Incursion of European Bat Lyssavirus 1 (EBLV-1) in Serotine Bats in the United Kingdom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. UK Lyssavirus Surveillance
2.2. Bat Speciation and Lyssavirus Diagnostic Assays
2.3. Immunohistochemical Identification of Viral Antigens from EBLV-1 Infected Bat Tissue
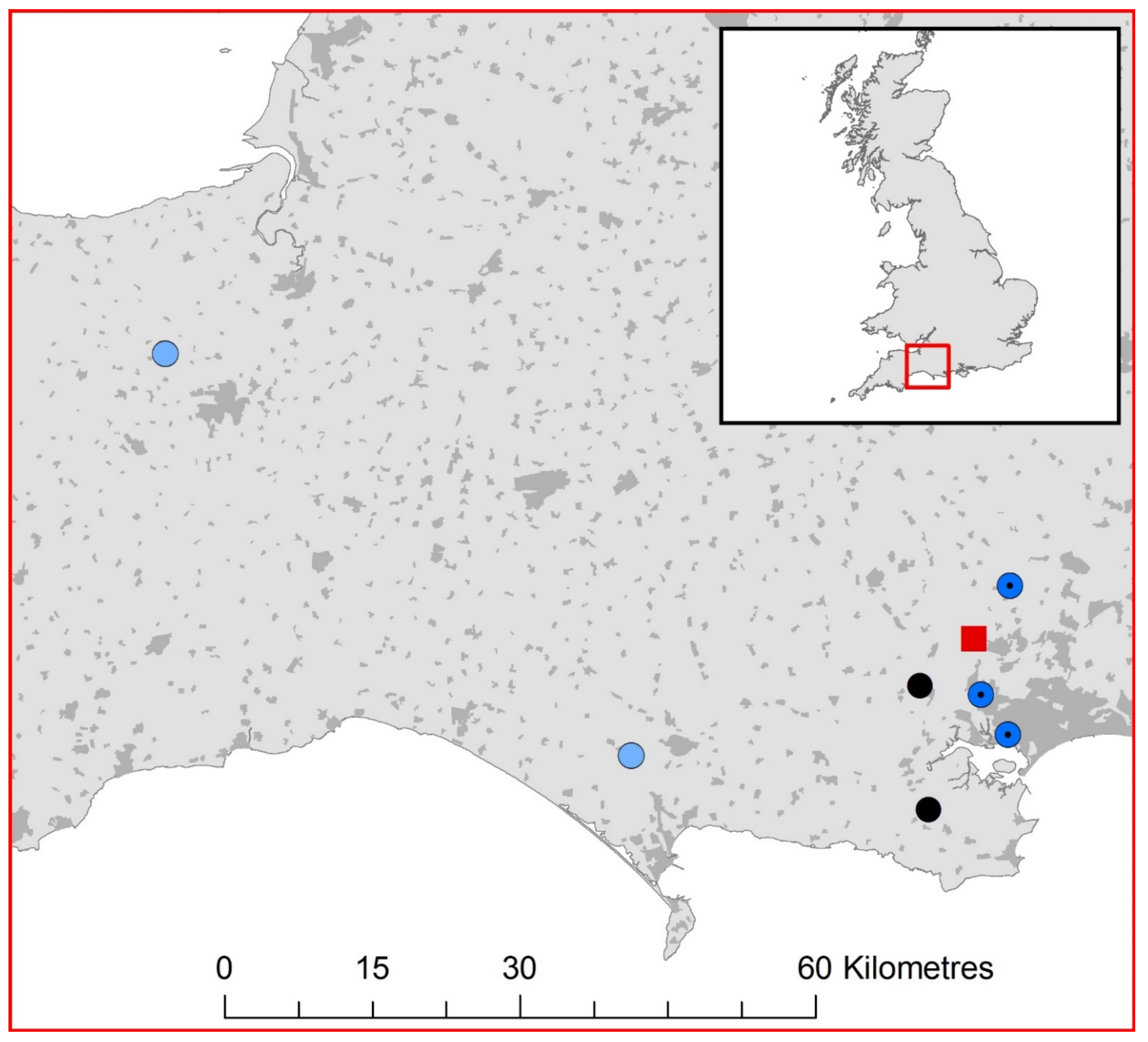
3. Results
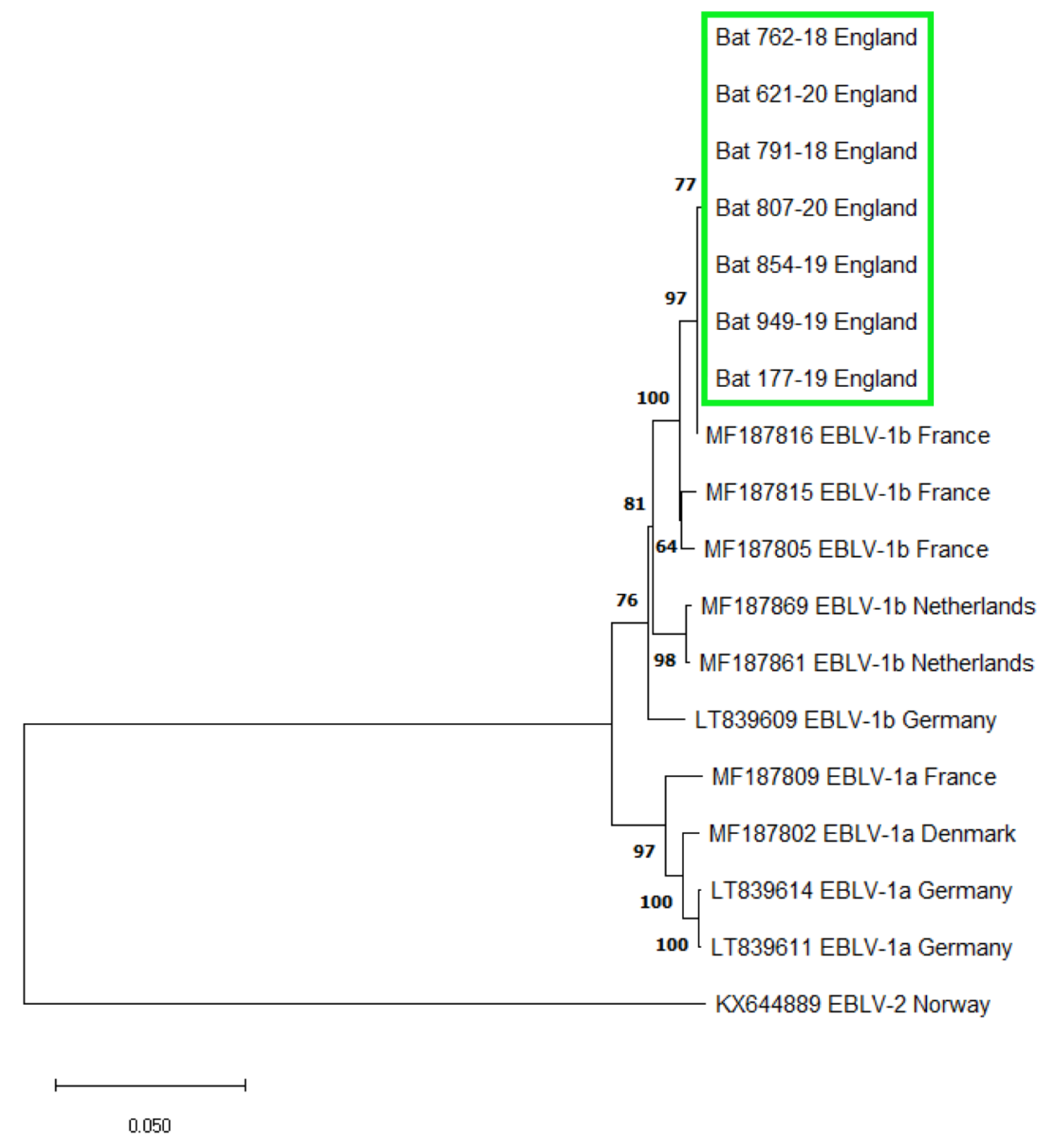
3.1. EBLV-1 Detection and Sequence Analysis
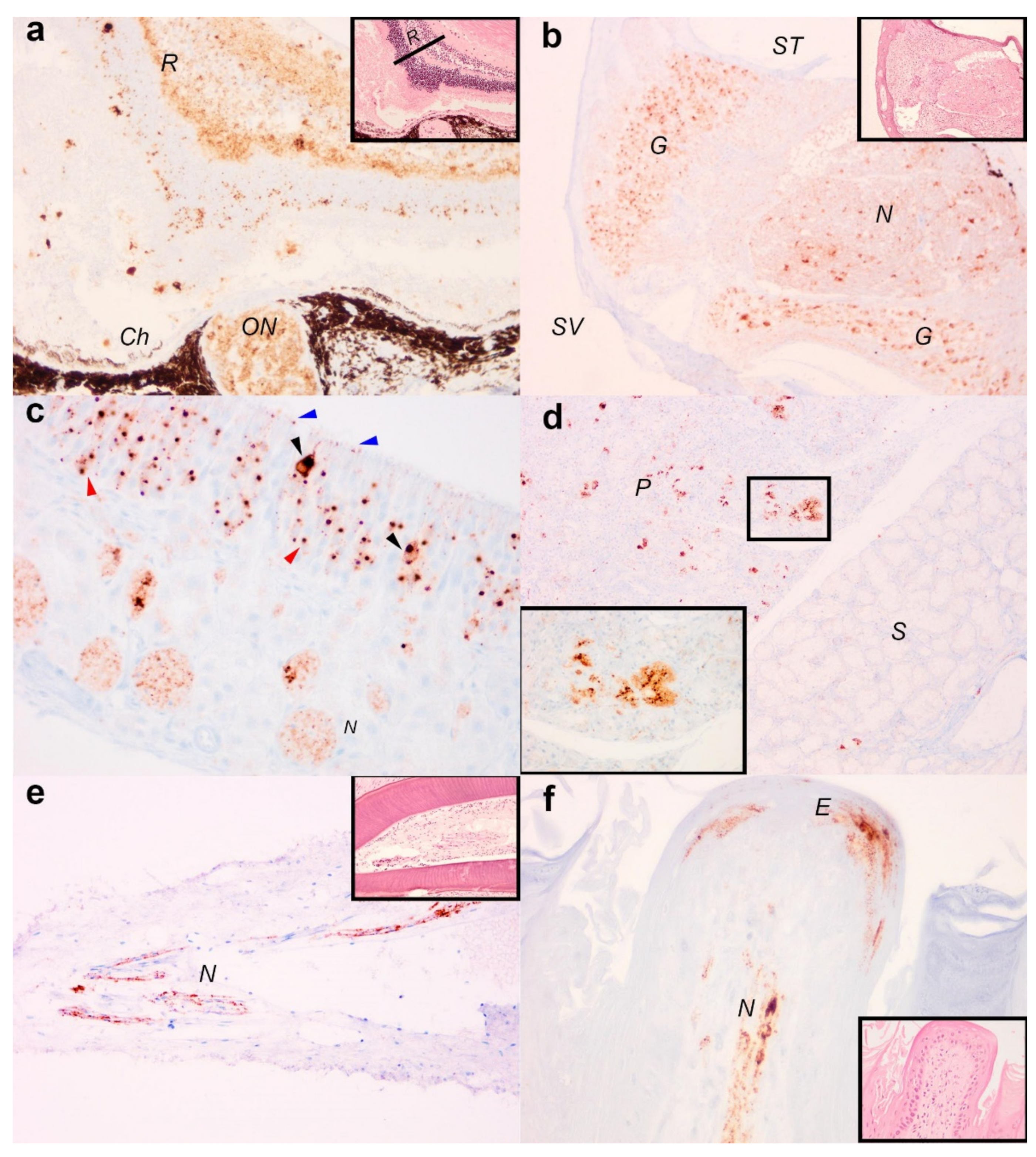
3.2. Immunohistochemical Detection of Viral Antigens in EBLV-1 Infected Tissue
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Leug, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopardi, S.; Blake, D.; Puechmaille, S.J. White-nose syndrome fungus introduced from Europe to North America. Curr. Biol. 2011, 25, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savage, A.E.; Gratwicke, B.; Hope, K.; Bronikowski, E.; Fleischer, R.C. Sustained immune activation is associated with susceptibility to the amphibian chytrid fungus. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 2889–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszak, P.; Cunningham, A.A.; Hyatt, A.D. Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife—Threats to biodiversity and human health. Science 2000, 287, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.A.; Schmidt, J.P.; Bowden, S.E.; Drake, J.E. Rodent reservoirs of future zoonotic diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7039–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, N.G.; Abbott, S.; Barnard, R.C.; Jarvis, C.I.; Kucharski, A.J.; Munday, J.D.; Pearson, C.A.B.; Russell, T.W.; Tully, D.C.; Washburne, A.D.; et al. Estimated transmissibility and impact of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 in England. Science 2021, 372, eabg3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claas, E.C.J.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; van Beek, R.; De Jong, J.C.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Senne, D.A.; Krauss, S.; Shortridge, K.F.; Webster, R.G. Human influenza A H5N1 virus related to a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus. Lancet 1998, 351, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fooks, A.R.; Banyard, A.C.; Horton, D.L.; Johnson, N.; Mcelhinney, L.M.; Jackson, A.C. Current status of rabies and prospects for elimination. Lancet 2014, 384, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhy, H.; Kissi, B.; Lafon, M.; Sacramento, D.; Tordo, N. Antigenic and molecular characterisation of bat rabies virus in Europe. