IFNα and β Mediated JCPyV Suppression through C/EBPβ-LIP Isoform
Abstract
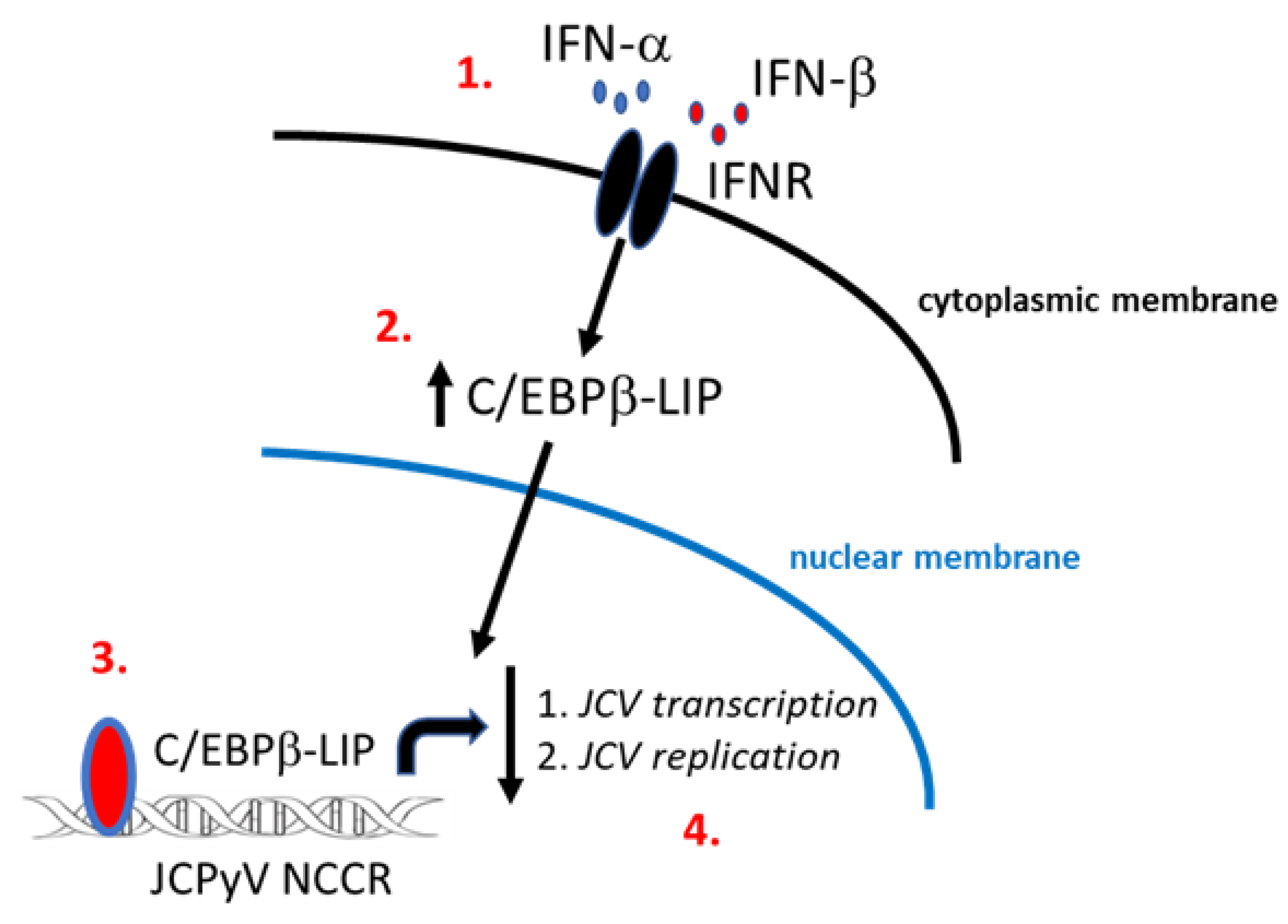
1. Introduction
1.1. The Human Polyomavirus JC
1.2. C/EBPβ-LIP Isoform
1.3. Type I IFNs and Antiviral Responses
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Plasmids
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. Recombinant Human IFNα and IFNβ Treatment
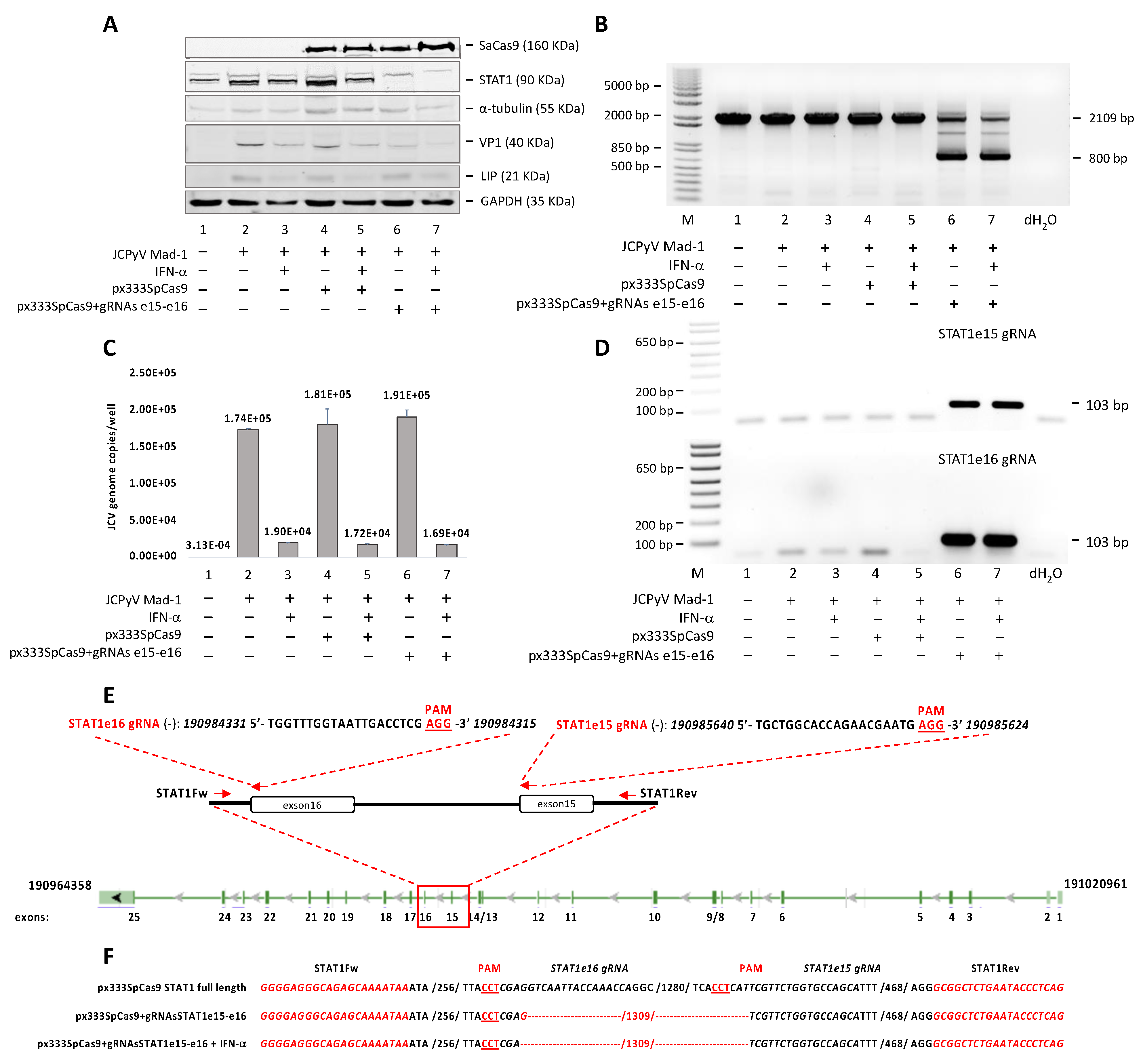
2.4. CRISPR Cas9 Knockout of STAT1
2.5. Production of Clonal Derivatives of SVGA Expressing SpCas9 and STAT1-Specific gRNAs
2.6. Reverse Transcriptase Reaction
2.7. Analysis of STAT1 Gene Sequence Excision
2.8. Infection/Transfection/shRNA Depletion of pLIP
2.9. Luciferase Assays
2.10. Western Blots
2.11. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (Q-PCR)
2.12. Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
2.12.1. MTT Assay
2.12.2. Cell Fractionation
2.12.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
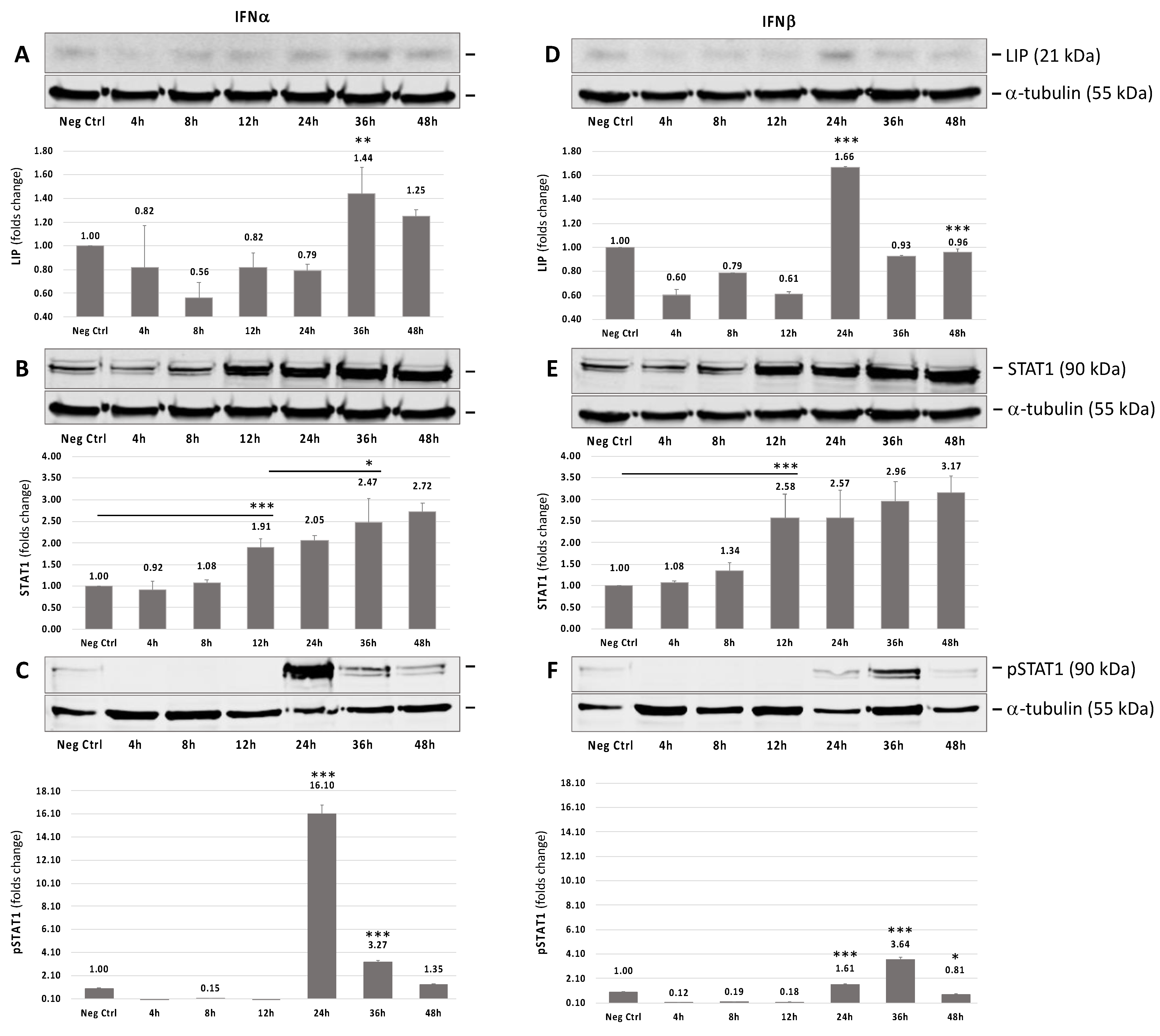
3.1. IFNα or IFNβ Induces Endogenous Expression of C/EBPβ-LIP
3.2. STAT1-Independent Interferon Signaling
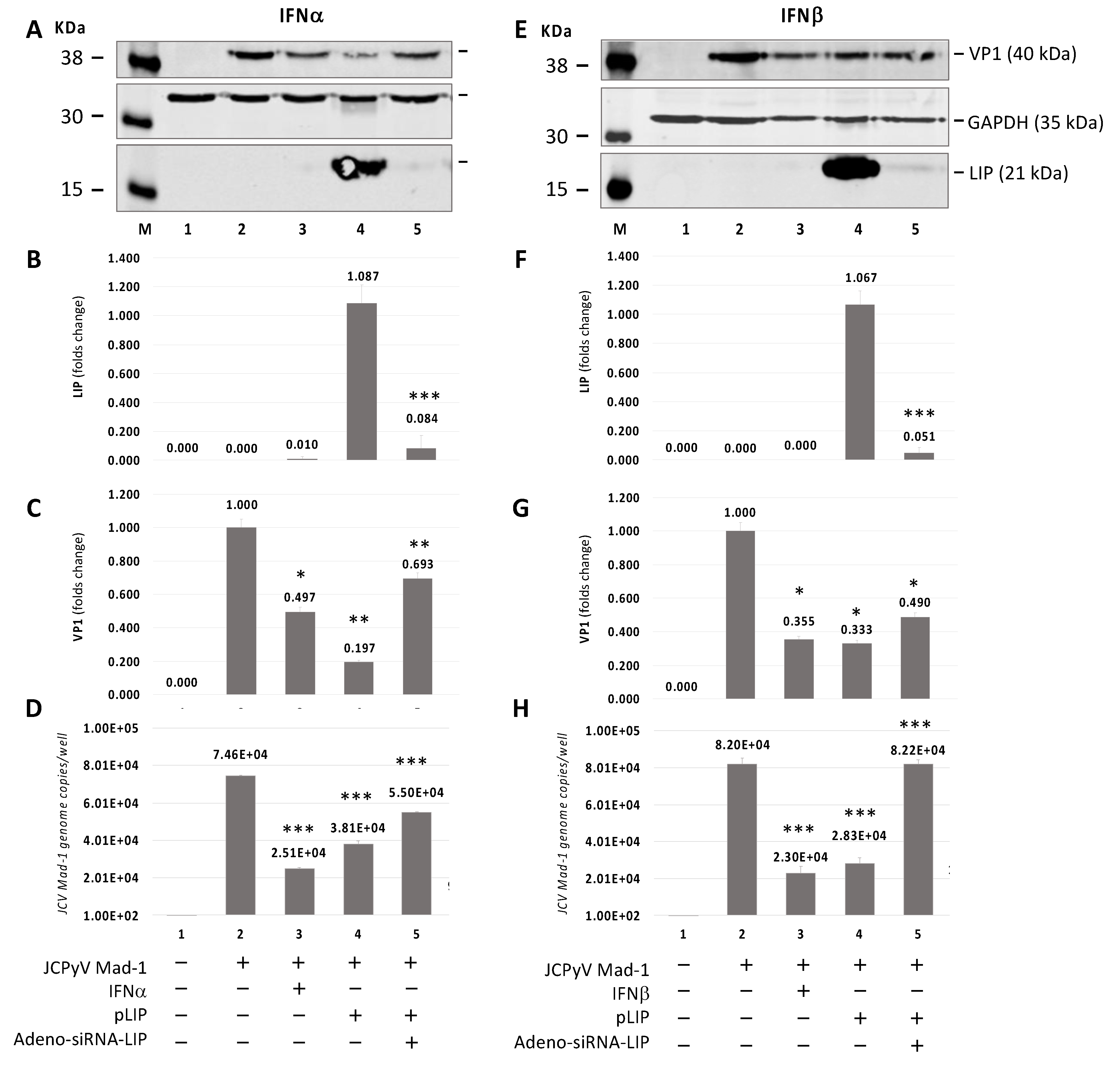
3.3. Additive Effect of IFNα or IFNβ and C/EBPβ-LIP on Inhibition of JCPyV Early and Late Transcription by Promoter Activity
3.4. Silencing of C/EBPβ-LIP by an Adeno-shRNA Reverses the Inhibitor Effect of LIP on JCPyV Replication
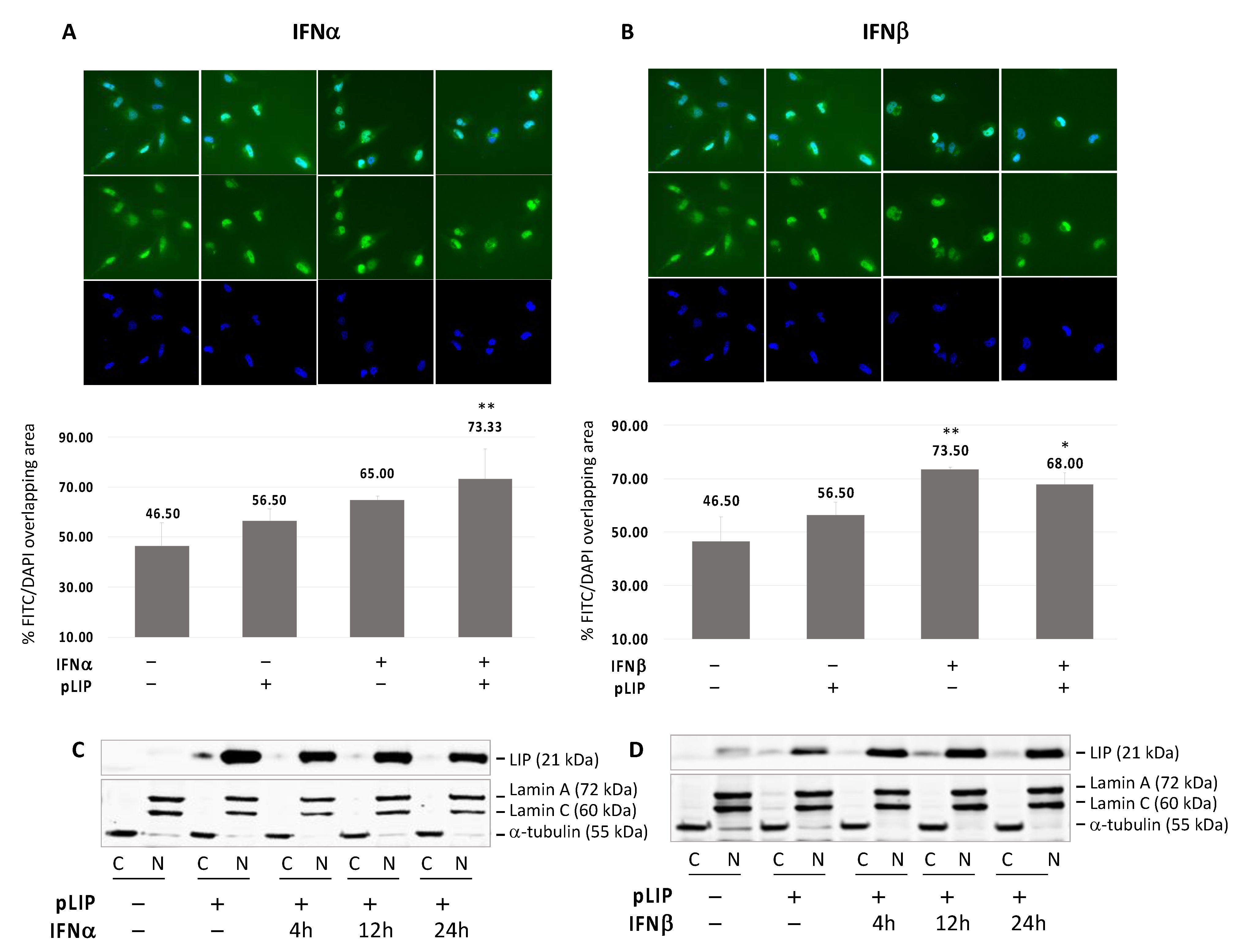
3.5. Translocation of C/EBPβ-LIP to the Nucleus after IFNα or IFNβ Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berger, J.R. The clinical features of PML. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2011, 78 (Suppl. 