A Preliminary Study of the Virome of the South American Free-Tailed Bats (Tadarida brasiliensis) and Identification of Two Novel Mammalian Viruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area, Sample Collection, and Ethics Statement
2.2. Sample Processing and Viral DNA Enrichment
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), Read Quality Control, and Sequence Filtering
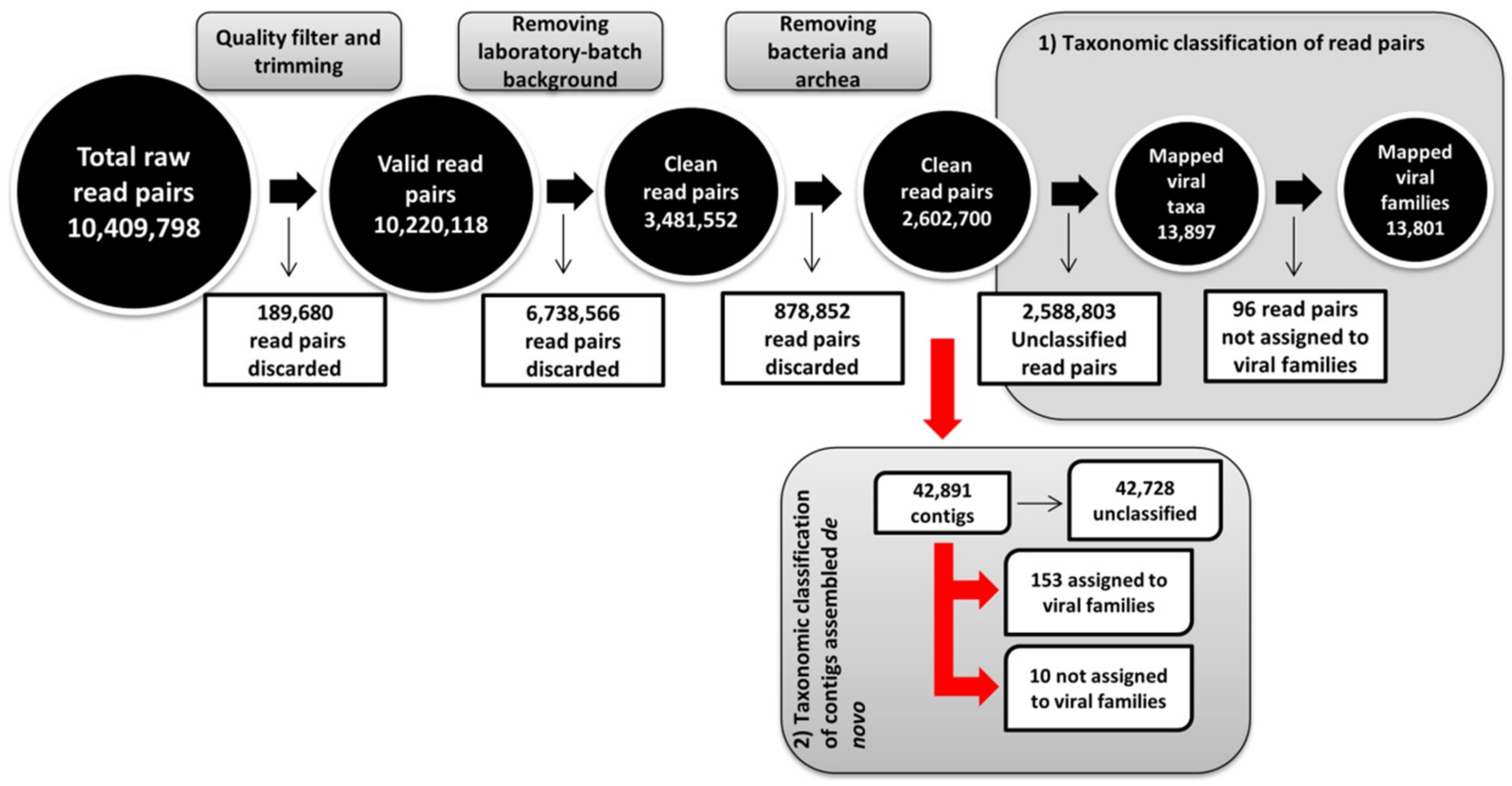
2.4. Metagenomic Analysis Workflow