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 2419–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mcelhinney, L.M.; Marston, D.A.; Leech, S.; Freuling, C.M.; van der Poel, W.H.M.; Echevarria, J.; Vazquez-Moron, S.; Horton, D.L.; Muller, T.; Fooks, A.R. Molecular epidemiology of bat lyssaviruses in Europe. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitby, J.E.; Heaton, P.R.; Black, E.M.; Wooldridge, M.; McElhinney, L.M.; Johnstone, P. First isolation of a rabies related virus from a Daubenton’s bat in the United Kingdom. Vet. Rec. 2000, 147, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fooks, A.R.; Brookes, S.M.; Johnson, N.; McElhinney, L.; Hutson, A.M. European bat lyssaviruses: An emerging zoonosis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2003, 131, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, E.; Marston, D.; Banyard, A.C.; Goharriz, H.; Selden, D.; MacLaren, N.; Goddard, T.; Johnson, N.; McElhinney, L.M.; Brouwer, A.; et al. Passive surveillance of United Kingdom bats for lyssaviruses (2005–2015). Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 2445–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fooks, A.R.; McElhinney, L.M.; Pounder, D.J.; Finnegan, C.J.; Mansfield, K.; Johnson, N.; Brookes, S.M.; Parsons, G.; White, K.; McIntyre, P.G.; et al. Case report: Isolation of a European bat lyssavirus type-2a from a fatal human case of rabies encephalitis. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 71, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.L.; Holmes, E.; Larrous, F.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Tjørnehøj, K.; Alonso, W.; Bourhy, H. Phylogeography, population dynamics, and molecular evolution of European bat lyssaviruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10487–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Troupin, C.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Dellicour, S.; Casademont, I.; Kergoat, L.; Lepelletier, A.; Dacheux, L.; Baele, G.; Monchâtre-Leroy, E.; Cliquet, F.; et al. Host genetic variation does not determine spatio-temporal patterns of European Bat 1 Lyssavirus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 3202–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Picard-Meyer, E.; Barrat, J.; Tissot, E.; Verdot, A.; Patron, C.; Barrat, M.J.; Cliquet, F. Bat rabies surveillance in France, from 1989 through May 2005. Dev. Biol. 2006, 125, 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Roig-Lopez, M.; Bourhy, H.; Lavenir, R.; Serra-Cobo, J. Seroprevalence