Differential Viral-Host Immune Interactions Associated with Oseltamivir-Resistant H275Y and Wild-Type H1N1 A(pdm09) Influenza Virus Pathogenicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oseltamivir-Resistant and Wild-Type Viruses
2.2. In Vitro Infection and Viral Load
2.3. Ethical Statement
2.3.1. Mice Infection, Clinical Signs, and Sampling
2.3.2. Ferret Infection, Clinical Signs, and Sampling
Ferret Acute Phase Proteins
Viral RNA Detection and IAV Antigen Expression and Quantification in Ferret Lungs
Ferret Innate Immune Gene Expression Profiles
2.3.3. Histopathology
2.3.4. Hemagglutination Inhibition (HI) Assay
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
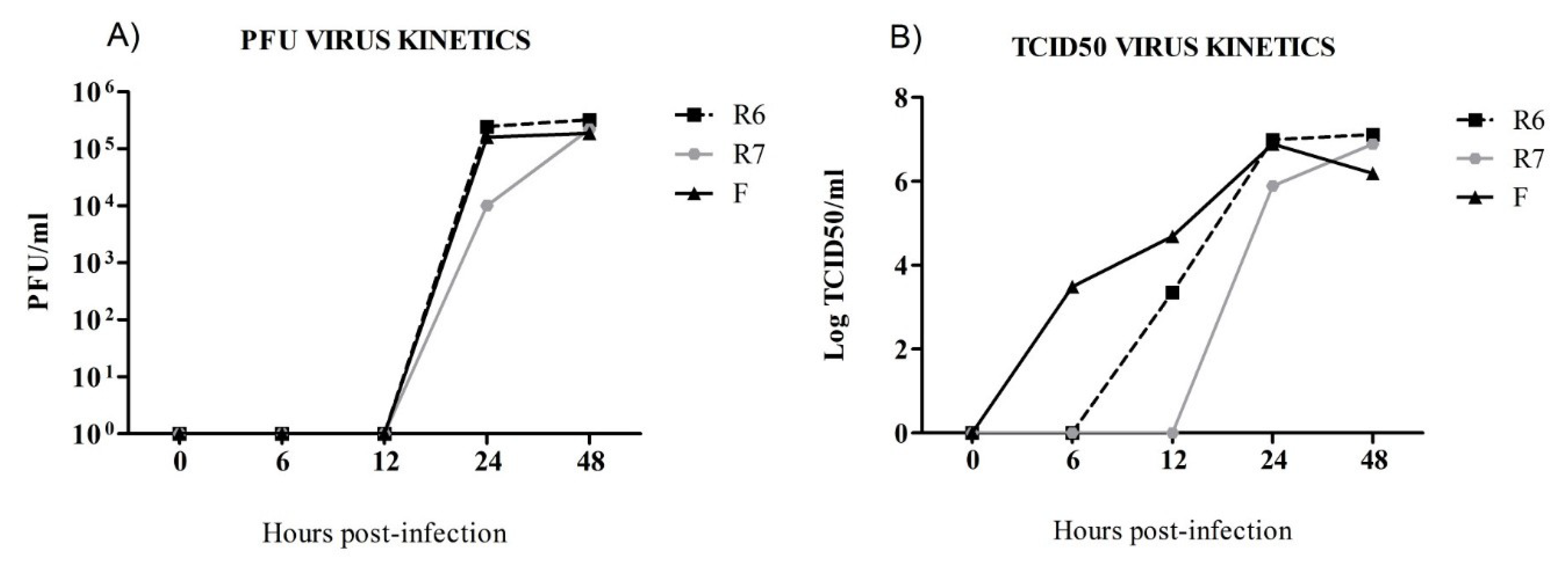
3.1. Oseltamivir-Sensitive (F) and Oseltamivir-Resistant (R6) Replicate Faster than the R7 Virus In Vitro
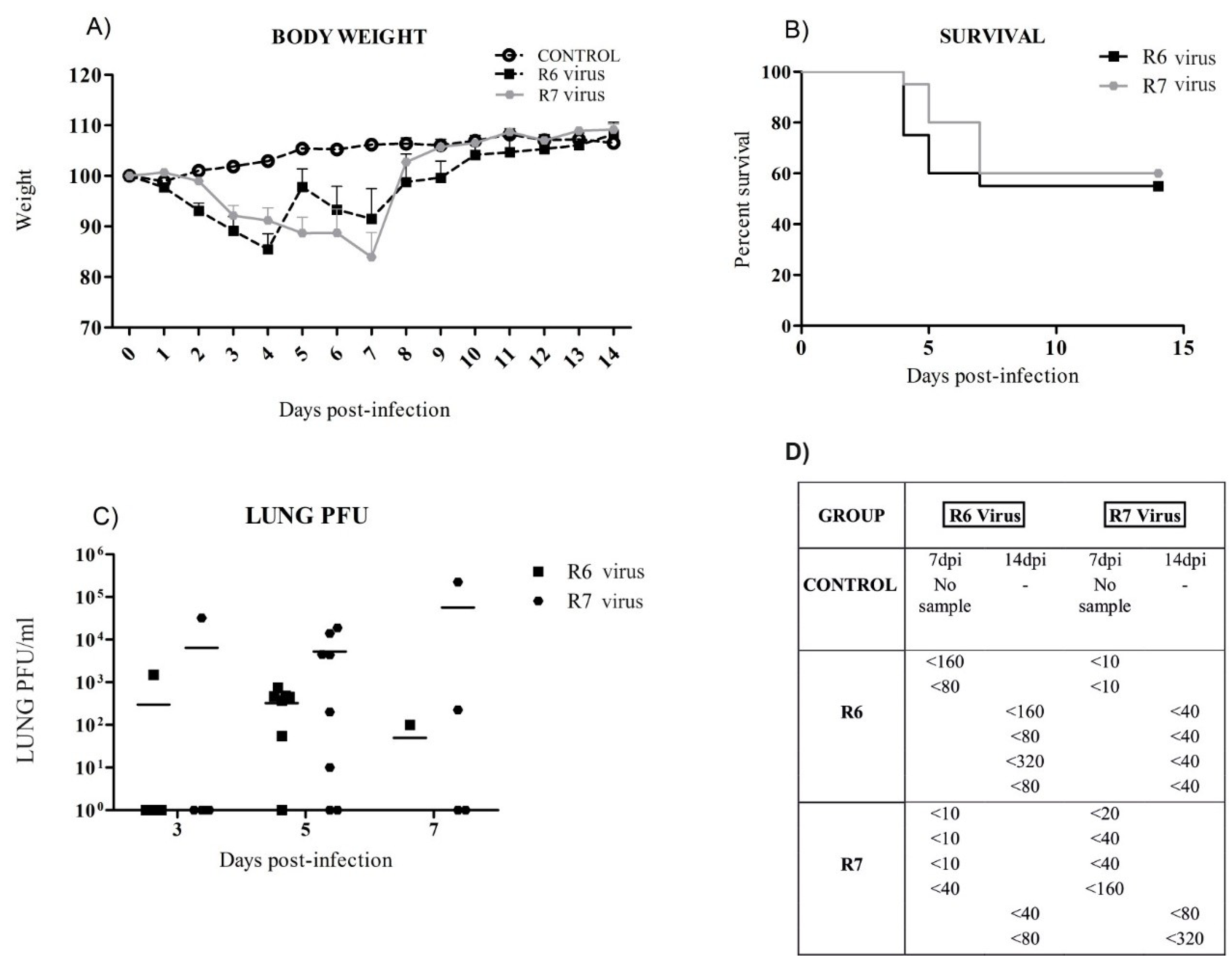
3.2. R6-Infected Mice Presented Earlier Clinical Signs and Higher Mortality Rates than R7-Infected Mice
3.3. Virus Replication in Mice
3.4. R6 and R7 Presented Similar Mice Antibody Responses
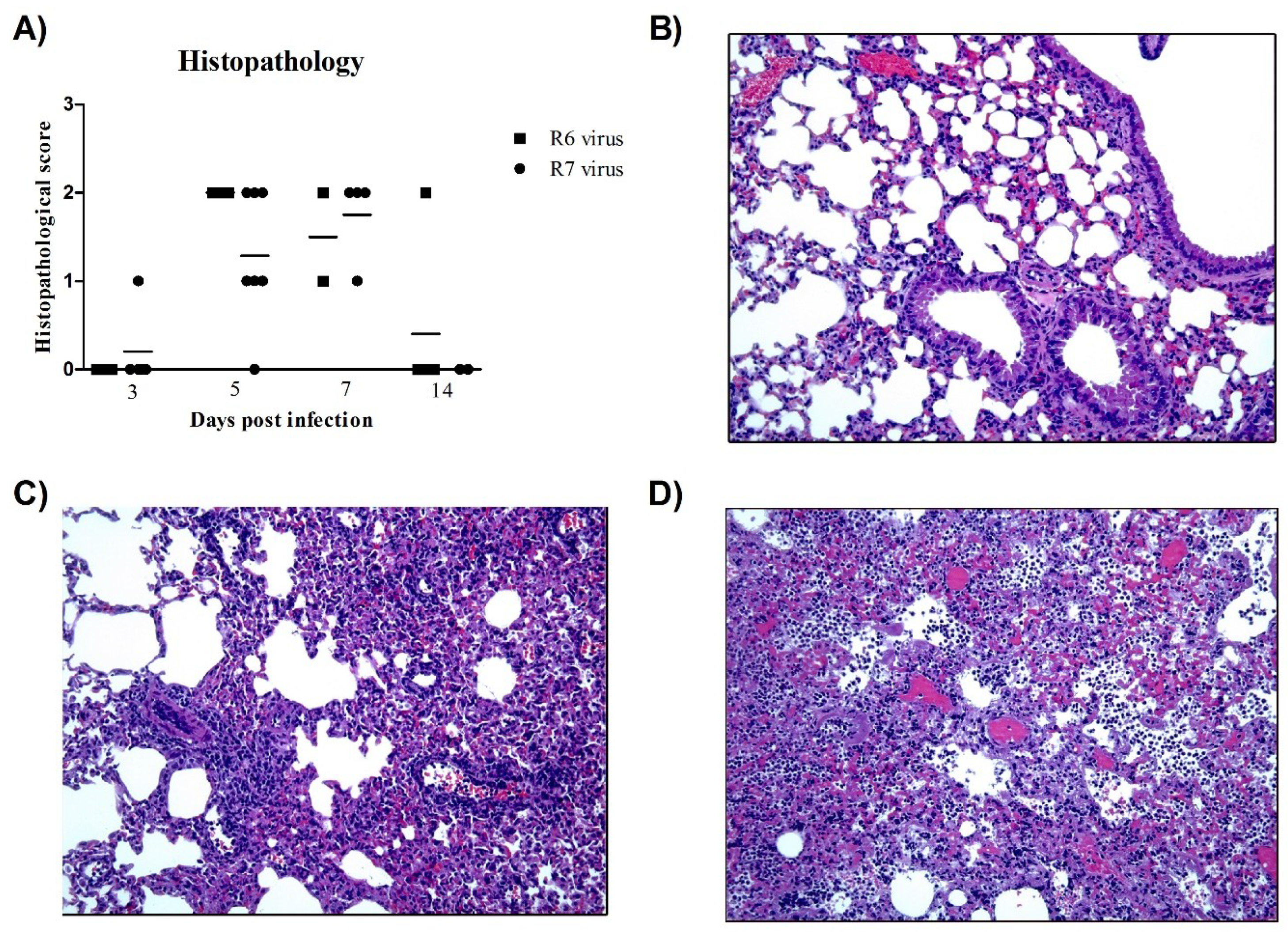
3.5. R6-Infected Mice Showed More Severe Histopathological Lesions than R7-Infected Mice
3.6. A/Baleares/RR6121/2009 (R6), (A/Madrid/RR7495/2011) (R7), and A/CastillaLaMancha/RR5911/2009 (F) Viruses Show Aminoacidic Differences
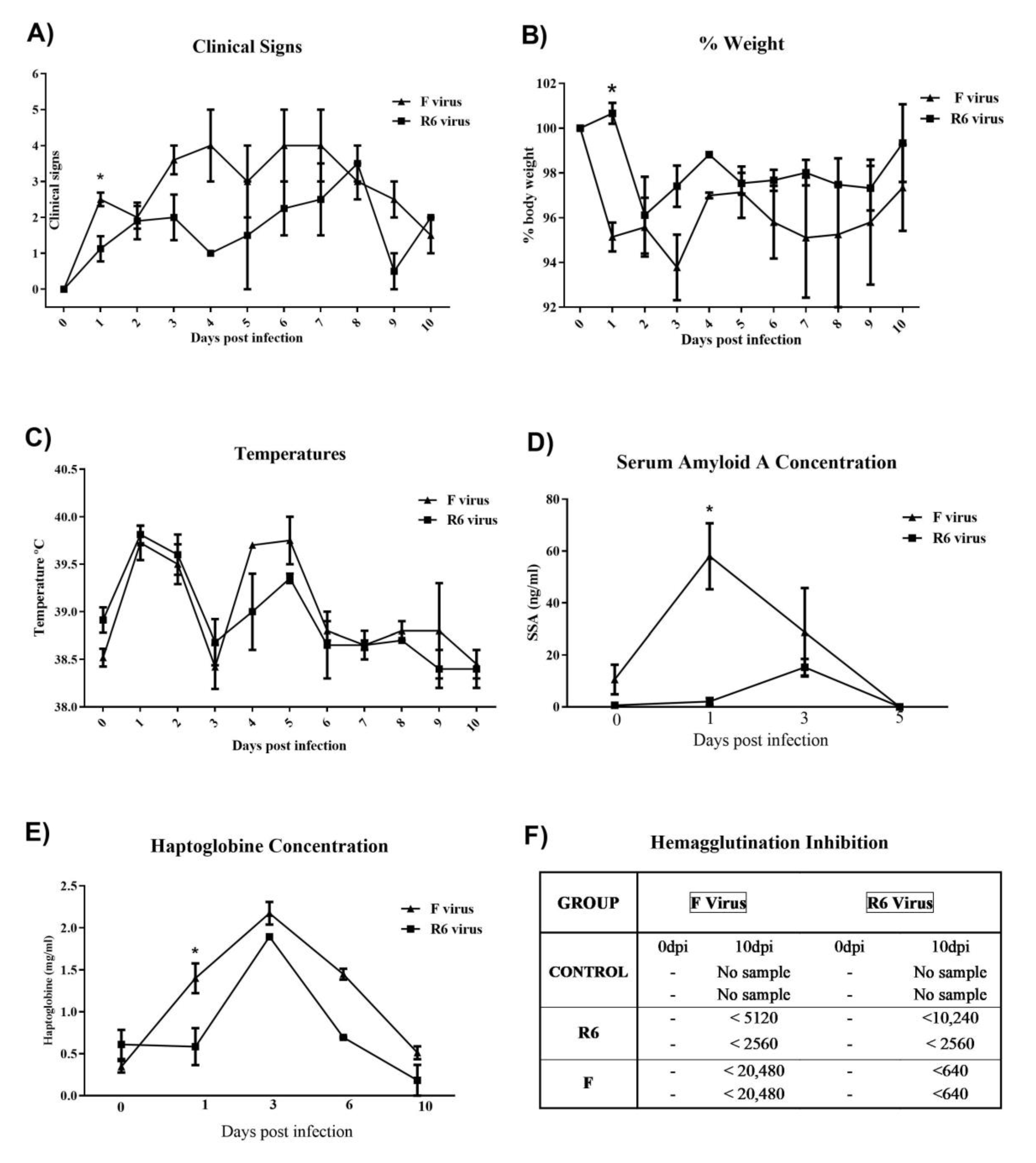
3.7. F-Infected Ferrets Presented More Severe Clinical Signs, and Higher Blood APP and Antibody Responses than the R6-Infected Group
3.8. F-Infected Ferrets Showed More Severe Histopathological Lesions and Higher IAV Antigen Immunostaining than R6-Infected Ferrets
3.9. F-Infected Ferrets Presented Higher Viral Loads than R6-Infected Ferrets
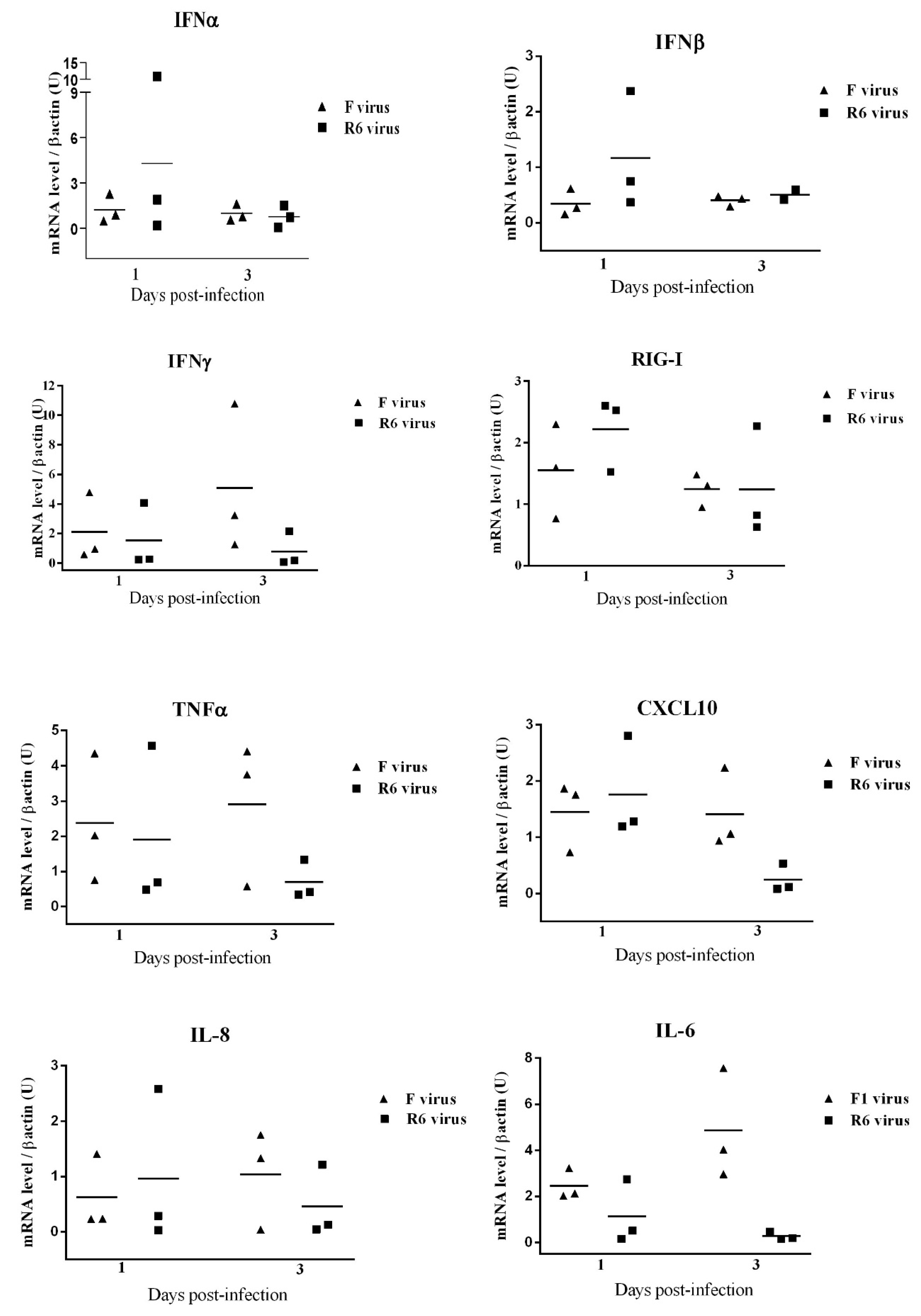
3.10. F- and R6-Infected Animals Showed Different Innate Immune Genetic Profiles in the Lungs throughout Infection
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donaldson, L.J.; Rutter, P.D.; Ellis, B.M.; Greaves, F.E.; Mytton, O.T.; Pebody, R.G.; Yardley, I.E. Mortality from pandemic A/H1N1 2009 influenza in England: Public health surveillance study. BMJ 2009, 339, b5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.J.; Vijaykrishna, D.; Bahl, J.; Lycett, S.J.; Worobey, M.; Pybus, O.G.; Ma, S.K.; Cheung, C.L.; Raghwani, J.; Bhatt, S.; et al. Origins and evolutionary genomics of the 2009 swine-origin H1N1 influenza A epidemic. Nature 2009, 459, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumbholz, A.; Schmidtke, M.; Bergmann, S.; Motzke, S.; Bauer, K.; Stech, J.; Durrwald, R.; Wutzler, P.; Zell, R. High