Retrieval of the Complete Coding Sequence of the UK-Endemic Tatenale Orthohantavirus Reveals Extensive Strain Variation and Supports Its Classification as a Novel Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Nucleic Acid Preparation
2.3. RT-PCR Screening
2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing
2.5. Retrieval of TATV’s Complete Coding sequence (CDS) Using PCR Primer-Walking
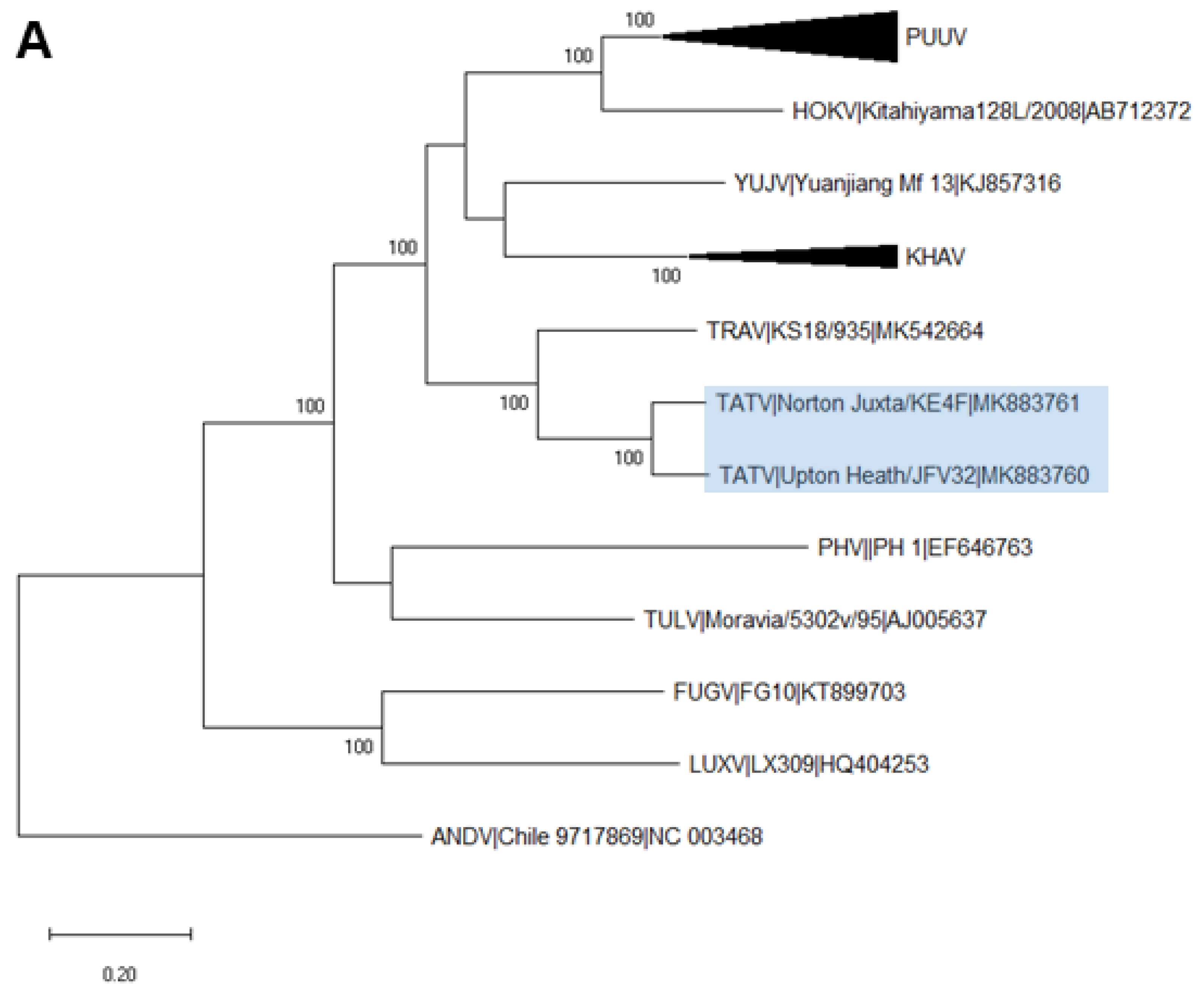
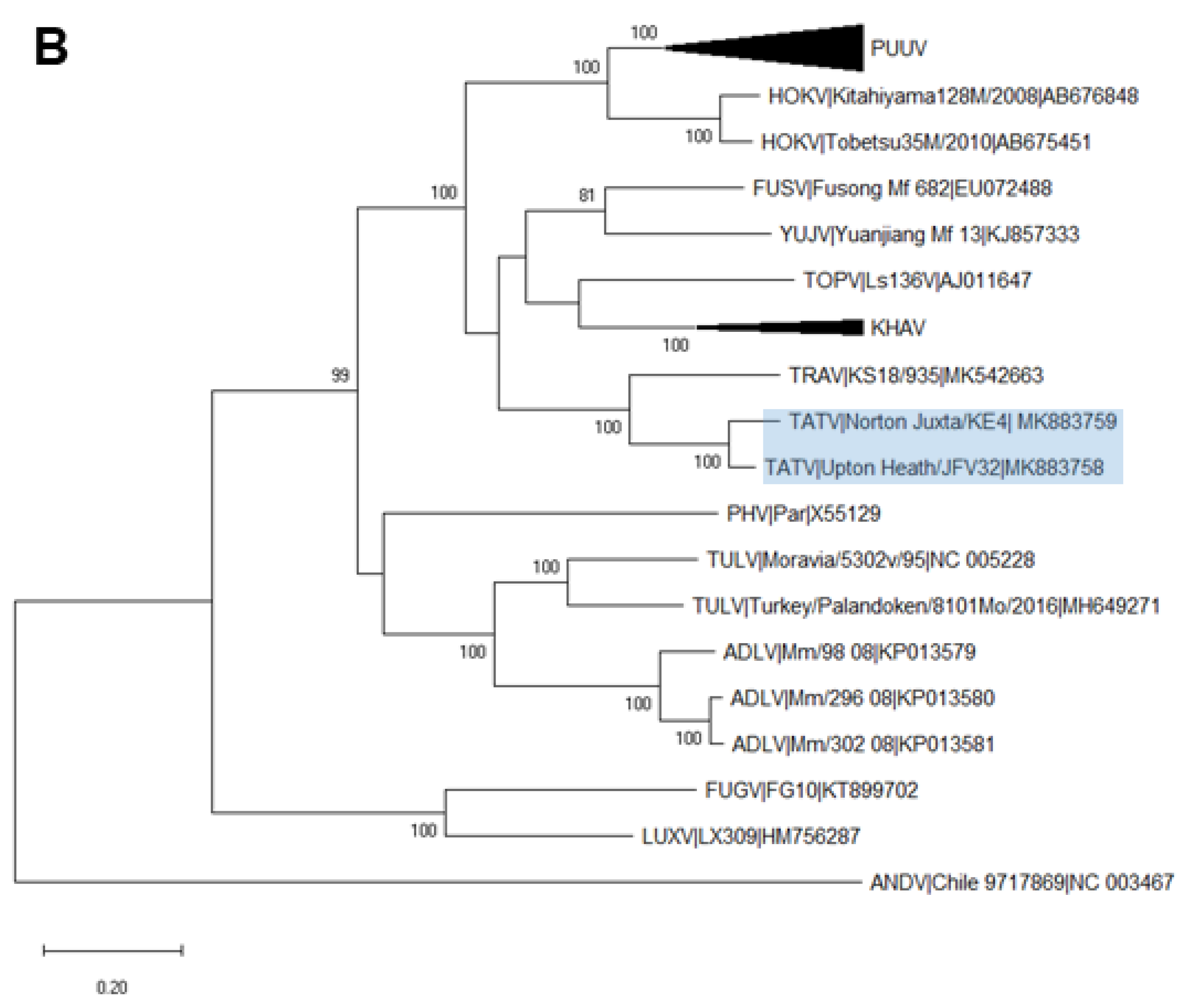
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Orthohantavirus RNA by RT-PCR
3.2. Recovery of Complete TATV CDS
3.3. Analysis of Complete TATV CDS
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plyusnin, A.; Vapalahti, O.; Vaheri, A. Hantaviruses: Genome structure, expression and evolution. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 2677–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, C.B.; Figueiredo, L.T.M.; Vapalahti, O. A global perspective on hantavirus ecology, epidemiology, and disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 412–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.; Witkowski, P.T.; Auste, B.; Nowak, K.; Weber, N.; Fahr, J. Hantavirus in Bat, Sierra Leone. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klempa, B.; Fichet-Calvet, E.; Lecompte, E.; Auste, B.; Aniskin, V.; Meisel, H.; Barrière, P.; Koivogui, L.; ter Meulen, J.; Krüger, D.H. Novel hantavirus sequences in Shrew, Guinea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laenen, L.; Vergote, V.; Kafetzopoulou, L.E.; Wawina, T.B.; Vassou, D.; Cook, J.A.; Hugot, J.-P.; Deboutte, W.; Kang, H.J.; Witkowski, P.T.; et al. A Novel Hantavirus of the European Mole, Bruges Virus, Is Involved in Frequent Nova Virus Coinfections. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermonval, M.; Baychelier, F.; Tordo, N. What Do We Know about How Hantaviruses Interact with Their Different Hosts? Viruses 2016, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaheri, A.; Strandin, T.; Hepojoki, J.; Sironen, T.; Henttonen, H.; Mäkelä, S.; Mustonen, J. Uncovering the mysteries of hantavirus infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macneil, A.; Nichol, S.T.; Spiropoulou, C.F. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. Virus Res. 2011, 162, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, J.; Maes, P.; Van Ranst, M. Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in the New, and Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome in the old world: Paradi(se)gm lost or regained? Virus Res. 2014, 187, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjertqvist, M.; Klein, S.L.; Ahlm, C.; Klingstrom, J. Mortality rate patterns for hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome caused by Puumala virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1584–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNeil, A.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Rollin, P.E. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome, United States, 1993–2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyman, P.; Ceianu, C.; Christova, I.; Tordo, N.; Beersma, M.; Joao Alves, M.; Lundkvist, A.; Hukic, M.; Papa, A.; Tenorio, A.; et al. A five-year perspective on the situation of haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and status of the hantavirus reservoirs in Europe, 2005–2010. Eurosurveillance 2011, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.G.; Williams, N.J.; Bennett, M.; Jennings, D.; Chantrey, J.; McElhinney, L.M. Detection of Seoul virus in wild brown rats (Rattus norvegicus) from pig farms in Northern England. Vet. Rec. 2019, 184, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, A.R.; Irving, W.L.; Ansell, I.D. Playing in a scrapyard and acute renal failure. Lancet 1997, 349, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.; Boyd, A.J.; Kudesia, G.; Pinkerton, I.W. A Scottish case of nephropathy due to Hantaan virus infection. J. Infect. 1985, 11, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, P.; Clement, J.; Matthys, P.; Coyle, P.V.; McCaughey, C. Serological evidence of hantavirus disease in Northern Ireland. J. Med. Virol. 