2.5. Characterization of Novel Viral Genome Sequences and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Complete Papillomavirus Genome Confirmation
2.7. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Number
3. Results
3.1. Global Analysis of High-Throughput Sequencing Data
3.2. Identification of Novel Bat Viruses
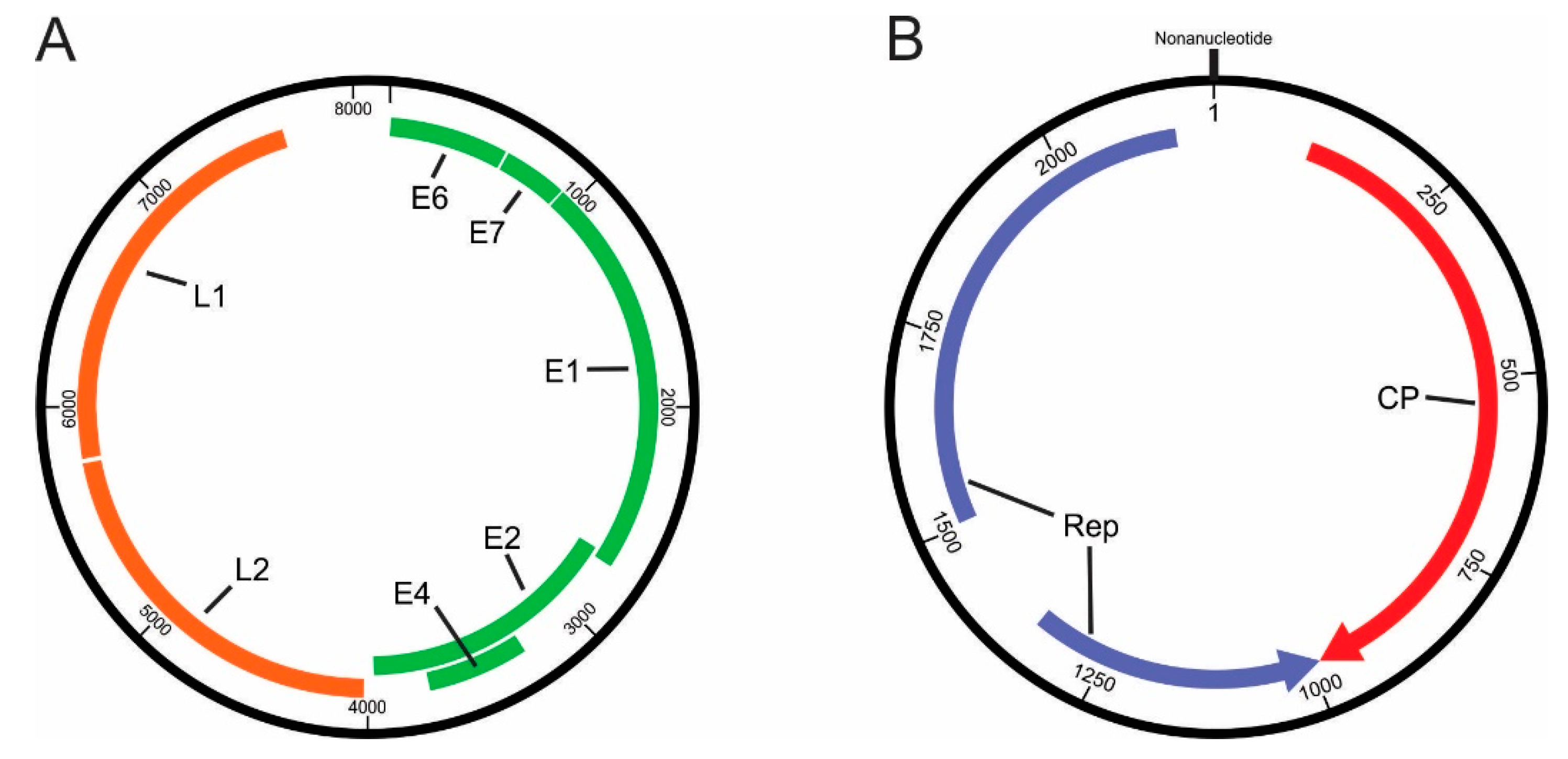
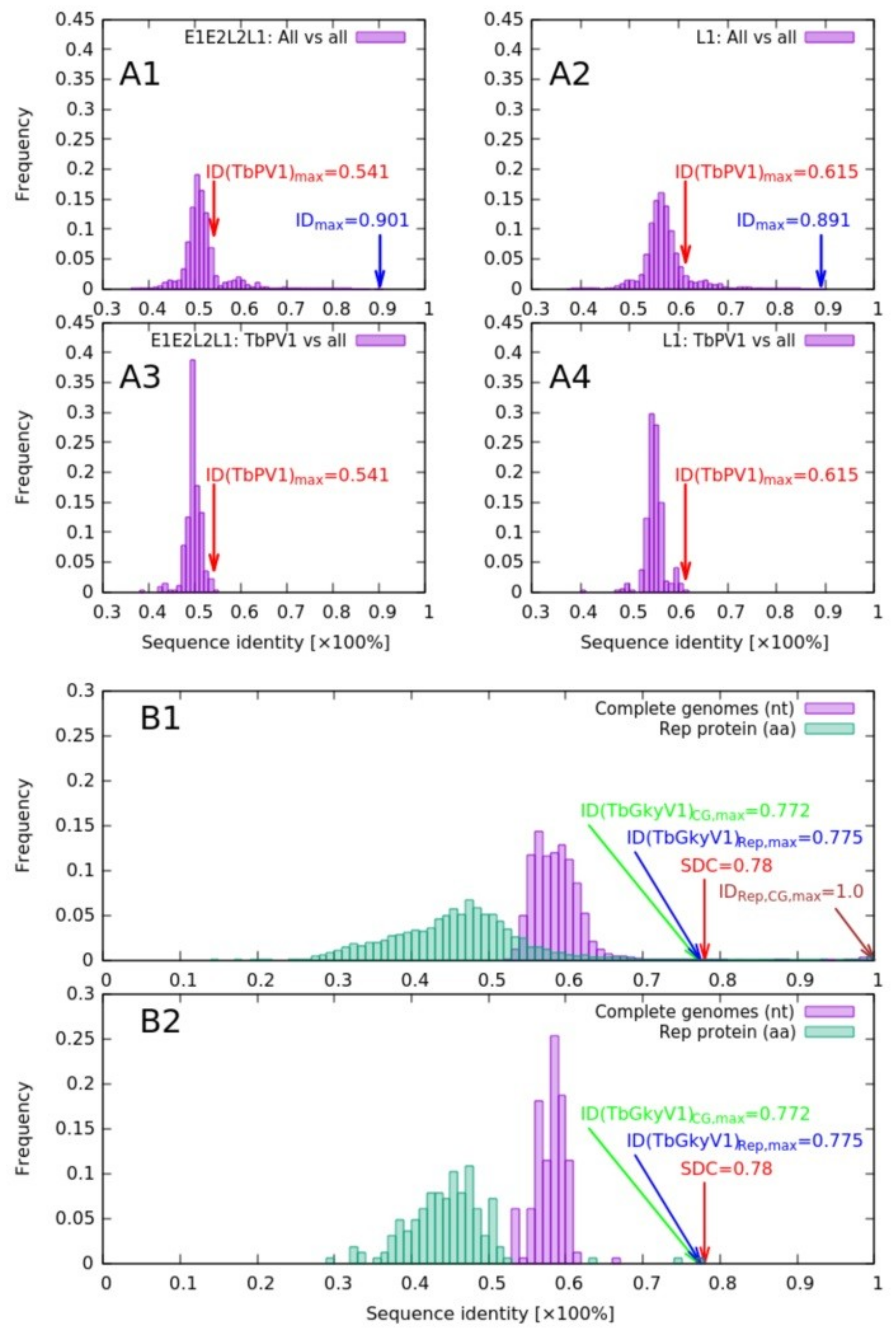
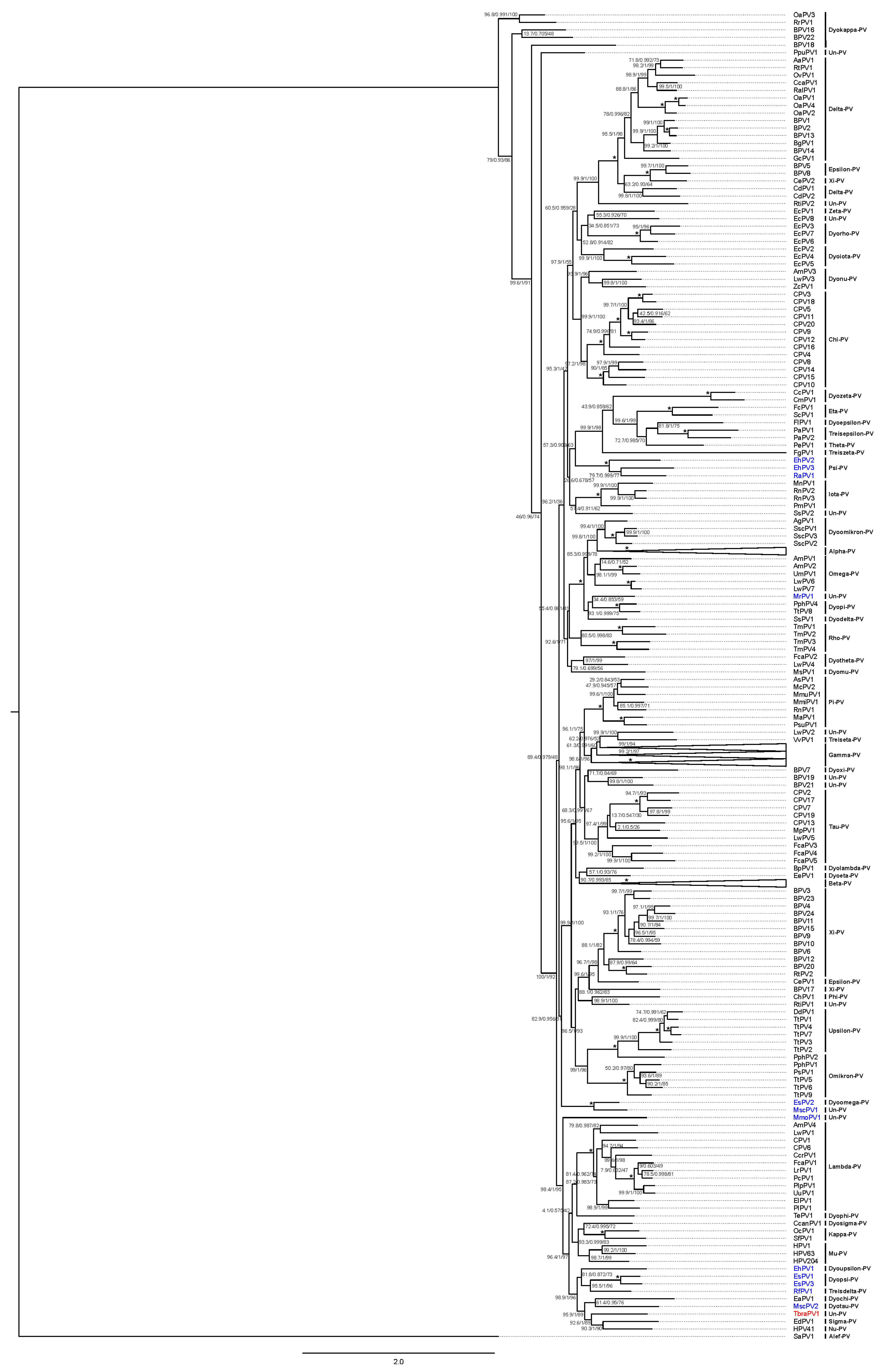
3.2.1. Papillomaviridae