prevalence of amantadine resistance among circulating European porcine influenza A viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, F.S.; Jain, S.; Finelli, L.; Shaw, M.W.; Lindstrom, S.; Garten, R.J.; Gubareva, L.V.; Xu, X.; Bridges, C.B.; Uyeki, T.M. Emergence of a novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus in humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2605–2615. [Google Scholar]
- Zambon, M.; Hayden, F.G. Position statement: Global neuraminidase inhibitor susceptibility network. Antivir. Res. 2001, 49, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiso, M.; Shinya, K.; Shimojima, M.; Takano, R.; Takahashi, K.; Katsura, H.; Kakugawa, S.; Le, M.T.; Yamashita, M.; Furuta, Y.; et al. Characterization of oseltamivir-resistant 2009 H1N1 pandemic influenza A viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Hong, E.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kwon, D.; Choi, J.H.; Choi, W.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, J.K.; Oh, H.B.; et al. Oseltamivir-resistant pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus, South Korea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1938–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Tan, M.; Guo, J.; Wei, H.; Zhao, X.; Lan, Y.; Xiao, N.; Wang, Z.; et al. Characteristics of oseltamivir-resistant influenza A (H1N1) pdm09 virus during the 2013–2014 influenza season in Mainland China. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Duan, S.; Boltz, D.A.; Seiler, P.; Li, J.; Bragstad, K.; Nielsen, L.P.; Webby, R.J.; Webster, R.G.; Govorkova, E.A. Oseltamivir-resistant pandemic H1N1/2009 influenza virus possesses lower transmissibility and fitness in ferrets. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.C. The epidemiology and spread of drug resistant human influenza viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 8C, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herlocher, M.L.; Truscon, R.; Elias, S.; Yen, H.L.; Roberts, N.A.; Ohmit, S.E.; Monto, A.S. Influenza viruses resistant to the antiviral drug oseltamivir: Transmission studies in ferrets. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 1627–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ives, J.A.; Carr, J.A.; Mendel, D.B.; Tai, C.Y.; Lambkin, R.; Kelly, L.; Oxford, J.S.; Hayden, F.G.; Roberts, N.A. The H274Y mutation in the influenza A/H1N1 neuraminidase active site following oseltamivir phosphate treatment leave virus severely compromised both in vitro and in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2002, 55, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscona, A. Global transmission of oseltamivir-resistant influenza. