First Evidence of Antibodies Against Lloviu Virus in Schreiber’s Bent-Winged Insectivorous Bats Demonstrate a Wide Circulation of the Virus in Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human and Bat Serum Samples
2.2. Recombinant LLOV GP Antigen
2.3. Detection of LLOV RNA by Real Time PCR
2.4. Detection of LLOV-Specific Antibodies by Immunoblot
2.5. Detection of LLOV-Specific Antibodies by Domain Programmable Arrays
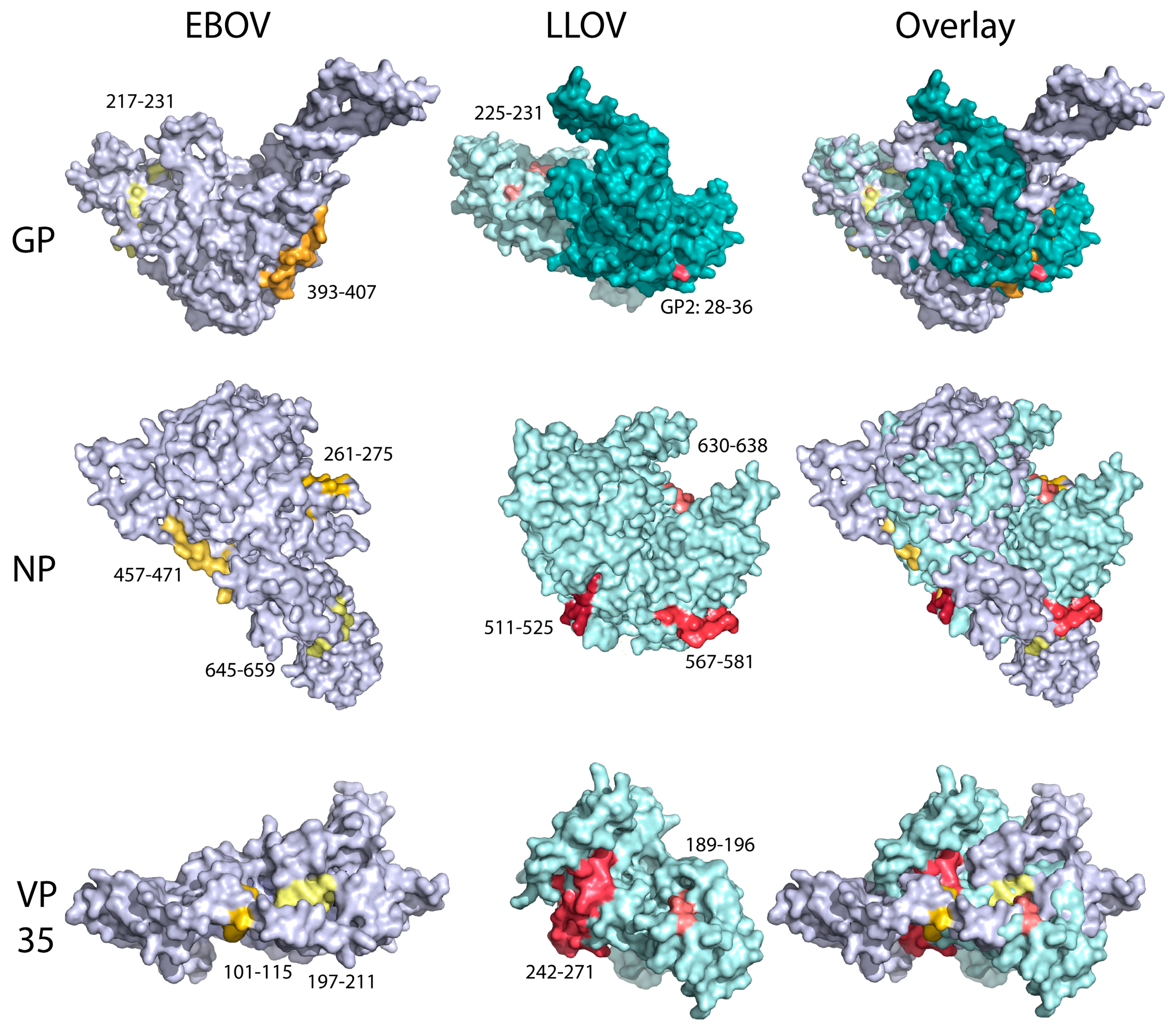
2.6. Protein Modelling and Surface Epitope Visualization
3. Results
3.1. Absence of LLOV RNA in the Schreiber’s Bent-Winged Bats
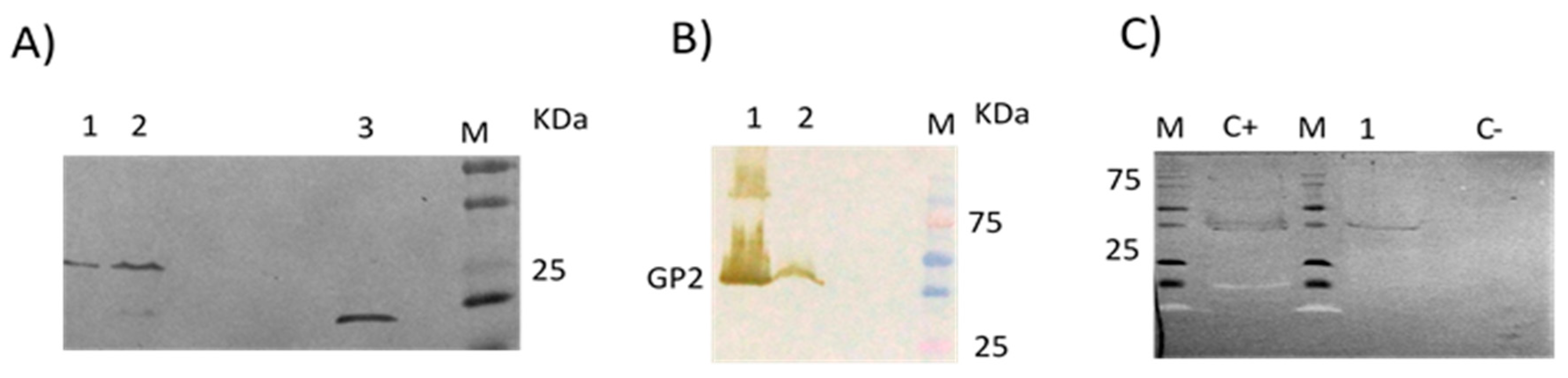
3.2. No Detectable Antibodies against LLOV GP2 Protein Were Found in the Human Samples by Immunoblot
3.3. Absence of Antibodies against LLOV GP2 Protein in Common Serotine Bats by Immunoblot
3.4. Presence of Antibodies against LLOV GP2 Protein in Schreiber’s Bent-Winged Bats by Immunoblot
3.5. Presence of Antibodies against LLOV Proteins in Schreiber’s Bent-Winged Bats Were Confirmed Using DPA
3.6. Detection of Significant Prevalence of LLOV in Schreiber’s Bent-Winged Bats
3.7. Immunodominance Epitope Analysis in Schreiber’s Bent-Winged Bats
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Negredo, A.; Palacios, G.; Vázquez-Morón, S.; González, F.; Dopazo, H.; Molero, F.; Juste, J.; Quetglas, J.; Savji, N.; de la Cruz Martínez, M.; et al. Discovery of an ebolavirus-like filovirus in Europe. PLoS Pathog 2011, 7, e1002304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, J.H.; Becker, S.; Ebihara, H.; Geisbert, T.W.; Johnson, K.M.; Kawaoka, Y.; Lipkin, W.I.; Negredo, A.I.; Netesov, S.V.; Nichol, S.T.; et al. Proposal for a revised taxonomy of the family Filoviridae: Classification, names of taxa and viruses, and virus abbreviations. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 2083–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yīmíng, B.; Gaya, K.A.; Christopher, F.B.; Bavari, S.; Bukreyev, A.; Chandran, K.; Dolnik, O.; Dye, J.M.; Ebihara, H.; Formenty, P.; et al. Implementation of Objective PASC-Derived Taxon Demarcation Criteria for Official Classification of Filoviruses. Viruses 2017, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemenesi, G.; Kurucz, K.; Dallos, B.; Zana, B.; Földes, F.; Boldogh, S.; Görföl, T.; Carroll, M.W.; Jakab, F. Re-emergence of Lloviu virus in Miniopterus schreibersii bats, Hungary, 2016. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanepoel, R.; Leman, P.A.; Burt, F.J.; Zachariades, N.A.; Braack, L.E.; Zachariades, N.A.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Rollin, P.E.; Zaki, S.R.; Peters, C.J. Experimental inoculation of plants and animals with Ebola virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1996, 2, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, E.M.; Kumulungui, B.; Pourrut, X.; Rouquet, P.; Hassanin, A.; Yaba, P.; Délicat, A.; Paweska, J.T.