1994, 43, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brus Sjölander, K.; Lundkvist, Å. Dobrava virus infection: Serological diagnosis and cross-reactions to other hantaviruses. J. Virol. Methods 1999, 80, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, L.J.; Logue, C.H.; Atkinson, B.; Baker, N.; Galbraith, S.E.; Carroll, M.W.; Brooks, T.; Hewson, R. The continued emergence of hantaviruses: Isolation of a Seoul virus implicated in human disease, United Kingdom, October 2012. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20344. [Google Scholar]
- Jameson, L.J.; Taori, S.K.; Atkinson, B.; Levick, P.; Featherstone, C.A.; van der Burgt, G.; McCarthy, N.; Hart, J.; Osborne, J.C.; Walsh, A.L.; et al. Pet rats as a source of hantavirus in England and Wales, 2013. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20415. [Google Scholar]
- Pounder, K.C.; Begon, M.; Sironen, T.; Henttonen, H.; Watts, P.C.; Voutilainen, L.; Vapalahti, O.; Klempa, B.; Fooks, A.R.; McElhinney, L.M. Novel Hantavirus in Field Vole, United Kingdom. Available online: http://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/19/4/12-1057_article (accessed on 22 January 2016).
- Thomason, A.G.; Begon, M.; Bradley, J.E.; Paterson, S.; Jackson, J.A. Endemic Hantavirus in Field Voles, Northern England. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1033–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeske, K.; Hiltbrunner, M.; Drewes, S.; Ryll, R.; Wenk, M.; Špakova, A.; Petraitytė-Burneikienė, R.; Heckel, G.; Ulrich, R.G. Field vole-associated Traemmersee hantavirus from Germany represents a novel hantavirus species. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoleridis, T.; Chappell, J.G.; Monchatre-Leroy, E.; Umhang, G.; Shi, M.; Bennett, M.; Tarlinton, R.E.; McClure, C.P.; Holmes, E.C.; Ball, J.K. Discovery and prevalence of divergent RNA viruses in European field voles and rabbits. Viruses 2019, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klempa, B.; Fichet-Calvet, E.; Lecompte, E.; Auste, B.; Aniskin, V.; Meisel, H.; Denys, C.; Koivogui, L.; ter Meulen, J.; Krüger, D.H. Hantavirus in African wood mouse, Guinea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICTV ICTV Ninth Report; Taxonomy Release. 2009. Available online: https://talk.ictvonline.org/ictv-reports/ictv_9th_report/negative-sense-rna-viruses-2011/w/negrna_viruses/205/bunyaviridae (accessed on 7 March 2019).