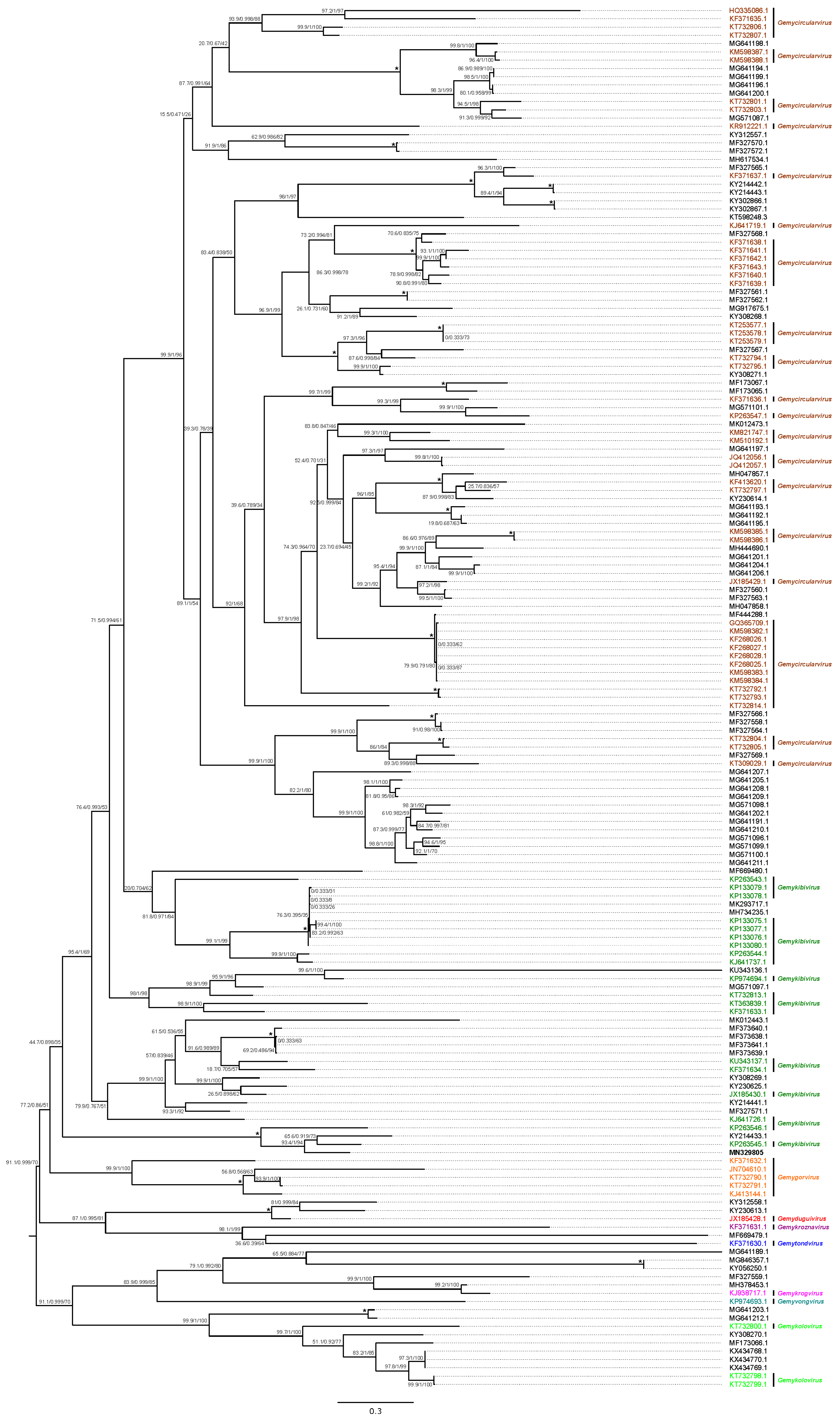
3.2.2. Genomoviridae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fenton, N.; Simmons, M. Bats, A World of Science and Mystery., 1st ed.; Univ. Chicago Press. Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 2015; p. 330. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, N.B.; Cirranello, A.L. Bat Species of the World: A taxonomic and geographic database. Available online: https://batnames.org/ (accessed on 10 October 2019).