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Swanepoel, R. Fruit bats as reservoirs of Ebola virus. Nature 2005, 438, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanepoel, R.; Smit, S.B.; Rollin, P.E.; Formenty, P.; Leman, P.A.; Kemp, A.; Burt, F.J.; Grobbelaar, A.A.; Croft, J.; Bausch, D.G.; et al. Studies of reservoir hosts for Marburg virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towner, J.S.; Pourrut, X.; Albariño, C.G.; Nkogue, C.N.; Bird, B.H.; Grard, G.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Nichol, S.T.; Leroy, E.M. Marburg virus infection detected in a common African bat. PLoS ONE 2007, 22, e764. [Google Scholar]
- Leroy, E.M.; Epelboin, A.; Mondonge, V.; Pourrut, X.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Muyembe-Tamfum, J.J.; Formenty, P. Human Ebola outbreak resulting from direct exposure to fruit bats in Luebo, Democratic Republic of Congo, 2007. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009, 9, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, S.; Watanabe, S.; Masangkay, J.S.; Omatsu, T.; Ikegami, T.; Alviola, P.; Ueda, N.; Iha, K.; Fujii, H.; Ishii, Y. Reston Ebolavirus antibodies in bats, the Philippines. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1559–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.F.; Shi, Z. Serological evidence of ebolavirus infection in bats, China. J. Virol. 2012, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayman, D.T.; Yu, M.; Crameri, G.; Wang, L.F.; Suu-Ire, R.; Wood, J.L.; Cunningham, A.A. Ebola virus antibodies in fruit bats, Ghana, West Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1207–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olival, K.J.; Islam, A.; Yu, M.; Anthony, S.J.; Epstein, J.H.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.U.; Crameri, G.; Wang, L.F.; Lipkin, W.I. Ebola virus antibodies in fruit bats, bangladesh. Emerg. Infect. Dis 2013, 19, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, T.1; Anthony, S.; Gbakima, A.; Bird, B.H.; Bangura, J.; Tremeau-Bravard, A.; Belaganahalli, M.N.; Wells, H.L.; Dhanota, J.K. The discovery of Bombali virus adds further support for bats as hosts of ebolaviruses. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towner, J.S.; Amman, B.R.; Sealy, T.K.; Carroll, S.A.; Comer, J.A.; Kemp, A.; Swanepoel, R.; Paddock, C.D.; Balinandi, S.; Khristova, M.L. Isolation of genetically diverse Marburg viruses from Egyptian fruit bats. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amman, B.R.; Carroll, S.A.; Reed, Z.D.; Sealy, T.K.; Balinandi, S.; Swanepoel, R.; Kemp, A.; Erickson, B.R.; Comer, J.A.; Campbell, S.; et al. Seasonal pulses of Marburg virus circulation in juvenile Rousettus aegyptiacus bats coincide with periods of increased risk of human infection. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, A.J.; Amman, B.R.; Jones, M.E.; Sealy, T.K.; Uebelhoer, L.S.; Spengler, J.R.; Martin, B.E.; Coleman-McCray, J.A.; Nichol, S.T.; Towner, J.S. Modelling filovirus maintenance in nature by experimental transmission of Marburg virus between Egyptian rousette bats. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changula, K.; Kajihara, M.; Mori-Kajihara, A.; Eto, Y.; Miyamoto, H.; Yoshida, R.; Shigeno, A.; Hang’ombe, B.; Qiu, Y.; Mwizabi, D.; et al. Seroprevalence of Filovirus Infection of Rousettus aegyptiacus Bats in Zambia. J. Infect. Dis 2018, 218, S312–S317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Tan, C.W.; Anderson, D.E.; Jiang, R.D.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Lim, X.F.; Zhou, P.; Liu, X.L.; et al. Characterization of a filovirus (Měnglà virus) from Rousettus bats in China. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.L.; Schountz, T.; Wang, L.F. Antiviral immune responses of bats: A review. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovich, S.S.; Lovett, S.P.; Koroleva, G.; Guito, J.C.; Arnold, C.E.; Nagle, E.R.; Kulcsar, K.; Lee, A.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Hume, A.J.; et al. The Egyptian Rousette Genome Reveals Unexpected Features of Bat Antiviral. Immunity Cell. 2018, 173, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, J.; Miyamoto, H.; Kajihara, M.; Ogawa, H.; Maeda, K.; Sakoda, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Takada, A. Characterization of the envelope glycoprotein of a novel filovirus, lloviu virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.; Ndungo, E.; Jangra, R.K.; Cai, Y.; Postnikova, E.; Radoshitzky, S.R.; Dye, J.M.; Ramírez de Arellano, E.; Negredo, A.; Palacios, G.; et al. Cell entry by a novel European filovirus requires host endosomal cysteine proteases and Niemann-Pick C1. Virology 2014, 468–470, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagins, A.R.; Basler, C.F. Lloviu virus VP24 and VP35 proteins function as innate immune antagonists in human and bat cells. Virology 2015, 485, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, A.; Robison, C.; Goto, H.; Sanchez, A.; Murti, K.G.; Whitt, M.A.; Kawaoka, Y. A system for functional analysis of Ebola virus glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14764–14769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wool-Lewis, R.J.; Bates, P. Characterization of Ebola virus entry by using pseudotyped viruses: Identification of receptor-deficient cell lines. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 3155–3160. [Google Scholar]
- Prehaud, C.; Hellebrand, E.; Coudrier, D.; Volchkov, V.E.; Volchkova, V.A.; Feldmann, H.; Le Guenno, B.; Bouloy, M. Recombinant Ebola virus nucleoprotein and glycoprotein (Gabon 94 strain) provide new tools for the detection of human infections. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 2565–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellquist-Riemenschneider, J.L.; Garrison, A.R.; Geisbert, J.B.; Saikh, K.U.; Heidebrink, K.D.; Jahrling, P.B.; Ulrich, R.G.; Schmaljohn, C.S. Comparison of the protective efficacy of DNA and baculovirus-derived protein vaccines for EBOLA virus in guinea pigs. Virus Res. 2003, 92, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, E.; Yokoyama, A.; Miyamoto, H.; Igarashi, M.; Kishida, N.; Matsuno, K.; Marzi, A.; Feldmann, H.; Ito, K.; Saijo, M.; et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of filovirus species-specific antibodies. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.; Delisle, J.; Konduru, K.; Bradfute, S.; Radoshitzky, S.R.; Retterer, C.; Kota, K.; Bavari, S.; Kuhn, J.H.; Jahrling, P.B.; et al. Development and characterization of rabbit and mouse antibodies against ebolavirus envelope glycoproteins. J. Virol. Methods. 2011, 174, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.S.; de Jong, C.E.; Field, H.E. Sampling small quantities of blood from microbats. Acta Chiropterologica 2010, 1, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panning, M.; Laue, T.; Olschlager, S.; Eickmann, M.; Becker, S.; Raith, S.; Courbot, M.C.; Nilsson, M.; Gopal, R.; Lundkvist, A.; et al. Diagnostic Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction kit for filoviruses based on the strain collections of all European biosafety level 4 laboratories. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, S199–S204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lockhart, M.; Reyes, D.S.; Gonzalez, J.C.; Garcia, K.Y.; Villa, E.C.; Pfeffer, B.P.; Trefry, J.C.; Kugelman, J.R.; Pitt, M.L.; Palacios, G.F.; et al. Qualitative Profiling of the Humoral Immune Response Elicited by rVSV-ΔG-EBOV-GP Using a Systems Serology Assay, Domain Programmable Arrays. Cell. Rep. 2018, 24, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protocols 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quetglas, J.; Gonzalez, F.; Paz, O. Estudian la extraña mortandad de miles de murciélago de cuevas. Quercus 2003, 203, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Schuh, A.J.; Amman, B.R.; Sealy, T.K.; Kainulainen, M.H.; Chakrabarti, A.K.; Guerrero, L.W.; Nichol, S.T.; Albarino, C.G.; Towner, J.S. Antibody-mediated virus neutralization is not a universal mechanism of Marburg; Ebola or Sosuga virus clearance in Egyptian rousette bats. J. Infect. Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changula, K.; Yoshida, R.; Noyori, O.; Marzi, A.; Miyamoto, H.; Ishijima, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Kajihara, M.; Feldmann, H.; Mweene, A.S.; et al. Mapping of conserved and species-specific antibody epitopes on the Ebola virus nucleoprotein. Virus Res. 2013, 176, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, R.; Overton, J.A.; Greenbaum, J.A.; Ponomarenko, J.; Clark, J.D.; Cantrell, J.R.; Wheeler, D.K.; Gabbard, J.L.; Hix, D.; Sette, A.; et al. The immune epitope database (IEDB) 3.0. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43, D405-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babirye, P.; Musubika, C.; Kirimunda, S.; Downing, R.; Lutwama, J.J.; Mbidde, E.K.; Weyer, J.; Paweska, J.T.; Joloba, M.L.; Wayengera, M. Identity and validity of conserved B cell epitopes of filovirus glycoprotein: Towards rapid diagnostic testing for Ebola and possibly Marburg virus disease. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobarzo, A.; Groseth, A.; Dolnik, O.; Becker, S.; Lutwama, J.J.; Perelman, E.; Yavelsky, V.; Muhammad, M.; Kuehne, A.I.; Marks, R.S.; et al. Profile and persistence of the virus-specific neutralizing humoral immune response in human survivors of Sudan ebolavirus (Gulu). J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becquart, P.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Nkoghe, D.; Leroy, E.M. Identification of continuous human B-cell epitopes in the VP35, VP40, nucleoprotein and glycoprotein of Ebola virus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Pools | Serum Number | Species | Year | Location | Gender | Animal Age | Sample Number | Pool Immunoblot | Individual Immunoblot | DPA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 4 | Human (H. sapiens) | 2003 | Sevilla | Female | Unknown | 1 | Neg | ND | ND |
| Male | Unknown | 2 | ND | ND | ||||||
| Male | Unknown | 3 | ND | ND | ||||||
| Male | Unknown | 4 | ND | ND | ||||||
| H2 | 4 | Human (H. sapiens) | 2004 | Sevilla | Female | Unknown | 5 | Neg | ND | ND |
| Male | Unknown | 6 | ND | ND | ||||||
| Male | Unknown | 7 | ND | ND | ||||||
| Male | Unknown | 8 | ND | ND | ||||||
| H3 | 5 | Human (H. sapiens) | 2006 | Vizcaya | Male | Unknown | 9 | Neg | ND | ND |
| Navarra | Male | Unknown | 10 | ND | ND | |||||
| La Rioja | Male | Unknown | 11 | ND | ND | |||||
| Vizcaya | Male | Unknown | 12 | ND | ND | |||||
| Murcia | Male | Unknown | 13 | ND | ND | |||||
| H4 | 5 | Human (H. sapiens) | 2006 | Badajoz | Female | Unknown | 14 | Neg | ND | ND |
| Vizcaya | Male | Unknown | 15 | ND | ND | |||||
| Madrid | Male | Unknown | 16 | ND | ND | |||||
| Badajoz | Male | Unknown | 17 | ND | ND | |||||
| Vizcaya | Male | Unknown | 18 | ND | ND | |||||
| H5 | 2 | Human (H. sapiens) | 2007 | Barcelona | Female | Unknown | 19 | Neg | ND | ND |
| Sevilla | Female | Unknown | 20 | ND | ND | |||||
| H6 | 2 | Human (H. sapiens) | 2008 | Sevilla | Male | Unknown | 21 | Neg | ND | ND |
| Female | Unknown | 22 | ND | ND | ||||||
| E1 | 5 | Serotine bat (E. serotinus) | 2002 | Huelva | Unknown | Unknown | 1 | Neg | ND | ND |
| Unknown | Unknown | 2 | ND | ND | ||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | 3 | ND | ND | ||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | 4 | ND | ND | ||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | 5 | ND | ND | ||||||
| E2 | 5 | Serotine bat (E. serotinus) | 2000 | Huelva | Unknown | Unknown | 6 | Neg | ND | ND |
| Unknown | Unknown | 7 | ND | ND | ||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | 8 | ND | ND | ||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | 9 | ND | ND | ||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | 10 | ND | ND | ||||||