- Maes, P.; Klempa, B.; Clement, J.; Matthijnssens, J.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Krüger, D.H.; Van Ranst, M. A proposal for new criteria for the classification of hantaviruses, based on S and M segment protein sequences. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, L.J.; Newton, A.; Coole, L.; Newman, E.N.C.; Carroll, M.W.; Beeching, N.J.; Hewson, R.; Christley, R.M. Prevalence of antibodies against hantaviruses in serum and saliva of adults living or working on farms in Yorkshire, United Kingdom. Viruses 2014, 6, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species (Accession Number) | S | M | L |
|---|---|---|---|
| Norton-Juxta | |||
| Traemersee | 82.7 (96.8) | 79.8 (94.2) | 81.5 (96.4) |
| Khabarovsk | 79.2 (89.4) | 76.4 (87.5) | 77.9 (90.9) |
| Yuanjiang | 79.2 (88.5) | 75.3 (86.5) | 77.7 (90.4) |
| Fusong | 78.7 (88.2) | 75.2 (85.9) | -* |
| Puumala | 77.9 (87.8) | 74.8 (84.7) | 77.9 (88.1) |
| Hokkaido | 78.3 (87.5) | 75.5 (84.4) | 76.8 (88.5) |
| Upton-Heath | |||
| Traemersee | 83 (96.5) | 80.8 (94.3) | 81.5 (96.4) |
| Khabarovsk | 79.9 (88.9) | 77.1 (87.8) | 78 (90.7) |
| Yuanjiang | 78.9 (88.2) | 75.7 (86.5) | 77.7 (89.6) |
| Fusong | 78.9 (88) | 76 (86.2) | -* |
| Puumala | 78.4 (87.8) | 75.5 (84.6) | 77.6 (87.5) |
| Hokkaido | 79 (87.8) | 75.7 (84.4) | 76.7 (87.9) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chappell, J.G.; Tsoleridis, T.; Onianwa, O.; Drake, G.; Ashpole, I.; Dobbs, P.; Edema, W.; Kumi-Ansah, F.; Bennett, M.; Tarlinton, R.E.; et al. Retrieval of the Complete Coding Sequence of the UK-Endemic Tatenale Orthohantavirus Reveals Extensive Strain Variation and Supports Its Classification as a Novel Species. Viruses 2020, 12, 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040454
Chappell JG, Tsoleridis T, Onianwa O, Drake G, Ashpole I, Dobbs P, Edema W, Kumi-Ansah F, Bennett M, Tarlinton RE, et al. Retrieval of the Complete Coding Sequence of the UK-Endemic Tatenale Orthohantavirus Reveals Extensive Strain Variation and Supports Its Classification as a Novel Species. Viruses. 2020; 12(4):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040454
Chicago/Turabian StyleChappell, Joseph G., Theocharis Tsoleridis, Okechukwu Onianwa, Gabby Drake, Ian Ashpole, Phillipa Dobbs, William Edema, Frederick Kumi-Ansah, Malcolm Bennett, Rachael E. Tarlinton, and et al. 2020. "Retrieval of the Complete Coding Sequence of the UK-Endemic Tatenale Orthohantavirus Reveals Extensive Strain Variation and Supports Its Classification as a Novel Species" Viruses 12, no. 4: 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040454
APA StyleChappell, J. G., Tsoleridis, T., Onianwa, O., Drake, G., Ashpole, I., Dobbs, P., Edema, W., Kumi-Ansah, F., Bennett, M., Tarlinton, R. E., Ball, J. K., & McClure, C. P. (2020). Retrieval of the Complete Coding Sequence of the UK-Endemic Tatenale Orthohantavirus Reveals Extensive Strain Variation and Supports Its Classification as a Novel Species. Viruses, 12(4), 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040454