- Mühldorfer, K.; Speck, S.; Kurth, A.; Lesnik, R.; Freuling, C.; Müller, T.; Kramer-Schadt, S.; Wibbelt, G. Diseases and causes of death in European bats: Dynamics in disease susceptibility and infection rates. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29773. [Google Scholar]
- Munshi-South, J.; Wilkinson, G.S. Bats and birds: Exceptional longevity despite high metabolic rates. Ageing Res. Rev. 2010, 9, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendergast, B.J.; Freeman, D.A.; Zucker, I.; Nelson, R.J. Periodic arousal from hibernation is necessary for initiation of immune responses in ground squirrels. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 282, R1054–R1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luis, D.; O’Shea, T.; Hayman, A. A comparison of bats and rodents as reservoirs of zoonotic viruses: Are bats special? Proc. R. Soc. B. 2013, 280, 20122753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, M.; Ren, W.; Smith, C.; Epstein, J.H.; Wang, H.; Crameri, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Bats Are Natural Reservoirs of SARS-Like Coronaviruses. Science 2005, 310, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, E.M.; Kumulungui, B.; Pourrut, X.; Rouquet, P.; Hassanin, A.; Yaba, P.; Délicat, A.; Paweska, J.T.; Gonzalez, J.-P.; Swanepoel, R. Fruit bats as reservoirs of Ebola virus. Nature 2005, 438, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.A.; Hassan, S.S.; Olival, K.J.; Mohamed, M.; Chang, L.-Y.; Hassan, L.; Saad, N.M.; Shohaimi, S.A.; Mamat, Z.C.; Naim, M.S.; et al. Characterization of Nipah virus from naturally infected Pteropus vampyrus bats, Malaysia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1990–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpin, K.; Young, P.L.; Field, H.E.; Mackenzie, J.S. Isolation of Hendra virus from pteropid bats: A natural reservoir of Hendra virus. J. Gen. Virol 2000, 81, 1927–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, K. Tadarida brasiliensis. Mamm. Species 1989, 331, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquez, R.; Diaz, M.; Gonzalez, E.; Rodriguez, A.; Incháustegui, S.; Arroyo-Cabrales, J. Tadarida brasiliensis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015: e.T21314A22121621. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T21314A22121621.en (accessed on 20 July 2019).
- Eger, J.L. Family Molossidae. In Mammals of South America. Volume 1. Marsupials, Xenarthrans, Shrews, and Bats; Section Molossidae; Gardner, A.L., Ed.; The University Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2007; pp. 399–439. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, M.; Trouwborst, A. Bonn convention on the conservation of migratory species of wild animals 1979. In Elgar Encyclopedia of Environmental Law; Faure, M., Ed.; Edward Elgar Publishing Limited: Cheltenham, UK, 2017; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Calisher, C.H.; Childs, J.E.; Field, H.E.; Holmes, K.V.; Schountz, T. Bats: Important Reservoir Hosts of Emerging Viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moratelli, R.; Calisher, C.H. Bats and zoonotic viruses: Can we confidently link bats with emerging deadly viruses? Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Li, Z.; Yang, F.; Zheng, J.; Feng, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, N.; Zhang, F.; et al. Virome profiling of bats from Myanmar by metagenomic analysis of tissue samples reveals more novel Mammalian viruses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61950. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Ai, L.; Yang, L.; Ye, F.; Ding, C.; Chen, J.; He, B.; Zhu, J.; et al. Virome analysis for identification of novel mammalian viruses in bats from Southeast China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geldenhuys, M.; Mortlock, M.; Weyer, J.; Bezuidt, O.; Seamark, E.C.J.; Kearney, T.; Gleasner, C.; Erkkila, T.H.; Cui, H.; Markotter, W. A metagenomic viral discovery approach identifies potential zoonotic and novel mammalian viruses in Neoromicia bats within South Africa. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, K.S.; Leggett, R.M.; Bexfield, N.H.; Alston, M.; Daly, G.; Todd, S.; Tachedjian, M.; Holmes, C.E.G.; Crameri, S.; Wang, L.-F.; et al. Metagenomic study of the viruses of African straw-coloured fruit bats: Detection of a chiropteran poxvirus and isolation of a novel adenovirus. Virology 2013, 441, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacheux, L.; Cervantes-Gonzalez, M.; Guigon, G.; Thiberge, J.M.; Vandenbogaert, M.; Maufrais, C.; Caro, V.; Bourhy, H. A preliminary study of viral metagenomics of French bat species in contact with humans: Identification of new mammalian viruses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, C.; Kurth, A. European bats as carriers of viruses with zoonotic potential. Viruses 2014, 6, 3110–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Victoria, J.G.; Wang, C.; Jones, M.; Fellers, G.M.; Kunz, T.H.; Delwart, E. Bat guano virome: Predominance of dietary viruses from insects and plants plus novel mammalian viruses. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6955–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, E.F.; Haskew, A.N.; Gates, J.E.; Huynh, J.; Moore, C.J.; Frieman, M.B. Metagenomic Analysis of the Viromes of Three North American Bat Species: Viral Diversity among Different Bat Species That Share a Common Habitat. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 13004–13018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.F.; Corman, V.M.; Müller, M.A.; Maganga, G.D.; Vallo, P.; Binger, T.; Gloza-Rausch, F.; Cottontail, V.M.; Rasche, A.; Yordanov, S.; et al. Bats host major mammalian paramyxoviruses. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmier, A.; Tirera, S.; de Thoisy, B.; Franc, A.; Darcissac, E.; Donato, D.; Bouchier, C.; Lacoste, V.; Lavergne, A. Virome analysis of two sympatric bat species (Desmodus rotundus and Molossus molossus) in French Guiana. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinero, C.; Gury Dohmen, F.; Beltran, F.; Martinez, L.; Novaro, L.; Russo, S.; Palacios, G.; Cisterna, D.M. High diversity of rabies viruses associated with insectivorous bats in Argentina: Presence of several independent enzootics. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simas, P.V.M.; de Souza Barnabé, A.C.; Durães-Carvalho, R.; de Lima Neto, D.F.; Caserta, L.C.; Artacho, L.; Jacomassa, F.A.F.; Martini, M.C.; Bianchi dos Santos, M.M.A.; Felippe, P.A.N.; et al. Bat Coronavirus in Brazil Related to Appalachian Ridge and Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Viruses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sales Lima, F.E.; Cibulski, S.P.; Witt, A.A.; Franco, A.C.; Roehe, P.M. Genomic characterization of two novel polyomaviruses in Brazilian insectivorous bats. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1831–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sales Lima, F.E.; Cibulski, S.P.; Dos Santos, H.F.; Teixeira, T.F.; Varela, A.P.M.; Roehe, P.M.; Delwart, E.; Franco, A.C. Genomic characterization of novel circular ssDNA viruses from insectivorous bats in Southern Brazil. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118070. [Google Scholar]
- Cibulski, S.P.; Teixeira, T.F.; de Sales Lima, F.E.; do Santos, H.F.; Franco, A.C.; Roehe, P.M. A Novel Anelloviridae Species Detected in Tadarida brasiliensis Bats: First Sequence of a Chiropteran Anellovirus. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e01028-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.C. Behavior and demography in an urban colony of Tadarida brasiliensis (Chiroptera: Molossidae) in Rosario, Argentina. Rev. Biol. Trop. 1999, 4, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Montani, M.E.; Auil, S.; Duque, C.M.; Romano, M.C.; Cordini, M.C. Estado actual de la colonia de Tadarida brasiliensis (Chiroptera, Molossidae) del SICOM “Facultad de Derecho”, Rosario, Argentina. 2015. Available online: http://www.sarem.org.ar/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/SAREM_Resumenes-XXVIII-JAM_2015.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2015).