| C1 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Cantabria | Male | Young | 2 | Pos | Neg | Neg |
| Male | Young | 3 | Neg | Neg | ||||||
| Female | Young | 4 | Pos | Neg | ||||||
| Female | Adult | 1 | Neg | ND | ||||||
| Female | Young | 5 | Neg | Neg | ||||||
| C2 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Cantabria | Female | Adult | 6 | Pos | Pos | Neg |
| Female | Adult | 7 | Pos | Pos | ||||||
| Female | Adult | 8 | Pos | Pos | ||||||
| Female | Young | 12 | Neg | ND | ||||||
| Female | Young | 11 | Pos | Pos | ||||||
| C3 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Cantabria | Male | Young | 13 | Pos | ND | Neg |
| Male | Young | 14 | ND | Pos | ||||||
| Female | Young | 15 | ND | Pos | ||||||
| Female | Adult | 16 | ND | Pos | ||||||
| Female | Adult | 18 | ND | Neg | ||||||
| C4 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Cantabria | Female | Young | 19 | Pos | ND | Neg |
| Male | Young | 20 | ND | Pos | ||||||
| Female | Adult | 21 | ND | ND | ||||||
| Male | Young | 22 | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Male | Young | 23 | ND | Neg | ||||||
| C5 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Cantabria | Female | Young | 24 | Pos | ND | Neg |
| Female | Adult | 25 | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Female | Young | 26 | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Male | Young | 27 | ND | Pos | ||||||
| Female | Young | 32 | ND | Neg | ||||||
| C6 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Cantabria | Male | Young | 33 | Pos | ND | Neg |
| Male | Young | 34 | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Female | Young | 35 | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Male | Young | 36 | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Female | Young | 37 | ND | Pos | ||||||
| C7 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Cantabria | Female | Young | 39 | Pos | ND | Neg |
| Female | Young | 40 | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Female | Young | 42 | ND | Pos | ||||||
| Male | Young | 43 | ND | Pos | ||||||
| Female | Young | 44 | ND | Pos | ||||||
| A4 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Asturias | Male | Young | 01A | Pos | ND | Pos |
| Male | Young | 02A | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Male | Young | 03A | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Female | Young | 04A | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Male | Young | 05A | ND | Neg | ||||||
| A5 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Asturias | Male | Young | 06A | Pos | ND | Pos |
| Female | Young | 07A | ND | Pos | ||||||
| Male | Young | 08A | ND | Pos | ||||||
| Male | Young | 26B | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Male | Young | 27B | ND | Neg | ||||||
| A1 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Asturias | Male | Young | 01B | Pos | ND | Pos |
| Male | Adult | 02B | ND | Pos | ||||||
