulatory activity of guanine nucleoside analogs: Activation of Toll-like receptor 7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6646–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kmonickova, E.; Potmesil, P.; Holy, A.; Zidek, Z. Purine P1 receptor-dependent immunostimulatory effects of antiviral acyclic analogues of adenine and 2,6-diaminopurine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 530, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potmesil, P.; Krecmerova, M.; Kmonickova, E.; Holy, A.; Zidek, Z. Nucleotide analogues with immunobiological properties: 9-[2-Hydroxy-3-(phosphonomethoxy)propyl]-adenine (HPMPA), -2,6-diaminopurine (HPMPDAP), and their N6-substituted derivatives. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 540, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchjorsen, J.; Risor, M.W.; Sogaard, O.S.; O’Loughlin, K.L.; Chow, S.; Paludan, S.R.; Ellermann-Eriksen, S.; Hedley, D.W.; Minderman, H.; Ostergaard, L.; et al. Tenofovir selectively regulates production of inflammatory cytokines and shifts the IL-12/IL-10 balance in human primary cells. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2011, 57, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Ohto, U.; Nomura, S.; Kibata, K.; Motoi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Fukui, R.; Ishimoto, T.; Sano, S.; et al. Guanosine and its modified derivatives are endogenous ligands for TLR7. Int. Immunol. 2016, 28, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Asano, M.; Matsumoto, A.; Sugiyama, M.; Nishida, N.; Tanaka, E.; Inoue, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Enomoto, N.; Shirasaki, T.; et al. Induction of IFN-lambda3 as an additional effect of nucleotide, not nucleoside, analogues: A new potential target for HBV infection. Gut 2018, 67, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, M.; Tsuge, M.; Murakami, E.; Mori, N.; Ohishi, W.; Uchida, T.; Fujino, H.; Nakahara, T.; Abe-Chayama, H.; Kawaoka, T.; et al. The association between serum cytokine and chemokine levels and antiviral response by entecavir treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients. Antivir. Ther. 2018, 23, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenne, T.; Bridgeman, A.; Rigby, R.E.; Rehwinkel, J. Deoxyguanosine is a TLR7 agonist. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Lai, C.L.; Leung, N.; Yao, G.B.; Cui, Z.Y.; Schiff, E.R.; Dienstag, J.L.; Heathcote, E.J.; Little, N.R.; Griffiths, D.A.; et al. Long-term safety of lamivudine treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.P.; Reijnders, J.G.; Perquin, M.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L. Frequency and clinical outcomes of flares related to nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral. Hepat. 2011, 18, e252–e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenney, D.J.; Rose, R.E.; Baldick, C.J.; Pokornowski, K.A.; Eggers, B.J.; Fang, J.; Wichroski, M.J.; Xu, D.; Yang, J.; Wilber, R.B.; et al. Long-term monitoring shows hepatitis B virus resistance to entecavir in nucleoside-naive patients is rare through 5 years of therapy. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow-Lampart, A.; Chappell, B.; Curtis, M.; Zhu, Y.; Myrick, F.; Schawalder, J.; Kitrinos, K.; Svarovskaia, E.S.; Miller, M.D.; Sorbel, J.; et al. No resistance to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate detected after up to 144 weeks of therapy in patients monoinfected with chronic hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 2011, 53, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathcart, A.L.; Chan, H.L.; Bhardwaj, N.; Liu, Y.; Marcellin, P.; Pan, C.Q.; Shalimar; Buti, M.; Cox, S.; Parhy, B.; et al. No Resistance to Tenofovir Alafenamide Detected through 96 Weeks of Treatment in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manns, M.P.; Akarca, U.S.; Chang, T.T.; Sievert, W.; Yoon, S.K.; Tsai, N.; Min, A.; Pangerl, A.; Beebe, S.; Yu, M.; et al. Long-term safety and tolerability of entecavir in patients with chronic hepatitis B in the rollover study ETV-901. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2012, 11, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.Y.; Lee, H.A.; Ko, S.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Choe, W.H.; Kwon, S.Y. Clinical impact of the early alanine amininotransferase flare during tenofovir monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2017, 23, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jeng, W.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Liaw, Y.F. Great and rapid HBsAg decline in patients with on-treatment hepatitis flare in early phase of potent antiviral therapy. J. Viral. Hepat. 2018, 25, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shouval, D.; Lai, C.L.; Chang, T.T.; Cheinquer, H.; Martin, P.; Carosi, G.; Han, S.; Kaymakoglu, S.; Tamez, R.; Yang, J.; et al. Relapse of hepatitis B in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients who discontinued successful entecavir treatment: The case for continuous antiviral therapy. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.L.; Liaw, Y.F.; Hadziyannis, S.J. Systematic review: Cessation of long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honkoop, P.; de Man, R.A.; Niesters, H.G.; Zondervan, P.E.; Schalm, S.W. Acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B virus infection after withdrawal of lamivudine therapy. Hepatology 2000, 32, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.G.; Wai, C.T.; Rajnakova, A.; Kajiji, T.; Guan, R. Fatal hepatitis B reactivation following discontinuation of nucleoside analogues for chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2002, 51, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.H.; Yang, H.C.; Tseng, T.C.; Liou, J.M.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S.; Liu, C.J.; Kao, J.H. Distinct Relapse Rates and Risk Predictors After Discontinuing Tenofovir and Entecavir Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liem, K.S.; Fung, S.; Wong, D.K.; Yim, C.; Noureldin, S.; Chen, J.; Feld, J.J.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L.A. Limited sustained response after stopping nucleos(t)ide analogues in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Results from a randomised controlled trial (Toronto STOP study). Gut 2019, 68, 2206–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.L.; Wong, D.K.; Wong, G.T.; Seto, W.K.; Fung, J.; Yuen, M.F. Rebound of HBV DNA after cessation of nucleos/tide analogues in chronic hepatitis B patients with undetectable covalently closed. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.L.; Chan, H.L.; Yuen, B.W.; Tse, Y.K.; Luk, H.W.; Yip, T.C.; Hui, V.W.; Liang, L.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Lui, G.C.; et al. The safety of stopping nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, L.; Allweiss, L.; Guerrieri, F.; Pediconi, N.; Volz, T.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M.; Levrero, M. IFN-alpha inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, U.S.; Peppa, D.; Micco, L.; Singh, H.D.; Carey, I.; Foster, G.R.; Maini, M.K.; Kennedy, P.T. Interferon Alpha Induces Sustained Changes in NK Cell Responsiveness to Hepatitis B Viral. Load Suppression In Vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micco, L.; Peppa, D.; Loggi, E.; Schurich, A.; Jefferson, L.; Cursaro, C.; Panno, A.M.; Bernardi, M.; Brander, C.; Bihl, F.; et al. Differential boosting of innate and adaptive antiviral responses during pegylated-interferon-alpha therapy of chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouse, J.; Kalinke, U.; Oxenius, A. Regulation of antiviral T cell responses by type I interferons. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flink, H.J.; Sprengers, D.; Hansen, B.E.; van Zonneveld, M.; de Man, R.A.; Schalm, S.W.; Janssen, H.L.; Group, H.B.V.S. Flares in chronic hepatitis B patients induced by the host or the virus? Relation to treatment response during Peg-interferon {alpha}-2b therapy. Gut 2005, 54, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter Borg, M.J.; Hansen, B.E.; Bigot, G.; Haagmans, B.L.; Janssen, H.L. ALT and viral load decline during PEG-IFN alpha-2b treatment for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 42, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneveld, M.J.; Zoutendijk, R.; Flink, H.J.; Zwang, L.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L. Close monitoring of hepatitis B surface antigen levels helps classify flares during peginterferon therapy and predicts treatment response. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, S.; Abiru, S.; Komori, A.; Sasaki, R.; Bekki, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Saeki, A.; Yamasaki, K.; Migita, K.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Hepatic flares promote rapid decline of serum hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in patients with HBsAg seroclearance: A long-term follow-up study. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, E89–E99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, Y.; Seo, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Hatazawa, Y.; Hirano, H.; Minami, A.; Kawano, Y.; Saito, M.; Ninomiya, T.; Sugano, M.; et al. Factors associated with the decrease in hepatitis B surface antigen titers following interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Is interferon and adefovir combination therapy effective? Biomed. Rep. 2017, 7, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wirth, S.; Zhang, H.; Hardikar, W.; Schwarz, K.B.; Sokal, E.; Yang, W.; Fan, H.; Morozov, V.; Mao, Q.; Deng, H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Peginterferon Alfa-2a (40KD) in Children With Chronic Hepatitis B: The PEG-B-ACTIVE Study. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Farag, M.; Brouwer, W.P.; Sonneveld, M.J.; Feld, J.J.; De Man, R.A.; Hansen, B.; Janssen, H. Early PEG-interferon-related ALT Flares of High Magnitude Lead to HBsAg Decline and Loss. A Study of 639 Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, T.L.; Goldstein, A.L. Thymosins: Structure, function and therapeutic applications. Thymus 1984, 6, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, P.H.; Mutchnick, M.G. Thymus-derived peptides in the treatment of viral chronic hepatitis. Dig. Dis. 1996, 14, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, P.H.; Mutchnick, M.G. Immunotherapy for hepatitis B in the direct acting antiviral era: Reevaluating the thymosin alpha1 efficacy trials in the light of a combination therapy approach. J. Viral. Hepat. 