dynamics of European bat lyssavirus type-1 in a multispecies bat colony. Viruses 2014, 6, 3386–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banyard, A.C.; Evans, J.S.; Luo, T.R.; Fooks, A.R. Lyssavirus and bats: Emergence and zoonotic threat. Viruses 2014, 6, 2974–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marston, D.A.; Banyard, A.C.; Mcelhinney, L.M.; Freuling, C.M.; Finke, S.; de Lamballerie, X.; Muller, T.; Fooks, A.R. The lyssavirus host specificity conundrum-rabies virus- the exception not the rule. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 28, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.; Cox, J.; Peter, W.; Schafer, R.; Johnson, N.; Mcelhinney, L.M.; Geue, J.L.; Tjornehoj, K.; Fooks, A.R. Spill-over of European bat lyssavirus type-1 into a stone martin (Martes foina) in Germany. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2004, 51, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjørnehøj, K.; Fooks, A.R.; Agerholm, J.S.; Rønsholt, L. Natural and experimental infection of sheep with European bat lyssavirus type-1 of Danish bat origin. J. Comp. Pathol. 2006, 134, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacheux, L.; Larrous, F.; Mailles, A.; Boisseleau, D.; Delmas, O.; Biron, C.; Bouchier, C.; Capek, I.; Muller, M.; Ilari, F.; et al. European bat lyssavirus transmission among cats, Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selnikova, O.P.; Antonova, L.A.; Moiseeva, A.B.; Botbinkin, A.D. Human rabies after a bat bite in Ukraine. Epidemiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 5, 55–56. [Google Scholar]
- Regnault, B.; Evrard, B.; Plu, I.; Dacheux, L.; Troadec, E.; Cozette, P.; Chrétien, D.; Duchesne, M.; Vallat, J.-M.; Jamet, A.; et al. First case of lethal encephalitis in Western Europe due to European bat lyssavirus type 1. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, ciab443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catto, C.M.C.; Hutson, A.M.; Raccey, P.A.; Stephenson, P.J. Foraging behaviour and habitat use of the serotine bat (Eptesicus serotinus) in Southern England. J. Zool. 1996, 238, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.; Vos, A.; Freuling, C.; Tordo, N.; Fooks, A.R.; Müller, T. Human rabies due to lyssavirus infection of bat origin. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 142, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, D.L.; Breed, A.C.; Arnold, M.E.; Smith, G.C.; Aegerter, J.N.; McElhinney, L.M.; Johnson, N.; Banyard, A.C.; Raynor, R.; Mackie, I.; et al. Between roost contact is essential for maintenance of European bat lyssavirus type -2 in Myotis daubentonii bat reservoir: ‘The swarming hypothesis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.S.; Horton, D.; Easton, A.J.; Fooks, A.R.; Banyard, A.C. Rabies virus vaccines: Is there a need for a pan-lyssavirus vaccine? Vaccine 2012, 52, 7447–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.L.; Aegerter, J.N.; Brookes, S.M.; McElhinney, L.M.; Jones, G.; Smith, G.C.; Fooks, A.R. Targeted surveillance for European bat lyssaviruses in English bats (2003–06). J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, N.; Selden, D.; Parsons, G.; Fooks, A.R. European bat lyssavirus type -2 in a bat in Lancashire. Vet. Rec. 2002, 151, 455–456. [Google Scholar]
- Marston, D.A.; Jennings, D.L.; MacLaren, N.C.; Dorey-Robinson, D.; Fooks, A.R.; Banyard, A.C.; McElhinney, L.M. Pan-lyssavirus Real Time RT-PCR for rabies diagnosis. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 149, e59709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakeley, P.R.; Johnson, N.; Mcelhinney, L.M.; Marston, D.; Sawyer, J.; Fooks, A.R. Development of a real-time TaqMan Reverse Transcription-PCR assay for detection and differentiation of lyssavirus genotypes 1, 5 and 6. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2786–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McElhinney, L.M.; Leech, S.; Marston, D.A.; Fooks, A.R. Rabies virus. In Molecular Detection of Human Viral Pathogens, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 425–435. [Google Scholar]
- Shipley, R.; Wright, E.; Lean, F.Z.X.; Selden, D.; Horton, D.L.; Fooks, A.R.; Banyard, A.C. Assessing rabies vaccine protection against a novel lyssavirus, Kotalahti bat lyssavirus. Viruses 2021, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussy, C.; Atterby, H.; Griffiths, A.G.F.; Allnut, T.R.; Mathews, F.; Smith, G.C.; Aegerter, J.N.; Bearhop, S.; Hosken, D.J. Population genetic structure of serotine bats (Eptesicus serotinus) across Europe and implications for the potential spread of bat rabies (European bat lyssavirus EBLV-1). Heredity 2015, 115, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogdanowicz, W.; Lesinski, G.; Sadkowska-Todys, M.; Gajewska, M.; Rutkowski, R. Population genetics and bat rabies: A case study of Eptesicus serotinus in Poland. Acta Chiropt. 