- Bolatti, E.M.; Chouhy, D.; Hošnjak, L.; Casal, P.E.; Kocjan, B.J.; Bottai, H.; Stella, E.J.; Sanchez, A.; Bussy, R.F.; Poljak, M.; et al. Natural history of human papillomavirus infection of sun-exposed healthy skin of immunocompetent individuals over three climatic seasons and identification of HPV209, a novel betapapillomavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Chouhy, D.; Gorosito, M.; Sanchez, A.; Serra, E.C.; Bergero, A.; Fernandez Bussy, R.; Giri, A.A. New generic primer system targeting mucosal/genital and cutaneous human papillomaviruses leads to the characterization of HPV 115, a novel Beta-papillomavirus species 3. Virology 2010, 397, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolatti, E.M.; Hošnjak, L.; Chouhy, D.; Re-Louhau, M.F.; Casal, P.E.; Bottai, H.; Kocjan, B.J.; Stella, E.J.; Gorosito, M.D.; Sanchez, A.; et al. High prevalence of Gammapapillomaviruses (Gamma-PVs) in pre-malignant cutaneous lesions of immunocompetent individuals using a new broad-spectrum primer system, and identification of HPV210, a novel Gamma-PV type. Virology 2018, 525, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslund, O.; Antonsson, A.; Nordin, P.; Stenquist, B.; Hansson, B.G. A broad range of human papillomavirus types detected with a general PCR method suitable for analysis of cutaneous tumours and normal skin. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 2437–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forslund, O.; Ly, H.; Reid, C.; Higgins, G. A broad spectrum of human papillomavirus types is present in the skin of Australian patients with non-melanoma skin cancers and solar keratosis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2003, 149, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Pan, Y.Q.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Hang, D.; Shen, N.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Abliz, A.; Deng, Q.; et al. Improved detection of human papillomavirus harbored in healthy skin with FAP6085/64 primers. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 193, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varsani, A.; Kraberger, S.; Jennings, S.; Porzig, E.L.; Julian, L.; Massaro, M.; Pollard, A.; Ballard, G.; Ainley, D.G. A novel papillomavirus in Adélie penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae) faeces sampled at the Cape Crozier colony, Antarctica. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1352–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yinda, C.K.; Rector, A.; Zeller, M.; Conceição-Neto, N.; Heylen, E.; Maes, P.; Ghogomu, S.M.; Van Ranst, M.; Matthijnssens, J. A single bat species in Cameroon harbors multiple highly divergent papillomaviruses in stool identified by metagenomics analysis. Virol. Reports 2016, 6, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van Doorslaer, K.; Ruoppolo, V.; Schmidt, A.; Lescroël, A.; Jongsomjit, D.; Elrod, M.; Kraberger, S.; Stainton, D.; Dugger, K.M.; Ballard, G.; et al. Unique genome organization of non-mammalian papillomaviruses provides insights into the evolution of viral early proteins. Virus Evol. 2017, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Song, L.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Salzberg, S.L. Centrifuge: Rapid and sensitive classification of metagenomic sequences. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitwieser, F.P.; Salzberg, S.L. Pavian: Interactive analysis of metagenomics data for microbiome studies and pathogen identification. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1303–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinformatics 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, H.U.; Burk, R.D.; Chen, Z.; van Doorslaer, K.; Hausen, H.Z.; de Villiers, E.M. Classification of papillomaviruses (PVs) based on 189 PV types and proposal of taxonomic amendments. Virology 2010, 401, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView Version 4: A Multiplatform Graphical User Interface for Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, M.; Gil, M.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Dessimoz, C.; Gascuel, O. Survey of branch support methods demonstrates accuracy, power, and robustness of fast likelihood-based approximation schemes. Syst. Biol. 2011, 60, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.; De Silva, N.; Otto, T.D.; Parkhill, J.; Keane, J.A.; Harris, S.R. Circlator: Automated circularization of genome assemblies using long sequencing reads. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhire, B.M.; Varsani, A.; Martin, D.P. SDT: A virus classification tool based on pairwise sequence alignment and identity calculation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108277. [Google Scholar]
- Escalera-Zamudio, M.; Mendoza, M.L.Z.; Heeger, F.; Loza-Rubio, E.; Rojas-Anaya, E.; Méndez-Ojeda, M.L.; Taboada, B.; Mazzoni, C.J.; Arias, C.F.; Greenwood, A.D. A Novel Endogenous Betaretrovirus in the Common Vampire Bat (Desmodus rotundus) Suggests Multiple Independent Infection and Cross-Species Transmission Events. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5180–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Perez, R.; Gottschling, M.; Wibbelt, G.; Bravo, I.G. Multiple evolutionary origins of bat papillomaviruses. Vet. Microbiol 2013, 165, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Pérez, R.; Ibáñez, C.; Godínez, J.M.; Aréchiga, N.; Garin, I.; Pérez-Suárez, G.; De Paz, O.; Juste, J.; Echevarría, J.E.; Bravo, I.G. Novel papillomaviruses in free-ranging Iberian bats: No virus-host co-evolution, no strict host specificity, and hints for recombination. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorbar, J. The E4 protein; structure, function and patterns of expression. Virology 2013, 445, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oštrbenk, A.; Kocjan, B.J.; Hošnjak, L.; Li, J.; Deng, Q.; Šterbenc, A.; Poljak, M. Identification of a Novel Human Papillomavirus, Type HPV199, Isolated from a Nasopharynx and Anal Canal, and Complete Genomic Characterization of Papillomavirus Species Gamma-12. PLoS ONE 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullman, C.G.; Haris, P.I.; Galloway, D.A.; Emery, V.C.; Perkins, S.J. Predicted alpha-helix/beta-sheet secondary structures for the zinc-binding motifs of human papillomavirus E7 and E6 proteins by consensus prediction averaging and spectroscopic studies of E7. Biochem J. 1996, 319, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, A.S.; Anderson, J.M. PDZ domains: Fundamental building blocks in the organization of protein complexes at the plasma membrane. J. Clin. Invest. 