| Female | Young | 04B | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Male | Adult | 06B | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Female | Adult | 08B | ND | Pos | ||||||
| A2 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Asturias | Male | Adult | 10B | Pos | ND | Neg |
| Male | Adult | 12B | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Male | Young | 13B | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Female | Young | 15B | ND | Neg | ||||||
| Male | Adult | 16B | ND | Neg | ||||||
| A3 | 5 | Schreibers’ bat (M. schreibersii) | 2015 | Asturias | Male | Young | 18B | Pos | ND | ND |
| Male | Young | 22B | ND | ND | ||||||
| Male | Young | 23B | ND | ND | ||||||
| Male | Young | 24B | ND | ND | ||||||
| Female | Young | 25B | ND | ND |
| Cantabria Cave | Epitopes | ||||||
| Sample Number | DPA | Protein | Inferred Epitope | EXP | Start | End | Shared |
| 7 | Pos | GP1 | KPMTDHQEFILQPHS | 94 | 329 | 343 | |
| 8 | Pos | GP2 | ETSSKSAT | >100 | 28 | 35 | GP2.28 |
| 11 | Pos | NP | QTQESSDRSDYSRRP | 58 | 511 | 525 | NP.511 |
| VP40 | ASPDKIKS | >100 | 231 | 238 | VP40.231 | ||
| 14 | Pos | GP2 | LLGSVSNNSSIQELETSSKSAT | >100 | 14 | 35 | GP2.28 |
| L | GASFVTDLEKYNLAFRFEFTRPFIEYC | 28 | 622 | 648 | L.620 | ||
| 15 | Pos | NP | QTQESSDRSDYSRRP | >100 | 511 | 525 | NP.511 |
| NP | GDRPHTTQ | >100 | 532 | 539 | NP.532 | ||
| 16 | Pos | NP | WKQPTSPLSTIPEEE | >100 | 630 | 644 | NP.630 |
| 20 | Pos | VP35 | DSPQCALIQITKRIPIFGETPP | 36 | 243 | 271 | VP35.243 |
| GP2 | LLGSVSNNSSIQELETSSKSAT | 33 | 14 | 35 | GP2.28 | ||
| 27 | Pos | VP35 | TERTFGKP | 49 | 189 | 196 | VP35.189 |
| NP | QTQESSDRSDYSRRP | 15 | 511 | 525 | NP.511 | ||
| NP | RTLPLISFDDNEGEI | 4 | 567 | 581 | NP.567 | ||
| 37 | Pos | VP35 | DSPQCALIQITKRIPIFGETPP | 5 | 243 | 271 | VP35.243 |
| NP | QTQESSDRSDYSRRP | 9 | 511 | 525 | NP.511 | ||
| NP | RTLPLISFDDNEGEI | 5 | 567 | 581 | NP.567 | ||
| 42 | Pos | GP2 | ETSSKSAT | 32 | 28 | 35 | GP2.28 |
| 43 | Pos | VP35 | PLIEPKTSANKSTQTENIYQSDQVLREIK | 23 | 42 | 70 | VP35.42 |
| NP | QTQESSDRSDYSRRP | 13 | 511 | 525 | NP.511 | ||
| NP | RTLPLISFDDNEGEI | 22 | 567 | 581 | NP.567 | ||
| 44 | Pos | VP35 | VREAFDRLEKTEEVTE | 7 | 175 | 190 | VP35.175 |
| GP2 | HNATTTSK | >100 | 98 | 105 | GP2.98 | ||
| GP2 | KTRRRRQVNPVPPTITQQTSTSINTSHHP | >100 | 105 | 133 | GP2.105 | ||
| Asturia Cave | Epitopes | ||||||
| Sample | DPA | Protein | Inferred Epitope | EXP | Start | End | |
| 01A | Pos | VP30 | NSRITPGDWQCQPCDYPKARFK | 12.5 | 77 | 98 | |
| VP35 | LEKTEEVTERTFGKP | 20 | 182 | 196 | VP35.189 | ||
| NP | RTLPLISFDDNEGEILDDKSD | 3 | 567 | 583 | NP.567 | ||
| 06A | Pos | NP | SQDPNNRQKQSDTQQTQESSDRSDYSRRP | 4.2 | 497 | 525 | NP.511 |
| NP | RTLPLISFDDNEGEILDDKSDLPAPDTHS | 14 | 567 | 595 | NP.567 | ||
| GP2 | ETSSKSATELTTPINHSQSLQL | 9.6 | 28 | 49 | GP2.28 | ||
| VP40 | LVPRLMSKDDLGGRDLVMSTKGSCENCYYPGASPTQ | 72 | 287 | 322 | |||
| 07A | Pos | GP1 | TTTLDYDV | 20 | 224 | 231 | GP1.224 |
| VP35 | VREAFDRLE | 4.4 | 175 | 183 | |||