2), S8–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carruthers, R.L.; Berger, J. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and JC Virus-related disease in modern neurology practice. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2014, 3, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavazzi, E.; White, M.K.; Khalili, K. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: Clinical and molecular aspects. Rev. Med. Virol. 2012, 22, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.K.; Khalili, K. Pathogenesis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy–revisited. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollebo, H.S.; White, M.K.; Gordon, J.; Berger, J.R.; Khalili, K. Persistence and pathogenesis of the neurotropic polyomavirus JC. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padgett, B.L.; Walker, D.L.; ZuRhein, G.M.; Hodach, A.E.; Chou, S.M. JC Papovavirus in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J. Infect. Dis. 1976, 133, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCaprio, J.A.; Garcea, R.L. A cornucopia of human polyomaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollebo, H.S.; Del Valle, L.; Safak, M.; Khalili, K.; White, M.K. Role for tumor necrosis factor-alpha in JC virus reactivation and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 233, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wollebo, H.S.; Cotto, B.; Adiga, R.; Langford, D.; White, M.K. Expression of Signaling Molecules in Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Curr. HIV Res. 2016, 14, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, L.; Wollebo, H.S.; Deshmane, S.L.; Mukerjee, R.; Del Valle, L.; Safak, M.; Khalili, K.; White, M.K. Modulation of JC virus transcription by C/EBPβ. Virus Res. 2009, 146, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollebo, H.S.; Melis, S.; Khalili, K.; Safak, M.; White, M.K. Cooperative Roles of NF-кB and NFAT4 in polyomavirus JC regulation at the KB control element. Virology 2012, 432, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollebo, H.S.; Woldemichaele, B.; Khalili, K.; Safak, M.; White, M.K. Epigenetic regulation of polyomavirus JC. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Co, J.K.; Verma, S.; Gurjav, U.; Sumibcay, L.; Nerurkar, V.R. Interferon-alpha and -beta restrict polyomavirus JC replication in primary human fetal glial cells: Implications for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assetta, B.; De Cecco, M.; O’Hara, B.; Atwood, W.J. JC polyomavirus infection of primary human renal epithelial cells is controlled by a type I IFN-induced response. mBio 2016, 7, e00903-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramji, D.P.; Foka, P. CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: Structure, function and regulation. Biochem. J. 2002, 365 Pt 3, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellizzi, A.; White, M.K.; Wollebo, H.S. Degradation of polyomavirus JC T-antigen by stress involves the LIP isoform of C/EBP. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2075–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesmer, V.M.; Rajadhyaksha, A.; Babin, J.; Bina, M. NF-IL6-mediated transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7298–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, Y.; Rogers, L.; Nakata, K.; Zhao, B.Y.; Pine, R.; Nakai, Y.; Kurosu, K.; Rom, W.N.; Weiden, M. Type