1999, 103, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radulescu, R.T.; Bellitti, M.R.; Ruvo, M.; Cassani, G.; Fassina, G. Binding of the LXCXE insulin motif to a hexapeptide derived from retinoblastoma protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 206, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titolo, S.; Pelletier, A.; Sauve, F.; Brault, K.; Wardrop, E.; White, P.W.; Amin, A.; Cordingley, M.G.; Archambault, J. Role of the ATP-binding domain of the human papillomavirus type 11 E1 helicase in E2-dependent binding to the origin. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5282–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, F.; Banks, L. The human papillomavirus E6 protein and its contribution to malignant progression. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7874–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A.; Mills, R.E.; Lange, C.J.; Stewart, M.; Devine, S.E.; Corbett, A.H. Classical nuclear localization signals: Definition, function, and interaction with importin alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5101–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradet-Turcotte, A.; Moody, C.; Laimins, L.A.; Archambault, J. Nuclear export of human papillomavirus type 31 E1 is regulated by Cdk2 phosphorylation and required for viral genome maintenance. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11747–11760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.W.; Roden, R.B. L2, the minor capsid protein of papillomavirus. Virology 2013, 445, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Schwartz, S. Regulation of human papillomavirus gene expression by splicing and polyadenylation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varsani, A.; Krupovic, M. Sequence-based taxonomic framework for the classification of uncultured single-stranded DNA viruses of the family Genomoviridae. Virus Evol. 2017, 3, vew037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Rosario, K.; Breitbart, M.; Duffy, S. Eukaryotic Circular Rep-Encoding Single-Stranded DNA (CRESS DNA) Viruses: Ubiquitous Viruses With Small Genomes and a Diverse Host Range. In Advances in Virus Research; Academic Press Inc: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 103, pp. 71–133. ISBN 9780128177228. [Google Scholar]
- Heyraud-Nitschke, F.; Schumacher, S.; Laufs, J.; Schaefer, S.; Schell, J.; Gronenborn, B. Determination of the origin cleavage and joining domain of geminivirus Rep proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laufs, J.; Schumacher, S.; Geisler, N.; Jupin, I.; Gronenborn, B. Identification of the nicking tyrosine of geminivirus Rep protein. FEBS Lett. 1995, 377, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timchenko, T.; de Kouchkovsky, F.; Katul, L.; David, C.; Vetten, H.J.; Gronenborn, B. A single rep protein initiates replication of multiple genome components of faba bean necrotic yellows virus, a single-stranded DNA virus of plants. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 10173–10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Ilyina, T. V Geminivirus replication proteins are related to prokaryotic plasmid rolling circle DNA replication initiator proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 2763–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, B.M.; Hanley-Bowdoin, L. Conserved sequence and structural motifs contribute to the DNA binding and cleavage activities of a geminivirus replication protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 24448–24456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, T.E.; Dallas, M.B.; Reyes, M.I.; Buhrman, G.K.; Ascencio-Ibañez, J.T.; Hanley-Bowdoin, L. Functional analysis of a novel motif conserved across geminivirus Rep proteins. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Koonin, E.V.; Wolf, Y.I. A new superfamily of putative NTP-binding domains encoded by genomes of small DNA and RNA viruses. FEBS Lett. 1990, 262, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V. A common set of conserved motifs in a vast variety of putative nucleic acid-dependent ATPases including MCM proteins involved in the initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, N.R.; Malik, P.S.; Singh, D.K.; Islam, M.N.; Kaliappan, K.; Mukherjee, S.K. The oligomeric Rep protein of Mungbean yellow mosaic India virus (MYMIV) is a likely replicative helicase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 6362–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerot, D.; Bernardi, F. DNA Helicase Activity Is Associated with the Replication Initiator Protein Rep of Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Geminivirus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11322–11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asplund, M.; Kjartansdóttir, K.R.; Mollerup, S.; Vinner, L.; Fridholm, H.; Herrera, J.A.R.; Friis-Nielsen, J.; Hansen, T.A.; Jensen, R.H.; Nielsen, I.B.; et al. Contaminating viral sequences in high-throughput sequencing viromics: A linkage study of 700 sequencing libraries. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Miller, S.; Chiu, C.Y. Clinical Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing for Pathogen Detection. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2019, 14, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simner, P.J.; Miller, H.B.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Pinilla Monsalve, G.; Pardo, C.A.; Salzberg, S.L.; Sears, C.L.; Thomas, D.L.; Eberhart, C.G.; Carroll, K.C. Development and Optimization of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing Methods for Cerebrospinal Fluid Diagnostics. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00472-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, A.; Pichon, M.; Picard, C.; Casalegno, J.S.; Valette, M.; Schuffenecker, I.; Billard, L.; Vallet, S.; Vilchez, G.; Cheynet, V.; et al. Quality control implementation for universal characterization of DNA and RNA viruses in clinical respiratory samples using single metagenomic next-generation sequencing workflow. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z. Metagenomic Analysis of Viruses from Bat Fecal Samples Reveals Many Novel Viruses in Insectivorous Bats in China. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4620–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.J.; Wang, J.; Todd, A.K.; Bissielo, A.B.; Yen, S.; Strydom, H.; Moore, N.E.; Ren, X.; Huang, Q.S.; Carter, P.E.; et al. Evaluation of rapid and simple techniques for the enrichment of viruses prior to metagenomic virus discovery. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 195, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywkowski, T.; Kühnemund, M.; Wu, D.; Nilsson, M. Limited reverse transcriptase activity of phi29 DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 3625–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; Ren, X.; He, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Qian, Z.; Dong, J.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Deciphering the bat virome catalog to better understand the ecological diversity of bat viruses and the bat origin of emerging infectious diseases. ISME J. 2016, 10, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñero, C.; Dohmen, F.; Beltran, F.; Martinez, L.; Novaro, L.; Russo, S.; Palacios, G.; Cisterna, D.M. High diversity of rabies viruses associated with insectivorous bats in Argentina: Presence of several independent enzootics. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Villiers, E.M.; Fauquet, C.; Broker, T.R.; Bernard, H.U.; zur Hausen, H. Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology 2004, 324, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, I.G.; de Sanjosé, S.; Gottschling, M. The clinical importance of understanding the evolution of papillomaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rector, A.; Mostmans, S.; Van Doorslaer, K.; McKnight, C.A.; Maes, R.K.; Wise, A.G.; Kiupel, M.; Van Ranst, M. Genetic characterization of the first chiropteran papillomavirus, isolated from a basosquamous carcinoma in an Egyptian fruit bat: The Rousettus aegyptiacus papillomavirus type 1. Vet. Microbiol 2006, 117, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.Y.; Qiu, M.; Guan, W.J.; Li, J.M.; Chen, S.W.; Cheng, M.J.; Huo, S.T.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, L.N.; et al. Viral metagenomics of six bat species in close contact with humans in southern China. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, H.; Tsang, A.K.; Tsoi, H.W.; Leung, A.S.; Ho, C.C.; Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Yuen, K.Y. Identification of a novel bat papillomavirus by metagenomics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doorslaer, K.; Chen, Z.; Bernard, H.U.; Chan, P.K.S.; Desalle, R.; Dillner, J.; Forslund, O.; Haga, T.; McBride, A.A.; Villa, L.L.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Papillomaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 989–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupovic, M.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Jiang, D.; Varsani, A. Genomoviridae: A new family of widespread single-stranded DNA viruses. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Khalafalla, A.I.; Paden, C.R.; Yusof, M.F.; Eltahir, Y.M.; Al Hammadi, Z.M.; Tao, Y.; Queen, K.; Al Hosani, F.; Gerber, S.I.; et al. Identification of diverse viruses in upper respiratory samples in dromedary camels from United Arab Emirates. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceição-Neto, N.; Zeller, M.; Heylen, E.; Lefrère, H.; Mesquita, J.R.; Matthijnssens, J. Fecal virome analysis of three carnivores reveals a novel nodavirus and multiple gemycircularviruses. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceição-Neto, N.; Theuns, S.; Cui, T.; Zeller, M.; Yinda, C.K.; Christiaens, I.; Heylen, E.; Van Ranst, M.; Carpentier, S.; Nauwynck, H.J.; et al. Identification of an enterovirus recombinant with a torovirus-like gene insertion during a diarrhea outbreak in fattening pigs. Virus Evol. 2017, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceição-Neto, N.; Godinho, R.; Álvares, F.; Yinda, C.K.; Deboutte, W.; Zeller, M.; Laenen, L.; Heylen, E.; Roque, S.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F.; et al. Viral gut metagenomics of sympatric wild and domestic canids, and monitoring of viruses: Insights from an endangered wolf population. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 4135–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.G.; Mori, D.; Deng, X.; Rajindrajith, S.; Ranawaka, U.; Fan Ng, T.F.; Bucardo-Rivera, F.; Orlandi, P.; Ahmed, K.; Delwart, E. Small circular single stranded DNA viral genomes in unexplained cases of human encephalitis, diarrhea, and in untreated sewage. Virology 2015, 482, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Assis, M.R.; Vieira, C.B.; Fioretti, J.M.; Rocha, M.S.; de Almeida, P.I.N.; Miagostovich, M.P.; Fumian, T.M. Detection and Molecular Characterization of Gemycircularvirus from Environmental Samples in Brazil. Food Environ. Virol. 2016, 8, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, S.; She, X.; Lan, G.; Varsani, A.; He, Z. Identification and molecular characterization of a single-stranded circular DNA virus with similarities to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum hypovirulence-associated DNA virus 1. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Male, M.F.; Kami, V.; Kraberger, S.; Varsani, A. Genome Sequences of Poaceae-Associated Gemycircularviruses from the Pacific Ocean Island of Tonga. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemenesi, G.; Kurucz, K.; Zana, B.; Földes, F.; Urbán, P.; Vlaschenko, A.; Kravchenko, K.; Budinski, I.; Szodoray-Parádi, F.; Bücs, S.; et al. Diverse replication-associated protein encoding circular DNA viruses in guano samples of Central-Eastern European bats. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V.; Krupovic, M.; Varsani, A.; Wolf, Y.I.; Yutin, N.; Zerbini, F.M.; Kuhn, J.H. Global Organization and Proposed Megataxonomy of the Virus World. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Host | Family | No. of Read Pairs | No. of Contigs | Genome Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria, Archea | Inoviridae | 9908 | 8 | ssDNA-C |