2013, 15, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juste, J.; Bilgin, R.; Muñoz, J.; Ibáñez, C. Mitochondrial DNA signatures at different spatial scales: From the effects of the Straits of Gibraltar to population structure in the meridional serotine bat (Eptesicus isabellinus). Heredity 2009, 103, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robardet, E.; Borel, C.; Mornet, M.; Jouan, D.; Wasniewski, M.; Barrat, J.; Boue, F.; Montchatre-Leroy, E.; Servat, A.; Gimenez, O.; et al. Longitudinal survey of two serotine bat (Eptesicus serotinus) maternity colonies exposed to EBLV-1 (European bat lyssavirus type 1): Assessment of survival and serological status variations using capture-recapture models. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pons-Salort, M.; Serra-Cobo, J.; Jay, F.; López-Roig, M.; Lavenir, R.; Guillemot, D.; Letort, V.; Bourhy, H.; Opatowski, L. Insights into persistence mechanisms of a zoonotic virus in bat colonies using a multispecies metapopulation model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banyard, A.C.; Johnson, N.; Voller, K.; Hicks, D.; Nunez, A.; Hartley, M.; Fooks, A.R. Repeated detection of European bat lyssaviruse type 2 in dead bats found at a single roost in the UK. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1847–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, P.T.; Fraser, G.C.; Foster, R.A.; Storie, G.J. Histopathology and immunohistochemistry of bats infected by Australian bat lyssavirus. Aust. Vet. J. 1999, 77, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatz, J.; Teifke, J.; Mettenleiter, T.; Aue, A.; Stiefel, D.; Müller, T.; Freuling, C. Lyssavirus distribution in naturally infected bats from Germany. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 169, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, N.; Phillpotts, R.; Fooks, A.R. Airborne transmission of lyssaviruses. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freuling, C.; Vos, A.; Johnson, N.; Kaipf, I.; Denzinger, A.; Neubert, L.; Mansfield, K.; Hicks, D.; Nunez, A.; Tordo, N.; et al. Experimental infection of serotine bats (Eptesicus serotinus) with European bat lyssavirus type 1a. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2493–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Morón, S.; Juste, J.; Ibanez, C.; Ruiz-Villamor, E.; Avellon, A.; Vera, M.; Echevarría, J.E. Endemic circulation of European bat lyssavirus type 1a in Serotine bats, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begeman, L.; Kooi, E.A.; Van Weezep, E.; Van De Bildt, M.W.G.; Reusken, C.B.E.M.; Lina, P.H.C.