Detection of Norovirus in Saliva Samples from Acute Gastroenteritis Cases and Asymptomatic Subjects: Association with Age and Higher Shedding in Stool
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Definitions and Sample Collection
2.2. HuNoV Testing
2.3. Secretor Status Genotyping
2.4. HuNoV Genotyping
2.5. HuNoV PMAxx-Viability RTqPCR
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiological Features of Studied Outbreaks
3.2. Occurrence of HuNoV RNA in Saliva Samples
3.3. Analysis of Factors Associated with HuNoV RNA Saliva Positivity
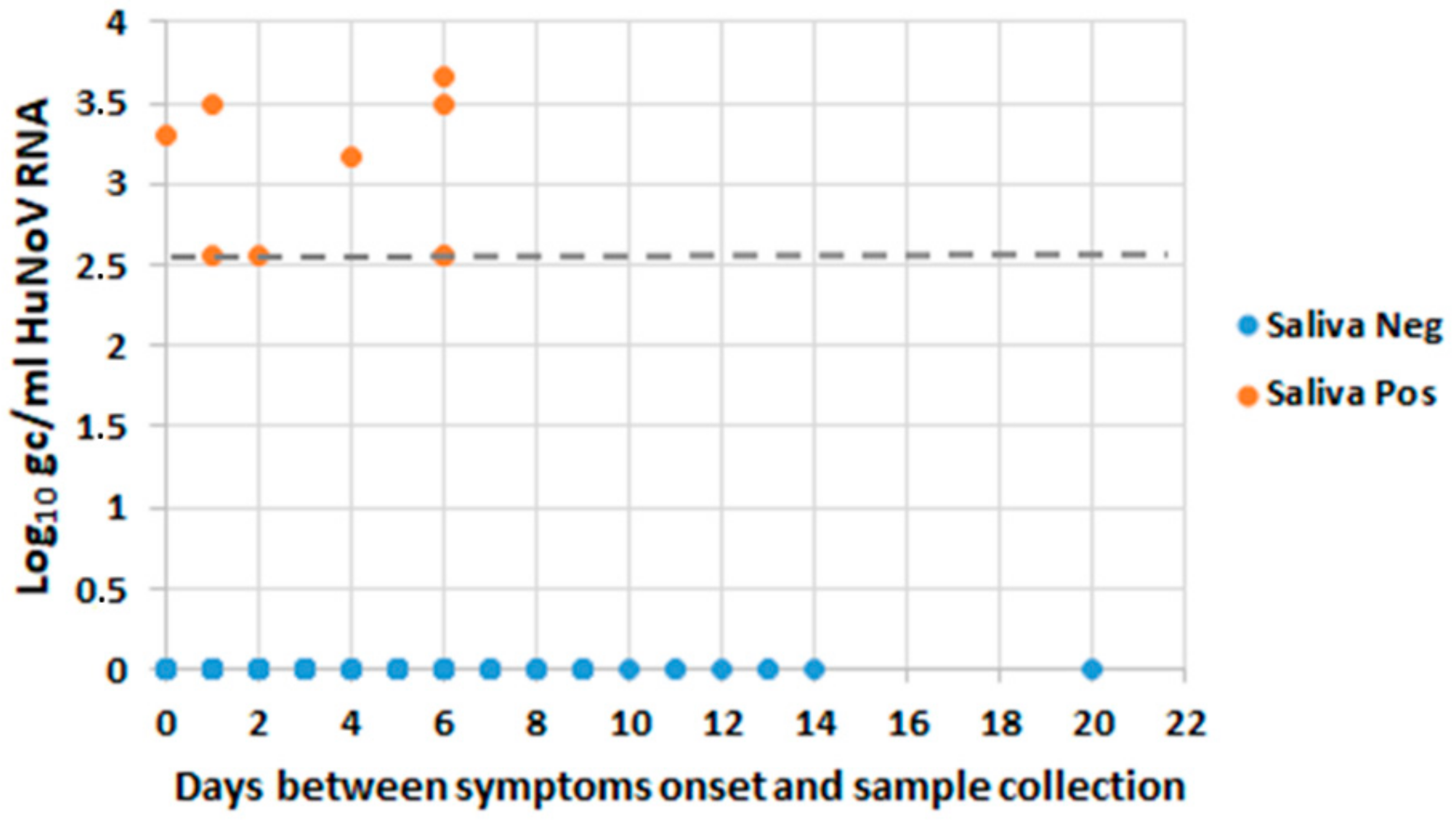
3.4. Occurrence of HuNoV RNA in Saliva and Levels of Shedding in Stool
3.5. Analysis of HuNoV Capsid Integrity in Saliva Using a Viability PMA RTqPCR Assay
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopman, B.A.; Steele, D.; Kirkwood, C.D.; Parashar, U.D. The vast and varied global burden of Norovirus: Prospects for prevention and control. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1001999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmar, R.L.; Ramani, S.; Estes, M.K. Human noroviruses: Recent advances in a 50-year history. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, M.; van Beek, J.; Koopmans, M.P. Human norovirus transmission and evolution in a changing world. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wit, M.A.; Widdowson, M.A.; Vennema, H.; de Bruin, E.; Fernandes, T.; Koopmans, M. Large outbreak of norovirus: The baker who should have known better. J. Infect. 2007, 55, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, L.A.; Murphy, J.J.; Kaplan, J.E.; Pinsky, P.F.; Chacon, D.; Walmsley, S.; Schonberger, L.B.; Phillips, A.; Forward, K.; Goldman, C.; et al. 25- to 30-nm virus particle associated with a hospital outbreak of acute gastroenteritis with evidence for airborne transmission. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1988, 127, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, P.; de Graaf, M.; Parra, G.I.; Chan, M.C.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Wang, Q.; White, P.A.; Katayama, K.; Vennema, H.; et al. Updated classification of norovirus genogroups and genotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordgren, J.; Svensson, L. Genetic susceptibility to human norovirus infection: An update. Viruses 2019, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guix, S.; Fuentes, C.; Pinto, R.M.; Blanco, A.; Sabria, A.; Anfruns-Estrada, E.; Garrido, V.R.; Alonso, M.; Bartolome, R.; Cornejo, T.; et al. Infectivity of norovirus GI and GII from bottled mineral water during a waterborne outbreak, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currier, R.L.; Payne, D.C.; Staat, M.A.; Selvarangan, R.; Shirley, S.H.; Halasa, N.; Boom, J.A.; Englund, J.A.; Szilagyi, P.G.; Harrison, C.J.; et al. Innate susceptibility to norovirus infections influenced by FUT2 genotype in a United States pediatric population. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, A.; Dove, W.; Ashton, L.; Hopkins, M.; Cunliffe, N.A. Detection of norovirus in mouthwash samples from patients with acute gastroenteritis. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 48, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, V.C.C.; Wong, S.C.; Chiu, K.H.Y.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Wong, S.C.Y.; Yuen, K.Y. Detection of norovirus in air samples in a non-vomiting patient: Implications of testing saliva for norovirus in an immunocompromised host. J. Hosp. Infect. 2019, 103, 357–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, R.; Parsons, B.D.; Lee, B.E.; Drews, S.J.; Chui, L.; Louie, M.; Crago, B.; Freedman, S.B.; Ali, S.; Pang, X. Identification of enteric viruses in oral swabs from children with acute gastroenteritis. J. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 20, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudero-Abarca, B.I.; Rawsthorne, H.; Goulter, R.M.; Suh, S.H.; Jaykus, L.A. Molecular methods used to estimate thermal inactivation of a prototype human norovirus: More heat resistant than previously believed? Food Microbiol. 2014, 41, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, W.; Lopez-Galvez, F.; Allende, A.; Aznar, R.; Sanchez, G. Evaluation of viability PCR performance for assessing norovirus infectivity in fresh-cut vegetables and irrigation water. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 229, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randazzo, W.; Khezri, M.; Ollivier, J.; Le Guyader, F.S.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J.; Aznar, R.; Sanchez, G. Optimization of PMAxx pretreatment to distinguish between human norovirus with intact and altered capsids in shellfish and sewage samples. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 266, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabria, A.; Pinto, R.M.; Bosch, A.; Bartolome, R.; Cornejo, T.; Torner, N.; Martinez, A.; de Simon, M.; Dominguez, A.; Guix, S. Molecular and clinical epidemiology of norovirus outbreaks in Spain during the emergence of GII.4 2012 variant. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 60, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO15216-2:2019. Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for Determination of Hepatitis A Virus and Norovirus Using Real-Time RT-PCR—Part 2: Method for Detection; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ISO15216-1:2017. Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for Determination of Hepatitis A Virus and Norovirus Using Real-Time RT-PCR—Part 1: Method for Quantification; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Marionneau, S.; Ruvoen, N.; Le Moullac-Vaidye, B.; Clement, M.; Cailleau-Thomas, A.; Ruiz-Palacois, G.; Huang, P.; Jiang, X.; Le Pendu, J. Norwalk virus binds to histo-blood group antigens present on gastroduodenal epithelial cells of secretor individuals. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, J.; van der Eijk, A.A.; Fraaij, P.L.; Caliskan, K.; Cransberg, K.; Dalinghaus, M.; Hoek, R.A.; Metselaar, H.J.; Roodnat, J.; Vennema, H.; et al. Chronic norovirus infection among solid organ recipients in a tertiary care hospital, the Netherlands, 2006–2014. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroneman, A.; Vennema, H.; Deforche, K.; Avoort, H.v.d.; Peñaranda, S.; Oberste, M.S.; Vinjé, J.; Koopmans, M. An automated genotyping tool for enteroviruses and noroviruses. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 51, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.; Guix, S.; Fuster, N.; Fuentes, C.; Bartolome, R.; Cornejo, T.; Pinto, R.M.; Bosch, A. Norovirus in bottled water associated with gastroenteritis outbreak, Spain, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1531–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.M.; Dean, A.; Soe, M.M. OpenEpi: A web-based epidemiologic and statistical calculator for public health. Public Health Rep. 2009, 124, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, B.; Kindberg, E.; Buesa, J.; Rydell, G.E.; Lidón, M.F.; Montava, R.; Mallouh, R.A.; Grahn, A.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.; Bellido, J.; et al. The G428A nonsense mutation in FUT2 provides strong but not absolute protection against symptomatic GII.4 norovirus infection. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.C.; Sung, J.J.; Lam, R.K.; Chan, P.K.; Lee, N.L.; Lai, R.W.; Leung, W.K. Fecal viral load and norovirus-associated gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1278–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, V.P.; Cooper, E.M.; Hardaker, H.L.; Lee, L.E.; Bierhoff, M.; Biggs, C.; Cieslak, P.R.; Hall, A.J.; Vinje, J. Epidemiologic, virologic, and host genetic factors of norovirus outbreaks in long-term care facilities. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.K.C.; Kwok, K.; Zhang, L.Y.; Mohammad, K.N.