2018, 25, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, S.; Toyota, J.; Kumada, H.; Kiyosawa, K.; Kakumu, S.; Sata, M.; Suzuki, H.; Martins, E.B. The efficacy and safety of thymosin alpha-1 in Japanese patients with chronic hepatitis B; results from a randomized clinical trial. J. Viral. Hepat. 2005, 12, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, R.N.; Liaw, Y.F.; Chen, T.C.; Yeh, C.T.; Sheen, I.S. Efficacy of thymosin alpha1 in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology 1998, 27, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadelka, S.; Dahari, H.; Ciupe, S.M. Understanding the antiviral effects of RNAi-based therapy in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B infection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.F.; Wong, D.K.; Schluep, T.; Lai, C.L.; Ferrari, C.; Locarnini, S.; Lo, R.C.; Gish, R.G.; Hamilton, J.; Wooddell, C.I.; et al. Long-term serological, virological and histological responses to RNA inhibition by ARC-520 in Chinese chronic hepatitis B patients on entecavir treatment. Gut 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F. HBV RNAi inhibitor RG6346 in Phase 1b-2a trial was safe, well tolerated, and resulted in subatantial and durable reductions in serum HBsAg levels. In Proceedings of the AASLD 2020 Late Breakong Oral Presentation, 11–16 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vaillant, A. REP 2139: Antiviral Mechanisms and Applications in Achieving Functional Control of HBV and HDV Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulon, R.; Blanchet, M.; Lemasson, M.; Vaillant, A.; Labonte, P. Characterization of the antiviral effects of REP 2139 on the HBV lifecycle in vitro. Antiviral Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, M.; Sinnathamby, V.; Vaillant, A.; Labonte, P. Inhibition of HBsAg secretion by nucleic acid polymers in HepG2.2.15cells. Antiviral Res. 2019, 164, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahtab, M.; Bazinet, M.; Vaillant, A. Safety and Efficacy of Nucleic Acid Polymers in Monotherapy and Combined with Immunotherapy in Treatment-Naive Bangladeshi Patients with HBeAg+ Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, M.; Pantea, V.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Albrecht, J.; Schmid, P.; Le Gal, F.; Gordien, E.; Krawczyk, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of REP 2139 and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus co-infection (REP 301 and REP 301-LTF): A non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, M.; Pantea, V.; Placinta, G.; Moscalu, I.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Iarovoi, L.; Smesnoi, V.; Musteata, T.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of 48 Weeks REP 2139 or REP 2165, Tenofovir Disoproxil, and Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2a in Patients With Chronic HBV Infection Naive to Nucleos(t)ide Therapy. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2180–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazinet, M.; Pantea, V.; Placinta, G.; Moscalu, I.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Iarovoi, L.; Smesnoi, V.; Musteata, T.; et al. Benefit of transaminase elevations in establishing functional cure of HBV infection during NAP-based combination therapy. J. Viral. Hepat. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streinu-Cercel, A.; Bazinet, M.; Elsner, C.; Dittmer, U.; Roggendorf, H.; Roggendorf, M.; Vaillant, A. Interferon free clearance of HDV RNA and HBsAg seroconversion in a cirrhotic subject with chronic HBV/HDV co-infection with TDF and REP 2165-Mg. Hepatology 2020, 72, 505A. [Google Scholar]
- Poh, Z.; Goh, B.B.; Chang, P.E.; Tan, C.K. Rates of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B and the role of surveillance: A 10-year follow-up of 673 patients. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidrich, B.; Serrano, B.C.; Idilman, R.; Kabacam, G.; Bremer, B.; Raupach, R.; Onder, F.O.; Deterding, K.; Zacher, B.J.; Taranta, A.; et al. HBeAg-positive hepatitis delta: Virological patterns and clinical long-term outcome. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manesis, E.K.; Vourli, G.; Dalekos, G.; Vasiliadis, T.; Manolaki, N.; Hounta, A.; Koutsounas, S.; Vafiadis, I.; Nikolopoulou, G.; Giannoulis, G.; et al. Prevalence and clinical course of hepatitis delta infection in Greece: A 13-year prospective study. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoofnagle, J.H.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Waggoner, J.G.; Park, Y. Interferon alfa for patients with clinically apparent cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 1993, 104, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.L.; Cheng, J.S.; Chien, R.N.; Liaw, Y.F. Hepatitis Flares Are Associated With Better Outcomes Than No Flare in Patients With Decompensated Cirrhosis and Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2064–2072 e2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Yurdaydin, C.; Hardtke, S.; Caruntu, F.A.; Curescu, M.G.; Yalcin, K.; Akarca, U.S.; Gurel, S.; Zeuzem, S.; Erhardt, A.; et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for hepatitis D (HIDIT-II): A randomised, placebo controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).