| NP | LNVDHTIVRKKSIPLFEIGNSDQVCNWIIQIIEAGV | 7.1 | 28 | 63 | |||
| NP | WKQPTSPLSTIPEEEGGHEANNDNSESDL | 76.8 | 630 | 658 | NP.630 | ||
| L | QVLGGLSFLNPEKCF | >100 | 903 | 917 | |||
| 08A | Pos | VP30 | YQQHNQES | 20 | 175 | 182 | |
| VP35 | QSDQVLREIK | 13.4 | 63 | 70 | |||
| L | AEDIIRPFCEARINLPVQELFKLLPSHYSGNIVHRY | 12.9 | 1232 | 1267 | |||
| 01B | Pos | VP24 | VKHDLCNFLVTTTITGWDVYWAGHLFHVPNKGIALL | 72 | 196 | 231 | |
| GP1 | TTTLDYDV | >100 | 224 | 231 | GP1.224 | ||
| VP35 | VREAFDRLEKTEEVTERTFGKP | 6.9 | 175 | 196 | VP35.189 | ||
| NP | STKESSSYTASRTEEDRNNYNS | 60 | 441 | 462 | NP.441 | ||
| NP | RTLPLISFDDNEGEILDDKSDLPAPDTHS | 8.8 | 567 | 595 | NP.567 | ||
| NP | WKQPTSPLS | 4.2 | 630 | 638 | NP.630 | ||
| L | ANTVMTSLLADMNNA | 19.6 | 1421 | 1435 | |||
| 02B | Pos | VP35 | LEKTEEVTERTFGKP | 3.1 | 182 | 196 | VP35.189 |
| NP | NVDHITDLLGVGSRDKSLRKTLSALEFEP | 12.5 | 112 | 140 | |||
| 08B | Pos | VP35 | VREAFDRLEKTEEVTERTFGKP | 36 | 175 | 196 | VP35.189 |
| NP | STKESSSYTASRTEEDRNNYNS | >100 | 441 | 462 | |||
| GP2 | ETSSKSAT | 57 | 28 | 35 | GP2.28 | ||
| GP2 | LASVTNTPTP | 28.7 | 49 | 56 | |||
| L | DHVQVRGASFVTDLEK | 53.7 | 616 | 637 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez de Arellano, E.; Sanchez-Lockhart, M.; Perteguer, M.J.; Bartlett, M.; Ortiz, M.; Campioli, P.; Hernández, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Garcia, K.; Ramos, M.; et al. First Evidence of Antibodies Against Lloviu Virus in Schreiber’s Bent-Winged Insectivorous Bats Demonstrate a Wide Circulation of the Virus in Spain. Viruses 2019, 11, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040360
Ramírez de Arellano E, Sanchez-Lockhart M, Perteguer MJ, Bartlett M, Ortiz M, Campioli P, Hernández A, Gonzalez J, Garcia K, Ramos M, et al. First Evidence of Antibodies Against Lloviu Virus in Schreiber’s Bent-Winged Insectivorous Bats Demonstrate a Wide Circulation of the Virus in Spain. Viruses. 2019; 11(4):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040360
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez de Arellano, Eva, Mariano Sanchez-Lockhart, Maria J. Perteguer, Maggie Bartlett, Marta Ortiz, Pamela Campioli, Ana Hernández, Jeanette Gonzalez, Karla Garcia, Manolo Ramos, and et al. 2019. "First Evidence of Antibodies Against Lloviu Virus in Schreiber’s Bent-Winged Insectivorous Bats Demonstrate a Wide Circulation of the Virus in Spain" Viruses 11, no. 4: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040360
APA StyleRamírez de Arellano, E., Sanchez-Lockhart, M., Perteguer, M. J., Bartlett, M., Ortiz, M., Campioli, P., Hernández, A., Gonzalez, J., Garcia, K., Ramos, M., Jiménez-Clavero, M. Á., Tenorio, A., Sánchez-Seco, M. P., González, F., Echevarría, J. E., Palacios, G., & Negredo, A. (2019). First Evidence of Antibodies Against Lloviu Virus in Schreiber’s Bent-Winged Insectivorous Bats Demonstrate a Wide Circulation of the Virus in Spain. Viruses, 11(4), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040360






