Dual Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals a Delayed Antiviral Response of Haliotis diversicolor supertexta against Haliotid Herpesvirus-1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Abalone Mortalities and Viral DNA Quantification
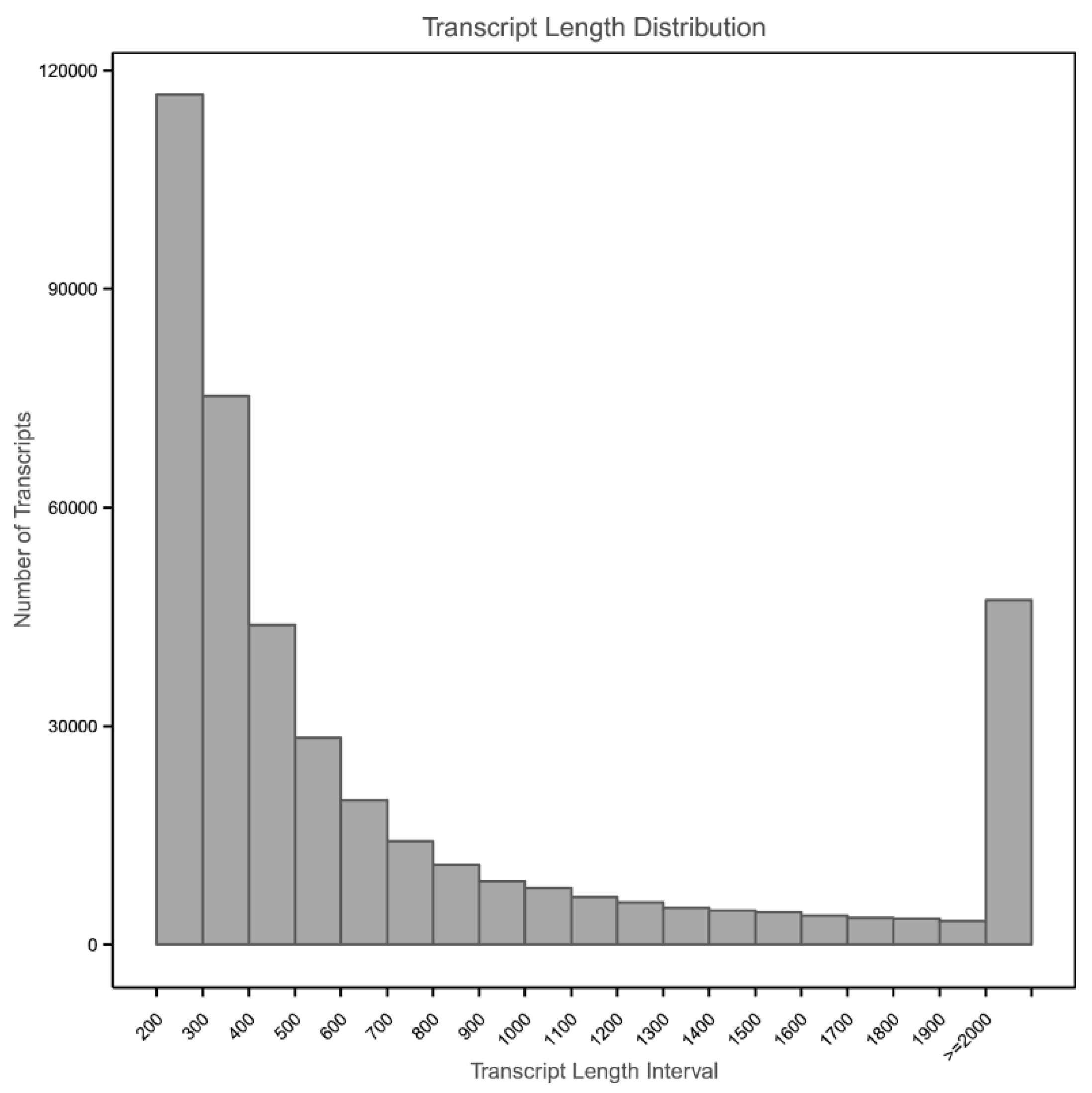
3.2. Transcriptome Assembly and Functional Annotation
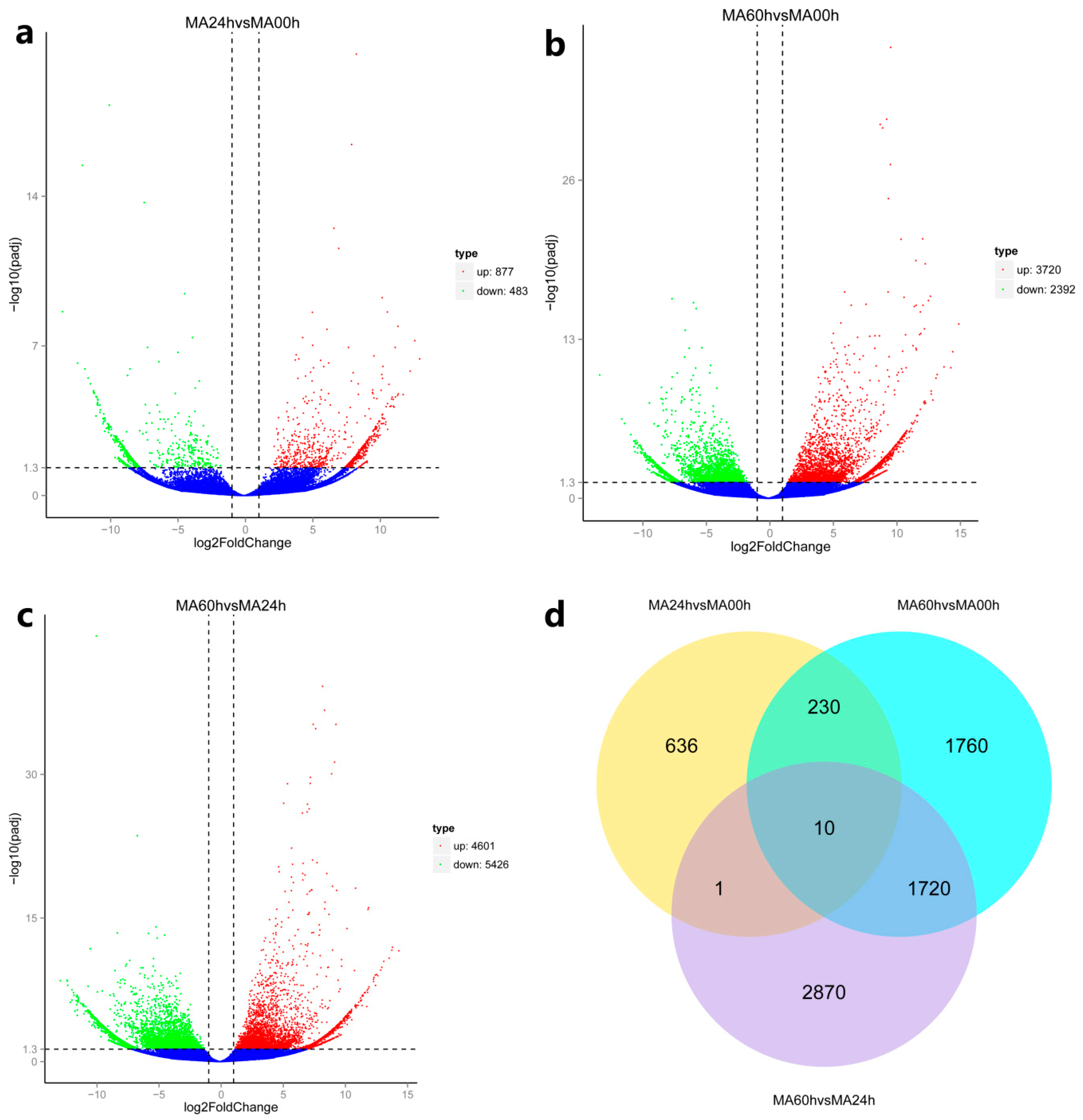
3.3. Analysis of the HaHV-1 Expression Profile
3.4. Analysis of DEGs Related to Immune Activities
3.4.1. The Delayed Immune Response of Abalone to HaHV-1 Infection
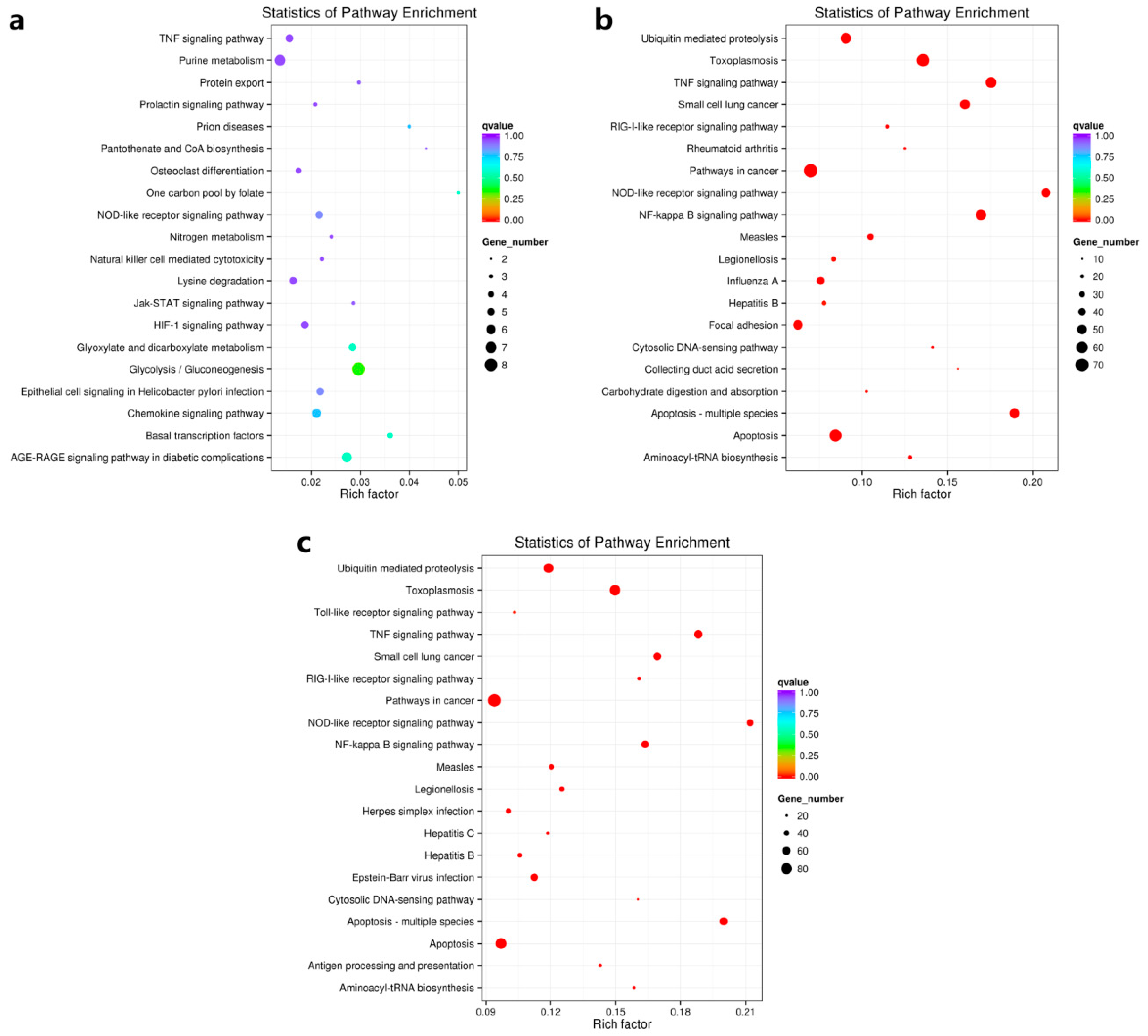
3.4.2. A Rich Set of Immune-Related Pathways in Abalone in Response to HaHV-1 Infection
3.5. Validation of RNA-Seq Results by RT-qPCR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, P.H.; Kuo, S.T.; Lai, S.H.; Yang, H.S.; Ting, Y.Y.; Hsu, C.L.; Chen, H.C. Herpes-like virus infection causing mortality of cultured abalone Haliotis diversicolor supertexta in Taiwan. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2005, 65, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savin, K.W.; Cocks, B.G.; Wong, F.; Sawbridge, T.; Cogan, N.; Savage, D.; Warner, S. A neurotropic herpesvirus infecting the gastropod, abalone, shares ancestry with oyster herpesvirus and a herpesvirus associated with the amphioxus genome. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, C.; Hardy-Smith, P.; Handlinger, J. Ganglioneuritis causing high mortalities in farmed Australian abalone (Haliotis laevigata and Haliotis rubra). Aust. Vet. J. 2007, 85, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Z.; Feng, J.; Liu, G.; Xu, L.; Chen, B.; Pan, J. Virus infection in cultured abalone, Haliotis diversicolor Reeve in Guangdong Province, China. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.M.; Li, Y.N.; Chang, P.H.; Jiang, J.Z.; Xin, L.S.; Li, C.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, C.M. Susceptibility of two abalone species, Haliotis diversicolor supertexta and Haliotis discus hannai, to Haliotid herpesvirus 1 infection. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 160, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Deuff, R.M.; Renault, T. Purification and partial genome characterization of a herpes-like virus infecting the Japanese oyster, Crassostrea gigas. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, A.J.; Trus, B.L.; Cheng, N.; Steven, A.C.; Watson, M.S.; Cunningham, C.; Le Deuff, R.M.; Renault, T. A novel class of herpesvirus with bivalve hosts. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, A.J. Evolution of the herpesviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 86, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, T.A.; Rouse, B.T. Herpesviruses—Immune escape artists? Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 14, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, B.D.; Verweij, M.C.; Wiertz, E.J. Herpesviruses and immunity: The art of evasion. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verweij, M.C.; Ressing, M.E.; Knetsch, W.; Quinten, E.; Halenius, A.; van Bel, N.; Hengel, H.; Drijfhout, J.W.; van Hall, T.; Wiertz, E.J. Inhibition of mouse TAP by immune evasion molecules encoded by non-murine herpesviruses. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Azab, W.; Osterrieder, N. Equine herpesviruses type 1 (EHV-1) and 4 (EHV-4)--masters of co-evolution and a constant threat to equids and beyond. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, D.; Ressing, M.E.; Wiertz, E.J. Exploiting human herpesvirus immune evasion for therapeutic gain: Potential and pitfalls. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.J.; Speck, P. Antiviral Defense and Innate Immune Memory in the Oyster. Viruses 2018, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, P.; Moreau, K.; Segarra, A.; Tourbiez, D.; Travers, M.A.; Rubinsztein, D.C.; Renault, T. Autophagy plays an important role in protecting Pacific oysters from OsHV-1 and Vibrio aestuarianus infections. Autophagy 2015, 11, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segarra, A.; Mauduit, F.; Faury, N.; Trancart, S.; Dégremont, L.; Tourbiez, D.; Haffner, P.; Barbosa-Solomieu, V.; Pepin, J.F.; Travers, M.A.; et al. Dual transcriptomics of virus-host interactions: Comparing two Pacific oyster families presenting contrasted susceptibility to ostreid herpesvirus 1. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renault, T.; Faury, N.; Barbosa-Solomieu, V.; Moreau, K. Suppression substractive hybridisation (SSH) and real time PCR reveal differential gene expression in the Pacific cupped oyster, Crassostrea gigas, challenged with Ostreid herpesvirus 1. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segarra, A.; Baillon, L.; Tourbiez, D.; Benabdelmouna, A.; Faury, N.; Bourgougnon, N.; Renault, T. Ostreid herpesvirus type 1 replication and host response in adult Pacific oysters, Crassostrea gigas. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.M.; Morga, B.; Rosani, U.; Shi, J.; Li, C.; Xin, L.S.; Wang, C.M. Long-range PCR and high-throughput sequencing of Ostreid herpesvirus 1 indicate high genetic diversity and complex evolution process. Virology 2019, 526, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burioli, E.A.V.; Prearo, M.; Houssin, M. Complete genome sequence of Ostreid herpesvirus type 1 microVar isolated during mortality events in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas in France and Ireland. Virology 2017, 509, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martenot, C.; Travaille, E.; Lethuillier, O.; Lelong, C.; Houssin, M. Genome exploration of six variants of the Ostreid Herpesvirus 1 and characterization of large deletion in OsHV-1 mu Var specimens. Virus Res. 2013, 178, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, T.; Moreau, P.; Faury, N.; Pepin, J.F.; Segarra, A.; Webb, S. Analysis of clinical ostreid herpesvirus 1 (Malacoherpesviridae) specimens by sequencing amplified fragments from three virus genome areas. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5942–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martenot, C.; Oden, E.; Travaille, E.; Malas, J.P.; Houssin, M. Detection of different variants of Ostreid Herpesvirus 1 in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas between 2008 and 2010. Virus Res. 2011, 160, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosani, U.; Varotto, L.; Domeneghetti, S.; Arcangeli, G.; Pallavicini, A.; Venier, P. Dual analysis of host and pathogen transcriptomes in ostreid herpesvirus 1-positive Crassostrea gigas. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4200–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Jouaux, A.; Ford, S.E.; Lelong, C.; Sourdaine, P.; Mathieu, M.; Guo, X. Transcriptome analysis reveals strong and complex antiviral response in a mollusc. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.M.; Rosani, U.; Xin, L.S.; Li, G.Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.C.; Wang, C.M. Dual transcriptomic analysis of Ostreid herpesvirus 1 infected Scapharca broughtonii with an emphasis on viral anti-apoptosis activities and host oxidative bursts. Fish. Shellfish Immun. 2018, 82, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorgeril, J.; Lucasson, A.; Petton, B.; Toulza, E.; Montagnani, C.; Clerissi, C.; Vidal-Dupiol, J.; Chaparro, C.; Galinier, R.; Escoubas, J.M.; et al. Immune-suppression by OsHV-1 viral infection causes fatal bacteraemia in Pacific oysters. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martenot, C.; Gervais, O.; Chollet, B.; Houssin, M.; Renault, T. Haemocytes collected from experimentally infected Pacific oysters, Crassostrea gigas: Detection of ostreid herpesvirus 1 DNA, RNA, and proteins in relation with inhibition of apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morga, B.; Faury, N.; Guesdon, S.; Chollet, B.; Renault, T. Haemocytes from Crassostrea gigas and OsHV-1: A promising in vitro system to study host/virus interactions. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 150, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martenot, C.; Segarra, A.; Baillon, L.; Faury, N.; Houssin, M.; Renault, T. In situ localization and tissue distribution of ostreid herpesvirus 1 proteins in infected Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 136, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Cheng, A.C.; Wang, M.S.; Jia, R.Y.; Sun, K.F.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.F.; et al. The suppression of apoptosis by alpha-herpesvirus. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.L.; Blaho, J.A. Apoptosis during herpes simplex virus infection. Adv. Virus Res. 2007, 69, 67–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goodkin, M.L.; Morton, E.R.; Blaho, J.A. Herpes simplex virus infection and apoptosis. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 23, 141–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzul, I.; Corbeil, S.; Morga, B.; Renault, T. Viruses infecting marine molluscs. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 147, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schikorski, D.; Renault, T.; Saulnier, D.; Faury, N.; Moreau, P.; Pepin, J.F. Experimental infection of Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas spat by ostreid herpesvirus 1: Demonstration of oyster spat susceptibility. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, B.H.; Kwak, W.; Kim, Y.O.; Kim, D.G.; Kong, H.J.; Kim, W.J.; Kang, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; An, C.M.; Moon, J.Y.; et al. Genome sequence of pacific abalone (Haliotis discus hannai): The first draft genome in family Haliotidae. Gigascience 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.D.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.M.; Rosani, U.; Li, Y.N.; Zhang, S.M.; Xin, L.S.; Wang, C.M. RNA-seq of HaHV-1-infected abalones reveals a common transcriptional signature of Malacoherpesviruses. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.Z.; Cai, T.; Olyarchuk, J.G.; Wei, L.P. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Mangalam, A.K.; Dwivedi, S.; Naik, S. Primer premier: Program for design of degenerate primers from a protein sequence. Biotechniques 1998, 24, 318–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-M.; Bai, C.-M.; Li, Y.N.; Xin, L.-S.; Wang, C.-M. Selection of reference genes as internal control for gene expression in adult abalone Haliotis diversicolor supertexta. J. Invertebr. Pathol. submitted.
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.X.; Chen, Z.S.; Ke, C.H.; Zhao, J.; You, W.W.; Zhang, J.; Dong, W.T.; Chen, J. Pyrosequencing of Haliotis diversicolor transcriptomes: Insights into early developmental molluscan gene expression. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushegian, A.; Karin, E.L.; Pupko, T. Sequence analysis of malacoherpesvirus proteins: Pan-herpesvirus capsid module and replication enzymes with an ancient connection to “Megavirales”. Virology 2018, 513, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettenleiter, T.C. Initiation and spread of alpha-herpesvirus infections. Trends Microbiol. 1994, 2, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, P.; Agosto, L.M.; Munro, J.B.; Mothes, W. Cell-to-cell transmission of viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, J.C.; Yokota, H.; Craven, R.C.; Schmitt, A.; Wills, J.W. The HSV-1 mechanisms of cell-to-cell spread and fusion are critically dependent on host PTP1B. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbeil, S.; McColl, K.A.; Williams, L.M.; Mohammad, I.; Hyatt, A.D.; Crameri, S.G.; Fegan, M.; Crane, M.S. Abalone viral ganglioneuritis: Establishment and use of an experimental immersion challenge system for the study of abalone herpes virus infections in Australian abalone. Virus Res. 2012, 165, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, C.; Slocombe, R.; Day, R.; Crawford, S. Leucopenia associated with abalone viral ganglioneuritis. Aust. Vet. J. 2012, 90, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Gao, W.; Wang, C.; Yu, T.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J. Identification and characterization of ostreid herpesvirus 1 associated with massive mortalities of Scapharca broughtonii broodstocks in China. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2016, 118, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, T.; Le Deuff, R.M.; Chollet, B.; Cochennec, N.; Gerard, A. Concomitant herpes-like virus infections in hatchery-reared larvae and nursery-cultured spat Crassostrea gigas and Ostrea edulis. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2000, 42, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hine, P.; Thorne, T. Replication of herpes-like viruses in haemocytes of adult flat oysters Ostrea angasi an ultrastructural study. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1997, 29, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abergel, C.; Rudinger-Thirion, J.; Giege, R.; Claverie, J.M. Virus-encoded aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: Structural and functional characterization of mimivirus TyrRS and MetRS. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12406–12417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouquet, B.; Nikolic, J.; Larrous, F.; Bourhy, H.; Wirblich, C.; Lagaudriere-Gesbert, C.; Blondel, D. Focal Adhesion Kinase Is Involved in Rabies Virus Infection through Its Interaction with Viral Phosphoprotein P. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1640–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.L.; Schattgen, S.A.; Pisitkun, P.; Jorgensen, J.P.; Hilterbrand, A.T.; Wang, L.J.; West, J.A.; Hansen, K.; Horan, K.A.; Jakobsen, M.R.; et al. Evasion of Innate Cytosolic DNA Sensing by a Gammaherpesvirus Facilitates Establishment of Latent Infection. J. Virol. 2015, 194, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, B.; Raftos, D. Immune responses to infectious diseases in bivalves. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 131, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, B.; Gillet, L.; Vanderplasschen, A.; Wattiez, R. Structural Proteomics of Herpesviruses. Viruses 2016, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | Sample | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Clean Bases | Error (%) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA00h | MA01 | 48,448,828 | 46,980,888 | 7.05G | 0.02 | 96.66 | 91.55 | 44.66 |
| MA02 | 46,479,558 | 44,978,850 | 6.75G | 0.01 | 97.43 | 93.28 | 45.49 | |
| MA03 | 59,916,192 | 58,047,078 | 8.71G | 0.02 | 97.31 | 93.01 | 44.71 | |
| MA24h | MA13 | 44,682,338 | 43,431,308 | 6.51G | 0.02 | 97.2 | 92.7 | 43.94 |
| MA14 | 49,698,546 | 48,290,308 | 7.24G | 0.02 | 97.13 | 92.52 | 44.02 | |
| MA15 | 49,009,274 | 47,443,952 | 7.12G | 0.02 | 97.26 | 92.77 | 43.23 | |
| MA60h | MA49 | 51,712,402 | 50,051,266 | 7.51G | 0.02 | 97.17 | 92.69 | 46.16 |
| MA50 | 41,758,974 | 40,566,558 | 6.08G | 0.02 | 96.7 | 91.62 | 45.68 | |
| MA51 | 56,555,122 | 54,822,210 | 8.22G | 0.01 | 97.37 | 93.12 | 44.81 |