| Siphoviridae | 666 | 29 | dsDNA-C | |
| Myoviridae | 120 | 18 | dsDNA-L | |
| Podoviridae | 33 | 6 | dsDNA-L | |
| Rudiviridae | 6 | 0 | dsDNA-L | |
| Sphaerolipoviridae | 3 | 0 | dsDNA-L | |
| Microviridae | 1 | 0 | ssDNA-C | |
| Leviviridae | 1 | 0 | ssRNA-L | |
| Total | 8 | 10,738 | 61 | 7 DNA; 1 RNA |
| Insects and other invertebrates | Baculoviridae | 34 | 7 | dsDNA-C |
| Ascoviridae | 34 | 0 | dsDNA-C | |
| Iridoviridae | 29 | 6 | dsDNA-C | |
| Nudiviridae | 15 | 0 | dsDNA-C | |
| Hytrosaviridae | 4 | 2 | ssDNA-C | |
| Dicistroviridae | 3 | 0 | ssRNA-L | |
| Polydnaviridae | 2 | 0 | dsDNA-C | |
| Solinviviridae | 2 | 3 | ssRNA-L | |
| Asfarviridae | 1 | 1 | dsDNA-L | |
| Nimaviridae | 1 | 0 | dsDNA-C | |
| Total | 10 | 125 | 19 | 8 DNA; 2 RNA |
| Plants | Phycodnaviridae | 42 | 6 | dsDNA-C |
| Potyviridae | 10 | 0 | ssRNA-L | |
| Geminiviridae | 8 | 0 | ssDNA-C | |
| Caulimoviridae | 1 | 0 | dsDNA-RT-C | |
| Tymoviridae | 1 | 1 | ssRNA-L | |
| Total | 5 | 62 | 7 | 3 DNA; 2 RNA |
| Protists | Mimiviridae | 1825 | 0 | dsDNA-L |
| Marseilleviridae | 65 | 1 | dsDNA-C | |
| Narnaviridae | 1 | 0 | ssRNA-L | |
| Totiviridae | 1 | 0 | dsRNA-L | |
| Pithoviridae | 1 | 0 | dsDNA-C | |
| Total | 5 | 1893 | 1 | 3 DNA; 2 RNA |
| Vertebrates | Retroviridae | 461 | 22 | ssRNA-RT-L |
| Genomoviridae | 258 | 6 | ssDNA-C | |
| Herpesviridae | 113 | 4 | dsDNA-L | |
| Papillomaviridae | 90 | 14 | dsDNA-C | |
| Poxviridae | 36 | 6 | dsDNA-L | |
| Alloherpesviridae | 10 | 1 | dsDNA-L | |
| Rhabdoviridae | 3 | 2 | ssRNA-L | |
| Reoviridae | 3 | 0 | dsRNA-L | |
| Astroviridae | 2 | 0 | ssRNA-L | |
| Circoviridae | 2 | 0 | ssDNA-C | |
| Adenoviridae | 1 | 0 | dsDNA-L | |
| Polyomaviridae | 1 | 0 | dsDNA-C | |
| Coronaviridae | 1 | 0 | ssRNA-L | |
| Paramyxoviridae | 1 | 0 | ssRNA-L | |
| Flaviviridae | 1 | 0 | ssRNA-L | |
| Total | 15 | 983 | 55 | 8 DNA; 7 RNA |
| Total sequences assigned to viral families | 43 | 13,801 | 143 | 29 DNA; 14 RNA |
| Viral sequences not assigned to families | 96 | 10 | ||
| Total viral sequences | 13,897 | 153 | ||
| Genomic Regions/ORFs | Length (nt) | Nucleotide Sequence (Pre-Stop Codon) (nt) | Protein Size (aa) | HPV Motifs and Domains (Consensus Sequences) | Nucleotide Position | Amino Acid Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| URR | 416 | 7735–8151 | Polyadenylation site [AATAAA] | 7700–7705 | ||
| 7906–7911 | ||||||
| 7924–7929 | ||||||
| TATA box [TATAAA] | 7686–7691 | |||||
| 7824–7829 | ||||||
| E1-binding site [CCATGAGAAATTGTTGTT] | 8038–8055 | |||||
| E2-binding site [ACC(N)6GGT] | 7885–7896 | |||||
| 7934–7945 | ||||||
| 7992–8003 | ||||||
| E6 | 603 | 1–603 | 200 | Zinc-binding domain [CXXC(X)29CXXC] | 256–366 | 86–122 |
| 475–585 | 159–195 | |||||
| PDZ-binding domain [X(T/S)X(L/V)] | 136–147 | 46–49 | ||||
| 202–213 | 68–71 | |||||
| 238–249 | 80–83 | |||||
| 277–228 | 93–96 | |||||
| E7 | 327 | 605–931 | 108 | Zinc-binding domain [CXXC(X)29CXXC] | 794–907 | 64–101 |
| pRB-binding site [(LXCXE)] | 668–682 | 22–26 | ||||
| E1 | 1848 | 934–2781 | 615 | Bipartite-like NLS [KRK(X)24KXXK] | 1180–1272 | 83–113 |
| NES | 1213–1242 | 94–103 | ||||
| [L(X)2-3L(X)2(L,I,V)X(L,I)] | ||||||
| ATP-binding site [GXXXXGK(T/S)] | 2260–2283 | 443–450 | ||||
| Cdk-phosphorylation site [(S/T)P] | 1216–1221 | 95–96 | ||||
| 1825–1830 | 298–299 | |||||
| 2362–2367 | 477–478 | |||||
| 2623–2628 | 564–565 | |||||
| 1198–1203 | 89–90 | |||||
| 1528–1533 | 199–200 | |||||
| 1243–1248 | 104–105 | |||||
| E2 | 1248 | 2717–3964 | 415 | Leucine zipper domain [L(X)6L(X)6L(X)6L] | Absent | Absent |
| E4 | 426 | 3300–3725 | 141 | Leucine motif [LLXLL] | Absent | Absent |
| L2 | 1758 | 4019–5776 | 585 | Polyadenylation site [AATAAA] | 5232–5237 | |
| Furin cleavage motif [RX(K/R)R] | 5744–5758 | 576–579 | ||||
| Transmembrane-like domain [G(X)26G] | 4187–4270 | 57–84 | ||||
| L1 | 1548 | 5787–7334 | 516 |
| Genome Regions | Length (nt) | Nucleotide Sequence (nt) | Protein Size (aa) | Motifs and Domains (Consensus Sequences) | Nucleotide Position | Amino Acid Position | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large intergenic region | 69 | 2162–2196, 1–36 | Nonanucleotide at the putative stem-loop | 1–9 | |||
| WATAWWHAN | |||||||
| Replicase (Rep) | Catalytic domain | 668 | 2162–1494 | 223 | Motif I [uuTYxQ] | 2073–2090 | 25–30 |
| Motif II [xHxHx] | 1965–1979 | 62–66 | |||||
| Motif III [YAxK] | 1842–1853 | 104–107 | |||||
| GRS domain [(x)2FD(x)4HPN(x)5] | 1875–1925 | 80–95 | |||||
| Central domain | 375 | 1381–1006 | 125 | Walker A [G(x)4GKT] | 1325–1348 | 7–14 | |
| Walker B [xFDDx] | 1220–1234 | 45–49 | |||||
| Walker C [W/Y(x)2N] | 1091–1102 | 89–92 | |||||
| Capsid (Cap/CP) | 974 | 36–1010 | 324 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bolatti, E.M.; Zorec, T.M.; Montani, M.E.; Hošnjak, L.; Chouhy, D.; Viarengo, G.; Casal, P.E.; Barquez, R.M.; Poljak, M.; Giri, A.A. A Preliminary Study of the Virome of the South American Free-Tailed Bats (Tadarida brasiliensis) and Identification of Two Novel Mammalian Viruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040422
Bolatti EM, Zorec TM, Montani ME, Hošnjak L, Chouhy D, Viarengo G, Casal PE, Barquez RM, Poljak M, Giri AA. A Preliminary Study of the Virome of the South American Free-Tailed Bats (Tadarida brasiliensis) and Identification of Two Novel Mammalian Viruses. Viruses. 2020; 12(4):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040422
Chicago/Turabian StyleBolatti, Elisa M., Tomaž M. Zorec, María E. Montani, Lea Hošnjak, Diego Chouhy, Gastón Viarengo, Pablo E. Casal, Rubén M. Barquez, Mario Poljak, and Adriana A. Giri. 2020. "A Preliminary Study of the Virome of the South American Free-Tailed Bats (Tadarida brasiliensis) and Identification of Two Novel Mammalian Viruses" Viruses 12, no. 4: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040422
APA StyleBolatti, E. M., Zorec, T. M., Montani, M. E., Hošnjak, L., Chouhy, D., Viarengo, G., Casal, P. E., Barquez, R. M., Poljak, M., & Giri, A. A. (2020). A Preliminary Study of the Virome of the South American Free-Tailed Bats (Tadarida brasiliensis) and Identification of Two Novel Mammalian Viruses. Viruses, 12(4), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040422