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, J.D.; Gong, L.I.; Baltimore, D. Permissive secondary mutations enable the evolution of influenza oseltamivir resistance. Science 2010, 328, 1272–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, Y.; Pizzorno, A.; Bouhy, X.; Rheaume, C.; Boivin, G. Impact of potential permissive neuraminidase mutations on viral fitness of the H275Y oseltamivir-resistant influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus in vitro, in mice and in ferrets. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, J.D.; Nayak, J.S.; Baltimore, D. A computational-experimental approach identifies mutations that enhance surface expression of an oseltamivir-resistant influenza neuraminidase. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.C.; Chotpitayasunondh, T.; Cox, N.J.; Daniels, R.; Fry, A.M.; Gubareva, L.V.; Hayden, F.G.; Hui, D.S.; Hungnes, O.; Lackenby, A.; et al. Antiviral resistance during the 2009 influenza A H1N1 pandemic: Public health, laboratory, and clinical perspectives. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Vries, E.; Stittelaar, K.J.; van Amerongen, G.; Veldhuis Kroeze, E.J.; de Waal, L.; Fraaij, P.L.; Meesters, R.J.; Luider, T.M.; van der Nagel, B.; Koch, B.; et al. Prolonged influenza virus shedding and emergence of antiviral resistance in immunocompromised patients and ferrets. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, J.; Baillie, J.K.; Cao, B.; Hayden, F.G. Antiviral combinations for severe influenza. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.C.; Hardie, K.; Wilson, N.J.; Deng, Y.M.; Osbourn, M.; Leang, S.K.; Lee, R.T.; Iannello, P.; Gehrig, N.; Shaw, R.; et al. Characteristics of a widespread community cluster of H275Y oseltamivir-resistant A(H1N1)pdm09 influenza in Australia. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashita, E.; Ejima, M.; Itoh, R.; Miura, M.; Ohnishi, A.; Nishimura, H.; Odagiri, T.; Tashiro, M. A community cluster of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus exhibiting cross-resistance to oseltamivir and peramivir in Japan, November to December 2013. Euro. Surveill 2014, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashita, E.; Kiso, M.; Fujisaki, S.; Yokoyama, M.; Nakamura, K.; Shirakura, M.; Sato, H.; Odagiri, T.; Kawaoka, Y.; Tashiro, M. Characterization