I interferon induces inhibitory 16-kD CCAAT/ enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) beta, repressing the HIV-1 long terminal repeat in macrophages: Pulmonary tuberculosis alters C/EBP expression, enhancing HIV-1 replication. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, S.; Ishii, K.J.; Coban, C.; Akira, S. Innate immune response to viral infection. Cytokine 2008, 43, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetson, D.B.; Medzhitov, R. Type I Interferons in Host Defense. Immunity 2006, 25, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Hertzog, P.J.; Holland, K.A.; Sumarsono, S.H.; Tymms, M.J.; Hamilton, J.A.; Whitty, G.; Bertoncello, I.; Kola, I. A null mutation in the gene encoding a type I interferon receptor component eliminates antiproliferative and antiviral responses to interferons α and β and alters macrophage responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11284–11288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, U.; Steinhoff, U.; Reis, L.F.L.; Hemmi, S.; Pavlovic, J.; Zinkernagel, R.M.; Aguet, M. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science 1994, 264, 1918–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, B.P.; Holman, D.W.; Cruz-Orengo, L.; Jujjavarapu, H.; Durrant, D.M.; Klein, R.S. Viral pathogen-associated molecular patterns regulate blood-brain barrier integrity via competing innate cytokine signals. mBio 2014, 5, e01476-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Daniels, B.P.; Pinto, A.K.; Huang, A.C.; Vick, S.C.; Doyle, S.E.; Gale, M.; Klein, R.S.; Diamond, M.S. Interferon-λ restricts West Nile virus neuroinvasion by tightening the blood-brain barrier. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 284ra59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Schoggins, J.W.; Diamond, M.S. Shared and Distinct Functions of Type I and Type III Interferons. Immunity 2019, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forero, A.; Ozarkar, S.; Li, H.; Lee, C.H.; Hemann, E.A.; Nadjsombati, M.S.; Hendricks, M.R.; So, L.; Green, R.; Roy, C.N.; et al. Differential Activation of the Transcription Factor IRF1 Underlies the Distinct Immune Responses Elicited by Type I and Type III Interferons. Immunity 2019, 51, 451–464.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkhoven, C.F.; Muller, C.; Leutz, A. Translational control of C/EBPα and C/EBPβ isoform expression. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1920–1932. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, B.E.; Rohr, O.; Aunis, D.; Schaeffer, E. Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor, a transcriptional activator of HIV-1 gene expression in human brain cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23572–23576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollebo, H.S.; Bellizzi, A.; Kaminski, R.; Hu, W.; White, M.K.; Khalili, K. CRISPR/Cas9 System as an agent for eliminating polyomavirus JC infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.K.; Skowronska, A.; Gordon, J.; Del Valle, L.; Deshmane, S.L.; Giordano, A.; Khalili, K. Analysis of a mutant p53 protein arising in a medulloblastoma from a mouse transgenic for the JC virus early region. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 4079–4092. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, M.K.; Kaminski, R.; Khalili, K.; Wollebo, H.S. Rad51 activates polyomavirus JC early transcription. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ng, C.T.; Mendoza, J.L.; Garcia, K.C.; Oldstone, M.B. Alpha and beta type 1 interferon signaling: Passage for diverse biologic outcomes. Cell 2016, 164, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, C.E. Antiviral actions of interferons. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 778–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnoli, L.; Sariyer, I.K.; Tung, J.; Feliciano, M.; Sawaya, B.E.; Del Valle, L.; Ferrante, P.; Khalili, K.; Safak, M.; White, M.K. Early growth response-1 protein is induced by JC virus infection and binds and regulates the JC virus promoter. Virology 2008, 375, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudaronek, J.M.; Barber, S.A.; Clements, J.E. CUGBP1 is required for IFNβ-mediated induction of dominant-negative CEBPbeta and suppression of SIV replication in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7262–7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, F.I.; Sariyer, R.; Otalora, Y.L.; Yarandi, S.; Craigie, M.; Gordon, J.; Sariyer, I.K. IFN-gamma inhibits JC virus replication in glial cells by suppressing T-antigen expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Major, E.O. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients on immunomodulatory therapies. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010, 61, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| gRNAs | Nucleotide Positions * | Strand | Sequence (PAM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAT1e16 | 190984331–190984315 | Minus | 5′-TGGTTTGGTAATTGACCTCG AGG-3′ |