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Lee, N.; Nelson, E.A.S.; Lai, R.W.M.; Leung, T.F.; Chan, P.K.S.; et al. Higher viral load of emerging norovirus GII.P16-GII.2 than pandemic GII.4 and epidemic GII.17, Hong Kong, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, K.L.; Moe, C.L.; Kirby, A.E.; Flanders, W.D.; Parkos, C.A.; Leon, J.S. Norovirus in symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals: Cytokines and viral shedding. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 184, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Hung, C.H.; Jiang, D.D.; Wu, F.T. A norovirus outbreak in a nursing home: Norovirus shedding time associated with age. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 56, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.E.; Rubenstein, J.H. Presentation and epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirato, H.; Ogawa, S.; Ito, H.; Sato, T.; Kameyama, A.; Narimatsu, H.; Xiaofan, Z.; Miyamura, T.; Wakita, T.; Ishii, K.; et al. Noroviruses distinguish between type 1 and type 2 histo-blood group antigens for binding. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 82, 10756–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenck, R.; Bernstein, D.I.; Xia, M.; Huang, P.; Zhong, W.; Parker, S.; Dickey, M.; McNeal, M.; Jiang, X. Predicting susceptibility to norovirus GII.4 by use of a challenge model involving humans. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, M.; van Beek, J.; Vennema, H.; Podkolzin, A.T.; Hewitt, J.; Bucardo, F.; Templeton, K.; Mans, J.; Nordgren, J.; Reuter, G.; et al. Emergence of a novel GII.17 norovirus—End of the GII.4 era? Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 21178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.F.; Huang, Q.; Long, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, T.; Tan, M.; Zhang, Q.L.; Huang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Ding, Y.Q.; et al. An outbreak caused by GII.17 norovirus with a wide spectrum of HBGA-associated susceptibility. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisanic, N.; Ballard, S.B.; Colquechagua, F.D.; Francois, R.; Exum, N.; Yori, P.P.; Schwab, K.J.; Granger, D.A.; Detrick, B.; Olortegui, M.P.; et al. Minimally invasive saliva testing to monitor norovirus infection in community settings. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, V.P.; Cooper, E.M.; Hardaker, H.L.; Lee, L.E.; DeBess, E.E.; Cieslak, P.R.; Hall, A.J.; Vinje, J. Humoral and mucosal immune responses to human norovirus in the elderly. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 1864–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettayebi, K.; Crawford, S.E.; Murakami, K.; Broughman, J.R.; Karandikar, U.; Tenge, V.R.; Neill, F.H.; Blutt, S.E.; Zeng, X.L.; Qu, L.; et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids. Science 2016, 353, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, K.Y.; Kaufman, S.S.; Nagata, B.M.; Chaimongkol, N.; Kim, D.Y.; Levenson, E.A.; Tin, C.M.; Yardley, A.B.; Johnson, J.A.; Barletta, A.B.F.; et al. Human norovirus targets enteroendocrine epithelial cells in the small intestine. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, O.J.; Lim, Y.K.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, M.K. Fecal respiratory viruses in acute viral respiratory infection and nasopharyngeal diarrheal viruses in acute viral gastroenteritis: Clinical impact of ectopic viruses is questionable. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabilla, N.; Nunes Vieira Almeida, T.; Carvalho Reboucas Oliveira, A.; Kipnis, A.; Neres Silva, T.; Souza Fiaccadori, F.; Teixeira de Sousa, T.; de Paula Cardoso, D.D.; Souza, M. Norovirus in feces and nasopharyngeal swab of children with and without acute gastroenteritis symptoms: First report of GI.5 in Brazil and GI.3 in nasopharyngeal swab. J. Clin. Virol. 2017, 87, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, S.; Daleno, C.; Scala, A.; Senatore, L.; Ascolese, B.; Principi, N. Detection of norovirus in respiratory secretions in children with respiratory tract infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Hagbom, M.; Nordgren, J.; Frodlund, J.; Hinkula, J.; Ledin, T.; Svensson, L. Detection of rotavirus- and norovirus-specific IgG memory B cells in tonsils. J. Med. Virol. 2019, 91, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmar, R.L.; Opekun, A.R.; Gilger, M.A.; Estes, M.K.; Crawford, S.E.; Neill, F.H.; Ramani, S.; Hill, H.; Ferreira, J.; Graham, D.Y. Determination of the 50% human infectious dose for Norwalk virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, A.E.; Teunis, P.F.; Moe, C.L. Two human challenge studies confirm high infectivity of Norwalk virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thebault, A.; Teunis, P.F.; Le Pendu, J.; Le Guyader, F.S.; Denis, J.B. Infectivity of GI and GII noroviruses established from oyster related outbreaks. Epidemics 2013, 5, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Feature | Description a |
|---|---|
| Type of transmission | Person-to-person (21); Foodborne (3); Waterborne (1) |
| Setting | Nursing homes (12); Youth hostels/Campgrounds (4); Socio-health centers (3); Kindergartens/Preschool centers (3); Schools (2); Hotel (1) |