of a large cluster of influenza A (H1N1) pdm09 viruses cross-resistant to oseltamivir and peramivir during the 2013–2014 influenza season in Japan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kossyvakis, A.; Mentis, A.A.; Tryfinopoulou, K.; Pogka, V.; Kalliaropoulos, A.; Antalis, E.; Lytras, T.; Meijer, A.; Tsiodras, S.; Karakitsos, P.; et al. Antiviral susceptibility profile of influenza A viruses; keep an eye on immunocompromised patients under prolonged treatment. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis 2017, 36, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leang, S.K.; Deng, Y.M.; Shaw, R.; Caldwell, N.; Iannello, P.; Komadina, N.; Buchy, P.; Chittaganpitch, M.; Dwyer, D.E.; Fagan, P.; et al. Influenza antiviral resistance in the Asia-Pacific region during 2011. Antivir. Res. 2013, 97, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okomo-Adhiambo, M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Abd Elal, A.; Sleeman, K.; Fry, A.M.; Gubareva, L.V. Drug susceptibility surveillance of influenza viruses circulating in the United States in 2011–2012: Application of the WHO antiviral working group criteria. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2013, 8, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragstad, K.; Hungnes, O.; Litleskare, I.; Nyrerod, H.C.; Dorenberg, D.H.; Hauge, S.H. Community spread and late season increased incidence of oseltamivir-resistant influenza A(H1N1) viruses in Norway 2016. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2019, 13, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, A.M.; Azhar, E.I.; Shalhoub, S.; Abujamel, T.S.; Othman, N.A.; Al Zahrani, A.B.; Abdullah, H.M.; Al-Alawi, M.M.; Sindi, A.A. Genetic characterization and diversity of circulating influenza A/H1N1pdm09 viruses isolated in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia between 2014 and 2015. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Orellana, P.; Martorell, J.; Vidana, B.; Majo, N.; Martinez, J.; Falcon, A.; Rodriguez-Frandsen, A.; Casas, I.; Pozo, F.; Garcia-Migura, L.; et al. Clinical response to pandemic h1n1 influenza virus from a fatal and mild case in ferrets. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoint. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Almansa, R.; Martinez-Orellana, P.; Rico, L.; Iglesias, V.; Ortega, A.; Vidana, B.; Martinez, J.; Exposito, A.; Montoya, M.; Bermejo-Martin, J.F. Pulmonary transcriptomic responses indicate a dual role of inflammation in pneumonia development and viral clearance during 2009 pandemic influenza infection. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets, N.; Segales, J.; Cordoba, L.; Mussa, T.; Crisci, E.; Martin-Valls, G.E.; Simon-Grife, M.; Perez-Simo, M.; Perez-Maillo, M.; Nunez, J.I.; et al. Experimental infection with H1N1 European swine influenza virus protects pigs from an infection with the 2009 pandemic H1N1 human influenza virus. Vet. Res. 2010, 41, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidana, B.; Martinez, J.; Martinez-Orellana, P.; Garcia Migura, L.; Montoya, M.; Martorell, J.; Majo, N. Heterogeneous pathological outcomes after experimental pH1N1 influenza infection in ferrets correlate with viral replication and host immune responses in the lung. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, E.; Elton, D.; Medcalf, L.; Digard, P. Functional domains of the influenza A virus PB2 protein: Identification of NP- and PB1-binding sites. Virology 2004, 321, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarendeau, F.; Crepin, T.; Guilligay, D.; Ruigrok, R.W.; Cusack, S.; Hart, D.J. Host determinant residue lysine 627 lies on the surface of a discrete, folded domain of influenza virus polymerase PB2 subunit. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, Y.; Ishihama, A. Identification of two nucleotide-binding domains on the PB1 subunit of influenza virus RNA polymerase. J. Biochem. 1997, 122, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guu, T.S.; Dong, L.; Wittung-Stafshede, P.; Tao, Y.J. Mapping the domain structure of the influenza A virus polymerase acidic protein (PA) and its interaction with the basic protein 1 (PB1) subunit. Virology 2008, 379, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Krug, R.M.; Tao, Y.J. The mechanism by which influenza A virus nucleoprotein forms oligomers and binds RNA. Nature 2006, 444, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Suzuki, Y. Molecular basis of the structure and function of H1 hemagglutinin of influenza virus. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2012, 88, 226–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtyrya, Y.A.; Mochalova, L.V.; Bovin, N.V. Influenza virus neuraminidase: Structure and function. Acta Nat. 2009, 1, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamelin, M.E.; Baz, M.; Abed, Y.; Couture, C.; Joubert, P.; Beaulieu, E.; Bellerose, N.; Plante, M.; Mallett, C.; Schumer, G.; et al. Oseltamivir-resistant pandemic A/H1N1 virus is as virulent as its wild-type counterpart in mice and ferrets. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; Shin, K.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, C. Mammalian pathogenesis of oseltamivir-resistant pandemic (H1N1) 2009 influenza virus isolated in South Korea. Virus Res. 2014, 185, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memoli, M.J.; Davis, A.S.; Proudfoot, K.; Chertow, D.S.; Hrabal, R.J.; Bristol, T.; Taubenberger, J.K. Multidrug-resistant 2009 pandemic influenza A(H1N1) viruses maintain fitness and transmissibility in ferrets. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 203, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibert, C.W.; Kaminski, M.; Philipp, J.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Albrecht, R.A.; Schwalm, F.; Stertz, S.; Medina, R.A.; Kochs, G.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; et al. Oseltamivir-resistant variants of the 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza A virus are not attenuated in the guinea pig and ferret transmission models. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11219–11226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baz, M.; Abed, Y.; Simon, P.; Hamelin, M.E.; Boivin, G. Effect of the neuraminidase mutation H274Y conferring resistance to oseltamivir on the replicative capacity and virulence of old and recent human influenza A(H1N1) viruses. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Falcon, A.; Cuevas, M.T.; Pozo, F.; Guerra, S.; Garcia-Barreno, B.; Martinez-Orellana, P.; Perez-Brena, P.; Montoya, M.; Melero, J.A.; et al. Characterization in vitro and in vivo of a pandemic H1N1 influenza virus from a fatal case. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goka, E.A.; Vallely, P.J.; Mutton, K.J.; Klapper, P.E. Mutations associated with severity of the pandemic influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological evidence. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 3167–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.C.; Nor’e, S.S.; McCaw, J.M.; Fryer, H.R.; Mosse, J.; McLean, A.R.; Barr, I.G. Assessing the viral fitness of oseltamivir-resistant influenza viruses in ferrets, using a competitive-mixtures model. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 9427–9438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzette, N.; Caffrey, D.R.; Zeldovich, K.B.; Liu, P.; Gallagher, G.R.; Aiello, D.; Porter, A.J.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Bolon, D.N.; Poh, Y.P.; et al. Evolution of the influenza A virus genome during development of oseltamivir resistance in vitro. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.; Hooper, K.A.; Petrie, S.; Lee, R.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Reh, L.; Guarnaccia, T.; Baas, C.; Xue, L.; Vitesnik, S.; et al. Estimating the fitness advantage conferred by permissive neuraminidase mutations in recent oseltamivir-resistant A(H1N1)pdm09 influenza viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Govorkova, E.A.; Bahl, J.; Zaraket, H.; Baranovich, T.; Seiler, P.; Prevost, K.; Webster, R.G.; Webby, R.J. Epistatic interactions between neuraminidase mutations facilitated the emergence of the oseltamivir-resistant H1N1 influenza viruses. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brand, J.M.; Stittelaar, K.J.; van Amerongen, G.; Reperant, L.; de Waal, L.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Kuiken, T. Comparison of temporal and spatial dynamics of seasonal H3N2, pandemic H1N1 and highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus infections in ferrets. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, C.; Kushner, I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keynan, Y.; Malik, S.; Fowke, K.R. The role of polymorphisms in host immune genes in determining the severity of respiratory illness caused by pandemic H1N1 influenza. Public Health Genom. 2013, 16, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauad, T.; Hajjar, L.A.; Callegari, G.D.; da Silva, L.F.; Schout, D.; Galas, F.R.; Alves, V.A.; Malheiros, D.M.; Auler, J.O., Jr.; Ferreira, A.F.; et al. Lung pathology in fatal novel human influenza A (H1N1) infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, M.; Klauschen, F.; Kuchen, S.; Germain, R.N. A systems analysis identifies a feedforward inflammatory circuit leading to lethal influenza infection. Cell 2013, 154, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zeng, X.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Lu, C. Innate and adaptive immune responses in patients with pandemic influenza A(H1N1)pdm09. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2267–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidana, B.; Martinez, J.; Martorell, J.; Montoya, M.; Cordoba, L.; Perez, M.; Majo, N. Involvement of the different lung compartments in the pathogenesis of pH1N1 influenza virus infection in ferrets. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Protein | Portion Compared | Mutated Position | F | R6 | Frequency | Domain | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB2 | 1-757 | 127 | Y | H | 127H 98.8% (1837) | N-terminal-PB1,NP interaction | [33] |