| Database | Number of Annotated Unigenes | Percentage of Annotated Unigenes (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Annotated in Nr | 40,934 | 19.66 |
| Annotated in NT | 71,597 | 34.39 |
| Annotated in KO | 29,322 | 14.08 |
| Annotated in SwissProt | 57,899 | 27.81 |
| Annotated in Pfam | 81,908 | 39.35 |
| Annotated in GO | 82,047 | 39.41 |
| Annotated in KOG | 29,895 | 14.36 |
| Annotated in all databases | 6029 | 2.89 |
| Annotated in at least one database | 131,904 | 63.37 |
| Total unigenes | 208,144 | 100.00 |
| Pathway Name | Pathway ID | MA60h VS MA00h | MA60h VS MA24h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rich Factor | q Value | Gene No. | Rich Factor | q Value | Gene No. | ||
| Apoptosis—multiple species | ko04215 | 0.19 | 1.80E-18 | 54 | 0.20 | 7.33E-15 | 57 |
| TNF signaling pathway | ko04668 | 0.18 | 3.21E-18 | 56 | 0.19 | 7.33E-15 | 60 |
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | ko04621 | 0.21 | 3.21E-18 | 48 | 0.21 | 4.48E-14 | 49 |
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | ko04064 | 0.17 | 1.64E-17 | 55 | 0.16 | 2.12E-11 | 53 |
| Toxoplasmosis | ko05145 | 0.14 | 2.02E-17 | 69 | 0.15 | 3.14E-14 | 76 |
| Small cell lung cancer | ko05222 | 0.16 | 1.05E-16 | 55 | 0.17 | 5.89E-13 | 58 |
| Apoptosis | ko04210 | 0.08 | 2.61E-08 | 67 | 0.10 | 9.32E-07 | 77 |
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | ko04120 | 0.09 | 1.12E-07 | 54 | 0.12 | 2.03E-09 | 71 |
| Measles | ko05162 | 0.10 | 3.44E-06 | 34 | 0.12 | 1.74E-05 | 39 |
| Pathways in cancer | ko05200 | 0.07 | 7.87E-06 | 70 | 0.09 | 1.65E-07 | 94 |
| Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis | ko00970 | 0.13 | 4.28E-05 | 21 | 0.16 | 1.45E-05 | 26 |
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | ko04622 | 0.11 | 0.0003 | 20 | 0.16 | 4.55E-06 | 28 |
| Influenza A | ko05164 | 0.08 | 0.0003 | 41 | 0.08 | 0.0122 | 44 |
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | ko04623 | 0.14 | 0.0003 | 15 | 0.16 | 0.0007 | 17 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | ko05323 | 0.13 | 0.0020 | 14 | 0.12 | 0.0469 | 13 |
| Focal adhesion | ko04510 | 0.06 | 0.0024 | 52 | / | / | / |
| Collecting duct acid secretion | ko04966 | 0.16 | 0.0033 | 10 | / | / | / |
| Legionellosis | ko05134 | 0.08 | 0.0033 | 24 | 0.13 | 1.90E-05 | 36 |
| Carbohydrate digestion and absorption | ko04973 | 0.10 | 0.0043 | 16 | / | / | / |
| Hepatitis B | ko05161 | 0.08 | 0.0057 | 25 | 0.11 | 0.0007 | 34 |