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Brand, J.M.A.V.D.; Kuiken, T. Faeces as a novel material to estimate lyssavirus prevalence in bat populations. Zoonosis Public Health 2019, 67, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard-Meyer, E.; Servat, A.; Wasniewski, M.; Gaillard, M.; Borel, C.; Cliquet, F. Bat rabies surveillance in France: First report of unusual mortality among Serotine bats. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.; Brookes, S.; Jones, G.; Hutson, A.; Racey, P.; Aegerter, J.; Smith, G.; McElhinney, L.; Fooks, A. European bat lyssaviruses: Distribution, prevalence and implications for conservation. Bio. Conserv. 2006, 131, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.; Calvelage, S.; Schlottau, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Eggerbauer, E.; Müller, T.; Freuling, C. Retrospective enhanced bat lyssavirus surveillance in Germany between 2018–2020. Viruses 2021, 13, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvelage, S.; Freuling, C.M.; Fooks, A.R.; Höper, D.; Marston, D.A.; McElhinney, L.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Finke, S.; Beer, M.; Muller, T. Full-genome sequences and phylogenetic analysis of archived Danish European bat lyssavirus 1 (EBLV-1) emphasize a higher genetic resolution and spatial segregation for sublineage 1a. Viruses 2021, 13, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjørnehøj, K.; Rønsholt, L.; Fooks, A.R. Antibodies to EBLV-1 in a domestic cat in Denmark. Vet. Rec. 2004, 155, 571–572. [Google Scholar]
- Cliquet, F.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Barrat, J.; Brookes, S.M.; Healy, D.M.; Wasniewski, M.; Litaize, E.; Biarnais, M.; Johnson, L.; Fooks, A.R. Experimental infection of Foxes with European bat Lyssaviruses type-1 and 2. BMC Vet. Res. 2009, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health England. Bat Contact and Rabies Risks. 2020. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/902947/Bat_Contact_Rabies_Risk_Leaflet_2020126.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- Parize, P.; Robledo, I.C.T.; Cervantes-Gonzalez, M.; Kergoat, L.; Larrous, F.; Serra-Cobo, J.; Dacheux, L.; Bourhy, H. Circumstances of human-bat interactions and risk of lyssavirus transmission in meteropolitan France. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fooks, A.R. The challenge of emerging lyssaviruses. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2004, 3, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Bat Species and Unique ID | Date Received | Gender | Age | County | TaqMan RT-PCR Result (Cycle Threshold) | Case Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. serotinus, Bat 762-18 | 08/10/2018 | Male | Adult | Dorset | Positive EBLV-1 (19.84) | Found dead, possible animal attack. |