| 191 | K | E | 191E 97.5% (1812) | ||||
| 221 | T | A | 221A 99.7% (1854) | ||||
| 660 | K | R | 660R 2.5% (47) | 627Domain – host range | [34] | ||
| PB1 | 1-757 | 257 | T | A | 257A 0.5% (10) | Nucleotide binding site | [35] |
| PB1-F2 | 1-11 TRUNCATED | - | |||||
| PA | 1-716 | 328 | R | K | 328K 99.8% (1855) | PB1 interaction | |
| 529 | N | D | 529D 99.8% (1855) | [36] | |||
| 716 | K | E | 716E 0.5% (9) | ||||
| NP | 2-497 | 400 | R | K | 400K 98.8% (1836) | Body | [37] |
| HA | 34-349 | 38 | E | K | 38K 0.1% (1) | Fusion HA1 chain | [38] |
| 127 | L | S | 127S 99.8% (1860) | Receptor binding HA1 chain | |||
| NA | 188-420 | 275 | H | Y | 275Y 0.8% (14) | Head domain | [39] |
| M1 | 1-252 | - | |||||
| M2 | 1-97 | - | |||||
| NS1 | 1-219 | 93 | M | I | 93I 2.2% (40) | N/A | |
| NS2 | 1-121 | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vidaña, B.; Martínez-Orellana, P.; Martorell, J.M.; Baratelli, M.; Martínez, J.; Migura-Garcia, L.; Córdoba, L.; Pérez, M.; Casas, I.; Pozo, F.; et al. Differential Viral-Host Immune Interactions Associated with Oseltamivir-Resistant H275Y and Wild-Type H1N1 A(pdm09) Influenza Virus Pathogenicity. Viruses 2020, 12, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080794
Vidaña B, Martínez-Orellana P, Martorell JM, Baratelli M, Martínez J, Migura-Garcia L, Córdoba L, Pérez M, Casas I, Pozo F, et al. Differential Viral-Host Immune Interactions Associated with Oseltamivir-Resistant H275Y and Wild-Type H1N1 A(pdm09) Influenza Virus Pathogenicity. Viruses. 2020; 12(8):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080794
Chicago/Turabian StyleVidaña, Beatriz, Pamela Martínez-Orellana, Jaime M. Martorell, Massimiliano Baratelli, Jorge Martínez, Lourdes Migura-Garcia, Lorena Córdoba, Mónica Pérez, Inmaculada Casas, Francisco Pozo, and et al. 2020. "Differential Viral-Host Immune Interactions Associated with Oseltamivir-Resistant H275Y and Wild-Type H1N1 A(pdm09) Influenza Virus Pathogenicity" Viruses 12, no. 8: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080794
APA StyleVidaña, B., Martínez-Orellana, P., Martorell, J. M., Baratelli, M., Martínez, J., Migura-Garcia, L., Córdoba, L., Pérez, M., Casas, I., Pozo, F., Fraile, L., Majó, N., & Montoya, M. (2020). Differential Viral-Host Immune Interactions Associated with Oseltamivir-Resistant H275Y and Wild-Type H1N1 A(pdm09) Influenza Virus Pathogenicity. Viruses, 12(8), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080794