| Human norovirus (HuNoV) genotype(s) | GII.17[P17] (5); GI.4[P4] (4); GII.4[P31] (3); GII.4[P16] (2); GI.1[P1] (2); GII.2[P16] (3); GI.6[P11] (2); GII.1[P33] (1); mixed GI.3[P13] + GI.2 (1); mixed GI.4[P4] + GII.4[P16] (1); mixed GI.3[P13] + GII.17[P17] (1) |
| Duration of outbreak in days: range [median] b | 1–25 [9] |
| Number of affected individuals: range [median] | 7–87 [24] |
| Attack rate (%): average ± standard deviation c | 32 ± 20 |
| Days passed between the onset of the outbreak and date of sampling: range [median] c | 0–17 [5] |
| Link with the Institution | Symptom Status | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | No Cases | No Data | Total | |
| Users (residents, students, etc.) | 237 | 67 | 0 | 304 |
| Workers | 71 | 125 | 1 | 197 |
| No Data | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 |
| Total | 310 | 195 | 1 | 506 |
| Symptomatic Cases | Asymptomatic Exposed Subjects | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype | No. of Outbreaks | No. of Analyzed Samples | No. of Positive Samples (%) | No. of Analyzed Samples | No. of Positive Samples (%) | No. of Analyzed Samples | No. of Positive Samples (%) |
| GI.1[P1] | 2 | 25 | 0 (0%) | 15 | 0 (0%) | 40 | 0 (0%) |
| GI.3[P13] | 1 | 10 | 0 (0%) | 10 | 0 (0%) | 20 | 0 (0%) |
| GI.4[P4] | 4 | 25 | 0 (0%) | 20 | 0 (0%) | 45 | 0 (0%) |
| GI.6[P11] | 2 | 11 | 0 (0%) | 5 | 0 (0%) | 16 | 0 (0%) |
| GI.3[P13] + GI.2 | 1 | 4 | 0 (0%) | 4 | 0 (0%) | 8 | 0 (0%) |
| Total GI | 10 | 75 | 0 (0%) | 54 | 0 (0%) | 129 | 0 (0%) |
| GII.1[P33] | 1 | 13 | 0 (0%) | 18 | 0 (0%) | 31 | 0 (0%) |
| GII.2[P16] | 3 | 23 | 6 (26.1%) | 10 | 0 (0%) | 33 | 6 (18.2%) |
| GII.4[P16] | 4 | 30 | 5 (16.7%) | 14 | 2 (14.2%) | 44 | 7 (15.9%) |
| GII.4[P31] | 2 | 17 | 3 (17.6%) | 0 | 0 (0%) | 17 | 3 (17.6%) |
| GII.17[P17] | 6 | 57 | 11 (19.3%) | 54 | 3 (5.5%) | 111 | 14 (12.6%) |
| Total GII | 16 | 140 | 25 (17.9%) | 96 | 5 (5.2%) | 236 | 30 (12.7%) |
| Factor | Saliva+ | Saliva− | HuNoV Positivity in Saliva | Odds Ratio | CI 95% | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vomiting (n = 105) | Yes | 16 | 66 | 19.5% | 0.687 | 0.233–2.021 | 0.501 |
| No | 6 | 17 | 26.1% | ||||
| Nausea (n = 90) | Yes | 12 | 28 | 30.0% | 2.633 | 0.924–7.497 | 0.074 |
| No | 7 | 43 | 14.0% | ||||
| Fever (n = 94) | Yes | 1 | 17 | 5.6% | 0.176 | 0.0220–1.416 | 0.067 |
| No | 19 | 57 | 25.0% | ||||
| Diarrhea (n = 109) | Yes | 16 | 52 | 23.5% | 1.495 | 0.557–4.013 | 0.440 |
| No | 7 | 34 | 17.1% | ||||
| Abdominal pain (n = 95) | Yes | 11 | 40 | 21.6% | 1.069 | 0.397–2.88 | 0.900 |
| No | 9 | 35 | 20.5% | ||||