| E. serotinus, Bat 791-18 | 17/10/2018 | Female | Juvenile | Dorset | Positive EBLV-1 (22.63) | Died in captivity. Possible animal attack, found grounded near roost. |
| E. serotinus, Bat 177-19 | 25/05/2019 | Male | Adult | Dorset | Positive EBLV-1 (19.37) | Died in captivity. Flew into window and fell to the ground. |
| E. serotinus, Bat 854-19 | 30/08/2019 | Male | Juvenile | Dorset | Positive EBLV-1 (23.99) | Euthanised. Recovered from a public space. Possible animal attack. |
| E. serotinus, Bat 949-19 | 13/09/2019 | Male | Juvenile | Dorset | Positive EBLV-1 (18.54) | Euthanised. Found on public highway path. Signs of animal attack. |
| E. serotinus, Bat 621-20 | 14/09/2020 | Female | Adult | Dorset | Positive EBLV-1 (21.61) | Euthanised. Found grounded. |
| E. serotinus, Bat 807-20 | 23/12/2020 | Female | Adult | Somerset | Positive EBLV-1 (19.55) | Euthanised. Recovered crawling on public road, unable to fly. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Folly, A.J.; Marston, D.A.; Golding, M.; Shukla, S.; Wilkie, R.; Lean, F.Z.X.; Núñez, A.; Worledge, L.; Aegerter, J.; Banyard, A.C.; et al. Incursion of European Bat Lyssavirus 1 (EBLV-1) in Serotine Bats in the United Kingdom. Viruses 2021, 13, 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101979
Folly AJ, Marston DA, Golding M, Shukla S, Wilkie R, Lean FZX, Núñez A, Worledge L, Aegerter J, Banyard AC, et al. Incursion of European Bat Lyssavirus 1 (EBLV-1) in Serotine Bats in the United Kingdom. Viruses. 2021; 13(10):1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101979
Chicago/Turabian StyleFolly, Arran J., Denise A. Marston, Megan Golding, Shweta Shukla, Rebekah Wilkie, Fabian Z. X. Lean, Alejandro Núñez, Lisa Worledge, James Aegerter, Ashley C. Banyard, and et al. 2021. "Incursion of European Bat Lyssavirus 1 (EBLV-1) in Serotine Bats in the United Kingdom" Viruses 13, no. 10: 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101979
APA StyleFolly, A. J., Marston, D. A., Golding, M., Shukla, S., Wilkie, R., Lean, F. Z. X., Núñez, A., Worledge, L., Aegerter, J., Banyard, A. C., Fooks, A. R., Johnson, N., & McElhinney, L. M. (2021). Incursion of European Bat Lyssavirus 1 (EBLV-1) in Serotine Bats in the United Kingdom. Viruses, 13(10), 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101979