| STAT1e15 | 190985640–190985624 | Minus | 5′-TGCTGGCACCAGAACGAATG AGG-3′ |
| Oligonucleotides gRNA cloning | Nucleotide positions * | Strand | Sequence |
| STAT1e16Fw | - | - | 5′-CAC CGT GGT TTG GTA ATT GAC CTC G-3′ |
| STAT1e16Rev | - | - | 5′-AAA CCG AGG TCA ATT ACC AAA CCA C-3′ |
| STAT1e15Fw | - | - | 5′-CAC CGT GCT GGC ACC AGA ACG AAT G-3′ |
| STAT1e15Rev | - | - | 5′-AAA CCA TTC GTT CTG GTG CCA GCA C-3′ |
| Primers | Nucleotide Positions * | Strand | Sequence |
| STAT1Fw | 190984026–190984046 | Plus | 5′-GGGGAGGGCAGAGCAAAATAA-3′ |
| STAT1Rev | 190986115–190986134 | Minus | 5′-CTGAGGGTATTCAGAGCCGC-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
May, D.; Bellizzi, A.; Kassa, W.; Cipriaso, J.M.; Caocci, M.; Wollebo, H.S. IFNα and β Mediated JCPyV Suppression through C/EBPβ-LIP Isoform. Viruses 2021, 13, 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101937
May D, Bellizzi A, Kassa W, Cipriaso JM, Caocci M, Wollebo HS. IFNα and β Mediated JCPyV Suppression through C/EBPβ-LIP Isoform. Viruses. 2021; 13(10):1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101937
Chicago/Turabian StyleMay, Dana, Anna Bellizzi, Workineh Kassa, John M. Cipriaso, Maurizio Caocci, and Hassen S. Wollebo. 2021. "IFNα and β Mediated JCPyV Suppression through C/EBPβ-LIP Isoform" Viruses 13, no. 10: 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101937
APA StyleMay, D., Bellizzi, A., Kassa, W., Cipriaso, J. M., Caocci, M., & Wollebo, H. S. (2021). IFNα and β Mediated JCPyV Suppression through C/EBPβ-LIP Isoform. Viruses, 13(10), 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101937