| Consumption of proton pump inhibitors (n = 85) | Yes | 5 | 12 | 29.4% | 1.607 | 0.485–5.322 | 0.450 |
| No | 14 | 54 | 20.6% | ||||
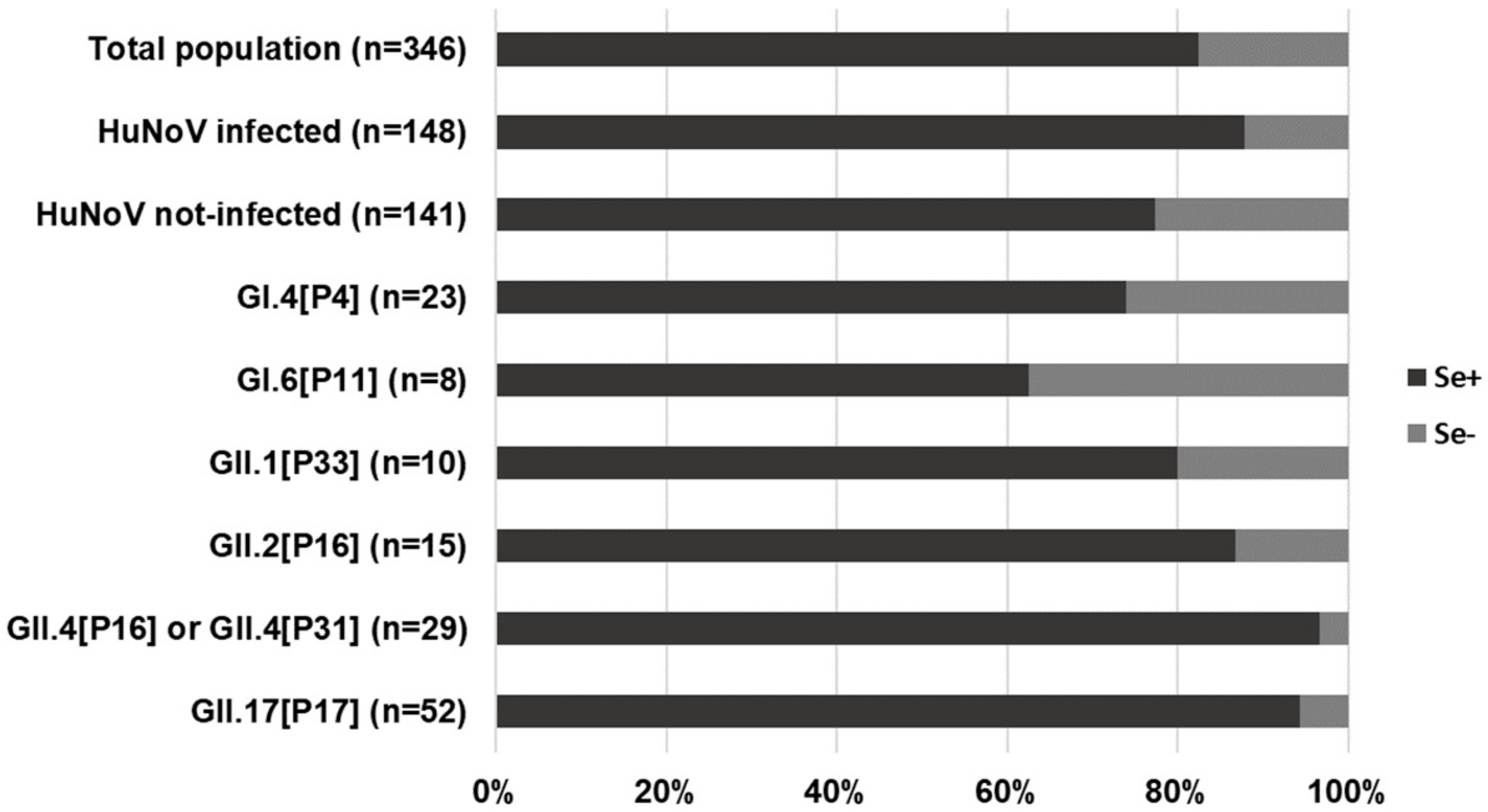
| Secretor Status (n = 130) | Pos | 24 | 94 | 20.3% | 2.809 | 0.345–22.830 | 0.352 |
| Neg | 1 | 11 | 8.3% | ||||
| Age (n = 129) | ≥65 years | 18 | 48 | 27.3% | 3.000 | 1.155–7.791 | 0.022 |
| <65 years | 7 | 56 | 11.1% | ||||
| Sex (n = 131) | Male | 4 | 30 | 11.8% | 0.482 | 0.153–1.523 | 0.216 |
| Female | 21 | 76 | 21.6% | ||||
| Sample | Treatment | PMA | HuNoV RNA Log Genome Copies/mL | Log Reduction * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artificially contaminated saliva | Untreated | - | 6.72 ± 0.01 | 0.03 |
| + | 6.69 ± 0.01 | |||
| 5 min at 95 °C | - | 2.91 ± 0.03 | 0.97 | |
| + | 1.94 ± 0.47 | |||
| Patient | Untreated | - | 3.45 | 0.30 |
| + | 3.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anfruns-Estrada, E.; Sabrià, A.; Fuentes, C.; Sabaté, S.; Razquin, E.; Cornejo, T.; Bartolomé, R.; Torner, N.; Izquierdo, C.; Soldevila, N.; et al. Detection of Norovirus in Saliva Samples from Acute Gastroenteritis Cases and Asymptomatic Subjects: Association with Age and Higher Shedding in Stool. Viruses 2020, 12, 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121369
Anfruns-Estrada E, Sabrià A, Fuentes C, Sabaté S, Razquin E, Cornejo T, Bartolomé R, Torner N, Izquierdo C, Soldevila N, et al. Detection of Norovirus in Saliva Samples from Acute Gastroenteritis Cases and Asymptomatic Subjects: Association with Age and Higher Shedding in Stool. Viruses. 2020; 12(12):1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121369
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnfruns-Estrada, Eduard, Aurora Sabrià, Cristina Fuentes, Sara Sabaté, Efrén Razquin, Thais Cornejo, Rosa Bartolomé, Nuria Torner, Conchita Izquierdo, Nuria Soldevila, and et al. 2020. "Detection of Norovirus in Saliva Samples from Acute Gastroenteritis Cases and Asymptomatic Subjects: Association with Age and Higher Shedding in Stool" Viruses 12, no. 12: 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121369
APA StyleAnfruns-Estrada, E., Sabrià, A., Fuentes, C., Sabaté, S., Razquin, E., Cornejo, T., Bartolomé, R., Torner, N., Izquierdo, C., Soldevila, N., Coronas, L., Dominguez, A., Pintó, R. M., Bosch, A., Guix, S., & on behalf of the Working Group for the Study of Outbreaks of Acute Gastroenteritis in Catalonia (PI16/02005). (2020). Detection of Norovirus in Saliva Samples from Acute Gastroenteritis Cases and Asymptomatic Subjects: Association with Age and Higher Shedding in Stool. Viruses, 12(12), 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121369