| Epstein-Barr virus infection | ko05169 | 0.06 | 0.0057 | 34 | 0.11 | 9.32E-07 | 56 |
| Cysteine and methionine metabolism | ko00270 | 0.09 | 0.0064 | 20 | / | / | / |
| Ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes | ko03008 | 0.09 | 0.0098 | 17 | / | / | / |
| Starch and sucrose metabolism | ko00500 | 0.09 | 0.0115 | 17 | / | / | / |
| Hepatitis C | ko05160 | 0.08 | 0.0157 | 18 | 0.12 | 0.0009 | 26 |
| Herpes simplex infection | ko05168 | 0.06 | 0.049 | 25 | 0.10 | 0.0006 | 39 |
| Antigen processing and presentation | ko04612 | / | / | / | 0.14 | 6.49E-05 | 26 |
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | ko04141 | / | / | / | 0.08 | 0.0100 | 48 |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | ko04620 | / | / | / | 0.10 | 0.0082 | 25 |
| Osteoclast differentiation | ko04380 | / | / | / | 0.10 | 0.0162 | 23 |
| Endocytosis | ko04144 | / | / | / | 0.08 | 0.0247 | 47 |
| Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | ko00400 | / | / | / | 0.20 | 0.0299 | 7 |
| RNA transport | ko03013 | / | / | / | 0.08 | 0.0414 | 39 |
| Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis | ko00900 | / | / | / | 0.15 | 0.0414 | 9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, C.-M.; Zhang, S.-M.; Li, Y.-N.; Xin, L.-S.; Rosani, U.; Wang, C.-M. Dual Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals a Delayed Antiviral Response of Haliotis diversicolor supertexta against Haliotid Herpesvirus-1. Viruses 2019, 11, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040383
Bai C-M, Zhang S-M, Li Y-N, Xin L-S, Rosani U, Wang C-M. Dual Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals a Delayed Antiviral Response of Haliotis diversicolor supertexta against Haliotid Herpesvirus-1. Viruses. 2019; 11(4):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040383
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Chang-Ming, Shu-Min Zhang, Ya-Na Li, Lu-Sheng Xin, Umberto Rosani, and Chong-Ming Wang. 2019. "Dual Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals a Delayed Antiviral Response of Haliotis diversicolor supertexta against Haliotid Herpesvirus-1" Viruses 11, no. 4: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040383
APA StyleBai, C.-M., Zhang, S.-M., Li, Y.-N., Xin, L.-S., Rosani, U., & Wang, C.-M. (2019). Dual Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals a Delayed Antiviral Response of Haliotis diversicolor supertexta against Haliotid Herpesvirus-1. Viruses, 11(4), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040383







